Mo含量对含β相TiAl合金组织和力学性能的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2017年第4期
论文作者:徐文臣 黄凯 武世峰 宗影影 单德彬
文章页码:820 - 828
关键词:TiAl合金;β相;显微组织;力学性能;均匀化热处理
Key words:TiAl alloy; β phase; microstructure; mechanical properties; homogenization treatment
摘 要:采用非自耗真空电弧熔炼Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y (x=0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2)合金试样,研究Mo含量变化对含β相TiAl合金显微组织和力学性能的影响规律。研究表明, Mo元素的偏聚使β相呈不连续网状分布于γ/α2 片层团边界。当Mo含量超过0.8%时,β相在枝晶间微偏析区易形成γ相。在Tα转变温度以上进行均匀化热处理可使β和γ相得到有效消除。对初始铸态和均匀化热处理态TiAl合金的组织性能进行对比分析发现,添加过量的Mo元素容易引起微偏聚,从而降低材料的强度和显微硬度,而均匀化热处理可使得其力学性能得到明显改善。
Abstract: The influence of Mo content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y (x=0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2) alloys was studied using small ingots produced by non-consumable electrode argon arc melting. The results show that small quantities of β phase are distributed along γ/α2 lamellar colony boundaries as discontinuous network in the TiAl alloys owing to the segregation of Mo element. The γ phase forms in the interdentritic microsegregation area when the Mo addition exceeds 0.8%. The β and γ phases can be eliminated effectively by subsequent homogenization heat treatment at the temperature above Tα. The evolution of the strength, microhardness and ductility at different Mo contents under as-cast and as-homogenization treated conditions was analyzed, indicating that excessive Mo addition is prone to cause the microsegregation, thus decreasing the strength and microhardness obviously, which can be improved effectively by subsequent homogenization heat treatment.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27(2017) 820-828
Wen-chen XU1,2, Kai HUANG1, Shi-feng WU1, Ying-ying ZONG1, De-bin SHAN1,2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China;
2. National Key Laboratory for Precision Hot Processing of Metals, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Received 8 January 2016; accepted 27 August 2016
Abstract: The influence of Mo content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y (x=0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2) alloys was studied using small ingots produced by non-consumable electrode argon arc melting. The results show that small quantities of β phase are distributed along γ/α2 lamellar colony boundaries as discontinuous network in the TiAl alloys owing to the segregation of Mo element. The γ phase forms in the interdentritic microsegregation area when the Mo addition exceeds 0.8%. The β and γ phases can be eliminated effectively by subsequent homogenization heat treatment at the temperature above Tα. The evolution of the strength, microhardness and ductility at different Mo contents under as-cast and as-homogenization treated conditions was analyzed, indicating that excessive Mo addition is prone to cause the microsegregation, thus decreasing the strength and microhardness obviously, which can be improved effectively by subsequent homogenization heat treatment.
Key words: TiAl alloy; β phase; microstructure; mechanical properties; homogenization treatment
1 Introduction
Intermetallic γ-TiAl-based alloys are considered as promising high temperature materials for high- temperature applications in aviation and automobile fields due to their attractive properties such as low density, elevated-temperature strength, excellent oxidation and creep resistance [1-3]. Particularly, high Nb-containing TiAl alloy can withstand temperatures up to 800 °C with acceptable mechanical properties, extending the service range of conventional TiAl alloys toward higher stresses and temperatures [4-6]. Although great progress has been achieved in the investigation of the TiAl-based alloys, the developed alloys cannot be put into large-scale use due to their low ductility and damage tolerance at room temperature as well as poor workability at elevated temperatures [7,8]. An effective way to improve the hot workability of TiAl alloys is to introduce disordered β phase, which provides a sufficient number of independent slip systems at elevated temperatures [9-12]. Conventional high Nb-containing TiAl alloys can only be deformed under isothermal conditions since only small volume fraction of β phase appears at hot working temperatures, which is not an economical processing route for industrial applications [13,14]. In recent years, the β-stablized TNMTM alloys with a baseline composition of Ti-(41-45)Al-(3-5)Nb-(0.1-2)Mo-(0.1-0.2)B have attracted much attention because of their high creep strength, excellent oxidation resistance and good hot workability, which can even be processed by nearly conventional forging on a conventional forging equip- ment with minor and inexpensive modification [15,16]. In the TNMTM alloys, β phase is introduced into TiAl alloys by the addition of β-stablized elements, such as Nb and Mo, through the β solidification process, exhibiting equiaxed, isotropic and texture-free microstructure. Moreover, the transformation of various phases during the β solidification process has been simulated by means of the ThermoCalc software using a commercially available TiAl database, indicating that the TiAl-Nb-Mo alloys solidify via the β phase [17]. Mo is a stronger β/β0 stabilizer than Nb [18], which is verified by other studies [19]. However, the segregation of alloying elements occurs and chemical inhomogeneity induces microstructural change during solidification due to the pronounced solute redistribution of refractory elements, producing retained interdendritic β phase and unstable γ/α2 lamellae [20,21]. To avoid the adverse effect of high β phase contents on creep behavior and room-temperature ductility, it is necessary to design TiAl alloys consisting of appropriate β phase that allows to minimize or eliminate the β phase fraction by subsequent heat treatments [22,23]. However, little attention is given to analyze the influence of the Mo content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of β-containing TiAl alloys.
