矿物的解理性质及表面能:各向异性的表面断裂因素
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2014年第9期
论文作者:高志勇 孙 伟 胡岳华
文章页码:2930 - 2937
Key words:surface broken bonds; cleavage; surface energy; pyrite; sphalerite; cassiterite; rutile; hematite
摘 要:利用Materials Studio 软件计算研究几种属于立方、四方、六方或单斜晶系等不同晶系的典型硫化矿、氧化矿和含氧酸盐矿物的表面断裂键性质,分析这些矿物的解理特性,并建立表面断裂键密度与表面能的关系。结果表明:表面断裂键性质可以用来预测大部分矿物的解理特性,预测结果与文献报道一致。对于某种矿物,表面断裂键的密度与表面能成正比,决定系数R2皆大于0.8,表明表面断裂键的密度大小是决定表面能的关键因素。同时,表面断裂键的数目可用来预测矿物表面的稳定性及表面原子的反应活性。
Abstract: The population of surface broken bonds of some typical sulfide, oxide and salt-type minerals which may belong to cubic, tetragonal, hexagonal, or orthorhombic system, were calculated. In terms of the calculation results, the cleavage natures of these minerals were analyzed, and the relationship between surface broken bonds density and surface energy was also established. The results show that the surface broken bonds properties could be used to predict the cleavage nature of most of minerals, and the predicted cleavage planes agree well with those reported in previous literature. Moreover, this work explored a rule that, surface broken bonds density is directly related to surface energy with determination coefficient (R2) of over 0.8, indicating that the former is a dominant factor to determine the latter. Therefore, anisotropic surface broken bonds density can be used to predict the stability of mineral surface and the reactivity of surface atoms.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 2930-2937
Zhi-yong GAO, Wei SUN, Yue-hua HU
School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 30 August 2013; accepted 3 December 2013
Abstract: The population of surface broken bonds of some typical sulfide, oxide and salt-type minerals which may belong to cubic, tetragonal, hexagonal, or orthorhombic system, were calculated. In terms of the calculation results, the cleavage natures of these minerals were analyzed, and the relationship between surface broken bonds density and surface energy was also established. The results show that the surface broken bonds properties could be used to predict the cleavage nature of most of minerals, and the predicted cleavage planes agree well with those reported in previous literature. Moreover, this work explored a rule that, surface broken bonds density is directly related to surface energy with determination coefficient (R2) of over 0.8, indicating that the former is a dominant factor to determine the latter. Therefore, anisotropic surface broken bonds density can be used to predict the stability of mineral surface and the reactivity of surface atoms.
Key words: surface broken bonds; cleavage; surface energy; pyrite; sphalerite; cassiterite; rutile; hematite
1 Introduction
The comprehensive and efficient utilization of complicated, low grade, fine-grained and refractory mineral resources is a world-wide thorny problem in the field of mineral processing. Froth flotation, a surface-chemistry based method, is used largely in mineral separation operations. Adjustment and modification of the mineral surface properties (hydrophobicity particularly) play a dominant role in achieving efficient and selective flotation separation of complex minerals [1].
