海洋环境下混凝土相对湿度响应
金祖权,赵铁军,王本臻,常洪雷
(青岛理工大学 土木学院,山东 青岛,266033)
摘要:混凝土放置于青岛室内大气环境、海洋大气区、浪溅区环境以及模拟干燥的恒温恒湿、45°C烘干环境,模拟湿润的毛细吸水环境,测试混凝土深度为10~40 mm的相对湿度演变。研究结果表明:饱和混凝土相对湿度受环境湿度影响先稳定、再快速下降然后缓慢下降,包括水气饱和期和相对湿度减小期。混凝土内部相对湿度对环境湿度响应时间上存在滞后性,离表层越近响应速度越快,环境湿度越小,影响深度越大。室内大气环境、海洋大气区、海洋浪溅区、恒温恒湿及烘干环境下养护42 d,混凝土10~20 mm深度的相对湿度分别为90%~92%,85%~90%,90%~95%,89%~92%和57%~58%。干燥过程中混凝土相对湿度与时间变化关系受水分向外扩散过程控制;混凝土表观湿度扩散系数随深度增加而线性增加,表面层平均相对湿度与深度的关系符合对数函数关系。在湿润过程中,表面层相对湿度演变可用毛细传输系数公式进行分析,内部相对湿度演变是传输与扩散共同作用所致。
关键词:混凝土;相对湿度;海洋环境;演变机制
中图分类号:TU528.01 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2014)10-3608-06
Relative humidity response of concrete under marine environment
JIN Zuquan, ZHAO Tiejun, WANG Benzheng, CHANG Honglei
(School of Civil Engineering, Qingdao Technological University, Qingdao 266033, China)
Abstract: Concretes were placed in marine environment including indoor atmospheric zone, marine atmospheric zone, splash zone, and placed in simulated marine tidal zone including drying environment and wetting environment. Then the inner relative humidity (RH) evolution of concrete under above-mentioned environments was systematically investigated. The results show that the inner RH evolution of concrete includes vapor phase saturation stage and relative humidity decrease stage. The RH of concrete keeps steady firstly, and then rapidly decreases with time, lastly slowly declines. The inner RH response of concrete lags behind the environment humidity and the RH response speed of surface zone are faster than those of interior zone. The smaller the environmental humidity, the bigger the influence depth. The RH of concrete in 10-20 mm depth, which occurred in indoor atmospheric zone, marine atmospheric zone, marine splash zone, constant temperature and humidity environment and in drying environment for 42 d, is 90%-92%, 85%-90%, 90%-95%, 89%-92% and 57%-58%, respectively. The inner RH change of concrete under drying environment is controlled by water diffusion from the interior to exterior, and can be described by the revised diffusion flux law. The apparent humidity diffusion coefficient decreases with depth, and the relationship between mean relative humidity of surface zone and depth can be represented by logarithmic function. In the wetting environment, the RH evolution in surface zone of concrete can be analyzed by the water capillary transport function, but the interior RH change is due to the capillary absorption and diffusion mechanism.
