生物浸出体系中中等嗜热菌对锌冶炼窑渣中金属的提取及其电化学特性的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2012年第12期
论文作者:蒋凯琦 郭朝晖 肖细元 韦小颖
文章页码:3120 - 3125
关键词:锌冶炼窑渣;嗜热菌;生物浸出;化学浸出;电化学行为
Key words:zinc smelting slag; thermophilic bacteria; bioleaching; chemical leaching; electrochemical behavior
摘 要:研究中等嗜热菌对锌冶炼窑渣中金属提取的影响以及生物浸出过程中锌冶炼窑渣碳糊电极的电化学特性。结果表明,在矿浆浓度2%、pH1.0、温度65 °C、转速为120 r/min的浸出条件下,去除生物浸出体系中吸附菌后,废渣中Fe、Cu和Zn的浸出率分别为86.7%、90.3%和66.7%,而在没有去除吸附菌体系中3种金属的浸出率分别为91.9%、96.0%和84.5%。对生物浸出渣和酸浸渣表面细菌分泌物进行FT-IR测试分析可知,生物浸出渣颗粒表面出现了新的官能团振动峰,如1007 cm-1和1193 cm-1处的峰,间接说明残渣颗粒表面吸附细菌的存在。生物浸出体系和空白体系的循环伏安曲线和塔菲尔曲线特性进一步表明生物浸出体系中细菌促进了锌冶炼窑渣中有价金属的溶出。
Abstract: The effects of moderately thermophilic bacteria on the extraction of metals from zinc smelting slag and electrochemical characteristics of zinc smelting slag carbon paste electrode in bioleaching process were studied. The results show that the extraction rates of Fe, Cu and Zn from the slag reach 86.7%, 90.3% and 66.7% after adsorbed bacteria sterilize, while those with adsorbed bacteria are 91.9%, 96.0% and 84.5% in conditions of pulp density 2%, pH 1.0, temperature 65 °C and stirring rate 120 r/min, respectively. Some stretching peaks of functional groups from bacterial secretes on the bioleached residue surface, such as 1007 cm-1 and 1193 cm-1, turn up through FI-IR analysis and indirectly reveal the presence of the adsorbed bacteria on the slag particles surface. Besides, the corrosion of zinc smelting slag is enhanced by bacteria according to the characteristics of cyclic voltametry and Tafel curves in bioleaching system.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 3120-3125
JIANG Kai-qi, GUO Zhao-hui, XIAO Xi-yuan, WEI Xiao-ying
Institute of Environmental Engineering, School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 27 April 2012; accepted 25 September 2012
Abstract: The effects of moderately thermophilic bacteria on the extraction of metals from zinc smelting slag and electrochemical characteristics of zinc smelting slag carbon paste electrode in bioleaching process were studied. The results show that the extraction rates of Fe, Cu and Zn from the slag reach 86.7%, 90.3% and 66.7% after adsorbed bacteria sterilize, while those with adsorbed bacteria are 91.9%, 96.0% and 84.5% in conditions of pulp density 2%, pH 1.0, temperature 65 °C and stirring rate 120 r/min, respectively. Some stretching peaks of functional groups from bacterial secretes on the bioleached residue surface, such as 1007 cm-1 and 1193 cm-1, turn up through FI-IR analysis and indirectly reveal the presence of the adsorbed bacteria on the slag particles surface. Besides, the corrosion of zinc smelting slag is enhanced by bacteria according to the characteristics of cyclic voltametry and Tafel curves in bioleaching system.
Key words: zinc smelting slag; thermophilic bacteria; bioleaching; chemical leaching; electrochemical behavior
1 Introduction
Zinc smelting slag from metallurgical industries contains relatively high levels of metals and poses a potential threat to environment [1]. Chemical leaching processes for disposal of the slag have been widely investigated. For example, the extraction rates of Cd, Ni and Zn from a zinc plant residue could excess 95% by using 1.22 mol/L H2SO4, at 25 °C for 60 min, but with negligible dissolution of Pb [2]. The extraction rates of Zn and Pb from a zinc leached residue can exceed 71.9% and 91.0% through both acid leaching and brine leaching, respectively [3]. However, secondary contamination and the waste of leaching agent would be produced by these hydrometallurgical methods [4]. Bioleaching has been employed in sulfide minerals, which is potentially applied in treatment of smelting slag [5,6].
