电解工艺对NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷 阳极耐腐蚀性能的影响
来源期刊:中南大学学报(自然科学版)2004年第6期
论文作者:秦庆伟 赖延清 孙小刚 李新征 李劼 刘业翔
文章页码:891 - 895
关键词:铝电解;惰性阳极;金属陶瓷;腐蚀; NiFe2O4
Key words:aluminum electrolysis; inert anode; cermet; corrosion; NiFe2O4
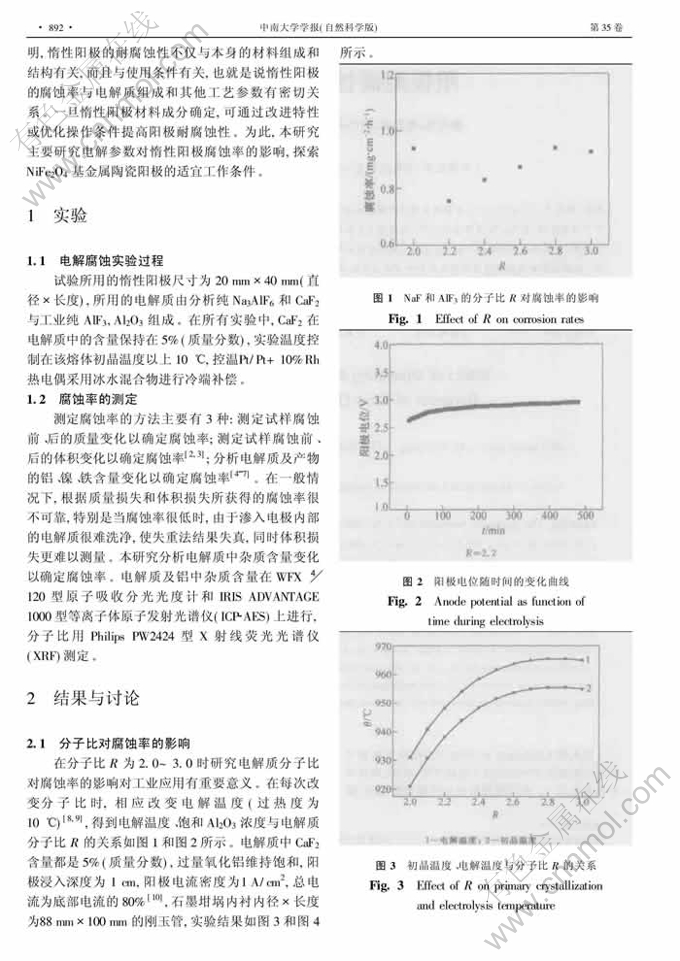
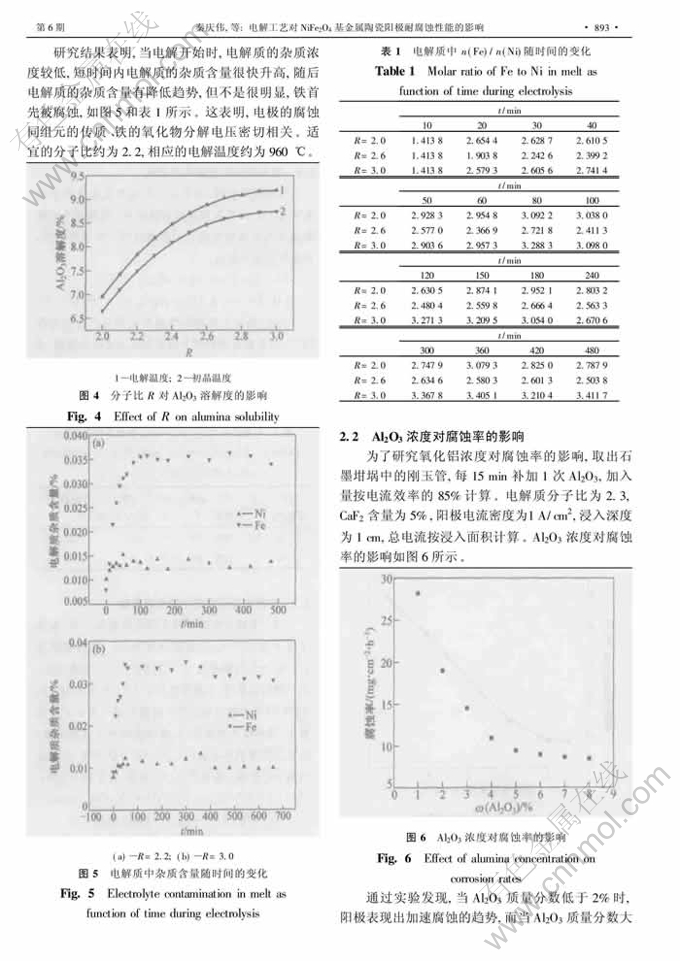
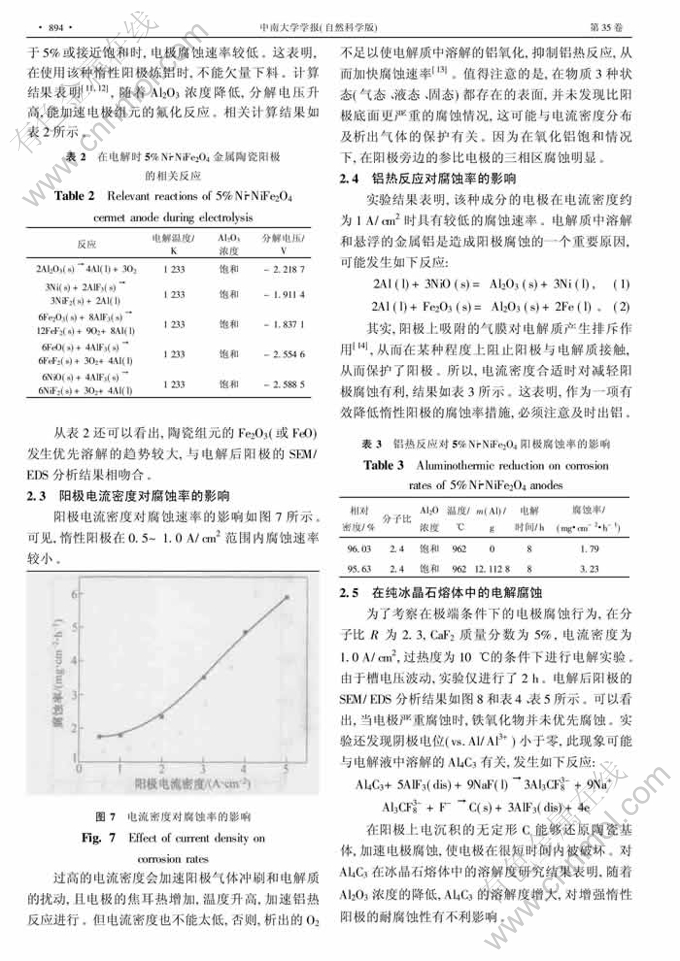
摘 要:研究了5%Ni- NiFe2O4金属陶瓷惰性阳极在冰晶石-氧化铝熔体中的腐蚀行为及电解参数对腐蚀率的影响。研究结果表明:当Al2O3质量分数大于5%或接近饱和时,电极腐蚀率较低;当Al2O3质量分数小于2%时,电极腐蚀加快;当在冰晶石熔体中不加Al2O3时,会发生灾变腐蚀;当分子比为2.2~2.4,电解温度为960℃时,腐蚀率较低;溶解的铝和高电流密度对惰性阳极的正常工作不利,电流密度适当时有利于降低阳极的腐蚀率;导致惰性阳极腐蚀的主要原因有铝热还原,碳化铝的溶解及电沉积、陶瓷基体的氟化反应。
Abstract: The corrosion behavior of 5%Ni- NiFe2O4 inert anodes in cryolite-alumina melts, and the corrosion rates as a function of some operating parameters were investigated. The results showthatthe corrosion rates increase rather slowly with Al2O3 concentration at saturated or above 5%; followed by a sharp increase at low concentrations(<2%). Depletion of alumina may lead to catastrophic corrosion. The anodes perform well in the cryolitic ratio range from2.2 to 2.4 at about 960℃. Dissolved aluminium metal and high current density have a detrimental effect on anode performance. Proper current density is of benefit to decrease corrosion rate.The principal corrosionmechanism appears to be the aluminothermic reductionwith dissolved aluminiummetal, fluoridation of anode matrix and subsequent dissolution in the bath.