Key words: concrete; relative humidity; marine environment; evolution mechanism
跨海大桥、海港码头钢筋混凝土在海洋水下区、潮汐区、浪溅区和大气区服役时,由于海洋潮汐、盐雾及日照作用,钢筋混凝土表面环境湿度将随其所处位置、季节不同而不同[1]。环境湿度演变必将影响到混凝土内部湿度演变和水饱和度,从而影响到腐蚀离子在混凝土中的传输[2-5]。为获得混凝土内部相对湿度随环境湿度演变规律,Norris等[6-7]开发了混凝土内部湿度演变与水分蒸发监测设备,Jin等[8]也利用环形电极等监测设备对海底隧道衬砌混凝土湿度演变进行了监测。Nilsson等[9-10]对暴露在自然环境、人工环境中高强混凝土和普通混凝土内部相对湿度变化规律进行了研究。马文彬[11]探讨了环境变化对混凝土内部微环境的影响。考虑到胶凝材料水化的自干燥作用以及水分扩散导致的混凝土内部湿度演变,蒋正武等[12]开展了系统研究。在试验研究基础上,Li等[13]对干湿交替下混凝土表层内水分传输过程进行了理论和试验研究,张君等[14]基于内部湿度试验求解了早龄期混凝土水分扩散系数。为获得海洋环境下混凝土内部相对湿度演变规律与机理,本文对暴露与青岛沿海室内环境、海洋大气区和浪溅区混凝土的相对湿度演变进行了测试与模型分析。并采用干燥、毛细吸水模拟海洋潮汐作用,测试混凝土不同深度、不同龄期相对湿度演变规律。通过上述研究,不仅可揭示混凝土相对湿度随环境演变机理,而且可为海洋工程不同区域腐蚀离子传输机理分析与腐蚀防护提供依据。
1 实验
1.1 原材料及配合比
山东山水集团青岛分公司提供的P·O·52.5水泥。青岛电厂鲁青Ⅰ级粉煤灰,烧失量为3.56%。粗骨料为花岗岩,粒度为5~25 mm连续级配,压碎值为13.7。大沽河中砂,细度模数为2.7。采用江苏博特聚羧酸高效减水剂,通过合理掺量将混凝土坍落度控制在160~180 mm。试验所用混凝土原材料(水泥、砂、石、水) 质量比为435:565:1 143:157,混凝土养护28 d的抗压强度为42 MPa。
1.2 实验方法
成型长×宽×高为100 mm×100 mm×100 mm的混凝土试件,为保证水分沿试件高度方向的1维传输。试件成型后,用环氧树脂密封试件的4个面,只留下相对的2个端面与外界接触。混凝土养护28 d后,采用冲击钻在未用环氧树脂封闭的表面钻孔,钻孔深度分别为10,20,30和40 mm。之后将混凝土放回养护室养护一段时间,以保证各孔相对湿度达到100%。选用S2WS-SH710电容式温湿度数字传感器,湿度测量范围为0~100%,误差为±3%,温度测定范围0~120 ℃,误差为±0.5 ℃。用橡皮套将传感器的测头端部包裹住,塞入到预先钻好的孔洞中,直至探头接触到孔洞底部,探头顶部与混凝土之间用环氧树脂封闭。
将埋入传感器的试件放置在室内大气、海洋大气区、海洋浪溅区,以及采用恒温恒湿(相对湿度HR=65%,t=20 ℃)于45 ℃烘干、烘干后吸水构成的模拟环境中。每隔一定时间读取湿度变化并记录。
2 结果与分析
2.1 混凝土在室内大气环境下的内部湿度响应
混凝土在相对湿度为70%~80%的室内大气环境中放置,其不同深度的相对湿度演变规律如图1所示。由图1可见:混凝土内部相对湿度受环境湿度影响短期内呈现出忽高忽低的折线形态,在长期随养护龄期增加而下降,可分为水气饱和期(阶段Ⅰ,HR=100%)和随后的湿度减小期(阶段Ⅱ,HR<100%) 2个阶段。其中混凝土20,30和40 mm深度处的水气饱和期时间大约为2,3和12 d。因此,混凝土阶段Ⅰ时间长短及阶段Ⅱ湿度降低的幅度、速率与混凝土水泥水化速率、混凝土致密程度及传感器埋设位置密切有关。
