搅拌速度对搅拌摩擦工艺制备的Cu/B4C表面复合材料显微组织和滑动磨损行为的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第1期
论文作者:R. SATHISKUMAR I. DINAHARAN N. MURUGAN S. J. VIJAY
文章页码:95 - 102
关键词:表面复合材料;搅拌摩擦工艺;搅拌速度;磨损率;显微组织
Key words:surface composite; friction stir processing; rotational speed; wear rate; microstructure
摘 要:采用搅拌摩擦工艺合成Cu/B4C表面复合材料,并分析搅拌速度对该复合材料显微组织和滑动磨损行为的影响。搅拌速度以200 r/min从800变化至1200 r/min,横向速度、轴向力、沟槽宽度及搅拌头外形保持不变。采用光学和扫描电子显微镜对所制备表面复合材料的显微组织进行观察。采用销盘滑动磨损试验装置研究该表面复合材料的滑动磨损性能。结果表明:搅拌速度对表面材料的面积和B4C颗粒的分布具有显著影响。在较高的搅拌速度下此复合材料中B4C颗粒分布均匀;而在低搅拌速度下B4C颗粒分布均匀性较差。此外,本文报道搅拌速度对复合材料的颗粒尺寸、硬度、磨损率、磨损表面和磨屑的影响。
Abstract: An attempt was made to synthesize Cu/B4C surface composite using friction stir processing (FSP) and to analyze the influence of tool rotational speed on microstructure and sliding wear behavior of the composite. The tool rotational speed was varied from 800 to 1200 r/min in step of 200 r/min. The traverse speed, axial force, groove width and tool pin profile were kept constant. Optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy were used to study the microstructure of the fabricated surface composites. The sliding wear behavior was evaluated using a pin-on-disc apparatus. The results indicate that the tool rotational speed significantly influences the area of the surface composite and the distribution of B4C particles. Higher rotational speed exhibits homogenous distribution of B4C particles, while lower rotational speed causes poor distribution of B4C particles in the surface composite. The effects of tool rotational speed on the grain size, microhardness, wear rate, worn surface and wear debris were reported.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 95-102
R. SATHISKUMAR1, I. DINAHARAN2, N. MURUGAN1, S. J. VIJAY3
1. Department of Mechanical Engineering, Coimbatore Institute of Technology, Coimbatore 641014, Tamil Nadu, India;
2. Department of Mechanical Engineering, V V College of Engineering, Tisaiyanvilai 627657, Tamil Nadu, India;
3. School of Mechanical Sciences, Karunya University, Coimbatore 641114, Tamil Nadu, India
Received 18 December 2013; accepted 7 August 2014
Abstract: An attempt was made to synthesize Cu/B4C surface composite using friction stir processing (FSP) and to analyze the influence of tool rotational speed on microstructure and sliding wear behavior of the composite. The tool rotational speed was varied from 800 to 1200 r/min in step of 200 r/min. The traverse speed, axial force, groove width and tool pin profile were kept constant. Optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy were used to study the microstructure of the fabricated surface composites. The sliding wear behavior was evaluated using a pin-on-disc apparatus. The results indicate that the tool rotational speed significantly influences the area of the surface composite and the distribution of B4C particles. Higher rotational speed exhibits homogenous distribution of B4C particles, while lower rotational speed causes poor distribution of B4C particles in the surface composite. The effects of tool rotational speed on the grain size, microhardness, wear rate, worn surface and wear debris were reported.
Key words: surface composite; friction stir processing; rotational speed; wear rate; microstructure
1 Introduction
Higher strength and wear resistance are essential properties desirable for industrial applications such as electrical sliding contacts, bearings, bushes and antifriction materials. Copper matrix composites (CMCs) have high potential for such applications [1,2]. But the reinforcement of hard, non deformable ceramic particles into the copper matrix results in the loss of ductility and toughness of CMCs. The nature and properties of component surface play a crucial role in determining its lifespan. If the surface of the components alone is modified by reinforcing with ceramic particles, the inner matrix will retain its ductility and toughness. Surface composite is the term used to denote such modified surfaces [3,4].