Surface broken bonds property of a certain mineral, as the primary surface property after its cleavage and/or fracture in the external stress, i.e. crushing and grinding, attracted some attention in recent years. MOON and FUERSTENAU [2] calculated the broken bonds population and broken ionic bond strength per unit area at four spodumene surfaces, and concluded that the cleavage of spodumene occurred along the weakest {110} plane. The continuative study by RAI et al [3] revealed that each Al site on {110} surface had two dangling bonds as compared to only one bond on {001}, resulting in the preferential chemisorption of oleate on {110} surface. XU et al [4] reported that the decreasing number of Mn—O or Fe—O broken bonds on {001}, {010}, and {100} surfaces of ferberite reflected the order of decreasing hydrophobicity of these crystal surfaces in sodium oleate solutions. HU et al [5] demonstrated in previous reports that, for diaspore and aluminosilicate minerals, the presence of broken (dangling) bonds affected the physicochemical properties of the cleaved surfaces and their interactions with flotation reagents, which in turn determined flotation separation performance [5]. To be specific, the ratio of the Al—O to Si—O broken bonds per unit area on edge surface was in the order of diaspore >> kaolinite > illite > pyrophyllite, which reversed the order of hydrophobicity of these minerals in cationic surfactant solutions. The latest work by GAO et al [6] and HU et al [7] indicated that surface broken bonds density was directly proportional to surface energy for calcium-containing minerals, namely scheelite, calcite and fluorite. Moreover, with the aid of the calculation results concerning surface broken bonds and surface energy, the commonly exposed surfaces of these three minerals were predicted and confirmed by XRD analysis. COOPER and de LEEUW [8] suggested that the adsorption of one water molecule on Ca site (with two broken bonds) of {001} surface of scheelite releases the energy of 22.1 kJ/mol using atomistic simulations, while on Ca atom with 4 dangling bonds of {103} surface, an average of 78.2 kJ/mol was released as a result of one water molecule adsorption. LONGO et al [9] concluded that the under-coordination number at Ca atom could be used to explain the stability order of {101} and {001} scheelite surfaces, since the three broken bonds per Ca atom on {101} surface induced more distortions than two dangling bonds per Ca site on {001}.
Given the above, anisotropic surface broken bonds can be used to predict the cleavage nature and morphologies of mineral crystal, to evaluate the reactivity of mineral surface species, and to account for the anisotropic adsorption and wetting behaviors of water and flotation reagents on mineral surfaces. This work will focus on the anisotropic surface broken bonds of several typical sulfide, oxide, and salt-type minerals which may belong to cubic, tetragonal, hexagonal, or orthorhombic system, in an attempt to build the relationship between surface broken bonds density and surface energy, and to establish the validity and suitability of calculation of surface broken bonds density for predicting the commonly cleaved or exposed surfaces of these minerals. To be sure, the conclusions in this work will be universal for most of the minerals, and help to improve the understanding of the differences in wetting and adsorption behaviors by flotation reagents on various minerals.
2 Calculation of surface broken bonds
All calculations were performed in Accelrys Material Studio 5.0 (MS) modeling package. The crystal structures of various minerals were built in Build Crystal module using the structure data reported in previous literature, as listed in Table 1.
A range of surface slabs were created from the bulk unit cell of mineral crystal at its Miller indices by cleave surface module in MS. The density of interplanar bonds broken for the creation of a certain surface was calculated according to the equation as follows:
Db=Nb/A (1)
where Db and Nb are the surface broken bonds density and the broken bonds number per unit cell area on a certain surface, respectively; A is mesh area of the surface unit cell.
Taking the galena {100} surface for example, the number of surface broken bonds could be evaluated as follows. As shown in Fig. 1, there are two Pb-S bonds between adjacent two layers within a unit cell along the direction of {100} surface. The mesh area (A) of a unit cell for {100} surface, could be evaluated by U×V×sin θ, while these three parameters (U, V and θ) could be automatically provided by the MS software. The A of {100} surface was calculated to be 0.1762 nm2. Then the surface broken bonds density (Db) of {100} surface could be calculated by 2/0.1762 according to Eq. (1), i.e. 11.35 nm-2.
The general requirements for the creation of a certain surface are as follows: 1) The stronger covalent bonds, such as S—O in barite, should not be broken; 2) The least possible number of cation-anion bonds per unit area should be broken.
