
Plastic anisotropy and fracture behavior of AZ31 magnesium alloy
LIU Pei 1, XIN Yun-chang1, LIU Qing1, 2
1. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China;
2. National Engineering Research Center for Magnesium Alloys, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China;
Received 25 September 2010; accepted 20 December 2010
Abstract: The effects of texture and abnormal large grains on the plastic anisotropy and fracture behavior of hot-rolled AZ31 magnesium alloy were investigated. Uniaxial tensile deformation behaviors of samples with tensile axis tilting 0°, 15°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 75° and 90° to normal direction (ND) respectively were addressed. Tensile deformation anisotropy was observed for samples with different angles to ND. The results show that the specimens with the angle from 0° to 30° exhibit relatively lower yielding strength due to the 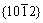 extension twinning. However, basal slip and prismatic slip are the dominant deformation modes for the specimens with angles larger than 45°. Macro-fractures are parallel to the length direction of abnormal large grains in the specimens with angles less than 60°, while those are serrated fracture edge for specimens with angles 75° and 90°.
extension twinning. However, basal slip and prismatic slip are the dominant deformation modes for the specimens with angles larger than 45°. Macro-fractures are parallel to the length direction of abnormal large grains in the specimens with angles less than 60°, while those are serrated fracture edge for specimens with angles 75° and 90°.
Key words: AZ31 magnesium alloy; anisotropy; deformation mechanism; fracture
1 Introduction
The increasing demand for low carbon economy and high operating efficiency has prompted intensive research into lightweight structural materials. Magnesium with a density of 1.74 g/cm3, two thirds of the density of aluminum and one third of the density of iron, offers great potential for automobile construction. Many studies have been concentrated on the characterization of texture formation and deformation behavior of single crystals or polycrystalline wrought alloys[1]. The limited number of active deformation systems in hexagonal close packed metals and twinning systems caused low formability of the magnesium alloys. A few groups tried to establish a qualitative or quantitative correlation among deformation mechanisms, texture and mechanical anisotropy[2-4].
However, much less attention has been paid to the effect of inhomogeneous microstructure on the plastic deformation and fracture behavior of magnesium alloys. The present study aims at investigating the effect of texture and abnormal large grains on the plastic anisotropy and fracture behaviors of an AZ31 magnesium alloy, which will depend on the understanding on plastic deformation mechanism of magnesium alloy and contribute to the development of effective secondary processing techniques.
2 Experimental
The composition of material used in this study was Mg-3Al-1Zn-0.3Mn (mass fraction, %) AZ31. The cast alloys were homogenized at 500 °C for 12 h followed by water quenching. The specimens were hot-rolled to a sheet with dimensions of 1 200 cm × 600 cm × 70 cm. The universal testing machine was used for tensile testing at room temperature with a constant strain rate of 10-4s-1. Tensile tests were carried out for the sheets in seven types with tension direction tilting 0° 15°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 75° and 90° to ND, respectively, as illustrated in Fig.1. Here, RD, ND and TD refer to rolling direction, normal direction and transverse direction, respectively. The dimensions of samples are 25 mm in gauge length, 2 mm in thickness and 10 mm in width. Extensometer was used to measure the strain in length during the tests.
The microstructures of as-received materials and deformed sample were monitored with optical microscope. The average grain size was determined by the intercept method. Crystal orientation (electron backscatter diffraction, EBSD) measurements were carried out using a FEI Nova400 field emission gun (FEG) SEM equipped with an Oxford Instruments–HKL Technology Nordlys EBSD system, using a step size of 2 μm.
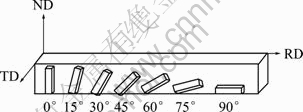
Fig.1 Sketch showing sample tensile axis for tensile test
3 Results
The microstructure in the as-received AZ31 magnesium alloy in the transverse section (TD) is demonstrated in Fig.2. The sample is characterized by inhomogeneous microstructure with both abnormal large grains (400 mm in width and about 1 mm in length) and fine grains (42 mm). The abnormal large grain is elongated along RD. Figure 3 shows the stress—strain curves of samples. At 0 °, 15° and 30°, samples have the similar stress—strain curves with a terrace after yielding, and the slope of curves increases with strain. At 45°, 60°, 75° and 90°, the terrace in strain—stress curves disappears and the slope of curves decreases with strain, which is more obvious at 75° and 90°. At 45°, specimen exhibits higher stress level near the strain 0.2% than at 0°, 15° and 30°. Taking into account the error bar, 0.2% stress is almost constant for sample at 0°, 15°, 30° and 45°, and increases fast when orientation angle is larger than 45°, as shown in Fig.4. The yield strength of specimen at 90° is more than 2 times that of specimen at 45°.
