J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. (2009) 16: 0230-0235
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-009-0039-x
A novel salt-tolerant Micrococcus sp. DUT_AHX capable of degrading nitrobenzene
AI Hai-xin(艾海新)1, 2, ZHOU Ji-ti(周集体)2, L? Hong(吕 红)2
(1. School of Life Science, Liaoning University, Shenyang 110036, China;
2. School of Environment and Biological Science and Technology, Dalian University of Technology,
Dalian 116024, China)
Abstract: A novel strain of Micrococcus sp. DUT_AHX, which was isolated from the sludge of a nitrobenzene (NB)-manufacturing plant and could utilize NB as the sole carbon source, was identified on the basis of physiological and biochemical tests and 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) sequence analysis. It can grow at the temperature up to 40 ℃ or in the presence of NaCl concentration up to 12 g/L in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium. The optimal degradation conditions are as follows: temperature 37 ℃, pH 7.0, and shaking speed 150 r/min. The strain involves a partial reductive pathway due to the release of ammonia and can also utilize 2-aminophenol as the sole carbon source. Furthermore, the enzyme activity tests show that crude extracts of NB-grown strain DUT_AHX mainly contain 2-aminophenol 1, 6-dioxygenase activity. The exploitation of salt-tolerant bacteria will be a remarkable improvement in NB bioremediation and wastewater treatment at high salinity and high temperature.
Key words: Micrococcus; 16S rDNA; nitrobenzene; degradation; salt-tolerant
1 Introduction
Hyper-salinity chemical industrial wastewater usually contains a lot of chemicals that include nitroaromatic compounds, phenol, aniline, dyes, and so on. Nitroaromatic compounds are widely used in the chemical industry for the production of explosives, dyes, polymers, plastics, and pesticides. Many of these compounds are highly toxic even at low concentrations and recalcitrant to biodegradation. Nitrobenzene (NB) is one of the seven nitroaromatic compounds on the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s list of priority pollutants [1].
Some physical, chemical and biological methods were established for the treatment of NB-contaminated wastewater. In contrast, biological methods that can mineralize NB at lower cost are usually preferred. However, NB industrial wastewater usually contains high inorganic salts (specifically NaCl). When the mass concentration of Na+ is above 3 g/L, it can generally cause moderate inhibition of most bacterial activities [2]. Since the growth of most microorganisms is inhibited at high salinity, traditional biological treatments are out of action.
NB degradation has been studied mainly in Pseudomonas and Comamonas species, such as Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes JS45 [3], Pseudomonas putida HS12 [4], Pseudomonas putida ZWL73 [5], Comamonas sp. strain JS765 [6], and Comamonas sp. CNB-1 [7]. The aerobic NB degradation involves two major pathways: a widespread partial reductive pathway characterized by the release of ammonia [3-4] and an oxidative pathway characterized by the release of nitrite [6]. In the partial reductive pathway, as illustrated in Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes JS45, Pseudomonas putida HS12, Pseudomonas putida ZWL73 and Comamonas sp. CNB-1, the degradation of NB leads to the formation of 2-aminophenol. In the oxidative pathway described in Comamonas sp. strain JS765, NB is converted to catechol. However, little is so far reported on the ability of Micrococcus species to degrade NB. Furthermore, there are much fewer studies on NB degradation at high salinity. Thus, exploiting salt-tolerant bacteria will be a great enhancement in conventional biotreatment systems. In this work, we described the isolation and characterization of a novel Micrococcus sp. strain DUT_AHX that is able to utilize NB as the sole carbon source under high salt concentration and high temperature conditions.
2 Experimental
2.1 Isolation and growth of bacteria
The mineral salts basal (MSB) medium with pH= 7.0, which was used for microbial growth and degradation studies, contained 7 g/L Na2HPO4·12H2O, 1 g/L KH2PO4, 10 mg/L CaCl2·2H2O, 1 mg/L FeCl3, 20 mg/L MgSO4·7H2O, 1 g/L (NH4)2SO4 and 100 mg/L NB. The media were supplemented with 15 g/L agar and appropriate NaCl as described in the text.
Strain DUT_AHX was isolated from the sludge of a NB-manufacturing facility (Jinan, China) by the enrichment culture technique. After 60 d of enrichment, samples were spread directly on MSB agar plates with 30 g/L NaCl and 100 mg/L NB as the sole carbon source. The plates were incubated at 30 ℃ for 72 h. Individual colonies on the plates were picked up and strain DUT_AHX was obtained by repeatedly streaking culture on new plates from a single colony.
