晶粒细化和残余元素对A713铸态铝合金热裂行为的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2016年第7期
论文作者:Anil Kumar BIRRU D. BENNY KARUNAKAR
文章页码:1783 - 1790
关键词:铝合金;热裂;浇铸温度;晶粒细化
Key words:aluminium alloy; hot tearing; pouring temperature; grain refinement
摘 要:为减少或防止热裂现象的产生,研究具有长程凝固区A713铸态铝合金的热裂行为。对添加不同晶粒细化剂如Al-2.5Ti-0.5C和Al-3.5Ti-1.5C的合金在不同浇铸温度(700、750和780 °C)条件下进行热裂实验。结果表明:添加晶粒细化剂Al-3.5Ti-1.5C能减少热裂现象的产生,但仅添加晶粒细化剂不能完全阻止A713铸态铝合金中热裂现象的产生。这与早期一些研究者得出的结论相矛盾。考察了铁元素对A713铸态铝合金热裂行为的影响。结果显示,同时添加晶粒细化剂和铁元素能减少A713铝合金的内部枝晶分离,从而沿晶界产生枝晶间的联锁。因此,铁元素作为工业铝中的一种杂质元素,能阻止A713铝合金热裂现象的产生。
Abstract: Some investigations have been carried out on hot tears in the A713 cast alloy, which is one of the long freezing range alloys, with objective to minimize/prevent hot tears. Experiments were conducted by varying pouring temperatures at 700, 750, and 780 °C on the alloy with the addition of grain refiners like Al-2.5Ti-0.5C and Al-3.5Ti-1.5C. It was found that hot tearing was minimized by the addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiner, but grain refinement alone could not prevent hot tearing in A713 cast alloy. This has contradicted the findings of some earlier researchers. Experiments conducted on hot tearing with the addition of iron were found to be interesting. It was found that grain refinement along with iron addition to the A713 alloy has reduced the inter-dendritic separation so that interlocking could take place along the grain boundaries. Thus, iron, which comes as an impurity in commercial aluminum, can prevent hot tearing of A713 alloy.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26(2016) 1783-1790
Anil Kumar BIRRU1, D. BENNY KARUNAKAR2
1. Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Manipur, Imphal-795004, India;
2. Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, Uttrakhand-247667, India
Received 13 August 2015; accepted 16 February 2016
Abstract: Some investigations have been carried out on hot tears in the A713 cast alloy, which is one of the long freezing range alloys, with objective to minimize/prevent hot tears. Experiments were conducted by varying pouring temperatures at 700, 750, and 780 °C on the alloy with the addition of grain refiners like Al-2.5Ti-0.5C and Al-3.5Ti-1.5C. It was found that hot tearing was minimized by the addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiner, but grain refinement alone could not prevent hot tearing in A713 cast alloy. This has contradicted the findings of some earlier researchers. Experiments conducted on hot tearing with the addition of iron were found to be interesting. It was found that grain refinement along with iron addition to the A713 alloy has reduced the inter-dendritic separation so that interlocking could take place along the grain boundaries. Thus, iron, which comes as an impurity in commercial aluminum, can prevent hot tearing of A713 alloy.
