J. Cent. South Univ. (2016) 23: 1823-1830
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-016-3236-4
Tuning microstructure and surface chemistry of reduced graphene oxide by mild reduction
LENG Xian(冷娴), LIU Ru-tie(刘如铁), ZOU Jian-peng(邹俭鹏), XIONG Xiang(熊翔), HE Han-wei(何捍卫)
State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Abstract: Reduced graphene oxide (RGO) sheets with varied contents and types of oxygenated groups were synthesized by Hummers treatment of natural graphite powders followed by different nontoxic and mild reduction methods, which include thermal and chemical reduction with ethylene glycol, KOH and Fe powder. The changes in microstructure and surface chemistry of RGOs were extensively characterized by SEM, TEM, AFM, XRD, XPS and Raman spectrum. The results show that significant exfoliation occurs during oxidation and is retained in reduction processes, along with the formation of curled wavy morphology. Compared with large d spacing (0.852 nm) of graphene oxide (GO), the (002) plane distance decreases to 0.358-0.384 nm of RGOs, indicating efficient tuning of surface functionalities through mild reduction methods. The ID/IG ratio of RGOs is about 1.0-1.15, indicating that reconstructed sp2 domains have smaller sizes and larger quantity. The content of sp2 bonded C in GO (36.93%, molar fraction) increases to 45.48%-72.92% (molar fraction) in RGOs, along with a drastic decrease in hydroxyl and epoxy and minor changes in carbonyl and carboxyl. Thermal reduction or chemical reduction produces RGOs with residual functionalities, which may render different chemical activity and is desirable in various applications.
Key words: graphene oxide; reduction; oxygen functionality; surface chemistry
1 Introduction
Graphene and its derivatives have received much attention in recent years because of its technological potential and significant theoretical values [1-2]. Graphene, a two-dimensional nanostructure material made of sp2 hybridized carbon atoms, possesses superior physical properties originating from its unique microstructure and it is a promising candidate for next-generation electronics [3-4]. From an application perspective, batch production of graphene and fabrication of graphene-based composites are of interest. To realize large-scale synthesis of graphene, massive efforts have been made in chemical exfoliation and reduction routes starting with graphene oxide (GO) and graphite intercalated compound (GIC) [5-6]; but the precise structure is still a controversial issue [7]. However, the π conjugation network is seldom fully recovered and the resulting RGO (reduced graphene oxide) retains partial oxygen-containing groups [8-9]. Residual oxygen functionalities offer special chemistry and opportunities for further modification [10]. For instance, graphene oxide reduced by hydrazine exhibits a field-effect response [11], and can readily form well-dispersed colloids benefiting from remaining carboxylic acid groups [12]. The presence of oxygenated groups on the surface of carbon materials promotes capacitance by producing pseudocapacitance [13-14]. In addition, pristine graphene without hydrophilic or hydrophobic groups is hardly compatible with inorganic and organic solvents that prohibit practical utilization. In contrast, chemically modified graphene with oxygen- containing functional groups introduces active sites and compatibility for composite reinforcement with respect to electrical, thermal and mechanical properties that can be realized through in situ reaction or liquid phase blending method [15-17]. Theoretically, the amount, distribution and nature of surface functions influence catalysis, absorption and electrochemistry performance [18-19]. The dependence of intercalation on graphitization degree and sp2-carbon domain sizes has been reported [20-21]. Detailed studies on surface functions and their influence on the structure of graphene are needed for better understanding and industrial applications.
Currently, investigations of RGO reported in the literature have highlighted in rigorous reduction and repeated purification, and yet little emphasis has been seen on the processability and intriguing practical values provided by the existence of functionalities. Mild reduction is energy-saving, easy to conduct and desirable for adjusting surface functionalities gradually. The aim of the present work is to study the impact of functionalization on the surface and structural properties, as well as to get a deeper understanding of oxygen functionalities reduction evolution, which may eventually lead to stoichiometrical control with minimum influence on the unique attributes of graphene.
