2024铝合金热裂敏感性预测模型
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2018年第5期
论文作者:M. H. GHONCHEH S. G. SHABESTARI A. ASGARI M. KARIMZADEH
文章页码:848 - 857
关键词:2024铝合金;枝晶搭接;直接激冷铸造;热分析;热裂
Key words:2024 aluminum alloy; dendrite coherency; direct-chill casting; thermal analysis; hot tearing
摘 要:对比研究Katgerman和Clyne-Davies预测热裂敏感性的理论模型。制备晶粒细化的和未细化的2024铝合金,凝固冷却速度为0.4-17.5 °C/s。采用热分析检测枝晶搭接点和共晶反应温度,基于牛顿法测绘固相线和液相线以确定热裂敏感区。实验结果显示,2024铝合金中可能发生热裂的最敏感区域为在糊状区的最后阶段,Al2CuMg金属间化合物作为共晶相形成的区域。另外,在熔铸过程中的高冷却速率下,两个模型具有较好的一致性;而在低至中等冷却速率下,Clyne-Davies 模型预测热裂倾向更准确。
Abstract: Two theoretical criteria represented by Katgerman, and Clyne and Davies for prognosticating hot tearing sensitivity were compared. Both unrefined and grain-refined samples of Al2024 alloy were solidified at various cooling rates ranging from 0.4 to 17.5 °C/s. Thermal analysis was used to detect dendrite coherency point and temperature of eutectic reaction. Curves of solid and liquid fractions were plotted based on Newtonian method to determine hot tearing susceptible areas. The experimental results show that the most susceptible zone in which hot tearing can occur in Al2024 is where Al2CuMg intermetallic compound forms as a eutectic phase at last stage of mushy-state interval. Also, both criteria are in a good agreement with each other at high cooling rates used in direct-chill casting process while Clyne and Davies’ model is more acceptable to determine hot tearing tendency from low to medium cooling rates.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28(2018) 848-857
M. H. GHONCHEH1, S. G. SHABESTARI2, A. ASGARI3, M. KARIMZADEH1
1. School of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology, 16846-13114, Tehran, Iran;
2. Center of Excellence for High Strength Alloys Technology, School of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology, 16846-13114, Tehran, Iran;
3. School of Mechanical Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology, 16846-13114, Tehran, Iran
Received 1 April 2017; accepted 5 August 2017
Abstract: Two theoretical criteria represented by Katgerman, and Clyne and Davies for prognosticating hot tearing sensitivity were compared. Both unrefined and grain-refined samples of Al2024 alloy were solidified at various cooling rates ranging from 0.4 to 17.5 °C/s. Thermal analysis was used to detect dendrite coherency point and temperature of eutectic reaction. Curves of solid and liquid fractions were plotted based on Newtonian method to determine hot tearing susceptible areas. The experimental results show that the most susceptible zone in which hot tearing can occur in Al2024 is where Al2CuMg intermetallic compound forms as a eutectic phase at last stage of mushy-state interval. Also, both criteria are in a good agreement with each other at high cooling rates used in direct-chill casting process while Clyne and Davies’ model is more acceptable to determine hot tearing tendency from low to medium cooling rates.
Key words: 2024 aluminum alloy; dendrite coherency; direct-chill casting; thermal analysis; hot tearing
1 Introduction
Al2024 alloy is a famous heat treatable alloy widely used in automotive and aerospace industries due to its low density and good damage tolerance [1,2]. Direct- chill (DC) casting is the industrial process to produce billets of Al2024 alloy [3]. Centerline hot tearing is the most abundant solidification defects faced the DC casting particularly, when it is being used to cast high-strength alloys and large-scale flat ingots. Hot tears severity is attributed to many factors, e.g., high thermal gradient, severe thermal contraction during solidification, and high cooling rates ranging from 17 to 20 °C/s [4-6].
To control the hot tearing tendency in DC cast metals, several criteria have been developed [7-9]. These criteria can be mainly divided into two categories: mechanical and nonmechanical. The mechanical criteria involve critical stress, critical strain, or critical strain rate; however, nonmechanical models deal with vulnerable temperature range, phase diagram, and process parameters represented by Clyne and Davies, Feurer and Katgerman [3,10]. Criteria of Clyne and Davies, and Katgerman as well-known and comprehensive indexation methods are applied in this work, and are explained in more details as follows.
Clyne and Davies criterion is relied on the idea that in the last stage of mushy-state solidification in which fraction of solid varies between 0.90 and 0.99, the liquid cannot freely flow and easily percolate into interdendritic channels so that the strain applied during this stage cannot be accommodated by mass feeding [3]. The last stage of solidification is considered the most susceptible interval to hot tearing. On further reducing the liquid fraction, however, bridging between adjacent dendrites is established so that the mush acquires some strength, e.g., at solid fraction above 0.99. According to this criterion, the hot cracking sensitivity coefficient (HCSC, C) is formulated as the ratio between the vulnerable time period, tV, and time available for stress relief, tR [11,12]:
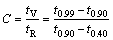 (1)
(1)
where t is the time at the solid fraction denoted by indices. This criterion works well in prognosticating the effect of composition on hot tearing, i.e., the lambda curve given in some literatures [3,4,13].
