文章编号:1004-0609(2010)04-0620-08
Sc、Zr和Er微合金化Al-5Mg填充合金的焊接热裂敏感性
杨福宝,刘恩克,徐 骏,张志峰,石力开
(北京有色金属研究总院 国家有色金属复合材料工程技术研究中心,北京 100088)
摘 要:采用鱼骨状试样裂纹试验、SEM和DSC等分析方法研究Sc、Zr和Er的复合添加对新型Al-5.6Mg-1.0Zn-0.6Mn基填充合金焊接热裂敏感性的影响。结果表明:Sc、Zr和Er(含Ti)参与形核核心Al3(Sc,X)的生成,Er(Ti)元素在晶界处形成富Er相,这对试验合金焊道熔池区域的晶粒度和晶间相富集状态影响显著;优化的Sc、Zr和Er成分配比能获得优异的晶粒细化效果,并抑制含Er相对晶界结合的恶化作用,使合金获得较高的焊接热裂抗力;焊接热裂敏感性降低的机理为合金偏析程度的降低、凝固终了温度的相对提高、细小晶粒的转动滑移和细晶晶界应力的分散。
关键词:Al-Mg合金;填充合金;微合金化;熔焊;热裂敏感性
中图法分类号:TG422.3 文献标志码:A
Hot-cracking susceptibility of (Sc, Zr, Er)-microalloyed Al-5Mg filler metals
YANG Fu-bao, LIU En-ke, XU Jun, ZHANG Zhi-feng, SHI Li-kai
(National Engineering and Technology Research Center for Non-ferrous Metal Matrix Composites,
General Research Institute for Non-ferrous Metals, Beijing 100088, China)
Abstract: The influence of Sc, Zr and Er additions on the welding hot-cracking susceptibility of Al-5.6Mg-1.0Zn-0.6Mn alloys was investigated by fishbone specimen hot-cracking test, SEM and DSC. The results show that Sc, Zr and Er including Ti participate from the melts in the Al3(Sc, X) nucleus, and Er (Ti) subsequently generates Er-riched phases at the grain boundaries. This significantly affects the grain size and phase enrichment state at the grain boundaries of the specimen molten pools. Optimized composition match of Sc, Zr and Er gives excellent grain-refining effect and suppresses the worsening effects of Er-bearing phases on the grain boundary binding, which endues the alloy with high hot-cracking resistance. The mechanism of lowering hot-cracking susceptibility is reduction of solute segregation, rise of finishing temperature, rotation and intergranular movement of refined grains and stress dispersion effect of large amounts of grains.
Key words: Al-Mg alloy; filler metal; microalloying; fusion welding; hot-cracking susceptibility
ER5356及5A56 Al-Mg系填充合金(焊丝)是目前常用的铝合金熔焊填充材料[1]。由于合金中含有Ti和Zr等常规细化剂,因而可以使焊件获得较高的接头强度和较好的抗热裂能力。但在高强铝合金厚板结构件的焊接中,尤其是焊后不可热处理的焊接中,它们已不能同时满足接头强度和抗热裂能力的要求,开发高强低热裂细晶铝合金填充合金成为必要。目前,国内外相继对含Sc新型铝填充合金开展相关研究,并取得一定的成果[2-4]。