2 Experimental
2.1 Preparation
Graphite flakes (99.8%, 43 μm, Alfa Aesar) were used as raw material for preparation of GO by Hummers method [22], during which, intercalation of graphene layers and functionalization of graphene planes and edges simultaneously happened. Centrifugation and sonication were performed to purify and exfoliate as-prepared kinetically stable GO colloid with a solid content of 0.5%. RGOs were prepared through four different eco-friendly procedures as follows: (1) 10 mL ethylene glycol was added to 10 mL GO colloid while stirring, and subjected to ultrasound (200 W, 40 kHz) for 1 h in 70 °C. The obtained product was labelled as RGO-1. (2) The pH value of GO colloid was adjusted to 10 with 1 mol/L KOH aided by continuous stirring. After that, the solution was treated in ultrasound for 1 h at 70 °C. The precipitates were washed with deionized water and named as RGO-2. (3) RGO-3 was prepared according to Fe powder reduction used in the Ref. [23]. Briefly, 2 g of Fe powder was added slowly to 20 mL GO, then 40 mL HCl (35%) was added drop by drop and the chemical reaction was carried out for 6 h under stirring. Finally, 20 mL HCl (35%) was dropped to consume the remaining Fe powder. This is sample RGO-3. (4) 30 mL GO was transferred to a Teflon-lined autoclave and kept at 180 °C for 18 h, and the sample was labelled as RGO-4.
All chemicals used in this work were of analytical grade and all solutions were prepared with 18 MΩ·cm water (Milli-Q SP. Japan).
2.2 Characterization
The morphology and element content were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, FEI NOVA Nano230) and energy-dispersive spectrometry (EDS). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and selected area electron diffraction (SAED) were performed by using a JEOL 2010II microscope. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) images were taken with VEECO Nano man VS instrument. X-ray diffraction analysis (Rigaku Ltd., Japan, D/max 2550VB, Cu Kα radiation, U=40 kV, I=250 mA) and Raman spectroscopy (HORIBA Scientific, France, Labram Aramis, laser excitation source: λ=532 nm) were employed to characterize crystalline information. XPS analysis (K-Alpha 1063, UK) was carried out to identify the reduction level and residual oxygen functional groups.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Morphology
Morphologies of pristine graphite, GO and as-prepared RGOs are shown in Fig. 1. Graphite (Fig. 1(a)) exhibits typical layered stacking structure and relatively smooth surface. GO (Fig. 1(b)) exhibits relatively flat appearances with slight spontaneous rippling. The oxygen contents in GO is 29.22% from EDS, which implies the existence of plenty of oxygen- containing groups and severe structural perturbations. Due to self-assembling along with deoxygenation [24], RGO-1 (Fig. 1(c)) and RGO-2 (Fig. 1(d)) show rougher surface compared to graphite in Fig. 1(a), and their oxygen contents are 25.3% and 20.42% respectively. So, ethylene glycol and KOH show partial reducing effect on GO. Curled wavy morphologies emerge on the surfaces of RGO-3 (Fig. 1(e)) and RGO-4 (Fig. 1(f)), and the increasing level of warping may be attributed to adjustment of local defects in graphitic lattices, or caused by carbon attaching OH groups in a distorted tetrahedral configuration [25-26]. The corresponding EDS results show much less residual oxygen content of 10.86% and 9.72%, respectively. The oxygen content in RGO reduced by the violent reducing agent of hydrazine hydrate is 11.5% [27]. It is worth noting that the mild methods of Fe powder reduction and hydrothermal reduction show comparable reducing effect compared with hydrazine hydrate reduction. Therefore, mild reduction methods provide reliable application potential for graphene-based composites and others because of their eco-friendliness.
