Characteristics of hot tensile deformation and microstructure evolution oftwin-roll cast AZ31B magnesium alloys
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2010年第5期
论文作者:刘志民 邢书明 鲍培玮 李楠 姚淑娜 张密兰
文章页码:776 - 782
Key words:magnesium; AZ31B alloy; twin-roll cast; processing map; dislocation creep; effective diffusion coefficient
Abstract: High temperature tensile properties and microstructure evolutions of twin-roll-cast AZ31B magnesium alloy were investigated over a strain rate range from 10-3 to 1 s-1. It is suggested that the dominant deformation mechanism in the lower strain rate regimes is dislocation creep controlled by grain boundary diffusion at lower temperature and by lattice diffusion at higher temperatures, respectively. Furthermore, dislocation glide and twinning are dominant deformation mechanisms at higher strain-rate. The processing map, the effective diffusion coefficient and activation energy map of the alloy were established. The relations of microstructure evolutions to the transition temperature of dominant diffusion process, the activation energy platform and the occurrence of the full dynamic recrystallization with the maximum peak efficiency were analyzed. It is revealed that the optimum conditions for thermo-mechanical processing of the alloy are at a temperature range from 553 to 593 K, and a strain rate range from 7×10-3 to 2×10-3 s-1.
基金信息:supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing, China
supported by the Science Foundation of Beijing Jiaotong University

LIU Zhi-min(刘志民), XING Shu-ming(邢书明), BAO Pei-wei(鲍培玮), LI Nan(李 楠),
YAO Shu-qing(姚淑娜), ZHANG Mi-lan(张密兰)
School of Mechanical, Electronic and Control Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University,
Beijing 100044, China
Received 1 September 2009; accepted 15 December 2009
Abstract: High temperature tensile properties and microstructure evolutions of twin-roll-cast AZ31B magnesium alloy were investigated over a strain rate range from 10-3 to 1 s-1. It is suggested that the dominant deformation mechanism in the lower strain rate regimes is dislocation creep controlled by grain boundary diffusion at lower temperature and by lattice diffusion at higher temperatures, respectively. Furthermore, dislocation glide and twinning are dominant deformation mechanisms at higher strain-rate. The processing map, the effective diffusion coefficient and activation energy map of the alloy were established. The relations of microstructure evolutions to the transition temperature of dominant diffusion process, the activation energy platform and the occurrence of the full dynamic recrystallization with the maximum peak efficiency were analyzed. It is revealed that the optimum conditions for thermo-mechanical processing of the alloy are at a temperature range from 553 to 593 K, and a strain rate range from 7×10-3 to 2×10-3 s-1.
Key words: magnesium; AZ31B alloy; twin-roll cast; processing map; dislocation creep; effective diffusion coefficient
1 Introduction
Magnesium alloys have high potential as structural materials, since they are the lightest structural alloys[1-3]. However, high market price and poor formability at room temperature prevent their wide applications, so the reduction of manufacturing costs and the improvement of formability are highly demanded[4-6]. Recently, twin-roll cast (TRC) gained much attention as the integrated producing process, magnesium alloy sheets produced by TRC have not only the cost-effective advantage of flat rolled products processed by one-step but also beneficial effects of microstructure such as reducing segregation and grain size. In addition, they also utilize alloying elements that have limited solid solubility in Mg[7-8], which are usually avoided in ingot casting since these elements form coarse intermetallic particles at low solidification rate[9]. It is expected that TRC can disperse these particles on a fine scale, which might result in improvement in tensile properties. Although in the present study, high temperature deformation behavior of TRC ZK60 alloy was examined[9], the hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of TRC-Mg alloy was rarely systematically investigated.
Therefore, the aim of the present investigation is to explore the mechanisms of hot deformation over a wide range of temperature and strain rate, and to obtain the optimum conditions for thermo-mechanical processing and the controlling microstructure in industrial components of the alloy. For these purposes, three approaches were adopted: 1) analysis of the stress-strain behaviors; 2) evaluation of the effective diffusion coefficient; and 3) development of processing maps. Finally, the correlation of microstructure with thermo-mechanical processing parameters was also studied.
