文章编号:1004-0609(2016)-09-1967-09
微合金化元素Zr对热障涂层关键界面的强化效应及机理
蓝国强1, 2,江 勇1, 2, 3, 4,江 亮3, 4
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 教育部有色金属材料重点实验室,长沙 410083;
3. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083;
4. 中南大学 深圳研究院,深圳 518057)
摘 要:针对高温热障涂层中关键的过渡层/热生长层界面,通过第一性原理界面热力学建模和密度泛函计算,考察微量锆元素对g-Ni(Al)/α-Al2O3界面结构、偏析、和界面结合的影响,以及在基体中对杂质(硫)的钉扎。结果显示:锆具有与同族元素铪类似的界面强化作用,其强化机理可以归纳为3种,即在基体中有效钉扎硫,以抑制硫的有害界面偏析、在界面处置换硫,以减轻偏析硫对界面的危害以及在界面偏析以直接强化界面结合,可使较弱的理想化学计量比界面的分离功提高3倍。
关键词:热障涂层;界面强度;微合金化;锆;第一性原理
中图分类号:TG132.32 文献标志码:A
自20世纪60年代以来,运用微合金化技术对基础系合金进行成分改造,逐渐成为国内外新合金材料研发的重要途径之一。微合金化通常是指在原有主合金元素的基础上,通过添加一种或多种微量的金属或非金属元素,配合恰当的变形和热处理,以明显改善合金的力学性能、耐蚀性、耐热性等。微量元素的加入量因合金体系而异,如非调质结构钢加入量一般小于0.1%(摩尔分数,下同),耐热钢和不锈钢加入量约为0.5%,铝合金加入量一般小于1%,高温合金加入量为1%~2%。虽然绝大多数微合金化的作用机理并不明确,但微合金化技术已经广泛地应用于各类新合金材料的设计、制备、和生产实践中。由于微合金化元素的加入量很少,一般可以推断其工作机理应与固溶强化关系不大,而主要与形核和长大、以及与位错、亚结构、或界面等发生的相互作用有关。
镍基合金高温热障涂层(Thermal barrier coatings, TBCs)在航空发动机、燃气轮机、和高温固体燃料电池等众多重要材料系统中发挥着关键性作用。在涂层制备或服役过程中,在镍基过渡层合金(Bond coat, BC)表面逐渐形成数量级在100 μm左右的热生长层(Thermally-grown oxide, TGO)氧化铝,其作用可有效缓解层间热应力,并为基体合金提供一定的抗高温氧化能力;但大量实验和服役经验证明,热生长形成的BC/TGO层界面最容易发生脱粘,进而造成整个绝热涂层(YSZ)的直接剥落。换而言之,BC/TGO界面结合强度及其退化演变,是决定高温热障涂层可靠性和服役寿命的关键。EVANS等[1]、GLEESON [2]以及国内蒋显亮等[3]先后以研究综述形式,对BC/TGO界面失效机制及相应BC合金优化设计,进行过详尽的分析和总结。大量实验研究表明,BC合金中残留的或从燃料中渗入的主要杂质元素(如S)容易在BC/TGO界面上发生强烈偏聚,进而严重弱化界面结合,是造成整个绝热层完全失效的重要机制[4-6]。在BC合金中添加微量稀土或近稀土元素(如 Hf、Y、Ce、Zr等)后,界面剥落的现象均可得到不同程度地缓解[7-12]。这些微合金化元素的作用机制,一般有两种基本假设:1) 可在合金基体中有效钉扎杂质S,从而阻滞后者向界面的有害偏析;2) 在界面参与成键,直接强化界面结合。这些假设可以很好地解释众多的实验观察,但尚未获得直接的实验验证[9]。在实际服役工况条件下,这些机制可能单独或同时发生作用,并相互影响。单纯依赖实验方法和技术,目前还难以充分揭示微合金化元素的复杂界面效应。
热障涂层界面研究所遇到的这些困难,是当前界面科学中的共性难题,比如如何预测一个界面的理想结合强度,如何确定界面强度的主要影响因素以及各因素间的相互关系,是否存在超过理想界面强度的可能,以及如何基于界面开展材料设计优化等。回答这些问题,必须首先充分认识界面结构和界面强度与制备或服役工况条件,以及合金内部化学成分的相关性。李志林等[13]运用经验电子理论和汤姆斯-费米-狄拉克-陈(Thomas-Fermi-Dirac-Cheng, TFDC)理论,通过界面价电子密度与界面结合因子计算,初步评估合金元素Cr偏析对陶瓷绝热层(YSZ)/BC合金界面结合的影响。然而,经验电子理论和TFDC理论研究复杂体系的准确性非常有限,而且YSZ与BC合金之间实际上还存在着TGO层,BC/TGO界面才是目前公认为整个热障涂层系统中最危险的界面。近年来,第一性原理计算方法逐渐成熟并成功应用于界面研究,为揭示这类基础性的界面相关问题提供了新的研究手段。CARLING[14]和JARVIS等[15]先后开展针对BC/TGO界面的第一性原理计算研究,进而预测不同合金元素对界面结合的强弱化影响。但这些研究未考虑各元素在界面的偏聚能力和竞争性,也未考虑各元素对杂质S的可能钉扎,特别是忽视了TGO界面的热力学生长特点,完全不考虑合金元素活度和温度的影响,从而割裂了界面微观结构与热力学条件的重要相关性,因此,其计算和讨论结果都缺乏说服力。
