文章编号:1004-0609(2011)12-3042-08
热暴露对Ti-44Al-4Nb-4Zr-0.2Si-1B合金显微结构及力学性能的影响
朱小龙,黄泽文
(西南交通大学 材料先进技术教育部重点实验室,成都 610031)
摘 要:采用扫描电镜、透射电镜以及拉伸和高周疲劳等试验手段研究10 000 h、700 ℃大气热暴露过程对Ti-44Al-4Nb-4Zr-0.2Si-1B合金显微结构和力学性能的影响。结果表明:复合含Nb-Zr的TiAl合金的α2+γ层片组织显示出较高的热力学稳定性,合金的α2+γ层片晶团在热暴露过程中,α2→γ和α2+γ→B2(ω)相变并不普遍。合金中B2(ω)晶粒由若干微米胞构成,长期的高温热暴露导致胞壁处具有较高有序度的D88相结构的ω颗粒明显长大,且胞内也大量析出这种脆性的D88相结构的ω颗粒;同时,在B2(ω)晶内还析出微米级别的γ相,这是该合金 10 000 h热暴露过程后脆性明显增加的主要原因。此外,该合金拉伸强度和条件屈服强度在热暴露过程中变化不大,室温疲劳极限甚至还有所提高。
关键词:钛铝合金;热暴露;显微结构;力学性能
中图分类号:TG146.4 文献标志码:A
Effect of thermal exposure on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-44Al-4Nb-4Zr-0.2Si-1B alloy
ZHU Xiao-long, HUANG Ze-wen
(Key Laboratory of Advanced Technologies of Materials, Ministry of Education,
Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, China)
Abstract: The effect of thermal exposure at 700 ℃ in air for 10 000 h on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-44Al-4Nb-4Zr-0.2Si-1B alloy was investigated using scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy and tensile and high cycle fatigue test. The results show that the decomposition of α2 lamellae through α2→γ and the formation of B2(ω) through α2+γ→B2(ω) are not prevail inside the α2+γ colonies. This tends to suggest that the α2+γ lamellae are at a high level of thermodynamic stability. B2(ω) grains consist of many micron-sized cells, in which ω particles with D88 highly ordered structure in cell-wall regions grow significantly during the long-term exposure. Such D8 8-ω particles also form widely inside the cells. Moreover, the micron-sized equiaxed γ phase also precipitates from B2(ω) grains. The tensile ductility in the exposed alloy reduces remarkably. While the long-term exposure does not cause detrimental effect on tensile strength and high cycle fatigue limit. The proof stress is still at level of larger than 600 MPa, while fatigue limit increases noticeably after 10 000 h exposure.
Key words: TiAl-based alloy; thermal exposure; microstructure; mechanical property
