DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.10.053
铅锌尾矿制备水泥熟料及重金属固化特性
何哲祥1, 2,肖祈春1,周喜艳1,李翔1,肖威1
(1. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院环境工程研究所,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 国家重金属污染防治工程技术研究中心,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:以桥口铅锌尾矿为原料制备水泥熟料,主要研究生料的易烧性、熟料的重金属固化、浸出毒性及水泥的强度。利用X线衍射(XRD)和扫描电镜(SEM)分析不同尾矿掺量及煅烧温度下水泥熟料的矿物相和微观结构,用电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法(ICP-AES法)分析熟料中重金属的质量分数。研究结果表明:当煅烧温度超过1 350 ℃且加入铅锌尾矿质量分数为15%~16%时,可生产出符合GB 175—2007标准的硅酸盐水泥,其硅酸三钙(C3S)质量分数最高可达49.2%,28 d抗压强度为53.99 MPa;掺入铅锌尾矿,熟料中游离氧化钙(f-CaO)的质量分数低于0.5%,改善了生料的易烧性;在煅烧过程中,重金属Zn,As,Cd和Pb的平均固化率分别为89.76%,83.62%,73.20%和15.19%;熟料Zn,As,Cd和Pb的浸出毒性远低于危险废物的国家标准。
关键词:铅锌尾矿;水泥熟料;浸出毒性;重金属固化;f-CaO
中图分类号:X753 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2015)10-3961-08
Solidification of heavy metal and production of cement clinker by lead-zinc tailings
HE Zhexiang1, 2, XIAO Qichun1, ZHOU Xiyan1, LI Xiang1, XIAO Wei1
(1. Department of Environment Engineering, School of Metallurgy and Environment,
Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Chinese National Engineering Research Center for Control & Treatment of
Heavy Metal Pollution, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Taking Qiaokou lead-zinc tailings as a kind of main raw materials to produce cement, the burn-ability of raw meal, the heavy metal curing, leaching toxicity and the strength of clinker were studied. The mineral phases and microstructure of cement clinker were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM), respectively, and the mass fractions of heavy metals in clinker were analyzed by the method of ICP-AES. The results show that portland cement which is in accordance with GB 175—2007 can be produced under the calcination temperature over 1 350 ℃ with 15%-16% mass fraction of lead-zinc tailings, the mass fraction of C3S reaches the maximum of 49.2%, and the compressive strength of cement in 28 d is 53.99 MPa. After incorporating the lead-zinc tailings, the mass fraction of f-CaO in clinker is less than 0.5%, and it improves the burn-ability of raw material. The averaged curing degrees of Zn, As, Cd and Pb are 89.76%, 83.62%, 73.20% and 15.19%, respectively. The leaching toxicities of As, Cd, Pb and Zn are far below the national standard of hazardous waste.