TEM images as shown in Fig. 2 also corroborate the morphology change caused by oxidation and subsequent reduction. Graphite (Fig. 2(a)) shows thick flakes with clear edges, which indicates lots of stacking. The corresponding SAED (Fig. 2(b)) reveals monocrystlline structure with high crystallization. After oxidation, GO flakes (Fig. 2(c)) exhibit veil-like appearance with slight folding, indicating delamination in the graphite. SAED of GO (Fig. 2(d)) shows multicrystalline structure with reassembly of graphene oxide along the c-axis, and the graphene oxide lamellae can be further separated to unillamelar sheet by in situ growing or anchoring of metal or metal oxide nanoparticles. Figure 2(e) shows that RGO-1 shares similar extent of crinkling as the GO surface (marked by arrows). For other reduction procedures, more wrinkles and corrugations appear in RGO-2, RGO-3 and RGO-4 (Figs. 2(f), (g), (h)). The possible reason is that less electrostatic repulsion and stronger π-π attractive interactions caused by functionalities and restored π conjugation take place in RGO-2, RGO-3 and RGO-4 [18]; these show good agreement with representative morphologies of RGOs [28-29]. Figure 2(i) shows the dispersion ring of the SAED result of RGO-4, which indicates multicrystalline structure with little difference compared with GO (Fig. 2(d)).
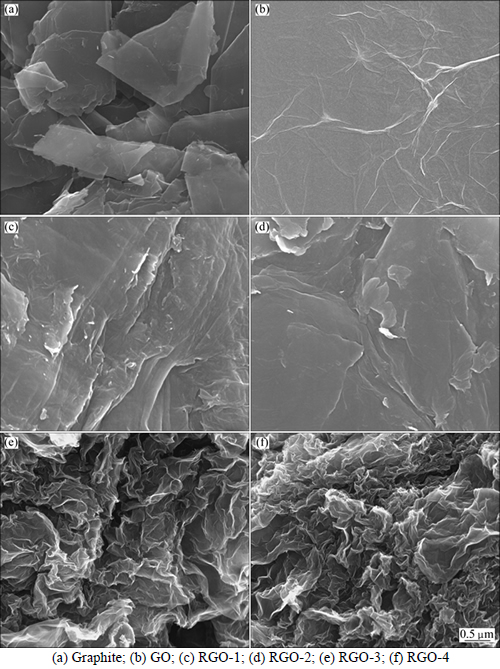
Fig. 1 SEM images:
The average thickness of GO and RGO-1 obtained from AFM images are plotted in Fig. 3. The GO flakes are about 1.711 nm thick, suggesting that GO lamellae are effectively exfoliated to ultrathin sheets of only few layers. The RGO-1 (Figs. 3(c) and (d)) is about 1.385 nm thick, indicative of 3-4 stacking layers. Analogously, other RGO samples not shown here have little change in lateral dimensions and the same trend of decrease in height during reduction results from removal of oxide groups on both sides of graphene planes [30].
3.2 XRD analysis
Figure 4 shows the X-ray diffraction patterns of pristine graphite, GO and RGOs measured at the state of flakes. Interplanar distance plays an important role in providing the structure and crystallinity information of carbon materials. Graphite (Fig. 4(a)) shows a sharp diffraction peak at 2θ=26.40° assigned to (002) plane with d=0.337 nm according to the Bragg equation. After severe oxidation by the Hummers method, diffractions from graphite structure disappear and a relatively broad peak at 2θ=10.37° with d=0.852 nm appears (Fig. 4(b)), which corresponds to a looser stacking of carbon layers in c-axis caused by accommodation of the functionalities and water molecules. As seen in Figs. 4(c)-(f), extended conjugated sp2 networks are restored after reduction along with the decomposition of oxygen functionalities. Figure 4 shows the (002) characteristic diffraction peak of RGOs at 2θ=23.12°, 23.83°, 24.87° and 24.58° with d values of 0.384, 0.373, 0.358 and 0.362 nm, respectively [23, 31]. The possible reason for slight enlarging of d-values and (002) peak broadening of RGOs compared to that of raw graphite might be the residual functionalities, which would lower the crystallinity and weaken the van der Waals forces between the layers.