晶粒细化作为一种组织控制方法,能同时提
料的力学性能并降低其凝固热裂敏感性[5-7]。因此,在熔焊过程中,对熔池组织进行晶粒细化能有效改善焊接接头的综合性能。由于焊件接头的组织受填充合金的直接影响,因而填充合金的抗焊接热裂能力则首要地取决于填充合金的热裂敏感性。对于填充合金,焊接热裂敏感性是其十分重要的性能指标[1, 8]。从材料本身来看,材料焊接热裂敏感性主要受合金晶界状态的影响,包括晶界面积的大小和晶间富集物的组成及存在形式。晶界面积的大小对应于晶粒细化的程度,而晶间富集物主要受凝固偏析程度及微合金化元素存在形式等因素影响。研究表明,细化晶粒能提高合金的抗热裂能力,对于铝合金尤其如此[9-12]。溶质或杂质元素在晶界的偏析,亦即低熔点相的存在,将使晶界的凝固明显落后于晶粒,脆性温度区间增大,热裂敏感性增强[13-15]。在新型填充合金开发中,Sc、Zr及Er细化剂对填充合金组织改善的研究尚未深入,需要对这些方面进行必要探索。
本文作者在ER5356填充合金的基础上,引入微量Sc、Zr及新型Er细化剂元素,重点研究3种元素对合金微观组织和热裂性能的影响,为低热裂细晶铝合金填充合金的开发提供理论分析和实验依据。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料
在本实验中将高纯Al (99.99%)、高纯Mg (99.99%)、高纯Zn (99.9%)和Al-10%Mn、Al-4.77%Zr、Al-5.5%Ti、Al-2.12%Sc及Al-10%Er中间合金配制试验合金。合金熔炼在中频真空感应炉中进行,采用氩气保护。为充分溶解中间合金中的粗大金属间化合物粒子,采用780~800 ℃保温熔炼20 min,于730 ℃浇铸,采用铜模浇铸成板状铸锭。
1.2 实验方法
采用鱼骨状试样裂纹试验来评价Al-5Mg试验合金的热裂敏感性。在试验中,合金中Mg、Mn和Zn基体元素的具体含量相对于ER5356填充合金做了适当调整,4种合金的名义成分如表1所列。
将试验合金铸锭切割成厚度为矩形薄板(3 mm×90 mm×50 mm),其示意图如图1所示。每种合金加工出同样规格的薄板6块。按图示尺寸在薄板上加工出深度逐渐增加的槽,以造成沿试板长度方向的不同拘束度。采用不添丝自动TIG焊接方法,在试板中心线熔融出一条焊缝。通过测量和统计焊缝裂纹长度来评价合金的焊接热裂敏感性。
表1 鱼骨试样热裂试验合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of experimental alloys (mass fraction, %)
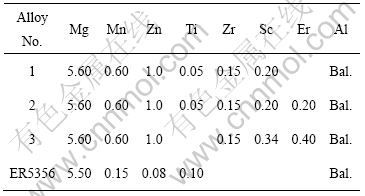

图1 鱼骨状试样及其尺寸示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of fishbone specimen (mm)
在该评价方法中,试验合金的热裂纹敏感性系数K1和近缝区液化裂纹敏感性系数K2可计算为

作为铝合金热裂敏感性控制指标,K1≤10%,K2=0即可认为材料的热裂敏感性较小,焊接性良好[1]。
试验采用自动TIG焊(交流脉冲钨极氩弧自动焊)。试验时,在试件下方垫上铜板,焊接方向从高拘束端(左端)向低拘束端,焊道宽度为8~10 mm。为防止试验合金不产生裂纹,首先选定组织最细小的试样(抗热裂性能可能最好)在一定的焊接参数下施焊,使其产生微小裂纹,确定该工艺参数如表2所列。其他试样按此工艺参数施焊。
焊道断面组织观察及微区成分分析采用扫描电镜(SEM,Hitachi-S4800)及其附带的X射线能谱仪(EDS)进行,加速电压20 kV。采用示差扫描量热分析仪(DSC,NETZSCH-STA 409PC)测定不同试样焊道中心相同部位的凝固温度,氩气流保护,升温速率为 10 K/min。
表2 鱼骨试样热裂试验工艺参数
Table 2 Welding parameters of hot-cracking test for fishbone specimen
2 实验结果
2.1 合金铸锭的宏观组织