针对这些局限性,本文作者提出了第一性原理界面热力学研究方法,即通过缺陷热力学建模,结合界面相结构与界面能量学计算,预测界面相图,并基于界面相图,预测和评估给定热力学条件下的界面平衡相结构、理想界面结合强度、微量合金和杂质元素的界面偏聚及其效应、以及基体内合金元素与杂质原子可能的相互作用。通过多年的研究实践,本文作者先后揭示了微合金化元素Hf、Y、Ce、和Pt对BC/TGO界面的强化效应和机理[16-20],并将第一性原理界面热力学成功推广到了其他界面体系[21-23]。本文作者在所有以往工作的基础上,进一步考察和评估微合金化元素Zr对BC/TGO(γ-Ni(Al)/α-Al2O3)界面的强化效应及其机理,并将其与同族元素Hf的界面效应进行对比,为BC合金的优化设计提供科学指导。具体包括以下几项主要研究内容:
1) 计算确定1300 K下γ-Ni(Al)/α-Al2O3界面相图的等温截面;
2) 根据活度计算,确定该温度下的界面平衡相结构;
3) 计算和比较偏聚前后界面分离功(Wsep)的变化,评估界面偏聚对结合强度的影响;
4) 计算Zr和S界面偏聚的驱动力和可能的偏析路径;
5) 计算评估高温下Zr对Ni基体内杂质S的钉扎能力。
所有计算采用第一性原理电子密度泛函通用程序包VASP[24]。其中交换关联能采用广义梯度近似,电子与核之间的相互作用采用Vanderbilt超软赝势,平面波展开采用较高能量截断(400 eV)。有关Al活度的计算,采用包含单个Al原子的2×2×2 面心γ-Ni超点阵,布里渊区能量积分在6×6×6 Monkhorst-Pack (M-P) k-网格中进行。温度对能量的贡献通过直接超胞法的声子计算和准简谐近似估算[25]。界面采用三明治型共格γ-Ni(111)/α-Al2O3(0001)超胞模型,包含8层Ni原子、12层Al原子、6层O原子、和至少12 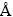 的真空层,布里渊区能量积分采用3×3×1 M-P k-网格。基体计算采用包含单个Zr-S原子对的3×3×3面心 γ-Ni的超点阵和2×2×2 M-P k-网格。所有计算为完全驰豫计算,收敛判据为Hellmann-Feymann原子净力小于20 meV/
的真空层,布里渊区能量积分采用3×3×1 M-P k-网格。基体计算采用包含单个Zr-S原子对的3×3×3面心 γ-Ni的超点阵和2×2×2 M-P k-网格。所有计算为完全驰豫计算,收敛判据为Hellmann-Feymann原子净力小于20 meV/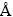 (1eV/
(1eV/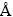 =1.6 nN)。计算中考虑自璇极化,但忽略声子-电子的相互作用以及磁性转变。
=1.6 nN)。计算中考虑自璇极化,但忽略声子-电子的相互作用以及磁性转变。
1 界面结构与界面强度
高温热障涂层中BC/TGO界面形成过程中,BC合金中固溶的Al元素在其表面获得择优氧化生成Al2O3层。同时,由于Al元素的不断消耗,BC合金中临近界面处的内部组织发生相应转变,由通常的两相(γ/β或γ/γ′)转变成单相(γ)。整个氧化过程因Al的逐渐消耗和Al2O3层的不断增厚而逐渐减缓,最终形成接近或达到热力学稳定的γ-Ni(Al)/α-Al2O3界面。EVANS等[26]对典型多层热障涂层系统的界面体系组成及各组元层的基本功能有清楚描述。因此,与一般第一性原理研究常规异相界面的方法[14-15]不同,本文作者研究这类界面的结合强度,首先考虑热生长过程的热力学平衡条件,即从计算界面平衡相图开始。
1.1 界面平衡相结构的确定
由于异相界面两侧晶格常数的差异,界面形成时不可避免出现失配位错。构建一个足够大的异型界面超胞,将这类失配位错“自然”包含在内,将导致极大的计算量。在γ-Ni/α-Al2O3界面附近晶格中引入尽可能小的变形量,以形成接近理想共格的界面原子结构模型。在计算界面强度(即界面分离功)时,由于界面和两个分离表面之间的能量相消,可以最大程度地消除应变对界面分离功数值的影响。
图1所示为3种典型界面原子结构类型的构建关系(即模型Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ),分别代表3种典型的界面取向和共格应变的组合[16]。其中,具有γ-Ni(111)(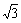 ×