With the application of bioleaching in waste solid disposal, the mechanism of bioleaching was focused to enhance the feasibility of bioleaching. The mechanisms of bioleaching are usually considered as non-contact, contact interaction of microorganism as well as electrochemical mechanism [7]. In the non-contact mechanism, Fe3+ is depleted through the oxidation of mineral, can significantly recover Cu from enargite in bioleaching process and the extraction rate reaches 90.9% [8]. While the adhesion of bacteria to sulfide minerals surface and mineral dissolution referring to the contact mechanism are definitely concerned [9]. Especially, the dissolution behavior of sulfide minerals in bioleaching can be known through electrochemical technologies. For instance, the electrochemical responses of massive chalcopyrite electrodes bioleached for various periods up to 20 d using cyclic voltametry showed that the oxidation peak of chalcopyrite disappeared at the late stage of bioleaching while those of intermediate species (CuxS (1
The bioleaching mechanism of zinc smelting slag by moderately thermophilic microorganisms, however, is ambiguous. The electrochemical responses were analyzed based on the similar behaviors of some compounds like Cu2S, FeS2 and ZnS containing in chalcopyrite and pyrite ores during bioleaching [10,11], the electrochemical behavior of zinc smelting slag electrode in bioleaching also remains enigmatic. The aims of this work are to determine the effect of adsorbed bacteria on Fe, Cu and Zn solubilization and the adsorption characteristics of bacteria on zinc smelting slag surface by FT-IR analysis and, to elucidate the electrochemical behaviors between zinc smelting slag carbon paste electrode and moderately thermophilic bacteria through cyclic voltametry and Tafel curves in bioleaching system.
2 Experimental
2.1 Zinc smelting slag and microorganism
Zinc smelting slag, a historical solid waste, was collected from an abandoned pile in Hengyang district, Hunan Province of China. The slag was dried at 60 °C and crushed using ball mill and then passed through a 0.25 mm sieve. The chemical composition and characterization of the slag are listed in Table 1 and Fig. 1.
Table 1 Element compositions of zinc smelting slag

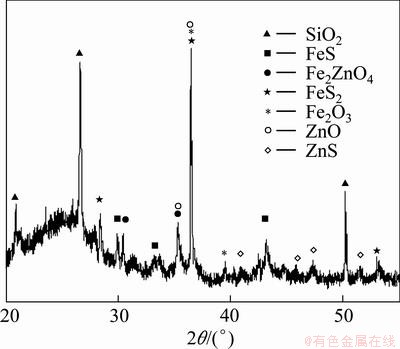
Fig. 1 XRD pattern of zinc smelting slag
Based on the results of chemical analysis, the contents of Fe, Cu and Zn in smelting slag are 18.5%, 0.84% and 2.53%. The mineralogical phases of zinc smelting slag mainly included SiO2, FeS, Fe2ZnO4, FeS2, Fe2O3, ZnO and ZnS by XRD analysis.
The indigenous moderate thermophilic bacteria in biological system are mainly affiliated with Bacillus spp., Sporosarcina spp. and Pseudomonas spp. [6]. The bacteria were conducted by centrifugation with velocity of 1157 g for 5 min to isolate slag from solution. Then, the bacteria in solution were separated with velocity of 12587 g for 20 min, which was conducted repeatedly until bacteria concentration reached 108 cells/mL, then the bacteria can be inoculated. The culture medium included 0.5 g/L (NH4)2SO4, 0.2 g/L NaCl, 0.3 g/L MgSO4·7H2O, 0.2 g/L KH2PO4, 0.07 g/L Ca(NO3)2·4H2O and 0.2% yeast extract.