图2所示为ER5356和3#合金板状铸锭横断面的宏观组织。由图2可以看出,ER5356合金呈现出粗大非均匀的组织形态,且存在一个垂直于铸锭侧面的发达柱状晶区。由于Sc和Zr的联合添加,并在Er元素的进一步促进下,3#合金整个铸锭内部组织形态由非常细小均匀的球晶组成,无柱状晶区存在。这些结果与本文作者的前期工作一致[16-17]。在此基础上,铸锭凝固收缩区表现出迥异的凝固热裂敏感性。在本实验熔炼和浇铸条件下,ER5356合金产生明显的凝固热裂纹,裂纹扩展方向沿柱状晶发展方向,而3#合金则形成连续平滑的凝固终了区域,无凝固裂纹产生,表现出良好的抗热裂能力。由此可以认为,在凝固收缩过

图2 ER5356合金和3#合金铸锭的宏观组织
Fig.2 Macrostructures of ingots: (a) ER5356; (b) Alloy 3
程中,铝合金粗大组织具有明显的热裂敏感性,而微合金化产生的细晶组织对合金凝固热裂有显著的改善作用。
2.2 鱼骨状试样焊道形貌及合金热裂敏感性
图3所示为ER5356合金和3#合金鱼骨试样经电弧扫描后的实物照片,沿试板中心线处为焊道凝固后的形貌。在电弧扫描过程中,虽然在试板的另一侧也观察到电弧的热影响形态,但焊道下方试板内的合金熔化并未穿透整个试板。由图3可看到,ER5356合金试样的焊道产生约30 mm长的裂纹(见图3(a)中箭头所指),而3#合金试样未发现裂纹产生。由于各个试样线切割切取铸锭的不同部位也会带来一定的成分和性能差异,试验中每种合金的6个试样产生的裂纹也不尽相同。合金的不同鱼骨试样裂纹长度及平均裂纹长度如表3所列。精细打磨焊道近缝区后观察确认,合金均未出现液化裂纹。由式(1)计算出的热裂敏感性系数K1及其变化趋势如图4所示。在本试验施焊工艺过程中,ER5356合金的热裂敏感性系数为23.1%,大于10%,而1#和3#合金的热裂敏感性系数分别降至18.0%和5.0%,但2#合金的热裂敏感性系数增大至27.0%。
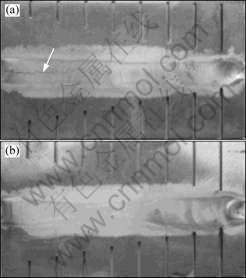
图3 鱼骨试样热裂试验样品形貌
Fig.3 Optical morphologies of fishbone specimens:(a) ER5356; (b) Alloy 3
表3 不同的鱼骨试样裂纹长度
Table 3 Hot-cracking length of fishbone specimens

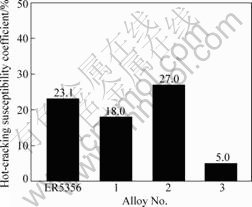
图4 合金鱼骨试样的热裂敏感性系数
Fig.4 Hot-cracking susceptibility coefficient K1 for fishbone specimens of ER5356, alloy 1, alloy 2 and alloy 3 (K1 of alloy 2 exhibits abnormal value)
3 分析与讨论
3.1 晶粒细化对合金热裂敏感性的影响
图5所示为鱼骨试样焊接起始端热裂断面低倍
SEM像。从图5可看出,发生严重热裂纹的ER5356、1#和2#合金在靠近焊弧的上侧倾向于焊弧移动的方向均产生大量取向结晶组织。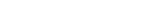
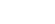 明显不同的是,3#合金试板的短小热裂纹的断面则显示出均匀的组织,无取向组织存在。这说明在同样的施焊条件下,在前3种合金中没有形成高密度等轴细小晶粒,而3#合金仍然形成均匀细化的晶粒组织。同时,前3种合金焊道的取向组织均起源于试板中心厚度处,这与焊道下方未熔化基体的均匀组织形貌形成鲜明的对比。相比而言,3#合金试板的断面形貌中则无明显不均匀性,这说明3#合金在鱼骨焊接条件下仍然保持与其普通浇铸铸锭接近的性质。图6所示为4种合金的SEM像。由图6可看出,前3种合金中的取向组织均为典型的胞状枝晶组织。由于焊接热流较大,枝晶生长速度很快,枝晶主干间距较小,形成的二次枝晶臂不能自由发展而受到抑制,枝干上生长出规则排列的短小二次枝突[1]。3#合金呈细小的粒状等轴晶。由于热裂断面为凝固后期区域,相对于基体内部溶质富集严重,剩余液相的热力学条件改变较大,相对于其铸锭时的晶粒组织,晶粒形态发生异常,等轴晶表现出界面失稳和晶粒粘连的迹象。