In the present study, Mo is introduced to a β-containing TiAl alloy with the composition of Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y (x=0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2) as a β stabilization element to improve its strength, room temperature ductility and oxidation resistance as well as hot workability. However, large quantities of β phase owing to Mo addition may lead to the decrease of mechanical properties of the TiAl alloy. Therefore, the present investigation aims at analyzing the influence of Mo content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the β-containing TiAl alloy, which will provide a guidance on the development of high temperature TiAl alloys with better hot workability. Additionally, it is reported that the microstructure can be refined by the introduction of Y element into TiAl alloys [24], thus, 0.3% Y is added into the β-containing TiAl alloys in this study.
2 Experimental
Small ingots of four TiAl alloys with nominal compositions of Ti-45Al-5Nb-Mo-0.3Y (x=0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2, mole fraction, %), with 30 mm in diameter and 8 mm in height, were produced by non-consumable electrode argon arc melting. Each ingot was remelted four times to ensure the homogeneity of alloy composition. In order to eliminate or reduce the β phase, the homogenization heat treatments were performed at 1340 °C for 10 min, which was above the temperature Tα where the ordered γ phase disappeared completely according to the analysis results reported by IMAYEV et al [7] and CLEMENS et al [18,25].
The compression tests were conducted on an Instron-5500R testing machine at room temperature and 800 °C with a strain rate of 1.5×10-4 s-1. The compression specimens with 4 mm in diameter and 6 mm in height were spark machined from the ingots and mechanically polished before hot compression experiments. The yield strength (YS) and ductility (maximum compression to failure, εmax) were determined by the load-displacement curves obtained from the hot compression experiments. The microhardness measurement was conducted on an HV-5 microhardness tester at a load of 500 g for 15 s. In this study, the microhardness values were given as arithmetic mean values with at least 5 single hardness measurements for each specimen.
The OM observation was conducted on an Olympus-PMG3 optical microscope, and the SEM analysis was carried out on a Quanta 200FEG scanning electron microscope in back-scattered electron mode (SEM-BSE) with the accelerated voltage 20 kV. The polished specimens for OM observation were etched in a modified Kroll’s reagent of 10% HF, 4% HNO3 and 86% H2O (volume fraction). The alloy phases were determined using cuboid samples with 4 mm × 4 mm × 6 mm by X-ray diffractometer (XRD), which was carried out using Cu Kα radiation (λ =0.154157 nm) and 2θ from 20° to 90°. The volume fractions of various phases were measured qualitatively by adiabatic method based on the XRD analysis. In addition, the volume fraction of β/B2 phase was calculated from the SEM images of TiAl alloys by the Image-Pro-Plus6 software.
3 Results
3.1 Influence of Mo content on microstructures of TiAl alloys
Figure 1 shows the X-ray diffraction patterns of the Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y (x=0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2) alloys as-cast (in red color) and after homogenization treatment (in black color). Two phases γ (TiAl) and α2 (Ti3Al) can be identified in the TiAl alloys, and β/B2 phase can also be found except in the as-cast Ti-45Al-5Nb-0.6Mo- 0.3Y alloy. After homogenization treatment at 1340 °C for 10 min, it can be seen that the β phase can be eliminated almost completely.
Figure 2 shows the OM and SEM microstructures of the as-cast Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y alloys. The SEM images indicate that the microstructures of the TiAl alloys mainly consist of γ/α2 lamellar colony (in gray color) and small amount of β phase (in gray-white color) distributed along γ/α2 lamellar colony boundaries. According to the OM and SEM microstructures, the average colony size of the as-cast ingots is quite small (40-60 μm), partly attributed to the introduction of Y element beneficial for the refinement of γ/α2 lamellar colony. In addition, the Y-rich phase particles (in bright-white color) are occasionally visible along the γ/α2 lamellar colony boundaries or in the colony interiors. When the Mo addition exceeds 1.0%, the black areas can be found in the TiAl alloys (Figs. 2(f) and (h)), exhibiting the interdentritic microsegregation abundant in Al and depleted in Nb and Mo, which is verified by the EDS analysis in Fig. 3. The high Al-containing interdentritic microsegregation zone comes into being during the β solidification process and transforms to γ phase during cooling to room temperature, as shown in Fig. 2(h), which will be discussed in the following section. In addition, the β phase is rich in Mo element (about 3.33%) and the Al content is far below the average content (Table 1).