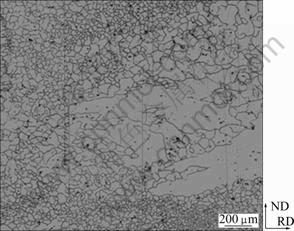
Fig.2 Optical micrograph showing inhomogeneity of as- received AZ31 magnesium alloy
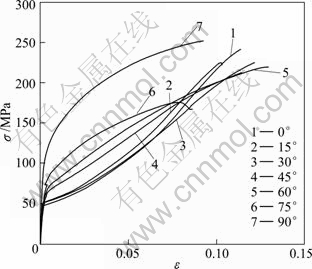
Fig.3 Representative stress—strain curves of samples with different tensile types
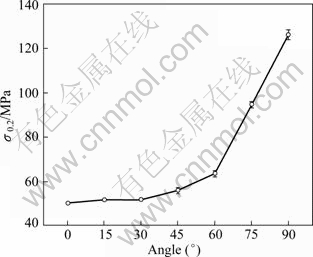
Fig.4 0.2% stress of samples with different tensile types
Figure 5 shows the EBSD microstructures of samples with 4% elongation. The red lines represent 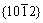 extension twinning boundaries. At 0°, the twin volume fraction is the highest and the twinning microstructure is more complicate compared with that of the other two samples. While at 90°, sample has a certain amount of low angle boundaries, which implies that the slip is the dominant deformation mechanism of sample at 90°. However, the sample at 90° has a small fraction of twins too.
extension twinning boundaries. At 0°, the twin volume fraction is the highest and the twinning microstructure is more complicate compared with that of the other two samples. While at 90°, sample has a certain amount of low angle boundaries, which implies that the slip is the dominant deformation mechanism of sample at 90°. However, the sample at 90° has a small fraction of twins too.
Figure 6 demonstrates the deformation traces on the sample surfaces at the strain of 4%. These deformation traces include the protuberances and lower-lying parts appearing alternatively with a width of about 1 mm. At the same time, the macro fracture angle is almost parallel to these deformation traces in the samples with angles less than 60°. The fracture angles almost linearly increase with the increase tension angles of samples to ND. There are small serrations on the macro-fracture surface of sample at 0° and the macro-fracture surface is serrated in the sample at 90°. Figure 7 shows the lower-lying parts of the deformation traces corresponding to the abnormal large grains and the protuberant parts are areas with small grains.
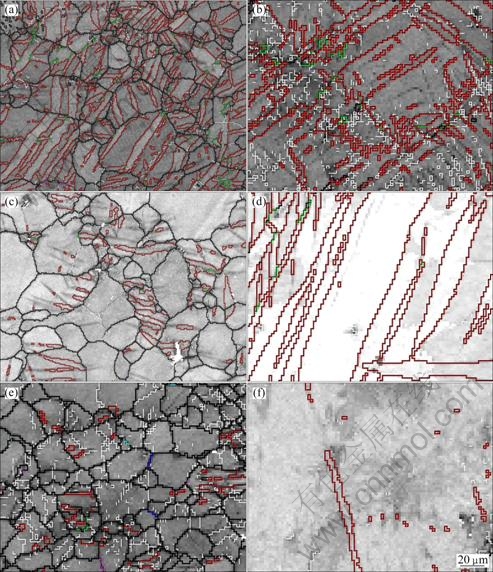
Fig.5 Deformation microstructures of fine grains and abnormal large grains in samples at deformation strain of 4% at 0°(a, b), 45°(c, d) and 90°(e, f)
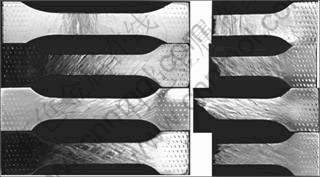
Fig.6 Micrograph showing deformation traces on surface of samples with deformation strain of 4% (left) and macro- fracture (right) (The tensile angles of samples from top to bottom are 0°, 30°, 60° and 90°, respectively.)