明显不同的是,3#合金试板的短小热裂纹的断面则显示出均匀的组织,无取向组织存在。这说明在同样的施焊条件下,在前3种合金中没有形成高密度等轴细小晶粒,而3#合金仍然形成均匀细化的晶粒组织。同时,前3种合金焊道的取向组织均起源于试板中心厚度处,这与焊道下方未熔化基体的均匀组织形貌形成鲜明的对比。相比而言,3#合金试板的断面形貌中则无明显不均匀性,这说明3#合金在鱼骨焊接条件下仍然保持与其普通浇铸铸锭接近的性质。图6所示为4种合金的SEM像。由图6可看出,前3种合金中的取向组织均为典型的胞状枝晶组织。由于焊接热流较大,枝晶生长速度很快,枝晶主干间距较小,形成的二次枝晶臂不能自由发展而受到抑制,枝干上生长出规则排列的短小二次枝突[1]。3#合金呈细小的粒状等轴晶。由于热裂断面为凝固后期区域,相对于基体内部溶质富集严重,剩余液相的热力学条件改变较大,相对于其铸锭时的晶粒组织,晶粒形态发生异常,等轴晶表现出界面失稳和晶粒粘连的迹象。
由前期工作可知[17],3#合金的铸锭由直径约为20 μm的球状等轴晶组成。在凝固过程中,熔体中高密度的高温质点Al3(Sc,X)(X=Zr,Er)快速析出,弥散分布在熔体中。Al3(Sc,X)质点为L12型晶格结构,
图5 鱼骨状试样裂纹断面SEM像
Fig.5 SEM images of hot-cracking surface for fishbone specimens: (a) ER5356; (b) Alloy 1; (c) Alloy 2; (d) Alloy 3 (Locating positions of arrows indicate upper side of welded-bead and their directions display moving directions of welding arc during hot-cracking test)
图6 鱼骨状试样裂纹断面的SEM像
Fig.6 SEM images of hot-cracking surfaces of fishbone specimens: (a) ER5356; (b) Alloy 1; (c) Alloy 2; (d) Alloy 3
与α(Al)仅存在约1.04%的错配度[18],成为α(Al)的有效形核核心。大量初始α(Al)晶粒在Al3(Sc,X)粒子基底上外延生长,晶粒在其尺寸较小时即迅速相遇,形成细小的等轴晶粒。同时,稀土Er所带来的成分过冷也进一步促进晶粒的细化。在鱼骨试验凝固过程中,足量的有效Al3(Sc,X)形核核心使3#合金获得细小均匀的等轴晶组织。由前期工作[16]也知,虽然1#和2#试验合金铸锭的微合金化成分使合金获得粒径约52 μm 和43 μm的晶粒组织,但鱼骨试验焊道中胞状枝晶的产生则说明在该施焊条件下,其Al3(Sc,X) (X=Zr,Ti,Er)粒子的有限生成不能使熔体中产生大量的细小晶粒,因而不能抑制胞状枝晶的发展。5356合金中的Al3Ti为DO22晶格结构,且其与α(Al)基体的错配度为4.3%,一般仅使合金获得100 μm量级的细化程度,远不及Al3(Sc,X)粒子对铝合金的细化能力。
根据METZ等[19-20]的研究结果,在外力作用下,合金在固液两相区内的变形方式主要有两种:一是晶粒的调整滑移,其变形抗力较小;二是晶粒的变形及弯曲,其变形抗力较大。对于3#合金,高密度Al3(Sc,X)质点使熔体在极短的时间内形成大量的细小球晶,细小的等轴晶容易实现晶粒的旋转和晶间滑动,具有良好的流动性和补缩能力, 降低热应力及拘束应力的存储,不易发生晶间分离。同时,细晶组织的形成使合金具有大规模的晶界,对于已形成的裂纹,裂纹尖端在扩展过程中会被高密度的晶界所分散,单位面积晶界的应变量降低,避免局部应力集中的发生。因而,3#合金具有优异的焊接热裂抗力。在前3种合金中,发达的取向胞状枝晶组织的调整难以进行,合金的变形只能通过枝晶主干的弯曲来实现,其变形抗力较大,易产生晶间分离而启裂,裂纹沿胞状枝晶间隙沿晶发展。这使得前3种合金均表现出较高的焊接热裂敏感性。
3.2 晶间状态对合金热裂敏感性的影响
为探明合金化元素在合金凝固后期的分布情况,对4种合金热裂断面进行选区EDS分析,结果如图7所示。图7(b)所示的半定量成分分析表明,与合金添加量相比,凝固终了热裂断面上富集高浓度的Mg、Zn、Mn和Er元素,在断面上未检测出Ti、Sc和Zr微合金化元素。4种合金中的Mg含量均为5.9%,而在热裂断面上,Mg的富集高达12%以上。根据固溶体的生长规律,凝固过程中发生溶质再分配,溶质元素的局部富集将使焊道中心的合金固相线温度降低。在凝固后期,这将导致低熔点液膜存在于胞状枝晶间隙。4种合金的Mg、Zn和Mn元素在热裂断面上的偏析程度依次减弱,对应图4中合金的热裂敏感系数变化趋势。同时,注意到2#和3#合金中的Er在热裂断面上约3%和2%的富集,其中,3#合金的偏析程度最低。至此也可以看出,影响合金组织的微合金化元素Ti、Sc、Zr和Er一方面参与Al3(Sc,X)质点在高温熔体中的形成;另一方面其中的大原子稀土元素Er还会偏聚于晶界,将以低温离异共晶Al3Er及低熔点Al(Er)固溶体的形式存在。因此,影响合金晶间状态的因素有溶质元素和低熔点Al3Er相在晶界的富集。