2.2 Experimental
2.2.1 Zinc smelting by bioleaching
First, slag was leached in the system of pH 1.0, pulp density 2%, inoculation 10% with bacteria concentration of 108 cell/mL at 65 °C during the first 12 h. Then, the slag and liquid were separated by centrifugation with velocity of 1157 g for 5 min. The separated slag was boiled in deionized water at 100 °C for 5 min in order to detach adsorbed bacteria from slag surface. Whereas the separated supernatant was added back to the boiled slag and the mixture was adjusted to pH 1.0 again. The bioleaching was continued for an additional 72 h. The whole leaching process sustained for 84 h to observe the changes of Fe, Cu and Zn extraction rates. Accordingly, two control experiments accompanied in the process, one was pH 1.0 with bacteria leaching for 84 h, another was bacteria-free, which was sterilized in an Oualtex autoclave at 121 °C for 20 min and added 2 mL saturated HgCl2 for sterilization during bioleaching process. Deionized water was added to the erlenmeyer flasks to compensate for evaporation losses. The concentrations of Fe, Cu and Zn in leachates were periodically analyzed. The first sample collected was 12 h, the second was 18 h and the third was 36 h, the remainders were taken for 12 h interval. Each experiment was triplicates.
2.2.2 Electrochemical experiments using cyclic voltametry and Tafel curves
Carbon paste electrode was prepared according to the method of CRUZ et al [12]. Working electrodes were prepared with zinc smelting slag (0.075 mm), graphite powder and paraffin wax and the mass ratio was 7(slag):1(graphite powder):1(paraffin wax). Zinc smelting slag and graphite powder were mixed and stirred homogeneously. The molten paraffin wax was added into the mixture immediately and was stirred in water bath at 65 °C. Finally, the mixture with zinc smelting slag, graphite powder and paraffin wax was molded into a cylinder with diameter of 13.5 mm and height of 8 mm using the bead machine (YP-250, China). The electrode surface was polished on 1200-grit silicon carbide paper, as far as possible, with no visible imperfections. It was sequentially cleaned by acetone, ethanol and deionized water, respectively.
A three-electrode system was used for the electrochemical determination. The cell consisted of a zinc smelting slag carbon paste electrode, a platinum counter electrode and a saturated calomel reference electrode. The electrochemical experiments were carried out at 30 °C and pH 1.0 using an electrochemical workstation (LK2005, China). All scannings were initiated from the open circuit potential (ocp). The electrode was immersed in solution for approximately 30 min in order to reach a constant ocp value before any voltammetric perturbation. Cycles of Tafel curves were performed from 0 to 800 mV (positive-going potential scan), then to -800 mV (negative-going potential scan), and back to 0 mV (positive-going potential scan) with scanning rate of 20 mV/s. Tafel curves were performed from 200 to 500 mV with scanning rate of 1 mV/s.
2.3 Analysis
Concentrations of Cu, Fe and Zn in leachates were determined by an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES, IRIS Intrepid II XSP, USA). The residues from bioleaching and acid leaching were dried in vacuum desiccator, and characterized by FT-IR [13], respectively.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of adsorbed bacteria on metal solubilization
The effects of adsorbed bacteria on the extraction rates of Fe, Cu and Zn from zinc smelting slag during bioleaching are shown in Fig.2. The extraction rates of Fe, Cu and Zn were significantly increased in the first 12 h. After adsorbed bacteria sterilized, the extraction rates of Fe and Cu slowed down compared with those adsorbed bacteria and maintained steady after 12 h. The extraction rates of Fe and Cu were 86.7% and 90.3%, while those of leaching with adsorbed bacteria reached 91.9% and 96.0% after leaching for 36 h, respectively. However, Zn extraction rate after adsorbed bacteria sterilized slightly changed leaching for 18-36 h and only reached 66.7%, while that of leaching with adsorbed bacteria significantly increased after 12 h and reached as high as 84.5%. Zn extraction rate gradually increased after 36 h in bioleaching system after adsorbed bacteria sterilized. The results showed that the solubilization of Fe and Cu only had a slight change after adsorbed bacteria sterilized, so it could be implied that free bacteria played a vital role in dissolving Fe and Cu in zinc smelting slag. Zn, however, was definitely linked to adsorbed bacteria and the extraction rates were 21.0% and 17.8% with both free and adsorbed bacteria, respectively, suggested that both adsorbed and free bacteria were fairly significant in solubilization of Zn in the slag.
