文章编号:1004-0609(2012)08-2163-11
薄壁铝合金压铸充型沿程的组织与力学性能
朱必武1, 2,李落星1, 2,刘 筱1, 2,王水平1, 2,张立强1, 2
(1. 湖南大学 汽车车身先进设计与制造国家重点实验室,长沙 410082;
2. 湖南大学 机械与运载工程学院,长沙 410082)
摘 要:采用压铸制备薄壁AlSi10MnMg铝合金铸件,用金相技术、密度、拉伸性能等分析方法讨论浇注温度对薄壁铝合金压铸充型沿程的组织与力学性能的影响。结果表明:随着浇注温度的升高,试样流动临界长度增加,气孔增多,α(Al)枝晶变细,抗拉强度和断后伸长率先增加后降低。随着充型沿程流动长度的增加,气孔先减少后增加,α(Al)枝晶变化不大。当浇注温度为650和680 ℃时,试样抗拉强度和断后伸长率沿充型流动长度的增加而减小;当浇注温度为710和740 ℃时,试样抗拉强度和断后伸长率沿充型流动长度的增加变化较小。
关键词:薄壁铝合金;压铸;组织;力学性能
中图分类号:TG249.2 文献标志码:A
Microstructure and mechanical properties along fluidity length of thin-wall aluminum alloy under high pressure die casting conditions
ZHU Bi-wu1, 2, LI Luo-xing1, 2, LIU Xiao1, 2, WANG Shui-ping1, 2, ZHANG Li-qiang1, 2
(1. State Key Laboratory of Advanced Design and Manufacturing for Vehicle Body, Hunan University,Changsha 410082, China;
2. College of Mechanical and Vehicle Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China)
Abstract: The thin-wall AlSi10MnMg aluminum alloy samples were prepared by high pressure die casting. The effects of pouring temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties along the fluidity length were discussed by metallographic techniques, density measurement and tensile tests. The results show that, with the pouring temperature increasing, the critical fluidity length and porosity increase, and α(Al) grain size decreases and the ultimate tensile strength and elongation to fracture increase firstly, and then decrease. With the increase of the fluidity length, the porosity