2.2 Identification of bacteria
Microorganism isolated from the enrichment culture was identified by the standard procedures described in Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology [8]. The NaCl tolerance was tested from 1 to 15 g/L. The ability to utilize other aromatic substrates as the sole carbon source was tested on MSB medium plates. The total DNA isolation from strain DUT_AHX was performed by the modified SDS method [9]. The G + C content of the DNA was determined by the thermal denaturation method [10], with E. coli K-12 as the reference.
A PCR was also performed in order to amplify the 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) of strain DUT_AHX [11-13]. One individual colony was dissolved in 50 ?L ultrapure water, boiled for 10 min and centrifuged at 12 000 r/min and 4 ℃ for 10 min. The supernatant fluids were used as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) templates. The 27f and 1522r universal primers were used to amplify the 16S rDNA of strain DUT_AHX. The PCR products were purified using the TaKaRa Agarose Gel DNA Purification Kit Ver 2.0 (TaKaRa Biotechnology, Dalian, China), and then directly sequenced on an ABI model 3730XL automatic DNA analyzer by using the BigDye Teminator V3.1 Kit (Applied Biosystems, USA). The 16S rDNA sequence analysis was performed with BLAST program at National Center for Biotechnology Information. The phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbour-joining method using the MEGA 3.1 software [14] after multiple alignment of data by the CLUSTAL X 1.8 software. The relationship stability was assessed by performing the bootstrap analysis of neighbor-joining data based on 1 000 resamplings.
2.3 Effect of different environmental factors
Keeping other parameters constant, the effect on NB degradation was investigated under different NaCl concentrations (0-15 g/L), temperatures (20-45 ℃), pH values (5.0-10.0) and shaking speeds (50-250 r/min) in MSB medium for 24 h. The cell-free cultures with NB and cell cultures without NB served as the control.
2.4 Preparation of cell-free extracts
For experiments with induced cells, cultures were grown in MSB medium (200 mL) at 150 r/min and 37 ℃ for 48 h. Then cultures were inoculated into 4 L MSB medium and incubated under the above conditions. Due to the toxic effect of NB on the microbial growth, NB was added intermittently after the depletion. Cultures grown in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium served as the control.
Cells were harvested by centrifugation (8 000 r/min) at 4 ℃ for 10 min, washed twice with the fresh 0.02 mol/L phosphate buffer (pH=7.2), and then resuspended in the same buffer. For preparation of crude extracts, cells were disrupted by an ultrasonic disruptor CPX750 (20% amplitude, Cole-Parmer, USA) and centrifuged (21 000 r/min) at 4 ℃ for 60 min. The pellets were discarded and the supernatants were stored on ice until used.
2.5 Enzyme assays
2-Aminophenol 1, 6-dioxygenase activity was measured by monitoring the increase in the absorbance of the 2-aminophenol ring cleavage product at 380 nm [3]. Catechol 1, 2-dioxygenase and catechol 2, 3- dioxygenase were determined as described in Ref.[15]. Reaction mixtures contained 2-aminophenol or catechol (0.3 ?mol), sodium phosphate (29.5 ?mol, pH=7.2), and cell extracts (0.3-1.0 mg of protein) in a final volume of 3 mL at room temperature.