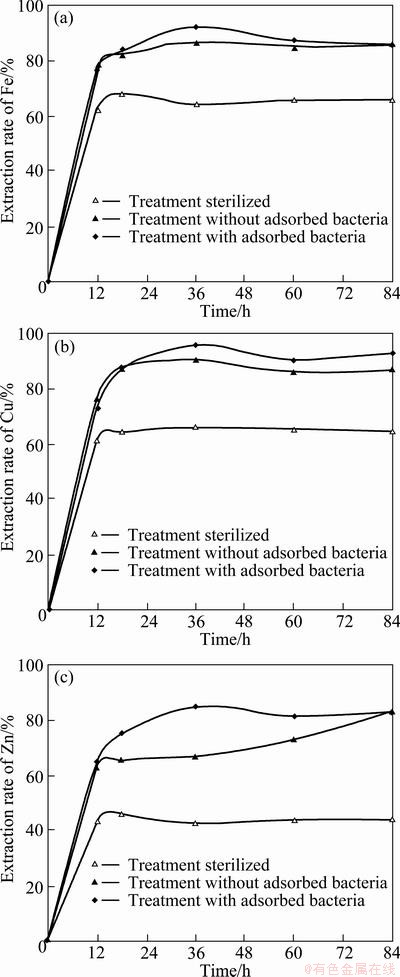
Fig. 2 Extraction rates of Fe (a), Cu (b) and Zn (c) with or without adsorbed bacteria
3.2 FT-IR spectroscopy of leached residues
The FT-IR spectrum of leached residue is helpful to reveal the characteristic functional groups of bacterial secretes. The interpretation of infrared spectra involves the correlation of absorption bands in the spectrum of an unknown compound with the known absorption frequencies for different types of bonds. It is critical to note that new absorption peaks of functional groups from bacterial secretes on the bioleached residue surfaces, such as 1007 cm-1 and 1193 cm-1, turn up in comparison with those from the acid leached residue (Fig. 3(a)). The frequency range of 1000-1200 cm-1 was assigned to C—O—C and C—O stretching, corresponded to the presence of carbohydrates [14]. The frequency range of 3570-3120 cm-1 was assigned to O—H and absorption peak centered at 3500-3300 cm-1 corresponded to N—H stretching of amide relative to polysaccharide [15,16]. The results suggested that FT-IR spectrum of functional groups from bacterial secretes on bioleached residue confirmed the possible presence of abundant carbohydrates, polysaccharide, polysaccharide and protein, which could be inferred that the bacteria existed on the slag particle surfaces.
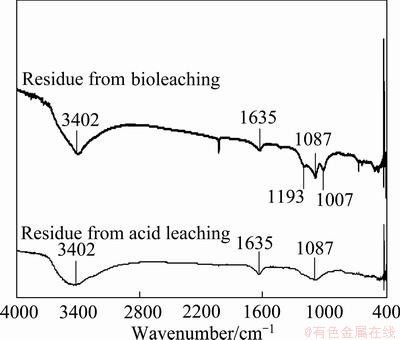
Fig. 3 FT-IR spectra of bioleached residue and acid leached residue
3.3 Cyclic voltammetry
The electrochemical behaviors of the electrode in different leaching systems are shown in Fig. 4. Four anodic peaks, such as (a), (b), (c) and (d), and a cathodic peak (e) turned up. New anodic peaks of (a), (b) and (c) appeared and sharply increased in the potential range from -0.25 to 0.5 V. In varied electrolytes, the anodic reactions of pyrite and chalcopyrite were fairly well discussed [10,16]. The anodic peak at -0.25 V was associated with reaction (1).
Cu2S Cu1.92S+0.08Cu2++0.16e (1)
Cu1.92S+0.08Cu2++0.16e (1)
As voltage increased above 0 V, the peaks of (b) and (c) ranging from 0 to 0.5 V, were related to a series of reactions as follows:
Cu1.92S Cu1.60S+0.32Cu2++0.64e (2)
Cu1.60S+0.32Cu2++0.64e (2)
Cu1.60S CuS+0.60Cu2++1.20e (3)
CuS+0.60Cu2++1.20e (3)
Some reactions, however, existed simultaneously due to the complexity of zinc smelting slag. When the potential value was kept at 0-0.6 V, pyrite began to oxdize and a series of FexS oxidation reactions occurred as follows:
FeS2+8H2O→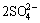 +Fe3++16H++15e (4)
+Fe3++16H++15e (4)
FeS1.12→2Fe2++1.16S+2e (5)
FeS2+Fe3++4.48H2O→ +2Fe2++8.96H++7.72e (6)
+2Fe2++8.96H++7.72e (6)
FeS2+4.48H2O→ +Fe2++8.96H++8.72e (7)
+Fe2++8.96H++8.72e (7)
When the voltage exceeded 0.5 V, peak of (d) attributed to the oxidation of ZnS.
