文章编号:1004-0609(2011)01-0152-07
AlN陶瓷表面状态对Ti/Ni金属化薄膜粘结性能的影响
占玙娟, 周灵平1, 朱家俊, 李德意, 彭 坤
(湖南大学 材料科学与工程学院, 长沙 410082)
摘 要:采用电子束蒸发技术在AlN衬底上蒸镀Ti/Ni双层金属化薄膜,通过SEM、EDS和AES等方法分析抛光AlN表面状态及与金属化薄膜间的相互作用。结果表明:离子束清洗可去除AlN衬底表面疏松层,改变AlN衬底表面状态,提高衬底表面能。结合热蒸发原子的作用,膜基界面处Al、N和Ti元素之间产生相互扩散现象,AlN陶瓷和Ti膜的附着机制由未清洗前的简单附着改变为扩散附着,极大提高了金属化薄膜粘结性能,其拉脱强度达300 MPa以上,且无需后续退火处理。
关键词:氮化铝;表面状态;金属化;粘结性能;离子束
中图分类号:TB43,TN305 文献标志码:A
Influence of AlN ceramic surface state on adhesion of Ti/Ni metallized thin films
ZHAN Yu-juan, ZHOU Ling-ping1, ZHU Jia-jun, LI Di-yi, PENG Kun
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China)
Abstract: Metallized thin films of Ti and Ni on AlN substrate were deposited by E-beam evaporation. AlN ceramic surface state and interaction with metallized thin films were investigated by SEM, EDS and AES. The results indicate that a loosened layer of AlN substrate surface is wiped off by ion beam sputter-cleaning, which can change the state of AlN ceramic surface, and then increase the surface energy. Because of the increasing surface energy and the influence of hot evaporation atoms, the spread among Al, N and Ti exists at the interface, and the adherence mechanism for Ti film and AlN is changed from simple adhesion to spread adhesion during ion beam sputter-cleaning. Thus, the adhesion strength of metallized thin films is improved greatly. So the sample shows a high adhesion strength over 300 MPa and needs no anneal treatment.
Key words: aluminum nitride; surface state; metallization; adhesion strength; ion beams