2.6 Analytical methods
NB was determined by measuring the maximum absorbance at 268 nm using an UV-visible spectrophotometer V-560 (JASCO, Japan) via the Beer-Lambert law. The relationship between absorbance and concentration was linear in the NB concentration range of 0-30 mg/L. Cell concentration was determined by measuring the optical density (OD) at 600 nm. Nitrite and ammonia releases were measured by standard methods [16]. The total organic carbon (TOC) was determined using a TOC-5000 analyzer (Shimadzu, Japan). Protein was measured by BRADFORD assay [17] with bovine serum albumin as the protein standard. All experiments were conducted three times, and the mean values of the data were presented.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Identification of strain DUT_AHX
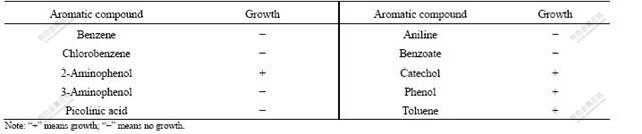
After 60 d of enrichment, strain DUT_AHX capable of utilizing NB as the sole carbon and energy sources was isolated by the repeatedly streaking culture. Cells of strain DUT_AHX are spherical (diameter, 0.5-1.0 ?m) and occur mostly in tetrads or irregular clusters of tetrads (Fig.1). Strain DUT_AHX is aerobic and nonmotile. It does not form spores. Colonies that are 0.5-1.5 mm in diameter on LB agar plates are creamy yellow, convex, smooth, entire, and circular. The optimum temperature for growth is 37 ℃ (Fig.2). Strain DUT_AHX grows well in LB medium containing NaCl up to 10 g/L; the growth is weak in the presence of 12 g/L NaCl; and no growth is observed in the presence of 15 g/L NaCl (Fig.3). The physiological and biochemical characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Strain DUT_AHX was examined for the growth on MSB medium plates with a variety of aromatic substrates as the sole carbon source (Table 2). The DNA G + C content of strain DUT_AHX is 70.2% (molar fraction). Thus, the strain is identified as a Micrococcus sp. and designated strain DUT_AHX on the basis of these phenotypic properties and the 16S rDNA gene sequence analysis (GenBank No. DQ409081). The closest phylogenetic relative of strain DUT_AHX is Micrococcus luteus (16S rDNA gene sequence identity is 99%, Fig.4).
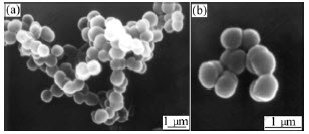
Fig.1 Scanning electron micrographs of Micrococcus sp. DUT_AHX: (a) Bacterial clusters; (b) Single tetrad
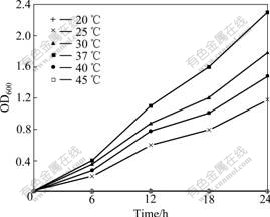
Fig.2 Growth of Micrococcus sp. DUT_AHX in LB medium at different temperatures
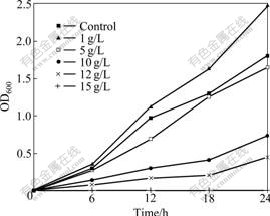
Fig.3 Growth of Micrococcus sp. DUT_AHX in LB medium with different NaCl concentrations
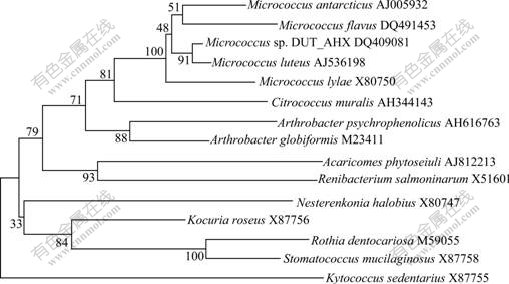
Fig.4 Phylogenetic tree of Micrococcus sp. DUT_AHX
Table 1 Taxonomic characteristics of strain DUT_AHX
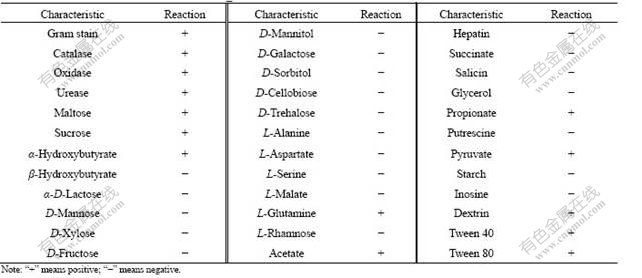
Table 2 Growth of strain DUT_AHX using aromatic compounds as sole carbon source under aerobic conditions
3.2 Effect of different factors on growth and NB degradation
Since NB industrial wastewater usually contains inorganic salts that can influence the performance of biological process, NB degradation by strain DUT_AHX at high salinity was tested (Fig.5). Strain DUT_AHX grows well in the absence of NaCl. It grows in the presence of NaCl concentrations up to 12 g/L in LB medium but only up to 10 g/L in MSB medium. Strain DUT_AHX can tolerate moderately NaCl but does not require NaCl for the growth. Hence, it is not halophilic but halotolerant [18]. Furthermore, the growth rate is faster and the NB degradation rate is higher in the presence of NaCl concentrations below 5 g/L than those above 5 g/L. When cells are subjected to the salt stress (5-15 g/L), they may shut off most metabolic activity and protein synthesis and then the growth is consequently inhibited [19].