×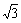 )//α-Al2O3(0001)(1×1)取向关系的结构中(模型Ⅰ和Ⅱ),共格的金属Ni一侧均承受拉伸应变,与类似界面(Nb/Al2O3)的高分辨电镜(HRTEM)观察[27]较符合。据此判断,模型Ⅰ和Ⅱ较为合理,其中模型Ⅱ所需共格应变量相对最小,因而在后续计算中采用。
)//α-Al2O3(0001)(1×1)取向关系的结构中(模型Ⅰ和Ⅱ),共格的金属Ni一侧均承受拉伸应变,与类似界面(Nb/Al2O3)的高分辨电镜(HRTEM)观察[27]较符合。据此判断,模型Ⅰ和Ⅱ较为合理,其中模型Ⅱ所需共格应变量相对最小,因而在后续计算中采用。
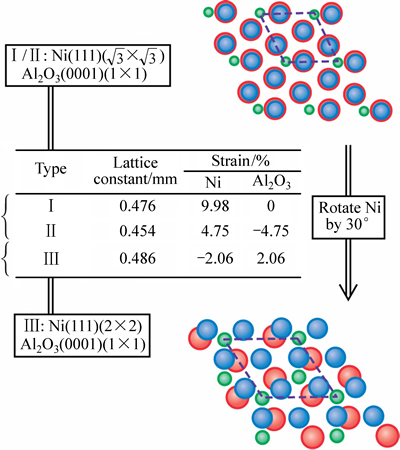
图1 典型界面结构的界面取向和共格应变关系(Ni、Al、O 原子分别用蓝、绿、红色标示)
Fig. 1 Typical commensuration types for γ-Ni/α-Al2O3 interface with different orientations and coherent strains (Ni, Al and O atoms are represented by dark blue, green and red spheres, respectively)
1.1.1 界面原子化学配比的影响
BC/TGO界面的平衡相结构,由实际热生长条件(如温度和化学反应气氛)决定,其中化学气氛可由氧分压或合金中的Al活度表征,它直接决定着实际参与界面化学反应的各元素原子的相对含量,即界面附近的原子化学计量比。参考表面终端(Termination)的概念,可以假设3种典型的界面原子化学配比类型,即理想化学计量比(Ni/Al2O3)、富Al(Ni/AlAl2O3)和富O型(Ni/OAl2O3)[16]。分别计算对应的界面分离功,结果表明:相比于界面取向和共格应变,界面原子化学配比是决定界面结合强度的主要因数。界面结构类型不同,但原子化学配比类型相同,界面分离功相差最大不超过50%;而界面结构类型相同,但原子化学配比不同,界面强度相差则可达数倍以上。以模型II界面为例,富Al和富O型界面的界面强度,分别是理想化学计量比界面的4倍和6倍。这些结果表明,对于BC/TGO这类热生长界面,任何无视界面原子化学配比的计算研究,其结果和讨论至少是不完整。分别计算对应的界面能,并通过界面能与温度和Al活度之间的热力学关系,可计算界面平衡相图,从而可以预测形成高结合强度的富Al和富O型界面所需的热力学条件。
1.1.2 Al活度与界面平衡相图的关系
根据缺陷热力学,不难推导出热力学平衡条件下Ni/AlB2BOB3B界面能的表达式[28]
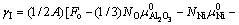
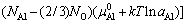 (1)
(1)
式中:Fo是整个超胞的Helmholtz自由能,上标 ‘0’表示各组元的纯净态;Ni和μi分别是各组元元素i的原子个数和化学势;A是界面面积。由于前四项自由能之间存在大量相消,温度对界面能的影响主要体现在最后一项,即kT lnaAl,其中aAl是γ-Ni(Al)基体的Al活度,可计算如下[25]
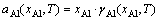 (2)
(2)
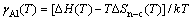 (3)
(3)
式中:γAl是基体Ni(Al)合金中的Al活度因子,在较低浓度(xAl≤10%~15%)时一般可认为与浓度无关,即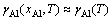 。DH和DSn-c分别为单个Al原子从纯净单质固溶到γ-Ni(Al)基体中所发生的焓变和非形熵变[25]。图2所示为计算得到的Al活度因子随温度的变化关系[29-32]。与相关实验值比较,计算值与实测值在高温区间普遍吻合较好,但在较低温度(980 K)时偏差在4个数量级左右。这主要是由于接近Al熔点的温度下,对蒸汽分压的实测值误差太大。相比之下,理论计算从热力学原理出发,不受实验条件局限,可涵盖较广泛的温度区间,所得预测更为可靠。本研究中将主要针对高温区间为1300~1600 K。
。DH和DSn-c分别为单个Al原子从纯净单质固溶到γ-Ni(Al)基体中所发生的焓变和非形熵变[25]。图2所示为计算得到的Al活度因子随温度的变化关系[29-32]。与相关实验值比较,计算值与实测值在高温区间普遍吻合较好,但在较低温度(980 K)时偏差在4个数量级左右。这主要是由于接近Al熔点的温度下,对蒸汽分压的实测值误差太大。相比之下,理论计算从热力学原理出发,不受实验条件局限,可涵盖较广泛的温度区间,所得预测更为可靠。本研究中将主要针对高温区间为1300~1600 K。