A model suggested by Katgerman combines the assumptions of Clyne and Davies and Feurer. In Feurer’s model, sufficient feeding of the forming solid phase with the liquid is requisite for the continuity of the solid phase and, therefore, acts an important role in hot tearing phenomenon. Katgerman’s criterion is specifically derived for hot tearing during DC casting of light alloys, at which the effects of casting speed, ingot diameter, and alloy composition are considered [10]. Based on this model, the hot tearing index is defined as follows:
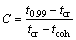 (2)
(2)
where tcr is the time when the after-feeding becomes inadequate, tcoh is the time at dendrite coherency point (DCP), and t0.99 and t0.40 are defined as same as Clyne and Davies’ criterion.
Regarding the potential influence that secondary phases may have on the flow of liquid into interdendritic channels, the vulnerable time period and the time period for accommodation can be rewritten as follows [11]:
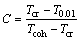 (3)
(3)
where T0.01 is the temperature at which the fraction of liquid is 0.01; Tcoh and Tcr are the temperatures at DCP and insufficient liquid after-feeding, respectively.
Based on Feurer’s model, Tcr is obtained when the velocity of volume contraction is equal to the maximum volumetric flow rate per unit volume. To take this into account, Tcr can be defined as the temperature when a given portion of the interdendritic volume is occupied by secondary phases [14]. Regarding a volume fraction of 0.02, Tcr takes place when the Eq. (4) can be established:
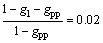 (4)
(4)
where gl and gpp are the volume fractions of the liquid and the primary phase, respectively. Synergy between thermal analysis technique and two mentioned criteria can be widely used to simply evaluate the hot tearing resistivity of DC cast alloys under different solidification conditions, e.g., various cooling rates, and adding different amounts of grain refinements.
In this work, the HCSC of Al2024 alloy was investigated at seven different cooling rates and in two conditions of unrefined and grain-refined microstructure. The aim of using high cooling rates was experimentally to simulate the solidification condition of DC casting process. To calculate different terms given in both criteria of Katgerman and Clyne and Davies, cooling curves associated with its first derivative and solid/liquid fraction curves were plotted using thermal analysis technique.
2 Experimental
The chemical composition of commercial Al2024 alloy used in this work is given in Table 1. To obtain a wide range of cooling rates between 0.4 and 17.5 °C/s, different types of molds having the same dimensions were used to evaluate the effect of cooling rates on the HCSC predicted by two criteria. In each experiment, 300 g of Al2024 alloy were melted in an electrical resistance furnace, and the melt was held for about 10 min at a constant temperature of (750±5) °C for homogenizing. Through the same melting procedure, the other samples were refined by adding 0.06% (mass fraction) Ti in the form of Al-5Ti-1B rod master alloy. The melt was regularly stirred to homogenize the chemical composition. In order to minimize the volume percentage of gas porosities in microstructure, degassing process was finally performed for 5 min using nitrogen-based degasser tablets. Neither water-circulated iron mold nor molds with low cooling rates were preheated before casting of molten metal.
Table 1 Chemical compositions of 2024 aluminum alloy

Two K-type thermocouples produced by OMEGA (OMEGA Engineering Inc., Stamford, Connecticut, USA) were inserted into the mold to measure the temperature of the melt continuously. They were connected to a high-speed data acquisition system associated with analogue to digital convertor with resolution of 2-16, and response time of 0.02. FIBERFRAX (Trademark of Standard Oil Engineering Materials Co., Niagara Falls, NY) insulation board was used above and below the molds to minimize heat loss in the axial directions. To detect onset temperature of dendrites impingement, the first thermocouple was inserted at the center of the mold while the other was located near the inner wall. Thermocouples were calibrated with solidifying high purity aluminum (99.99%, mass fraction), and were fixed at the same height from the bottom of the mold. Temperature-time data were recorded with the frequency of 10 readings per second, and were plotted as cooling curves via Origin pro (Origin Lab Corporation, Northampton, MA) 9.2 software. Furthermore, the DCP was measured via ΔT-t curve in which ΔT was the temperature difference between central and peripheral zones of the melt recorded by two thermocouples. Newtonian technique was applied to plot curves of solid and liquid fractions during solidification. Figure 1 illustrates the thermal analysis setup and dimensions of the mold.
