DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2018.03.022
电石渣/偏高岭土固化铜污染土的浸泡试验研究
陈永贵1,潘侃1,谭邦宏1, 2,叶为民1,陈宝1
(1.同济大学 岩土及地下工程教育部重点实验室,上海,200092;
2. 广西交通投资集团南宁高速公路运营有限公司,广西 南宁,530022)
摘要:针对电石渣/偏高岭土地聚合物固化铜污染土开展去离子水和盐酸条件下的浸泡试验,研究固化污染土无侧限抗压强度变化规律,分析浸泡条件对固化污染土稳定性的影响。研究结果表明:在未浸泡条件下,固化污染土无侧限抗压强度随着电石渣掺量的增加而增大;当电石渣掺量较低时,固化污染土的应力随应变增加而缓慢增大,无明显峰值;当电石渣质量分数超过9%时,应力随应变增加而较快增大,强度峰值明显;在去离子水和盐酸浸泡条件下,固化污染土的无侧限抗压强度变化趋势基本一致,随着电石渣掺量增加而增大,且明显低于未浸泡固化污染土的无侧限抗压强度;当电石渣质量分数为10%,偏高岭土质量分数为5%时,电石渣/偏高岭土地聚合物对铜污染土具有较强的抗酸稳定性,修复效果良好。
关键词:铜污染土;固化/稳定化;电石渣;浸泡试验
中图分类号:TU411 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2018)03-0678-06
Soaking experimental study on solidification/stabilization of Cu2+ contaminated soils with carbide slag and metakaolin
CHEN Yonggui1, PAN Kan1, TAN Banghong1, 2, YE Weimin1, CHEN Bao1
(1. Key Laboratory of Geotechnical and Underground Engineering of Ministry of Education, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China;
2. Nanning Highway Operation Limited Company, Guangxi Communication Investment Group Co. Ltd., Nanning 530022, China)
Abstract: Geopolymer prepared from carbide slag(CS) and metakaolin(MK) was used for solidification/stabilization of Cu2+ contaminated soils. The immersion tests were conducted on the soils under deionized water or hydrochloric acid conditions to investigate the unconfined compressive strength(UCS), and the long-term stability of the soils was evaluated. The results show that UCS increases with the increase of the CS content. When the CS content is lower than 9%, the stress increases slightly with the increase of the strain and there is no significant peak. However, when the CS content reaches 9%, the stress grows rapidly and there appears a peak. The change in UCS is almost the same in soaked deionized water and hydrochloric acid, and the UCS increases with the increase of the CS content, but it’s obvious lower than that of the soils without soaking. The geopolymer with the CS content of 10% and MK content of 5% is confirmed to be the best for remediation of Cu2+ contaminated soils.