2 ExperimentalThe TRC-Mg alloy sheet used in this study was a commercial Mg-Al-Zn alloy AZ31B fabricated by the twin-roll cast technique. The chemical composition of the alloy was as follows: Al 3.010%; Zn 0.950%; Mn 0.510%; Si 0.100%; Cu 0.050%; Ni 0.005%; and balance Mg (mass fraction). Tensile specimens with a size of 7.5 mm×3.3 mm×20 mm were machined directly from the TRC sheet. These specimens were tested with a Gleeble-1500D thermal simulator testing machine. Tensile tests were conducted with the sample gauge axes parallel to the rolling direction at different temperatures (473, 523, 573 and 623 K) and different strain rates ranging from 1 to 1×10-3 s-1. The deformed specimens were water cooled and then sectioned parallelly to the deformation direction, ground, polished and etched for the metallographic examination.
A typical longitudinal microstructure of the as- received TRC-Mg alloy is shown in Fig.1(a). It exhibits a dendritic structure with coarse-grain sizes from 60 to 120 μm close to the surface layer of the sheet, and has an equiaxial grain with an average size of about 25 μm in the center respectively. In addition, some semi-solid grains with an average size of 8-10 μm are found in the center, as shown in Fig.1(b).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Flow stress characteristics
The true stress—true strain curves at different deformation temperatures are shown in Fig.2. It can be
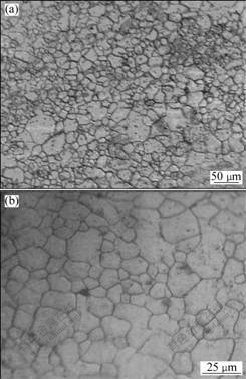
Fig.1 Optical micrographs of AZ31B TRC-Mg alloy in longitudinal orientation: (a) Equiaxial grains with coarse grains; (b) Semi-solid grains

Fig.2 Flow stress of TRC AZ31B alloy sheet at various temperatures: (a) ![]() =1 s-1; (b)
=1 s-1; (b) ![]() =0.1 s-1; (c)
=0.1 s-1; (c) ![]() =0.01 s-1; (d)
=0.01 s-1; (d) ![]() =0.001 s-1
=0.001 s-1
seen that all stress curves exhibit a sharp increase in the initial stage of the strain and then increase to a transient equilibrium when the stress arrives at the maximum value. Subsequently, the stress decreases and drives to a steady value with increasing the strain, especially when the material is deformed at high temperature above 573 K and at the low strain rate range below 1×10-2 s-1, the stress value in the flow curves is extremely low at 623 K, less than 25 MPa. Meanwhile, the flow curve exhibits a severe strain hardening at low temperature and high strain rate, especially when the materials is deformed at a high strain rate of 1 s-1 and a low temperature of 473 K.
In previous studies, the constitutive equations were formulated for conventionally hot magnesium alloys[10-12]. They include three forms, namely, a power law (Eq.(1)) at low stresses, an exponential law (Eq.(2)) at high stresses and hyperbolic sine function (Eq.(3)) for all stress ranges, respectively[4, 9-10]:
![]() (1)
(1)
![]() (2)
(2)
![]() (3)
(3)
where A, A1, A2, α, ?, n and n1 are all constants; ![]() is the strain rate; T is temperature; R is universal gas constant with the value of 8.31 J/(mol?K); and Q is the deformation activity energy.
is the strain rate; T is temperature; R is universal gas constant with the value of 8.31 J/(mol?K); and Q is the deformation activity energy.
By taking natural logarithms for Eq.(3), the deformation activity energy can be expressed as[4]:
![]() (4)
(4)
The variation in flow stress as a function of deformation temperature is shown in Fig.3(a) for all strain rates examined. The flow stress for each strain rate was determined by the peak stress. It is evident that the flow stress monotonically decreases with elevated deformation temperatures. The variations of flow stress as a function of strain rate over the temperature ranges tested are plotted in Figs.3(b)-(c). The slope of the curve in Fig.3(b) indicates that the stress exponent n is a function of strain-rate and it increases from about 5.3 to 8.1 as temperature decreases.