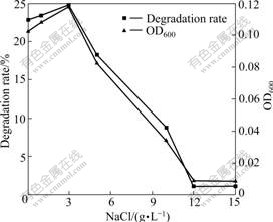
Fig.5 Effect of NaCl concentration on growth and degradation of NB by Micrococcus sp. DUT_AHX
Some environmental factors (temperature, pH, and oxygen supply), which can affect growth and NB degradation of strain DUT_AHX in MSB medium, were also tested. Most studies on NB degradation were carried out at the optimal temperature of 30 ℃ [3-7]. However, strain DUT_AHX can degrade NB at the optimal temperature of 37 ℃ (Fig.6). These results indicate that strain DUT_AHX will be broadly applied in degrading NB in high temperature and high salinity environment. The pH range from 5.0 to 10.0 with an optimum of 7.0, which is suitable for NB degradation, is observed (Fig.7). This reason may be that the internal environment of bacterial cells is approximately neutral. Oxygen plays an important role in the degradation process of organic pollutants. Different concentrations of oxygen are obtained by adjusting the shaking speed. As shown in Fig.8, the degradation rate of NB reaches 23.4% at the shaking speed of 150 r/min and increases slightly with the increase of shaking speed (150-250 r/min). Hence, the optimal shaking speed is 150 r/min.
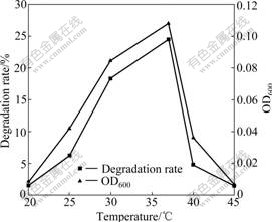
Fig.6 Effect of temperature on growth and degradation of NB by Micrococcus sp. DUT_AHX
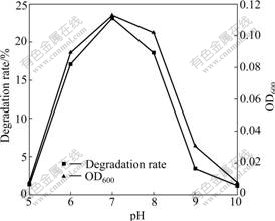
Fig.7 Effect of pH on growth and degradation of NB by Micrococcus sp. DUT_AHX
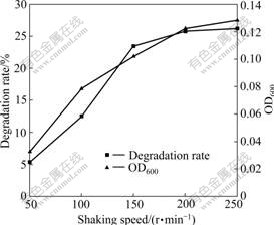
Fig.8 Effect of shaking speed on growth and degradation of NB by Micrococcus sp. DUT_AHX
3.3 Bacterial growth and degradation of NB
NB-grown cells were washed twice to remove NB and then cultured in 0.02 mol/L phosphate buffer (pH= 7.2) containing 100 mg/L NB. As shown in Fig.9, the NB concentration rapidly decreases and cell density gradually increases with the increase of culture time. Ammonia is detected in the culture medium, but the amount of released ammonia is not stoichiometric to that of NB consumed. This is due to the fact that a significant amount of released ammonia is taken up by the microorganism as the nitrogen source for the cell growth [4]. There is no change in optical density in control cultures without NB. No nitrite release is detected in the culture medium. This suggests that NB degradation by strain DUT_AHX involves a partial reductive pathway [3].
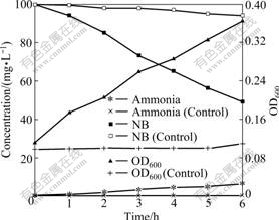
Fig.9 Degradation of NB by NB-grown cells of Micrococcus sp. DUT_AHX in phosphate buffer
99% of 100 mg/L NB is degraded by strain DUT_AHX after about 80 h and over 98% TOC is removed under the optimal conditions but the NB concentration does not decrease in the control experiment. This indicates that NB is mineralized by strain DUT_AHX.
3.4 Enzyme activities in cell-free extracts
The cell-free extracts grown in MSB medium contain activities of 2-aminophenol 1, 6-dioxygenase, catechol 2, 3-dioxygenase and catechol 1, 2-dioxygenase (Table 3). The cell-free extracts grown in LB medium include none of three enzyme activities. These results suggest that the enzymes of NB degradation are induced by NB.
Table 3 Enzyme activities in cell-free extracts of Micrococcus sp. DUT_AHX
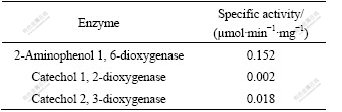
4 Conclusions
(1) The isolated strain DUT_AHX is capable of utilizing NB as the sole carbon source. It is a moderately halotolerant bacterium and identified as a Micrococcus sp. by physiological and biochemical tests and 16S rDNA sequence analysis.
(2) At high salinity (10 g/L NaCl) and high temperature (40 ℃), strain DUT_AHX can degrade NB and the optimal degradation conditions are 3 g/L NaCl, 37 ℃, pH 7.0 and 150 r/min.