AlN陶瓷具有高热导率、低介电常数和低介电损耗等优良物理性能,其膨胀系数和介电性能分别与Si和Al2O3陶瓷接近,是高密度和高性能电子封装领域的一种理想基板材料[1],但表面金属化是制约其广泛应用的因素之一。一般情况下,大部分金属与AlN陶瓷的润湿性很差,而在实际应用中,金属化层粘接牢固及其稳定性是至关重要的。Ti、Ta和W等金属因能与N形成高晶格能化合物,常被选作金属化体系的底层材料[2-5]。YASUMOTO等[6]认为在700~950 ℃退火时,Ti与AlN发生反应,并向AlN中扩散形成TiAl3,而N扩散到Ti膜中形成TiN,通过化合结合提高粘结强度。HE等[5, 7]认为AlN/Ti体系退火后Ti与AlN衬底反应生成TiAl3、TiN、Ti4N3-x和Ti2N,形成化合物附着层。金属化薄膜粘结性能及其稳定性取决于界面的附着机制,而膜/基界面的附着机制除与膜层材料有关外,还与陶瓷基体表面状态有关。长期以来,人们主要是通过金属化体系的选择和制备方法的改进来提高薄膜的粘结强度[8-10],而忽视了AlN陶瓷基体表面状态的影响。仅有少数文献研究了高温及化学溶液对AlN陶瓷表面金属化薄膜粘结强度的影 响[11],而AlN陶瓷基体表面状态对薄膜粘结强度的影响尚未见深入报道。目前,国内研制的金属化膜层粘结性能不稳定,其中一个重要的原因就是对AlN陶瓷表面状态未给予足够重视。AlN陶瓷基板表面状态一方面受制备和抛光方法的影响,另一方面受金属化镀膜前清洗方式的影响。因此,本文作者采用电子束蒸发镀膜的方法在AlN衬底上制备Ti/Ni双层薄膜,研究衬底表面状态对AlN表面Ti/Ni金属化薄膜粘结强度的影响。
1 实验
实验所用AlN衬底为国内市售产品,表面抛光,AlN衬底放入真空室前经乙酸乙酯浸泡、丙酮和酒精超声清洗、120 ℃烘干处理;镀膜前采用600 eV、70 mA的低能离子束对AlN衬底表面进行溅射清洗15 min,对比样未进行离子束清洗。
使用ZZS500型电子束蒸发镀膜机在AlN衬底上蒸镀金属化薄膜。本底真空度为5.0×10-4 Pa。衬底不加热不水冷,镀膜料为纯度99.99%的Ti颗粒和纯度99.99%的Ni颗粒。电子束蒸发参数如下:工作电压为6~8 kV,电子束流为100~150 mA。在AlN衬底上依次蒸镀约200 nm厚的Ti膜及约400 nm厚的Ni膜,镀膜过程中采用FCM-Ⅱ型膜厚控制仪监控膜厚。退火在管式炉中进行,保护气氛为Ar气,退火温度为400~ 550 ℃,保温时间1 h。
采用Hitachi S4800型扫描电子显微镜和Quanta 200型环境扫描电镜测试样品表面形貌和薄膜厚度,采用Horiba 7395-H型能谱仪测试金属化膜层及AlN
衬底表面成分分布。采用日本ULVAC-PHI公司生产的型号PHI-700 纳米扫描俄歇系统进行AES测试,使用同轴电子枪和CMA能量分析器,电子枪高压为 5 kV, 能量分辨率为0.1%,入射角为30°,分析室真空度为5.2×10-7 Pa。采用拉脱法测试金属化薄膜粘结性能,具体方法参照GB5210—85执行。
2 结果与分析
2.1 AlN陶瓷表面金属化薄膜粘结性能分析
AlN陶瓷表面Ti/Ni金属化薄膜粘结性能采用拉脱强度来表征,不同表面处理和退火处理的样品拉脱强度测试结果如表1所列。由表1可以看出,AlN衬底表面经离子束清洗后,所沉积的金属化薄膜的粘结性能得到根本改善。当衬底表面未采用离子束清洗时,样品从真空室中取出数分钟后,有些样品薄膜直接脱落;对于薄膜没有脱落的样品,用尖锐的镊子划破其金属化薄膜时,膜部分脱落且卷曲,可清晰看到白色的AlN衬底,其后在很短时间内其他部分膜也脱落卷起,直至表面所镀Ti/Ni双层膜全部卷起脱落。因此,可以认为其粘结强度几乎为0。当衬底表面采用离子束清洗时,情况就大不相同,使用尖锐的镊子一般无法划破金属化薄膜,即使尽力刻划也只能见到薄膜表面细小划痕,没有任何卷曲和脱落。拉脱试验表明,薄膜被拉脱部分是从AlN陶瓷内部剥离的,其膜层附着力值大于300 MPa,远超过对良好金属化膜层附着力(常温大于150 MPa)的要求[12]。因此,低能离子束清洗通过改变AlN陶瓷表面状态可极大地改善金属化薄膜的粘结强度,这正如文献[13]指出:离子清洗的重要作用之一是提高薄膜的附着力。
表1 AlN陶瓷表面Ti/Ni金属化薄膜拉脱强度
Table 1 Stretch strength of Ti/Ni metallized thin films on AlN substrate