Key words: aluminium alloy; hot tearing; pouring temperature; grain refinement
1 Introduction
Hot tearing is a severe defect encountered in alloy castings and perhaps the key issue defining alloy’s castability. It is identified as a crack, either on the inner or outer surfaces of the casting. Once the hot tear arises in a casting, the casting has to be repaired or scraped, which results in a significant loss. CAO and KOU [1] studied the hot tearing susceptibility of Mg-4Al-0.5Ca, Mg-4Al-1.5Ca, Mg-4Al-2.5Ca, Mg-4Al-3.5Ca, Mg- 5Al-2.5Ca, and Mg-6Al-2.5Ca alloys and found that the hot tearing susceptibility decreased significantly with increase in Ca content but did not change much with the Al content. Mg-4Al-0.5Ca alloy had the widest freezing range and the lowest eutectic content and was the most susceptible to hot tearing, while Mg-4Al-3.5Ca and Mg-6Al-2.5Ca alloys were the opposite. RYOSUK et al [2] studied the crack susceptibility of Al-Mg alloy and found that the addition of 0.08Ti-0.016B could prevent the susceptibility to cracking of the alloy. However, it was revealed from the microstructure analysis that the addition of Ti and B was the most effective in reducing globular grain size, which resulted in minimization of the susceptibility to cracking. WANG et al [3] studied the effects of zinc and rare earth additions on Mg-9Al alloy and found that zinc additions decreased the end-solidifying temperature, promoted the precipitation of Mg17Al12 phase along the grain boundaries and increased the hot tearing susceptibility. Precipitation of Al4RE phase slowed down the temperature drop at the initial stage of solidification. ESKIN and KATGERMAN [4] studied the fracture mode of hot tearing at the nucleation and observed that the brittle and intergranular mode fracture occurred mostly when the grain boundaries were covered with liquid metal. The effects of casting speed and alloy composition on the structure formation and hot tearing during the casting of Al-Cu alloys were studied by SUYITNO et al [5] and they found that the grain size depended on the chemical composition. Mostly, coarser structure was observed at low contents of copper of less than 2% at low casting speeds. The phenomenon of hot tearing, a serious defect in castings, has been known for a long time. CAMPBELL [6] defined hot tear as a uniaxial tensile failure, which results in cracks on the outer or inner surface of the casting. However, the precise mechanism of hot tearing was not understood for quite some time. ESKIN et al [7] have made reviews on hot tearing, which show that hot tearing is a complex phenomenon. It lies at the intersection of heat flow, fluid flow and mass flow, and various factors influence its formation. Recently, RAVI [8] has concluded that hot tears usually result during the solidification of a casting in a location that has a high temperature, high gradient, and high cooling rate, coupled with a sharp corner. High temperature contributes to low strength; high gradient and high cooling rates contribute to stresses; and a sharp corner contributes to crack initiation. LANCASTER [9] cited factors influencing solidification cracking of aluminium and its alloys during welding. It was mentioned that the addition of small amounts of Ti and B (grain refinement) had resulted in reducing solidification cracking. Further, it was concluded that enhanced grain refinement could prevent solidification cracking completely.
ZHANG and SINGER [10] studied two types of Ni-based superalloys of IN792 and found that the effect of Ti content on IN792 is quite interesting. Castings without any crack or only with tiny cracks were obtained when the Ti content was dropped to 2%, compared with the original 3.9% in IN792. Moreover, ZHANG [11] studied the effects of Ti and Ta contents on the solidification behavior and castability of IN792 alloy. Good castability was achieved by proper control of the Ti/Ta ratio. This was due to the increased solidification temperature of remaining liquid in the final stages of solidification, which reduced the possibility of the formation of the detrimental interdendritic liquid film. The hot tearing susceptibility has therefore reduced. KORI [12] investigated the effect of grain refinement and modification of some hypoeutectic and eutectic Al-Si alloys with the addition of various binary and ternary-grain refiners namely, Al-3Ti, Al-3B, Al-3Ti-1B, Al-1Ti-3B, Al-5Ti-1B and Al-1Ti-5B at different addition levels. The holding time was varied from 0 to 120 min. The results revealed that the above grain refiners could fairly refine the grains in the hypoeutectic and eutectic Al-Si alloys. Based on these experimental results, REDDY et al [13] made an attempt to model the grain refinement behaviour of Al-7Si alloy. A feed forward neural network with back-propagation learning algorithm was developed for the prediction of the grain size, as a function of Ti and B addition levels and holding time during grain refinement of Al-7Si alloy. Comparison of the predicted and experimental results showed that the neural network model could predict the grain size of Al-7Si alloy with good learning precision and generalization.
KARUNAKAR et al [14] studied the hot tearing in Al-1Sn alloy with the addition of Al-5Ti-1B grain refiner, and found that grain refinement alone could not prevent hot tearing, but grain refinement plus Fe addition could prevent cracking completely. GUO and ZHU [15] made a correlation between the crack susceptibility coefficient and aluminium content for Mg-Al alloys and also predicted the conditions favouring hot tearing. They found that the addition of carbon had a significant effect on the reduction of hot tearing susceptibility. However, a few of researchers made an attempt on hot tearing of magnesium alloys and super alloys [16-19]. Recently, few researchers also made various defects [20,21] and the investigations and conclusions made by BIRRU et al [22] showed that A713 alloy was extremely prone to hot tearing. Hence, the aim of the present work is to conduct investigations on A713 aluminum cast alloys, which have long freezing range and are sensitive to hot tearing, which will help the foundrymen to minimize such defects that are associated with cracking. The conditions that would result in complete prevention of hot tearing have been investigated.
