文章编号:1004-0609(2011)06-1404-05
Cu/Nb纳米多层膜延性及其断裂行为
张 欣,张金钰,牛佳佳,雷诗莹,刘 刚,孙 军
(西安交通大学 金属材料强度国家重点实验室,西安 710049)
摘 要:通过单轴拉伸试验研究恒定调制周期的聚酰亚胺基体Cu/Nb纳米金属多层膜的延性对调制比的依赖性,并采用聚焦离子束/扫描电子显微镜(FIB/SEM)截面定量表征技术深入分析多层膜的异质约束效应对断裂行为的影响。结果表明:随着调制比的增加,多层膜的延性单调减小,出现由剪切型向张开型断裂模式的转变。当调制比小于某一临界值时,调制周期越小,多层膜延性越高;反之,则多层膜延性越差。这是由于软相Cu层对脆相Nb层中萌生的微裂纹扩展的约束作用。
关键词:纳米金属多层膜;延性;断裂行为;调制比
中图分类号:TG113 文献标志码:A
Ductility and fracture behavior of
Cu/Nb nanostructured multilayers
ZHANG Xin, ZHANG Jin-yu, NIU Jia-jia, LEI Shi-ying, LIU Gang, SUN Jun
(State Key Laboratory for Mechanical Behavior of Materials, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China)
Abstract: The dependent of ductility of polyimide-based Cu/Nb nanostructured metallic multilayers with constant modulation period on the modulation ratio was investigated by uniaxial tensile testing. The heterogeneity restriction effect of the multilayers affecting the fracture behavior was further studied through quantitative focused ion beam(FIB) and scanning electron microscope (SEM) cross-section characterization technique. The results show that the ductility of multilayers decreases with increasing modulation ratio, and the fracture mode transforms from opening to shear mode. When the modulation ratio decreases to less than a critical value, the ductility increases with decreasing modulation period. When the modulation ratio is larger than the critical value, the ductility decreases with decreasing modulation period. This can be attributed to the ductile Cu layer that can arrest the microcracks initiated in the brittle Nb layer.
Key words: nanostructured metallic multilayers; ductility; fracture behavior; modulation ratio
金属多层膜广泛应用于微电子器件中,特别是微电子机械系统(MEMS)的兴起和发展对多层膜的力学和物理性能提出了更高的要求[1-2]。目前,微电子元器件和微机电系统具有多层异质膜结构所用材料尺度逐渐减小到微米至纳米级,即处于宏观与微观之间的的介观范畴,加之其电/热/力的多场环境,材料性能与服役行为的尺度、界面和异质约束效应[3]等愈加凸现,成为影响微器件服役可靠性的重要因素[4],膜/基和多层异质膜结构将因尺寸效应、异质界面约束和多场耦合效应等多种效应表现出不同的损伤失效形式[5-8]。因此,对材料介观性能的表征成为当前材料科学研究的前沿和热点之一。