Key words: Cu2+ contaminated soils; stabilization/solidification; carbide slag; immersion experiment
随着我国经济快速发展,城市化进程加快,大量化工厂、金属冶炼厂等污染企业逐步搬离城市,但原有场地已经被严重污染,对这些污染场地的再次利用已成为城市可持续发展的重要内容[1]。铜在工业生产以及日常生活中使用非常广泛,由铜所引起的土壤及地下水污染日益严重[2]。目前,许多学者认为固化/稳定化技术是修复重金属污染土最有效的方法,在固化剂作用下,污染土的强度明显提高,浸出离子浓度显著降低。常用的固化/稳定化添加剂包括水泥、粉煤灰、高炉矿渣等。水泥作为固化剂能有效改善污染土的性质,但水泥本身是一种高能耗物质,在生产过程中会排放大量大气污染物,造成严重的二次污染。另一方面,目前我国每年都产生大量的电石渣、偏高岭土等工业废料,这些工业废料的无序堆放会导致土体钙化,污染土体和地下水。研究表明,电石渣、偏高岭土的主要化学成分与水泥作为固化剂的有效成分一致[3-4]。利用电石渣、偏高岭土等工业废料固化/稳定化处理重金属污染土,对实现变废为宝、降低能耗具有重要意义。虽然污染土固化后的强度有较大提高,但其长期稳定性问题仍然为人们所关注[5]。查甫生等[5]发现水泥固化污染土强度随着干湿循环次数增多先增大后减小,浸出离子浓度先降低后增大。章定文等[6]开展了水泥固化铅污染土碳化试验,发现碳化后的试样Pb2+累计溶出量是标准养护试样的0.68~0.91倍,Pb2+低浓度时溶出机制为表面侵蚀。STANFORTH等[7]研究了固化铅污染土在不同气候条件下的稳定性,对比分析了不同固化剂作用下污染土的稳定性特征。李磊等[8]发现水泥掺量达到一定值后,才能降低水浸泡对固化污染土强度的不利影响。FITCH等[9]研究了经水泥和粉煤灰固化后重金属污染场地10 a后的工程性质,发现表层土重金属离子量增大而深层土减少。刘晶晶[10]研究了NaCl侵蚀环境下水泥/粉煤灰固化重金属污染土的工程特性,发现随着NaCl浓度增大,固化污染土的无侧限抗压强度降低,Cr3+浸出浓度增大,而Pb2+浸出浓度降低。蒋宁俊等[11]研究了酸雨入渗对水泥固化铅污染土淋滤特性的影响,发现当酸雨pH=2.5时,滤出液pH明显降低,钙离子浓度显著增大,而铅离子浓度明显减小。ZHANG等[12-13]研究了电石渣或偏高岭土地聚合物对重金属离子的固定、吸附特性,结果表明电石渣或偏高岭土具有良好的固化、吸附效果。杜延军等[14]对水泥固化锌污染高岭土强度及微观特性进行了研究。大量研究表明,固化/稳定化修复后的污染土在干湿循环、碳化等作用下强度不断降低,大部分重金属离子浸出量增大。目前,人们对固化污染土长期强度的研究主要集中在不同浓度或离子类型的盐溶液条件,但大量的重金属污染场地均处于酸性条件。为此,本文作者针对不同掺入量的电石渣/偏高岭土固化铜污染土开展酸性条件下的浸泡试验,研究固化污染土的无侧限抗压强度变化规律,分析酸性条件下固化剂对固化污染土长期稳定性的影响。
1 材料和方法
1.1 试验材料
试验用土为上海第2①层粉质黏土,取自上海某工地未受污染的天然原状土;自然风干后,挑除其中石砾和植物残体,过2 mm筛获得试验用样。采用的固化/稳定化材料包括电石渣和偏高岭土,其中电石渣取自南京某一电石生产乙炔厂家,主要成分为CaO;偏高岭土由巴斯夫催化剂有限责任公司提供。选取部分土样、电石渣和偏高岭土,分别过0.075 mm筛后,放入温度为120 ℃的烘箱中烘干3 h,用X线荧光光谱仪(XRF)测试黏土、电石渣和偏高岭土的化学成分,结果见表1。
因硝酸根离子对水化反应影响较小,且硝酸铜具有较高溶解度和较强离子活动性[15],试验中采用硝酸盐(Cu(NO3)2)作为铜污染源制备铜污染土。选用质量分数为1%的HCl作为酸性溶剂配制浸泡溶液[16]。
表1 土样及固化剂化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Component of soil samples and additives %