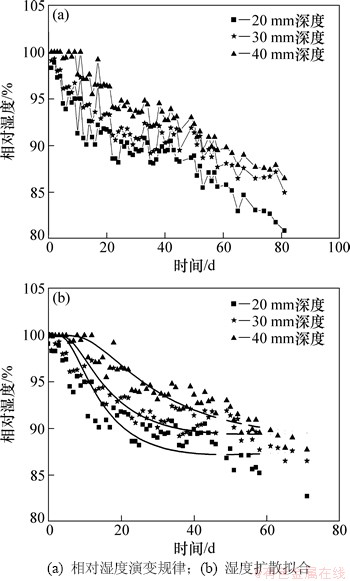
图1 室内大气环境中混凝土内部相对湿度演变规律及模拟
Fig. 1 Inner relative humidity evolution and its simulation of concrete cured in indoor atmospheric environment
此外,混凝土20 mm处的相对湿度波动幅度较大,30和40 mm处的相对湿度波动较小,这说明距离外部环境越近,受到环境湿度影响越大。当测试时间80 d时,20 mm处达到的相对湿度为81%,30 mm处为85%,40 mm处则是87%,仍未与环境湿度达到平衡。因此,混凝土内部湿度对环境湿度响应存在时间上的滞后性。
混凝土在环境作用下内部湿度变化主要为内部水分从内向外迁移导致了混凝土内部水饱和度下降。因此,其相对湿度演变仍可用Fick第二定律进行描述,则其不同深度的扩散通量为: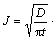
 。在环境湿度小于混凝土内部湿度(100%)的干燥过程中,其水分传输将由内向外。因此,混凝土相对湿度随时间的演变关系则可用式(1)表示。
。在环境湿度小于混凝土内部湿度(100%)的干燥过程中,其水分传输将由内向外。因此,混凝土相对湿度随时间的演变关系则可用式(1)表示。
 (1)
(1)
其中:HR为混凝土相对湿度(%),D 为表观湿度扩散系数(cm2/d), t 为扩散时间(d), x为混凝土深度(cm),CS为混凝土表面层平均相对湿度(%)。
按照式(1)对混凝土在室内环境下的相对湿度演变进行拟合,其结果如图1(b)所示。显然,通过对扩散通量公式进行修正,可实现混凝土内部相对湿度随深度及环境演变关系的模拟,其相关系数在0.85~ 0.98。通过拟合,混凝土20~40 mm深度的表观湿度扩散系数分别为0.0406,0.0797和0.07859 cm2/d。与之相关的表面层平均相对湿度分别为86.95%,91.72%和88.575%。显然,混凝土内部相对湿度不同,其水分扩散系数也不应相同。干燥过程中,混凝土表层的平均水分扩散系数小,内部扩散系数大。
2.2 混凝土在海洋大气区和浪溅区环境下的内部湿度响应
混凝土在青岛小麦岛海洋暴露站大气区和浪溅区环境下的内部相对湿度演变如图2所示,统计该暴露站1984—1995年大气环境的相对湿度演变,其结果如图3所示。由图2可见:混凝土在深度0~20 mm内其湿度可较快的随环境湿度演变,但其30 mm深处的相对湿度几乎保持在100%不变。经过近50 d的环境暴露,混凝土10 mm深度的相对湿度与环境湿度仍相差40%左右,混凝土表层湿度仍为85%~95%。因此,环境湿度对混凝土内部湿度有重要影响,但混凝土内部湿度随环境湿度响应速度较慢。海洋浪溅区服役混凝土的相对湿度大于大气区服役混凝土的相对湿度。
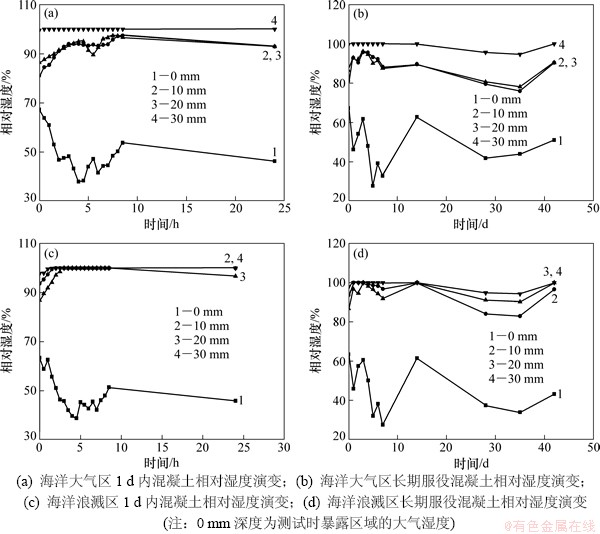
图2 海洋环境下混凝土内部湿度演变
Fig. 2 Inner relative humidity evolution of concrete cured in marine environment
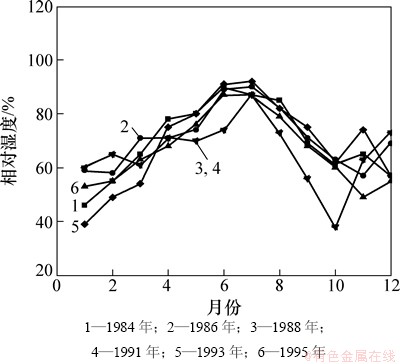
图3 青岛暴露站大气环境相对湿度演变