Key words: lead-zinc tailings; cement clinker; leaching toxicity; heavy metal solidification; f-CaO
桥口铅锌矿区位于湘江上游郴州东江湖区域,于1957年开始开采,至今已累积尾矿上千万吨。尾矿中的重金属等有害物质渗入地表及地下水,已成为湘江流域水源重大的安全隐患。目前,将铅锌尾矿作矿化剂、铁质原料、黏土质原料等制备水泥熟料已成为处理铅锌尾矿的研究热点[1-8]。王学武等[9]以质量分数为3.5%的铅锌尾矿替代黏土生产高强度水泥熟料,其水泥各龄期强度均得到提高,龄期为28 d时抗压强度可达62 MPa。宣庆庆等[10]以质量分数为9.5%的铅锌尾矿为原料制备硅酸盐水泥熟料,其3 d和28 d抗压强度分别达到35.2 MPa和68.4 MPa,性能比黏土配料的水泥试样的好。铅锌尾矿成分复杂,因地域差异尾矿中有价组分的种类及质量分数差别很大,导致以铅锌尾矿为原料生产水泥熟料的研究结果不同。朱建平等[11]采用质量分数为6.6%的铅锌尾矿在工业回转窑中生产硅酸盐水泥熟料,其硅酸三钙的质量分数高达70.71%。施正伦等[12]研究尾矿作水泥矿化剂和铁质原料,以5%的尾矿为原料生产的硅酸三钙质量分数为56.79%的水泥熟料。以上文献主要研究熟料的煅烧特性及水泥的基本性质,但对水泥中重金属的固化特性报道很少。Lim等[13]研究以水泥固定污泥中的重金属,通过TCLP(浸出毒性浸出方法)对固定效果进行分析,其Pb的固化率可达90%以上,而Zn的固化率则低于40%。本文作者以质量分数为15%以上的铅锌尾矿为原料替代石英采矿废石及有色金属灰渣制备硅酸盐水泥,并研究铅锌尾矿的基本性质、生料易烧性、水泥强度和熟料重金属固化特性等,以解决桥口铅锌矿尾矿重金属污染问题,同时通过尾矿资源化利用为水泥厂提供原料。
1 材料与试验方法
1.1 原材料
湖南金磊南方水泥有限公司目前生产水泥的主要原料是石灰石、有色金属灰渣、石英采矿废石和粉煤灰等。本试验所用原材料除铅锌尾矿采自湖南桥口铅锌尾矿库,其余均由湖南金磊南方水泥有限公司提供。桥口铅锌尾矿为浅灰色砂状,粒度较小,含水量(质量分数)约为10%。原料化学成分见表1。从表1可以看出:该铅锌尾矿中SiO2质量分数较高,与石英采矿废石成分接近,是理想的黏土质替代材料,且增加了原料中CaO,Al2O3和Fe2O3等成分,可部分替代石灰石、有色金属灰渣和粉煤灰。表2所示为原料中主要重金属的质量分数。由表2可知:原料中Pb和Zn的质量分数较高,As和Cd质量分数较低。与石英采矿废石相比,铅锌尾矿中重金属的质量分数明显偏高,其中Pb和As的质量分数分别为前者的4.40倍及41.19倍。用XRD分析原料的物相组成,原料的XRD谱见图1。从图1可以看出:铅锌尾矿的主要物相为石英,峰形明显,成分稳定,与石英采矿废石成分接近,可替代石英采矿废石。
表1 水泥原料的化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Chemical analysis of cement materials %

表2 水泥原料中主要重金属的质量分数
Table 2 Mass fractions of heavy metals in cement materials mg·kg-1
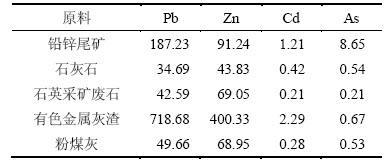

图1 水泥原料的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of cement materials
1.2 方案设计
试验以水泥厂配方S1为对照,通过分析生料易烧性,熟料强度性能、物相组成及重金属固化特性等,研究以铅锌尾矿全部替代石英采矿废石制备硅酸盐水泥的可行性。设计以质量分数为15%~18%的铅锌尾矿全部替代石英采矿废石、部分替代其他原料,其煅烧温度分别为1 350 ℃和1 400 ℃。在水泥生产过程中,常用CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-Fe2O3体系中各氧化物之间的质量比(即饱和石灰比αKH,SiO2质量与Al2O3和Fe2O3质量和之比MS,Al2O3与Fe2O3质量之比MI)来表征生料的化学成分及矿物组成对水泥熟料的性能和煅烧的影响。在生料配料过程中,通过调节原料的配比,使水泥生产3大率控制在:αKH=0.820~0.940,MS=1.70~ 2.70,MI=0.80~1.70。不同配方的生料化学成分质量分数和比值见表3。