针对不同的界面相结构,计算任意给定温度下界面能与Al活度的对应关系,就可以得到界面平衡相图的一个等温截面。图3所示为通过式(1)~(2)计算得到的T=1300 K等温截面及相应的界面相结构。热生长界面形成后,界面附近Al的大致浓度范围为1≤ xAl≤15%,结合Al活度因子的计算结果,可以推断界面附近Ni(Al)一侧Al元素的大致活度范围。根据等温截面相图,可以判断该温度下界面平衡相应是富Al相(Ni/AlAl2O3),但靠近理想化学配比相的相界。
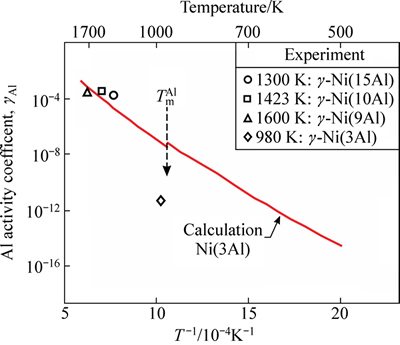
图2 计算预测的Al活度因子随温度的变化及其与相应实验值[29-32]的比较
Fig. 2 Comparison of calculated Al activity coefficient in γ-Ni(Al) and experimental values[29-32]
由图3还可看出,在足够高的Al活度(即乏氧气氛)条件下,界面甚至可直接生成镍铝金属间化合物(Ni3Al)。而随着Al活度不断降低(对应于氧分压的不断升高),该温度下界面平衡相可能逐步转变为理想化学计量比相(Ni/Al2O3)、富O相(Ni/OAl2O3)、复合氧化物(NiAl2O4)、直至氧化镍(NiO),其中复合氧化物和氧化镍界面相的形成,在一些特殊方法制备的BC/TGO界面上都得到了实验证实[30, 33]。
由于环境中的氧分压与合金中的Al活度之间存在一定的换算关系,可以由择优氧化反应:Al(solid)+O2(gas)=Al2O3(solid)的热力学平衡条件推导[24],因此,根据界面平衡相图,可以进一步预测形成不同界面相结构所需的对应热力学生长条件,帮助实验人员分析和解释众多实验现象好而结果,以及指导实验制备工艺的设计优化,在此不再赘述。
1.2 界面偏析与界面强度
在计算微合金化元素Zr的界面偏析时,为谨慎起见,将同时考虑两种界面(即富Al型和理想化学计量比型界面)的偏析行为,并进而比较其对界面分离功的影响。
1.2.1 界面偏析能和偏析路径的关系
如前所述,同样的基体,在不同生长条件(温度和气氛)下得到的界面平衡相可能不同,因此,合金和杂质元素的界面偏析能力也会相应不同,从而直接影响到它们对界面的影响和作用。界面偏析能力,可以通过计算和比较偏析前后界面超胞总能的变化(即界面偏析能)来评估。正值的界面偏析能代表从基体向界面的偏析趋势,反之亦然。比较同一元素对界面不同位置的偏析能,可以确定该元素的偏析路径。比较不同元素的界面偏析能,可以确定元素之间的偏析优先权。
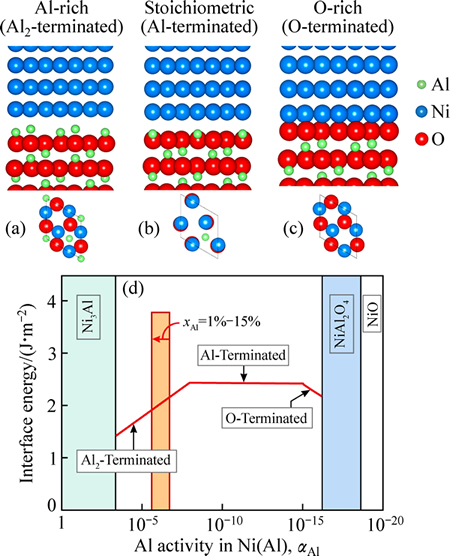
图3 富Al相(Ni/AlAl2O3)、理想化学配比相(Ni/Al2O3)以及富O相(Ni/OAl2O3)的界面原子结构以及计算得到的界面平衡相图中T=1300 K的等温截面(图中橙色柱代表计算获知的界面附近Al活度的大致范围)
Fig. 3 Atomic structures of Al-rich (Ni/AlAl2O3) (a), stoichiometric (Ni/Al2O3) (b) and O-rich (Ni/OAl2O3) interfaces (c) and calculated interfacial phase diagram for T=1300 K (d) (Approximate variation range of near-interface Al activity is represented as orange bar)
图4所示为计算预测的元素Zr对界面的偏析能力,并与之前杂质S偏析的计算结果[12, 14]对比。结果显示:1) 对于理想化学计量比界面,杂质S有强烈的偏析能力。在界面的填隙位(SI)和Ni置换位(SNi),S的偏析能分别为1.74和1.44 eV/atom。不过,元素Zr的界面偏析能力更强,在界面填隙位(ZrI)和Ni置换位(ZrNi),Zr的偏析能分别达到2.34和2.02 eV/atom;2) 对于富Al型界面,S的偏析能力大大降低,在界面Ni置换位(SNi)和填隙位(SI)上,S的偏析能仅分别为0.44 和0.20 eV/ atom。相对而言,Zr依然具有很强的偏析能力,在Al置换位(ZrAl)上偏析能为1.08 eV/atom。对比之前的计算结果[17],可以发现,在这两类界面上,Zr的偏析能力比同族的Hf略强,且均明显强于杂质S。S能否在界面偏析,将不得不取决于先期抵达界面的Zr原子占位。以理想化学计量比界面(见图4(b))为例,偏析到界面的杂质S可以先后占据Ni置换位(SNi)和填隙位(SI),体系总能进一步降低0.87 ev/atom。如果界面已有偏析Zr存在,杂质S的偏析仍然可以继续进行,并抢占Ni置换位(SNi),在界面上出现Zr和S的“共同偏析”,体系总能进一步降低。从图4(a)可以看到,类似的共同偏析也可以在富Al相的界面上出现。界面偏析(包括共同偏析)对界面强度的影响,可以通过直接计算相应的界面分离功定量评估。