Table 1 Lattice parameters used for crystal building for various minerals

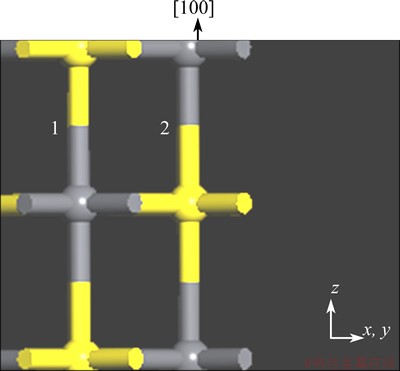
Fig. 1 Side view of {100} surface of galena (one unit cell, Pb=dark gray, S=yellow)
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Relationship between surface broken bonds density and cleavage nature of minerals
3.1.1 Sulfide minerals
Pyrite (FeS2) is the most common sulfide mineral, and has an important (but undesired in most cases) role in the field of mineral processing, as it often coexists with other more valuable minerals such as sphalerite (ZnS) and galena (PbS). It is of great importance to study the surface properties of these three sulfide minerals, so as to achieve the selective separation from each other.
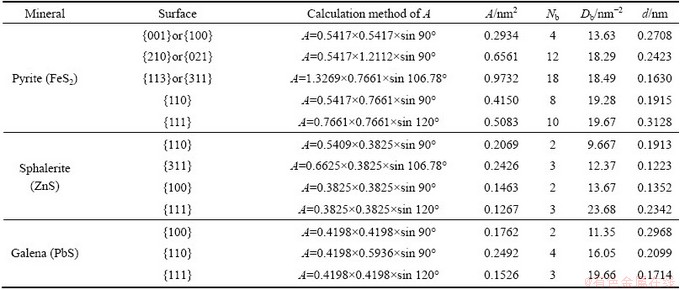
Pyrite consists of both Fe2+—S22- ionic bonds and S—S covalent bonds. It was reported by NESBITT et al [10] that Fe2+—S22- bond energy was greater than 300 kJ/mol while S—S bond energy was a lower value of 245 kJ/mol. Analysis of bond energies indicates that S—S and Fe—S bonds are both likely to be broken when pyrite is cleaved or fractured. For sphalerite and galena, cleavage requires the breaking of only Zn—S or Pb—S bonds. The results of surface broken bonds densities of pyrite, sphalerite and galena, calculated according to Eq. (1), are listed in Table 2.
From Table 2, for pyrite, the surface broken bonds density (Db), follows the order: {111}>{311}>{110}> {021}>>{001}, while the interlayer spacing (d) is in the order: {111}>{001}>{021}>{110}>{311}. COOPER and LEEUW [11] reported that when the mineral particles were crushed in the first stage of flotation process, the minerals would mainly cleave or fracture along surfaces that had large interlayer spacing and few interplanar bonds. The {001} surface has the smallest broken bonds density (Db) and the second largest interlayer spacing (d) of five surfaces calculated, and is expected to be the most common cleavage surface for natural pyrite, which was in good agreement with experimental observations [12,13]. {021} surface, with the second smallest Db and a larger d, is also predicted to be a strong cleavage plane of pyrite. MARIANO and BEGER [14] found that the {021} cleavage pyritohedron was also the most dominant of complementary merohedral forms in pyrite. {111} surface has the largest d and a larger Db, taking into account electrostatic repulsive force between S22-—S- adjacent layers, and hence the cleavage may occur parallel to this surface. MUROWCHICK and BARNES [12] observed some cleavage pyritohedral crystals for pyrite, terminated by {021} surface and to a less extent {111} surface, respectively. {110} and {311} cleavages can rarely occur, which could be explained by their larger surface broken bonds densities and smallest interlayer distances. It was concluded that pyrite cleaves parallel to {001}, {021} and {111} in a decreasing order of rank.
For sphalerite, along the {111}, {311} or {100} surface, the alternating arrangements of Zn2+ layer and S2- layer with each other cause a relatively strong electrostatic attraction between neighbouring layers. In addition, in consideration of its largest broken bonds density, the {111} cleavage cannot be existent, though the interlayer spacing along this surface is the largest. {100} or {311} surface, with the smallest interlayer distance and a moderate broken bonds density, is also rarely seen in sphalerite minerals. {110} surface with stoichiometry and charge neutrality, has the smallest broken bonds density and second largest interlayer spacing of four surfaces calculated as listed in Table 2, and therefore is the only perfect cleavage plane [15].