2 Experimental
2.1 Experimental setup
The hot tear experiments included mould preparation, melting of the charge and pouring. Green sand was prepared with standard binders and the mould properties like permeability and green compression strength, were maintained to be the same for all the experiments. For the present investigation, a special gated pattern has been designed, similar to the one incorporated by KARUNAKAR et al [14], which would produce four rings on four sides simultaneously. The dimensions of a single pattern are shown in Fig. 1. A photograph of the gated pattern designed for the present investigation along with the metallic cores is shown in Fig. 2. The gated pattern was kept inside the lower moulding box (drag) and the green sand was compacted around the pattern. The cope was placed over the drag, filled with the green sand properly and rammed manually. The cope was separated from the drag and the gated pattern was withdrawn from the drag. The steel cores were polished with an emery paper and painted with zirconium so that they could be withdrawn easily from the solidified casting. After the steel cores were kept at the centre of each ring mould in the drag, the cope was placed over the drag and clamped together using dovetail pins. The unwrapped green sand mould, along with the steel cores, is shown in Fig. 3. The above alloys were melted in an induction furnace and poured into separate moulds. The molten metal was poured into three different moulds at three different pouring temperatures of 700, 750 and 780 °C.
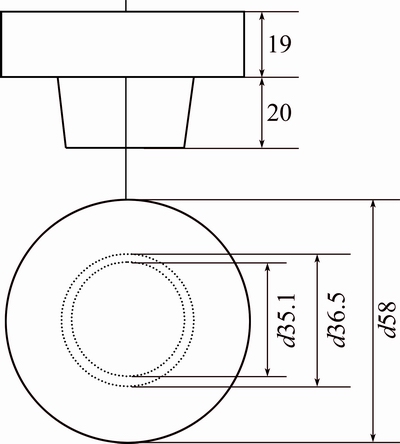
Fig. 1 Dimensions of single wooden pattern (unit: mm)
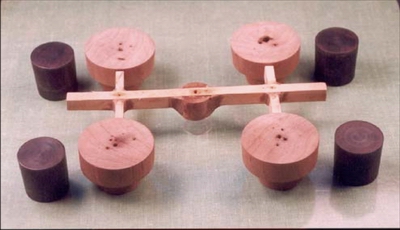
Fig. 2 Gated pattern designed for present investigation with metallic cores [14]
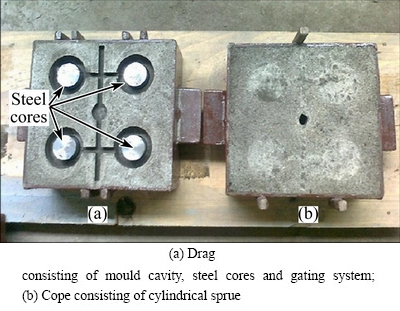
Fig. 3 Sand moulds made for investigating hot tearing
The temperature was measured by a K-type thermocouple, with an accuracy of ±1 °C. The casting rings developed cracks on all the four sides (outside, inside, top and bottom). The cracks visible on each ring were measured on all the four sides using a thread and the same was transferred to a ruled scale. The total crack length on each ring was the sum of the crack lengths obtained on all the four sides. Thus, the total crack lengths were determined for all the four rings of each casting and the average crack length was determined.
2.2 Experimental work
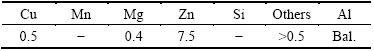
The alloy used in the present study is A713 alloy. The chemical composition of the alloy is shown in Table 1. Initially, hot tear investigations were carried out on A713 alloy with the addition of grain refiner. Following this, investigations were carried out with the addition of grain refiner and residual element with a motive to prevent the hot tearing.