Friction stir processing (FSP) is a novel solid state technique to synthesize surface composites. MISHRA et al [5] developed FSP based on the principles of friction stir welding (FSW). One of the methods to produce surface composite using FSP is to make a groove of required depth, compact with ceramic particles, plunge the tool and traverse along the groove [6]. The frictional heat softens the matrix alloy and the ceramic particles distribute within the plasticized matrix alloy due to the stirring action of the tool. FSP has been effectively explored by several investigators to synthesize the surface composite on aluminum, magnesium, steel and titanium alloys [7]. BARMOUZ et al [8-11] successfully applied the FSP technique to synthesize Cu/SiC surface composites in recent times.
Some studies on the effect of tool rotational speed on the properties of surface composites synthesized by FSP were reported in literatures [8,12-17]. BARMOUZ et al [8] produced Cu/SiC surface composite by FSP and noticed insignificant change in the grain size with an increase in tool rotational speed. MAHMOUD et al [12] synthesized AA1050/SiC surface composite by FSP and reported the formation of defects at higher tool rotational speeds. LIM et al [13] prepared AA6111/CNT surface composite by FSP and found enhanced distribution of carbon nanotubes at higher tool rotational speeds. ASADI et al [14] produced AZ91/SiC surface composite using FSP and observed a decrease in the grain size with an increase in tool rotational speed. KURT et al [15] developed AA1050/SiC surface composite by FSP and concluded that increasing tool rotational speed affected the thickness of the surface composite, grain size, distribution of the precipitates and reinforcing particles. ASADI et al [16] fabricated AZ91/SiC surface composite using FSP and recorded an increase in grain size and a decrease in hardness when the tool rotational speed increased. AZIZIEH et al [17] produced AZ91/Al2O3 surface composite by FSP and observed an enhanced distribution of particles at high tool rotational speeds.
In the present work, an attempt is made to synthesize Cu/B4C surface composite by FSP and study the effect of tool rotational speed on the microstructure and sliding wear behavior of the surface composites. Boron carbide (B4C) has excellent chemical and thermal stability, high hardness and low density and is used for manufacturing of armor tank, neutron shielding material etc [18,19]. B4C coating is applied on copper and steel by various methods and is extensively used in nuclear industries [20].

Fig. 1 Optical micrograph of copper (a) and SEM image of B4C particles (b)
2 Experimental
Commercially available pure copper plates with 100 mm in length, 50 mm in width and 6 mm in thickness were used in this work. The optical micrograph of as- received copper plate which was etched with a color etchant containing 20 g chromic acid, 2 g sodium sulphate, 1.7 mL HCl (35%, mass fraction) in 100 mL distilled water is shown in Fig. 1(a). A groove of 0.7 mm in breadth and 2.5 mm in depth was cut in the middle of the plate using wire EDM and compacted with B4C powders. The SEM image of B4C particles is shown in Fig. 1(b). The average size of B4C particles is 4 μm. A pinless tool was initially employed to cover the top of the groove after filling with B4C particles to prevent the particles from scattering during the FSP. A tool made of double tempered hot working steel as shown in Fig. 2 was used in this work. The tool had a shoulder diameter of 20 mm, pin diameter of 5 mm and pin length of 3 mm. The FSP was carried out on an indigenously built FSW machine. The traverse speed (40 mm/min) and axial force (10 kN) were kept constant. The tool rotational speed was varied from 800 to 1200 r/min in step of 200 r/min. The FSP procedure to produce the surface composite is schematically shown in Fig. 3. The theoretical and actual volume fractions of B4C particles were calculated using the following expressions:
φt=(Sg/S)×100% (1)
φa=(Sg/Sc)×100% (2)
Sg=WgHg (3)
St=DpLp (4)
where φt and φa are the theoretical and actual volume fractions of B4C particles, respectively; Sg is the area of groove; St is the projected area of tool pin; Sc is the area of the surface composite; Wg is the groove width; Hg is the groove depth; Dp is the pin diameter; Lp is the pin length.

Fig. 2 Fabricated friction stir processing tool

Fig. 3 FSP procedure to fabricate surface composite
Specimens were prepared from the centre of the friction stir processed plates and polished as per standard metallographic procedure. The digital image of the macrostructure of the etched specimens was captured using a digital optical scanner. The microstructure was observed by a metallurgical microscope and a scanning electron microscope. The microstructures were analyzed using the software Image J. The interparticle spacing (d) was calculated as
d=[1-(Sg/100)]/N (5)
The grain size was measured following the procedure explained elsewhere [21]. The microhardness was measured using a microhardness tester at 500 g load applied for 15 s at various locations in the surface composite and its average value was calculated. The sliding wear rate of Cu/B4C surface composites was measured with a pin-on-disc wear apparatus (DUCOM TR20-LE) at room temperature according to ASTM G99-04 standard. The specimens with dimensions of 3 mm×5 mm×20 mm were prepared from the FSP zone by wire EDM. The wear test was conducted at a sliding velocity of 1.5 m/s, normal force of 30 N and sliding distance of 3 km. The polished surface of the pin was slid on a tempered chromium steel disc (AISI 52100). A computer aided data acquisition system was used to monitor the loss of height. The volumetric loss was calculated by multiplying the cross sectional area of the test pin with its loss of height. The wear rate was obtained by dividing volumetric loss to sliding distance. The worn surfaces of the test specimens were observed by SEM. The wear debris which were scattered on the face of the counter-face were carefully collected and characterized by SEM.