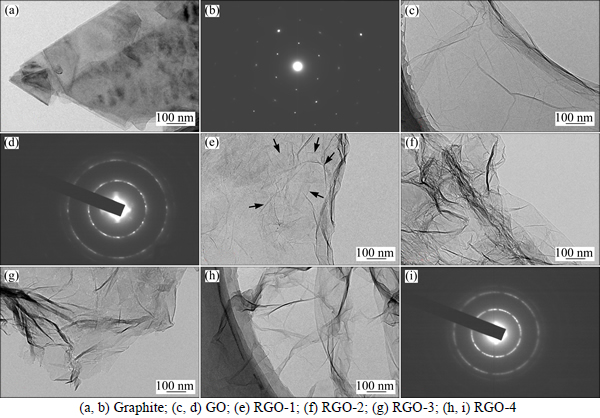
Fig. 2 TEM images and corresponding SAED:
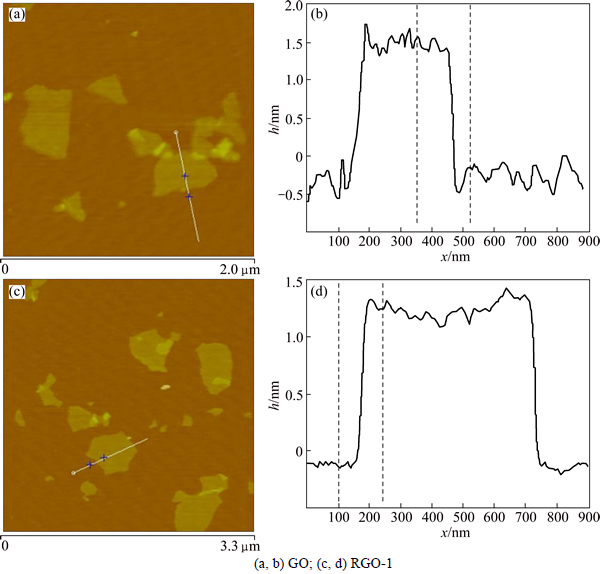
Fig. 3 Typical AFM images and height profiles:
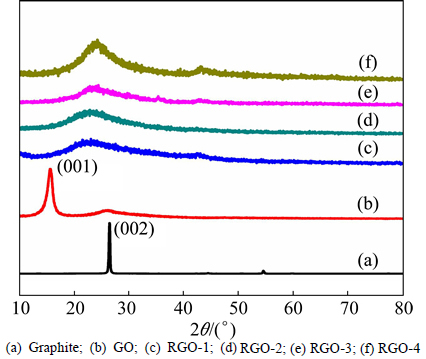
Fig. 4 XRD patterns:
3.3 Raman analysis
To characterize the changes in p-conjugation extent and defect density, Raman spectra of pristine graphite, GO and RGOs are examined, as shown in Fig. 5. The spectra mainly exhibit D band, G band and weak 2D band in graphite, GO and RGOs, which is consistent with typical curves of chemically converted graphene [32-33]. The G band of GO at 1589.49 cm-1 is blue shifted compared with that of graphite at 1582.40 cm-1, which denotes in-plane hexagonal vibration. The G band may overlap with D′ band (1620 cm-1) with increased defects. However, isolated double bonds segregated by functional groups may appear [34]. The G bands of RGOs are at about 1582.73-1586.11 cm-1 and shift to lower wave numbers compared with those of GO, suggesting transformation from amorphous states to nanocrystalline or enhanced graphitic crystallinity [35]. The G bands of RGOs are blue shifted compared with original graphite flakes, which is a sign for the decrease in stacking layers and in agreement with the reported shift trend of G band in graphene [36-37]. D band at about 1350 cm-1 reflects defects that lower crystal symmetry. The ID/IG ratio is used to evaluate the graphitic crystallinity and integrity of the structure. Assuming that ID/IG in GO is 1, ID/IG of RGOs is in the range of 1.0-1.15. ID/IG increases with reduction, as shown in previous studies [38], which is attributed to rebuilding sp2 domains of smaller sizes and larger amount in comparison with those of GO. The 2D band, which arises from a two phonon double resonance, of both GO and RGO are wide and limited in intensity, indicative of multilayered nanosheet structure [39].