All samples were sectioned horizontally through the place where the tip of the thermocouples was located. They were mechanically polished, and then etched via Keller’s reagent. The prepared surfaces were assessed using Olympus optical microscope, and Tescan-Vega scanning electron microscope aided by energy dispersive X-ray analysis which is used to determine the chemical composition of the phases. To detect the elemental distribution in the solidified samples, X-ray mapping of the elements was also performed.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructural analysis
Figure 2 demonstrates the effect of cooling rate and grain refiner on microstructural morphology of Al2024. According to this figure, fine dendrite arms have been achieved where cooling rate enhances within its range commonly used in DC casting. More fraction of solid can be formed during mushy state due to larger surface of dendrite interfaces. Dendrites refinement can occur as a result of:
1) Intensifying the nucleation frequency of high-potential sites of primary α(Al) phase by increasing the cooling rate [3,6]. Thus, increasing the nucleation to growth ratio in primary and secondary dendrites will lead to form higher fraction of solid at a constant volume of Al2024 liquid phase [4].
2) Significant key roles of diffusion rate and solidification time on dendrite arm spacing [7]. Narrow interdendritic channels can be obtained at high cooling rates due to accelerated nucleation and growth rate of dendrite arms [7,10].
Apart from that, 0.06% (mass fraction) Ti addition as a grain refiner leads to change of the morphology of structure from dendritic to globular. EASTON and St. JOHN [15] reported that two main mechanisms can be considered to form grains in grain-refined castings: 1) Initial thermal undercooling occurred adjacent to the mold wall and 2) constitutional undercooling as a predominant factor in central region of the melt container. The growth restriction factor is a determinant term due to its proportional relationship with constitutional undercooling. Both Ti and B elements intensify the value of the growth restriction factor leading to refined microstructure. To explain dendritic to globular transition, the growth mode of solid phase should be considered. Increasing the constitutional undercooling persuades the mode of dendritic growth. However, the presence of grain refiner intensifies both the constitutional undercooling and the growth restriction factor. The reciprocal trace of these two terms causes to activate high-potential substrates in solidifying melt. Thus, high nucleation frequency will be responsible for nucleation of large number of grains and constraining the growing dendrites to form secondary and tertiary dendrite arms.
Figure 3 shows the X-ray mapping and EDS profiles of unrefined sample cast at cooling rate of 0.74 °C/s. As seen in Fig. 3, the microstructure includes primary α(Al) as a dark grey phase and connected network of intermetallic compounds formed by rejection of elements into interdendritic regions during solidification. High copper concentration in these regions prepares high potential sites for nucleation and growth of Cu-richened intermetallics, e.g., Al2Cu and Al2CuMg phases [16]. Al2CuMg compound possibly supported by some Al2Cu and Mg2Si phases is mainly responsible for precipitation strengthening of the Al2024 alloy during heat treating process [17]. As reported in some literatures [16-19], the microstructure of Al2024 alloy contains intermetallic compounds with intricate chemical composition like Al15(CuFeMn)3Si2, Al20Cu2Mn3, Al12(FeMn)3Si2 and Al7Cu2Fe phases. Also, the presence of Mg2Si at low volume fraction is represented in some interdendritic regions [16].
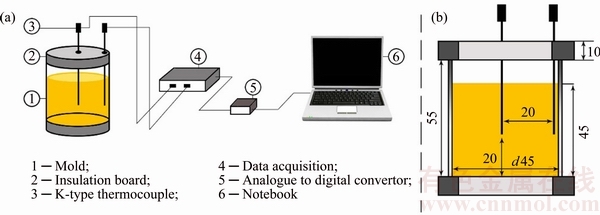
Fig. 1 Setup of two-thermocouple thermal analysis (a), and dimensions of mold (units in mm) (b)
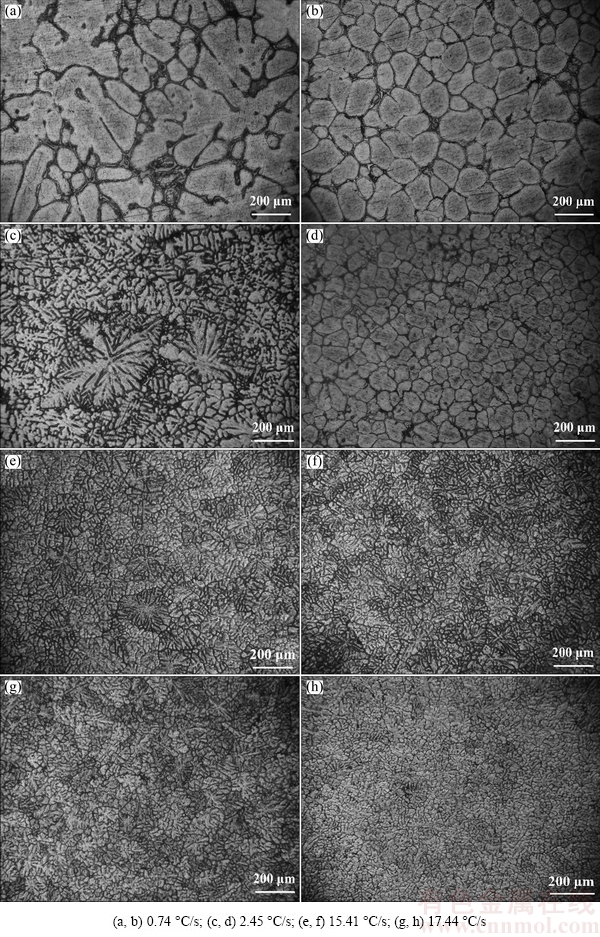
Fig. 2 Microstructures of unrefined (a, c, e, g) and grain-refined (b, d, f, h) Al2024 alloy at different cooling rates
In Al2024 alloy, intermetallics can be divided into three categories based on their formation temperature and time: pre-eutectic, near-eutectic, and eutectic phases [17].