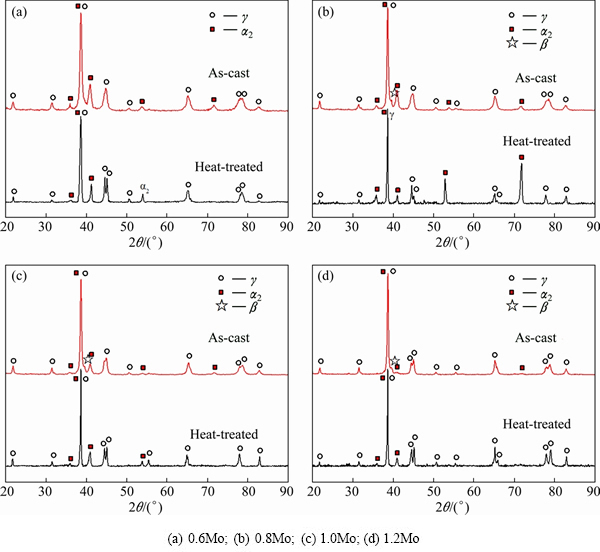
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y alloys as-cast and after homogenization heat treatment
Figure 4 shows the OM and SEM microstructures of Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y alloys after homogenization heat treatment. The fully lamellar microstructures are observed from the OM images in the TiAl alloys. When the Al content is no more than 0.8%, nearly no β phase is found from the SEM images since small amount of β phase is almost completely dissolved in the TiAl alloy matrix. As the Al content reaches 1.0% or more, retained β phase is visible particular in the vicinity of the γ/α2 colony boundaries. Compared with as-cast TiAl alloys, the microstructures are evidently coarsened to over 100 μm after homogenization heat treatment at 1340 °C for 10 min. Moreover, the average size of γ/α2 lamellar colony reduces from 160 to 110 μm when the Mo content increases from 0.6% to 1.2%. Obviously, the retained β phase hinders the over coarsening of lamellar colony at higher Mo content. Besides, γ grains can be found at triple conjunctions of γ/α2lamellar colonies, and Y-rich phase segregates along colony boundaries at higher Mo content (see Figs. 4(f) and (h)).
Figure 5 shows the evolution of the volume fractions of γ, α2 and β phases with varying Mo content in the Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y alloys mainly by XRD analysis. For the as-cast TiAl alloys, the β phase cannot be detected by XRD analysis until the Mo addition reaches 0.8%, and then it keeps continuous increase with the increase of the Mo content. As shown in Fig. 5(a), the β phase increases to 6.9% at the Mo addition of 1.2%. Also, the measurement of β phase fraction from SEM microstructures verifies the increasing tendency of β phase content with the increase of Mo addition (see Fig. 5(a)). Meanwhile, the volume fraction of γ phase increases from 61.6% to 82.3% with the Mo addition increasing from 0.6% to 1.2%, whereas that of α2 phase reduces from 37.8% to 10.8%. After homogenization heat treatment, the β phase is hard to be detected by XRD analysis, and the variation tendency of volume fraction of other phase fractions is similar to that of the as-cast alloys.
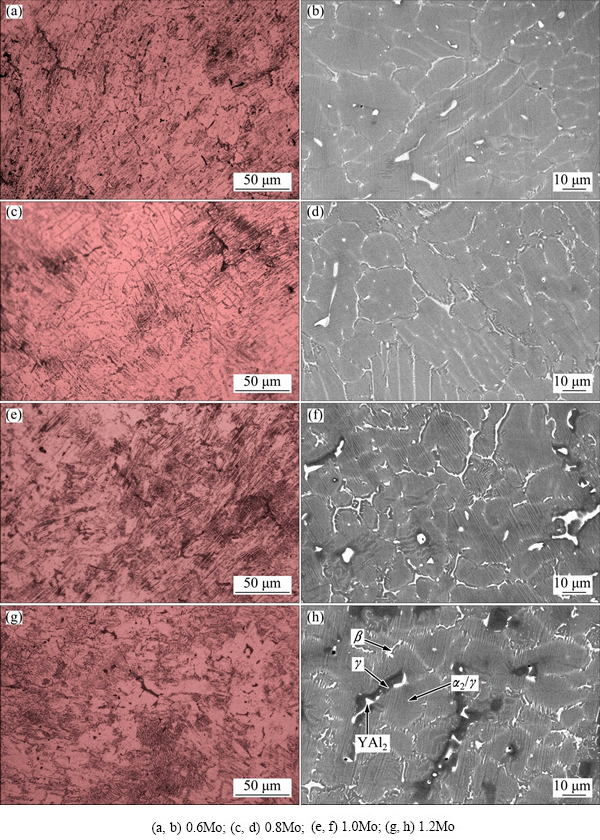
Fig. 2 OM (a, c, e, g) and SEM (b, d, f, h) microstructures of as-cast Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y alloys