decreases firstly and then increases, but the α(Al) grain size is insignificant. The ultimate tensile strength and elongation to fracture decrease along the fluidity length under pouring temperatures of 650 and 680 ℃. However, the difference of the ultimate tensile strength and elongation to fracture along the fluidity length under pouring temperatures of 710 and 740 ℃ is insignificant.
Key words: thin-wall aluminum alloy; high pressure die casting; microstructure; mechanical properties
薄壁铝合金铸件具有轻质、力学性能优良等特点,近年来,广泛应用于汽车车身与底盘等结构件[1]。这类零件尺寸大且精度要求高、壁厚薄且结构复杂,其流动充型能力成为此类零件成形的基本问题,因为合金熔体的流动充型能力直接关系到零件是否能完整成形,同时也影响铸件的组织力学性能[2-5]。压铸作为一种快速的近净成型工艺,具有生产效率高、尺寸精度高和力学性能优异等特点,特别适合于此类零件的生产[6]。薄壁铝合金铸件在压铸充型过程中,铝合金熔体以很快的速度呈喷射状压入型腔,然后在压力下凝固,其组织会经历一系列动态变化,这种变化反过来又会影响充型过程和成形零件的性能。如果成形后零件的组织不均匀,就会产生力学性能的不均匀。目前的研究主要集中在各因素对铝合金熔体流动充型能力的影响[7-10]、成形工艺参数对成形后零件组织力学性能的影响[11-14],对于充型过程中组织如何演变、成形工艺参数对充型过程中组织力学性能的影响研究还很少见。
为了探索薄壁铝合金充型过程中组织力学性能沿充型长度的变化规律,本文作者采用压铸方法铸造薄壁AlSi10MnMg铝合金试样,研究压铸过程中浇注温度对压铸流动长度和组织力学性能的影响,同时探讨充型沿程流动长度上铸件组织力学性能规律。这对优化此类大型复杂薄壁件压铸工艺参数、改善压铸件力学性能均有积极意义。
1 实验
1.1 合金熔炼
实验材料选用自配制的AlSi10MnMg铝合金,其配比成分(质量分数)为10%Si、0.6%Mn、0.4%Mg、0.2%Ti、0.02%Sr,其余为Al。通过热力学计算分析和实验测得其液、固相线温度分别为624和552 ℃。熔炼采用井式电阻石墨坩埚炉,C2Cl6精炼除气,Al-5Ti-B细化,Al-10%Sr变质,然后将合金液静置,准备实验。
1.2 试样制备
实验所用设备为江苏灌南125T压铸机,采用二级压射速度,开始150 mm距离压射速度为300 mm/s,最后150 mm距离压射速度为2.4 m/s,压射比压为20 MPa,无设置增压,模具试压5~6模预热至80~150 ℃,涂料为压铸用脱模剂,浇注温度分别为650、680、 710、740 ℃。
1.3 测试分析
