文章编号:1004-0609(2010)06-1075-08
原位合成Mg2Si/Mg-2Al-Zn-2Gd复合材料的微观组织与断裂行为
王旭东,杜文博,王朝辉,李淑波
(北京工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,北京 100124)
摘 要:采用多次循环塑性变形-原位反应方法制备Mg2Si/Mg-2Al-Zn-2Gd复合材料。采用XRD、SEM和TEM对复合材料的成分及微观组织进行分析和观察。结果表明:多次循环塑性变形过程对镁合金基体组织和原位合成的Mg2Si第二相粒子均有细化和均化作用;随着Mg2Si颗粒含量的增加,复合材料的弹性模量和屈服强度增加,同时断裂强度和伸长率均下降;原位反应合成的Mg2Si第二相粒子与基体结合良好,材料断裂时裂纹优先在基体中形成,断裂时Mg2Si第二相粒子能起到阻碍裂纹扩展的作用;Mg2Si/Mg-2Al-Zn-2Gd复合材料的强化机制主要为第二相强化和基体晶粒细化。
关键词:Mg2Si/Mg-2Al-Zn-2Gd复合材料;断裂行为;多次循环塑性变形;原位合成;Mg2Si
中图法分类号:TG 146.2;TG 146.4 文献标志码:A
Microstructure and fracture behavior of in-situ synthesized Mg2Si/Mg-2Al-Zn-2Gd composite
WANG Xu-dong, DU Wen-bo, WANG Zhao-hui, LI Shu-bo
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China)
Abstract: The Mg2Si reinforced Mg-2Al-Zn-2Gd composite was synthesized by in-situ solid state reaction and repeated plastic deformation (RPW) process. The XRD, SEM and TEM analysis results indicate that the RPW method can significantly decrease the second phase particle size as well as the matrix crystalline size, and the elastic modulus and yield strength of the composite increase with increasing the volume fraction of Mg2Si whereas the fracture strength and strain decrease. The interface between Mg2Si and matrix is smooth, and no crack initiation source has been found on the interface. The propagation of cracks formed in matrix during fracture can be obstructed by the second phase, and the increase of mechanical properties of the composite is attributed to the dispersed Mg2Si second phase particle and the refined matrix grain size.
Key words: Mg2Si/Mg-2Al-Zn-2Gd composite; fracture behavior; repeated plastic deformation; in-situ synthesis; Mg2Si
镁被誉为“21世纪的绿色工程材料”,加速其开发和应用是实现社会可持续发展的重要课题之一。作为最轻的绿色结构材料,镁合金及其复合材料因具有密度小、比强度和比刚度高、阻尼性和切削加工性好等优点而正得到日益广泛的应用[1-3]。