The activation energy for deformation is calculated through the hyperbolic sine model (Eq.(4)), and the activation energy at various temperatures and strain rates are illustrated in Fig.4. The results reveal that the activation energy increases with elevated temperature. The average activation energy from 473 to 523 K is about 100 kJ/mol, which is close to that of grain-boundary diffusion of magnesium (92 kJ/mol)[13].
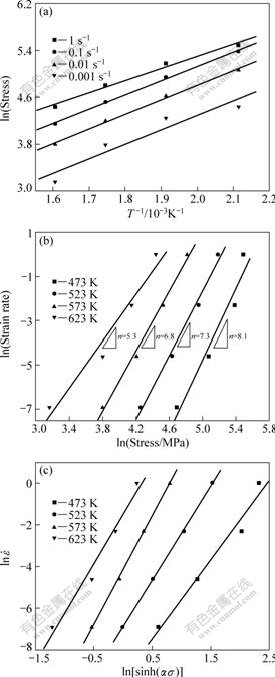
Fig.3 Peak stress of TRC AZ31B Mg as function of deformation temperatures and strain rates: (a) Flow stress—deformation temperatures; (b) Strain rates—peak stress; (c) ln![]() —ln[sinh(ασ)]
—ln[sinh(ασ)]
In contrast, the average activation energy from 523 to 623 K is about 135 kJ/mol, which is equal to that for lattice diffusion of magnesium (135 kJ/mol)[13]. In addition, a small activation energy platform region was found in a temperature range from 553 to 608 K and a strain rate range of 7×10-3 to 2×10-3 s-1. It means that if the material deformed in the small platform region, the microstructure is in a relatively steady state. The reason that activation energy varies with different strain rates
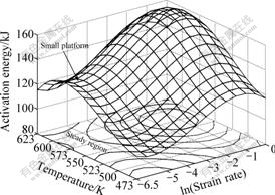
Fig.4 Activation energies at various temperatures and strain rates
may be the existence of some semi-solid grains in the TRC produced sheet. For the semi-solid grains construction, the solid-state and liquid-state grains separate and the construction is broken out during the tension test. The variation of dislocations and twins in the deformation may be another reason.
3.2 Microstructure evolution and deformation mechanism
The stress exponent, n, observed in the present material was 5.3-8.1 (shown in Fig.3(b)), which suggests that climb controlled dislocation creep can be a dominant deformation process[11]. The deformation temperature and stress relationships at different strain rate (shown in Fig.3(a)) indicate that the stress level decreases with temperature increasing, and the analyses reveal that the flow behavior at the high strain rate of 1 s-1 is represented by a conventional creep[11]. In order to confirm the deformation mechanism, the optical microstructures of testing specimens were examined, as shown in Fig.5. As seen in Figs.5(a), highly dense deformation twins are formed in the material, some dislocation ripple glide-bands are observed in the material deformed at T=473 K, ![]() =1 s-1, but fewer twins are shown in Figs.5(b) and (c). This indicates that the TRC-Mg alloy may deform by dislocation glide and twinning at high strain rates even at high temperatures. In addition, when the material deformed at T=623 K,
=1 s-1, but fewer twins are shown in Figs.5(b) and (c). This indicates that the TRC-Mg alloy may deform by dislocation glide and twinning at high strain rates even at high temperatures. In addition, when the material deformed at T=623 K, ![]() =0.001 s-1, as shown in Fig.5(d), the grains present a nearly equiaxed structure, and the grains become coarse.
=0.001 s-1, as shown in Fig.5(d), the grains present a nearly equiaxed structure, and the grains become coarse.