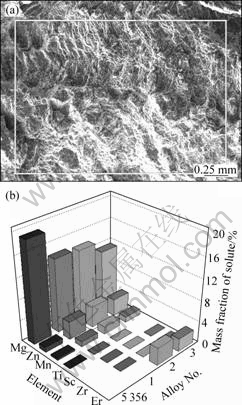
图7 试样热裂断面的SEM像及选区EDS谱
Fig.7 SEM image (a) and EDS pattern (b) of hot-cracking surfaces for alloys
图8所示为4种合金的DSC热分析结果。从图8可以看出,1#合金具有最窄的凝固温区,这主要是由于该合金中含0.15Zr+0.2Sc的细化元素,合金中胞状枝晶数量有限,同时在晶界处无稀土Er的偏聚。
相比而言,ER5356在591 ℃附近存在一个吸热峰,其原因是合金中的Ti细化能力最弱,合金晶粒组织粗大,晶粒长大过程中产生的严重偏析使胞状枝晶晶界处存在溶质富集,既形成低熔点的Al(Mg)液膜,又生成(Al,Zn)49Mg32 低熔点相。这使得该合金具有更低的凝固终了温度,因此也具有更大的热裂敏感系数。在1#合金的基础上,在2#合金中添加0.2%Er,其
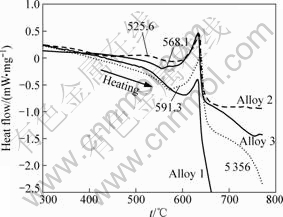
图8 不同合金鱼骨试样焊道部位的样品DSC热分析结果
Fig.8 DSC analysis of samples taken from welding centre-line of ER5356, alloy 1, alloy 2 and alloy 3 (Melting temperatures of different matrix materials are all near 635 ℃)
热裂断面上富集了约3%Er,这使合金的凝固终了温度降至525 ℃以下。3#合金中含0.4%Er,但其凝固终了温度在568 ℃附近,热裂断面富集仅为2%Er。从热裂断面SEM像(见图9)可以进一步看出,在合金2和3中的枝晶突起及等轴晶间隙的液窝中,离散分布着尺寸约5 μm的颗粒,EDS分析这些颗粒为富Er相。结合前期工作可知:对于2#合金,该颗粒为(Al,Mg)20Ti2Er相及Al3Er离异共晶相;对于3#合金,由于合金中无Ti元素,颗粒仅为Al3Er离异共晶相。这说明2#合金中晶界处较多的(Al,Mg)20Ti2Er和Al3Er颗粒相及低熔点固溶体相,给合金带来严重的凝固拖尾现象,增大拘束应力的作用时间,也降低晶界结合强度,使得该合金产生高达27.0%的热裂敏感系数。这一现象同已有的铝、镁合金的研究结果一致。邱武等[21]对ZL201合金的热裂现象进行研究,发现合金中Si元素含量过高,沿晶界存在大量的脆性Al2Cu和AlSiCu低熔点共晶相,导致合金凝固热裂敏感性增大。WANG等[22]研究Zn对Mg-9Al合金凝固行为的影响,同样发现凝固过程中Zn 和Al 元素在晶界的富集,增加晶界低熔点相的量,降低晶界处低熔点相的凝固温度,延长凝固后期晶界液相膜存在的时间,造成Mg-9Al-xZn合金具有较大热裂倾向性。3#合金中含有0.4%Er,但仍呈现出较强的热裂抗力,这是由于3#合金中的高效Al3(Sc,X) (X=Zr,Er) 异质形核核心强烈地细化了合金组织,这不仅使合金获得均匀的组织,降低合金的热裂敏感性,同时在晶粒长大过程中也具有较短的溶质偏析距离,缩小了合金凝固温度区间,进一步提高了合金的抗热裂能力。均匀细小的合

图9 2#和3#合金热裂断面的SEM像及3#合金晶间颗粒相的EDS谱
Fig.9 SEM images of hot-cracking surfaces of alloy 2 (a) and alloy 3 (b) and EDS pattern (c) of alloy 3 with Er-riched intergranular particles
金组织使合金具有较低的热裂敏感性的结果也已被诸多研究证实[23-24]。在该合金中,细小晶粒又进一步地离散了Al3Er离异共晶颗粒和Al(Er)稀固溶体,使得3#合金的Er偏析比2#合金还弱,而它们不会像连续液膜一样对晶间结合力构成显著威胁。尽管如此,在填充合金成分设计中,在考虑适量含量的Er细化晶粒的前提下,应控制Ti和Er元素的含量,减少 (Al,Mg)20Ti2Er及Al3Er晶间相的偏聚,以避免其对合金晶界状态的严重恶化。
4 结论