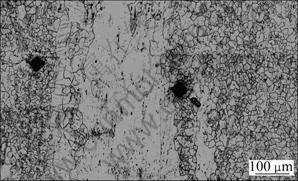
Fig.7 Microstructure in deformation traces of sample deformed at 0° to deformation strain of 4 %

Fig.8 Crack propagation along large grain
4 Discussion
The main deformation modes in magnesium and magnesium alloys are basal slip, 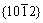 twin, prismatic slip and áa+c? slip[3, 5]. The critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) ratio between these deformation modes is 1:0.7:2:15. Since Burgers vector of basal slip lies in the basal plane, no plastic strain parallel to the c-axis can be accommodated by this slip system. However, such strain can be accommodated by
twin, prismatic slip and áa+c? slip[3, 5]. The critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) ratio between these deformation modes is 1:0.7:2:15. Since Burgers vector of basal slip lies in the basal plane, no plastic strain parallel to the c-axis can be accommodated by this slip system. However, such strain can be accommodated by 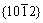 twinning and prismatic slip.
twinning and prismatic slip. 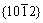 twinning is the easiest twinning that can be activated at room temperature. Taking into account the prismatic slip
twinning is the easiest twinning that can be activated at room temperature. Taking into account the prismatic slip 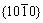 and {
and {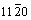 } observed in the deformed AZ31 magnesium alloy, the plastic deformation can be estimated by calculating the CRSS ratio to mean orientation factor (M), CRSS/M and the deformation mechanism at yield points can be semi-quantitatively inferred that the sample deforms mainly by basal slip,
} observed in the deformed AZ31 magnesium alloy, the plastic deformation can be estimated by calculating the CRSS ratio to mean orientation factor (M), CRSS/M and the deformation mechanism at yield points can be semi-quantitatively inferred that the sample deforms mainly by basal slip, 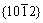 twinning and prismatic slip. Slight increase of the yield stress for samples at 0°-45° is probably related to the presence of
twinning and prismatic slip. Slight increase of the yield stress for samples at 0°-45° is probably related to the presence of 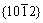 tension twinning and its lower CRSS [5]. The disappearance of the yielding terrace from the orientation of 45° can be ascribed to activation of other deformation mechanism. When the angle between tensile axis and c axis of the grains is around 35°, the CRSS/M values for
tension twinning and its lower CRSS [5]. The disappearance of the yielding terrace from the orientation of 45° can be ascribed to activation of other deformation mechanism. When the angle between tensile axis and c axis of the grains is around 35°, the CRSS/M values for 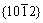 twinning and basal slip are almost identical and after that, the CRSS/M for the basal slip is smaller, which means that the basal slip is the major mode for plastic deformation theoretically. When the orientation is equal to or larger than 75°, prismatic slip is expected to be dominant in tension deformation, which is in consistent with the earlier report that 50% and 60% of the grains were predicted to deform by the prismatic slip[5]. Flow curves of samples at 0°, 15° and 30°run at a higher stress level up to a total strain of about 0.08, 0.09, and 0.1, respectively, where they intersect once again.
twinning and basal slip are almost identical and after that, the CRSS/M for the basal slip is smaller, which means that the basal slip is the major mode for plastic deformation theoretically. When the orientation is equal to or larger than 75°, prismatic slip is expected to be dominant in tension deformation, which is in consistent with the earlier report that 50% and 60% of the grains were predicted to deform by the prismatic slip[5]. Flow curves of samples at 0°, 15° and 30°run at a higher stress level up to a total strain of about 0.08, 0.09, and 0.1, respectively, where they intersect once again.
In order to understand detailed microstructure of the protuberances and the lower-lying parts, the indents from a micro-hardness tester were used to mark the protuberant parts and lower-lying parts on sample surfaces deformed to the deformation strain of 4%. The microstructure was obtained by using optical microscope and the results are presented in Fig.7. It indicates that the protuberances and the lower-lying parts are caused by inhomogeneity of the microstructure. The abnormal large grains are the soft area in the microstructure where the twinning is supposed to form easily. As observed in macro features of fracture, the macro fractures in samples at 0°, 30° and 60°are parallel to the length direction of abnormal large grains, while are serrated in sample at 90°. The small serrate on the fracture surfaces is found to propagate along the twins, which is probably linked up with the loss in the load-bearing capacity due to void development in twins in the abnormal large grains[6]. In samples at 30° and 60°, the length direction of abnormal large grains is close to the maximum shear stress direction during tension, so the macro-fracture surface is much smoother, compared with that of sample at 0°. In sample at 90°, however, the serrated macro-fracture surface is composed of cracks both along large twins in abnormal large grains and small twins in adjacent small grains. These twins are connected due to the complex local stress-strain state during the fracture, the void development in twins in the abnormal large grains and the localization of deformation within the double twins is probably responsible for the initiation of cracks[7]. In most of the samples, macroscopic cracks along the grain boundary regions[8] were observed and the failure of magnesium alloy is very sensitive to the constraint[9]. Figure 8 shows the microstructure of the crack propagation along the large grain in sample at 60°. The white line is the crack which propagates along the abnormal large grain. This mainly results from the strain constrain between the small grains and the large grain. After the crack is formed, it propagates along the high strain direction.