TiAl基合金具有高熔点、低密度、高弹性模量、低扩散系数、优良的抗腐蚀性能及良好的结构稳定性[1-2],这些优点使其在航空航天和汽车工业等领域有广泛的应用前景。但γ-TiAl合金在室温下具有较低的抗损伤能力,比如较低的室温塑性、较低的断裂韧性和较高的裂纹扩展速率。这些都增加了材料失效的可能性[3-6]。工程用γ-TiAl合金通常是在Ti-(44%~49%)Al二元系的基础上加入适量合金元素熔炼而成的。近年来,低铝高合金含量的Ti-44Al-8X-1B(X为Nb、Zr、Ta和Hf等)系列γ-TiAl合金,由于能提供更高的力学性能而得到了广泛的关注和研究。在γ-TiAl合金中适当降低铝的含量,加入较多的难熔合金元素,目的是想改善合金的脆性,提高合金的高温成型加工能力和综合力学性能,尤其是Nb和Zr等元素的加入,能够显著改善合金的高温蠕变性能和抗氧化性能[7-8]。但 这类合金在高温长时间服役时的热稳定性能尚无定论。已有的针对44Al-8Nb合金的研究发现,其力学性能在长时间热暴露后发生了明显的衰退[9]。Zr被认为是比Nb更为稳定的难熔合金元素,有助于减缓TiAl合金组织在高温时的分解。因此,用Zr部分取代Nb,复合添加Nb-Zr对TiAl合金高温热稳定性的影响值得认真探索。本文作者采用扫描电镜和透射电镜技术以及拉伸和高周疲劳力学性能测试手段,系统地研究了含4Nb-4Zr的TiAl合金在长时间高温环境下热暴露过程对合金组织结构和性能稳定性的影响,着重研究了一系列高温热暴露处理对该合金的显微结构、拉伸性能以及高周疲劳性能等力学性能的影响,为进一步发展高强度多元稳态TiAl合金提供参考数据。
1 实验
1.1 样品准备
实验所用原材料为英国伯明翰大学提供的4-4-1合金,其名义成分为Ti-44Al-4Nb-4Zr-0.2Si-1B(摩尔分数,%)。合金经二次真空电弧重熔,并利用冷壁坩埚磁悬浮熔炼炉在保护气氛中制成直径为100 mm的铸锭,对其进行热等静压处理,其工艺制度为1 260 ℃、150 MPa、4 h,以得到致密的近片层组织(NL),然后采用电火花线切割加工,制备成尺寸为70 mm×10 mm×10 mm和d 10 mm×70 mm 的试样,将试样在700 ℃下的空气气氛中分别进行1 000、3 000、5 000和10 000 h的热暴露处理,热暴露过程温度偏差为 ±5 ℃。
1.2 显微结构及形貌表征
采用FEI公司的Quanta200 ESEM环境扫描电子显微镜(SEM)分别对热暴露前后的试样进行显微结构分析。采用背散射电子(BSE)成像,电压为20 kV,定量分析显微结构中各主要组元在随热暴露时间的变化。使用型号为Tecnai G F20 S-TWINd场发射透射电子显微镜(TEM)对合金组织形貌进行观察,并分析确定热暴露过程中发生的相变反应。采用标准电解双喷工艺制备透射样品,电解液溶液的成分为:65%甲醇+30%正丁醇+5%高氯酸(体积分数,%),双喷温度为-35~-25 ℃,工作电压为30 V。
1.3 力学性能试验
拉伸试验分别在室温和700 ℃的高温下采用WDW3100型微机控制电子万能试验机进行,试验温度由分布在加热炉的上、中、下3段的热电偶循环监控(±5 ℃), 采用圆形截面试样,试样表面抛光到1 μm, 每一实验数据来自3根试样的平均值。由于钛铝合金为脆性材料,在本研究中采用较低的应变速率,其值为0.7×10-4 s-1。
四点弯曲疲劳试验在室温下进行。对疲劳试样的最大拉应力受力面采用例行的磨抛程序,最后抛光到1 μm。每组试样共10根。所使用设备型号为PLG-100型微机控制高频疲劳实验机,最小应力与最大应力比为0.1,试验频率为100~120 Hz之间。测定出材料在交变疲劳应力作用下的最大断裂应力(σmax)和相应的疲劳失效周次(N)。 当样品在经历107周次仍然不断裂时,则停机,此时的最大应力定义为该规范的条件疲劳强度。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 热暴露时间对显微结构的影响
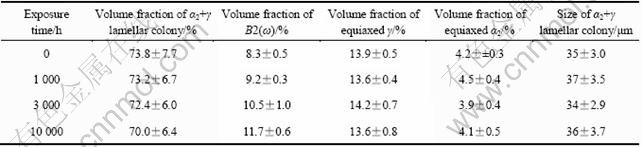
合金4-4-1的微观组织为典型的近片层(Near lamellar)组织(见图1)。图1所示为未进行热暴露的铸造态合金的显微组织,由大量α2+γ层片交替重叠构成的片层团,少量B2(ω)相和等轴γ相,以及更少量的等轴α2相组成。从图1可以看到,片层晶团(Lamellar)占据体积分数约为74%(见表1),分布在片层团的晶界处和片层团内部的白色块状组织为富含元素Nb和Zr的等轴B2(ω)相,分布在层团晶界处的灰色和黑色块状组织分别为富Al的等轴γ相和贫Al富Ti的等轴α2相[7],此3种等轴相的体积分数约占总体积的26%。