采用颗粒增强方法制备镁基复合材料是改善镁合金性能的重要手段。有许多增强相都被证明具有良好的强化作用,如硅化物、碳化物、氧化物、硼化物、氮化物、准晶以及碳纤维。其中,Mg2Si等陶瓷颗粒因具有高硬度、高耐磨性及高温抗蠕变性,其增强效果明显[4-6]。
目前,颗粒增强镁基复合材料的重要研究方向是选择合适的制备工艺,以提高增强相与基体的润湿性和弥散分布程度,实现性能的进一步跨越。采用原位反应法获得自生增强相的复合材料与外加颗粒增强相复合材料相比,具有颗粒细小、表面洁净、与基体相容性良好以及界面结合强度高的优点[7-8]。DU等[9]通过在AZ31基体中添加SiO2颗粒,采用多次循环塑性变形/固相反应的方法制备Mg2Si+MgO强化的Mg基复合材料。相比于传统粉末冶金方法,该方法降低了固相反应温度,改善了增强体在基体中分布的均匀性,细化了基体与增强体颗粒的尺寸。
本研究采用多次循环塑性变形加工方法将Mg-2Al-Zn-2Gd稀土镁合金与不同含量的Si粒子混合,再经过固相原位合成,挤压成型制备颗粒增强镁基复合材料,重点分析多次循环塑性变形加工方法对Si颗粒的分散和复合材料显微组织的影响,不同Si含量对原位反应得到的Mg2Si颗粒大小与基体界面的影响以及复合材料的强化机理。
1 实验
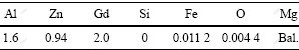
本试验中所用的合金是使用纯镁(99.9%)、纯铝(99.9%)、纯Zn(99.9%)和Mg-Gd中间合金在SG-7.5-12型坩埚电阻炉中熔炼得到的Mg-2Al-Zn-2Gd合金。先将纯Mg和纯Al升温至780 ℃熔化,然后分别加入一定比例的纯Zn和Mg-Gd中间合金,待完全熔化并搅拌均匀后,静置10 min浇铸到低碳钢模具中,为了防止镁合金的氧化和燃烧,整个熔炼过程采用自制覆盖剂保护。用Philips X射线荧光光谱仪对合金成分测定,结果如表1所列。
表1 实验合金化学成份
Table 1 Chemical composition of studied alloy (mass fraction, %)
将铸造得到的合金制备成70~150 μm粉末,再与Si(纯度大于99.99%)混合,放入多次循环塑性变形设备,经过200次循环塑性变形后,得到直径为35 mm的复合胚体。将复合胚体放在红外加热炉中固相反应,在挤压机中挤压,挤压比为25?1,挤压速率为5 mm/s,模具温度为400 ℃,制备得直径为8 mm的复合材料棒材。使用二硫化钼锂基脂与石墨粉的混合物作为挤压过程中的润滑剂。
利用D/MAX-3C型旋转阳极X-射线衍射仪分析相组成和晶粒尺寸,采用Cu靶,扫描速度为2(?)/min。用配备Genesis 7000能谱仪的HITACHI S-450扫描电镜(SEM)进行组织观察和相分析,观察断口形貌。TEM分析在配备OXFORD能谱系统的JEM-2010型透射电镜(TEM)上进行。拉伸试验在MTS810试验机上进行,拉伸速度为1 mm/min。
2 结果
2.1 X-射线衍射分析
基体合金、多次循环塑性变形制备的复合胚体和原位反应并挤压的复合材料型材的XRD谱如图1所示。从图1可以看出,合金铸态的XRD谱由Mg的衍射峰和稀土相的衍射峰组成;添加3%Si(质量分数)的复合胚体的XRD谱中Si单质的衍射峰比铸态的多,但没有Mg2Si的衍射峰,说明在反复塑性加工过程中并未发生原位反应;添加3%Si制备的复合材料的XRD谱有Mg2Si的衍射峰,Si单质的衍射峰在原位反应后消失,说明原位反应可以使其发生Mg+Si→Mg2Si反应[10],生成Mg2Si颗粒;在添加5%Si复合材料的XRD谱中,不但有Mg2Si的衍射峰,而且还有Si单质的衍射峰,说明有部分Si未与Mg反应。
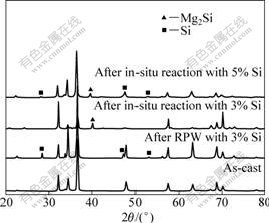
图1 原位合成Mg2Si反应前、后材料的XRD谱
Fig.1 XRD patterns of Mg2Si before and after in-situ synthesis
2.2 扫描电镜的分析结果