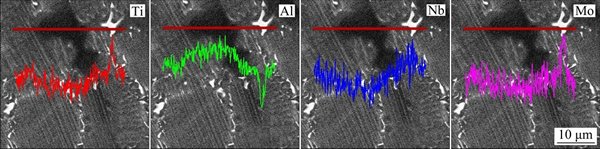
Fig. 3 EDS profiles of interdentritic microsegregations in Ti-45Al-5Nb-1.2Mo-0.3Y alloy
Table 1 EDS data for morphologies of microsegregations in Ti-45Al-5Nb-1.2Mo-0.3Y alloys in Fig. 3 (mole fraction, %)
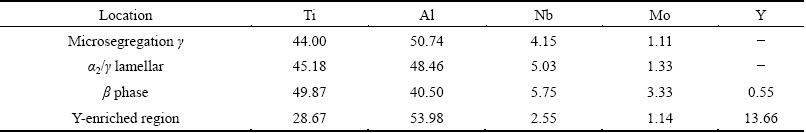
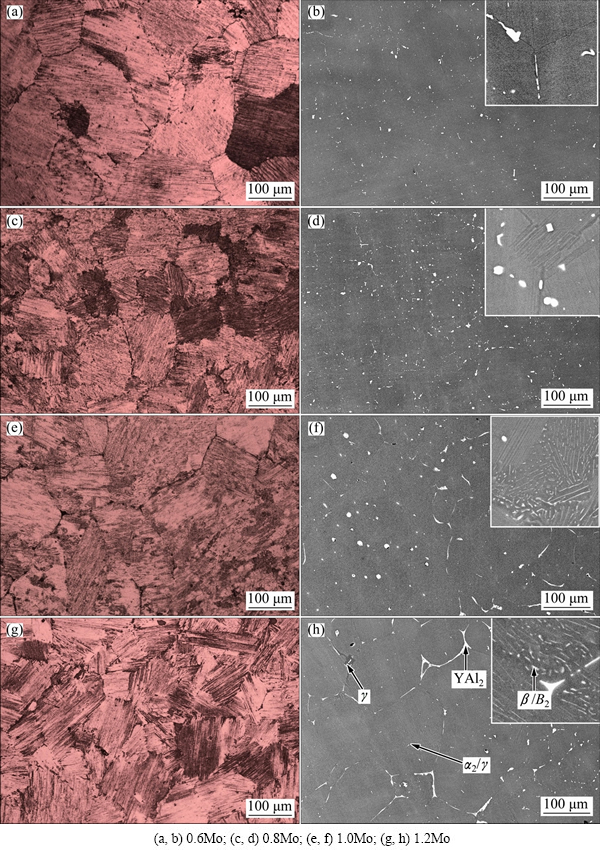
Fig. 4 OM (a, c, e, g) and SEM (b, d, f, h) microstructures of Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y alloys after homogenization heat treatment at 1340 °C for 10 min
3.2 Influence of Mo content on mechanical properties
Figure 6 shows the compression mechanical properties of Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y alloys as-cast and after homogenization heat treatment at room temperature and 800 °C, respectively. It can be seen that the mechanical properties have obvious Mo dependence, exhibiting the similar variation trend of the YS (yield stress) and the εmax (maximum compression to failure, %) both for the TiAl alloys as-cast and as-homogenized. At room temperature, the YS decreases continuously while the εmax increases gradually with the increase of Mo content. For the as-cast TiAl alloys, the YS decreases from 954 to 607 MPa and the εmax increases from 14.7% to 28.3% when the Mo content increases from 0.6% to 1.2%. After homogenization heat treatment, the YS increases relative to the as-cast TiAl alloy, which is more evident when the Mo addition surpasses 1.0%, but the εmax reduces slightly. At 800 °C, the YS decreases obviously when the Mo content exceeds 1.0% both for the as-cast and homogenized TiAl alloys. However, compared with the as-cast alloy, the YS reduces when the Mo content is below 0.8% but enhances when Mo content is higher than 1.0% after homogenization treatment.
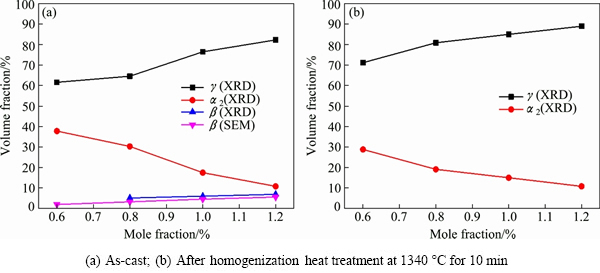
Fig. 5 Evolution of volume fractions of various phases in Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y alloys
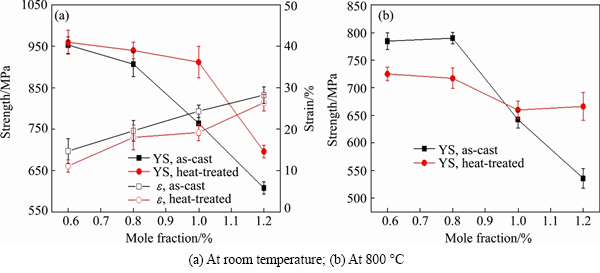
Fig. 6 Compression mechanical properties of Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y alloys
Figure 7 shows the microhardness evolution of Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y alloys. It indicates that the microhardness decreases with the increase of Mo content no matter in casting condition or after homogenization heat treatment. Furthermore, there is an increase of the microhardness after homogenization heat treatment, especially at lower Mo content (≤0.8%).