Fig. 3 Relative humidity evolution of atmospheric environment in Qingdao marine exposure station
由图3可见:青岛海洋大气环境湿度为45%~90%,其中5~8月份的湿度在75%以上;随混凝土服役时间延长,处于大气区和浪溅区服役的海工混凝土内部相对湿度将小于100%,但表层混凝土则会随环境湿度变化而变化。
2.3 混凝土在模拟干燥环境下的湿度响应
将混凝土试件放入HR=65%、温度t=20 ℃的恒温恒湿环境中,以及置于鼓风式烘箱中45 ℃恒定温度下烘干,测试混凝土相对湿度演变,并按照式(1)进行拟合,其结果如图4所示。
由图4可见:与实际环境相比,混凝土在恒温恒湿和烘干环境下的内部湿度短期内波动较小;随时间增加,混凝土内部各个深度处相对湿度均逐步降低;环境湿度越小、温度越高,表面层相对湿度下降越快,且其影响深度也越大。但即便在恒温恒湿放置120 d,烘干环境放置70 d,混凝土40 mm深度的相对湿度仍高于环境湿度,这足以说明混凝土内部的湿度对环境湿度存在时间上的滞后效应。此外,采用扩散定律对恒温恒湿环境下混凝土相对湿度演变模拟的相关性好,但对于烘干环境模拟相关性差。因此,在45 ℃烘干环境下混凝土中水分向外传输不仅有扩散作用,而且存在毛细抽吸作用。

图4 混凝土内部相对湿度随模拟环境演变规律及模拟
Fig. 4 Inner relative humidity evolution of concrete in simulative dry environment
针对恒温恒湿、室内大气和烘干环境下混凝土不同深度的相对湿度演变,按照式(1)回归得到混凝土不同深度的表观湿度扩散系数和混凝土表面层平均相对湿度,其结果如表1所示。
为建立混凝土表观湿度扩散系数以及表面层平均湿度与混凝土深度的关系,对10 mm深度的上述2项数值进行归一化处理。显然,混凝土表观湿度扩散系数与深度的关系可用线性函数拟合,混凝土表面层平均相对湿度与深度关系可用对数函数关系拟合,其拟合结果如图5所示。依据拟合公式分析得出:随混凝土深度增加,其表观湿度扩散系数线性增加,其表面层平均相对湿度先增加后趋于稳定。
表1 不同环境下混凝土表观湿度扩散系数与表面层平均相对湿度
Table 1 Apparent humidity diffusion coefficient and average relative humidity of concrete in different depth and environment

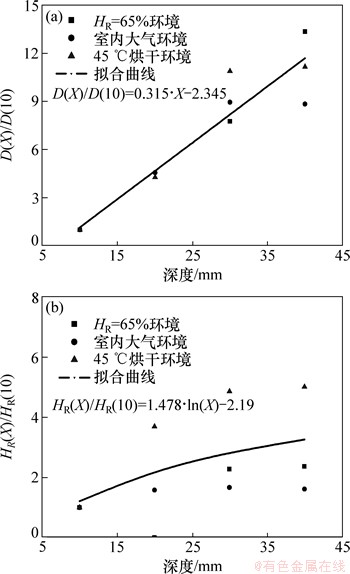
图5 混凝土湿度扩散系数、表面层平均相对湿度与深度的关系
Fig. 5 Relationship among humidity diffusion coefficient, average relative humidity and depth of concrete
2.4 混凝土在模拟湿润过程中的湿度响应
考虑潮汐区服役海工混凝土在干燥后将受到海水湿润作用,为了解非饱和混凝土在毛细吸水过程中的相对湿度演变,对45 ℃时烘干的混凝土试件进行毛细吸水试验,测试混凝土不同深度的相对湿度演变,其结果如图6所示。