压铸制得的薄壁AlSi10MnMg铝合金试样如图1所示:流动试样(Fluidity specimen)壁厚1.5 mm、宽10 mm、总长908 mm,且定义压铸充型流动产生第一个明显铸造缺陷的长度为临界长度(Critical length),拉伸试样取样至临界长度处,总的充型长度为极限长度(Limiting length),分别测量记录其临界长度和极限长度。

图1 压铸流动试样照片
Fig. 1 Photo of fluidity specimen
金相组织采用德国蔡司Axiovert 40 MAT金相显微镜观察。密度测量采用天平/浮力法,用密度定性反映铸件的气孔率,密度越小,气孔率越大。
力学性能在WDW-1000微机控制电子万能材料试验机上进行。拉伸试样取样位置如图2所示,其中心位置离流动试样入口处的距离分别为45、135、235、330、410、495、575、645、715、805 mm。拉伸试样尺寸如图3所示。

图2 拉伸试样取样示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of position for tensile specimens
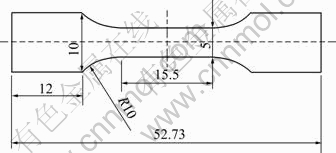
图3 拉伸试样尺寸
Fig. 3 Dimensions of tensile specimen (mm)
2 结果与讨论
2.1 浇注温度对充型流动长度的影响
图4所示为压射力20 MPa、2.4 m/s压射速度条件下试样压铸充型流动极限长度、临界长度随浇注温度变化的规律。从图4可以看出,薄壁试样压铸充型流动极限长度、临界长度均随浇注温度的升高而增 加,且流动临界长度均大于530 mm。RAVI等[7]研究发现铝合金熔体的流动性随熔体过热的增大而增强;HAN和XU[8]研究发现在相同浇注温度条件下,铝合金压铸充型流动长度随其固相线温度的降低而增大。提高浇注温度,铝合金熔体的表观黏度减小,充型过程中阻力减小,流动能力增强,因此充型流动长度增加;同时,较高的浇注温度会增加铝合金熔体的过热,熔体冷却凝固的时间变长,充型时间增加,充型流动长度变长。从图4还可以看出,试样充型流动长度末端大部分集中在铸件样件拐角处(Corner point),拐角位置见图2,试样的形状很大程度上决定铸件的充型。铝合金熔体流经这些拐角处时,由于冲击碰撞引起铝合金熔体各质点流速的大小和方向发生急剧变化形成阻力[15],充型能力减小,因此,铝合金熔体很容易在拐角处停止流动。
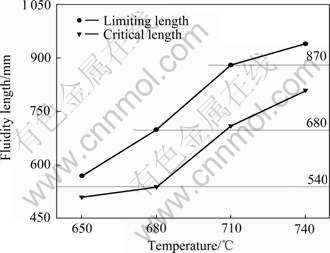
图4 流动试样流动长度随浇注温度的变化
Fig. 4 Change of fluidity length of fluidity specimen with pouring temperature
2.2 浇注温度对气孔和组织的影响
图5所示为压射力20 MPa、2.4 m/s压射速度条件下薄壁流动试样45 mm处金相组织。从低倍金相图5(a)~(d)可以看出,随着浇注温度的升高,流动试样入口处的气孔逐渐增多,形态从大尺寸卷气型气孔转变成弥散分布气孔。压铸过程中,铝合金熔体以高速、高压方式压入型腔,充型过程中会产生强烈的紊流、喷射,合金液前端会产生断裂,甚至局部产生雾化,使得型腔中部分空气来不及排出,卷入到金属液内部一起充填型腔,并在后续的压力作用下缩小、变形,最终留在铸件内部形成卷气、孔洞等缺陷[11-12]。且浇注温度越高,铝合金熔体充型流动能力越好,充型速度越快,产生紊流、卷气的可能性越大,气孔越多。