For galena, the broken bonds density follows the order: {111}>{110}>{100}, while the interlayer spacing decreases in this order: {100}, {110} and {111}. {100} surface has the smallest Db and largest d, and accordingly it is the most prominent cleavage surface when galena minerals are crushed and ground. {110} surface with moderate Db and d, is also a possible fracture plane for galena. Owing to its largest Db and smallest d, {111} cleavage surface is nonexistent.
Table 2 Calculation of surface broken bonds population of different sulfide minerals
3.1.2 Oxide minerals
Cassiterite, rutile, anatase, and hematite are the main mineral ores for the extraction of tin, titanium, and ferrum metals. Therefore, the separation of these minerals with other gangue minerals has been some of the main objects in the field of mineral processing in recent years. As a consequence, it is necessary to investigate the bulk and surface properties of these minerals such as cleavage nature, surface broken bonds rule, and surface energy to further provide theoretical guidance for the efficient concentration of these minerals. The calculation results of surface broken bonds densities of cassiterite, rutile, antase and hematite are listed in Table 3.
Table 3 Calculation of surface broken bonds population of different oxide minerals
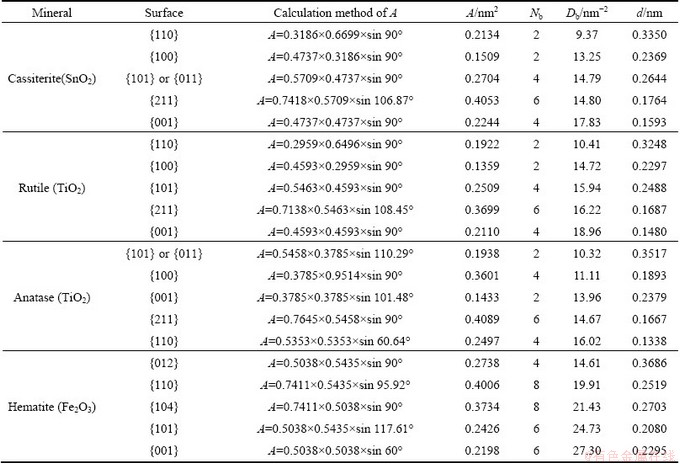
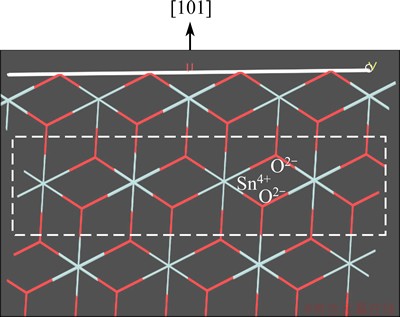
Fig. 2 Side view of {101} surface of cassiterite (Sn = grey blue, O=red)
Cassiterite has a rutile-type tetragonal structure. In this structure each tin (or titanium) cation is surrounded by six oxygen atoms in an octahedron, while each oxygen anion has a trigonal planar coordination to three surrounding tin (or titanium) atoms. As listed in Table 3, for cassiterite (SnO2) and rutile (TiO2), the order of broken bonds densities of five surfaces is as follows: {001}>{211}≥{101}>{100}>{110}. The interlayer distance decreases in the order: {110}>{101}>{100}> {211}>{001}. Taking cassiterite for instance, the {110} surface of charge neutrality, with the smallest Db and largest d of five surfaces considered, is the excellent cleavage plane. {101} or {100} surface is built up from O2-—Sn4+—O2- triple layers of 0.2644 or 0.2369 nm distance and terminated by oxygen ions, as shown in Fig. 2. Because of the electrostatic repulsion of adjacent O2- layers between two triple layers and a relatively large d and small Db, {101} and {100} cleavages can easily occur in cassiterite. {211} surface possesses a comparatively lower Db, leading to a very weak cleavage parallel to this surface in the presence of external stress. {001} cleavage cannot occur as a result of its largest Db and lowest d. In brief, the predominant cleavage in cassiterite is {110}, followed by moderate {100} and {101}, and finally a very weak {211}. Obviously, rutile has the same cleavage nature as cassiterite.