由图6可见:在距离吸水面10 mm处,混凝土内部湿度从测试时间1.5 h开始逐渐增加,增长速率由慢逐渐变快,湿度增加最快的时间段出现在3~4 h,在这1 h内湿度增大了8.8%;之后,增大速度又逐渐减缓,直到测试时间为15.7 h时,10 mm处相对湿度达到100%,说明混凝土距离吸水面10 mm以内已达到饱水状态;距离吸水面20 mm处,湿度从6 h开始明显增加,151 h时湿度达到100%;在距离吸水面为30 mm处,湿度开始增大的时间最晚,增长速度最慢,达到饱和状态所需时间最长。总体而言,距离吸水面越近,湿度增大越快增幅越大,达到饱水状态所需时间越短。

图6 吸水过程中混凝土不同深度处相对湿度演变规律及模拟
Fig. 6 relative humidity evolution and its simulation curves of concrete during process of water uptake
此外,混凝土各个深度相对湿度在毛细吸水1 h时并未明显增大,说明在1 h内水分在毛细吸力作用下的渗入深度未达到10 mm。在毛细吸水12 h时, 10 mm和20 mm处的湿度已经明显增大,其相对湿度分别达到93.1%和59.2%,但30 mm处的湿度还未显著增大,仅为39.2%。考虑青岛地区潮汐为正规半日潮,在6 h左右的涨潮期,非饱和混凝土内部湿度很难达到饱和。
将混凝土吸水过程中的相对湿度演变与毛细吸水过程中的水分演变曲线(参见文献[15])进行对照,二者具有良好的线性关系。按照毛细吸水公式(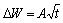 )对非饱和混凝土吸水曲线进行回归。显然,表层混凝土的相对湿度演变采用HR=A·t0.5+B(其中HR为相对湿度,t为湿润时间,A和B为回归常数)拟合具有很好的相关性,但在20~30 mm层采用该公式拟合,相关性很差。因此,吸水过程中混凝土表层相对湿度演变可用毛细吸附定律描述,内部的相对湿度演变是水分毛细吸附与扩散共同作用所致。
)对非饱和混凝土吸水曲线进行回归。显然,表层混凝土的相对湿度演变采用HR=A·t0.5+B(其中HR为相对湿度,t为湿润时间,A和B为回归常数)拟合具有很好的相关性,但在20~30 mm层采用该公式拟合,相关性很差。因此,吸水过程中混凝土表层相对湿度演变可用毛细吸附定律描述,内部的相对湿度演变是水分毛细吸附与扩散共同作用所致。
3 结论
1) 混凝土内部相对湿度演变包括水气饱和期和相对湿度减小期。环境湿度越小,其表层相对湿度越小,与外部达到平衡的时间越短。随混凝土深度增加,水气饱和期时间延长,内部相对湿度变化幅度减小,并在时间上存在滞后效应。
2) 干燥过程中混凝土相对湿度随时间演变受水分由内向外扩散过程控制,可用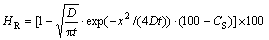 进行拟合。混凝土表观湿度扩散系数随深度增加而线性增加,表面层平均相对湿度与深度的关系符合对数函数关系。
进行拟合。混凝土表观湿度扩散系数随深度增加而线性增加,表面层平均相对湿度与深度的关系符合对数函数关系。
3) 在湿润过程中,距离吸水面越近,混凝土相对湿度增加越早,增幅越大,达到饱水状态所需的时间越短。非饱和混凝土表面层相对湿度演变可用毛细传输系数公式进行分析,内部则是传输与扩散共同作用所致。
4) 室内大气环境中养护80 d,混凝土20 mm深度的相对湿度为80%,30~40 mm深度相对湿度为86%左右。海洋大气区环境下养护42 d,其表层10~20 mm深度的相对湿度为85%~90%,海洋浪溅区环境下表层10~20 mm深度的相对湿度为90%~95%。
参考文献:
[1] 侯保荣, 李伟华, 金祖权, 等. 海洋钢筋混凝土腐蚀与修复补强技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012: 7-9.