1) Pre-eutectic compounds: Pre-eutectic phases of Al15(CuFeMn)3Si2 and Al20Cu2Mn3 immediately form after nucleation and growth of primary α(Al) dendrites.
2) Near-eutectic compounds: Al2Cu and Mg2Si continually precipitate as near-eutectic phases up to end of solidification.
3) Eutectic compound: Formation of Al2CuMg eutectic intermetallic is followed by precipitation of near-eutectic compounds.
Based on Katgerman’s criterion, determining the nucleation point of eutectic phase and its relevant volume fraction of liquid is main factor to measure Tcr. For this purpose, thermal analysis is a suitable candidate to determine all parameters represented in Katgerman’s and Clyne and Davies’ criteria under different solidification conditions.
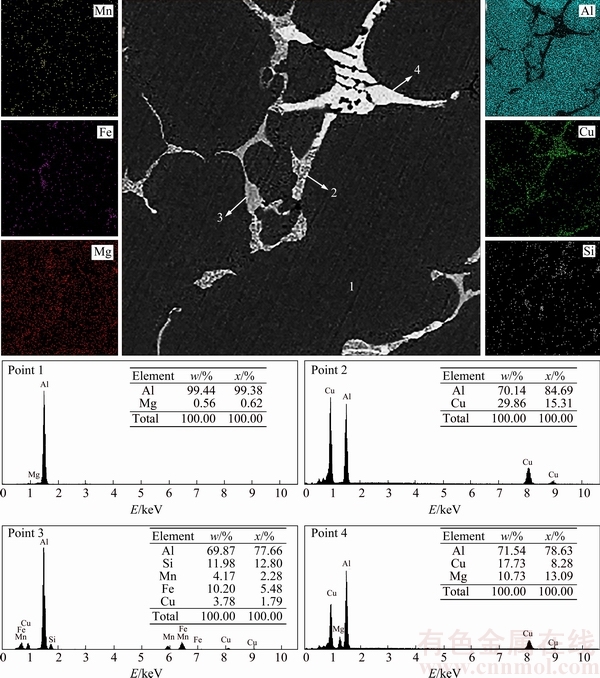
Fig. 3 SEM micrograph, EDS profiles and elemental distributions in Al2024 alloy at cooling rate of 0.74 °C/s
3.2 Thermal analysis curves
As seen in Fig. 4, merged graphs of cooling curves in both central and peripheral regions, and temperature difference, ΔT, versus time illustrate the DCP in both unrefined and grain-refined conditions. A sharp valley in temperature difference caused by higher thermal conductivity of the solid phase rather than the liquid is in accordance with the DCP [20,21]. At the DCP, dendrites tips impinge together, and a skeleton network of solidifying alloy rapidly forms and therefore, high thermal conductive path between central and peripheral regions leads to dropping down of the value of ΔT.
The other key parameter obtained from this figure is nucleation temperature of eutectic phases which is defined as a minimum point just before the last peak of intermetallic formation marked on the first derivative curve. This peak is attributed to precipitation of Al2Cu, and Al2CuMg phases which cause to release high value of latent heat during last stage of mushy zone [16,22]. The first derivative curve is plotted based on temperature-time data recorded by central thermocouple. Since the solidification process progresses within movement of solid/liquid front towards the middle of the mold, the last residual melt enriched by rejected elements will be solidified in the vicinity of the central thermocouple. Trapping the eutectic phases into interdendritic channels leads to reverse segregation in this region so that inadequate volume fraction of liquid cannot be adopted with shrinkage tension [23,24]. Therefore, to predict the centerline hot tearing, first derivative data obtained from central regions are more critical compared with peripheral areas.
The DCP characteristics and nucleation point of eutectic phases at different cooling rates, under both unrefined and grain-refined conditions have been summarized in Table 2 [16,20]. Based on these results, the fraction of solid at the DCP varies with the cooling rate and addition amount of grain refiner. In spite of Clyne and Davies’ criterion in which the solid fraction is equalized to constant value of 0.40, Katgerman considers various solid fractions based on solidification conditions.