ZnS→Zn2++S+2e (8)
Inversely, a peak of (e) arose, which was expected to associate with the Fe3+ reduction:
Fe3++e→Fe2+ (9)
When the potential value was less than 0.6 V, peak (f) after bacteria sterilized was observed, indicating that the reactions of bioleaching were irreversible compared with acid leaching. The results showed that some substances could be solubilized in bioleaching according to the cyclic voltammetry of zinc smelting slag electrode in the presence or absence of bacteria, and the moderately thermophilic microorganisms can positively influence the metal oxidation of zinc smelting slag.
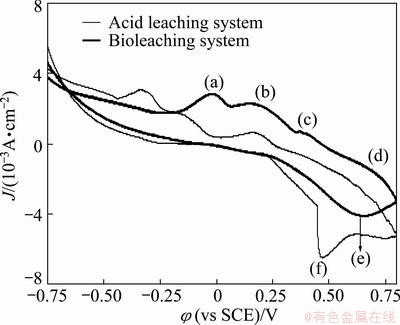
Fig. 4 Cyclic voltammetry curves of zinc smelting slag electrode of bioleaching and control system
3.4 Tafel curves
Tafel curves of zinc smelting slag carbon paste electrode were carried out to examine the corrosion kinetics of the electrode (Fig. 5). A series of kinetic parameters, such as corrosion potential, corrosion current and Tafel slope (anodic ba and cathodal bc), were calculated and listed in Table 2 according to the linear polarization of equation (10):
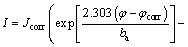
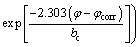 (10)
(10)
It can be observed obviously that corrosion potential and corrosion current increased, whereas the anodic and cathodic Tafel slope decreased in bioleaching compared with that of the control (Table 2). With the increase of electron transfer coefficient, Tafel slope decreased and indicated that electron transfer and exchange enhanced in bacteria system. The results show that the corrosion kinetics of zinc smelting slag oxidation is accelerated by bacteria and improves the dissolution of metals from the slag.

Fig. 5 Tafel curve of zinc smelting slag electrode in presence (a) or absence (b) of bacteria
Table 2 Tafel parameters of zinc smelting slag electrode in presence or absence of bacteria

4 Conclusions
1) The extraction rates of Fe, Cu and Zn from a zinc smelting slag with adsorbed bacteria are 91.9%, 96.0% and 84.5% while those after adsorbed bacteria sterilized are 86.7%, 90.3% and 66.7%, respectively. The solubilization of Fe and Cu in the slag is heavily affected by the free bacteria while that of Zn is significantly affected by both adsorbed and free bacteria.
2) Based on the FI-IR spectroscopy of functional groups from bacterial secretes on bioleached residues, the stretching peaks of C—O—C, C—O, O—H and N—H corresponded to carbohydrates, polysaccharide, polysaccharide and protein infer that the bacteria exist on the slag particles surface. At the same time, the cyclic voltammetry and Tafel curves conclude that bacteria enhance the corrosion of zinc smelting slag during bioleaching.
References
[1] FARAHMAND F, MORADKHANI D, SAFARZADEH M S, RASHCHI F. Brine leaching of lead-bearing zinc plant residues: Process optimization using orthogonal array design methodology [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 95(3-4): 316-324.
[2] SAFARZADEH M S, MORADKHANI D, ILKHCHI M O, GOLSHAN N H. Determination of the optimum conditions for the leaching of Cd-Ni residues from electrolytic zinc plant using statistical design of experiments [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2008, 58(3): 367-376.
[3] RUSEN A, SUNKAR A S, TOPKAYA Y A. Zinc and lead extraction from  leach residues by using hydrometallurgical method [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 93(1-2): 45-50.
leach residues by using hydrometallurgical method [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 93(1-2): 45-50.
[4] PARK Y J. Stabilization of a chlorine-rich fly ash by colloidal silica solution [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 162(2-3): 819-822.
[5] CARRANZA F, ROMERO R, MAZUELOS A , IGLESIAS N, FORCAT O. Biorecovery of copper from converter slags: Slags characterization and exploratory ferric leaching tests [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 97(1-2): 39-45.