实验材料铸态、复合胚体和复合材料型材的显微组织及Mg2Si的EDAX谱如图2所示。由图2可看出,合金中有多边形块状和针形菊花状两种形貌的稀土相,这些稀土相在基体中分布不均匀,有偏聚倾向(见图2(a));合金铸态的针形菊花状稀土相已被完全破碎,成颗粒状,相比铸态均匀分布在基体中,同时还可见组织中有一些空隙,Si粒子的形貌和分布在金相图上并不易看出(见图2(b)),需要再进一步结合能谱分析观察。结合能谱图(见图2(e))分析可确定为Mg2Si相,在背散射电子像中可以看到Mg2Si相与基体颜色不同,色调要略亮于基体,又因Mg2Si要比Mg更耐腐蚀,所以在图2(c)图中Mg2Si如小平台。
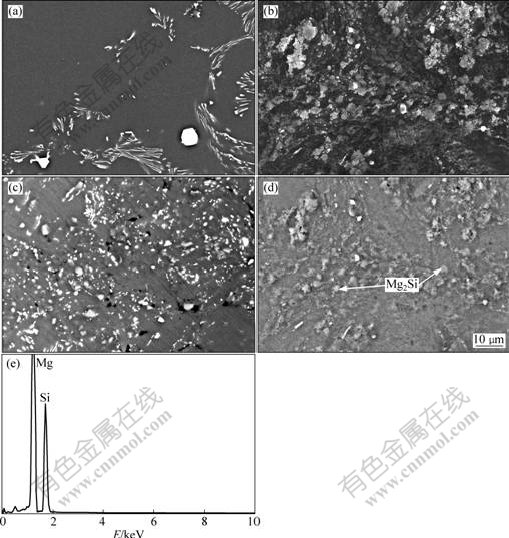
图2 实验材料组织的显微组织和Mg2Si的EDAX谱
Fig.2 Microstructures of studied alloys and EDAX spectrum of Mg2Si phase: (a) SEM image, as-cast; (b) SEM image, after RPW; (c) SEM image, after in-situ reaction; (d) BSE image, at same position as (c); (e) EDAX spectrum of Mg2Si in Fig.(d)
2.3 能谱分析
多次塑性变形制备的复合胚体的SEM像以及同位置Si元素的面扫描如图3所示。由图3(a)和(b)可看出,经多次塑性变形后,Si颗粒尺寸小于10 μm,其中尺寸为1 μm的颗粒占总颗粒数的60%以上,分布较均匀,说明当多次循环变形达到一定的次数后,Si元素可较好地分布于基体之中。由图3(c)和(d)可看出,当Si的含量增加后,出现明显团聚现象。
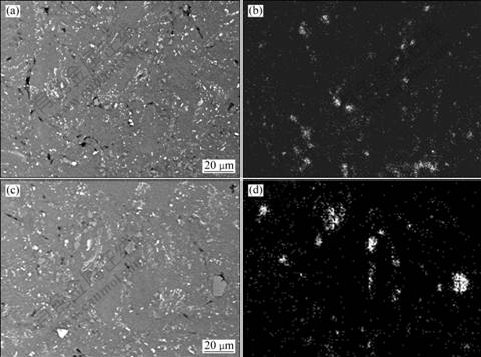
图3 多次塑性变形制备的复合材料胚体的SEM像以及Si元素的面扫描
Fig.3 SEM images ((a), (c)) and mapping analysis of Si element ((b), (d)) in composite fabricated by repeated plastic deformation: (a), (b) 3%Si; (c), (d) 5%Si
2.4 透射电镜的分析结果
复合材料中Mg2Si颗粒与基体析出物的形貌如图4所示。由图4(a)看到,原位反应的Mg2Si颗粒与基体间的界面干净,Mg2Si颗粒大小为50~100 nm,多为球形,也有部分是长条形,间距为100 nm~400 nm。由图4(b)可看到,Mg2Si颗粒尺寸大于500 nm,界面结合干净、良好。
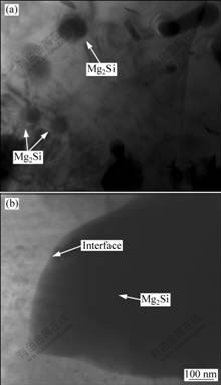
图4 Mg2Si与基体界面析出物的TEM像
Fig.4 TEM images of precipitates along Mg2Si/matrix interface: (a) Mg2Si with grain size less than 100 nm; (b) Mg2Si with grain size more than 500 nm
拉伸变形后复合材料中Mg2Si颗粒周围可见多位错,其TEM像如图5所示。由图5可看到,位错在晶界和缺陷处较多,Mg2Si颗粒附近未见位错的大量塞积。
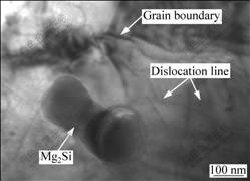
图5 Mg2Si周围的位错
Fig.5 Dislocation around Mg2Si
2.5 断口分析
基体合金、复合胚体和挤压后型材的断口形貌如图6所示。由图6可看出,铸态的断口特征主要是准解理断裂,断口处由解理刻面、撕裂棱和颗粒凸起组成,其中尺寸大于20 μm的解理刻面存在但不多,说明存在少量的穿晶断裂,撕裂棱较多,断裂裂纹起源于晶粒内部的铸造形成的空洞、夹杂物和第二相粒子(见图6(a))。与铸态相比呈现典型的准解理断裂特征,其裂纹由裂纹源向四周不连续传递,解理小平面远小于铸态,且存在深刻的二次裂纹。这主要是因为经过多次循环塑性变形后,破碎的稀土相,影响裂纹的扩展,致使裂纹不断改变方向所致,同时可见基体裂纹数量相比铸态增加(见图6(b))。当Si含量增加后Mg2Si颗粒的尺寸明显增加,这与图3的观察结果一致,裂纹起源主要是基体内部的缺陷、空洞和大尺寸的第二相粒子(见图6(c)和(d));小尺寸Mg2Si颗粒有明显的解理刻面,且刻面都小于2 μm,在Mg2Si颗粒周围由撕裂棱包裹着,内部有明显的二次裂纹,在Mg2Si颗粒与基体间无裂纹存在(见图6(e))。大尺寸Mg2Si颗粒也主要由小解理刻面组成,但是其与基体间有裂纹存在,在Mg2Si颗粒周围没有撕裂棱,内部也有二次裂纹存在(见图6(f))。