Compared to rutile, anatase has both an identical molecular formula and a different crystal structure. Table 3 also shows that, for anatase, the density of surface broken bonds follows the order: {110}>{211}>{001}> {100}>{101}, while the interplanar distance increases in the order: {110}<{211}<{100}<{001}<<{101}. Along the direction of {101} surface, the interlayer spacing is the largest, and the cleavage requires the breaking of the lowest bonds number per unit area of five surfaces calculated. Accordingly, {101} surface is the dominant cleavage plane of anatase. {100} surface possesses the second smallest Db and the moderate d, and consequently the cleavage can occur parallel to this surface. {001} surface has the second largest d and moderate Db, and this cleavage also can occur in the presence of external stress. {211} and {110} cleavage can rarely occur due to their highest Db and smallest d among five surfaces. It can be concluded that the predominant cleavage in anatase is {101} surface followed by moderate {100} and {001} surfaces.
For hematite, the surface broken bonds density follows the order: {001}>{101}>{104}>{110}>{012}, while the interlayer spacing decreases in the order: {012}>{104}>{110}>{001}>{101}, as listed in Table 3. {012}, {104} and {110} surfaces are built from alternating electroneutral O—Fe—O—Fe—O unit layers with largest interlayer spacings of all the surfaces considered, i.e., 0.3686, 0.2703 and 0.2519 nm, respectively. Owing to their lower densities of surface broken bonds and the electrostatic repulsion of adjacent O2- layers between two electroneutral unit layers, it is relatively easy for hematite to fracture parallel to {012}, {104} and {110} planes, though the literature reported that hematite had no distinct cleavage. Along {001} and {101} surfaces, the alternating arrangements of Fe3+ layer and O2- layer with each other cause a stronger electrostatic attraction between two adjacent layers. In addition, the largest Db also prohibits the cleavage or fracture to occur parallel to {001} and {101} planes. It should be noted that there is a dipole moment perpendicular to {001} or {101} surface formed by alternate layers of Fe3+ and O2-. Therefore, this dipolar surface is likely to be less stable. While dipolar surfaces can exist, and this normally leads to twinning of crystals to remove the dipole. That is why hematite usually exhibits {001} and {101} twinning types and shows a well-defined parting parallel to {001} and {101} planes. In this context, {012} and {104} surfaces could be considered the commonly exposed planes for hematite mineral particles.
3.1.3 Salt-type minerals
The latest research shows that, for the minerals containing tungstate and carbonate poly-anions, namely scheelite and calcite, the surface broken bonds density can be used to predict their commonly exposed cleavage planes [6,7]. Here, barite, another poly-anion bearing mineral, was chosen to verify the accuracy of the above conclusion.
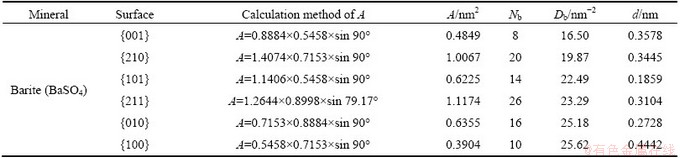
In barite bulk structure, each barium atom is coordinated by twelve oxygen atoms belonging to seven separate sulphate groups, while each oxygen atom is four-coordinated to three neighboring calcium atoms and one sulphur atom. As listed in Table 4, the surface broken bonds density of barite follows the order: {100}>{010}>{211}>{101}>{210}>{001}, while the interlayer spacing decreases in the order: {100}>{001}>{210}>{211}>{010}>{101}. All the six surfaces are of stoichiometry and charge neutrality. {001} and {210} surfaces have the smallest Db and much larger d among the six surfaces, and naturally are the perfect cleavage planes of barite minerals. {211} surface with a moderate Db and d, could be secondary cleavage plane of barite as a complementary form of {210} cleavage. {101} has the lowest d among six surfaces calculated and moderate Db, accordingly the cleavage cannot easily occur parallel to this direction. In consideration of the highest Db, {010} and {100} cleavages are hard to exist.