Table 1 Chemical composition of A713 alloy (mass fraction, %)
2.2.1 Experiments with addition of grain refiner
Initially, the hot tear investigations were carried out on A713 alloy with the addition of Al-2.5Ti-0.5C grain refiner. The A713 alloy was melted in an induction furnace and the grain refiner was added to the melt at 0.25% (mass fraction). The melt was then poured into three green sand moulds at the pouring temperatures of 700, 750 and 780 °C, respectively. After the melt in the moulds solidified, the castings were taken out, which are shown in Fig. 4. It was observed that with an increase in the pouring temperature, under the same grain refinement, the crack length gradually increased from a minimum value. However, it can be noted that refining the melt using Al-2.5Ti-0.5C grain refiner could not reduce hot tearing effectively. Further experiments were conducted with the addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiner and by increasing the pouring temperatures. It was observed that with the second grain refiner (Al-3.5Ti-1.5C), there was an appreciable decrement in the crack length at the lowest pouring temperature, which is shown in Fig. 5. In Fig. 5(c), it was observed that most outer surface cracked at the verge of the rings. The correlations between pouring temperature and crack length with both the grain refiners are shown in Figs. 6 and 7.
2.2.2 Experiments with addition of grain refiner and Fe master alloy
Experiments were carried out on A713 alloy with the addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiner and Al-3.0Fe master alloy chips and the melt was stirred thoroughly. The melt was then poured into three green sand moulds, by varying the pouring temperatures at 700, 750 and 780 °C. After the melt in the moulds solidified, the castings were taken out. The castings were thoroughly examined and no cracks were found in all the castings that were made at different pouring temperatures. These castings are shown in Fig. 8.
2.2.3 Metallographic analysis
Specimens of A713 alloy castings with the addition of grain refiners were sectioned at crack affected areas for the purpose of microstructure analysis. All such samples were polished and etched using Keller’s reagent (10 mL HF + 15 mL HCl + 25 mL HNO3 + 50 mL H2O) to reveal the microstructure. Buehler Omni Met image analysis software, in conjunction with an optical microscope, was used to characterize the microstructure and measure the grain sizes of the specimens. Grain size calculations were performed by linear intercept method. In photomicrograph, at any straight line, the length of the line, divided by the average number of grains intercepted by it, gives the average grain size. The grain sizes were measured at different locations for each specimen and the average grain size was determined. All the samples were analyzed with an optical microscope at a magnification of 200× and indicated the scale of 50 μm.
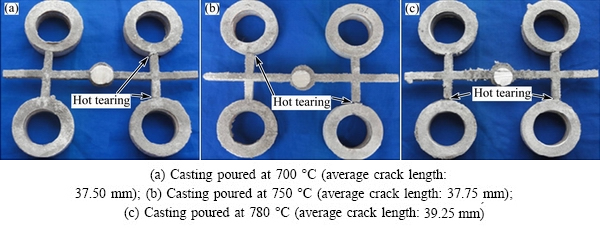
Fig. 4 Castings of A713 alloy with addition of Al-2.5Ti-0.5C grain refiner
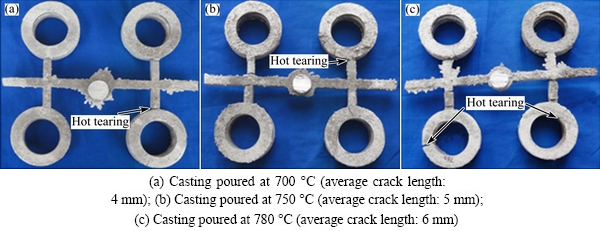
Fig. 5 Castings of A713 alloy with addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiner
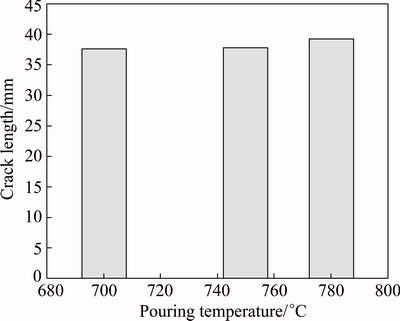
Fig. 6 Effect of pouring temperature on crack length in A713 alloy castings with addition of Al-2.5Ti-0.5C grain refiner
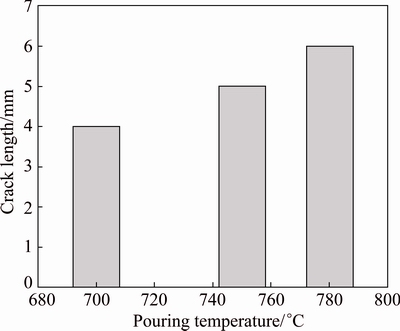
Fig. 7 Effect of pouring temperature on crack length in A713 alloy castings with addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiner
3 Results
Table 2 shows the average crack lengths and grain sizes obtained from the investigations on A713 alloy, with the additions of Al-2.5Ti-0.5C and Al-3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiners and by varying the pouring temperatures. Table 3 shows the details of the additions of grain refiner and Fe master alloy, crack lengths and corresponding grain sizes of the A713 castings, which exhibited zero crack length at all the pouring temperatures. It was observed that there was a slight increase in the grain sizes with an increase in the pouring temperature. The grain sizes were 37, 38 and 39 μm at the pouring temperatures of 700, 750 and 780 °C, respectively.