(3) The free-cell crude extracts of NB-grown strain DUT_AHX mainly contain 2-aminophenol 1, 6- dioxygenase activity. Moreover, NB degradation by strain DUT_AHX involves a partial reductive pathway due to the release of ammonia. So Micrococcus sp. strain DUT_AHX has a remarkable potential for application in hyper-salinity industrial wastewater treatment systems.
References
[1] KEITH L H, TELLIARD W A. Priority pollutants (I): A perspective view [J]. Environmental Science Technology, 1979, 13(4): 416-423.
[2] de BAERE L A, DEVOCHT M, ASSCHE P V, VERSTRAETE W. Influence of high NaCl and NH4Cl salt levels on methanogenic associations [J]. Water Research, 1984, 18(5): 543-648.
[3] NISHINO S F, SPAIN J C. Degradation of nitrobenzene by a Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes [J]. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 1993, 59(8): 2520-2525.
[4] PARK H S, LIM S J, CHANG Y K, LIVINGSTON A G, KIM H S. Degradation of chloronitrobenzenes by a coculture of Pseudomonas putida and Rhodococcus sp. [J]. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(3): 1083-1091.
[5] ZHEN Da, LIU Hong, WANG Shu-jun, ZHANG Jun-jie, ZHAO Fei, ZHOU Ning-yi. Plasmid-mediated degradation of 4-chloronitrobenzene by newly isolated Pseudomonas putida strain ZWL73 [J]. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 2006, 72(4): 797-803.
[6] NISHINO S F, SPAIN J C. Oxidative pathway for the biodegradation of nitrobenzene by Comamonas sp. strain JS765 [J]. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 1995, 61(6): 2308-2313.
[7] WU Jian-feng, SUN Cui-wei, JIANG Cheng-ying, LIU Zhi-pei, LIU Shuang-jiang. A novel 2-aminophenol 1, 6-dioxygenase involved in the degradation of p-chloronitrobenzene by Comamonas strain CNB-1: Purification, properties, genetic cloning and expression in Escherichia coli [J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2005, 183(1): 1-8.
[8] BUCHANAN R E, GIBBONS N E. Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology [M]. 8th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1984.
[9] SAMBROOK J, RUSSELL D W. Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual [M]. 3rd ed. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 2001.
[10] MARMUR J, DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from thermal denaturation temperature [J]. Journal Molecular Biology, 1962, 5: 109-118.
[11] ZHOU Hong-bo, LIU Xi, FU Bo, QIU Guan-zhou, HUO Qiang, ZENG Wei-min, LIU Jian-she, CHEN Xin-hua. Isolation and characterization of Acidithiobacillus caldus from several typical environments in China [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2007, 14(2): 163-169.
[12] YANG Yu, DIAO Meng-xue, SHI Wu-yang, LI Li, DAI Qin-yun, QIU Guan-zhou. Isolation and characterization of organic-sulfur degradation bacterial strain [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2007, 14(3): 324-329.
[13] LIU Jian-she, XIE Xue-hui, XIAO Sheng-mu, WANG Xiu-mei, ZHAO Wen-jie, TIAN Zhuo-li. Isolation of Leptospirillum ferriphilum by single-layered solid medium [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2007, 14(4): 467-473.
[14] KUMAR S, TAMURA K, NEI M. MEGA3: Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment [J]. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2004, 5(2): 150-163.
[15] SCHRAA G, BOONE M L, JETTEN M S M, van NEERVEN A R W, COLBERG P J, ZEHNDER A J B. Degradation of 1, 4- dichlorobenzene by Alcaligenes sp. strain A175 [J]. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 1986, 52(6): 1374-1381.
[16] GERHARDT P, MURRAY R G, WOOD W A, KRIEG N R. Methods for general and molecular bacteriology [M]. Washington: American Society for Microbiology, 1994.
[17] BRADFORD M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding [J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 1976, 72(1/2): 248-254.
[18] VREELAND R H. Mechanisms of halotolerance in microorganisms [J]. Critical Reviews Microbiology, 1987, 14(4): 311-356.
[19] DUCH? O, TR?MOULET F, GLASER P, LABADIE J. Salt stress proteins induced in Listeria monocytogenes [J]. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 2002, 68(4): 1491-1498.
Received date: 2008-07-25; Accepted date: 2008-09-13
Corresponding author: ZHOU Ji-ti, Professor; Tel: +86-411-84706252; E-mail: zjiti@dlut.edu.cn
(Edited by CHEN Wei-ping)