5 Conclusions
1) Tensile anisotropy was observed due to the different deformation mechanisms. For specimens at 0° to 30°, 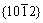 extension twinning is the dominant deformation mode, and for specimens at 75° and 90°, the prismatic slip plays a major role in plastic deformation.
extension twinning is the dominant deformation mode, and for specimens at 75° and 90°, the prismatic slip plays a major role in plastic deformation.
2) The macro-fractures are observed to be parallel to the length direction of abnormal large grains in the samples whose orientations are smaller than 60°, and are serrated in higher angle samples. While the micro-fractures are parallel to the twinning directions both in the abnormal large grains and the small grain area.
References
[1] KLIMANEK P, POTZSCH A. Microstructure evolution under compressive plastic deformation of magnesium at different temperatures and strain rates [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 324(1-2): 145-150.
[2] KLEINER S, UGGOWITZER P J. Mechanical anisotropy of extruded Mg-6%Al-1%Zn alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 379(1-2): 258-263.
[3] AGNEW S R, DUYGULU. Plastic anisotropy and the role of non-basal slip in magnesium alloy AZ31B [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2005, 21(6): 1161-1193.
[4] CHINO Y, KIMURA K, HAKAMADA M, MABUCHI M. Mechanical anisotropy due to twinning in an extruded AZ31 Mg alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 485(1-2): 311-317.
[5] BARNETT M R, KESHAVARZ Z, MA X. A semianalytical sachs model for the flow stress of a magnesium alloy [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2006, 37(7): 2283-2293.
[6] BARNETT M R, JACOB S, GERARD B F, MULLINS J G. Necking and failure at low strains in a coarse-grained wrought Mg alloy [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2008, 59(10): 1035-1038.
[7] BARNETT M R. Twinning and the ductility of magnesium alloys: Part II. "Contraction" twins [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 464(1-2): 8-16.
[8] SRIVATSAN T S, VASUDEVAN S, PETRAROLI M. The tensile deformation and fracture behavior of a magnesium alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 461(1-2): 154-159.
[9] YAN C, YE L, MAI Y W. Effect of constraint on tensile behavior of an AZ91 magnesium alloy [J]. Materials Letters, 2004, 58(25): 3219-3221.
AZ31镁合金的各向异性及断裂行为
刘 培1, 信运昌1, 刘 庆1, 2
1. 重庆大学 材料科学与工程学院,重庆 400044;2. 重庆大学 国家镁合金工程技术研究中心,重庆 400044
摘 要:研究织构和异常长大晶粒对热轧AZ31镁合金力学各向异性和断裂行为的影响。在拉伸轴与板材的法向方向分别呈0°、15°、30°、45°、60°、75° 和 90°下进行单轴拉伸实验,观察不同角度下样品的拉伸各向异性。结果表明:由于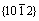 孪晶的出现,在0°-30°时样品表现出较低的屈服强度;当角度大于45°时,样品的主要的变形机制为基面和柱面滑移;当角度低于60°时,宏观断口平行于大晶粒拉长的方向;在75°和90°时样品的宏观断口呈锯齿状。
孪晶的出现,在0°-30°时样品表现出较低的屈服强度;当角度大于45°时,样品的主要的变形机制为基面和柱面滑移;当角度低于60°时,宏观断口平行于大晶粒拉长的方向;在75°和90°时样品的宏观断口呈锯齿状。
关键词:AZ31镁合金;各向异性;变形机制;断裂
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Foundation item: Project (2007CB613703) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Project (CDJXS11132227) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China
Corresponding author: LIU Qing; Tel:+86-23-65111295; E-mal: qingliu@cqu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60797-8