从高倍金相图5(a′)~(d′)可以看出,随着浇注温度的升高,流动试样45 mm处α(Al)枝晶越来越细。浇注温度较低时,试样α(Al)枝晶呈现不规则的块状,晶粒尺寸较粗大且分布不均匀,没有明显的二次枝晶臂;随着浇注温度的升高,试样α(Al)转变为不规则的蔷薇状或球状,晶粒尺寸明显细化、分布也更均匀。实验中试样壁厚只有1.5 mm,凝固过程中熔体凝固释放的凝固潜热有限,即使在不同的浇注温度条件下,模具被加热后的温升差别很小,因此,合金在凝固时的冷却速度差别亦很小,如果没有其他外界因素影响相同冷却速度条件下,α(Al)枝晶大小应该差别不大。然而,压铸过程中,铝合金熔体在冲头的速度和压力下充型凝固,且铝合金熔体从铸型表面向铸件中心顺序凝固,铸件中心流动性较好,铸件中心存在流动通道(Flow channel),冲头压力迫使铝合金熔体穿过流动通道,迫使枝晶破碎变细[13]。浇注温度越高,铝合金熔体的充型流动性越好,铝合金熔体穿过流动通道的速度和压力越大,冲头压力迫使α(Al)枝晶破碎变细的作用更明显,晶粒变细。
图6和7所示为压射力20 MPa、2.4 m/s压射速度条件下浇注温度为680 ℃时流动试样充型沿程流动长度上的金相组织。
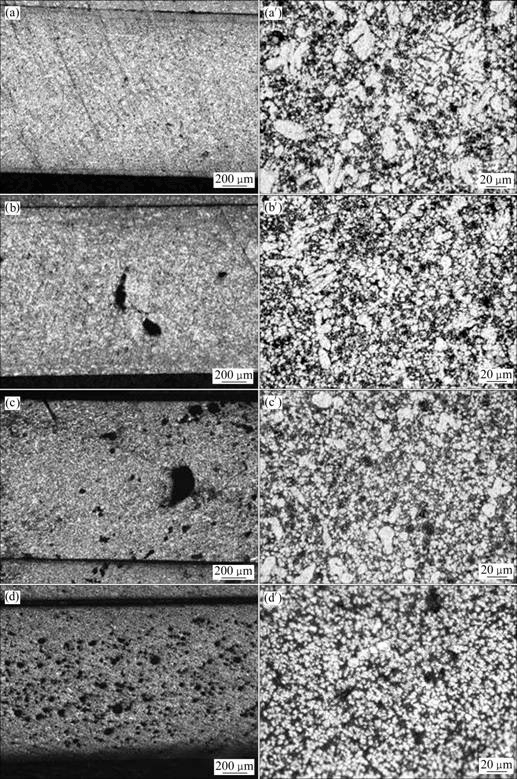
图5 流动试样45 mm处不同浇注温度下的金相组织
Fig. 5 Micrographs of fluidity specimens (at 45 mm) at different pouring temperatures: (a), (a′) 650 ℃; (b), (b′) 680 ℃; (c), (c′) 710 ℃; (d), (d′) 740 ℃
从图6低倍金相图(a)~(f)中可以看出,当浇注温度为680 ℃时,随着充型沿程流动长度的增加,试样中多为卷气型气孔,数量先减少后增加,但变化规律不明显。这是因为当浇注温度较低时,铝合金熔体表观粘度较大,充型流动能力差,型腔中气体排溢不通畅;随着充型沿程流动长度的增加,气体排溢有所改善;随着充型沿程流动长度的进一步增加,熔体温度进一步降低,熔体开始发生凝固,熔体固相率不断提高,熔体充型性变差,熔体前端长时间与空气接触,很容易形成氧化夹杂、卷气等缺陷。
从图7高倍金相图(a)~(f)中可以看出,当浇注温度为680 ℃时,随着充型沿程流动长度的增加,α(Al)枝晶大小变化不大。压铸中枝晶大小主要取决于冷却速度和加压条件,实验中试样壁厚只有1.5 mm,凝固过程中熔体凝固释放的凝固潜热有限,即使铝合金熔体温度在充型沿程过程中有所降低,但模具被加热后的温升差别很小,因此,合金在凝固时的冷却速度差别亦很小,α(Al)枝晶大小差别不大。
图8和9所示为压射力为20 MPa、压射速度为2.4 m/s、浇注温度为740 ℃时流动试样沿程流动长度上的金相组织。从图8低倍金相图(a)~(h)中可以看出,当浇注温度为740 ℃时,试样中的气孔先减少后增加。流动试样入口处为大量的弥散型气孔,随着充型沿程流动长度的增加,弥散气孔的尺寸变小、数量减少,随着充型沿程流动长度的进一步增加,气孔转变为卷气型气孔,数量增多,规律变化相比图6中浇注温度为680 ℃时明显。实验流动试样壁薄、充型流动长度长,压铸过程中,入口处位置熔体最先充型,大量气体来不及排溢,快速喷射状的紊流熔体迫使气体弥散分布于试样中;随着充型沿程流动长度增加,熔体温度不断降低、流动阻力增大、流速不断减慢,气体排溢效果较入口处变好,弥散气孔数量减少、大小变小;随着充型沿程流动长度的进一步增加,熔体温度进一步降低,熔体开始发生凝固,熔体固相率不断提高,熔体充型性变差,熔体前端长时间与空气接触,很容易形成氧化夹杂、卷气等缺陷。