3 Results and discussion
A typical crown appearance of friction stir processed copper with B4C particles is shown in Fig. 4. The crown displays a smooth appearance without depressions or prominences. Semicircular features similar to those formed during the conventional milling process are visible. The rubbing action of the tool shoulder on the copper plate forms such features. The chosen process parameters are sufficient to produce a defect-free crown. The process parameters were chosen based on trial experiments. It is essential to obtain a smooth crown appearance because each surface irregularity or defects in the crown lead to another kind of internal defects in the surface composite.

Fig. 4 Typical crown appearance of friction stir processed copper surface composites reinforced with B4C particles
3.1 Macrostructure of Cu/B4C surface composites

Fig. 5 Macrostructures of friction stir zone containing Cu/B4C surface composites at different tool rotational speeds
Table 1 Effect of tool rotational speed on properties of Cu/B4C surface composite
The variation of macrostructures when tool rotational speed increases from 800 to 1200 r/min is shown in Fig. 5. The traverse speed and axial force were kept constant. It is evident from the figure that the tool rotational speed significantly influences the area of friction stir processed zone that contains the surface composite. The area of the surface composite increases as the tool rotational speed increases. The area of the surface composite was measured using an image analyzing software and the values are listed in Table 1. Frictional heat is generated as a result of rubbing of the tool shoulder on the copper plate. The quantity of frictional heat generated is dependent upon the tool rotational speed [22]. The frictional heat causes copper to plasticize. The amount of plasticized copper is dependent upon the available frictional heat. As the tool rotational speed increases, the frictional heat generated increases. The amount of plasticized copper subsequently increases. The increase in the area of the surface composite leads to a reduction in the actual volume fraction of B4C particles in the surface composite as presented in Table 1 because the same amount of B4C particles packed in the groove is to be distributed to more amount of plasticized copper.
The macrostructure of Cu/B4C surface composites does not have any defect as shown in Fig. 5. The vigorous stirring action of the rotating tool causes an interaction between the plasticized copper and the packed B4C particles, which results in the formation of the surface composite. The amount of plasticized material and its transportation during FSP play a crucial role to obtain defect-free surface composite. The frictional heat generated during processing and the tool movement governs the amount of plasticized material and its flow. The frictional heat and tool movement are dependent upon the process parameters such as tool rotational speed, traverse speed and groove width. The selected process parameters in this work yield sound Cu/B4C surface composites.
3.2 Microstructure of Cu/B4C surface composites
It is evident from Table 1 that the grains are coarsened as the tool rotational speed increases. The increase in tool rotational speed produces higher frictional heat that leads to coarsening of grains. The effect of tool rotational speed on the microstructure of Cu/B4C surface composites is shown in Fig. 6. The optical micrographs in Fig. 6 clearly reveal the distribution of B4C particles in the copper matrix. The distribution is not uniform at 800 r/min due to the presence of B4C clusters at several places. Each cluster consists of closely located B4C particles. When the tool rotational speed increases, the clusters gradually disappear. The optical micrograph of Cu/B4C surface composite synthesized at 1200 r/min shows (Fig. 6(c)) better distribution of B4C particles. The SEM images as presented in Fig. 7 show the variation of microstructures at different tool rotational speeds with higher magnification. The average spacing between B4C particles increases when the tool rotational speed increases (Table 1). The tool rotational speed does two more functions apart from frictional heat generation. Tool rotation stirs the plasticized materials as well as influences material flow behavior across the friction stir processed zone. The formation of clusters at 800 r/min can be attributed to insufficient stirring and inadequate material flow from the advancing side to the retreating side. The B4C particles that are packed in the groove do not mix with the plasticized copper properly. Hence, clusters form. As the tool rotational speed increases, the amount of material flow increases. The friction stir processing zone where the surface composite is formed is subjected to high plastic strain. High plastic strain and enhanced stirring break the clusters into finely dispersed particles in the copper matrix. The increase in inter particle spacing can be attributed to the decrease in the actual volume fraction.