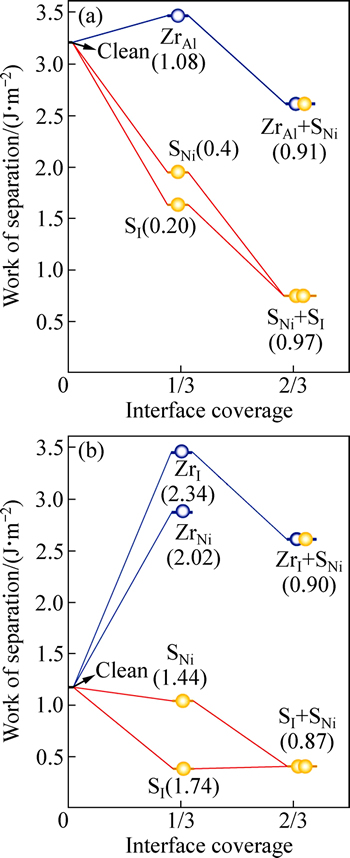
图4 富Al相和理想化学配比相界面的界面分离功(Wsep)随界面偏析度的变化(界面偏析度以Ni(111)层上每Ni原子为单位。括号中的数字代表各偏析进程对应的界面偏析能(单位:eV/atom))
Fig. 4 Work of separation, Wsep as function of interfacial coverage for Al-rich (a) and stoichiometric interfaces (b) (Interfacial coverage is valued as per Ni atom on Ni(111) layer, values in parentheses correspond to associated heats of segregation for each segregation step (Unit: eV/atom))
1.2.2 元素偏析对界面强度的影响
比较偏析前后界面结构的变化,计算相应的界面分离功(Wsep),可以定量评估元素偏析对界面结合强度的影响。有关界面分离功的计算结果可见图4和5。对于感兴趣的界面,可以结合相应的价电子密度分布云图(见图6),定性分析界面附近电子成键的特点,以及合金和杂质元素偏析对界面化学成键的影响。
相图预测为热力学平衡相的富Al相,其纯净界面具有较高的界面结合强度(Wsep=3.20 J/m2),约3倍于理想化学计量比界面的强度(1.14 J/m2),这是由于富Al相界面上形成有很强Ni—Al金属键(见图6(a)),远强于理想化学计量比相界面上的Ni—O键(共价-离子混和键,见图6(b))。在这两类界面上,特别是在理想化学计量比相界面上,杂质硫对界面强度危害极大,可降低界面分离功达60%~70%(见图4和5)。由于硫的界面偏析,界面上原本还算较强的Ni—O键被较弱的共价键S—O键和更弱的离子键S—Al键替换(见图6(d)),导致界面弱化。值得注意的是,合金元素Zr的界面偏聚效应与同族的Hf元素[17]非常类似。Zr偏聚对界面的强化作用,在相对较弱的理想化学计量比界面上表现得尤为明显(见图4(b)和5)。特别是当Zr偏析到填隙位置(ZrI),可使Wsep提升约300%。仔细观察计算得到的基态界面原子结构可知,这样显著的强化效果,实际上源自于界面原子结构的改变:Zr在理想化学计量比界面的填隙位上偏析(ZrI),恰巧复制Zr在富Al相界面上的Al置换位偏析(ZrAl)的界面结构。对应的界面价电子密度云图(见图6(c)) 清楚显示,Zr能够同时与界面两侧的Ni和O形成新键,新键键能远强于图6(b)中的Ni—O键,接近图6(a)中的Ni—Al金属键,从而使原本较弱的理想化学计量比界面强度提升近3倍,达到富Al相界面的理论结合强度。显然,Zr能够直接参与界面成键,从而强化界面。值得注意的是,图4(b)已清楚显示,Zr对界面的强化作用,容易遭后续偏析的S破坏而消减,因此,对于这两类界面,Zr和S的共同偏析需要尽可能地避免。只有设法将S有效地钉扎在基体中,避免其在界面的偏析,才有可能最大限度地发挥Zr的强化作用。
2 基体内的杂质钉扎
高温下直接表征基体合金中原子间的相互作用,目前的实验检测技术手段尚难以实现。运用第一性原理直接计算和比较Zr-S原子在γ-Ni(FCC)晶格中的最近邻(2.5  )距离和理论上无限远距离上的系统总能,以其差值可定量反映Zr-S之间相互作用的强弱。总能之差为正,Zr-S原子对在γ-Ni基体中就趋向分裂;反之,Zr-S原子对在γ-Ni基体中就趋向稳定,表明S能够被Zr有效钉扎。显然,总能差值越负,钉扎能力则越强。实际计算中,选择以FCC晶格中的第五近邻距离作为无限远近似(约为8.5
)距离和理论上无限远距离上的系统总能,以其差值可定量反映Zr-S之间相互作用的强弱。总能之差为正,Zr-S原子对在γ-Ni基体中就趋向分裂;反之,Zr-S原子对在γ-Ni基体中就趋向稳定,表明S能够被Zr有效钉扎。显然,总能差值越负,钉扎能力则越强。实际计算中,选择以FCC晶格中的第五近邻距离作为无限远近似(约为8.5  ),可以确保此时两个原子间距足够远,相互作用可忽略不计。
),可以确保此时两个原子间距足够远,相互作用可忽略不计。
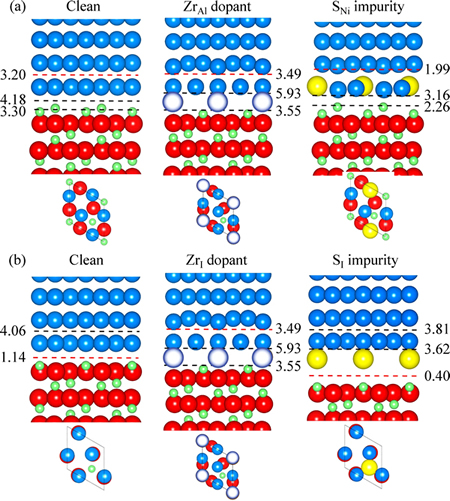