目前,主要通过对自由膜进行单轴拉伸来直接得到薄膜发生变形损伤的临界应变值[9-10],但是自由膜在制备和进行拉伸实验时存在很大的困难,且自由膜在变形时极易形成局部颈缩导致薄膜早期断裂,难以得到准确的薄膜延性指标。然而,当薄膜沉积在柔性基板上时,基板的均匀大变形将驱动薄膜整体变形,在抑制局部变形的基础上可以很好地反映薄膜的本征延性。柔性基板上金属薄膜材料变形延性的合理表征不但具有理论背景,同样具有很重要的应用背景,例如可用于评价柔性显示器用金属薄膜的变形能力。将多层膜沉积在柔性基板上并进行单轴拉伸,可以得到一个重要的薄膜延性指标——裂纹萌生临界应变(εc)。用裂纹萌生临界应变作为评价薄膜延性的判据比用自由膜的变形损伤的临界应变作为判据更加具有实际意义,因为一旦萌生裂纹,意味着薄膜已产生损伤,同时伴随着传输性能(如电学性能)的突变[11]。对于多层膜延性的尺寸依赖性,更多的是关注其随单层厚度或调制波长的变化规律[10, 12]。ZHANG等[12]对Cu/Cr纳米多层膜延性的研究结果表明,由于软相对硬相中微裂纹扩展的约束抑制,导致多层膜在某一临界调制波长出现最大值。然而,延性随调制比的变化规律研究较少。
目前,尺寸效应对多层膜断裂行为的影响也鲜见深入的研究报道,ZHU等[13]研究调制周期为20 nm的Cu/Ta多层膜单向拉伸变形与断裂行为,发现距裂纹尖端不同位置处发生了位移量为几纳米到几十纳米的剪切位移,进而得出位错在层中运动所需应力随调制周期减小逐渐增大,当调制周期(调制比为1)小于某一临界值时,位错将穿越界面形成剪切型断裂的结论。但对于断裂行为的尺寸依赖性仍缺乏系统深入的研究。综合以上对多层膜研究现状的分析,本文作者以Cu/Nb多层膜作为研究对象,系统研究调制比对其延性的影响,并分析其延性与断裂行为之间的关系。
1 实验
1.1 样品制备及微观结构表征
试验用的Cu/Nb金属多层膜试样是在125 μm厚的聚酰亚胺基体上用UDP450型闭合场非平衡磁控溅射离子镀设备获得的。溅射沉积前,采用1 keV Ar离子轰击清洗基体5 min,磁控溅射的本底真空约为1×10-4 Pa,镀膜偏压为75 V。沉积态的Cu/Nb纳米金属多层膜试样在真空腔中150 ℃退火2 h以稳定组织、消除残余应力。固定样品的总厚度为500 nm,调制波长λ为25和50 nm(λ定义为Nb单层厚度hNb与Cu单层厚度hCu之和,即λ=hCu+hNb),变换调制比η为0.11~3(η为Nb单层厚度hNb与Cu单层厚度hCu之比,即η=hNb/hCu),调制结构通过改变溅射时间来控制。通过7000S 型X射线衍射仪(XRD) (Cu Kα射线,40 mA,40 kV,θ-2θ扫描方式)和JEOL-2100F高分辨透射电子显微镜(HR-TEM)对多层膜的微观结构进行表征。
1.2 单轴拉伸试验
室温下采用Micro-Force Test System (MTS? Tytron 250)对聚酰亚胺基体Cu/Nb多层膜进行单轴拉伸试验,试样标距部分为30 mm×3 mm,应变速率为1×10-4 s-1。拉伸实验采用恒位移控制。薄膜/基体系的载荷及位移数据由试验机和高分辨率激光检测系统自动记录[11, 14]。在拉伸的同时,对试样进行原位电阻测试,得到电阻相对变化率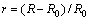 (R为实时电阻,R0为初始电阻)随应变的变化曲线,如图1所示。在小应变裂纹萌生以前可认为薄膜始终处于纯弹性变形。电阻相对变化与应变大致成线性关系。而产生微裂纹后,薄膜的电阻将显著增大,电阻相对变化率随应变的变化曲线将偏离原来的线性部分,此时可定义偏离点的应变为εc,如图1所示,定义这一点为裂纹萌生临界应变εc[11]。通过测试不同调制比下多层膜的裂纹萌生临界应变,即可得到延性随调制比的变化规律。通过FEI双束聚焦离子束/扫描电子显微镜(FIB/SEM)截面定量表征技术观察Cu/Nb多层膜的裂纹形貌,从而深入分析其断裂行为。