Table 4 Calculation of surface broken bonds population of salt-type mineral
3.2 Relationship between surface broken bonds density and surface energy of minerals
When a certain mineral surface was cleaved, surface species lost certain coordinate bonds with the surrounding atoms, and hence became under- coordinated. Consequently, this surface was unstable and had the tendency to adsorb foreign species. Generally speaking, the stability of the surface with or without adsorbed species depends on its surface energy. Surface energy, in turn can be assumed to be directly related to the bond energy and the number of broken bonds on the surface. It is clear that, in moving forward, for a certain mineral that has one type of bonds broken when cleaved, surface energy is a function of the density of surface broken bonds on the surface.
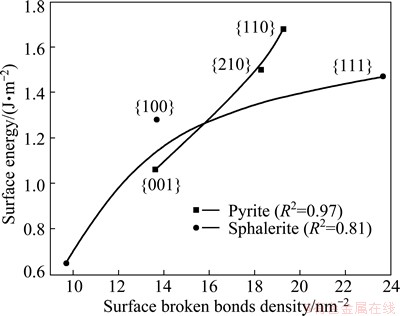
Fig. 3 Relationship between surface energy and surface broken bonds density of sulfide minerals
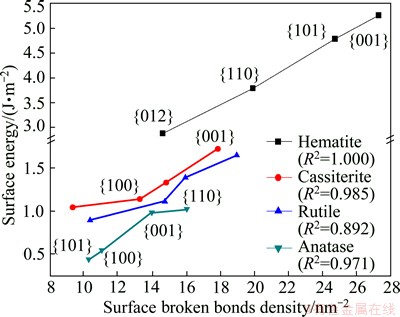
Fig. 4 Relationship between surface energy and surface broken bonds density of oxide minerals
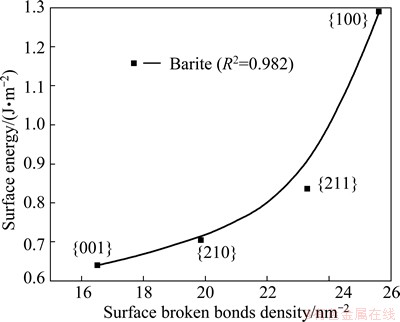
Fig. 5 Relationship between surface energy and surface broken bonds density of salt-type mineral
Using the previous published data [16-24], concerning surface energies of the minerals considered in this study, the relationship between surface energy and surface broken bonds density was evaluated and confirmed, as shown in Figs. 3-5. These figures clearly show that surface energies reported in literature are positively correlated with the densities of surface broken bonds calculated in this work, with determination coefficients of over 0.8. This implies that the number of broken bonds on the surface serves as a predominant factor that determines surface energy of the minerals considered in this study which may belong to cubic, tetragonal, hexagonal, or orthorhombic system. In addition, the latest study on fluorite, calcite and scheelite [6,7] also confirmed to the above finding. It is tenable to conclude that this is a universal rule which may apply to most of minerals.
Surface energy is commonly given by half the energy needed to cut a given crystal into two half crystals, and thus it provides a measure of the thermodynamic stability of a cleavage plane. In this way, the density of surface broken bonds and surface energy could be both used as a good measure to predict the cleavage nature and surface reactivity of minerals. However, compared to the calculation of surface broken bonds, the determination of surface energy is more costly and time-consuming [25]. Thus, compared to surface energy, the density of surface broken bonds is a better measure for the cleavage property and surface stability for a certain mineral with a relatively simple formula, and may provide a check on the accuracy of surface energy calculations.