图5 元素偏析对富Al相界面和理想化学计量比界面的结合强度
Fig. 5 Segregation structures and Wsep for Al-rich (a) and stoichiometric interface (b) at 1/3 monolayer coverage of Zr and S (Ni, Al, and O atoms are represented in dark blue, green and red, respectively. Zr and S atoms are represented in bright blue and yellow, respectively)
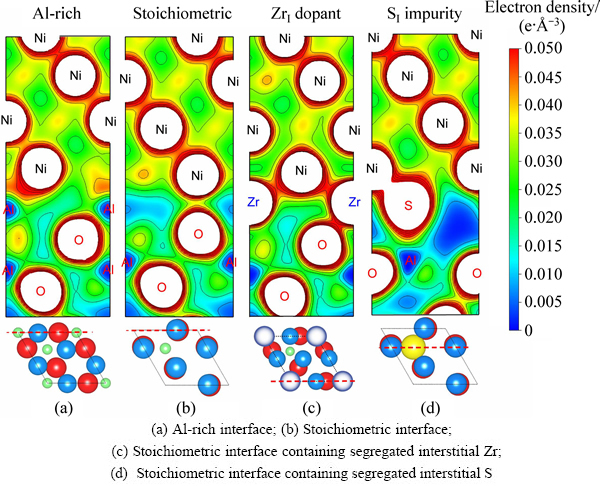
图6 界面价电子密度云图
Fig. 6 Interfacial valence electron density contours (Dash-dot lines at bottom correspond to positions of contour planes in top-views, (Unit: e/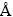 3))
3))
相关计算结果可见图7(a)。计算中充分考虑温度对晶格的振动熵的贡献(即热声子,Phonons)以及热电子效应[34]。从图7(a)看到,在0K下,即不考虑任何温度效应时,Ni基体中的Zr和S能形成稳定的原子对且相互作用较强,总能之差约为-0.21 eV/atom。随着温度的升高,晶格热膨胀效应会导致原子间距增大,高温下晶格热声子振动和热电子效应两个因素共同作用,会进一步影响Zr-S之间的相互作用。计算表明,在感兴趣的整个高温区间(1300~1600 K),Zr都能较强地钉扎S,钉扎能为-0.2~0.44 eV/atom,与同族的Hf钉扎能力接近[17]。图7(b)所示为所计算Ni基体中Zr-S原子对的价电子局域化函数分布(Electron localization function, ELF[35])。在Ni-Zr金属的均匀电子密度背景衬托下,电子密度主要在S附近且沿Zr方向相对集中,显示Zr-S的相互作用主要是离子键性质,并可能混合少量的共价成分。电子态密度分析也证实有微弱的Zr(5d,6s)-S(3p)轨道杂化。与同族Hf相同,Zr与S原子之间存在价电荷迁移,是其在γ-Ni基体中能够有效钉扎杂质S的微观机制。
图7 γ-Ni基体中Zr-S原子对相互作用能温度下随温度的变化和Zr-S原子对附近的电子局域化函数等势图
Fig. 7 Change of interaction energies of Zr-S pair in γ-Ni with temperature at high temperatures (a) and electron localization function (ELF) contours around Zr-S pair (b) (Dashed lines refer to interaction energies calculated at 0 K, reflecting low-temperature pair attraction)
3 结论
1) 热障涂层中BC/TGO关键界面的界面结构由生长气氛(Al活度或O分压)和环境温度决定。根据计算得到的界面平衡相图,在感兴趣的温度区间(1300~1600 K),界面平衡相为富Al相,但靠近理想化学计量比相的相界。富Al相界面结合强度较高(Wsep=3.20 J/m2),约三倍于理想化学计量比界面(1.14 J/m2)。但杂质S偏析到这两种界面上,均可降低界面结合强度达60%~70%。
2) 对可能共存的两种界面相,合金元素Zr均具有强烈的偏析能力,且偏析能力比同族元素Hf更强。
3) Zr微合金化明显有助于界面强化,其强化机理与同族元素Hf类似,主要包括3种:在Ni基体内有效钉扎杂质S抑制S的界面偏析,在界面处置换偏析杂质S减少S效应对界面的直接危害,或直接参与界面成键以强化界面结合。
4) 对于结合最弱的理想化学计量比界面,Zr微合金化可提高其界面分离功约3倍(Wsep=3.5 J/m2),超过富Al型界面的理论结合强度(3.20 J/m2)。
REFERENCES
[1] EVANS A G, MUMM D R, HUTCHINSON J W, MEIER G H, PETTIT F S. Mechanisms controlling the durability of thermal barrier coatings[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2001, 46(5): 505-553.