Fig. 6 Optical micrographs of Cu/B4C surface composites at different tool rotational speeds

Fig. 7 SEM images of Cu/B4C surface composites at different tool rotational speeds
It is evident from micrographs shown in Figs. 6 and 7 that the tool rotational speed is an important process parameter that significantly dictates the distribution of B4C particles. The interface between B4C particles and copper matrix appears (Fig. 7) to be clean and is not surrounded by any voids or reaction products. BARMOUZ et al [9] observed a lot of porosities around SiC particles in the Cu/SiC surface composite synthesized using FSP technique. FRAGE et al [23] noticed reaction products around SiC particles in the Cu/SiC composite synthesized using liquid metallurgy route. No porosity or reaction products can be seen in the higher magnification micrographs of the Cu/B4C surface composites around B4C particles, which confirms the presence of a clear interface. A clean interface provides good bonding between B4C particles and copper matrix.
3.3 Microhardness of Cu/B4C surface composites
The effect of tool rotational speed on the microhardness of Cu/B4C surface composites is presented in Table 1. The microhardness of the composite decreases as the tool rotational speed increases. The distribution and the interparticle spacing significantly affect the hardness of the composite [24]. The microhardness is inversely proportional to the interparticle spacing. It is evident from Table 1 that the interparticle spacing increases as the tool rotational speed increases. The increase in surface area and the decrease in the actual volume fraction make the increase of the interparticle spacing as tool rotational speed increases. Therefore, the microhardness of the surface composite drops. Further, coarsening of grains contributes to the decrease in microhardness.
3.4 Sliding wear behavior of Cu/B4C surface composites
The effect of the tool rotational speed on the wear rate of Cu/B4C surface composite is listed in Table 1. The wear rate decreases as tool rotational speed increases. The volume loss of the material (Vl) due to sliding wear is given as follows according to the Archard’s law of wear [25]:
Vl=(awpds)/Hm (6)
where aw is the wear coefficient of the material; p is the applied load; ds is the sliding distance; Hm is the hardness of the material.
The above expression indicates that volume loss is inversely proportional to the hardness of the surface composite. The higher the hardness of the material is, the lower the wear rate will be. The decrease in microhardness of the Cu/B4C surface composite reduces the resistance to metal removal during sliding wear. Hence, the wear rate increases as tool rotational speed increases.
The effect of the tool rotational speed on the worn surface of Cu/B4C surface composite is shown in Fig. 8. The worn surfaces are observed to be uniform and covered with wear debris. The debris does not adhere to the worn surface due to the hard nature of the B4C particles. Some pits are observed (Fig. 8(a)) on the worn surface of Cu/B4C surface composite produced at 800 r/min. This can be attributed to the bulk removal of B4C particle clusters during sliding wear. There are no apparent cracks or subsurface deformation (Figs. 8(b) and (c)) on the worn surface of Cu/B4C surface composite produced at 1000 and 1200 r/min. Those worn surfaces are flat in nature. The substantial reduction of clusters and uniform distribution of B4C particle result in such a worn surface. It is evident from Fig. 8 that the wear mode appears to be abrasive irrespective of the tool rotational speed.

Fig. 8 SEM images of worn surface of Cu/B4C surface composites at different tool rotational speeds
The effect of the tool rotational speed on the wear debris of Cu/B4C surface composite is shown in Fig. 9, which displays fine size of wear debris. The average size of wear debris increases slightly as the tool rotational speed increases. There is no appreciable change in wear debris size irrespective of the tool rotational speed. The formation of fine wear debris can be attributed to the decreased probability of direct contact between the wear specimen and the counter-face due to the presence of B4C particles. The detached B4C particles during sliding convert two-body abrasion wear into three-body abrasion wear, which results in the formation of fine debris. The formation mechanism of fine debris is analogous to high energy ball milling. The drop in the actual volume fraction of B4C particles may lead to a reduction in the milling action as the tool rotational speed increases. Hence, the size of wear debris increases.