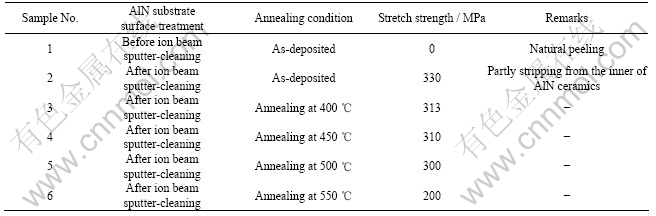
经离子束清洗的AlN表面所沉积的Ti/Ni薄膜样品经过400~550 ℃的退火,可以观察到样品表面形态和颜色发生了改变。未退火样品表面呈银灰色镜面;400和450 ℃退火样品表面仍然呈银灰色镜面,较未退火样品无明显改变;500 ℃退火样品表面呈银白色,无镜面;550 ℃退火样品表面呈灰色,无镜面,且样品中间部分颜色较边缘部更深。拉脱试验表明,经400~500 ℃的退火处理,金属化薄膜粘结性能没有明显变化,但当退火温度达到550 ℃时,其粘结强度显著降低。
2.2 离子束清洗对AlN衬底表面状态的影响
图1所示为未经离子束清洗和经离子束清洗的AlN衬底表面SEM像。由图1可以看出:未经离子束清洗的AlN衬底表面较疏松和粗糙(见图1(a));经离子束清洗后AlN衬底表面更加平整,凹坑和突起减少,去除了表面疏松层,同时降低了表面粗糙度(见图1(b))。这一结果也进一步表明本实验所选择的清洗工艺参数对AlN衬底有很好的溅射清洗作用。图2所示为 AlN表面沉积Ti/Ni金属化薄膜样品的断面SEM像,由图2可见:未经离子束清洗的AlN衬底和Ti膜接合处有一颗粒状物质组成的疏松层(见图2(a)中箭头标示处),这与图1(a)显示结果相对应,而AlN表面经离子束清洗后的膜基界面结合紧密(见图2(b))。图3所示为离子束清洗前后AlN表面的X射线能谱(EDS)分析结果。由图3可知:未经离子束清洗的AlN表面疏松层中N含量(摩尔分数)很高,达84.72%,尽管这是一种半定量结果,但也可判断其N与Al的原子比严重偏离1:1。这主要是AlN表面采用化学机械抛光引起Al原子的流失造成的,而经离子束清洗后AlN衬底表面N与Al的原子比约为1:1。由于离子束轰击具有选择性溅射和增强表层原子扩散效应,不会明显改变衬底表面成分,因此,离子束溅射清洗可去除AlN表面疏松层而得到新鲜表面。
2.3 AlN衬底表面状态对粘结强度的影响
AlN表面状态对金属化薄膜粘结性能的影响机制应从其界面相互作用来进行分析。图4所示为不同表面状态AlN表面沉积的Ti/Ni金属化薄膜的XRD谱。从图4可以看出:未经离子束清洗的AlN表面沉积

图1 未经离子束清洗和经离子束清洗的AlN衬底表面SEM像
Fig.1 SEM images of AlN substrate before ion beam sputter-cleaning (a) and after ion beam sputter-cleaning (b)
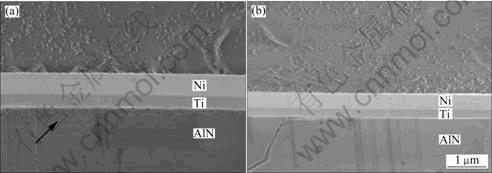
图2 未经离子束清洗和经离子束清洗的AlN表面Ti/Ni薄膜样品断面SEM像
Fig.2 SEM images of section of Ti/Ni metallized thin films on AlN substrate before ion beam sputter-cleaning (a) and after ion beam sputter-cleaning (b)

图3 未经离子束清洗和经离子束清洗的AlN表面的EDS谱
Fig.3 EDS spactra of AlN substrate before ion beam sputter-cleaning (a) and after ion beam sputter-cleaning (b)

图4 未经离子束清洗和经离子束清洗的AlN表面Ti/Ni薄膜样品的XRD谱
Fig.4 XRD patterns of Ti/Ni metallized thin films on AlN substrate before ion beam sputter-cleaning (a) and after ion beam sputter-cleaning (b)