表3 水泥生料化学成分(质量分数)和比例
Table 3 Chemical compositions and ratios of cement materials

1.3 试验方法
1.3.1 熟料制备
水泥原料经105 ℃烘干至恒质量,按照表3配制生料,加入质量分数约20%的水搅拌成型,切割成直径为5 cm、厚度为0.5 cm的半圆形切片,在105 ℃下预烘2 h。设置煅烧温度分别为1 350 ℃和1 400 ℃,将生料置于SO-12-16型电阻炉中,温度从室温升至950 ℃,恒温30 min后,再快速升温至煅烧温度恒温20 min,取出样品在空气中迅速冷却。熟料样品于SM-500型试验小磨中粉磨至通过0.074 mm标准筛,用FYS-150C型负压筛分仪测定筛余率,控制筛余率小于10%,制得熟料样品。
1.3.2 水泥试样制备
熟料掺加质量分数为4.5%的二水石膏,制成硅酸盐水泥。按水泥与ISO标准砂质量比为1:3,水灰比为0.5拌制成长×宽×高为40 mm×40 mm×160 mm的试块,试块连模在HBY-40B型水泥(砼)恒温、恒湿标准养护箱中养护,控制恒温为20 ℃,恒湿为95%,24 h后脱模,将试块置于水中恒温20 ℃养护至相应 龄期。
1.3.3 分析方法
1) 生料易烧性:根据JC/T 735—2005“水泥生料易烧性试验方法”分析生料的易烧性[14],采用甘油-酒精法测定熟料中f-CaO质量分数,用该f-CaO质量分数表征生料的煅烧难易程度。
2) 熟料微观特性。用日本理学D/max 2500型X线衍射仪对熟料进行物相成分分析,同时采用XRD-Rietveld全谱拟合法对熟料矿物进行定量分析,用SEM观察熟料的形貌。
3) 重金属固化率。采用硝酸-高氯酸-氢氟酸消解熟料,用ICP-AES法测定重金属质量分数,根据配料计算生料中重金属质量分数,依照生料及熟料中重金属质量分数计算煅烧过程重金属的固化率。固化率 G为
 (1)
(1)
式中:K为重金属元素在熟料中的质量分数,mg/kg;S为参加尾矿后的生料中重金属元素的质量分数,mg/kg;RLoss为生料的烧失率,%。
4) 水泥强度。硅酸盐水泥的强度性能按照GB/T 17671—1999“水泥胶砂强度检验方法(ISO)法”[15]分析,采用DKZ-5000型电动抗折试验机测定试块的抗折强度,采用TYA-100C型电液式抗折抗压试验机测量其抗压强度。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 生料易烧性
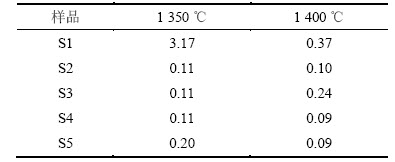
熟料中的f-CaO质量分数偏高会影响水泥的安定性及强度,合理的f-CaO质量分数应控制在1.0%以下[16]。不同温度不同尾矿质量分数下熟料的f-CaO质量分数见表4。从表4可以看出:当温度为1 350 ℃时,样品S1的f-CaO质量分数为3.17%,掺入铅锌尾矿后熟料中的f-CaO质量分数最高仅为样品S1的6.31%;随着铅锌尾矿质量分数的增加,熟料中f-CaO质量分数基本不变,且均不高于0.2%;当温度升至1 400 ℃时,样品S1的f-CaO质量分数降低至0.37%,掺入铅锌尾矿后,熟料中f-CaO质量分数在0.3%以下。掺入铅锌尾矿后,不同温度下煅烧得到的熟料的f-CaO质量分数均减少。试验结果表明:在煅烧温度t为1 350 ℃和1 400 ℃时,掺入铅锌尾矿均可降低熟料中的f-CaO质量分数,从而改善生料的易烧性。
表4 不同温度及不同配方下水泥熟料的f-CaO质量分数
Table 4 f-CaO mass fractions of cement clinker calcined at different temperatures and formulations %
2.2 熟料XRD分析
图2所示为不同配方下熟料的XRD谱。由图2可以看出:熟料的主要矿物组成为硅酸三钙(C3S)、硅酸二钙(C2S)、铝酸三钙(C3A)和铁铝酸四钙(C4AF)等,熟料形成较好;随着尾矿质量分数的增加,矿物组成基本不变,且不同配方的生料在煅烧过程中所呈现的反应特性基本相同;在掺入尾矿之后,熟料中均未见f-CaO的特征峰,表明熟料中f-CaO质量分数较低;熟料中硅酸盐物相的主衍射峰出现在33°附近,掺入铅锌尾矿后,硅酸盐物相的衍射峰位置无明显偏移,且没有新的、较强的衍射峰出现,表明铅锌尾矿不会诱导新的晶型出现。