图1(b)、(c)和(d)所示分别为1 000、3 000和 10 000 h热暴露后合金4-4-1的背散射SEM像。合金经过1 000、3 000和10 000 h的热暴露后,其微观结构在SEM观察条件下看起来无明显变化。与图1(a)相比,合金中白色的B2(ω)相的体积分数似稍有增多,与此相应,α2+γ片层晶团体积分数稍微减少,而等轴γ和等轴相的α2相体积分数几乎没有变化。热暴露过程中合金各组成相的体积分数的变化和α2+γ晶团尺寸的变化统计结果均列于表1。利用下面的公式对统计数据进行了95%置信度条件下的误差(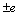 )分析:
)分析:
 (1)
(1)
式中:t为系数,t=2;S为标准差;N为测量次数。表1中还列出了不同高温热暴露时间的α2+γ层片晶团的尺寸。可以看出,α2+γ层片晶团的尺寸在10 000 h的长期热暴露过程中无明显改变。

图1 合金4-4-1的微观组织随热暴露时间变化的背散射SEM像
Fig.1 Back scattered SEM images of alloy 4-4-1 exposured in air at 700 ℃: (a) 0 h; (b) 1 000 h; (c) 3 000 h; (d) 10 000 h
表1 合金4-4-1热暴露过程中显微体积分数和尺寸
Table 1 Volume fractions and sizes of microstructural constituents in alloy 4-4-1 exposured in air at 700 ℃
在扫描电镜的BSE模式下高放大倍数下观察发现,700 ℃长期热暴露对在α2+γ片层晶团晶界处偏聚的等轴B2(ω)晶粒产生了明显的影响。如图2(a)所示,热暴露前,在热等静压条件下形成的B2(ω)等轴晶粒具有胞状组织的特征,尺寸为10 μm的晶粒其实是由若干个微米级别的B2(ω)胞组成,胞与胞之间分布着硬脆的ω颗粒,形成胞壁。前期采用TEM详细观察相结构发现,这种微米胞是B2+ω共生有序相结构,其中胞内的ω相为B82六方有序结构,而分布于胞壁的ω相却是一种有序度更高的D88相结构,而且胞壁处的B2+ω较胞内B2+ω更富集Nb和Zr[10]。在经历 5 000 h的高温热暴露后,如图2(b)所示,这些B2(ω)胞状结构胞壁处具有D88相结构的颗粒明显长大。此外,在B2(ω)晶内还有微米级别深色的贫Nb和Zr、但富Al的ω相形成。这种γ相在热暴露过程中从原先的B2(ω)晶内生成的现象在以前的研究中已经报道过[11]。
图3(a)采用TEM明场技术,揭示了这种B2(ω)共生有序的胞状结构的组织形貌。可以看出,这些微米胞的表面平滑,胞壁却因聚集微小尺寸的D88型ω颗粒而显得粗糙。图3(b)所示为取自平滑胞内的选区电子衍射谱,证实胞内的ω相为B82六方有序结构,有关相结构鉴定的具体细节可参考文献[8]。图3(c)所示的TEM明场像进一步揭示,经5 000 h热暴露后,在平滑的B2(ω)胞内也析出了很多细小的具有D88相结构的ω颗粒(如箭头所指),该图同样也显示了微米级别的γ相从B2(ω)晶内析出的事实。图3(d)所示为取自含有细小ω颗粒的胞内部选区的电子衍射谱。和图3(b)对比可以看出,经历700 ℃、5 000 h的大气热暴露后,析出的ω相是D88相结构,具有比B82六方有序结构更高的有序程度。

图2 合金4-4-1的B2(ω)等轴晶粒在700 ℃大气热暴露0 h和5 000 h的BSE像
Fig.2 BSE images of equiaxed B2(ω) grains in alloy 4-4-1 before exposure (a) and after 5 000 h exposure in air at 700 ℃(b)

图3 合金4-4-1的B2(ω)等轴晶粒中胞状结构在700 ℃大气热暴露0 h和5 000 h的TEM明场像和B2(ω)胞内的选区电子衍射谱
Fig.3 TEM bright field (BF)images showing cell structure composed of equiaxed B2(ω) grain in alloy 4-4-1 before exposure (a) and after 5 000 h exposure in air at 700 ℃ (c) and selected area diffraction patterns ((b), (d)) in B2(ω) cell