3.1 Experiments with addition of Al-2.5Ti-0.5C as grain refiner
The A713 alloy castings, with the addition of Al-2.5Ti-0.5C grain refiner, developed crack lengths of 37.50, 37.75 and 39.25 mm at the pouring temperatures of 700, 750 and 780 °C, respectively. Microstructures of the specimens of these castings are shown in Fig. 9. The alloy exhibited an increase in crack length from 37.50 to 37.75 mm and the grain size also increased from 72 to 76 μm with an increase in pouring temperature from 700 to 750 °C. With further increase in the pouring temperature, grain size increased to 78 μm and the crack length increased to 39.25 mm.
3.2 Experiments with addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C as grain refiner
The A713 alloy castings, with the addition of Al- 3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiner, developed crack lengths of 4.0, 5.0 and 6.0 mm at the pouring temperatures of 700, 750 and 780 °C, respectively. Microstructures of these castings are shown in Fig. 10. The alloy exhibited an increase in the crack length from 4.0 to 5.0 mm, when the pouring temperature was raised from 700 to 750 °C. Accordingly, grain size also increased from 42 to 45 μm. With further increase in the pouring temperature, grain size increased to 49 μm and the crack length increased to 6.0 mm.
3.3 Experiments with addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C as grain refiner and Al-3.0Fe master alloy
It was noticed that all the A713 alloy castings, poured at different temperatures, with the additions of grain refiner and Al-3.0Fe master alloy, exhibited zero crack length. It was also observed that there has been a slight increment in the grain size with an increase in the pouring temperature. However, globular grains were noticed in the microstructures of the castings obtained at all the pouring temperatures, which are shown in Fig. 11. The grain sizes obtained were 37, 38 and 39 μm at the pouring temperatures of 700, 750 and 780 °C, respectively.
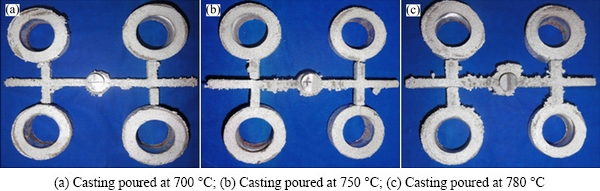
Fig. 8 Castings of A713 alloy with addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiner and Fe master alloy (zero crack length in all castings)
Table 2 Average crack lengths and grain sizes of A713 castings with addition of grain refiners
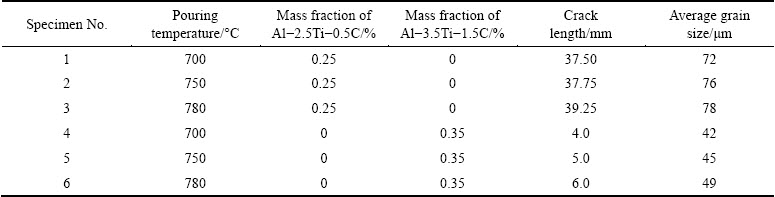
Table 3 Details of crack lengths and average grain sizes in A713 castings with addition of grain refiner and Fe master alloy
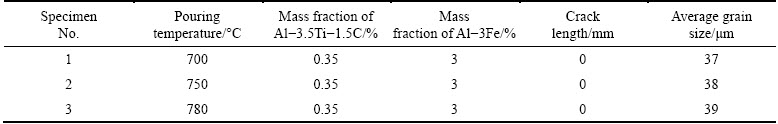

Fig. 9 OM images of A713 castings with addition of Al-2.5Ti-0.5C grain refiner, poured at 700 °C (a), 750 °C (b) and 780 °C (c)
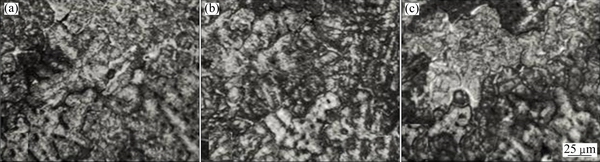
Fig. 10 OM images of A713 castings with addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiner, poured at 700 °C (a), 750 °C (b) and 780 °C (c)
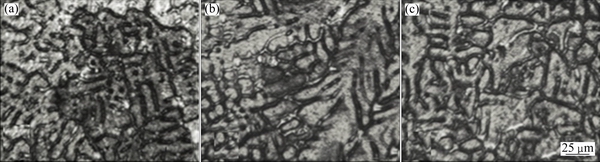