图2 不同配方下水泥熟料的XRD谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of cement clinker at different formulations
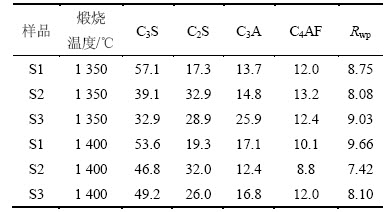
熟料的矿物组成直接影响硅酸盐水泥的质量。通常,熟料中C3S和C2S的质量分数约为75%,C3A和C4AF质量分数约为22%[17]。表5所示为熟料矿物成分的XRD-Rietveld分析结果。加权差方剩余因子(Rwp)表示总体计算图谱与实测图谱之间的吻合程度,若Rwp收敛且小于15%,则表示结果可靠;若Rwp小于10%,则结果更准确[18]。从表5可以看出:样品的Rwp为7.42%~9.66%,均小于10%,表明测试结果可靠。当温度为1 350 ℃时,样品S1中C3S质量分数达57.1%,C2S质量分数为17.3%,熟料中硅酸盐矿物形成良好。在掺入铅锌尾矿后,熟料中C3S质量分数降至40%以下,C2S质量分数则升至28%以上,样品S2和S3的硅酸盐矿物质量分数分别为72.0%和61.8%;当温度升至1 400 ℃时,样品S1中C3S质量分数为53.6%,C2S质量分数为19.3%;在掺入铅锌尾矿后,样品S2和S3中C3S质量分数略有降低,分别为46.8%和49.2%,而C2S质量分数则分别提高到32.0%和26.0%。表明当煅烧温度为1 350 ℃时,掺入铅锌尾矿,影响熟料中C3S的形成,使熟料中产生较多的C2S,导致硅酸盐水泥的早期强度较低;当温度为1 400 ℃时,铅锌尾矿对熟料中C3S的形成影响不大,但能促进C2S的生成。
表5 水泥熟料矿物成分的XRD-Rietveld分析结果
Table 5 XRD-Rietveld analysis of mineral compositions of cement clinker %
2.3 熟料SEM分析
通过SEM分别对样品S1和S3在温度为1 350℃及1 400 ℃下煅烧得到的熟料样品进行形貌分析,试验结果见图3所示。从图3可以看出:熟料中C3S颗粒较大,轮廓清晰,而C2S呈圆状小颗粒,填充在C3S间隙中;当温度为1 350 ℃时,样品S1中C3S颗粒较多,而掺入铅锌尾矿后,样品S3中形成了较多的C2S圆颗粒,分散在C3S周围;当温度为1 400 ℃时,样品S1和S3中C3S颗粒粒径增大,质量分数增大,而C2S质量分数明显减小,且与样品S1相比,样品S3中C2S的质量分数较高,表明掺入铅锌尾矿可增加熟料中C2S的质量分数;但当温度为1 350 ℃时,减少熟料中C3S的质量分数;当温度为1 400 ℃时,C3S的质量分数基本不变。在掺入铅锌尾矿后,升高煅烧温度,熟料中C3S颗粒粒径变大,质量分数增大,有利于C2S转化为C3S。

图3 不同配方下水泥熟料的SEM图
Fig. 3 SEM images of cement clinker at different formulations
2.4 重金属固定分析
在煅烧过程中,原料中含有Pb,Zn,Cd和As等重金属,一部分挥发或随着灰分扩散到空气中,另一部分固溶在熟料中。图4所示为1 350 ℃下熟料的重金属固化率,图5所示为1 400 ℃下熟料的重金属固化率。
从图4可以看出:As,Zn和Cd在熟料中的质量分数普遍比生料的高,表明其能很好地固定在熟料中;Pb在生料中的质量分数明显比熟料中的高,部分Pb由于高温挥发而造成损失;当温度为1 350 ℃时,Zn,As,Cd和Pb的平均固化率分别为93.57%,90.29%,70.21%和19.91%。
由图5可知:当温度升高至1400 ℃时,Zn,As,Cd和Pb的平均固化率分别为85.94%,76.94%,76.19%和10.46%;在高温煅烧过程中,As与CaO化合形成Ca3(AsO4)2,促进As的固化。Zn在中间相中相对集中,且较多分布于硅酸盐矿物中,能够很好地固溶在熟料矿物中。Cd属于半挥发性元素,在煅烧过程中部分挥发,部分转化为其他难溶盐等。Pb的熔点较低,挥发性强,易生成气态产物挥发到烟气中[19-20]。
2.5 水泥强度分析