3.3 Interpretation for reactivity of surface atom using surface broken bonds properties
The stability of a surface without adsorbed species depends on its surface energy. And surface energy is directly related to the strength and number of broken (dangling) bonds on the surface. It is acceptable to conclude that the reactivity of a surface atom arises from the unsatisfied valence or dangling bonds caused by the creation of this surface. For instance, COOPER and LEEUW [11] reported that on scheelite {101} and {103} surfaces, a methanoic acid molecule interacted with one surface calcium atom through its carbonyl oxygen atom. The adsorption of a mechanoic acid molecule on {103} surface releases more energy (138 kJ/mol) than that on {101} surface (102 kJ/mol). Since there is no steric hindrance existing during the adsorption process, the distinction in adsorption energy may be attributed to the different reactivity of calcium atoms on these two surfaces. It is easy to found that when creating the surfaces, the calcium ion on {101} surface loses three coordinate bonds to oxygen atoms, while for calcium ion on {103} surface, four bonds is lost. Therefore, the calcium on {103} surface is more reactive than that on {101} surface, leading to a more adsorption energy when a methanoic acid molecule is adsorbed.
4 Conclusions
1) The population of surface broken bonds of some typical sulfide, oxide and salt-type minerals which may belong to cubic, tetragonal, hexagonal, or orthorhombic system, were calculated in this work, through which the cleavage natures of these minerals were analyzed. This work shows that the anisotropic surface broken bonds could be used to correctly predict the cleavage nature of most of minerals, and the predicted cleavage planes accord well with those reported in previous literature.
2) The relationship between surface broken bonds density calculated in this work and surface energy published in previous literature, was established. It was found that surface broken bonds density was directly proportional to surface energy with determination coefficients of over 0.8, demonstrating that the former was a dominant factor determining the latter.
3) Compared to surface energy, anisotropic surface broken bonds is a better measure for the cleavage property and surface stability for a certain mineral with a relatively simple formula, and may provide a new idea for the evaluation of reactivity of surface atom.
References
[1] BRAGGS B, FORNASIERO D, RALSTON J, SMART R S. The effect of surface modification by an organosilane on the electrochemical properties of kaolinite [J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 1994, 42(2): 123-136.
[2] MOON K S, FUERSTENAU D W. Surface crystal chemistry in selective flotation of spodumene (LiAl[SiO3]2) from other aluminosilicates [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2003, 72(1-4): 11-24.
[3] RAI B, SATHISH P, TANWAR J, PRADIP, MOON K S, FUERSTENAU D W. A molecular dynamics study of the interaction of oleate and dodecylammonium chloride surfactants with complex aluminosilicate minerals [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2011, 362(2): 510-516.
[4] XU Z, HU Y, LI Y. Electrokinetics and wettability of huebnerite and ferberite [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1998, 198(2): 209-215.
[5] HU Y, LIU X, XU Z. Role of crystal structure in flotation separation of diaspore from kaolinite, pyrophyllite and illite [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2003, 16(3): 219-227.
[6] GAO Z, SUN W, HU Y, LIU X. Anisotropic surface broken bond properties and wettability of calcite and fluorite crystals [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(5): 1203-1208.
[7] HU Y, GAO Z, SUN W, LIU X. Anisotropic surface energies and adsorption behaviors of scheelite crystal [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2012, 415: 439-448.
[8] COOPER T G, de LEEUW N H. A combined ab initio and atomistic simulation study of the surface and interfacial structures and energies of hydrated scheelite: introducing a CaWO4 potential model [J]. Surface Science, 2003, 531(2): 159-176.
[9] LONGO V M, GRACIA L, STROPPA D G, CAVALCANTE L S, ORLANDI M, RAMIREZ A J, LEITE E R, ANDRES J, BELTRAN A, VARELA J A, LONGO E. A joint experimental and theoretical study on the nanomorphology of CaWO4 crystals [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(41): 20113-20119.
[10] NESBITT H W, BANCROFT G M, PRATT A R, SCAINI M J. Sulfur and iron surface states on fractured pyrite surfaces [J]. American Mineralogist, 1998, 83(9-10): 1067-1076.
[11] COOPER T G, de LEEUW N H. A computer modeling study of the competitive adsorption of water and organic surfactants at surfaces of the mineral scheelite [J]. Langmuir, 2004, 20(10): 3984-3994.