3.3 Transition of dominant diffusion process
Generally, the strain rate at which a material deforms at elevated temperature can be described as[14-15]
![]() (5)
(5)
where ![]() is the strain rate, A is a constant, Deff is the effective diffusion coefficient (Deff=D0exp[-Q/(RT)], σ is the flow stress, G is the shear modulus, k is the Boltzmann’s constant, d is the grain size, b is the Burgers vector, p is the grain size exponent, Q is the activation energy, R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, and n is the true stress exponent. In this work, since the dislocation climb and glide are the
is the strain rate, A is a constant, Deff is the effective diffusion coefficient (Deff=D0exp[-Q/(RT)], σ is the flow stress, G is the shear modulus, k is the Boltzmann’s constant, d is the grain size, b is the Burgers vector, p is the grain size exponent, Q is the activation energy, R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, and n is the true stress exponent. In this work, since the dislocation climb and glide are the
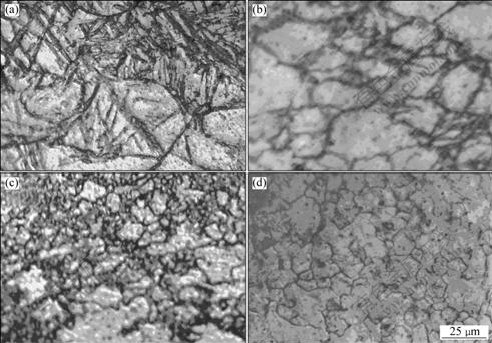
Fig.5 Optical microstructures deformed at: (a) T=473 K, ![]() =1 s-1; (b) T=473 K,
=1 s-1; (b) T=473 K, ![]() =0.001 s-1; (c) T=623 K,
=0.001 s-1; (c) T=623 K, ![]() =1 s-1; (d) T=623 K,
=1 s-1; (d) T=623 K, ![]() =0.001 s-1
=0.001 s-1
dominant diffusion mechanism, and the true stress exponent value n is closed to 4.5, the grain size exponent p value is equal to 0[14].
The effective diffusion coefficient, Deff, is given as[11]
![]() (6)
(6)
where DL is the lattice diffusion coefficient and Dgb is the grain boundary diffusion coefficient, β is a constant and is estimated to be 0.12 for AZ31 and AZ61 magnesium alloys, σ is the stress, and G is the shear modulus. Furthermore, DL and Dgb for AZ31 alloy are taken as that for pure magnesium[11].
The effective diffusion coefficients (Deff) vary at different deformation temperature and strain-rates, as illustrated in Fig.6. It can be clearly seen that the effective diffusion coefficients increase when the temperature increase, and the temperature within 593 to 613 K corresponds to the transition temperature between grain-boundary and lattice diffusions. This means that the contribution of grain-boundary diffusion remains dominant until it transits to lattice diffusion when the deformation temperature is higher than the transition temperature. Once this transition occurs, the microstructures of the material may be changed significantly. The reason that Deff varies with the strain rates may be the variation of semi-solid grains construction, dislocations and twins in the deformation.

Fig.6 Variation of effective diffusion coefficients at different deformation temperature and strain rates
3.4 Processing map
The processing maps were developed on the basis of Dynamic Materials Model[16]. In this model, the work-piece undergoing hot deformation is considered to be a dissipation of power, and the strain rate sensitivity (m) of flow stress is the factor that partitions power between deformation heat and microstructure changes. The efficiency of power dissipation through microstructure changes during deformation as a function of temperature and strain rate is given as[17]
![]() (7)
(7)
where m is the strain rate sensitivity of flow stress. The contour plot of the iso-efficiency η values on temperatures and strain rates field constitutes the processing map[18]. As the dissipation characteristics vary for different microstructural mechanisms, each domain on the map can be correlated to a single dominant mechanism operating those conditions and therefore, the processing-maps are known as power dissipation maps. In addition to the η contours, the instability criterion is given as[19]
≤
The variation of the instability parameter ξ with temperature and strain rate constitutes an instability map, which may be superimposed on the power dissipation map to obtain an instability map.