选取温度分别为1 350 ℃和1 400 ℃时煅烧的熟料样品S1,S2和S3,测定其龄期为3 d和28 d的抗折和抗压强度。不同温度不同龄期下水泥的强度测试结果见表6。从表6可以看出:当煅烧温度为1 350 ℃时,样品S2和S3的各龄期抗折、抗压强度均高于GB 175—2007中规定的42.5硅酸盐水泥标准[21]。与样品S1的性能相比,样品S2和S3的3 d抗折、抗压强度平均降低程度分别达26%和41%,28 d抗压强度降低16%,但28 d抗折强度得到提升,最高提升可达8.01 MPa;当温度升到1 400 ℃时,样品S2的3 d抗折、抗压强度分别为6.51 MPa和27.08 MPa,28 d抗折、抗压强度分别为8.21 MPa和47.90 MPa,超过42.5硅酸盐水泥标准,样品S3达到42.5硅酸盐水泥标准,其28 d抗压强度可达53.99 MPa;当煅烧温度升高至1 400 ℃时,水泥各龄期的抗压、抗折强度比温度为1 350 ℃时水泥的强度高;与样品S1的各龄期强度相比,掺入一定量的铅锌尾矿,3 d抗压强度降低,28 d抗压强度基本不变;抗折强度在温度为1 400 ℃时增大,其中样品S3的3 d和28 d的抗折强度分别为6.82 MPa和9.18 MPa。

图4 当温度为1 350 ℃时水泥熟料中重金属的固化率
Fig. 4 Curing ratios of heavy metals in cement clinker at 1 350 ℃

图5 当温度为1 400 ℃时水泥熟料中重金属的固化率
Fig. 5 Curing ratios of heavy metals in cement clinker at 1 400 ℃
表6 不同温度下水泥熟料的抗折及抗压强度
Table 6 Flexural and compressive strength of cement clinker at different temperatures

3 结论
1) 在煅烧温度为1 350 ℃和1 400 ℃时掺入15%~18%的铅锌尾矿,水泥熟料中的f-CaO质量分数均低于0.3%;未掺尾矿在1 350 ℃煅烧得到的熟料中f-CaO质量分数为3.17%。掺入铅锌尾矿后,可改善生料的易烧性,降低熟料的烧成温度。
2) 重金属Zn,As和Cd能较好地固溶在熟料中,大部分Pb由于高温挥发到烟气中。在煅烧温度为1 350 ℃时,熟料中Zn,As,Cd和Pb的平均固化率分别为93.57%,90.29%,70.21%和19.91%;当煅烧温度升高至1 400 ℃时,Zn,As,Cd和Pb的平均固化率分别为85.94%,76.94%,76.19%和10.46%。
3) 掺入铅锌尾矿后,熟料中的矿物组成不变,没有出现新的晶型。在煅烧温度为1 350 ℃时,铅锌尾矿影响熟料中C3S的生成,形成了较多的C2S圆颗粒分散在C3S周围;当煅烧温度升至1 400 ℃时,C3S颗粒变大,质量分数增大,掺入铅锌尾矿后熟料中C3S的质量分数可达49.2%。
4) 以铅锌尾矿为原料制备水泥熟料,当煅烧温度为1 350 ℃、尾矿掺量为16%时,水泥的3 d抗压、抗折强度分别为17.46 MPa和4.23 MPa,28 d抗压、抗折强度分别为48.46 MPa和7.36 MPa;当煅烧温度为1 400 ℃、尾矿质量分数为16%时,水泥的3 d抗压、抗折强度分别达到18.09 MPa和6.82 MPa,28 d抗压、抗折强度分别达到53.99 MPa和9.18 MPa。
参考文献:
[1] 赵武, 霍成立, 刘明珠, 等. 有色金属尾矿综合利用的研究进展[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2011, 29(3): 24-28.
ZHAO Wu, HUO Chengli, LIU Mingzhu, et al. Research progress on the comprehensive utilization of non-ferrous metal mine tailings[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2011, 29(3): 24-28.
[2] 周文, 孙志强, 刘华伟, 等. 铅锌尾矿综合利用中的合理用能诊断[J]. 金属材料与冶金工程, 2011, 39(2): 25-28.
ZHOU Wen, SUN Zhiqiang, LIU Huawei, et al. Diagnosis of rational energy use in comprehensive utilization of lead-zinc tailings[J]. Metal Materials and Metallurgy Engineering, 2011, 39(2): 25-28.