1.2 试验方案
试验中,针对Cu2+质量分数为2000 mg/kg的污染土,分别制备偏高岭土(以下简称MK)质量分数为5.0%以及电石渣(以下简称CS)质量分数分别为5.0%,7.5%,10.0%和12.5%的聚合物进行固化/稳定化修复,将标准养护条件下养护28 d后的固化土体分别放入质量分数为1%的盐酸和去离子水中浸泡14 d,然后取出测定土样的无侧限抗压强度,得到相应的应力-应变曲线。具体步骤如下。
1) 制样及养护。
① 将原状土自然风干后,挑除石砾和植物残渣等,过2 mm筛。
② 量取土样最优含水率22%所需的水和相对应的硝酸铜的质量,配置一定浓度的硝酸铜溶液,再均匀加入称量好的土样,在恒温恒湿箱(温度为(20±3) ℃,相对湿度≥95% )中养护15 d,得到稳定均匀的污染土。
③ 称量预设配比的电石渣、偏高岭土,搅拌均匀后加入污染土中,随后装入密封塑料袋,置于标准养护室内(温度为(20±3) ℃,相对湿度≥95% )。
④ 采用静压法制样,制备试样的干密度为最大干密度的90%,将制备好的试样置于标准养护箱中养护28 d。
2) 浸泡试验。
① 去离子水浸泡试验。将养护好的固化污染土样两端加上滤纸,用透水石封盖,并用胶带把试样侧边绑上。然后,将试样放入装有去离子水的容器中,控制单向侵蚀条件,浸泡14 d。浸泡完成后,根据JTG E40—2007“公路土工试验规程”开展无侧限抗压强度试验。
② 盐酸浸泡试验。配置质量分数为1%的HCl溶液。取养护28 d的固化土试样,两端加上滤纸并用透水石封盖,用胶带把试样侧边绑上。然后,将试样放入配制好的HCl溶液中,控制为单向侵蚀条件,浸泡14 d。浸泡完成后,根据JTG E40—2007“公路土工试验规程”开展无侧限抗压强度试验。
2 试验结果及分析
2.1 浸泡条件对固化污染土强度的影响
对偏高岭土质量分数为5%、不同质量分数的电石渣所固化的污染土,在不同浸泡条件下开展无侧限抗压强度测试,试验结果见图1。从图1可以看出:总体而言,固化污染土的无侧限抗压强度随着电石渣掺量的增大而增大;同时,未浸泡条件下固化污染土的强度大于浸泡条件下固化污染土的强度,而酸浸泡和水浸泡条件下的强度基本相同;在未浸泡情况下,污染土的无侧限抗压强度随着电石渣掺量的增加而增大,当电石渣质量分数大于5%时,固化污染土强度已经超过荷兰、法国等国家修复标准规定的1 MPa [17]。酸性浸泡条件与水浸泡条件时的强度变化规律基本一致。不同浸泡条件下,固化污染土的无侧限抗压强度相比未浸泡土的无侧限抗压强度明显降低,均随着电石渣掺量的增加而增大;当电石渣质量分数低于7%时,固化污染土无侧限抗压强度的增大不够明显;当电石渣质量分数大于7.5%时,固化污染土无侧限抗压强度随着电石渣掺量的增加而显著增大,而且当电石渣质量分数达到10%时,即使在去离子水条件下浸泡后,固化污染土的强度仍然达到0.95 MPa,超过英、美两国修复标准分别规定的0.75 MPa和0.35 MPa[17]。

图1 浸泡条件对固化污染土无侧限抗压强度的影响
Fig. 1 Effect of different conditions on unconfined compressive strength of stabilized soils
2.2 浸泡条件对固化污染土应力-应变关系的影响
对偏高岭土质量分数为5%、不同质量分数的电石渣所固化的污染土,分别测试未浸泡、去离子水浸泡和1%盐酸浸泡后的应力-应变曲线,结果分别见图2~4。从图2可知:在未浸泡条件下,当电石渣掺量较低时,固化污染土的应力随应变增加缓慢增大,无明显峰值,属硬化型;当电石渣质量分数大于9%后,固化污染土的应力随应变增加而较快增大,峰值强度变得明显。对比图3和图4可以看出:盐酸浸泡条件下,应力与应变的关系随电石渣掺量的变化与未浸泡时大致相同,但与水浸泡条件相比,酸性条件下固化污染土强度峰值出现较缓慢且对应的应变较小。这一现象表明:随着电石渣掺量增加,酸性条件对固化污染土强度的影响逐渐增大;掺量的变化与未浸泡时大致相同,但酸性条件下峰值强度下降明显且达到峰值强度所对应的应变减小。这是因为随着电石渣掺量增大,水合硅酸钙等水化产物将会增多,而水化产物易与酸反应,故影响增大。

图2 未浸泡条件下固化污染土的应力-应变曲线
Fig. 2 Stress-strain curves of copper contaminated soils under different contents of carbide slag