HOU Baorong, LI Weihua, JIN Zuquan, et al. Corrosion and reinforcement technology of steel reinforced concrete under marine environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012: 7-9.
[2] 王本臻, 金祖权, 卢峰, 等. 非饱和混凝土中氯离子的毛细吸附[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2012, 33(10): 864-866.
WANG Benzhen, JIN Zuquan, LU Feng, et al. Capillary absorption of chloride ions in instauration concrete[J]. Corrosion & Protection, 2012, 33(10): 864-866.
[3] Byung H O, Seung Y J. Effects of material and environmental parameters on chloride penetration profiles in concrete structures[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2007, 37(1): 47-53.
[4] Hall C, Hoff W D, Taylor S C, et al. Water anomaly in capillary liquid absorption by cement-based materials[J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1995, 14(1): 1178-1181.
[5] Rucker-Gramm P, Beddoe R E. Effect of moisture content of concrete on water uptake[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2010, 40(1): 102-108.
[6] Norris A, Saafi M, Romine P. Temperature and moisture monitoring in concrete structures using embedded nanotechnology/micro electromechanical systems (MEMS) sensors[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2008, 22(2): 111-120.
[7] de J. Cano-Barrita P F, Marble A E, Balcom B J, et al. Embedded NMR sensors to monitor evaporable water loss caused by hydration and drying in Portland cement mortar[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2009, 39 (4): 324-328.
[8] JIN Zuquan, ZHAO Tiejun, ZHANG Peng, et al. Durability monitoring of concrete structure of subsea tunnel[J]. Journal of the Chinese ceramic society, 2013, 41(2): 205-210.
[9] Nilsson L O. Long-term moisture transport in high performance concrete[J]. Materials and structures, 2002, 35(10): 641-649.
[10] Andrade C, Sarria J, Alonso C. Relative humidity in the interior of concrete exposed to natural and artificial weathering[J]. Cement and concrete research, 1999, 29(8): 1249-1259.
[11] 马文彬. 气候环境变化与混凝土内微环境的响应规律研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2007: 62-69.
MA Wenbin. Response regularity of microenvironment in concrete under climate variations[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2007: 62-69.
[12] 蒋正武, 孙振平, 王培铭. 高性能混凝土自身相对湿度变化的研究[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2003, 31(8): 770-773.
JIANG Zhengwu, SUN Zhenping, WANG Peiming. Study on autogenous relative humidity change in high performance concrete[J]. Journal of the Chinese ceramic society, 2003, 31(8): 770-773.
[13] LI Chunqiu, LI Kefei, CHEN Zhaoyuan. Numerical analysis of moisture influential depth in concrete and its application in durability design[J]. Tsinghua science and technology, 2008, 13(S1): 7-12.
[14] 张君, 侯东伟. 基于内部湿度试验的早龄期混凝土水分扩散系数求解[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 48(12): 2033-2035.
ZHANG Jun, HOU Dongwei. Calculation of moisture diffusion coefficient in early age concrete from interior humidity tests[J]. Journal of Tsinghu University (Sci&Tech), 2008, 48(12): 2033-2035.
[15] ZHANG Peng, Wittmann F H, ZHAO Tiejun, et al. Visualization and quantification of water movement in porous cement-based materials by real time thermal neutron radiography: Theoretical analysis and experimental study[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2010, 53(5): 1198-1207.
(编辑 邓履翔)
收稿日期:2013-10-25;修回日期:2013-12-28
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51178230);铁道部科技研究计划项目(2010G024);山东省高校优秀科研创新团队基金(2012);青岛市科技项目(13-1-4-176-jch,13-1-4-115-jch)(Project (51178230) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2010G024) supported by the Science Research Program of Ministry of Railways, China; Project (2012) supported by the College Science Innovation Team Foundation of Shandong Precise, China; Projects (13-1-4-176-jch, 13-1-4-115-jch) supported by the Science and Technology Program of Qingdao City, China)
通信作者:金祖权(1977-),男,四川南充人,博士,教授,从事海洋环境混凝土耐久性研究;电话:15964239984;E-mail:jinzuquan@126.com