[6] CHENG Yi, GUO Zhao-hui, LIU Xue-duan, YIN Hua-qun, QIU Guan-zhou, PAN Feng-kai, LIU Hong-wei. The bioleaching feasibility for Pb/Zn smelting slag and community characteristics of indigenous moderate-thermophilic bacteria [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2009, 100(10): 2737-2740.
[7] YU Run-lan, ZHONG Dai-li, MIAO Lei, WU Fa-deng, QIU Guan-zhou, GU Guo-hua. Relationship and effect of redox potential, jarosites and extracellular polymeric substances in bioleaching chalcopyrite by acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(7): 1634-1670.
[8] TAKATSUGI K, SASAKI K, HIRAJIMA T. Mechanism of the enhancement of bioleaching of copper from enargite by thermophilic iron-oxidizing archaea with the concomitant precipitation of arsenic [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 109(1-2): 90-96.
[9] YU Run-lan, QIU Guan-zhou, HU Yue-hua, TAN Jian-xi, YANG Peng. Bacterial extracellular polymeric substances and its contact- leaching sulfide mechanism [J]. Hydrometallurgy of China, 2008, 27(3): 72-75.
[10] ZHANG Li-min, PENG Juan-hua, WEI Man-man, DING Jian-nan, ZHOU Hong-bo. Bioleachingof chalcopyrite with Acidianus manzaensis YN25 under contact and non-contact conditions [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(10): 1981-1986.
[11] WANG Zhao-hui, XIE Xue-hui, XIAO Sheng-mu, LIU Jian-she. Comparative study of interaction between pyrite and cysteine by thermogravimetric and electrochemical techniques [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 101(1-2): 88-92.
[12] CRUZ R,  I. Acid dissolution influences bacterial attachment and oxidation of arsenopyrite [J]. Mineral Engineering, 2005, 18(10): 1024-1031.
I. Acid dissolution influences bacterial attachment and oxidation of arsenopyrite [J]. Mineral Engineering, 2005, 18(10): 1024-1031.
[13] YU Run-lan, TAN Jian-xi, YANG Peng, SUN Jing, OUYANG Xiong-jing, DAI Yun-jie. EPS-contact-leaching mechanism of chalcopyrite concentrates by A. ferrooxidans [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(6): 1427-1432.
[14] BRAMHACHARI P V, DUBEY S K. Isolation and characterization of exopolysaccharide produced by Vibrio harveyi strain VB23 [J]. Applied Microbiology, 2006, 43(5): 571-577.
[15] MISHRA A, JHA B. Isolation and characterization of extracellular polymeric substances from micro-algae Dunaliella salina under salt stress [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2009, 102(13): 87-90.
[16] WANG Zhao-hui, XIE Xue-hui, XIAO Sheng-mu. Adsorption behavior of glucose on pyrite surface investigated by TG, FTIR and XRD analyses [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 100(1-4): 3382-3386.
蒋凯琦,郭朝晖,肖细元,韦小颖
中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院 环境工程研究所,长沙 410083
摘 要:研究中等嗜热菌对锌冶炼窑渣中金属提取的影响以及生物浸出过程中锌冶炼窑渣碳糊电极的电化学特性。结果表明,在矿浆浓度2%、pH1.0、温度65 °C、转速为120 r/min的浸出条件下,去除生物浸出体系中吸附菌后,废渣中Fe、Cu和Zn的浸出率分别为86.7%、90.3%和66.7%,而在没有去除吸附菌体系中3种金属的浸出率分别为91.9%、96.0%和84.5%。对生物浸出渣和酸浸渣表面细菌分泌物进行FT-IR测试分析可知,生物浸出渣颗粒表面出现了新的官能团振动峰,如1007 cm-1和1193 cm-1处的峰,间接说明残渣颗粒表面吸附细菌的存在。生物浸出体系和空白体系的循环伏安曲线和塔菲尔曲线特性进一步表明生物浸出体系中细菌促进了锌冶炼窑渣中有价金属的溶出。
关键词:锌冶炼窑渣;嗜热菌;生物浸出;化学浸出;电化学行为
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Foundation item: Project (41271330) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: GUO Zhao-hui; Tel: +86-731-88836442; Fax: +86-731-88710171; E-mail: zhguo@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61580-X