(R为实时电阻,R0为初始电阻)随应变的变化曲线,如图1所示。在小应变裂纹萌生以前可认为薄膜始终处于纯弹性变形。电阻相对变化与应变大致成线性关系。而产生微裂纹后,薄膜的电阻将显著增大,电阻相对变化率随应变的变化曲线将偏离原来的线性部分,此时可定义偏离点的应变为εc,如图1所示,定义这一点为裂纹萌生临界应变εc[11]。通过测试不同调制比下多层膜的裂纹萌生临界应变,即可得到延性随调制比的变化规律。通过FEI双束聚焦离子束/扫描电子显微镜(FIB/SEM)截面定量表征技术观察Cu/Nb多层膜的裂纹形貌,从而深入分析其断裂行为。

图1 柔性基体上薄膜延性的电阻变化
Fig.1 Ductility of polymer-supported metal films by electrical resistance method
2 结果与分析
2.1 微观结构
图2所示为不同调制比Cu/Nb多层膜(λ=50 nm)的XRD谱。Cu层呈现(111)和(200)的取向,而Nb层具有(110)择优取向。随着调制比η的减小,Nb(110)减弱为漫散峰,呈现纳米晶的结构特征。其中Nb(110)峰往小角度方向偏移,而其他峰的偏移情况并不明显。这主要是由于Cu的原子体积(7.1 cm3/mol)明显小于Nb的原子体积(10.87 cm3/mol),在Cu往Nb层上溅射的过程中,Cu原子会不可避免地进入Nb的晶格中,造成Nb层中原子间距增大,从而导致Nb(110)衍射峰往小角度方向偏移,因此在界面处会出现一定厚度(约1.5 nm)的混合层[15-16]。
图3所示为Cu/Nb多层膜截面的TEM像和相应的选区电子衍射斑(SADP)。多层膜各层均匀连续、相互交替,具有良好的周期调制结构(其中深色区为Cu层,浅色区为Nb层)。其中Cu层呈柱状纳米晶,Nb层呈极细小的纳米晶。晶粒尺寸随着单层厚度的减小而减小。从SADP(见图3中插图)可以看出,Cu层呈现(111)择优取向,Nb层呈现(110)择优取向,与XRD谱的结果相符。
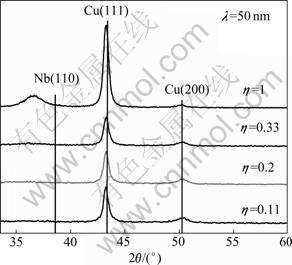
图2 调制波长为l=50 nm 的Cu/Nb 纳米金属多层膜的XRD谱
Fig.2 XRD patterns of Cu/Nb nanostructured metallic multilayers with modulation wavelength λ=50 nm
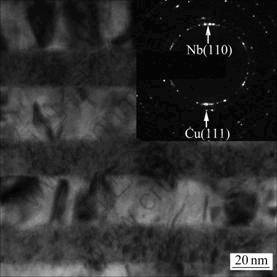
图3 Cu/Nb多层膜的截面TEM像(l =50 nm, h =1)
Fig.3 TEM image showing cross-section view of Cu/Nb multilayers (l = 50 nm, h =1)
2.2 多层膜延性及断裂行为
图4所示为调制周期分别为25 nm和50 nm的Cu/Nb纳米多层膜裂纹萌生临界应变(εc)随调制比的变化规律。由图4可以看出,在调制波长一定的情况下,多层膜的延性随着调制比的增加而单调减小。从图4中可以看出,当调制比小于0.5时,调制周期为25 nm的Cu/Nb多层膜的延性高于调制周期为50 nm的Cu/Nb多层膜的;反之,当调制比大于0.5时,后者的延性低于前者的。

图4 Cu/Nb纳米多层膜裂纹萌生临界应变(εc)随调制比h的变化规律(l=25 nm和50 nm)
Fig.4 Dependence of εc on modulation ratio η for Cu/Nb nanomultilayers (l=25 nm and 50 nm)
Cu/Nb多层膜在变形过程中,微裂纹始于脆相Nb层中,进一步的扩展则受到周围延性较好的Cu层的抑制[5]。而微裂纹扩展能否被抑制取决于以下两方面因素:裂纹尖端的应力场强度因子(ISF)和Cu层塑性变形对微裂纹扩展的抑制作用。其中铜层的塑性变形能力随着厚度的增加而提高。而Nb层中形成的微裂纹的ISF与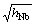 存在一个比例关系,即随着Nb层厚度的减小,ISF也减小。因此,以上两方面综合作用的结果导致Cu/Nb多层膜的延性随着调制比的减小而增加。与调制周期是50nm的Cu/Nb多层膜相比,调制波长为25nm的多层膜中Nb层的ISF明显较小,而铜层的塑性变形能力相差不大。当调制比较小(小于0.5)时,Cu层具有足够的塑性变形能力来阻止裂纹的扩展,因此,λ=25 nm的多层膜延性更好。而调制比较大(大于0.5)时,Cu层很薄,位错在亚层中难以形核运动,导致Cu层出现韧脆转变(Cu层相当于一种脆性层)[17],此时多层膜的结合相当于两种脆性材料的叠加,含有更多界面的λ=25 nm的多层膜延性反而不如λ=50 nm的多层膜。