The processing map obtained at a strain of 0.4 is illustrated in Fig.7. Normally, the processing maps can be partitioned into four domains: instability region, continuous dynamic recrystallization (CDRX) region, discontinuous dynamic recrystallization (DDRX) region and low Zener-Hollomon parameter Z (high temperature and low strain rate) region. As seen in Fig.7, the instability region appears at lower temperatures and higher strain rates and occupies the upper left part of the processing map. The microstructures of instability region in the material are shown in Figs.5(a), where the grains are visibly elongated and highly dense twins occur. In addition, some cavities are found in the grain boundaries or triple points. As seen in Fig.7, the CDRX region appears in a temperature range of 473 K to 535 K and a strain rate range of 0.001 to 0.002 s-1 and the peak efficiency at CDRX region is 38%. The DDRX region appears in the region of higher temperature and higher strain rate, and the peak efficiency at DDRX region is 42%. The optical microstructures of CDRX and DDRX grains are shown in Figs.8(a) and (b), respectively. It is obvious that the recrystallized grain feature has extremely fine grains (Fig.8(a)) and equiaxed grains with wavy grain boundaries (Fig.8(b)). Different mechanisms of crystal plasticity control different microstructure of DRX, and the mechanisms of DRX depend on the operating deformation mechanisms which change with temperatures. At low temperature, DRX is associated with the operation of twinning, basal slip and áa+c? dislocation glide; at intermediate temperature, CDRX is associated with the extensive cross-slip due to the Friedel-Escaing mechanism; at high temperatures, both bulging of original grain boundaries and subgrain growth are the operating DRX mechanisms and controlled by dislocation climb[13]; the obtained peak efficiency is 60% in the low Zener-Hollomon parameter Z region, when the temperature is in the range of 568 to 623 K and the strain rate in the range of 0.001 to 0.004 s-1. The obtained optical microstructure is shown in Fig.5 (e), which shows the recrystallized grain feature with the nearly equiaxed grains and even structure.

Fig.7 Processing map obtained at strain of 0.4 (ε=0.4)
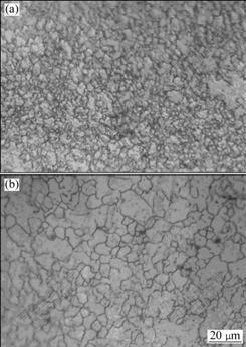
Fig.8 Optical microstructures in DRX domains: (a) CDRX; (b) DDRX
3.5 Optimization of thermo-mechanical processing
To obtain the optimum processing parameters of the TRC-Mg alloy, the processing map, activation energy map and the effective diffusion coefficient map should be taken into account together. As seen in Fig.4, the variation of activation energy has a small platform in the temperature range of 553 K to 608 K and strain rate range of 7×10-3 to 2×10-3 s-1. This means that the microstructures of the material have little sensitivity for processing parameters in the steady region. In addition, as shown in Fig.6, the variation of the effective diffusion coefficient indicates that the grain-boundary diffusion transits to the lattice diffusion when the deformation temperature is higher than the transition temperature. In this case, the microstructures of the material changed significantly. So the temperature of hot processing should be lower than the transition temperature. According to the processing map, two principles of the optimization should be adopted: 1) be apart from instability region (2) obtain the maximum peak efficiency with the occurrence of full dynamic recrystallization in the region. Based on the reasons mentioned above, the optimum conditions for thermo- mechanical processing of the TRC-Mg alloy are at the temperature range of 553 to 593 K and the strain rate range of 7×10-3 to 2×10-3 s-1.
4 Conclusions1) When the alloy deformed in the low strain rate range below 1×10-1 s-1, the dominant deformation mechanism is dislocation creep controlled by grain-boundary diffusion at low temperature and by the lattice diffusion at high temperatures. The deformation behaviors and microstructures at a high strain rate of 1 s-1 indicate that the dislocation glide and twinning are the dominant deformation mechanisms even at elevated temperatures.
2) The average activation energy is 100 kJ/mol at 473-523 K, and the average activation energy at 523-623 K is 135 kJ/mol. The small activation energy platform region is in the temperature range of 553 K to 608 K and the strain rate range of 7×10-3 to 2×10-3 s-1. The effective diffusion coefficients map reveals that the transition temperature between grain-boundary diffusion at low temperature and lattice diffusion at high temperatures varied in the range of 593 to 613 K.
3) The processing map suggests that the DDRX region appears in the higher temperature and higher strain rate, CDRX region appears in the temperature range of 473 K to 535 K and strain rate range from 0.001 to 0.002 s-1, and the flow instability region appears at the low temperature range under high deformation rates. Furthermore, the obtained optimum conditions for thermo-mechanical processing of the alloy is at the temperature range of 553 K to 593 K and strain rate range of 7×10-3 to 2×10-3 s-1.
References[1] YANG Yong-biao, WANG Fu-chi, TAN Cheng-wen, WU Yuan-yuan, CAI Hong-nian. Plastic deformation mechanisms of AZ31 magnesium alloy under high strain rate compression [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(5): 1043-1046.