1) Sc、Zr和Er(Ti)元素的加入显著影响Al-5.6Mg-1.0Zn-0.6Mn基合金的组织细化和晶间相形态。Sc、Zr和Er(含Ti)参与高温质点相Al3(Sc,X)的生成,对α(Al)晶粒的细化起到了关键作用,稀土Er所带来的成分过冷进一步促进α(Al)晶粒的细化;部分Er元素在晶界处富集形成低熔点Al(Er)稀固溶体、离异共晶Al3Er颗粒相及(Al,Mg)20Ti2Er颗粒相(含Ti合金中),这些相影响着合金的实际凝固终了温度,对合金凝固热裂有负作用。
2) 3#合金通过0.15%Zr+0.34%Sc+0.40%Er的复合添加,使焊道中发达的胞状枝晶转变为细小均一的等轴晶,降低合金凝固偏析的程度,提高凝固终了温度,并抑制含Er相对晶界结合的恶化作用。细小的晶粒所具有的良好流动性和补缩能力在焊道凝固后期能使晶粒发生及时的转动和滑移,高密度晶界的存在降低单位面积晶界的应变量,使拘束应力分散化,提高合金抗热裂的能力。
REFERENCES
[1] 中国机械工程学会焊接学会. 焊接手册(第2卷)[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2001.
Chinese Welding Society. Welding Handbook (Vol.2)[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2001.
[2] NORMAN A F, BIRLEY S S, PRANGNELL P B. Development of new high strength Al-Sc filler wires for fusion welding 7000 series aluminium aerospace alloys[J]. Sci Technol Weld Join, 2003, 8 (4): 235-245.
[3] 陈苏里, 姜 锋, 尹志民, 雷学锋, 聂 波. 含钪与不含钪铝镁钪合金焊接接头的组织与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16 (5): 835-840.
CHEN Su-li, JIANG Feng, YIN Zhi-min, LEI Xue-feng, NIE Bo. Microstructure and properties of Al-Mg-Sc alloy weld joints filled with Al-Mg-Zr and Al-Mg-Zr-Sc weld wires[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(5): 835-840.
[4] KOTESWARA RAO S R, KAMSALA DEVI B, SREENIVASA RAO K, PRASAD RAO K. Thermo-mechanical treatments of Sc- and Mg-modified Al-Cu alloy welds[J]. Int J Adv Manuf Technol, 2009, 45: 16-24
[5] MURTY B S, KORI S A, CHAKRABORTY M. Grain refinement of aluminium and its alloys by heterogeneous nucleation and alloying[J]. Int Mater Rev, 2002, 47(1): 3-29.
[6] NORMAN A F, HYDE K, COSTELLO F, THOMPSON S, BIRLEY S, PRANGNELL P B. Examination of the effect of Sc on 2000 and 7000 series aluminium alloy castings: for improvements in fusion welding[J]. Mat Sci Eng A, 2003, 354(1/2): 188-198.
[7] ESKIN D G, SUYITNO, KATGERMAN L. Mechanical properties in the semi-solid state and hot tearing of aluminium alloys[J]. Prog Mater Sci, 2004, 49: 629-711.
[8] 王业双, 王渠东, 丁文江, 卢 晨. 合金的热裂机理及其研究进展[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2000(2): 48-50.