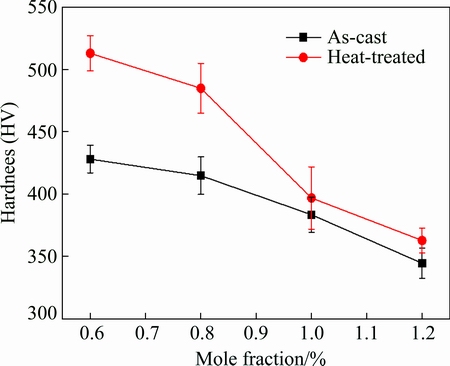
Fig. 7 Microhardness evolution of Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y alloys
4 Discussion
The phase transformation sequence for the Ti-43.5Al-(4-5)Nb-(1-1.5)Mo-0.1B (TNM) alloys under continuous cooling conditions has been proposed by CLEMENS et al [26]. Under equilibrium conditions, the solidification and transformation pathway is L→L+ β→β→β+α→α→α+γ→α+γ+B2→α2+γ+B2, indicating that the TNM alloys solidify completely via β phase. Furthermore, SCHMOELZER et al [17] have pointed out that no α single phase filed can be found under continuous cooling with moderate and high cooling rates because of the addition of low diffusive Nb and Mo elements, and the phase transformation sequence is as follows: L→L+β→β→β+α→α(+βm)→α+γ(+βm)→α+γ+ B2→α2+γ+B2, where βm denotes the metastable β phase. Similarly, there should be no single α phase field existing during the solidification process of the Ti-45Al- 5Nb-xMo-0.3Y (x=0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2) alloy in the present study. In addition, CHLADILA et al [27] have calculated the phase diagram of Ti-45Al-xNb alloys, which shows that Ti-45Al-xNb alloys solidify through the peritectic reaction 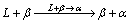 under equilibrium conditions when the Nb content is less than ~7.5%. Also, LUO et al [28] have verified the same solidification path in Ti-45Al-5Nb alloy based on thermodynamics calculation. For roughly predicting the solidification path by the “Al-equivalent” concept [29-31], the alloy composition of Ti-45Al-5Nb-(0.6-1.2)Mo-0.3Y approximately corresponds to the binary Ti-(45.7-45.8)Al alloy, suggesting the occurrence of the peritectic reaction
under equilibrium conditions when the Nb content is less than ~7.5%. Also, LUO et al [28] have verified the same solidification path in Ti-45Al-5Nb alloy based on thermodynamics calculation. For roughly predicting the solidification path by the “Al-equivalent” concept [29-31], the alloy composition of Ti-45Al-5Nb-(0.6-1.2)Mo-0.3Y approximately corresponds to the binary Ti-(45.7-45.8)Al alloy, suggesting the occurrence of the peritectic reaction 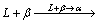
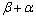 during the solidification process according to the Ti-Al binary phase diagram [32]. In any case, β phase is the primary phase in the equilibrium solidification process of the present TiAl alloys.
during the solidification process according to the Ti-Al binary phase diagram [32]. In any case, β phase is the primary phase in the equilibrium solidification process of the present TiAl alloys.
The primary β phase exhibits dentritic morphology containing low Al content and high β formation elements (Nb and Mo). Thus, the interdentritic black area presents microsegregation that is rich in Al and poor in Nb and Mo (see Fig. 3), which leads to the formation of transformed γ grains after cooling to room temperature. In addition, the L+β→β+α→α(+βm) phase transformation takes place in the process of temperature drop from β phase field to α phase field, wherein α grains are nucleated either in the interiors of or around the primary β grains. As the β/α transformation proceeds, the Al content in α phase increases and β stabilizers in ternary systems like Nb and Mo are pushed toward the opposite direction. Finally, the retained stable β phase area remains at the positions where α grains meet, which are abundant in Nb and Mo and depleted in Al, as can be verified by the EDS analysis in Table 1. Here, it should be noted that excessive addition of Mo element can cause severe microsegregation in interdentritic black area.