[2] HOU Li-feng, WEI Ying-hui, LIU Bao-sheng, XU Bing-she. Microstructure evolution of AZ91D induced by high energy shot peening [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(5): 1053-1057.
[3] YANG Lian-fa, MORI Ken-ichiro, TSUJI Hirokazu. Deformation behaviors of magnesium alloy AZ31 sheet in cold deep drawing [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(1): 86-91.
[4] GUAN Shao-kang, WU Li-hong, WANG Li-guo. Flow stress and microstructure evolution of semi-continuous casting AZ70 Mg-alloy during hot compression deformation [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(2): 315-320.
[5] SLOOFF F A, ZHOU J, DUSZCZYK J, KATGERMAN L. Constitutive analysis of wrought magnesium alloy Mg-Al4-Zn1 [J]. Scripta Mater, 2007, 57(8): 759-762.
[6] PEREZ-PRADO M T, DELVALLE J A, RUANO O A. Effect of sheet thickness on the microstructural evolution of an Mg AZ61 alloy during large strain hot rolling [J]. Scripta Mater, 2004, 50(5): 667-671.
[7] PARK S S, OH Y S, KANG D H, KIM N J. Microstructural evolution in twin-roll strip cast Mg-Zn-Mn-Al alloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2007, 449/451: 352-355.
[8] PARK S S, BAE G T, KANG D H, JUNG I-H, SHIN K S, KIM N J. Microstructure and tensile properties of twin-roll cast Mg-Zn-Mn-Al alloys [J]. Scripta Mater, 2007, 57(9): 793-796.
[9] SONG S X, HORTON J A, KIM N J, NIEH T G. Deformation behavior of a twin-roll-cast Mg-6Zn-0.5Mn-0.3Cu-0.02Zr alloy at intermediate temperatures [J]. Scripta Mater, 2007, 56(5): 393-395.
[10] WATANABE H, TSUTSUI H, MUKAI T, KOHZU M, TANABE S, HIGSHI K. Deformation mechanism in a coarse-grained Mg-Al-Zn alloy at elevated temperatures [J]. Int J Plas, 2001, 17(3): 387-397.
[11] ISHIKAWA K, WATANABE H, MUKAI T. High temperature compressive properties over a wide range of strain rates in an AZ31 magnesium alloy [J]. J Mater Sci, 2005, 40(7): 1577-1582.
[12] WANG Y N, HUANG J C. Transition of dominant diffusion process during superplastic deformation in AZ61 magnesium alloys [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2004, 35(2): 555-562.
[13] GALIYEV A, KAIBYSHEV R, GOTTSTEIN G. Correlation of plastic deformation and dynamic recrystallization in magnesium alloy ZK60 [J]. Acta Mater, 2001, 49(7): 1199-1207.
[14] LANGDON T G. Grain boundary sliding revisited: Developments in sliding over four decades [J]. J Mater Sci, 2006, 41(3): 597-609.
[15] RUANO O A, WADSWORTH J, SHERBY O D. Deformation of fine-grained alumina by grain boundary sliding accommodated by slip [J]. Acta Mater, 2003, 51(12): 3617-3634.
[16] SIVAKESAVAM O, PRASAD Y V R K. Characteristics of superplasticity domain in the processing map for hot working of as-cast Mg-11.5Li-1.5Al alloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, 323(1/2): 270-277.
[17] BALASUBRAHMANYAM V V, PRASAD Y V R K. Deformation behaviour of beta titanium alloy Ti-10V-4.5Fe-1.5Al in hot upset forging [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, 336(1/2): 150-158.
[18] SRINIVASAN N, PRASAD Y V R K, Rama RAO P. Hot deformation behaviour of Mg-3Al alloy—A study using processing map [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 476: 146-156.
[19] PENG W P, LI P J, ZENG P, LEI L P. Hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of twin-roll-cast Mg-2.9Al-0.9Zn alloy: A study with processing map [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 494(1/2): 173-178.
(Edited by FANG Jing-hua)
Foundation item: Project(3093024) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing, China; Project(2007XM035) supported by the Science Foundation of Beijing Jiaotong University
Corresponding author: XING Shu-ming; Tel: +86-10-51688614; E-mail: shumingxing1962@126.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(09)60213-2