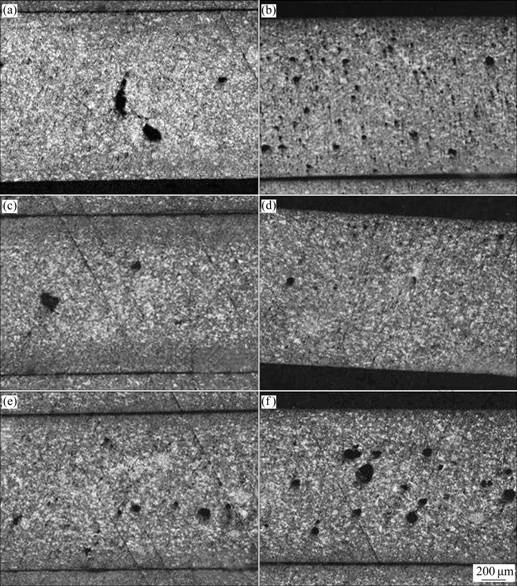
图6 流动试样在浇注温度为680 ℃时沿程流动长度上的低倍金相组织
Fig. 6 Macrostructures along fluidity length of fluidity specimen at pouring temperature of 680 ℃: (a) 45 mm; (b) 135 mm; (c) 235 mm; (d) 330 mm; (e) 410 mm; (f) 495 mm
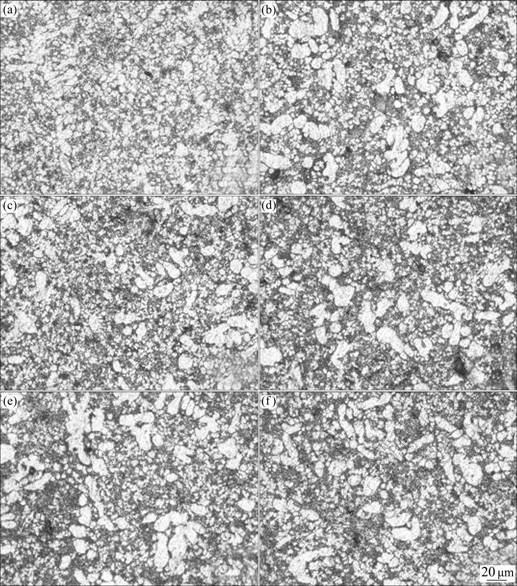
图7 流动试样浇注温度为680 ℃时沿程流动长度上的高倍金相组织
Fig. 7 Micrographs along fluidity length of fluidity specimen at pouring temperature of 680 ℃: (a) 45 mm; (b) 135 mm; (c) 235 mm; (d) 330 mm; (e) 410 mm; (f) 495 mm
从图9高倍金相图(a)~(h)中可以看出,当浇注温度为740 ℃时,随着充型沿程流动长度的增加,α(Al)枝晶大小变化亦不大。因此,综合图7和9可以说明,充型沿程流动长度对α(Al)枝晶大小影响很小。
2.3 浇注温度对密度的影响
图10所示为压射力20 MPa、2.4 m/s压射速度条件下流动试样45 mm处密度随浇注温度变化的规律。由图10可看出,流动试样入口处密度随浇注温度的升高先增加后减小。浇注温度越高,铝合金熔体中氢溶解度升高,熔体温度越高其流动充型性越好,越快的充型速度气体越难以排溢,因此会有更多的气体存于试样中,密度降低[11];另一方面,浇注温度越高熔体流动充型性越好,压射压力可以很好地作用其充型凝固,密度变大[12]。在两者的作用下,流动试样入口处的密度呈现随浇注温度的升高先增加后减小。
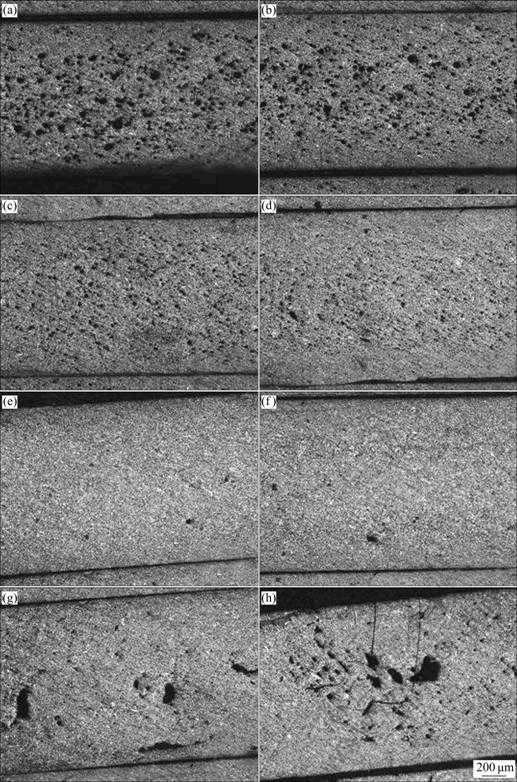
图8 流动试样浇注温度为740 ℃时沿程流动长度上的低倍金相组织
Fig. 8 Macrostructures along fluidity length of fluidity specimen at pouring temperature of 740 ℃: (a) 45 mm; (b) 235 mm; (c) 410 mm; (d) 495 mm; (e) 575 mm; (f) 645 mm; (g) 715 mm; (h) 805 mm
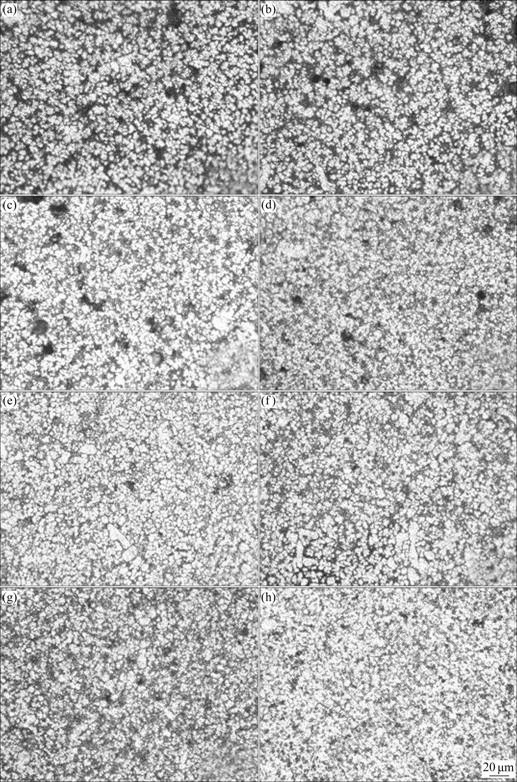

图9 流动试样浇注温度为740 ℃时沿程流动长度上的高倍金相组织
Fig. 9 Micrographs along fluidity length of fluidity specimen at pouring temperature of 740 ℃: (a) 45 mm; (b) 235 mm; (c) 410 mm; (d) 495 mm; (e) 575 mm; (f) 645 mm; (g) 715 mm; (h) 805 mm