After the β/α transformation is finished, α grains may transfer to α2+γ lamellar structure or near full lamellar structure during the cooling process, which mainly depends on Al content. Therefore, the retained stable β phase segregates around α2+γ lamellar colonies and transformed γ grain boundaries (interdentritic black area) in the TiAl alloys, which is more obvious at higher Mo addition. As indicated in Fig. 2, both network β phase and β blocks occur at colony boundaries as the Mo content exceeds 0.8%. Moreover, β phase formed by Nb and Mo segregation is visible in the colony interiors due to β/α transformation. In addition, it is clear that the homogenization treatment at 1340 °C for 10 min is able to eliminate the β and γ segregation nearly completely when the Mo content is no more than 0.8%, while the β phase is retained obviously and the Y-rich network comes into being along colony boundary when the Mo content reaches 1.0%, as illustrated in Fig. 4.
The yield strength and microhardness reduce with the increase of Mo content, exhibiting a negative effect on the mechanical properties of the TiAl alloy (Figs. 6 and 7). Under as-cast condition, the increase of Mo addition contributes to the interdentritic microsegregation (transformed γ phase) and the formation of retained β phase along colony boundaries, which leads to the decrease of the strength. Particularly at high temperature (800 °C), the obvious increase of softening β phase exacerbates the decrease of the high-temperature strength of the TiAl alloy when the Mo content exceeds 0.8%. With regard to the microhardness of various phases in TiAl alloy, SCHLOFFER et al [33] indicate that the β phase is slightly softer than α2 phase and evidently harder than γ phase for TiAl-Nb-Mo alloy. Therefore, with the increase of Mo addition, the rapid reduction of α2 phase and obvious increase of γ phase, as shown in Fig. 5, lead to descending in hardness and ascending in ductility (εmax), albeit with slight increase of β phase.
After homogenization treatment at 1340 °C, the evolution tendency of the strength, hardness and ductility is similar to that under as-cast condition since the volume fraction of γ phase increases while that of α2 phase reduces as the Mo content increases. Moreover, the retained β phase and segregated γ phase are dissolved nearly totally in the matrix, causing the considerable solution strengthening effect due to the addition of Nb and Mo elements [34,35] and thus higher strength and hardness and lower ductility compared with the as-cast alloys at room temperature. When compressed at high temperature (800 °C), the yield stress decreases more evidently when the Mo content reaches 1.0% (Fig. 6(b)). It should be attributed to the discontinuous network segregation of Y-rich phase along the colony boundaries, leading to the weakening of colony boundaries, as can be seen in Fig. 4. In addition, the yield stress is lower at lower Mo content (≤0.8%) and higher at higher Mo content (≥1.0%) relative to the corresponding cast alloys. At lower Mo content (≤0.8%), the reduction of the strength should be caused by the pronounced coarsening effect of the γ/α2 colony due to the homogenization heat treatment conducted above the temperature Tα. At higher Mo content (≥1.0%), the elimination or reduction of amounts of retained softening β phase and interdentritic microsegregation γ phase results in the obvious improvement of high-temperature strength, which confirms the adverse effect of excessive introduction of β phase on the high-temperature strength of γ-TiAl alloys.
To sum up, although the addition of Mo is beneficial to improving the hot workability of the Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y alloys through introduction of β phase, the excessive addition of Mo element can contribute to the formation of retained β phase and interdentritic microsegregation γ phase, thus leading to the decrease of the strength of the as-cast alloys, which can be improved by subsequent homogenization heat treatment at temperatures above Tα. The research provides a helpful guidance to optimize the Mo content for achieving the TiAl-Nb-Mo alloy with excellent mechanical properties and hot workability.
5 Conclusions
1) The influence of Mo content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y (x=0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 12) was analyzed in casting and homogenization treatment conditions.
2) Small quantities of β phase are distributed along γ/α2 lamellar colony boundaries as discontinuous network in the alloy matrix owing to the segregation of Mo element. The γ phase forms in the interdentritic microsegregation area when Mo addition reaches 1.0%. The homogenization heat treatment at temperatures above Tα can eliminate the β phase and γ phase almost completely, but cause the coarsening of γ/α2 lamellar colony.
3) With the increase of the Mo content, the yield stress (YS) and microhardness decrease continuously while the ductility (εmax) increases gradually both for the as-cast and homogenized alloys. After homogenization heat treatment, the TiAl alloy exhibits higher strength, microhardness and lower ductility at room temperature compared with the corresponding as-cast alloy. Moreover, the high-temperature strength is also higher at higher Mo content (≥1.0%) compared with the corresponding as-cast alloy.
4) The excessive Mo addition can exacerbate the segregation of retained β phase and interdentritic segregation γ phase and decrease the strength of the as-cast alloy, which can be improved by the solution strengthening effect of Nb and Mo through homogenization heat.
References
[1] APPEL F, BROSSMANN U, CHRISTOPH U. Recent progress in the development of gamma titanium aluminide alloys [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2000, 2: 699-720.