存在一个比例关系,即随着Nb层厚度的减小,ISF也减小。因此,以上两方面综合作用的结果导致Cu/Nb多层膜的延性随着调制比的减小而增加。与调制周期是50nm的Cu/Nb多层膜相比,调制波长为25nm的多层膜中Nb层的ISF明显较小,而铜层的塑性变形能力相差不大。当调制比较小(小于0.5)时,Cu层具有足够的塑性变形能力来阻止裂纹的扩展,因此,λ=25 nm的多层膜延性更好。而调制比较大(大于0.5)时,Cu层很薄,位错在亚层中难以形核运动,导致Cu层出现韧脆转变(Cu层相当于一种脆性层)[17],此时多层膜的结合相当于两种脆性材料的叠加,含有更多界面的λ=25 nm的多层膜延性反而不如λ=50 nm的多层膜。
利用FIB截面定量表征技术观察拉伸试样的裂纹形貌(见图5),分析其断裂方式。由FIB截面照片可以看出,Cu/Nb多层膜中,裂纹的扩展方向与膜基界面存在一个断裂角度q,如图5(a)所示。Cu/Nb多层膜呈现不同的断裂模式——剪切型断裂(见图5(a))、张开型断裂(见图5(b))以及张开与剪切的混合断裂模式。且当调制比小于1时,Cu/Nb多层膜呈现剪切型断裂;当调制比大于1时,Cu/Nb多层膜呈现张开型断裂;当调制比等于1时,Cu/Nb多层膜呈现张开+剪切型断裂。
图6所示为Cu/Nb多层膜的裂纹断裂角度(θ)与裂纹萌生临界应变(εc)的变化规律。由图6可看出,随着延性的增加,多层膜断裂角度的逐渐减小,曲线分为3个区域。在区域A,临界应变小于1%,θ随εc变化不大(θ约为83°±3°),Cu层的变形能力很小,几乎无法抑制萌生于Nb层的微裂纹的扩展,因此多层膜在Cu层和Nb层中均倾向于张开型断裂。在区域C,临界应变大于1.6%,θ几乎不随εc变化而变化(θ约为 52±3°),萌生于脆性Nb层的微裂纹可以被Cu层的塑性变形抑制而无法继续扩展,因此多层膜表现为剪切型断裂。在区域B,临界应变处于1%~1.6%之 间,多层膜呈现一种剪切+张开混合型断裂模式,因此,θ随着εc变化。调制波长为50 nm的断裂角(q)普遍大于调制波长为25 nm的,进一步证实较大的微裂纹(较大的hNb)更难被Cu层阻止。以上结果都表 明,多层膜延性及断裂行为的变化均对应着Nb层萌生微裂纹的裂纹尖端应力场强度与Cu层对微裂纹的抑制作用之间的竞争。

图5 裂纹尖端形变区内的剪切变形和张开变形的形貌
Fig.5 Morphologies of shear (a) and opening (b) deformation in microcrack deformation area

图6 Cu/Nb纳米多层膜断裂角度(q)随裂纹萌生临界应变(εc)的变化
Fig.6 Variation of fracture angle θ of Cu/Nb nanostructured multilayer as function of critical macroscopic strain εc
3 结论
1) Cu/Nb纳米金属多层膜在生长方向上呈现Cu(111)和Nb(110)的择优取向,多层膜各层均匀连续、相互交替,界面清晰平直。
2) Cu/Nb多层膜的延性及断裂行为均表现出明显的尺寸依赖性:随着调制比的增加,多层膜的延性单调减小;当调制比小于0.5时,调制周期为25 nm的延性高于50 nm的;当调制比大于0.5时,调制周期为50 nm的延性高于25 nm的。
3) 随着调制比的增加,多层膜的断裂角度逐渐增大,出现由剪切型向张开型断裂模式的转变。这主要是由于随着调制比的增加,软相Cu层对脆相Nb层中萌生的微裂纹扩展的约束作用逐渐减小。
REFERENCES
[1] WEN S P, ZONG R L, ZENG F, GAO Y, PAN F. Evaluating modulus and hardness enhancement in evaporated Cu/W multilayers[J]. Acta Mater, 2007, 55(1): 345-351.