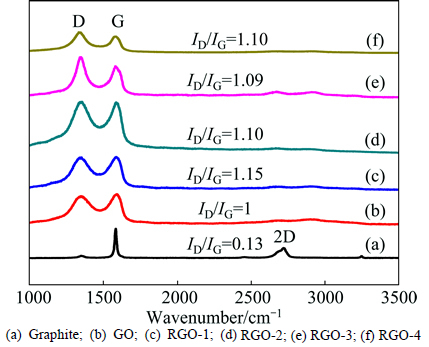
Fig. 5 Raman spectra:
3.4 XPS analysis
Removal of oxygen functional groups is confirmed by XPS survey spectra and deconvolution core-level spectra, as illustrated in Fig. 6. The O 1s signal gradually declines from GO to RGO-4, denoting that the oxygen content declines from 29.22% for GO to 26.15%, 21.48%, 13.12%, and 9.32% for RGO—1-4, respectively. The reduction level of RGO-4 is comparable with RGO reduced by hazardous hydrazine hydrate (C/O=10.3) [27]. The identification of different chemical groups of C 1s peaks (Figs. 6(b)-(f)) is based on binding energy values according to previous studies [40-41]. The C 1s peak separation of GO, RGO-1, RGO-2, RGO-3, RGO-4 are given in Figs. 6(b)-(f), respectively. The relative contents of carbon atoms in graphene planes (284.6 eV), hydroxyl and epoxy (286.4 eV), carbonyl in acetone/quinone (287.8 eV) and carboxyl in —COOR (R=H and alkyl) (289.0 eV) are summarized in Fig. 6(g). Among the changes of surface functional groups (C—OH, COC, C=O and O—C=O), hydroxyl and epoxy content attenuate notably from 23.59% for GO to 20.66%, 11.15%, 11.8% and 8.67% for RGO—1-4, respectively. It is also highlighted in O 1s peaks (Fig. 6(h)) that peaks at 532.6 eV suggesting C—O groups are progressively broadened, weakened and decreased from RGO-1 to RGO-4 compared with the minor changes of peaks at 531.2 eV denoting carbonyl and carboxyl groups [9].RGOs are incompletely deoxygenated because of differences in activity of oxygen functional groups. The XPS analyses further corroborate that manipulation of surface chemistry can be realized by monitoring the reduction extent through various mild procedures and it will facilitate the modification methods of graphene-based materials.
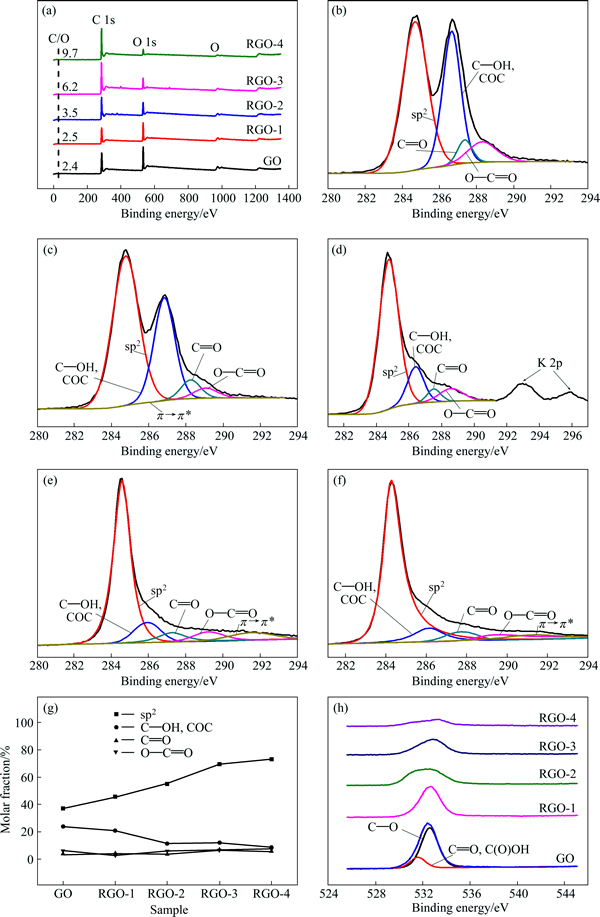
Fig. 6 XPS spectra of survey scan peaks (a); C 1s peaks of GO (b), RGO-1 (c), RGO-2 (d), RGO-3 (e) and RGO-4 (f); content of carbon in different chemical state (g); O 1s peaks (h)
4 Conclusions
This work explores the surface and structure changes of RGOs prepared through various reduction procedures. Graphene layers stacking along c-axis are disturbed and exfoliated to curved few-layer graphenes with residual oxygenated groups. RGOs reduced by Fe powders and hydrothermal process exhibit obvious distinction in surface and show heavily crumpled morphology. Effective delamination occurs in GO colloid and remains in few-layer structure during reduction. The surface groups significantly affect the structure of sp2 skeleton. It is found that interlayer distance declines to 0.358-0.384 nm and the ID/IG is about 1.0-1.15 in the RGOs owing to reduction. The evolution of surface-grafted functional groups indicates different electronic structure and extent of contribution to specific function. Deoxygenation mainly impacts the quantity of hydroxyl and epoxy. Moreover, RGOs with oxygen functionalities can reasonably accelerate its future application in reinforcement of composites and various other fields that need high aspect ratio carbons and mass production, such as hydrogen and energy storage.