[2] KOTHARI K, RADHAKRISHNAN R, WERELEY N M. Advances in gamma titanium aluminides and their manufacturing techniques [J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2012, 55: 1-16.
[3] CHEN R R, ZHENG D S, GUO J J, MA T F, DING H S, SU Y Q, FU H Z. A novel method for grain refinement and microstructure modification in TiAl alloy by ultrasonic vibration [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A , 2016, 653: 23-26.
[4] HADIN M, SHAFYEI A, MERATIAN M. A comparative study of microstructure and high temperature mechanical properties of a β-stabilized TiAl alloy modified by lanthanum and erbium [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 624: 1-8.
[5] XU X J, LIN J P, WANG Y L, GAO J F, LIN Z, CHEN G L. Microstructure and tensile properties of as-cast Ti-45Al-(8-9)Nb- (W, B, Y) alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 414: 131-136.
[6] FANG H Z, CHEN R R, ANTON G, GUO J J, DING H S, SU Y Q, FU H Z. Effect of cyclic heat treatment on microstructures and mechanical properties of directionally solidified Ti-46Al-6Nb alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 1872-1880.
[7] IMAYEV R M, IAYEV V M, OEHRING M, APPEL F. Alloy design concepts for refined gamma titanium aluminide based alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2007, 15: 451-460.
[8] SUN H F, LI X W, FANG W B. Microstructures of PM Ti-45Al-10Nb alloy fabricated by reactive sintering [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 1454-1459.
[9] TETSUI T, SHINDO K, KAJI S, KOBAYASHI S, TAKEYAMA M, Fabrication of TiAl components by means of hot forging and machining [J]. Intermetallics, 2005, 13(9): 971-978.
[10] CUI N, KONG F T, WANG X P, CHEN Y Y, ZHOU H T. Hot deformation behavior and dynamic recrystallization of a β-solidifying TiAl alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2016, 652: 231-238.
[11] HOLEC D, LEGUT D, ISAEVA L, SOUVATZIS P, CLEMENS H, MAYER S. Interplay between effect of Mo and chemical disorder on the stability of β/β0-TiAl phase [J]. Intermetallics, 2015, 61: 85-90.
[12] QIU C Z, LIU Y, HUANG L, LIU B, ZHANG W, HE Y H, HUANG B Y. Tuning mechanical properties for β(B2)-containing TiAl intermetallics [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 2593-2603.
[13] STARK A, BARTELS A, CLEMENS H, KREMMER S, SCHEIMANSKY F P, GERLING R. Microstructure and texture formation during near conventional forging of an intermetallic Ti-45Al-5Nb alloy [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2009, 12: 976-981.
[14] SOYAMA J, OEHRING M, LIMBERG W, EBEL T, KAINER K U, PYCZAK F. The effect of zirconium addition on sintering behaviour, microstructure and creep resistance of the powder metallurgy processed alloy Ti-45Al-5Nb-0.2B-0.2C [J]. Materials and Design, 2015, 84: 87-94.
[15] CLEMENS H, MAYER S. Design, processing, microstructure, properties, and applications of advanced intermetallic TiAl alloys [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2013, 15: 191-215.
[16] HUBERA D, WERNER R, CLEMENS H, STOCKINGER M. Influence of process parameter variation during thermo-mechanical processing of an intermetallic β-stabilized γ-TiAl based alloy [J]. Materials Characterization, 2015, 109: 116-121.
[17] SCHMOELZER T, LISS K D, GERALD A Z, WATSON I J, DROESSLER L M, WALLGRAM W, BUSLAPS T, STUDER A, CLEMENS H. Phase fractions, transition and ordering temperatures in TiAl-Nb-Mo alloys: An in- and ex-situ study [J]. Intermetallics, 2010, 18: 1544-1552.
[18] CLEMENS H, CHLADIL H F, WALLGRAM W, BOCK B, KREMMER S, OTTO A, GUTHER V, BARTELS A. A β-stabilized γ-TiAl based alloy for improved processing performance [C]//KIM Y W, MORRIS D, YANG R, LEYENS C. Structural Aluminides for Elevated Temperatures 2008. New Orleans, LA: The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society (TMS), 2008: 217-228.
[19] TAKEYAMA M, KOBAYASHI S. Physical metallurgy for wrought gamma titanium aluminides: Microstructure control through phase transformations [J]. Intermetallics, 2005, 13: 993-999.
[20] HUANG Z W. Inhomogeneous microstructure in highly alloyed cast TiAl-based alloys caused by microsegregation [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 52: 1021-1025.
[21] CHEN G L, XU X J, TENG Z K, WANG Y L, LIN J P. Microsegregation in high Nb containing TiAl alloyingots beyond laboratory scale [J]. Intermetallics, 2007, 15: 625-631.
[22] WALLGRAM W, SCHMOELZER T, CHA L, DAS G, GUTHER V, CLEMENS H. Technology and mechanical properties of advanced γ-TiAl based alloys [J]. International Journal of Materials Research, 2009, 100: 1021-1030.