图4所示分别为合金4-4-1未经历热暴露和经历了10 000 h的热暴露时α2+γ层片晶团内的α2+γ层片的TEM明场像。图4(a)显示0 h时晶团内部典型的α2+γ层片相间的组织。由图4可以看出,层片晶团在经历10 000 h热暴露以后,一些较粗的α2 片层发生了分解,形成细小的α2板条并被更细的γ板条分隔开来,如图4(b)中箭头所示,这表明此时发生了α2 → γ相变,由于所有新形成的α2/γ界面与原始的α2/γ界面是平行的,所以,这样的分解被称为“平行分解”。图4中的α2和γ板条的晶体学关系为 //
// 。此时的片层界面基本上是共格的,其界面能量最低[12-13]。产生α2平行分解的热力学原理是:铸造工艺的冷却特点使得该合金中形成了超过平衡态含量的α2相。在高温长时间热暴露时,这种亚稳定的α2相将分解成细小的α2和γ板条,以消除多余α2相,回归平衡[9]。
。此时的片层界面基本上是共格的,其界面能量最低[12-13]。产生α2平行分解的热力学原理是:铸造工艺的冷却特点使得该合金中形成了超过平衡态含量的α2相。在高温长时间热暴露时,这种亚稳定的α2相将分解成细小的α2和γ板条,以消除多余α2相,回归平衡[9]。

图4 合金4-4-1 α2+γ片层经700 ℃大气热暴露0 h和 10 000 h后的TEM明场像
Fig.4 TEM bright field images of α2+γ lamellae of alloy 4-4-1 before exposure (a) and after 10 000 h exposure in air at 700 ℃(b)
仔细观察图4(b)还可以看出,当经历10 000 h热暴露后,在分解中的α2+γ层片条束上形成了一些亚微米尺度的B2(ω)相,如图4(b)中箭头所指的白色块状物,从图4(b)中插入的选区衍射斑点可以证明这种六方相的存在。显然,这些地方的B2(ω)相的生成和长大都是靠消耗相邻的α2+γ板条而形成的,即在此处发生了α2+γ→B2(ω)相变。值得注意的是,在合金4-4-1中很少观察到单个粗大的α2 板条分解成B2(ω)相的现象,即“垂直分解”现象。这与HUANG和CONG[9]在研究合金Ti-44Al-8Nb-1B时得到的结果不同。
图5所示为热暴露0 h和10 000 h后α2+γ层片晶团内层片形貌的典型BSE像。广泛的SEM观察发现,在经历了10 000 h的热暴露后,α2+γ层片晶团中的α2层片的平行分解和α2+γ层片条束上形成B2(ω) 块状相的这两种相变(α2→α2+γ和α2+γ→B2(ω)进行得并不是很普遍。图5(a)显示的白色组织是经热等静压处理后在晶团边界偏聚的B2(ω),但α2+γ层片上没有这种白色的有序共生脆性相。经历10 000 h的热暴露后,并未发现α2片层的广泛分解,虽然有细小的B2(ω)晶块出现在晶团边界,甚至晶团内部。但和合金Ti-Al-8Nb-1B的情况相比[7],这样生成的B2(ω)的体积分数并不高。
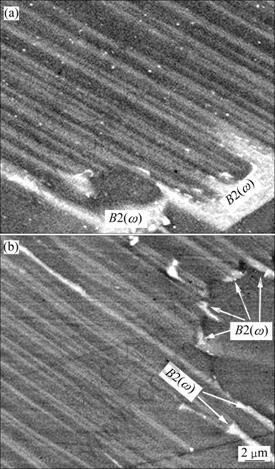
图5 合金4-4-1片层晶团内α2+γ片层组织在700 ℃大气热暴露0 h和10 000 h后的BSE像
Fig.5 BSE images of α2+γ lamellae colonies of alloy 4-4-1 before exposure (a) and after 10 000 h exposure in air at 700 ℃ (b)
2.2 热暴露时间对拉伸性能的影响
合金4-4-1的在室温和700 ℃高温的拉伸性能分别示于图6(a)和(b)。从图6(a)可以看出,合金4-4-1的室温拉伸强度(σ0.1)和0.1%条件屈服强度(σs)相对较高,前者在650 MPa以上,后者也达到了620 MPa。但是,该合金的室温塑性(δ)很差,这和合金4-4-1含有较高体积分数的硬脆的B2(ω)等轴晶粒有关。这些硬脆晶粒主要是偏聚在片层晶团的晶界处。Zr被认为是强烈稳定ω相的元素[14],添加4%(摩尔分数)的Zr使得该合金出现8%(体积分数)的B2(ω)胞状结构,其中,高有序度的ω相(D88型)呈细小颗粒偏聚于胞壁。这样,在硬脆的B2(ω)胞周围形成更脆的ω颗粒组成的网络。这会明显降低合金4-4-1的塑性变形能力。

图6 合金合金4-4-1的拉伸性能
Fig.6 Tensile properties of 4-4-1 alloy exposed at room temperature (a) and 700 ℃ in air (b)