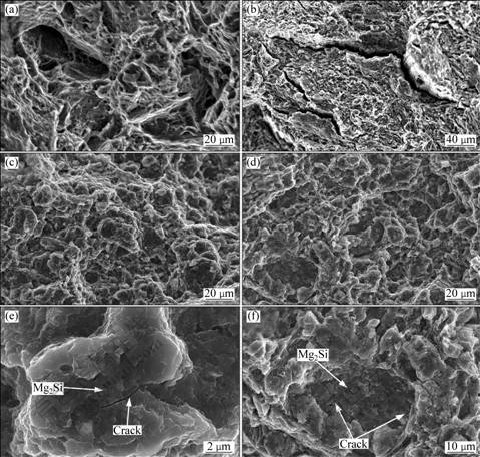
图6 实验材料的室温拉伸断口形貌
Fig.6 Tensile fractographs of studied alloys: (a) As-cast Mg-2Al-Zn-2Gd alloy; (b) After RPW, without Si; (c) After in-situ synthesis, with 3%Si; (d) After in-situ synthesis, with 5%Si; (e) Mg2Si particle fracture, with 3%Si; (f) Mg2Si particle fracture, with 5%Si
3 讨论与分析
3.1 多次循环塑性变形对组织性能的影响
细化晶粒尺寸可以增强材料的强度,其强化效果可以通过Hall-Petch来估算:

式中:σy为屈服强度;σ0为晶格摩擦力;d为晶粒直径;k为常数。在镁合金中k的取值范围多在135~ 270 MPa?μm-1/2,远高于铝合金的,因此细晶强化对于镁合金增强有重要意义[11]。
图7所示为利用XRD谱,根据Hall公式(2)计算[11]得到的铸态、多次循环塑性变形后预制胚体和挤压型材的晶粒尺寸。
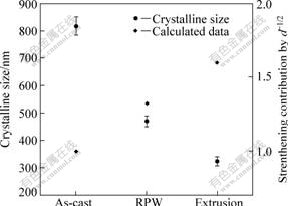
图7 晶粒尺寸
Fig.7 Crystalline sizes

式中:B是衍射峰的半高宽;λ是入射X射线的波长;D是晶粒尺寸;ε是有效应变;θ衍射角。可以看到,多次循环塑性变形方法有效地减小了基体晶粒尺寸,而挤压加工会使晶粒尺寸进一步降低。根据Hall-Petch公式,以铸态合金的晶粒尺寸d-1/2对合金强度的贡献为1,比较多次循环塑性变形和挤压加工方法细化效果对强度的贡献,分别达到了1.32和1.61,说明细化效果比较明显。
将图3(a)所示的Si元素的面扫描图平均分为9格,分别统计其中Si粒子数量,结果如图8所示。由图8可见,Si的分布比较均匀。
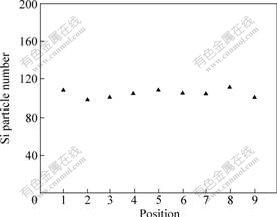
图8 Si颗粒的分布
Fig.8 Distribution of Si particles
对图2(b)分析后发现,多次循环塑性变形加工方法对基体中的第二相有明显的剪切破碎和均匀化的作用。观察图3(a)可以得到相同结论,添加的Si单质在反复变形后,比较均匀、细小的颗粒分布在基体之中。
综上所述,在反复塑性加工过程中,在剪切力的作用下基体合金的晶粒尺寸、Si粒子大小和第二相粒子大小都被降低,所以多次循环塑性加工方法具有细化作用。因为在反复塑性加工过程中,剪切和压实交替进行,因此材料在变形过程有流动性,随加工次数的增加,内部颗粒的分布均匀性增加,所以多次循环塑性变形加工方法也有均匀化分布的作用。
3.2 不同Si含量对组织性能的影响
修正的Eshelby公式[12-13]:

根据式(3),计算不同Mg2Si含量下复合材料的理论弹性模量,如图9所示。由图9可以看到,随着Mg2Si含量的增加,复合材料的弹性模量同时增加,这与实验值比较吻合。
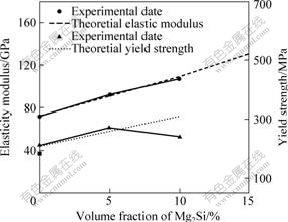
图9 复合材料的弹性模量和屈服强度随Mg2Si体积分数的变化
Fig.9 Changes of elastic modulus and yield strength of composite with volume fraction of Mg2Si
由Shear-Lag模型得到的公式(4)和(5)[14-15]:
