聚合物对微细粒蛇纹石的絮凝作用及机理
冯其明,龙涛,卢毅屏,欧乐明,张国范
(中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:通过浊度法沉降实验、Zeta电位测试和红外光谱测试,考察羧甲基纤维素(CMC)、聚丙烯酸钠(PAAS)、聚丙烯酰胺(PAM) 3种聚合物对金川硫化铜镍矿主要脉石矿物即蛇纹石的絮凝作用,并对上述不同类型聚合物在矿物表面的吸附机理进行分析。研究结果表明:CMC和PAM在蛇纹石表面的吸附以物理作用为主,而PAAS能够通过化学作用吸附在蛇纹石表面,进而通过聚合物分子的架桥作用使蛇纹石微细颗粒发生絮凝;颗粒间静电相互作用对聚合物的絮凝效果影响显著,静电斥力越小,絮凝效果越好;反之静电斥力越大,絮凝效果越差。
关键词:蛇纹石;聚合物;絮凝;浊度;红外光谱
中图分类号:TD9 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)09-2531-06
Mechanism of polymers effect on flocculation behavior of fine serpentine
FENG Qi-ming, LONG Tao, LU Yi-ping, OU Le-ming, ZHANG Guo-fan
(School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The effects of polymers, including CMC, PAAS and PAM, on the flocculation of serpentine gangue resulted from Jinchuan copper-nickel sulphide were investigated by turbidimetric sedimentation tests, zeta-potential measurements and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. And then the adsorption mechanism of the polymers on the serpentine surface was analyzed. The results show that CMC and PAM are mainly physically bonded onto the serpentine surface, but PAAS is chemically adsorbed onto the serpentine surface. The flocculation of the fine serpentine comes from the bridging action of adsorbed polymers molecules. Electrostatic interaction between the particles influences the flocculation behavior of the fine serpentine obviously. Less electrostatic repulsion induces the better flocculation of the fine serpentine, and vice versa.
Key words: serpentine; polymer; flocculation; turbidity; infrared spectrum