图3 水浸泡条件下固化污染土的应力-应变曲线
Fig. 3 Stress-strain curves of stabilized soils under different contents of carbide slag in soaked deionized water
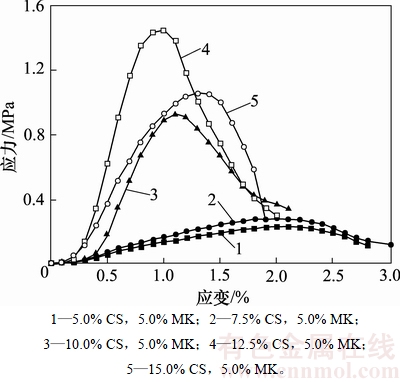
图4 酸浸泡条件下固化污染土的应力-应变曲线
Fig. 4 Stress-strain curves of stabilized soils under different contents of carbide slag in soaked acidic condition
2.3 浸泡条件对固化污染土破坏应变的影响
未浸泡、去离子水浸泡和酸浸泡条件下固化污染土的破坏应变见图5~7。由图5~7可知:3种条件下固化污染土的破坏应变均随着电石渣掺量的增加而减小;未浸泡条件下,固化污染土的破坏应变主要分布范围为2.10%~2.30%,平均破坏应变为 2.20%;水浸泡条件下,固化污染土的破坏应变主要分布范围为0.90%~2.30%,平均破坏应变为1.59%; 1%盐酸浸泡条件下,固化污染土的破坏应变主要分布范围为0.90%~2.00%,平均破坏应变为1.09%。对比分析可知:盐酸浸泡条件下的平均破坏应变最小,而未浸泡条件下的破坏应变分布更集中。

图5 未浸泡条件下固化污染土的破坏应变
Fig. 5 Failure strain of stabilized soils under different contents of carbide slag in unsoaked condition

图6 水浸泡条件下固化污染土的破坏应变值
Fig. 6 Failure strain of stabilized soils under different contents of carbide slag in soaked deionized water

图7 酸浸泡条件下固化污染土的破坏应变
Fig. 7 Failure strain of stabilized soils under different contents of carbide slag in soaked acidic condition
2.4 浸泡条件对固化污染土力学性能的影响机理
无论在未浸泡条件还是水和酸的浸泡条件下,固化污染土的无侧限抗压强度均随着电石渣掺量的增加而明显增大。这主要是因为电石渣和偏高岭土产生了水化水解反应,生成了大量的水合硅酸钙(C—S—H)和水合铝酸钙(C—A—H)等凝胶体,与污染土之间发生吸附、离子交换、硬凝等反应,形成整体性较好的结晶网状结构,不仅填充在土颗粒间的间隙中,而且将土体中的团粒体进一步连接起来,形成较大的稳定块状结构,从而起到固化/稳定化作用。研究表明,污染土中Cu2+的固化效果受pH影响显著,弱碱性环境下离子的迁移率最低[18]。增加电石渣掺量,使得污染土的pH提高,Cu2+被更好地固定在凝胶体表面,并且在碱性条件下生成Cu(OH)2沉淀,从而提高固化污染土的强度。
酸性浸泡条件下,溶液中的H+会与固化污染土中的水化产物水合硅酸钙以及Ca(OH)2发生如下反应:
Ca(OH)2+2H+→Ca2++2H2O
3Ca·2SiO2·3H2O+6H+→3Ca2++2SiO2·H2O+4H2O
随着浸泡时间延长,水合硅酸钙以及Ca(OH)2不断减少,使得固化污染土无侧限抗压强度降低。
同时,HCl溶液也会对固化污染土的强度产生影响。溶液中的Cl- 在土体中的渗透性较强[19],进入固化污染土的基质后会与电石渣/偏高岭土地聚合物水化产生的3CaO·Al2O3反应,减少钙矾石的生成;同时,还会与钙矾石反应生成可溶盐,进一步降低固化污染土的强度[20]。
水浸泡条件下,固化污染土的强度基本上与酸浸泡条件下的强度变化趋势一致,但其强度始终略高于酸浸泡条件下固化污染土的强度,尤其是当电石渣质量分数大于10%后,强度差异更加明显。这可能是因为当电石渣掺量较低时,地聚合物水解水化产生的C—S—H和C—A—H等凝胶体较少,土颗粒间的盐溶质胶结物也较少,此时,水对凝胶体或是胶结物的溶解作用与盐酸的作用差别不大,强度变化趋势一致。但是,随着电石渣掺量的增加,地聚合物水化水解产生的凝胶体以及沉淀物均增多,酸性溶液的溶解能力明显要强于去离子水,固化污染土中的水化产物C—S—H和Ca(OH)2沉淀以及钙矾石等被溶解,并且酸性条件阻止了地聚合物水化水解反应的进一步进行,阻碍了固化污染土体强度的增大,导致强度差距越来越大,破坏应变逐渐减小。