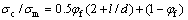 (4)
(4)
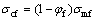 (5)
(5)
式中:σc和σm分别是基体和复合材料的屈服强度;l/d是添加粒子的长径比;σmf是基体的断裂强度;σcf是复合材料的断裂强度。
根据式(4)计算复合材料随Mg2Si含量的增加其屈服强度的变化情况,发现随着Mg2Si含量的增加,复合材料的理论屈服强度增加,这说明理论上弹性模量的增加会影响屈服强度,两者呈正比关系。与实验值比较,发现理论值与实验值在低于5%时(体积分数)吻合较好,但当Mg2Si含量高于5%时差别明显增大,可能因为此处已接近其理论的断裂强度而断裂(见图10),所以没有达到理论的屈服强度。
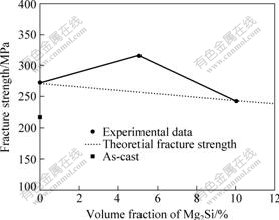
图10 复合材料的断裂强度随Mg2Si体积分数的变化
Fig.10 Change of fracture strength of composite with volume fraction of Mg2Si
根据式(5)计算,随Mg2Si含量的增加复合材料的理论断裂强度变化情况,如图10所示。由图10可以看出,理论上随着Mg2Si含量的增加,复合材料的理论断裂强度减小。在实验值小于5%(体积分数)时,与理论值趋势相反;但当Mg2Si含量高于5%后,与理论趋势相同,说明添加少量Mg2Si对复合材料性能提高具有帮助,但含量过高会导致复合材料性能下降。
3.3 Mg2Si颗粒的强化机制
根据位错理论,位错与第二相粒子的作用可以细分为可切过障碍物和不可切过障碍物,其切过和绕过机制如图11所示[16-17]。本质是当位错在应力作用下,在基体的一个滑移面上运动时,它会遇到第二相粒子,并与之交互作用,这种作用取决于颗粒大小和共格程度。在解理断裂过程中,如果是Orowan机制起作用,变形时位错会在颗粒周围大量塞积,当达到其界面结合强度时会引起颗粒与基体间产生新的界面,引起显微裂纹[18-19]。
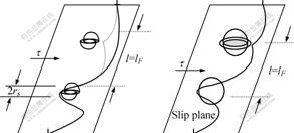
图11 位错切割机制和绕过机制示意图[16-17]
Fig.11 Schematic diagrams of mechanisms of Feriedl cutting and Orowan looping[16-17]
结合TEM像和断口SEM像,添加的Si含量在3%(质量分数)时,原位反应会生成大量尺寸约为100 nm的小尺寸Mg2Si颗粒。从其断口SEM像看,在断后Mg2Si颗粒与基体间没有观察到裂纹存在,说明在小尺寸Mg2Si颗粒的复合材料中,显微裂纹首先在稀土相、晶界和其他缺陷处产生,并聚集形成裂纹源,由此向四周扩散,并因为第二相粒子不断改变方向,形成解理裂纹,Mg2Si颗粒是裂纹扩展最后的汇聚地,在裂纹扩展到Mg2Si颗粒处时,有部分裂纹断在小颗粒内部,Mg2Si颗粒起到阻碍裂纹扩展的作用。添加的Si含量在5%时,因为部分Si团聚,原位反应有大于500 nm的大尺寸Mg2Si颗粒生成。其断口SEM像显示,大尺寸Mg2Si颗粒与基体间会有显微裂纹存在,强化作用降低,但当裂纹扩展到Mg2Si颗粒时,同样会被减弱或改变方向,可以起到阻碍裂纹扩展的作用。
4 结论
1) 随Mg2Si颗粒含量的增加,复合材料的弹性模量随之增加,同时屈服强度也随之增加,断裂强度先升高后下降,伸长率下降。
2) 原位反应的Mg2Si与基体结合良好,小尺寸Mg2Si颗粒的强化效果优于大尺寸Mg2Si颗粒的。Mg2Si颗粒与基体的界面强度高于稀土相与基体界面结合强度,裂纹优先在基体中形成。不同尺寸的Mg2Si颗粒起到阻碍裂纹扩展的作用,是复合材料的主要增强相。
3) 多次循环塑性变形制备的Mg2Si/Mg-2Al- Zn-2Gd复合材料的强化机制主要由于多次循环塑性变形对组织的细化和晶粒尺度的降低以及原位合成的Mg2Si对位错能量的消耗和阻碍和对裂纹扩展的影响。
REFERANCES
[1] 杜文博, 吴玉锋, 左铁镛. 镁合金在交通工具中的应用[J]. 世界有色金属, 2006(2): 19-21.