金川是我国最大的金属镍原料基地,拥有大型的硫化铜镍矿床。该类型矿床中,除有用矿物镍黄铁矿和黄铜矿外,还存在蛇纹石等硅酸盐脉石。其中,蛇纹石在破碎过程中易泥化,产生的微细粒级蛇纹石容易通过机械夹带进入浮选精矿[1-3],是导致精矿中镁含量过高的主要原因。因此,消除微细蛇纹石对硫化矿浮选的影响具有十分重要的意义。目前,针对金川镍精矿降镁的研究大多以开发蛇纹石脉石的抑制剂为主。邱显扬等[4]认为羧甲基纤维素能选择性吸附在蛇纹石表面,通过增强其亲水性而使蛇纹石受到抑制。夏启斌等[5]认为,六偏磷酸钠能增大蛇纹石表面电位的绝对值,提高颗粒间静电排斥作用能,从而使蛇纹石分散,降低精矿中的氧化镁含量。王德燕等[6]研究了水玻璃对蛇纹石脉石的抑制作用机理,认为硅酸钠水解后生成的胶状二氧化硅吸附于蛇纹石矿泥表面使其表面亲水性增大,从而降低可浮性。这些抑制剂都在一定程度上起到了降低镍精矿中氧化镁含量的作用,但对镍精矿降镁还需要开展更细致深入的研究。事实上,浮选过程中通过凝聚或絮凝等手段[7],使脉石矿物选择性聚团,可以减少夹带对目的矿物浮选的影响。其中,一些聚合物的分子链上有大量的活性官能团,这些官能团通过静电作用、氢键或形成化学键等方式选择性作用于矿物表面,并通过架桥作用将微细颗粒聚集在一起,形成大而松散的絮团,达到絮凝的目的[8-12]。利用聚合物的絮凝作用,不但能使微细矿物表观粒度增大,还能使脉石矿物表面亲水,从而使机械夹杂的程度降到最低,更有利于浮选过程的进行[13]。同时,有机絮凝剂在后续的冶炼中可受热分解,不会带入新的杂质。因此,采用有机聚合物对微细蛇纹石进行选择性絮凝,降低其对有用矿物浮选的影响,可以为硫化铜镍矿浮选精矿的降镁研究提供新的思路。在此,本文作者通过浊度法沉降实验、Zeta电位测试和红外光谱测试,研究阴离子型聚合物羧甲基纤维素(CMC)、聚丙烯酸钠(PAAS)和非离子型聚合物聚丙烯酰胺(PAM) 3种聚合物对微细蛇纹石的絮凝作用,并对其作用机理进行分析。
1 实验
1.1 矿样与试剂
实验所用蛇纹石取自江苏东海蛇纹石矿。块矿经锤碎手选后用瓷球磨、搅拌磨磨细,得到90%粉末粒径小于14 μm的微细粒蛇纹石单矿物样品。样品经X线衍射分析和化学分析,其纯度达90%以上。表1所示为蛇纹石单矿物试样主要元素的化学分析结果。
表1 蛇纹石单矿物试样化学分析结果(质量分数)
Table 1 Chemical analysis results of serpentine samples %

实验用盐酸和氢氧化钠为分析纯,羧甲基纤维素(CMC)、聚丙烯酰胺(PAM)和聚丙烯酸钠(PAAS)为化学纯。实验用水为一次蒸馏水。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 浊度法沉降实验
采用浊度来表征蛇纹石矿物在溶液中的聚集/分散状态。用天平称取微细粒蛇纹石100 mg,加入水溶液中并添加一定浓度的聚合物,搅拌5 min,再放入100 mL沉降筒沉降3 min,抽取上层悬浊液20 mL,放入试样瓶中,采用WGZ-3(3A) 散射光浊度仪测量浊度(浊度单位为NTU,1 mg/L SiO2悬浊液的浊度为1 NTU)。浊度较大时,表示沉降体系上层悬浊液中矿物颗粒数量较多,蛇纹石处于分散状态;反之,当浊度较小时,代表上层悬浊液中矿物颗粒数量较少,蛇纹石悬浊液处于聚集状态。
1.2.2 Zeta电位测试
将蛇纹石单矿物样品细磨至粒径小于2 μm,称取30 mg样品并将其放入烧杯中,加入50 mL蒸馏水,加入聚合物药剂并调节pH,用磁力搅拌器搅拌5 min,然后采用Coulter Delsa440sx Zeta电位分析仪进行Zeta电位测量,每个点均测3次后取平均值。实验所用支持电解质为1 mmol/L的KNO3溶液。
1.2.3 红外光谱测试
采用Nicolet FTIR-740型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪测定聚合物及其与蛇纹石作用前后的红外光谱。试样制备过程是:将蛇纹石单矿物样品细磨至粒径小于 2 μm,称取一定量的该样品加入合适浓度的聚合物溶液中,充分搅拌后,静置一段时间,待矿物完全沉降后,用吸管吸出上层清液,然后用蒸馏水充分洗涤矿物,固液分离后自然晾干,进行红外光谱检测。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 pH对微细粒蛇纹石聚集行为的影响