Fig. 11 OM images of A713 castings with addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiner and Al-3.0Fe master alloy poured at 700 °C (a), 750 °C (b) and 780 °C (c)
4 Discussion
4.1 Effect of grain refinement and pouring temperature
The above investigations were carried out with the addition of grain refiners with an aim to prevent hot tearing in A713 castings. Initially, the investigations were carried out with the addition of Al-2.5Ti-0.5C grain refiner, by varying the pouring temperatures. The grain size was minimized to some extent with this grain refiner. However, the crack length of the alloy was reduced at minimum pouring temperatures but not in an appreciable manner. Further experiments were carried out with the addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiner and varying the pouring temperatures. The crack lengths were minimized using both the grain refiners, especially, at minimum pouring temperatures. It was observed that titanium and carbon additions through the grain refiners into the A713 melt resulted in a refined equiaxed grains, promoting reduced hot tearing tendency. This was likely due to the fact that in the equiaxed grains (grain-refined) structures, mass feeding was facilitated and, consequently, healing of the tears occurred easily. The grain size was minimized to the possible extent with the grain refiner. Further, the crack length of the alloy was greatly reduced at the minimum pouring temperature but was not completely prevented.
4.2 Effect of grain refinement and residual element
In the further investigations, grain refiner along with iron, the residual element in the commercial aluminum, was added to the A713 alloy melt in the form of Al-3.0Fe master alloy. Iron reacted with aluminum and formed iron-aluminide, which underwent freezing at a temperature much higher than the temperature where zinc underwent freezing. From Al-Fe phase diagram [21], α(Al)-iron-aluminide eutectic underwent freezing at 652 °C. However, zinc underwent freezing at 419.5 °C. The dendrites undergoing shrinkage at this particular temperature were held together by the iron-aluminide, which acted as an anchoring agent. This resulted in the prevention of hot tearing.
Detailed analysis was carried out using the X-ray diffraction (XRD) for the specimens of A713 castings with the addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiner and Al-3.0Fe master alloy. The XRD pattern was mainly composed of Al3Ti0.75Fe0.25 and FeTi phases, which are shown in Fig. 12. Other FeC and Zn2Ti4C phases might not have affected the alloy system very much. Figure 13 shows the SEM microstructure analysis. It was found that there were some cluster compounds at the grain boundaries. Hence, it is difficult to pinpoint the exact compositions of the phases in the microstructure.