[23] DROESSLER L M, SCHMOELZER T, WALLGRAM W, CHA L, DAS G, CLEMENS H. Microstructure and tensile ductility of a Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B alloy [C]//Proceedings of Materials Research Society Symposia. Boston: Materials Research Society, 2009: 121-126.
[24] KONG F T, CHEN Y Y, LI B H. Influence of yttrium on the high temperature deformability of TiAl alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 499: 53-57.
[25] CLEMENS H, CHLADILA H F, WALLGRAM W, ZICKLER G A, GERLING R, LISS K D, KREMMER S, GUTHER V, SMARSLY W. In- and ex-situ investigations of the β-phase in a Nb and Mo containing γ-TiAl based alloy [J]. Intermetallics, 2008, 16: 827-833.
[26] CLEMENS H, BOECK B, WALLGRAM W, SCHMOELZER T, DROESSLER L M, ZICKLER G A. Experimental studies and thermodynamic simulations of phase transformations in Ti-(41-45)Al-4Nb-lMo-0.1B alloys [C]//Proceedings of Materials Research Society Symposia. Boston: Materials Research Society, 2009: 115-120.
[27] CHLADILA H F, CLEMENS H, ZICKLER G A, TAKEYAMA M, KOZESCHNIK E, BARTELS A, BUSLAPS T, GERLING R, KREMMER S, YEOH L, LISS K D. Experimental studies and thermodynamic simulation of phase transformations in high Nb containing γ-TiAl based alloys [J]. International Journal of Materials Research, 2007, 98: 1131-1137.
[28] LUO L S, LIU T, LI K, SU Y Q, GUO J J, FU H Z. Microstructures, micro-segregation and solidification path of directionally solidified Ti-45Al-5Nb alloy [J]. China Foudary, 2016, 13: 107-113.
[29] KIM S W, WANG P, OH M H, WEE D M, KUMAR K S. Mechanical properties of Si- and C-doped directionally solidified TiAl-Nb alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2004, 12: 499-509.
[30] JOHNSON D R, INUI H, MUTO S, OMIYA Y, YAMANAK T. Mechanical properties of Si- and C-doped directionally solidified TiAl-Nb alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54: 1077-1085.
[31] LIU Y, HU R, KOU H C, WANG J, ZHANG T B, LI J S, ZHANG J. Solidification characteristics of high Nb-containing γ-TiAl alloys with different aluminum contents [J]. Rare Metals, 2015, 34: 381-386.
[32] SU Y Q, LIU C, LI X Z, GUO J J, LI B S, JIA J, FU H Z. Microstructure selection during the directionally peritectic solidification of Ti-Al binary system [J]. Intermetallics, 2005, 13: 267-274.
[33] SCHLOFFER M, RASHKOVA B, SCHOBERL T, SCHWAIGHOFER E, ZHANG Z, CLEMENS H, MAYER S. Evolution of the ωo phase in a β-stabilized multi-phase TiAl alloy and its effect on hardness [J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 64: 241-252.
[34] ZHANG W J, DEEVI S C, CHEN G L. On the origin of superior high strength of Ti-45Al-10Nb alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2002, 10: 403-406.
[35] SCHWAIGHOFER E, RASHKOVA B, CLEMENS H, STARK A, MAYER S. Effect of carbon addition on solidification behavior, phase evolution and creep properties of an intermetallic β-stabilized γ-TiAl based alloy [J]. Intermetallics, 2014, 46: 173-184.
徐文臣1,2,黄 凯1,武世峰1,宗影影1,单德彬1,2
1. 哈尔滨工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,哈尔滨 150001;
2. 哈尔滨工业大学 金属精密热加工国家级重点实验室,哈尔滨 150001
摘 要:采用非自耗真空电弧熔炼Ti-45Al-5Nb-xMo-0.3Y (x=0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2)合金试样,研究Mo含量变化对含β相TiAl合金显微组织和力学性能的影响规律。研究表明, Mo元素的偏聚使β相呈不连续网状分布于γ/α2 片层团边界。当Mo含量超过0.8%时,β相在枝晶间微偏析区易形成γ相。在Tα转变温度以上进行均匀化热处理可使β和γ相得到有效消除。对初始铸态和均匀化热处理态TiAl合金的组织性能进行对比分析发现,添加过量的Mo元素容易引起微偏聚,从而降低材料的强度和显微硬度,而均匀化热处理可使得其力学性能得到明显改善。
关键词:TiAl合金;β相;显微组织;力学性能;均匀化热处理
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (51275132) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2008RFQXG040) supported by the Youth Science and Technology Project of Harbin, China
Corresponding author: Wen-chen XU; Tel: +86-451-86416221; Fax: +86-451-86418641; E-mail: xuwc_76@hit.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60094-3