图1所示为pH对微细粒蛇纹石聚集行为的影响。由图1中曲线1可以看出:在没有添加聚合物的水溶液中,pH<7时,浊度较大,蛇纹石颗粒间分散性较好;在pH=7附近时,浊度迅速降低,蛇纹石颗粒间聚集行为加强;当7<pH<12时,浊度保持稳定且略有下降,颗粒处于聚集状态;当pH>12时,颗粒又逐渐恢复到分散状态。
加入聚合物CMC,PAAS和PAM后,由图1中曲线2~4可以看出:沉降体系上层悬浊液的浊度降低,微细蛇纹石颗粒间的同相凝聚行为得到加强。但当 pH<6时,聚合物对蛇纹石颗粒的絮凝作用较弱,悬浊液浊度的降低不足100 NTU;当6<pH<8时,浊度迅速降低,蛇纹石微细颗粒迅速凝聚,聚合物的絮凝作用得到加强;当8<pH<12时,浊度稳定在一定范围,出现一个平台区,微细粒蛇纹石矿物颗粒絮凝作用非常强烈;但当pH>12后,浊度又有所回升,絮凝作用有所减弱。从图1还可以看出:在相同药剂浓度条件下,pH<6时,这3种聚合物的絮凝效果相似,但当pH>8时,PAM与PAAS的絮凝效果比CMC的好,前者能使悬浊液的浊度下降至260 NTU左右,而后者只能使浊度降低到400 NTU左右。
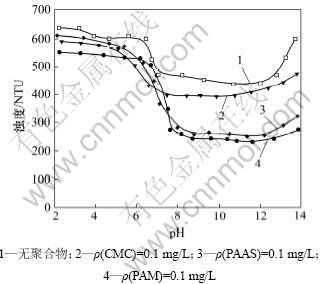
图1 pH对微细粒蛇纹石聚集行为的影响
Fig.1 Effect of pH on aggregation behavior of fine serpentine
2.2 聚合物用量对微细粒蛇纹石絮凝效果的影响
图2所示为pH=9时,聚合物用量对微细粒蛇纹石絮凝效果的影响。从图2可以看出:随着聚合物用量的增加,沉降体系上层悬浊液的浊度明显降低,聚合物对微细粒蛇纹石颗粒的絮凝作用显著增强;当聚合物用量增大到一定值后,悬浊液的浊度逐渐稳定下来,不再发生变化。对CMC来说,浊度曲线的拐点出现在用量为3 mg/L附近,在用量小于3 mg/L的阶段,随CMC用量增加,浊度下降很快,在用量为3~ 6 mg/L时,浊度下降趋势变缓,当用量大于6 mg/L时,浊度不再发生明显变化。对于PAM和PAAS来说,浊度曲线的拐点出现在0.5 mg/L左右。当用量大于1 mg/L之后,浊度值不再发生明显变化。3种聚合物对蛇纹石的絮凝作用均有一个临界值,当达到临界值后再继续增加聚合物的用量,浊度稳定下来,不会继续下降。临界值越低,絮凝效果越好。CMC只能使体系的浊度降至100 NTU左右,有部分微细蛇纹石颗粒仍然保持分散状态;而PAM能使体系的浊度降至 0 NTU附近,体系中几乎没有分散状态的蛇纹石颗粒,絮凝效果非常好。3种聚合物对蛇纹石絮凝效果由强到弱依次为:PAM,PAAS,CMC。
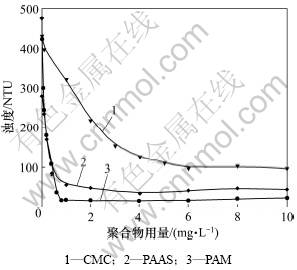
图2 聚合物用量对微细粒蛇纹石絮凝效果的影响(pH=9)
Fig.2 Effect of polymer concentration on flocculation behavior of serpentine at pH=9
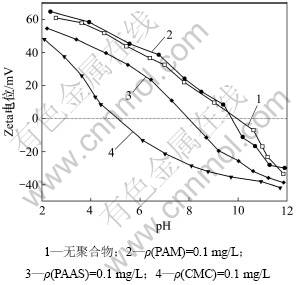
图3 不同pH时聚合物对蛇纹石Zeta电位的影响
Fig.3 Effect of polymers on Zeta-potential of serpentine at different pH values
2.3 聚合物对微细粒蛇纹石的絮凝作用机理
图3所示为3种聚合物对蛇纹石Zeta电位的影响。图3中曲线1所示为不同pH条件下蛇纹石自身的Zeta电位,可以看出:随着pH的增加,蛇纹石的Zeta电位不断降低,并在pH=10附近由正变为负,可知蛇纹石的零电点为10。结合图1可知:当pH<7时,蛇纹石表面带较强的正电,颗粒之间斥力较大,在水溶液中分散性较好;当7<pH<12时,蛇纹石表面电荷的绝对值较低,颗粒间斥力降低,分散性变差;当 pH>12时,蛇纹石表面负电荷将继续增加,颗粒间斥力上升,蛇纹石微细粒间的同相凝聚减弱。