References
[1] GEIM A K, NOVOSELOV K S. The rise of graphene [J]. Nature Materials, 2007, 6(3): 183-191.
[2] BROWNSON D A, BANKS C E. Graphene electrochemistry: An overview of potential applications [J]. Analyst, 2010, 135(11): 2768-2778.
[3] GAO Li-bo, REN Wen-cai, LIU Bi-lu, WU Zhong-shuai, JIANG Chuan-bin, CHENG Hui-ming. Crystallographic tailoring of graphene by nonmetal SiOx nanoparticles [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(39): 13934-13936.
[4] WORSLEY K A, RAMESH P, MANDAL S K, NIYOGI S, ITKIS M E, HADDON R C. Soluble graphene derived from graphite fluoride [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2007, 445(1): 51-56.
[5] SHANMUGHARAJ A M, CHOI W S, LEE C W, RYU S H. Electrochemical performances of graphene nanosheets prepared through microwave radiation [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(23): 10249-10253.
[6] BAE S Y, JEON I Y, YANG J, PARK N, SHIN H S, PARK S, RUOFF R S, DAI Li-ming, BAEK J B. Large-area graphene films by simple solution casting of edge-selectively functionalized graphite [J]. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(6): 4974-4980.
[7] SZABO T, BERKESI O, FORGO P, JOSEPOVITS K, SANAKIS Y, PETRIDIS D, DEKANY I. Evolution of surface functional groups in a series of progressively oxidized graphite oxides [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2006, 18(11): 2740-2749.
[8] WANG Guo-xiu, WANG Bei, PARK J, YANG J, SHEN Xiao-ping, YAO J. Synthesis of enhanced hydrophilic and hydrophobic graphene oxide nanosheets by a solvothermal method [J]. Carbon, 2009, 47(1): 68-72.
[9] MATTEVI C, EDA G, AGNOLI S, MILLER S, MKHOYAN K A, CELIK O, MASTROGIOVANNI D, GRANOZZI G, GARFUNKEL E, CHHOWALLA M. Evolution of electrical, chemical, and structural properties of transparent and conducting chemically derived graphene thin films [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2009, 19(16): 2577-2583.
[10] LEE S H, DREYER D R, AN J, VELAMAKANNI A, PINER R D, PARK S, ZHU Yan-wu, KIM S O, BIELAWSKI C W, RUOFF R S. Polymer brushes via controlled, surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) from graphene oxide [J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2010, 31(3): 281-288.
[11] GOMEZ-NAVARRO C, WEITZ R T, BITTNER A M, SCOLARI M, MEWS A, BURGHARD M, KERN K. Electronic transport properties of individual chemically reduced graphene oxide sheets [J]. Nano Letters, 2007, 7(11): 3499-3503.
[12] LI Dan, M LLER M B, GILJGE S, KANER R B, WALLACE G G. Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets [J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2008, 3(2): 101-105.
LLER M B, GILJGE S, KANER R B, WALLACE G G. Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets [J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2008, 3(2): 101-105.