Figure 5 demonstrates the Newtonian curves of solid and liquid fractions, fs and fl, versus time and temperature in both unrefined and grain-refined samples cast at cooling rate of 0.74 °C/s. According to both hot tears criteria, detecting time and temperature at which fs values are 0.40, 0.90, 0.99, and also fs at the DCP and eutectic reaction, 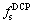 and
and 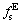 , are important terms to measure the HCSC. According to Figs. 4(b) and 5, total solidification interval of Al2024 alloy can be divided to pre-eutectic and eutectic regions. Since in solidification process of non-eutectic alloys, the solidifying samples chill within the range of mushy zone where its duration is mainly affected by chemical composition and cooling rate, each phase forming before isothermal eutectic reaction can be considered as a primary phase. Therefore, the value of solid fraction achieved before the nucleation point of eutectic phase (black star-shaped sign) can be regarded as gpp in Eq. (4).
, are important terms to measure the HCSC. According to Figs. 4(b) and 5, total solidification interval of Al2024 alloy can be divided to pre-eutectic and eutectic regions. Since in solidification process of non-eutectic alloys, the solidifying samples chill within the range of mushy zone where its duration is mainly affected by chemical composition and cooling rate, each phase forming before isothermal eutectic reaction can be considered as a primary phase. Therefore, the value of solid fraction achieved before the nucleation point of eutectic phase (black star-shaped sign) can be regarded as gpp in Eq. (4).
As seen in Table 3, contribution between cooling curve, its first derivative and solid/liquid fractions curves leads to attaining parameters which are prerequisite to predict the HCSC based on proposed criteria. It is worth being mentioned that gpp is measured by calculating of 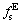 which is in accordance with solid fraction at eutectic transition point in Fig. 5, while gl is achieved from Eq. (4) by knowing the value of gpp. Since solidification process progresses in non-equilibrium condition, the average value of temperatures at which fs and fl become equal to gpp and gl is considered to determine TCr. It should be noted that based on Feurer’s criterion, TCr is defined as a critical temperature in which the maximum volumetric flow rate per unit volume, SPV, becomes equal to the velocity of volumetric solidification shrinkage caused by density difference between solid and liquid phases, SRG [4]. Therefore, it can be concluded that Katgerman’s criterion is more sensitive to total interval of solidification process like the TDCP, TCr and volume fraction of primary phases, whereas Clyne and Davies’ criterion is based on feeding condition at last stage of mushy zone between t0.90 and t0.99 [25].
which is in accordance with solid fraction at eutectic transition point in Fig. 5, while gl is achieved from Eq. (4) by knowing the value of gpp. Since solidification process progresses in non-equilibrium condition, the average value of temperatures at which fs and fl become equal to gpp and gl is considered to determine TCr. It should be noted that based on Feurer’s criterion, TCr is defined as a critical temperature in which the maximum volumetric flow rate per unit volume, SPV, becomes equal to the velocity of volumetric solidification shrinkage caused by density difference between solid and liquid phases, SRG [4]. Therefore, it can be concluded that Katgerman’s criterion is more sensitive to total interval of solidification process like the TDCP, TCr and volume fraction of primary phases, whereas Clyne and Davies’ criterion is based on feeding condition at last stage of mushy zone between t0.90 and t0.99 [25].
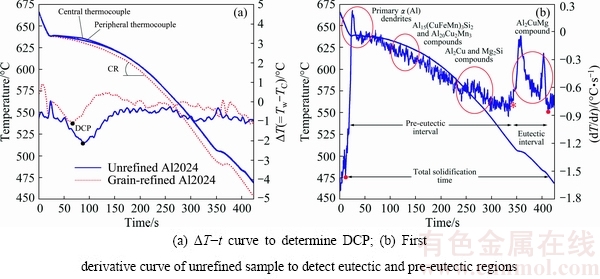
Fig. 4 Thermal analysis curves of Al2024 alloy cast at cooling rate of 0.74 °C/s
Table 2 Thermal analysis features of dendrite coherency and nucleation point of eutectic phase [16,20]
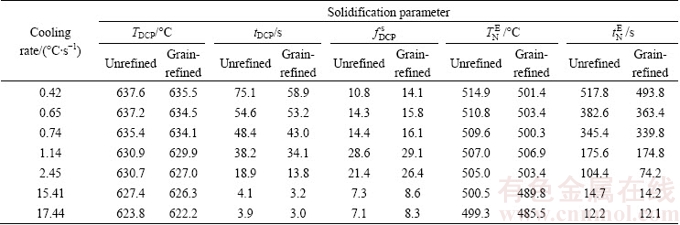
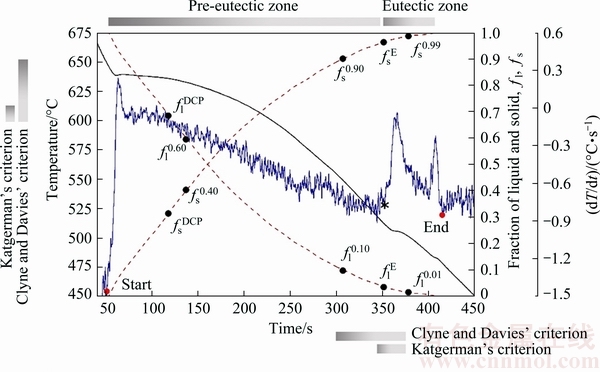