图3中曲线2所示为不同pH条件下蛇纹石与PAM作用后的Zeta电位。PAM为非离子型有机高分子聚合物,它对蛇纹石的Zeta电位没有产生明显的影响。图3中曲线3所示为不同pH条件下蛇纹石与PAAS作用后的Zeta电位。PAAS为阴离子型有机高分子聚合物,解离的—COO-能降低蛇纹石的表面电位,使矿物等电点向左移动到8附近。图3中曲线4所示为不同pH条件下蛇纹石与CMC作用后的Zeta电位。CMC为阴离子型有机高分子聚合物,与PAAS相比,CMC有—COO-和—O- 2种阴离子基团,对蛇纹石表面电位的影响更大,使矿物等电点向左移动到5附近。
有机高分子聚合物的分子量很大,可通过长碳链上的活性基团吸附在蛇纹石微粒颗粒表面,当其他颗粒接触到聚合物分子的外伸部分,就会发生同样的附着[7]。颗粒间借助聚合物的这种架桥作用彼此凝聚起来,沉降速度增加,颗粒表观粒度增大,微细矿物颗粒数量减少,蛇纹石的机械夹杂减轻,对硫化矿物可浮性的影响降低。聚合物的架桥作用受到颗粒表面电荷的影响[14],结合图1与图3可知:当pH<5时,蛇纹石颗粒表面带强正电,静电斥力较大,矿物颗粒间距离较远,超过聚合物分子链的链环、链尾所能达到的距离,此时蛇纹石微细颗粒的凝聚与分散状态受DLVO理论支配[15],聚合物的架桥不起主要作用,絮凝效果有限;当pH>8时,蛇纹石表面电荷的绝对值降低,颗粒间静电斥力减小,彼此距离缩短,架桥作用显著,蛇纹石颗粒通过聚合物发生强烈的絮凝。
图4所示为3种聚合物的红外吸收光谱。图4中曲线1所示为聚丙烯酸钠的红外谱图,其中3 432.6 cm-1处的峰为羟基的伸缩振动峰,2 945.5 cm-1处的峰为—CH3的伸缩振动峰,1 585.7和1 410.0 cm-1处的峰分别为羧基的不对称和对称伸缩振动峰[16];图4中曲线2所示为聚丙烯酰胺的红外谱图,3 428.2和 2 925.8 cm-1处的峰分别对应—OH和—CH3的伸缩振动,1 664.1,1 620.1和1 406.4 cm-1处的峰分别为酰胺键中C=O,N—H和C—N的特征吸收峰[17];图4中曲线3所示为羧甲基纤维素的红外谱图,3 442.2和2 918.2 cm-1处的峰分别对应—OH和—CH3的伸缩振动,1 623.4和1 423.2 cm-1处的峰分别为羧基的不对称和对称伸缩振动峰,1 057.9和1 018.6 cm-1处的峰分别对应C—O—C和C—O的弯曲振动[18]。
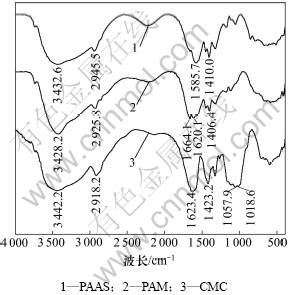
图4 聚合物的红外光谱
Fig.4 FTIR spectra of polymers
图5所示为蛇纹石与聚合物作用前后的红外光谱。图5中曲线1所示具有典型的蛇纹石红外光谱特 征[19-20],在3 686.0和612.3 cm-1处的峰分别对应 Mg—OH的伸缩和弯曲振动,975.8和451.1 cm-1处的峰分别为Si—O的伸缩和弯曲振动峰。蛇纹石与PAAS作用后(见图5中曲线2),在1 565.6 cm-1处出现了新的吸收峰,与PAAS光谱中1 585.7 cm-1处的羧基吸收峰相比,向低频端移动了20.1 cm-1,说明PAAS在蛇纹石表面发生了化学吸附[16],推测PAAS上的羧基与蛇纹石表面的镁生成了螯合产物;蛇纹石与PAM作用后(见图5中曲线3),在1 665.3 cm-1处出现了吸收峰,与PAM光谱中1 664.1 cm-1处的C=O振动峰对应,说明PAM在蛇纹石表面产生了物理吸附,推测其原因可能是PAM中的—NH2与蛇纹石表面的 Mg—OH发生了氢键吸附[15, 17, 21];蛇纹石与CMC作用后(见图5中曲线4),并没有出现明显的新吸收峰。结合图3中曲线4,CMC的加入显著降低了蛇纹石的Zeta电位,可知CMC通过物理吸附的方式作用于蛇纹石表面[18, 22]。
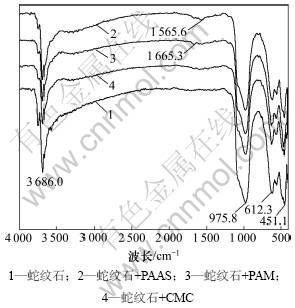
图5 蛇纹石与聚合物作用前后的红外光谱