DU Wen-bo, WU Yu-feng, ZUO Tie-yong. Application condition of magnesium alloy in transportation means[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2006(2): 19-21.
[2] MORDIKE B L, EBERT T. Magnesium properties-applications- potential[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2001, 302: 37-45.
[3] ZENG Rong-chang, ZHANG Jin, HUANG Wei-jiu, DIETZEL W, KAINER K U, BLAWERT C, KE Wei. Review of studies on corrosion of magnesium alloys[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2006, 16(S): s763-s771.
[4] LIAO Heng-cheng, SUN Yu, SUN Guo-xiong. Restraining effect of strontium on the crystallization of Mg2Si phase during solidification in Al-Si-Mg casting alloys and mechanisms[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2003, 358: 164-170.
[5] LU L, THONG K K, GUPTA M. Mg-based composite reinforced by Mg2Si[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2003, 63: 627-632.
[6] WU Yu-feng, DU Wen-bo, ZUO Tie-yong. Synthesis kinetics of Mg2Sn in Mg-Sn powder mixture using non-isothermal differential scanning calorimetry[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2009, 19: 1196-1200.
[7] ZHANG Cong-fa, FAN Tong-xiang, CA Wei, ZHANG Di. (AlN+Mg2Si)/Mg composites in situ synthesis and scale effect of particulate on damping capacity[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2009, 508: 190-194.
[8] WANG Qu-dong, WEI Yin-hong, CHEN Wen-zhou, ZHU Yan-ping, MA Chun-jiang, DING Wen-jiang. In situ surface composites of (Mg2Si+Si)/ZA27 fabricated by centrifugal casting[J]. Materials Letters, 2003, 57: 3851-3858.
[9] DU Wen-bo, KATSUYOSHI K, EIJI Y, TATSUHIKO A. In-situ solid-state synthesis of Mg2Si/MgO/Mg composite[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2003, 419/422: 783-788.
[10] XIONG Wei, QIN Xiao-ying, KONG Ming-guang, CHEN Li. Synthesis and properties of bulk nanocrystalline Mg2Si through ball-milling and reactive hot-pressing[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2006, 16: 987-991.
[11] LU L, LAI M O, HOE M L. Formation of nanocrystalline Mg2Si and Mg2Si dispersion strengthened Mg-Al alloy by mechanical alloying[J]. Nanostructured Materials, 1998, 10(4): 551-563.
[12] MORI T, TANAKA K. Average stress in matrix and average elastic energy of materials misfitting inclusions[J]. Acta Metall, 1973, 21: 571-574.
[13] LAU K C. Characterization and mechanical properties of SiC reinforced aluminum matrix composites[D]. Hongkong: City University of Hongkong, 1996.
[14] TAYA M, ARSENAULT R J. Metal matrix composites[M]. Oxford: Pergamon, 1989: 25-28.
[15] TAYA M, ARSENAULT R J. A comparison between a shear lag type model and an Eshelby type model in predicting the mechanical properties of a short fiber composite[J]. Scripta Metall, 1987, 21: 349-345.
[16] OROWAN E S. On interal stress in metals and alloys, session discussion[M]. London: Institute of Metals, 1948: 451-512.
[17] KOCKS U F. A statistical theory of flow stress and work-hardening[J]. Philosophical Magazine Letters, 1966, 13: 541-566.
[18] ZHANG Z, CHEN D L. Contribution of Orowan strengthening effect in particulate-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 483/484: 148-152.
[19] MOHLES V. Orowan process controlled dislocation glide in materials containing incoherent particles[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2001, 309/310: 265-269.
___________________________________
基金项目:国家重大基础研究发展计划资助项目(2007CB613706);北京市2009创新人才建设计划资助项目(PHR200906101);北京工业大学博士研究生创新计划资助项目(bcx-2009-072)
收稿日期:2009-11-15;修订日期:2010-01-18
通信作者:杜文博,教授,博士;电话/传真:010-67392917;E-mail:duwb@bjut.edu.cn
(编辑 李艳红)