Fig. 5 Critical parameters to determine hot tearing susceptible zones based on criteria represented by Katgerman, and Clyne and Davies (cooling rate of 0.74 °C/s)
Table 3 Measured parameters defined in equations of hot tearing criteria
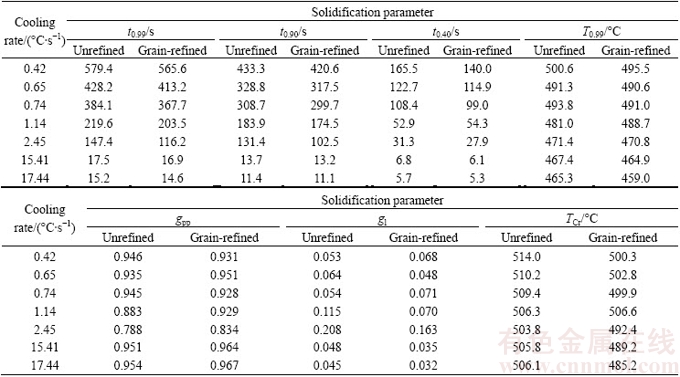
Based on Katgerman’s methodology, the fraction of primary phase, gpp, at medium cooling rates (1.14 and 2.45 °C/s) does not obey the Clyne and Davies’ assumptions. Clyne and Davies report that the most susceptible zone to hot tear is mushy zone interval where solid fraction varies between 0.90 and 0.99 while Katgerman believes that the susceptible zone is significantly affected by onset time and temperature of eutectic reaction which is accommodated to nucleation and growth of eutectic phase within interdendritic channels. Under this condition, grains are surrounded by a thin film of the molten metal, and inadequate volume fraction of the melt cannot undergo contraction occurred during solidification [26,27]. Based on Table 3, at cooling rates of 1.14 and 2.45 °C/s, measured gpp is less than solid fraction of 0.90, which means that eutectic reaction has commenced before starting point of hot tearing phenomenon represented by Clyne and Davies’criterion.
Also, the sum of gpp and gl is not 100% due to lack of sufficient residual molten metal, which eventually leads to the formation of centerline hot tears. The difference between 100% and summation of gpp and gl can qualitatively shows the hot tears severity in samples. Before using both criteria to measure the HCSC, it seems that Katgerman’s criterion predicts higher hot tearing tendency at medium cooling rates compared with its lower values, which is in conflict with results reported by some authors [28-31].
3.3 Hot tearing indexation
As illustrated in Fig. 6, the HCSC measured by both criteria shows different trends at some cooling rates. According to Clyne and Davies’ criterion, there is an optimum cooling rate at which the HCSC attains its minimum quantity [28]. In some literatures, there has been reported that hot tearing tendency will be intense at cooling rates used in DC casting process while its value will be minimum at minimum cooling rates due to the same rate of growing of dendrites in both lateral and longitudinal directions before the DCP [20,28]. Multipath growing of dendrites causes solid fraction to increase at the DCP so that mass to interdendritic feeding will be postponed [32]. On the other hand, at high cooling rates, the mushy-state interval expands due to deviation of solidus line from its equilibrium situation, and the solidifying alloy will be more exposed to temperature range of hot cracking susceptibility. Also, at high cooling rates, severe growing rate of dendrites in longitudinal direction leads to acceleration of dendrites impingement. Katgerman’s criterion represents similar trend at high cooling rates, but it seems that this model is not as practical as Clyne and Davies’ model to predict the HCSC at low to medium cooling rates. As mentioned before, Katgerman’s model is specifically derived for prediction of the HCSC during DC casting of alloys, in which the effects of cooling rates, casting speed, ingot diameter, and alloy composition are significant [4,7].

Fig. 6 Effects of cooling rate and grain refiner on hot cracking sensitivity coefficient
In both studied criteria, adding Al-5Ti-1B grain refiner leads to reduction of the HCSC at each cooling rate. The main reason is attributed to dendrite impingement at the DCP. By adding grain refiners, the DCP will be delayed, and casting defects during equiaxed growth, e.g., shrinkage porosities as well as hot tears, will be decreased [32,33]. Besides, the mode of eutectic distribution is highly affected by grain size [34,35]. In grain-refined samples, the presence of eutectic phase at the grain boundaries causes free movement of the grains to maximize, called showering crystals, and helps to undergo the contraction of the casting [36]. There are also other reasons based on pliability of mushy-state material in the presence of grain refiners, and changing the capillary pressures discussed by some researchers [20,25].