Ti/Ni薄膜衍射峰较宽且强度低,表明其晶粒细小,甚至存在非晶相,同时还发现微弱的Ti的氮化物衍射峰,这可能是由于抛光AlN表层Al严重流失,含有大量N的悬挂键,这样Ti与N更容易形成化合物。经离子束清洗的样品的金属化薄膜Ti和Ni衍射峰尖锐且强度高,说明结晶程度好,由于清洗后疏松层去除,Ti层直接沉积于AlN衬底上,减少了与N发生反应的概率,难以形成Ti与N的化合物。未经离子束清洗的AlN表面沉积Ti/Ni薄膜的化合物产生在衬底失Al的疏松层,膜基界面存在大量的孔洞和气体等,沉积薄膜在应力作用下极易剥落。
图5所示为经离子束清洗的AlN表面沉积Ti/Ni薄膜样品断面线扫描EDS谱,扫描范围为图5(a)中黑

图5 经离子束清洗的AlN衬底表面沉积Ti/Ni薄膜样品断面及其线扫描EDS谱
Fig.5 SEM image of section of Ti/Ni metallized thin films on AlN substrate after ion beam sputter-cleaning (a) and line scanning EDS spectra(b)
线部分。由图5可知,样品的表层为Ni层,厚约400 nm,Ti层厚约为200 nm,即图5(a)中黑线部分从左往右0~0.4 μm处为Ni层,0.4~0.6 μm处为Ti层。由图5(b)可知;Ni元素在距表层0~0.4 μm处含量最高;Ti元素分布在距表层1.1~1.6 μm处出现一高峰,表明金属化薄膜表层中主要元素为Ni,未发现Ti和Al等向Ni层的明显扩散,而Ti元素分布峰值不是出现在第二层Ti层处,即表明Ti已向AlN内部扩散;在距表层0.4~0.6 μm处有少量N和Al元素,说明少量N和Al已扩散至Ti层中;Ni在距表层0.4~1.6 μm范围呈梯度分布,说明表层Ni向Ti层和AlN衬底表层扩散。
图6所示为经离子束清洗的AlN表面沉积Ti/Ni薄膜样品的AES元素分布分析结果,标样热氧化SiO2/Si的溅射速率为36 nm/min。由图6和Ti、Ni等元素的溅射产额[14]可大致推测:溅射时间20~25 min处为Ni-Ti界面,40~45 min处为Ti-AlN界面。这进一步说明金属化薄膜表层中主要元素为Ni,同时表层Ni向Ti层和AlN衬底扩散。Ti、Al和N元素在Ti-AlN界面周围相互扩散,其中N元素已扩散至Ni-Ti界面。

图6 经离子束清洗的AlN衬底表面沉积Ti/Ni薄膜样品的AES分析结果
Fig.6 AES analysis results of Ti/Ni metallized thin films on AlN substrate after ion beam sputter-cleaning
从热力学角度考虑,CARTER等[15]预测指出,在温度为573 K时,金属Ti与AlN陶瓷倾向发生下述固-固界面反应:
4Ti+3AlN=3TiN+TiAl3, 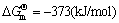
YASUMOTO等[6]认为上述反应存在3个过程,AlN的分解,Ti、Al和N的相互扩散以及化合物的形成。扩散驱动力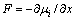 ,其中,负号表示扩散驱动力指向化学位降低的方向,x表示扩散距离,μi表示化学位,
,其中,负号表示扩散驱动力指向化学位降低的方向,x表示扩散距离,μi表示化学位,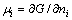 ,G为体系自由能。上述反应的体系自由能将促进Ti、Al和N的相互扩散。
,G为体系自由能。上述反应的体系自由能将促进Ti、Al和N的相互扩散。
离子束溅射清洗可去除衬底表面层,使之露出新鲜表面,提高了表面能;而在蒸发过程中,Ti先熔化后蒸发,蒸发源温度高于1 667 ℃,在真空环境中热的传导主要是以热辐射的形式,样品台未额外加热也可通过热辐射获得部分热能,即衬底温度会有一定程度的升高(热电偶测试表明可达100 ℃左右);蒸发过程中Ti原子或原子团的蒸发速率约为1 000 m/s,对应的平均动能为0.1~0.2 eV[15]。因此,热的Ti蒸发原子和原子团、AlN表面能的提高以及样品温度共同为上述扩散反应提供了驱动力。