Fig.5 FTIR spectra of serpentine in absence and presence of polymers
3 结论
(1) 3种聚合物PAM,PAAS和CMC对微细粒蛇纹石均有良好的絮凝作用,絮凝效果由强到弱依次为:PAM,PAAS,CMC。聚合物对蛇纹石的絮凝作用受pH影响较大,8<pH<12时絮凝效果最好。
(2) 蛇纹石的零电点为10。PAM为非离子型高分子聚合物,它的吸附对蛇纹石的Zeta电位影响不大; PAAS与CMC为阴离子型高分子聚合物,它们的吸附能使蛇纹石的Zeta电位降低。
(3) 3种聚合物对蛇纹石的絮凝效果受颗粒间静电力的影响。当颗粒间静电斥力较大时,聚合物的架桥作用有限,絮凝效果一般;当颗粒间静电斥力较小时,聚合物的架桥作用显著,絮凝效果强烈。
(4) 聚合物PAAS在蛇纹石表面的吸附为化学吸附,PAM与CMC在蛇纹石表面的吸附为物理吸附。
参考文献:
[1] 唐敏, 张文彬. 低品位铜镍硫化矿浮选中蛇纹石的行为研究[J]. 昆明理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2001, 26(3): 74-77.
TANG Min, ZHANG Wen-bin. A study on behavior of serpentine in the flotation of low-grade copper-nickel sulfide[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology: Science and Technology, 2001, 26(3): 74-77.
[2] Bremmell K E, Fornasiero D, Ralston J. Pentlandite-lizardite interactions and implications for their separation by flotation[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2005, 252(2/3): 207-212.
[3] 卢毅屏, 龙涛, 冯其明, 等. 微细粒蛇纹石的可浮性及其机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(8): 1493-1497.
LU Yi-ping, LONG Tao, FENG Qi-ming, et al. Flotation and its mechanism of fine serpentine[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(8): 1493-1497.
[4] 邱显扬, 俞继华, 戴子林. 镍黄铁矿浮选中抑制剂的作用[J]. 广东有色金属学报, 1999, 9(2): 86-89.
QIU Xian-yang, YU Ji-hua, DAI Zi-lin. Action of depressants in pentlandite flotation[J]. Journal of Guangdong Non-Ferrous Metals, 1999, 9(2): 86-89.
[5] 夏启斌, 李忠, 邱显扬, 等. 六偏磷酸钠对蛇纹石的分散机理研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2002, 22(2): 51-54.
XIA Qi-bin, LI Zhong, QIU Xian-yang, et al. Investigation of action mechanism between sodium hexametaphosphate and serpentine[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2002, 22(2): 51-54.