4 Conclusions
1) The hot tearing occurred at last stage of solidification at which Al2CuMg intermetallic compound as a eutectic phase formed in interdendritic channels. Based on Clyne and Davies’ criterion, this time interval was in accordance with susceptible zone where fraction of solid varied between 0.90 and 0.99. While in Katgerman’s model, TCr was a key parameter on hot tearing prediction intensively affected by eutectic distribution, dendrite coherency, and solid fraction of pre-eutectic and near-eutectic compounds.
2) At cooling rates of 1.14 and 2.45 °C/s, there was a conflict between assumptions defined in both criteria. According to Katgerman’s equation, the fraction of primary phase, gpp, was less than solid fraction of 0.90 which was defined as a starting point of vulnerable time interval in Clyne and Davies’ criterion. It was confirmed that the eutectic reaction commenced before susceptible zone, whereas Clyne and Davies and some researchers considered eutectic precipitation interval as a most vulnerable zone during equiaxed solidification.
3) Katgerman’s criterion was suitable candidate to detect the HCSC at cooling rates used in DC casting process while Clyne and Davies derived their numerical model to predict hot cracking sensitivity from low to medium values of cooling rate.
4) Thermal analysis technique was non-destructive test to easily evaluate solidification defects like hot tears and shrinkage porosities. Synergy among cooling curve, its first derivative and solid/liquid fraction curves and numerical criteria proposed to detect hot tears can be widely used for online monitoring of samples quality during solidification.
References
[1] TOTTEN G E, MACKENZIE D S. Handbook of aluminum. Vol. 1: Physical metallurgy and processes [M]. New York: Marcel Dekker, 2003.
[2] TOTTEN G E, MACKENZIE D S. Handbook of aluminum. Vol. 2: Alloy production and materials manufacturing [M]. New York: Marcel Dekker, 2003.
[3] ESKIN D G. Physical metallurgy of direct chill casting of aluminum alloys [M]. CRC Press: Taylor and Francis, 2008.
[4] ESKIN D G, SUYITNO, KATGERMAN L. Mechanical properties in the semi-solid state and hot tearing of aluminum alloys [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2004, 49: 629-711.
[5] QU Min, LIU Lin, TANG Feng-tao, ZHANG Jun, FU Heng-zhi. Effect of sample diameter on primary dendrite spacing of directionally solidified Al-4%Cu alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19: 1-8.
[6] MI Gua-fa, LIU Xiang-yu, ZHU Zhao-jun, WANG Hong-wei. Effects of chill casting processes on secondary dendrite arm spacing and densification of Al-Si-Mg alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17: 1012-1017.
[7] GRANDFIELD J F, ESKIN D G. Essential readings in light metals. Vol. 3: Cast shop for aluminum production [M]. Switzerland: Springer, 2016.
[8] RAPPAZ M, DREZET J M, GREMAUD M. A new hot-tearing criterion [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1999, 30: 449-455.
[9] BIRRU A K, KARUNAKAR B. Effects of grain refinement and residual elements on hot tearing of A713 aluminum cast alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26: 1783-1790.
[10] GRANDFIELD J F, ESKIN D G, BAINBRIDGE I F. Direct-chill casting of light alloys: Science and technology [M]. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2013.
[11] MIRZADEH H. Simple physically-based constitutive equations for hot deformation of 2024 and 7075 aluminum alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 1614-1618.
[12] SUYITNO D G E, KATGERMAN L. Hot tearing criteria evaluation for direct-chill casting of an Al-4.5%Cu alloy [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2005, 36: 1537-1546.
[13] XU Rong-fu, ZHENG Hong-liang, LUO Jie, DING Su-pei, ZHANG San-ping, TIAN Xue-lei. Role of tensile forces in hot tearing formation of cast Al-Si alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 2203-2207.
[14] KAMGA H, LAROUCHE D, BOURNANE M, RAHEM A. Hot tearing of aluminum-copper B206 alloys with iron and silicon additions [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 537: 7413-7423.
[15] EASTON M A, St. JOHN D. An analysis of the relationship between grain size, solute content, and the potency and number density of nucleant particles [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2005, 36: 1911-1920.
[16] SHABESTARI S, GHONCHEH M H, MOMENI H. Evaluation of formation of intermetallic compounds in Al2024 alloy using thermal analysis technique [J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2014, 589: 174-182.
[17] BACKERUD L, KROL E, TAMMINEN J. Solidification characteristics of aluminum alloys. Vol. 3: Wrought aluminum alloys [M]. Sweden: Skan Aluminum, 1986.
[18] PAREL T, WANG Shun-cai, STARINK M. Hardening of an Al-Cu-Mg alloy containing types I and II S phase precipitates [J]. Materials and Design, 2010, 31: s2-s5.
[19] WANG Shun-cai, STARINK M. Precipitates and intermetallic phases in precipitation hardening Al-Cu-Mg-(Li) based alloys [J]. International Materials Reviews, 2005, 50: 193-215.