[2] LIU M X, XU K W. Anomalous electronic transport in metallic nanomultilayer at all length scales: Influence of grain boundary and interface boundary[J]. J Mater Res, 2008, 23(6): 1658-1666.
[3] 张广平, 李远平, 朱晓飞, 张 滨. 几种金属多层薄膜的形变与断裂行为及其机制[J]. 南京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 45(2): 180-186.
ZHANG Guang-ping, LI Yuan-ping, ZHU Xiao-fei, ZHANG Bin. Deformation and fracture behavior of several metallic multilayers and mechanics[J]. Journal of Nanjing University: Natural Sciences Edition, 2009, 45(2): 180-186.
[4] SPEARING S M. Materials issues in microelectromechanical systems (MEMS)[J]. Acta Mater, 2000, 48(1): 179-196.
[5] 王阳元, 康晋锋. 超深亚微米集成电路中的互联问题—低k介质与Cu的互联集成技术[J]. 半导体学报, 2002, 23(11): 1121-1134.
WANG Yang-yuan, KANG Jin-feng. Development of ULSI interconnect integration technology—Copper interconnect with low k dielectrics[J]. Chinese Journal of Semiconductors, 2002, 23(11): 1121-1134.
[6] FAVENNEC L, JOUSSEAUME V, GERBAUD G, ZENASNI A, PASSEMARD G. Ultralow k using a plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition porogen approach: Matrix structure and porogen loading influences[J]. J Appl Phys, 2007, 102(6): 064107-1-9.
[7] FAYOLLE M, PASSEMARD G, LOUVEAU O, FUSALBA F, CLUZEL J. Challenges of back end of the line for sub 65 nm generation[J]. Microelectron Eng, 2003, 70(2): 255-266.
[8] NGUYEN H S, GAN Z H, CHEN Z, CHANDRASEKAR V, PRASAD K, MHAISALKAR S G, JIANG N. Reliability studies of barrier layers for Cu/PAE low-k interconnects[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2006, 46(8): 1309-1314.
[9] HUANG H B, SPAEPEN F. Tensile testing of free-standing Cu, Ag and Al thin films and Ag/Cu multilayers[J]. Acta Mater, 2000, 48(12): 3261-3269.
[10] MARA N A, BHATTACHARYYA D, HOAGLAND R G, MISRA A. Tensile behavior of 40 nm Cu/Nb nanoscale multilayers[J]. Scripta Mater, 2008, 58(10): 874-877.
[11] NIU R M, LIU G, WANG C, ZHANG G, DING X D, SUN J. Thickness dependent critical strain in submicron Cu films adherent to polymer substrate[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90(16): 161907, 1-3.
[12] ZHANG J Y, LIU G, ZHANG X, ZHANG G J, SUN J, MA E. A maximum in ductility and fracture toughness in nanostructured Cu/Cr multilayer films[J]. Scripta Mater, 2010, 62(6): 333-336.
[13] ZHU X F, LI Y P, ZHANG G P, TAN J, LIU Y. Understanding nanoscale damage at a crack tip of multilayered metallic composites[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 92(16): 161905-1-3.
[14] YU D Y W, SPAEPEN F. The yield strength of thin copper films on Kapton[J]. J Appl Phys, 2004, 95(6): 2991-2997.
[15] OUYANG G, WANG C X, YANG G W. Anomalous interfacial diffusion in immiscible metallic multilayers a size-dependent kinetic approach[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 86(17): 171914-1-3.
[16] CLEMENS B M, NIX W D, RAMASWAMY V. Surface-energy-driven intermixing and its effect on the measurement of interface stress[J]. J Appl Phys, 2000, 87(6): 2816-2820.
[17] HSIA K J, SUO Z, YANG W. Cleavage due to dislocation condinement in layered materials[J]. J Mech Phys Solids, 1994, 42(6): 877-896.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究计划资助项目(2010CB631003);国家自然科学基金资助项目(50971097)
收稿日期:2010-06-28;修订日期:2010-11-20
通信作者:刘 刚,教授;电话:15002989271;E-mail: lgsammer@mail.xjtu.edu.cn