拉伸结果表明,随着高温热暴露时间的增加,合金4-4-1的室温拉伸性能的变化不大,其伸强度基本维持在650 MPa左右,而0.1%条件屈服极限基本维持在630 MPa左右。这说明,合金4-4-1的室温强度对热暴露并不敏感。在室温条件下,合金4-4-1的塑性伸长率的整体水平较低,在长期的700 ℃大气热暴露过程中,室温塑性也一直维持在很低的水平,据此很难判断热暴露的影响。但在700 ℃的高温拉伸实验中(见图6(b))可以观察到,合金4-4-1的塑性伸长率随热暴露时间增加而呈逐渐下降的趋势。同时,700 ℃的拉伸强度和0.1%条件屈服极限也随热暴露时间略有降低。根据显微组织的变化,合金4-4-1塑性持续下降的主要原因应该是晶界偏聚的B2(ω)胞状结构在热暴露过程中的变化。如前所述,随着大气热暴露时间的增加,B2(ω)胞周围形成硬脆的颗粒开始逐渐粗化,而且在胞内也大量析出硬脆的D88型ω颗 粒[15]。这些均对合金4-4-1的塑性变形能力不利。对显微组织的观察认为,这种热暴露脆化与α2+γ层片晶团内α2层片的平行分解和α2+γ层片熔合形成B2(ω)块状相关系不大。因为这两种相变在合金4-4-1中进行得并不广泛。
2.3 热暴露时间对疲劳性能的影响
合金4-4-1在经过一系列的热暴露后的四点弯曲室温疲劳(S—N)曲线如图7所示。由图7可以看出,在未进行热暴露的情况下,它的最大应力—疲劳周次关系处于较低的应力水平,热暴露后,该关系对应的应力值呈现增加的趋势,而这个趋势在10 000 h的热暴露后变得更为明显。这样看来,合金4-4-1的疲劳抗力对长期高温热暴露所出现的显微组织的变化并不特别敏感,包括B2+ω的脆化变化、α2+γ层片晶团内α2层片的平行分解和α2+γ层片熔合形成B2(ω)块状相均未对合金4-4-1的疲劳强度构成伤害。相反,该合金出现了一种“热暴露疲劳强化”现象。目前的工作尚难对这种强化现象给出合理的解释。这种现象的具体原因需要进一步研究。

图7 合金4-4-1的疲劳性能
Fig.7 Fatigue properties of alloy 4-4-1
但是,仔细观察疲劳实验数据发现,热暴露后,样品断裂时的最大应力表现出较大幅度的波动。如图7所示,在1 000 h热暴露后,在490 MPa最大应力作用下,该样品的寿命可以不足104而也可超过107周次。同时也发现,在5 000 h热暴露后,在同样的最大应力作用下,样品的疲劳寿命可以小于104,也可以大于107。10 000 h后,疲劳数据的分散程度更为明显。这表明,在实验过程中,合金4-4-1的疲劳性能数据受到了多种因素的影响。这些因素包括样品加工缺 陷、最大受力面上的缺陷、样品最大受力面上可能存在的粗大硼化物、晶界处的等轴晶粒以及样品边缘的加工缺陷等。它们往往可能成为微裂纹萌生源,其作用甚至可以掩盖热暴露过程中的“组织脆化”对疲劳抗力的作用,从而使得疲劳断裂的数据出现如此的分散现象。
3 结论
1) 合金4-4-1在热等静压条件下呈现典型的近片层组织,该组织由大量的α2+γ层片晶团、分布在层片晶团晶界处的少量B2(ω)相和γ相和更少量的等轴α2相组成。
2) 经过长时间的热暴露,合金中B2(ω)相的体积分数稍有增加,α2+γ片层晶团体积分数稍微减少,而等轴γ相和等轴α2相的体积分数无明显变化。
3) 合金中的B2(ω)相具有胞状组织特征,其中胞内ω相为B82六方有序结构,胞壁处ω相却是一种有序度更高的D88相结构。长期的大气高温热暴露导致胞壁处具有D88相结构颗粒明显长大,且胞内也析出大量具有D88相结构的颗粒。此外,在B2(ω)晶内还有微米级别的ω相形成。
4) 经过10 000 h的热暴露以后,在合金中的α2+γ层片晶团中会发生两种相变(α2→γ和α2+γ→B2(ω)),这表明合金Ti-44Al-4Nb-4Zr-0.2Si-1B中的α2+γ层片组织比合金Ti-44Al-8Nb-1B中的层片组织稳定。
5) 在10 000 h的热暴露过程中,合金的拉伸强度和0.1%条件屈服强度变化不大,始终保持在较高水平,然而塑性伸长率明显降低。这与B2(ω)胞状组织内脆性的ω颗粒的明显长大和相结构变化有关。
6) 经过10 000 h热暴露处理以后,合金的室温疲劳极限并没有因合金脆性增加而降低。相反,还有所提高。
REFERENCES
[1] CHAN K S, WANG P, BHATE N, KUMAR K S. Intrinsic and extrinsic fracture resistance in lamellar TiAl alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52(15): 4601-4614.