[13] LOZANO-CASTELLO D, CAZORLA-AMOROS D, LINARES- SOLANO A, SHIRAISHI S, KURIHARA H, OYA A. Influence of pore structure and surface chemistry on electric double layer capacitance in non-aqueous electrolyte [J]. Carbon, 2003, 41(9): 1765-1775.
[14] ODA H, YAMASHITA A, MINOURA S, OKAMOTO M, MORMOTO T. Modification of the oxygen-containing functional group on activated carbon fiber in electrodes of an electric double-layer capacitor [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 158(2): 1510-1516.
[15] LEE S H, KIM H W, HWANG J O, LEE W J, KWON J, BIELAWSKI C W, RUOFF R S, KIM S O. Three-dimensional self-assembly of graphene oxide platelets into mechanically flexible macroporous carbon films [J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2010, 122(52): 10282-10286.
[16] LIU Ping-gui, GONG Ke-cheng, XIAO Peng, XIAO Min. Preparation and characterization of poly(vinyl acetate)-intercalated graphite oxide nanocomposite [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2000, 10(4): 933-935.
[17] VADUKUMPULLY S, PAUL J, MAHANTA N, VALIYAVEETTIL S. Flexible conductive graphene/poly (vinyl chloride) composite thin films with high mechanical strength and thermal stability [J]. Carbon, 2011, 49(1): 198-205.
[18] LI Ming-jie, LIU Chen-ming, XIE Yong-bing, CAO Hong-bin, ZHAO He, ZHANG Yi. The evolution of surface charge on graphene oxide during the reduction and its application in electroanalysis [J]. Carbon, 2014, 66: 302-311.
[19] PITTMAN C U Jr, JIANG W, YUE Z R, GARDNER S, WANG L, TOGHIANI H, LEONY LEON C A. Surface properties of electrochemically oxidized carbon fibers [J]. Carbon, 1999, 37(11): 1797-1807.
[20] SONEDA Y, TOYODA M, HASHIYA K, YAMASHITA J, KODAMA M, HATORI H, INAGAKI M. Huge electrochemical capacitance of exfoliated carbon fibers [J]. Carbon, 2003, 41(13): 2680-2682.
[21] SI Yong-chao, SAMULSKI E T. Synthesis of water soluble graphene [J]. Nano Letters, 2008, 8(6): 1679-1682.
[22] HUMMERS JR W S, OFFEMAN R E. Preparation of graphitic oxide [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1958, 80(6): 1339.
[23] FAN Zhuang-jun, KAI Wang, YAN Jun, WEI Tong, ZHI Lin-jie, FENG Jing, REN Yue-ming, SONG Li-ping, WEI Fei. Facile synthesis of graphene nanosheets via Fe reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide [J]. ACS Nano, 2010, 5(1): 191-198.
[24] OH Y J, YOO J J, KIM Y I, YOON J K, YOON H N, KIM J H, PARK S B. Oxygen functional groups and electrochemical capacitive behavior of incompletely reduced graphene oxides as a thin-film electrode of supercapacitor [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 116(10): 118-128.
[25] LERF A, HE He-yong, FORSTER M, KLINOWSKI J. Structure of graphite oxide revisited II [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 1998, 102(23): 4477-4482.
[26] HE H, KLINOWSKI J, FORSTER M, LERF A. A new structural model for graphite oxide [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 1998, 287(1): 53-56.
[27] STANKOVICH S, DIKIN D A, PINER R D, KOHLHAAS K A, KLEINHAMMES A, JIA Yuan-yuan, WU Yue, NGUYEN S T, RUOFF R S. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide [J]. Carbon, 2007, 45(7): 1558-1565.
[28] ZHU Yan-wu, MURALI S, STOLLER M D, VELAMAKANNI A, PINER R D, RUOFF R S. Microwave assisted exfoliation and reduction of graphite oxide for ultracapacitors [J]. Carbon, 2010, 48(7): 2118-2122.
[29] LV Wei, TANG Dai-ming, HE Yan-bing, YOU Cong-hui, SHI Zhi-qiang, CHEN Xue-cheng, CHEN Cheng-meng, HOU Peng-xiang, LIU Chang, YANG Quan-hong. Low-temperature exfoliated graphenes: Vacuum-promoted exfoliation and electrochemical energy storage [J]. ACS Nano, 2009, 3(11): 3730-3736.