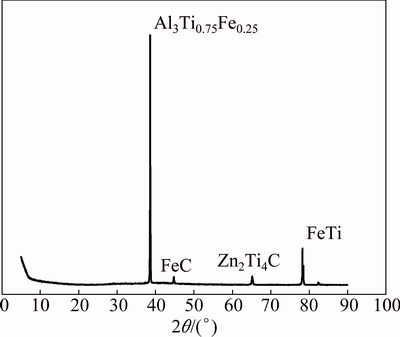
Fig. 12 XRD pattern of A713 alloy castings with addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiner and Al-3.0Fe master alloy
The EDAX chemical compositions at different grain boundaries (at positions A, B, C and D in Fig. 13) are shown in Table 4. The space between the interdendritic regions was reduced, which enabled interlocking between the neighbouring grains. The most pronounced Al3Ti0.75Fe0.25 and FeTi phases anchored the neighbouring grains, thus preventing the hot tearing in the aforesaid alloy. The SEM image showing the interlocking phenomenon is shown in Fig. 14 in which Al3Ti0.75Fe0.25 phase can be noticed. From the ternary phase diagram [23] of Al-Ti-Fe, it is evident that this Al3Ti0.75Fe0.25 phase frozen at about 670 °C, which is much higher than the freezing point of zinc. It can be inferred that this particular phase, which froze much earlier than zinc, became hard and strong and anchored the zinc grains, ultimately preventing the hot tearing. Thus, it can be confirmed that iron, which is the common residual element in commercial aluminum, together with titanium (grain refiner), enables to prevent hot tearing.
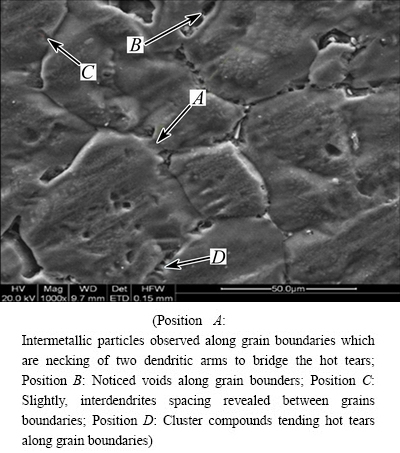
Fig. 13 SEM image of A713 alloy castings with addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C and Al-3.0Fe master alloy
Table 4 EDAX compositions of A713 cast specimens along positions A, B, C and D in Fig. 13
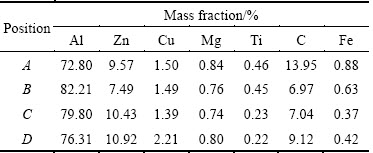

Fig. 14 SEM image showing different phases observed in A713 cast specimen with interlocking phenomenon along grain boundaries, after addition of Al-3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiner and Al-3.0Fe master alloy
5 Conclusions
1) Al-3.5Ti-1.5C grain refiner had significant influence on minimizing the hot tear tendency in A713 castings. At minimum pouring temperatures, the grain size was minimum, but the addition of grain refiner alone could not prevent hot tearing.
2) Iron, the common residual element in the commercial aluminum, together with the addition of grain refiner, could prevent hot tearing in the aforementioned alloy.
Acknowledgement
Anil Kumar BIRRU, the first author, would like to acknowledge the National Institute of Technology, Manipur, Imphal-795004, India.
References
[1] CAO G, KOU S. Hot tearing of ternary Mg-Al-Ca alloy castings [J]. Metallurgical and Material Transaction A, 2006, 37: 3647-3663.
[2] RYOSUK K, HARUAKI H, KENJI S, IZUMI M, ASADA J O, MAKOTO Y. Effects of grain refiner and grain size on the susceptibility of Al-Mg die casting alloy to cracking during solidification [J]. Journal of Material Processing Technology, 2009, 209: 210-219.
[3] WANG Ye-shuang, WANG Qu-dong, MA Chun-jiang, DING Wen-jiang, ZHU Yan-ping. Effects of Zn and RE additions on the solidification behavior of Mg-9Al magnesium alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 342: 178-182.
[4] ESKIN D G, KATGERMAN L. A quest for a new hot tearing criterion [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2007, 38: 1511-1519.
[5] SUYITNO, SAVRAN V I, KATGERMAN L, ESKIN D G. Effects of alloy composition and casting speed on structure formation and hot tearing during direct-chill casting of Al-Cu alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2004, 35: 3551-3556.
[6] Campbell J. Castings [M]. 2nd ed. Oxford: Butterworth- Heinemann, 1993.
[7] ESKIN D G, SUYITNO, KATGERMAN L. Mechanical properties in the semi-solid state and hot tearing of aluminum alloys [J]. Progress in Material Science, 2004, 49: 629-711.
[8] Ravi B. Metal casting [M]. 2nd ed. New Delhi: PHI, India, 2011.