[12] MUROWCHICK J B, BARNES H L. Effects of temperature and degree of supersaturation on pyrite morphology [J]. American Mineralogist, 1987, 72(24): 1241-1250.
[13] BLANCHARD M, WRIGHT K, GALE J D, CATLOW C R A. Adsorption of As(OH)3 on the (001) surface of FeS2 pyrite: A quantum-mechanical DFT study [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2007, 111(30): 11390-11396.
[14] MARIANO A N, BEGER R M. Cleavage in pyrite and cobalite [J]. The American Mineralogist, 1971, 56(11-12): 1867-1881.
[15] QIN W, JIAO F, SUN W, WANG X, LIU B, WANG J, ZENG K, WEI Q, LIU K. Effects of sodium salt of N,N-dimethyldi- thiocarbamate on floatability of chalcopyrite, sphalerite, marmatite and its adsorption properties [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2013, 421: 181-192.
[16] HUNG A, MUSCAT J, YAROVSKY I, RUSSO S P. Density-functional theory studies of pyrite (100) and (110) surfaces [J]. Surface Science, 2002, 513(3): 511-524.
[17] HUNG A, MUSCAT J, YAROVSKY I, RUSSO S P. Density-functional theory studies of pyrite (111) and (210) surfaces [J]. Surface Science, 2002, 520(1): 111-119.
[18] WRIGHT K, WATSON G W, PARKER S C, VAUGHAN D J. Simulation of the structure and stability of sphalerite ZnS surfaces [J]. American Mineralogist, 1998, 83(1-2): 141-146.
[19] OVIEDO J, GILLAN M J. Energetics and structure of stoichiometric SnO2 surfaces studied by first-principles calculations [J]. Surface Science, 2000, 463(2): 93-101.
[20] PERRON H, DOMAIN C, ROQUES J, DROT R, SIMONI E, CATALETTE H. Optimisation of accurate rutile TiO2 (110), (100), (101) and (001) surface models from periodic DFT calculations [J]. Theoretical Chemistry Accounts, 2007, 117(4): 565-574.
[21] PARKER S C, ALLEN J P, ARROUVEL C, SPAGNOLI D, KERISIT S, SAYLE D C. Molecular simulation of mineral surfaces and the role of impurities on surface stability [J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2007, 916: 268-287.
[22] MACKRODT W C. Atomistic simulation of oxide surfaces [J]. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 1988, 15(3): 228-237.
[23] JONES F, RICHMOND W R, ROHL A L. Molecular modeling of phosphonate molecules onto barium sulfate terraced surfaces [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2006, 110(14): 7414-7424.
[24] JIANG Y, XU C, LAN G. First-principles thermodynamics of metal-oxide surfaces and interfaces: A case study review [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(1): 180-192.
[25] WU W, NANCOLLAS G H. Determination of interfacial tension from crystallization and dissolution data: A comparison with other methods [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 1999, 79(2): 229-279.
高志勇,孙 伟,胡岳华
中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083
摘 要:利用Materials Studio 软件计算研究几种属于立方、四方、六方或单斜晶系等不同晶系的典型硫化矿、氧化矿和含氧酸盐矿物的表面断裂键性质,分析这些矿物的解理特性,并建立表面断裂键密度与表面能的关系。结果表明:表面断裂键性质可以用来预测大部分矿物的解理特性,预测结果与文献报道一致。对于某种矿物,表面断裂键的密度与表面能成正比,决定系数R2皆大于0.8,表明表面断裂键的密度大小是决定表面能的关键因素。同时,表面断裂键的数目可用来预测矿物表面的稳定性及表面原子的反应活性。
关键词:表面断裂键;解理;表面能;黄铁矿;闪锌矿;锡石;金红石;赤铁矿
(Edited by Chao WANG)
Foundation item: Project (50831006) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2012BAB10B05) supported by the National Key Technologies R&D Program of China
Corresponding author: Yue-hua HU; Tel: +86-731-88879299; Fax: +86-731-88830623; E-mail: hyh@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63428-2