[3] Stephan D, Mallmann R,  D, et al. High intakes of Cr, Ni, and Zn in clinker: Part II. Influence on the hydration properties[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1999, 29(12): 1959-1967.
D, et al. High intakes of Cr, Ni, and Zn in clinker: Part II. Influence on the hydration properties[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1999, 29(12): 1959-1967.
[4] 董璐, 高谦, 南世卿, 等. 超细全尾砂新型胶结充填料水化机理与性能[J]. 中南大学学报 (自然科学版), 2013, 44(4): 1571-1577.
DONG Lu, GAO Qian, NAN Shiqing, et al. Performance and hydration mechanism of new super fine cemented whole-tailings backfilling materials[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(4): 1571-1577.
[5] 梁亮, 李凝, 韦立宁, 等. 用有色金属尾矿制备水泥的工艺条件[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2013(4): 75-78.
LIANG Liang, LI Ning, WEI Lining, et al. The process conditions of cement preparation by nonferrous tailings[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2013(4): 75-78.
[6] 崔素萍, 兰明章, 张江, 等. 废弃物中重金属元素在水泥熟料形成过程中的作用及其固化机理[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2004, 32(10): 1264-1270.
CUI Suping, LAN Mingzhang, ZHANG Jiang, et al. Effect and incorporation mechanism of heavy metal elements in hazardous industrial wastes during clinker formation[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2004, 32(10): 1264-1270.
[7] 杨雷, 李飞, 管学茂, 等. 原料成分对烧制水泥熟料固化重金属的影响研究[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 29(6): 812-816.
YANG Lei, LI Fei, GUAN Xuemao, et al. Research of the impact of burning cement clinker raw ingredients on heavy metals in solidified[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Science and Technology), 2010, 29(6): 812-816.
[8] 杨雷, 罗树琼, 李飞. Pb对水泥熟料矿物烧成、组分的影响及其固化行为研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2012, 11(6): 4174-4178.
YANG Lei, LUO Shuqiong, LI Fei. Influence of Pb on sintering and components of cement clinker and study on its consolidation behavior[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2012, 11(6): 4174-4178.