[9] Lancaster J F. Metallurgy of welding [M]. 5th ed. London: Chapman & Hall, 1993.
[10] ZHANG J, SINGER R F. Hot tearing of nickel-based super alloys during directional solidification [J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50: 1869-1879.
[11] ZHANG J. Effect of Ti and Ta on hot cracking susceptibility of directionally solidified Ni-based super alloy IN792 [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2003, 48: 677-681.
[12] Kori S A. Studies on the grain refinement and modification of some hypoeutectic and eutectic Al-Si alloys [D]. Kharagpur: Indian Institute of Technology, 2000.
[13] REDDY N S, PRASAD R A K, CHAKRABORTY M, MURTY B S. Prediction of grain size of Al-7Si alloy by neural networks [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 391: 131-140.
[14] KARUNAKAR D B, NARESH RAI R A M, PATRA S, DATTA G L. Effects of grain refinement and residual elements on hot tearing in aluminum castings [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2009, 45: 851-858.
[15] GUO J, ZHU J Z. Prediction of hot tearing during alloy solidification [C]//Proceedings of the 5th Decennial International Conference on Solidification Processing. Sheffield, 2007: 549-553.
[16] SHI Zhao-xia, DONG Jian-xin, ZHANG Mai-cang, ZHENG Lei. Solidification characteristics and hot tearing susceptibility of Ni-based superalloys for turbocharger turbine wheel [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2014, 24: 2737-2751.
[17] XU Rong-fu, ZHENG Hong-liang, LUO Jie, DING Su-pei, ZHANG San-ping, TIAN Xue-lei. Role of tensile forces in hot tearing formation of cast Al-Si alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 2203-2207.
[18] LIU Zheng, ZHANG Si-bo, MAO Ping-li, WANG Feng. Effects of Y onhottearingsusceptibility of Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 907-914.
[19] HUANG Hao, FU Peng-huai, WANG Ying-xin, PENG Li-ming, JIANG Hai-yan. Effect of pouring and mold temperatures on hot tearing susceptibility of AZ91D and Mg-3Nd-0.2Zn-Zr Mg alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 922-929.
[20] ZHUYuan-zhi,WAN Qiang, LI Bing-liang, ZHOU Feng, ZHANG Ya-feng. Three-dimensional modeling of effect of surface intermetallic phase on surface defects of Al-Fe-Si aluminum foils during twin-roll casting [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 477-483.
[21] CHEN Wei, GUAN Ying-ping, WANG Zhen-hua. Hot deformation behavior of high Ti 6061 Al alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26: 369-377.
[22] BIRRU A K, BENNY KARUNAKAR D, MAHAPATRA M M. A study on the hot tearing susceptibility of Al-Cu, Al-Mg and Al-Zn alloys [J]. Transactions of Indian Institute of Metals, 2012, 65: 97-105.
[23] MASSALSKI T B. Binary alloy phase diagrams [M]. 2nd ed. Ohio: ASM International, 1990.
Anil Kumar BIRRU1, D. BENNY KARUNAKAR2
1. Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Manipur, Imphal-795004, India;
2. Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, Uttrakhand-247667, India
摘 要:为减少或防止热裂现象的产生,研究具有长程凝固区A713铸态铝合金的热裂行为。对添加不同晶粒细化剂如Al-2.5Ti-0.5C和Al-3.5Ti-1.5C的合金在不同浇铸温度(700、750和780 °C)条件下进行热裂实验。结果表明:添加晶粒细化剂Al-3.5Ti-1.5C能减少热裂现象的产生,但仅添加晶粒细化剂不能完全阻止A713铸态铝合金中热裂现象的产生。这与早期一些研究者得出的结论相矛盾。考察了铁元素对A713铸态铝合金热裂行为的影响。结果显示,同时添加晶粒细化剂和铁元素能减少A713铝合金的内部枝晶分离,从而沿晶界产生枝晶间的联锁。因此,铁元素作为工业铝中的一种杂质元素,能阻止A713铝合金热裂现象的产生。
关键词:铝合金;热裂;浇铸温度;晶粒细化
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Corresponding author: Anil Kumar BIRRU; Tel: +91-8331866984; E-mail: anilbirru@gmail.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64291-7