[2] GLEESON B. Thermal barrier coatings for aeroengine applications[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2006, 22(2): 375-383.
[3] 刘纯波, 林 锋, 蒋显亮. 热障涂层的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(1): 1-13.
LIU Chun-bo, LIN Feng, JIANG Xian-liang. Current state and future development of thermal barrier coating[J]. The Chinese Journal of NonferrousMetals, 2007, 17(1): 1-13.
[4] SMIALEK J L, JAYNE D T, SCHAEFFER J C, MURPHY W H. Effects of hydrogen annealing, sulfur segregation and diffusion on the cyclic oxidation resistance of superalloys: A review[J]. Thin Solid Films, 1994, 253(1/2): 285-292.
[5] GAUDETTE F G, SURESH S, EVANS A G. Effects of sulfur on the fatigue and fracture resistance of interfaces between gamma-Ni(Cr) and alpha-Al2O3[J]. Metall Trans A, 2000, 31(8): 1977-1983.
[6] KIELY J D, YEH T, BONNELL D A. Evidence for the segregation of sulfur to Ni-alumina interfaces[J]. Surf Sci, 1997, 393(1/3): L126-130.
[7] FUNKENBUSCH A W, SMEGGIL J G, BORNSTEIN N S. Reactive element-sulfur interaction and oxide scale adherence[J]. Metall Trans A, 1985, 16(6): 1164-1166.
[8] KHANNA A S, WASSERFUHR C, QUADAKKERS W J, NICKEL H. Addition of ytterium, cerium, and hafnium to combat the deleterious effect of sulfur impurity during oxidation of an Ni-Cr-Al alloy[J]. Mat Sci Eng, 1989, A120(1):185-191.
[9] HOU P Y. Segregation phenomena at thermally grown Al2O3/Alloy interfaces[J]. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2008, 38: 275-298.
[10] BARRETT C A. Effect of 0.1 at.% zirconium on the cyclic oxidation resistance of β-NiAl[J]. Oxidation of Metals, 1988, 30(5/6): 361-390.
[11] HAMADI S, BACOS M P, POULAIN M, SEYEUX A, MAURICE V, MARCUS P. Oxidation resistance of a Zr-doped NiAl coating thermochemically deposited on a nickel-based superalloy[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2009, 204(6/7): 756-760.
[12] OZFIDAN I, CHEN K Y, FU M, Effects of Additives and Impurity on the adhesive behavior of the NiAl(110)/Al2O3 (0001) interface: An ab initio study[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2011, 42(13): 4126-4136.
[13] 李志林, 吴远启. 粘接层中Cr对热障涂层界面结合因子的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(9): 1477-1482.
LI Zhi-lin, WU Yuan-qi. Influence of bonding layer Cr content of thermal barrier coatings on its interface conjunction factors[J]. The ChineseJournalof NonferrousMetals, 2004, 14(9): 1477-1482.
[14] CARLING K M, CARTER E A. Effects of segregating elements on the adhesive strength and structure of the α-Al2O3/β-NiAl interface[J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55: 2791-2830.
[15] JARVIS E A, CHRISTENSEN A, CARTER E A. Weak bonding of alumina coatings on Ni (111)[J]. Surface Science, 2001, 487(1/3): 55-76.
[16] SMITH J R, JIANG Y, EVANS A G. Adhesion of the gamma-Ni(Al)/alpha-Al2O3 interface[J]. International Journal of Materials Research (formerly Z. Metallkd.), 2007, 98(12): 1214-1221.
[17] JIANG Y, SMITH J R, EVANS A G. First principles assessment of metal/oxide interface adhesion[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(14): 141918.
[18] JIANG Y, SMITH J R. Pt effects in gamma-Ni(Al)/alpha-Al2O3 adhesion[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2009, 44(7): 1734-1740.
[19] 江 勇. 基于第一性原理揭示活性元素铪对热障涂层关键界面的强化机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(6): 1463-1472.
JIANG Yong. Strengthening mechanisms of reactive-element Hf on the key interface in thermal barrier coating systems from the first-principles[J]. The ChineseJournalof NonferrousMetals, 2011, 21(6): 1463-1472.
[20] LAN G Q, WANG Y R, JIANG Y. Effects of rare-earth dopants on the thermally grown Al2O3/Ni(Al) interface: the first-principles prediction[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2014, 49: 2640-2646.