[9] 王学武, 赵坚志, 李延林, 等. 利用电石渣和铅锌尾矿配料生产高强度水泥熟料[J]. 水泥, 2012(5): 17-18.
WANG Xuewu, ZHAO Zhijian, LI Yanlin, et al. The production of high strength cement clinker by using carbide slag and lead-zinc tailings[J]. Cement, 2012(5): 17-18.
[10] 宣庆庆, 李东旭, 罗治敏. 铅锌尾矿用于中热水泥的制备[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2009, 27(2): 266-270.
XUAN Qingqing, LI Dongxu, LUO Zhimin. Lead-zinc tailings applied in the production of moderate heat Portland cement[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Engineering, 2009, 27(2): 266-270.
[11] 朱建平, 李东旭, 邢锋. 铅锌尾矿对硅酸盐水泥熟料矿物结构与力学性能的影响[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2008, 36(Suppl 1): 180-184.
ZHU Jianping, LI Dongxu, XING Feng. Influence of Pb/Zn mine tailing on mineral structure and mechanical properties of Portland clinker[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2008, 36(Suppl 1): 180-184.
[12] 施正伦, 骆仲泱, 林细光, 等. 尾矿作水泥矿化剂和铁质原料的试验研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2008, 42(3): 506-510.
SHI Zhenglun, LUO Zhongyang, LIN Xiguang, et al. Experimental study on utilization of metallic tailings as cement mineralizer and iron raw material[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2008, 42(3): 506-510.
[13] Lim T T, Chu J, Goi M H. Effects of cement on redistribution of trace metals and dissolution of organics in sewage sludge and its inorganic waste-amended products[J]. Waste Management, 2006, 26(11): 1294-1304.
[14] JC/T 735—2005, 水泥生料易烧性试验方法[S].
JC/T 735—2005, Test method for burnability of cement raw meal[S].
[15] GB/T 17671—1999, 水泥胶砂强度检验方法(ISO法)[S].
GB/T 17671—1999, Method of testing cements-determination of strength[S].
[16] 王莹莹. 游离氧化钙质量分数对水泥安定性和强度的影响[J]. 福建建材, 2012(10): 11-12.
WANG Yingying. Influence of free CaO on the stability and strength of cement[J]. Fujian Building Materials, 2012(10): 11-12.
[17] 罗云峰, 樊粤明, 卢迪芬, 等. 水泥熟料矿物组成及矿物形态对水泥强度的影响[J]. 水泥, 2008(10): 5-9.
LUO Yunfeng, FAN Yueming, LU Difen, et al. Effect of cement strength on clinker mineral composition and morphology[J]. Cement, 2008(10): 5-9.
[18] 李华, 孙伟, 刘加平. XRD-Rietveld法用于水泥基材料物相的定量分析[J]. 混凝土, 2013(1): 1-5.
LI Hua, SUN Wei, LIU Jiaping. Quantitative analysis of phases for cement-based materials by XRD-Rietveld method[J]. Concrete, 2013(1): 1-5.
[19] Ract P G, Espinosa D C R, Tenório J A S. Determination of Cu and Ni incorporation ratios in Portland cement clinker[J]. Waste Management, 2003, 23(3): 281-285.
[20] Gineys N, Aouad G, Sorrentino F, et al. Effect of the clinker composition on the threshold limits for Cu, Sn or Zn[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2012, 42(8): 1088-1093.
[21] GB 175—2007, 通用硅酸盐水泥[S].
GB 175—2007, Common portland cement[S].
(编辑 刘锦伟)
收稿日期:2014-10-25;修回日期:2014-12-19
基金项目(Foundation item):国家“十二五”科技支撑计划项目(2012BAC09B02)(Project (2012BAC09B02) supported by the National Science and Technology Pillar Program During the 12th “Five-year” Plan)
通信作者:何哲祥,博士,教授,从事尾矿处理与综合利用研究;E-mail:hezx@csu.edu.cn