3 结论
1) 未浸泡条件下,固化污染土无侧限抗压强度随着电石渣掺量的增加而增大;当偏高岭土质量分数为5%、电石渣质量分数为5%时,固化污染土的无侧限抗压强度达到1 MPa。当电石渣掺量较低时,固化污染土的应力随应变增大缓慢,无明显峰值;当电石渣质量分数大于9%时,应力随应变增长较快,峰值强度明显。
2) 酸性浸泡条件与水浸泡条件下,固化污染土的无侧限抗压强度变化规律基本一致,均比未浸泡土的无侧限抗压强度明显降低,且随着电石渣掺量的增加而增大。
3) 当电石渣质量分数为10%,偏高岭土质量分数为5%时,去离子水和酸浸泡条件下固化污染土的无侧限抗压强度均满足有关修复标准,表明电石渣/偏高岭土地聚合物对铜污染土的修复效果良好,具有较强的抗酸稳定性。
参考文献:
[1] 薄煜琳, 于博伟, 杜延军, 等. 淋滤条件下GGBS-MgO固化铅污染黏土强度与溶出特性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(10): 2877-2891.
BO Yulin, YU Bowei, DU Yanjun, et al. W Strength and leachability of lead contaminated clay stabilized by GGBS-MgO[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(10): 2877-2891.
[2] MOON D H, CHEONG K H, KHIM J, et al. Stabilization of Pb2+ and Cu2+ contaminated firing range soil using calcined oyster shells and waste cow bones[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 91(9): 1349-1354.
[3] 毕金栋, 李昌勇, 曹华夏, 等. CO2气氛下电石渣配料生料和普通水泥生料在模拟预热器系统中的逆反应工程[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2012, 31( 6): 1621-1625.
BI Jindong, LI Changyong, CAO Huaxia, et al. The reverse reaction of cement raw meal with dosing of carbide slag and common cement raw meal in the simulated preheater system in CO2 atmosphere[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2012, 31(6): 1621-1625.
[4] CUISINIER O, BORGNE T L, DENEELE D, et al. Quantification of the effects of nitrates, phosphates and chlorides on soil stabilization with lime and cement[J]. Engineering Geology, 2011, 117(3/4): 229-235.
[5] 查甫生, 刘晶晶, 许龙, 等. 水泥固化重金属污染土干湿循环特性试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(7): 1246-1252.
ZHA Fusheng, LIU Jingjing, XU Long, et al. Cyclic wetting and drying tests on heavy metal contaminated soils solidified/ stabilized by cement[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(7): 1246-1252.