[30] FAN Xiao-bin, PENG Wen-chao, LI Yang, LI Xian-yu, WANG Shu-lan, ZHANG Guo-liang. ZHANG Feng-bao. Deoxygenation of exfoliated graphite oxide under alkaline conditions: A green route to graphene preparation [J]. Advanced Materials, 2008, 20(23): 4490-4493.
[31] NETHRAVATHI C, RAJAMATHI M. Chemically modified graphene sheets produced by the solvothermal reduction of colloidal dispersions of graphite oxide [J]. Carbon, 2008, 46(14): 1994-1998.
[32] WU Zhong-shuai, REN Wen-cai, XU Li, LI Feng, CHENG Hui-ming. Doped graphene sheets as anode materials with superhigh rate and large capacity for lithium ion batteries [J]. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(7): 5463-5471.
[33] WU Zhong-shuai, REN Wen-cai, GAO Li-bo, ZHAO Jin-ping, CHEN Zong-ping, LIU Bi-lu, TANG Dai-ming, YU Bing, JIANG Chuan-bin, CHENG Hui-ming. Synthesis of graphene sheets with high electrical conductivity and good thermal stability by hydrogen arc discharge exfoliation [J]. ACS Nano, 2009, 3(2): 411-417.
[34] RAMESHA G K, SAMPATH S. Electrochemical reduction of oriented graphene oxide films: An in situ Raman spectroelectrochemical study [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009, 113(19): 7985-7989.
[35] LIANG Yan-yu, FRISCH J, ZHI Lin-jie, NOROUZI-ARASI H, FENG Xin-liang, RABE J P, KOCH N, M LLEN K. Transparent, highly conductive graphene electrodes from acetylene-assisted thermolysis of graphite oxide sheets and nanographene molecules [J]. Nanotechnology, 2009, 20(43): 18968-18972.
LLEN K. Transparent, highly conductive graphene electrodes from acetylene-assisted thermolysis of graphite oxide sheets and nanographene molecules [J]. Nanotechnology, 2009, 20(43): 18968-18972.
[36] GUPTA A, CHEN G, JOSHI P, TADIGADAPA S, EKLUND P C. Raman scattering from high-frequency phonons in supported n-graphene layer films [J]. Nano Letters, 2006, 6(12): 2667-2673.
[37] GRAF D, MOLITOR F, ENSSLIN K, STAMPFER C, JUNGEN A, HIEROLD C, WIRTZ L. Spatially resolved Raman spectroscopy of single-and few-layer graphene [J]. Nano Letters, 2007, 7(2): 238-242.
[38] VINODGOPAL K, NEPPOLIAN B, LIGHTCAP I V, GRIESER F, ASHOKKUMAR M, KAMAT P V. Sonolytic design of graphene-Au nanocomposites. Simultaneous and sequential reduction of graphene oxide and Au(III) [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2010, 1(13): 1987-1993.
[39] FERRARI A C. Raman spectroscopy of graphene and graphite: Disorder, electron–phonon coupling, doping and nonadiabatic effects [J]. Solid State Communications, 2007, 143(1): 47-57.
[40] XU Chao, YUAN Ru-sheng, WANG Xin. Selective reduction of graphene oxide [J]. New Carbon Materials, 2014, 29(1): 61-66.
[41] ZHANG Jia-li, YANG Hai-jun, SHEN Guang-xia, CHENG Ping, ZHANG Jing-yan, GUO Shou-wu. Reduction of graphene oxide vial-ascorbic acid [J]. Chemical Communications, 2010, 46(7): 1112-1114.
(Edited by YANG Bing)
Foundation item: Project(51274248) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Projects(2015DFR50580, 2013DFA31440) supported by the International Scientific and Technological Cooperation Program of China
Received date: 2015-08-08; Accepted date: 2015-12-15
Corresponding author: ZOU Jian-peng, PhD, Professor; Tel: +86-731-88830376; E-mail: zoujp@csu.edu.cn