薄膜的附着是范德华力、扩散附着和机械咬合等综合作用结果,有4种类型:简单附着、扩散附着、通过中间层附着和宏观效应附着[16]。未经离子束清洗的AlN表面沉积Ti/Ni薄膜样品中存在颗粒状物质组成的疏松层,该疏松层对金属化薄膜的粘结强度有重大影响。一方面,金属化薄膜与疏松层不可能粘结牢固,因为疏松层所含杂质和气体等可能扩散到膜基界面,破坏了界面啮合,并成为界面裂纹源;另一方面,疏松层本身可能成为断裂带,在外力作用下很容易将金属化膜层一起剥离衬底表面。因此,未清洗的AlN陶瓷和Ti膜中的分子范德华力大大减弱,仅仅依靠弱范德华力结合,故其粘结强度极差;而经离子束清洗的AlN表面沉积Ti/Ni薄膜样品界面存在相互扩散现象,形成了扩散附着,从而极大地提高了薄膜的粘结强度。
这种扩散附着在以前的研究中都必须通过高温退火来实现[5-6],但高温退火不仅导致金属化底层膜与衬底间的相互扩散,也常常引起多层膜之间的互扩散,如果没有有效的抗高温扩散阻挡层就会导致金属化多层膜体系的失效[17]。经400 ℃退火样品可观察到双层膜,界面清晰。经550 ℃退火样品观察不到双层膜,仅观察到混合的膜层,膜基界面及膜表面界线不平整。图7所示为经550 ℃退火样品的断面线扫描EDS谱。由图7可见,Ti元素分布峰值先于Ni峰出现,与图5中各元素分布峰出现顺序相反,Ni元素向膜基界面扩散,Ti元素向表层扩散,表层Ti含量高于Ni含量。说明在550 ℃退火后Ti层与Ni层已发生较严重的相互扩散,样品表面宏观及微观形貌均发生改变,直接造成粘结强度的降低。
拉脱强度测试及微观结构和成分分布分析表明,经400和450 ℃退火的金属化AlN样品的Ti/Ni多层膜未被破坏,但拉脱强度不但没有改善,反而略有降低;经550 ℃退火样品的Ti/Ni多层膜互扩散严重,拉脱强度显著降低。因此,经离子束清洗后沉积金属化薄膜无需后续的退火处理。

图7 经550 ℃退火的AlN表面Ti/Ni薄膜样品断面线扫描EDS谱
Fig.7 EDS thought line scanning of section of Ti/Ni metallized thin films on AlN substrate after annealing at 550 ℃
3 结论
1) 抛光AlN表面由于Al原子的大量流失,存在一层Al和N原子比严重失配的疏松层,沉积的金属化薄膜粘结强度极弱。
2) 离子束溅射清洗可以完全去除抛光AlN表面的疏松层,从而改变其表面状态,提高 AlN陶瓷表面能。在较低衬底温度(约100 ℃)下,热蒸发原子Ti与衬底AlN间界面可以产生扩散,膜基形成了扩散附着,极大地提高了其粘结强度,薄膜拉脱强度大于300 MPa,远超过相应规范对良好金属化膜层附着力常温大于150 MPa的要求。
3) 较低温度退火对Ti/Ni金属化薄膜粘结强度没有明显影响,但当退火温度达到550 ℃时,薄膜粘结强度显著降低。因此,AlN表面经离子束清洗后沉积的Ti/Ni金属化薄膜无需后续的退火处理。
References
[1] 张兆生, 卢振亚, 陈志武. 电子封装用陶瓷基片材料的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2008, 22(11): 16-20.
ZHANG Zhao-sheng, LU Zhen-ya, CHEN Zhi-wu. Research progress in ceramic substrate material for electronic packaging[J]. Materials Review, 2008, 22(11): 16-20.
[2] GAO Jie, LI Chang-rong, WANG Na, DU Zhen-min. Study on the interfacial reactions of Ti/AlN joints[J]. Rare Metals, 2008, 27(2): 175-180.