[20] GHONCHEH M H, SHABESTARI S. Effect of cooling rate on the dendrite coherency point during solidification of Al2024 alloy [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2015, 46: 1287-1299.
[21] DJURDJEVIC M, HUBER G. Determination of rigidity point/temperature using thermal analysis method and mechanical technique [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 590: 500-506.
[22] GHONCHEH M H, SHABESTARI S, ABBASI M H. Effect of cooling rate on the microstructure and solidification characteristics of Al2024 alloy using computer-aided thermal analysis technique [J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2014, 117: 1253-1261.
[23] LIU Yong-qin, JIE Wan-qi, GAO Zhi-ming, ZHENG Yong-jian. Investigation on the formation of microporosity in aluminum alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 629: 221-229.
[24] LEMIEUX A, LANGLAIS J, BOUCHARD D, CHEN G. Effect of Si, Cu and Fe on mechanical properties of cast semi-solid 205 alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20: 1555-1560.
[25] ESKIN Dmitry, DU Qiang, RUVALCABA D, KATGERMAN L. Experimental study of structure formation in binary Al-Cu alloys at different cooling rates [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 405: 1-10.
[26] VANEETVELD G, RASSILI A, PIERRET J C, LECOMTE- BECKERS J. Conception of tooling adapted of thixoforming of high solid fraction hot-crack-sensitive aluminum alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20: 1712-1718.
[27] CHEN Rui, SHI Yu-feng, XU Qing-yan, LIU Bai-cheng. Effect of cooling rate on solidification parameters and microstructure of Al-7Si-0.3Mg-0.15Fe alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 1645-1652.
[28] SHABESTARI S, GHONCHEH M H. Investigation on the effect of cooling rate on hot tearing susceptibility of Al2024 alloy using thermal analysis [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2015, 46: 2438-2448.
[29] D’ELIA F, RAVINDRAN C, SEDIAKO D. Interplay among solidification, microstructure, residual strain and hot tearing in B206 aluminum alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 624: 169-180.
[30] LI Shi-min, SADAYAPPAN K, APELIAN D. Role of grain refinement in the hot tearing of cast Al-Cu alloy [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2013, 44: 614-623.
[31] EASTON M A, WANG Hao, GRANDFIELD J, DAVIDSON C, STJOHN D, SWEET L, COUPER M. Observation and prediction of the hot tear susceptibility of ternary Al-Si-Mg alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2012, 43: 3227-3238.
[32] LI Fa-guo, DONG Qing, ZHANG Jiao, DAI Yong-bing, FU Ya-nan, XIE Hong-lan, YIN Fu-cheng, SUN Bao-de. In situ on columnar-equiaxed transition and an axial columnar dendrite growth of Al-15%Cu alloy by synchrotron radiography [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 2112-2116.
[33] CHEN Ti-jun, LI Xiang-wei, GUO Hai-yang, HAO Yuan. Microstructure and crystal growth direction of Al-Cu alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 1399-1409.
[34] ROBLES HERNANDEZ F, SOKOLOWSKI J. Thermal analysis and microscopical characterization of Al-Si hypereutectic alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 419: 180-190.
[35] CRUZ H C, GONZALEZ-RIVERA C G, JUAREZ HERNANDEZ A, HERRERA M, JUAREZ J. Quantification of the microconstituents formed during solidification by the Newtonian thermal analysis method [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2006, 178: 128-134.
[36] NABAWY A, SAMUEL A, SAMUEL F, DOTY H. Influence of additions of Zr, Ti-B, Sr, and Si as well as of mold temperature on the hot-tearing susceptibility of an experimental Al-2%Cu-1%Si alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2012, 47: 4146-4158.
M. H. GHONCHEH1, S. G. SHABESTARI2, A. ASGARI3, M. KARIMZADEH1
1. School of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology, 16846-13114, Tehran, Iran;
2. Center of Excellence for High Strength Alloys Technology, School of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology, 16846-13114, Tehran, Iran;
3. School of Mechanical Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology, 16846-13114, Tehran, Iran
摘 要:对比研究Katgerman和Clyne-Davies预测热裂敏感性的理论模型。制备晶粒细化的和未细化的2024铝合金,凝固冷却速度为0.4-17.5 °C/s。采用热分析检测枝晶搭接点和共晶反应温度,基于牛顿法测绘固相线和液相线以确定热裂敏感区。实验结果显示,2024铝合金中可能发生热裂的最敏感区域为在糊状区的最后阶段,Al2CuMg金属间化合物作为共晶相形成的区域。另外,在熔铸过程中的高冷却速率下,两个模型具有较好的一致性;而在低至中等冷却速率下,Clyne-Davies 模型预测热裂倾向更准确。
关键词:2024铝合金;枝晶搭接;直接激冷铸造;热分析;热裂
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Corresponding author: S. G. SHABESTARI; Tel/Fax: +98-21-77240371; E-mail: shabestari@iust.ac.ir
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64718-1