WANG Ye-shuang, WANG Qu-dong, DING Wen-jiang, LU Chen. Research development of hot tear mechanism for cast alloys[J]. Special Casting and Nonferrous Alloy, 2000(2): 48-50.
[9] KIM H T, NAM S W, HANG S H. Study on the solidification cracking behaviour of high strength aluminum alloy welds: Effects of alloying elements and solidification behaviours[J]. J Mater Sci, 1996, 31(11): 2859-2864.
[10] JANAKI R G D, MITRA T K, SHANKAR V, SUNDARESAN S. Microstructural refinement through inoculation of type 7020 Al-Zn-Mg alloy welds and its effect on hot cracking and tensile properties[J]. J Mater Process Technol, 2003, 142(1): 174-181.
[11] 董晟全, 周敬恩, 严 文, 梁艳峰, 杨 通. Al-4.5Cu合金热裂倾向的研究[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2003, 26(1): 44-47.
DONG Cheng-quan, ZHOU Jing-en, YAN Wen, LIANG Yan-feng, YANG Tong. Research of hot tearing tendency of Al-4.5Cu alloy[J]. Ordnance Mater Sci Eng, 2003, 26(1): 44-47.
[12] ESKIN D G, KATGERMAN L. Effect of structure on hot tearing properties of aluminum alloys[C]. Mater Sci Forum, 2007, 561/65(2): 995-998.
[13] DEV S, MURTY B S, RAO K P. Effects of base and filler chemistry and weld techniques on equiaxed zone formation in Al-Zn-Mg alloy welds[J]. Sci Technol Weld Join, 2008, 13(7): 598-606.
[14] DING H, FU H Z. Effect of grain boundary's state on the hot cracking tendency of directionally solidified Al-Cu and Rene 125 alloys[J]. Rare Metal Mat Eng, 2000, 29(4): 228-230.
[15] MOUSAVI M G, CROSS C E, GRONG O. The effect of high-temperature eutectic-forming impurities on aluminum 7108 weldability[J]. Welding Journal, 2009, 88(S5): 104-110.
[16] LIU E K, YANG F B, XU J, SHI L K. Effects of microalloying on grain refinement behaviors and hardness properties of wedge-shaped Al-Mg-Mn castings[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2007, 17(S1): 308-313.
[17] 杨福宝, 刘恩克, 徐 骏, 石力开. Er对Al-Mg-Mn-Zn- Sc-Zr-(Ti)填充合金凝固组织与力学性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2008, 44: 911-916.
YANG Fu-bao, LIU En-ke, XU Jun, SHI Li-kai. Effects of Er on the microstructures and mechanical properties of as-cast Al-Mg-Mn-Zn-Sc-Zr-(Ti) filler metals[J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2008, 44: 911-916.
[18] HARADA Y, DUNAND D C. Microstructure of Al3Sc with ternary transition-metal additions[J]. Mat Sci Eng A, 2002, 329: 686-695.
[19] METZ S A, FLEMINGS M C. Hot tearing in cast metals[J]. AFS Trans, 1969, 77: 329-334.
[20] METZ S A, FLEMINGS M C. A fundamental study of hot tearing[J]. AFS Trans, 1970, 78: 453-460.
[21] 邱 武, 罗吉荣, 李东南. ZL201合金铸件裂纹产生的原因分析[J]. 中国铸造装备与技术, 2005(1): 27-29.
QIU Wu, LUO Ji-rong, LI Dong-nan. Analysis on crack causes of ZL201 Al alloy castings[J]. China Foundry Machinery & Technology, 2005(1): 27-29.
[22] WANG Y S, WANG Q D, WU G H, ZHU Y P, DING W J. Hot-tearing susceptibility of Mg-9Al-xZn alloy[J]. Mater Lett, 2002, 57(4): 929-934.
[23] DVORNAK M J, FROST R H, OLSON D L. The weldability and grain-refinement of Al-2.2Li-2.7Cu[J]. Weld J, 1989, 68(s8): 327-335.
[24] LIN S, ALIRAVCI C, PEKGULERYUZ N I O. Hot-tear susceptibility of aluminum wrought alloys and the effect of grain refining[J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2007, 38(5): 1056-1068.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2006CB605203);国家高技术研究发展计划资助项目(2006AA03Z115)
收稿日期:2009-05-19;修订日期:2009-12-18
通信作者:杨福宝,高级工程师,博士;电话:010-82241229;E-mail:yfubao@mail.grinm.com.cn