[21] LAN G Q, JIANG Y, YI D Q, LIU S J. Theoretical prediction on microstructure evolution during the internal oxidation fabrication of metal-oxide composites: the case of Cu-Al2O3[J]. RSC Advances, 2013, 3(36): 16136-16143.
[22] LAN G Q, JIANG Y, YI D Q, LIU S J. Theoretical prediction of impurity effects on the internally oxidized metal/oxide interface: The case study of S on Cu/Al2O3[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2012, 14(31): 11178-11184.
[23] 江 勇, 蓝国强, 王怡人, 周松松. 内氧化Cu/Al2O3界面热力学与杂质效应[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(11): 3154-3164.
JIANG Yong, LAN Guo-qiang, WANG Yi-ren, ZHOU Song-song. Interfacial thermodynamics and impurity effects on internally oxidized Cu/Al2O3 interface[J]. The ChineseJournalof NonferrousMetals, 2013, 23(11): 3154-3164.
[24] KRESSE G, FURTHM LLER J. VASP manual[EB/OL]// http://cms.mpi.univie.ac.at/vasp/vasp/vasp.html
LLER J. VASP manual[EB/OL]// http://cms.mpi.univie.ac.at/vasp/vasp/vasp.html
[25] JIANG Y, SMITH J R, EVANS A G. Temperature dependence of the activity of Al in dilute Ni(Al) solid solution[J]. Physical Review B, 2006, 74(22): 224110.
[26] EVANS A G, CLARKE D R, LEVI C G. The influence of oxides on the performance of advanced gas turbines[J]. J Euro Ceram Soc, 2008, 28(7): 1405-1419.
[27] VITEK V, GUTEKUNST G, MAYER J, RUHLE M. Atomic-structure of misfit dislocations in metal-ceramic interfaces[J]. Philosophical Magazine A, 1995, 71(6): 1219-1239.
[28] ZHANG W, SMITH J R, EVANS A G. The connection between ab initio calculations and interface adhesion measurements on metal/oxide systems: Ni/Al2O3 and Cu/Al2O3[J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50(15): 3803-3816.
[29] ESKOV V M, SAMOKHVAL V V, VECHER A A. Thermodynamic properties of Al-Ni hard alloys[J]. Russ Metall, 1974, 2: 118-119.
[30] STEINER A, KOMAREK K L. Thermodynamic activities of solid nickel-aluminum alloys[J]. Trans Metall Soc AIME, 1964, 230(4): 786-788.
[31] OFORKA N C. Thermodynamics of nickel-aluminum alloys[J]. Indian J Chem A, 1986, 25(11): 1027-1029.
[32] HILPERT K, MILLER M, GERADS H, NICKEL H K. Thermodynamic study of the liquid and solid alloys of the nickel-rich part of the Al-Ni phase-diagram including the AlNi3 phase[J]. Ber Bunsenges, Phys Chem, 1990, 94(1): 40-47.
[33] DAROONPARVAR M, YAJID A M M, YUSOF N M, FARAHANY S, HUSSAIN M S, BAKHSHESHI -RAD H R, VALEFI Z, ABDOLAHI A. Improvement of thermally grown oxide layer in thermal barrier coating systems with nano alumina as third layer[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(5): 1322-1333.
[34] JIANG Y, LIU R. Gettering of S in Ni from first-principles[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2010, 62(10): 782-785.
[35] BECKER A D, EDGECOMBE K E N. A simple measure of electron localization in atomic and molecular systems[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1990, 92(9): 5397-5403.
Strengthening effects and mechanisms of micro-alloying Zr on key interface in thermal barrier coating systems
LAN Guo-qiang1, 2, JIANG Yong1, 2, 3, 4, JIANG Liang3, 4
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Nonferrous Materials, Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. National Key Laboratory for Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
4. Shenzhen Research Institute, Central South University, Shenzhen 518057, China)
Abstract: Bond-coat/thermally-growth-oxide interface is the key interface in high-temperature thermal barrier coating systems. The first-principle interface thermodynamics modeling combined with density functional theory calculations were performed to investigate the effects of micro-alloying Zr on the γ-Ni(Al)/α-Al2O3 interface structure, segregation, and adhesion, and pinning impurity (S) in the matrix. The results show that Zr plays very similar roles as Hf. The addition of Zr substantially improves the adhesion through three strengthening mechanisms: pining S in bulk Ni(Al), displacing S from its interstitial interface sites and directly enhancing the interfacial binding. The binding strength of the weak stoichiometric interface can be enhanced by up to a factor of 3.
Key words: thermal barrier coating; interface adhesion; micro-alloying; zirconium; first-principles
Foundation item: Project(51171211) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2012AA03A514) supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China; Project(JCYJ20140509142357196) supported by the Shenzhen Science and Technology Program, China
Received date: 2015-03-03; Accepted date: 2016-07-04
Corresponding author: JIANG Yong; Tel: +86-731-88836320; E-mail: yjiang@csu.edu.cn
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金面上项目(51171211);国家高技术研究开发计划资助项目(2012AA03A514);深圳市科技计划项目(JCYJ20140509142357196)
收稿日期:2015-03-03;修订日期:2016-07-04
通信作者:江 勇,教授,博士;电话:0731-88836320;E-mail:yjiang@csu.edu.cn