[6] 王德燕, 戈保梁. 硫化铜镍矿浮选中蛇纹石脉石矿物的行为研究[J]. 有色矿冶, 2003, 19(4): 15-17.
WANG De-yan, GE Bao-liang. A study on behavior of serpentine in processing of copper-nickel sulphide[J]. Non-ferrous Mining and Metallurgy, 2003, 19(4): 15-17.
[7] 梁为民. 凝聚与絮凝[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1987: 29-52.
LIANG Wei-min. Agglomeration and flocculation[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1987: 29-52.
[8] McGuire M J, Addai-Mensah J, Bremmell K E. The effect of polymer structure type, pH and shear on the interfacial chemistry, rheology and dewaterability of model iron oxide dispersions[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2006, 275(1/3): 153-160.
[9] McFarlane A, Bremmell K, Addai-Mensah J. Improved dewatering behavior of clay minerals dispersions via interfacial chemistry and particle interactions optimization[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2006, 293(1): 116-127.
[10] Eriksson R, Merta J, Rosenholm J B. The calcite/water interface II. Effect of added lattice ions on the charge properties and adsorption of sodium polyacrylate[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2008, 326(2): 396-402.
[11] Burdukova E, van Leerdam G C, Prins F E, et al. Effect of calcium ions on the adsorption of CMC onto the basal planes of New York talc-A ToF-SIMS study[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2008, 21(12/14): 1020-1025.
[12] Parolis L A S, van der Merwe R, van Leerdamet G C, et al. The use of ToF-SIMS and microflotation to assess the reversibility of binding of CMC onto talc[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2007, 20(10): 970-978.
[13] Liu Q, Wannas D, Peng Y. Exploiting the dual functions of polymer depressants in fine particle flotation[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2006, 80(2/4): 244-254.
[14] Mpofu P, Addai-Mensah J, Ralston J. Temperature influence of nonionic polyethylene oxide and anionic polyacrylamide on flocculation and dewatering behavior of kaolinite dispersions[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2004, 271(1): 145-156.
[15] 卢寿慈, 翁达. 界面分选原理及应用[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1992: 243-268.
LU Shou-ci, WENG Da. Principle and application of interface separation[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1992: 243-268.
[16] Baigorri R, Garcia-Mina J M, Gonzalez-Gaitano G. Supramolecular association induced by Fe(III) in low molecular weight sodium polyacrylate[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2007, 292(2/3): 212-216.
[17] Chiem L T, Huynh L, Ralston J, et al. An in situ ATR-FTIR study of polyacrylamide adsorption at the talc surface[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2006, 297(1): 54-61.
[18] Cuba-Chiem L T, Huynh L, Ralston J, et al. In situ particle film ATR-FTIR studies of CMC adsorption on talc: The effect of ionic strength and multivalent metal ions[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2008, 21(12/14): 1013-1019.
[19] 江绍英. 蛇纹石矿物学及性能测试[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987: 84-104.
JIANG Shao-ying. Serpentine mineralogy and performance testing[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1987: 84-104.
[20] 冯其明, 杨艳霞, 刘琨, 等. 采用纤蛇纹石制备纳米纤维状多孔氧化硅[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 38(6): 1088-1093.
FENG Qi-ming, YANG Yan-xia, LIU Kun, et al. Preparation of porous silica with nanofibrous morphology from chrysotile[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2007, 38(6): 1088-1093.
[21] Liu P, Guo J. Polyacrylamide grafted attapulgite (PAM-ATP) via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization (SI-ATRP) for removal of Hg(II) ion and dyes[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2006, 282/283: 498-503.
[22] Bicak O, Ekmekci Z, Bradshaw D J, et al. Adsorption of guar gum and CMC on pyrite[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2007, 20(10): 996-1002.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2010-08-22;修回日期:2010-11-30
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划(“973”计划)项目(2007CB613602)
通信作者:冯其明(1962-),男,湖北天门人,教授,博士生导师,从事矿物加工与资源综合利用等研究;电话:0731-88836817;E-mail: qmfeng@csu.edu.cn