[6] 章定文, 张涛, 刘松玉, 等. 碳化作用对水泥固化/稳定化铅污染土溶出特性影响[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(1): 41-48.
ZHANG Dingwen, ZHANG Tao, LIU Songyu, et al. Effect of carbonation on leaching properties of cement stabilized/ solidified lead contaminated soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(1): 41-48.
[7] STANFORTH R, YAP C F, NAYAR R. Effects of weathering on treatment of lead contaminated soils[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2005, 131(1): 38-48.
[8] 李磊, 朱伟, 林城, 等. 干湿循环条件下固化污泥的物理稳定性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2009, 30(10): 3001-3004, 3012.
LI Lei, ZHU Wei, LIN Cheng, et al. Study of wet and dry properties of solidified sludge[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(10): 3001-3004.
[9] FITCH J R, CHEESEMAN C R. Characterisation of environmentally exposed cement-based stabilised/solidified industrial waste[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2003, 101(3): 239-255.
[10] 刘晶晶. 化学物质渗入作用下固化重金属污染土的稳定性研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学资源与环境工程学院, 2014: 45.
LIU Jingjing. The stability of solidified/stabilized heavy metal contaminated soils under erosive environment[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology. School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, 2014: 45.
[11] 蒋宁俊, 杜延军, 刘松玉, 等. 酸雨入渗对水泥固化铅污染土淋滤特性的影响研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(4): 739-744.
JIANG Ningjun, DU Yanjun, LIU Songyu, et al. Leaching behaviors of cement-based solidification/stabilization treated lead contaminated soils under effects of acid rain[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(4): 739-744.
[12] ZHANG Y S, SUN W, CHEN Q L, et al. Synthesis and heavy metal immobilization behaviors of slag based geopolymer[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 143(1/2): 206-213.
[13] CHENG T W, LEE M L, KO M S, et al. The heavy metal adsorption characteristics on metakaolin-based geopolymer[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2012, 56(1): 90-96.
[14] 杜延军, 蒋宁俊, 王乐, 等. 水泥固化锌污染高岭土强度及微观特性研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2012, 34(11): 2114-2120.
DU Yanjun, JIANG Ningjun, WANG Le, et al. Strength and microstructure characteristics of cement-based solidified/ stabilized zinc-contaminated kaolin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(11): 2114-2120.
[15] 武相萍, 陆雷, 曹常富, 等. 电石渣力学性能的研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2009, 28(2): 235-238.
WU Xiangping, LU Lei, CAO Changfu, et al. Study on mechanical properties of carbide slag[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2009, 28(2): 235-238.
[16] 刘汉龙, 朱春鹏, 张晓璐. 酸碱污染土基本物理性质的室内测试研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2008, 30(8): 1213-1217.
LIU Hanlong, ZHU Chunpeng, ZHANG Xiaolu. Fundamental physical properties of soil polluted by acid and alkali in laboratory[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2008, 30(8): 1213-1217.
[17] 许龙. 重金属污染土的固化修复及长期稳定性研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学资源与环境工程学院, 2012: 13.
XU Long. Research on remediation and long-term stability of solidified/stabilized heavy metal contaminated soil[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology. School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, 2012: 13.
[18] KUMPIENE J, LAGERKVIST A, MAURICE C. Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments: a review[J]. Waste Management, 2008, 28(1): 215.
[19] 熊厚金, 林天健, 李宁. 岩土工程化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 473.
XIONG Houjin, LIN Tianjian, LI Ning. Geotechnical Engineering Chemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 473.
[20] AL-AMOUDI O S B, MASLEHUDDIN M, ABDUL-AL Y A B. Role of chloride ions on expansion and strength reduction in plain and blended cements in sulfate environments[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 1995, 9(1): 25-33.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2017-05-10;修回日期:2017-07-22
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(41422207, 41772279) (Projects(41422207, 41772279) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:陈永贵,博士,教授,博士生导师,从事环境地质和非饱和土力学研究;E-mail: cyg@tongji.edu.cn