[3] 颜宁瑶. 从TiN铝化、Ti3Al氮化及TiN/Ti3Al界面反应探讨AlN/Ti界面生成机构[D]. 台北: 国立交通大学, 2007: 44-55.
YEN Nin-yau. Formation mechanisms of the AlN/Ti interface based upon nitrided Ti3Al, aluminized TiN and the interfacial reaction of TiN/Ti3Al[D]. Taibei: National Traffic University, 2007: 44-55.
[4] CHIU Chia-hsiang, LIN Chien-cheng. Microstructural development of the AlN/Ti diffusion couple annealed at 1 000 ℃[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(4): 1273-1280.
[5] HE Xiang-jun, TAO Kun, FAN Yu-dian. Interfacial reactions of metal films with AlN substrate[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 1996, 6(2): 81-85.
[6] YASUMOTO T, YAMAKAWA K, IWASE N, SHINOSAWA N. Reaction between AlN and metal thin films during high temperature annealing[J]. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 1993, 101(9): 969-973.
[7] HE Xiang-jun, YANG Si-ze, DU Yong, TAO Kun, FAN Yu-dian. Reaction layer formation at the interface between Ti or Zr and AlN[J]. Physica Status Solidi (A), 1996, 157(1): 99-106.
[8] CHIU C H, LIN C C. Formation mechanisms and atomic configurations of nitride phases at the interface of aluminum nitride and titanium[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2008, 23(8): 2221-2228.
[9] SHALISH I, SHAPIRA Y. Thermal stability of a Ti-Si-N diffusion barrier in contact with a Ti adhesion layer for Au metallization[J]. J Vac Sci Technol B, 1999, 17(1): 166-173.
[10] HOGLUND C, BECKERS M, SCHELL N, BORANY J V, BIRCH J, HULTMAN L. Topotaxial growth of Ti2AlN by solid state reaction in AlN/Ti(0001) multilayer thin films[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90: 174106-1-174106-3.
[11] 刘 刚, 王从香, 符 鹏. AlN基板表面处理对薄膜附着力的影响[J]. 电子元件与材料, 2005, 24(9): 44-47.
LIU Gang, WANG Cong-xiang, FU Peng. Influence of AlN ceramic substrate surface treatment on thin film adhesion[J]. Electronic Components and Materials, 2005, 24(9): 44-47.
[12] 黄岸兵, 崔 嵩, 张 浩. 功率电路基片首推氮化铝陶瓷[J]. 世界产品与技术, 2000(6): 50-52.
HUANG An-bing, CUI Song, ZHANG Hao. AlN ceramic: The most important power circuit substrate[J]. The World Product and Technology, 2000(6): 50-52.
[13] 张大伟, 张东平, 邵建达. 离子束清洗在激光薄膜中的应用[J]. 光学技术, 2005, 31(2): 238-240.
ZHANG Da-wei, ZHANG Dong-ping, SHAO Jian-da. The application of ion beam cleaning on the laser films[J]. Optical Technique, 2005, 31(2): 238-240.
[14] 刘金声. 离子束沉积薄膜技术与应用[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2003: 61-103.
LIU Jin-sheng. Ion beam deposition film technology and application[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 2003: 61-103.
[15] CARTER W B. Titamium and tantalum coatings on aluminum nitride[J]. J Vac Sci Technol A, 1992, 10(6): 3460-3464.
[16] 冯 亮, 李金山, 黄 磊, 常 辉, 崔予文, 周 廉. Ti-Mo二元合金在β相区的互扩散行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(10): 1766-1771.
FENG Liang, LI Jin-shan, HUANG Lei, CHANG Hui, CUI Yu-wen, ZHOU Lian. Interdiffusion behavior of Ti-Mo binary system in β phase[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(10): 1766-1771.
[17] 田民波. 薄膜技术与薄膜材料[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2006: 223-226.
TIAN Min-bo. Film technology and film material[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2006: 223-226.
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50501008)
收稿日期:2010-02-22;修订日期:2010-04-15
通信作者:周灵平,教授, 博士;电话:0731-88822663;E-mail:lpzhou@hnu.cn