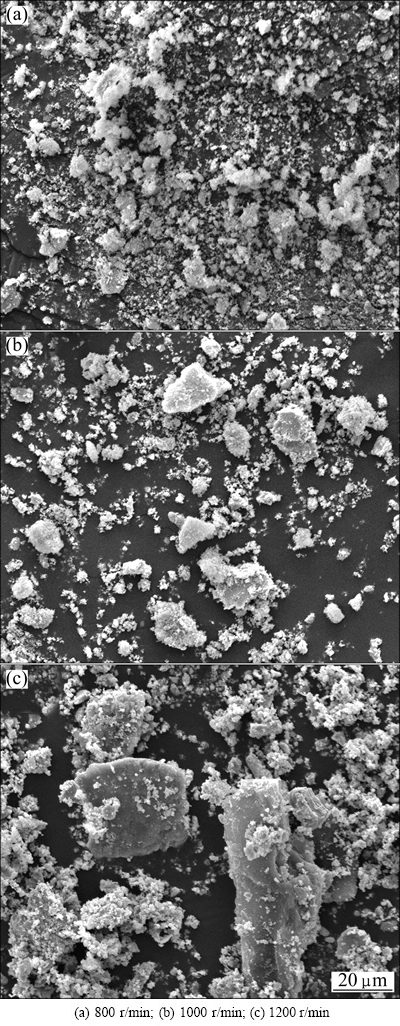
Fig. 9 SEM images of wear debris of Cu/B4C surface composite at different tool rotational speeds
4 Conclusions
1) The area of the Cu/B4C surface composite is significantly influenced by tool rotational speed. The area of the surface composite increases as tool rotational speed increases.
2) The distribution of B4C particles in the surface composites is influenced by the tool rotational speed. Low tool rotational speed results in the formation of B4C particle cluster and vice versa.
3) The microhardness of the surface composite decreases as the tool rotational speed increases.
4) The wear rate of the surface composite increases as the tool rotational speed increases. The worn surface shows the presence of pits at low tool rotational speeds. The size of wear debris increases slightly as the tool rotational speed increases.
References
[1] RAJKUMAR K, ARAVINDAN S. Tribological performance of microwave sintered copper- TiC-graphite hybrid composites [J]. Tribology International, 2011, 44(4): 347-358.
[2] RAJKUMAR K, ARAVINDAN S. Tribological studies on microwave sintered copper–carbon nanotube composites [J]. Wear, 2011, 270(9-10): 613-621.
[3] ATTIA A N. Surface metal matrix composites [J]. Materials and Design, 2001, 22(6): 451-457.
[4] ROMANKOV S, HAYASAKAB Y, SHCHETININC I V, YOON J M, KOMAROVD S V. Fabrication of Cu-SiC surface composite under ball collisions [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2011, 257(11): 5032-5036.
[5] MISHRA R S, MA Z Y, CHARIT I. Friction stir processing: A novel technique for fabrication of surface composite [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 341(1-2): 307-310.
[6] SOLEYMANI S, ZADEH A A, ALIDOKHT S A. Microstructural and tribological properties of Al5083 based surface hybrid composite produced by friction stir processing [J]. Wear, 2012, 278-279: 41-47.
[7] ARORA H S, SINGH H, DHINDAW B K. Composite fabrication using friction stir processing—A review [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2012, 61(9-12): 1043-1055.
[8] BARMOUZ M, GIVI M K B, SEYFI J. On the role of processing parameters in producing Cu/SiC metal matrix composites via friction stir processing: Investigating microstructure, microhardness, wear and tensile behavior [J]. Materials Characterization, 2011, 62(1): 108-117.
[9] BARMOUZ M, ASADI P, GIVI M K B, TAHERISHARGH M. Investigation of mechanical properties of Cu/SiC composite fabricated by FSP: Effect of SiC particles size and volume fraction [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528(3): 1740-1749.
[10] BARMOUZ M, GIVI M K B. Fabrication of in-situ Cu/SiC composites using multi-pass friction stir processing: Evaluation of microstructural, porosity, mechanical and electrical behavior [J]. Composites: Part A, 2011, 42(10): 1445-1453.
[11] BARMOUZ M, GIVI M K B, JAFARI J. Influence of tool pin profile on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of Cu/SiC metal matrix composites produced by friction stir processing [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 154-155: 1761-1766.
[12] MAHMOUD E R I, IKEUCHI K, TAKAHASHI M. Fabrication of SiC particle reinforced composite on aluminium surface by friction stir processing [J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2008, 13(7): 607-618.