[2] 张永刚, 韩雅芳, 陈国良. 金属间化合物结构材料[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2001: 705.
ZHANG Yong-gang, HAN Ya-fang, CHEN Guo-liang. Intermetallic compound material of construction[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industrial Press, 2001: 705.
[3] KUMPFERT J, KIM Y W, DIMIDUK D M. Effect of microstructure on fatigue and tensile properties of the gamma TiAl alloy Ti-46.5Al-3.0Nb-2.1Cr-0.2W[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1995, 192/193: 465-473.
[4] CHAN K S, KIM Y W. Effects of lamellae spacing and colony size on the fracture resistance of a fully-lamellar TiAl alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1995, 43(2): 439-451.
[5] 贺跃辉, 黄伯云, 周科朝. TiAl基合金显微组织对高温拉伸力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 1997, 7(1): 75-79.
HE Yue-hui, HUANG Bai-yun, ZHOU Ke-chao. Effects of microscopic structure on high temperature tensile mechanical property of TiAl-based alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1997, 7(1): 75-79.
[6] 张喜燕, 赵永庆, 白晨光. 钛合金及应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005: 145-151.
ZHANG Xi-yan, ZHAO Yong-qing, BAI Chen-guang. Titanium alloy and application[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005: 145-151.
[7] CHENG T T, LORETTO M H. The decomposition of the beta phase in Ti-44Al-8Nb and Ti-44Al-4Nb-4Zr-0.2Si alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 1998, 46(13): 4801-4819.
[8] 王桂生, 田荣璋. 钛的应用技术[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2007: 82-86.
WANG Gui-sheng, TIAN Rong-zhang. Applied technology of titanium[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2007: 82-86.
[9] HUANG Ze-wen, CONG Tao. Microstructural instability and embrittlement behaviour of an Al-lean, high-Nb γ-TiAl based alloy subjected to a long-term thermal exposure in air[J]. Intermetallics, 2010, 18: 161-172.
[10] HUANG Ze-wen. Ordered ω phases in a 4Zr-4Nb-containing TiAl-based alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2008, 56: 1689-1700.
[11] CHENG T T. Effects of thermal exposure on the microstructure and properties of α γ-TiAl based alloy containing 44Al+4Nb+ 4Zr+0.2Si+0.3B[J]. Intermetallics, 1999, 7: 995-999.
[12] APPEL F, BEAVEN P A, WAGNER R. Deformation processes related to interfacial boundaries in two-phase gamma-titanium aluminides[J]. Acta Metall Mater, 1993, 41: 1721-1725.
[13] APPEL F, BROSSMANN U, CHRISTOPH U, EGGERT S, JANSCHEK P, LORENZ U, MULLAUER J, OEHRING M, PAUL J D H. Recent progress in the development of gamma titanium aluminide alloys[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2000, 11(2): 699-720.
[14] JIANG H, HU D, WU X. Thermal stability of the omega phase in Zr-containing TiAl alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 475: 134-138.
[15] 孙红亮, 叶 飞, 黄泽文, 朱得贵. 等温热锻对铌锆TiAl合金组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属, 2009, 33(4): 472-476.
SUN Hong-liang, YE Fei, HUANG Ze-wen, ZHU De-gui. Effect of isothermal forging on microstructure and mechanical properties of 44Al+4Nb+4Zr+0.2Si+1B alloys[J]. Rare Metals, 2009, 33(4): 472-476.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50971106)
收稿日期:2010-10-26;修订日期:2011-04-02
通信作者:黄泽文,教授;电话:13679083423;E-mail: zxl200402040113@163.com