[13] LIM D K, SHIBAYANAGI T, GERLICH A P. Synthesis of multi-walled CNT reinforced aluminium alloy composite via friction stir processing [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 507(1-2): 194-199.
[14] ASADI P, FARAJI G, BESHARATI M K. Producing of AZ91/SiC composite by friction stir processing (FSP) [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2010, 51(1-4): 247-260.
[15] KURT A, UYGURB I, CETE E. Surface modification of aluminium by friction stir processing [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2011, 211(3): 313-317.
[16] ASADI P, GIVI M K B, ABRINIA K, TAHERISHARGH M, SALEKROSTAM R. Effects of SiC particle size and process parameters on the microstructure and hardness of AZ91/SiC composite layer fabricated by FSP [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2011, 20(9): 1554-1562.
[17] AZIZIEH M, KOKABI A H, ABACHI P. Effect of rotational speed and probe profile on microstructure and hardness of AZ31/Al2O3 nanocomposites fabricated by friction stir processing [J]. Materials and Design, 2011, 32(4): 2034-2041.
[18] KALAISELVAN K, MURUGAN N, PARAMESWARAN S. Production and characterization of AA6061–B4C stir cast composite [J]. Materials and Design, 2011, 32(7): 4004-4009.
[19] GUO J, AMIRA S, GOUGEON P, CHEN X G. Effect of the surface preparation techniques on the EBSD analysis of a friction stir welded AA1100-B4C metal matrix composite [J]. Materials Characterization, 2011, 62(9): 865-877.
[20] NANOBASHVILI S, MATEJICEK J, ZACEK F, STOCKEL J, CHRASKA P, BROZEK V. Plasma sprayed coatings for RF wave absorption [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2002, 307-311(2): 1334-1338.
[21] SATHISKUMAR R, MURUGAN N, DINAHARAN I, VIJAY S J. Characterization of boron carbide particulate reinforced in situ copper surface composites synthesized using friction stir processing [J]. Materials Characterization, 2013, 84: 16-27.
[22] RAJAKUMAR S, MURALIDHARAN C, BALASUBRAMANIAN V. Influence of friction stir welding process and tool parameters on strength properties of AA7075-T6 aluminium alloy joints [J]. Materials and Design, 2011, 32(2): 535-549.
[23] FRAGE N, FROUMIN N, AIZENSHTEIN M, DARIEL M P. Interface reaction in the B4C(Cu-Si) system [J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52(9): 2625-2635.
[24] IZADI H, NOLTING A, MUNRO C, BISHOP D P, PLUCKNETT K P, GERLICH A P. Friction stir processing of Al/SiC composites fabricated by powder metallurgy [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2013, 213: 1900-1907.
[25] KUMAR S, SARMA V S, MURTY B S. Influence of in situ formed TiB2 particles on the abrasive wear behaviour of Al-4Cu alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 465(1-2): 160-164.
R. SATHISKUMAR1, I. DINAHARAN2, N. MURUGAN1, S. J. VIJAY3
1. Department of Mechanical Engineering, Coimbatore Institute of Technology, Coimbatore 641014, Tamil Nadu, India;
2. Department of Mechanical Engineering, V V College of Engineering, Tisaiyanvilai 627657, Tamil Nadu, India;
3. School of Mechanical Sciences, Karunya University, Coimbatore 641114, Tamil Nadu, India
摘 要:采用搅拌摩擦工艺合成Cu/B4C表面复合材料,并分析搅拌速度对该复合材料显微组织和滑动磨损行为的影响。搅拌速度以200 r/min从800变化至1200 r/min,横向速度、轴向力、沟槽宽度及搅拌头外形保持不变。采用光学和扫描电子显微镜对所制备表面复合材料的显微组织进行观察。采用销盘滑动磨损试验装置研究该表面复合材料的滑动磨损性能。结果表明:搅拌速度对表面材料的面积和B4C颗粒的分布具有显著影响。在较高的搅拌速度下此复合材料中B4C颗粒分布均匀;而在低搅拌速度下B4C颗粒分布均匀性较差。此外,本文报道搅拌速度对复合材料的颗粒尺寸、硬度、磨损率、磨损表面和磨屑的影响。
关键词:表面复合材料;搅拌摩擦工艺;搅拌速度;磨损率;显微组织
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Corresponding author: R. SATHISKUMAR; Tel: +91-9943350848; E-mail: sathiscit2011@gmail.com, rsathiskumar@hotmail.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63583-X