图11所示为压射力20 MPa、压射速度2.4 m/s不同浇注温度条件下流动试样充型沿程流动长度上密度变化的规律。由图11可看出,浇注温度为650 ℃、680 ℃时,试样的密度随沿程流动长度的增加而减小;浇注温度为710 ℃、740 ℃时,试样密度随沿程流动长度的增加虽有波动,但变化不大。较低的浇注温度会减弱铝合金熔体的充型性,且较低浇注温度的熔体很容易发生凝固,压射压力对其凝固作用减弱,随着沿程流动长度的增加这种趋势越明显,密度下降;反之,较高的浇注温度会增强铝合金熔体的充型性,压射压力可以很好地作用其充型凝固,随着沿程流动长度的增加密度下降趋势变小,另一方面随着沿程流动长度的增加试样中气体更容易排溢,密度变大。
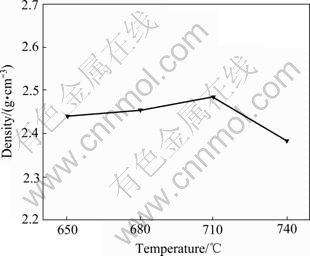
图10 流动试样45 mm处密度随浇注温度变化规律
Fig. 10 Change of density of fluidity specimens at position of 45 mm with different pouring temperature
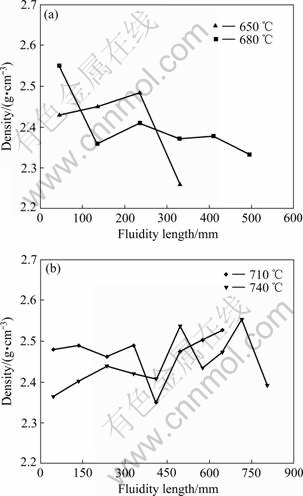
图11 不同浇注温度下沿程流动长度上密度的变化规律
Fig. 11 Change of density along fluidity length at different pouring temperatures
2.4 浇注温度对力学性能的影响
图12所示为压射力20 MPa、压射速度2.4 m/s条件下流动试样45 mm处抗拉强度、断后伸长率随浇注温度变化的规律。
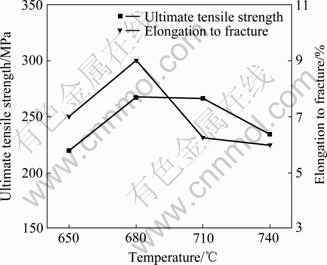
图12 流动试样45 mm处力学性能随浇注温度变化
Fig. 12 Change of mechanical properties of fluidity sample at position of 45 mm with pouring temperature
从图12可以看出,流动试样入口处抗拉强度、断后伸长率均随浇注温度的升高先增加后降低,此变化规律同图10中流动试样入口处的密度变化规律保持一致,峰值温度有所提前。压铸过程中,气孔是最为常见的缺陷之一,它能显著降低压铸件的力学性能。气孔率最常见的评定形式是铸件的密度,密度的大小可以定性判断压铸件内含有气孔的多少。密度越大,气孔越少,性能越好[11-12, 14]。因此,可以说气孔是影响薄壁压铸件性能的主要因素。
图13所示为压射力20 MPa、压射速度2.4 m/s不同浇注温度条件下流动试样充型沿程流动长度上抗拉强度、断后伸长率变化规律。
由图13可看出,当浇注温度为650和680 ℃时,试样的抗拉强度和断后伸长率沿程流动长度的增加而减小;温度为710 ℃和740 ℃时,试样的抗拉强度和断后伸长率沿程流动长度虽有波动,但变化不大。此变化规律和图11中流动试样沿程流动长度位置上密度变化规律一致,流动试样沿程流动长度位置上α(Al)枝晶变化不大,因此,可以说流动试样沿程流动长度位置上其力学性能主要取决于其气孔率,气孔率越大,性能越差。
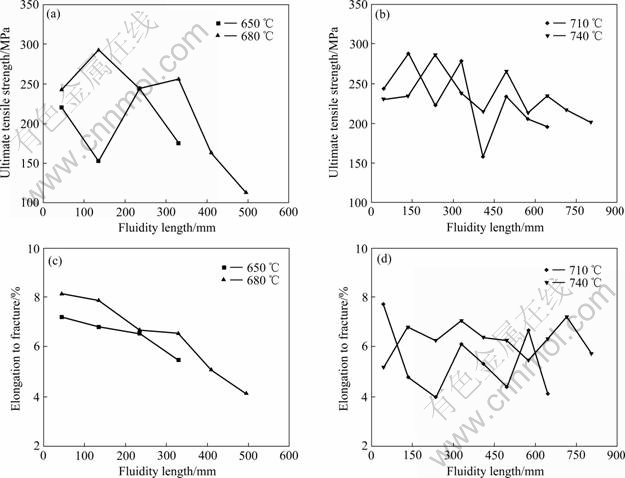
图13 不同浇注温度下流动试样沿程流动长度上抗拉强度和断后伸长率的变化
Fig. 13 Ultimate tensile strength ((a), (b)) and elongation ((c), (d)) along fluidity length at different pouring temperatures
3 结论
1) 1.5 mm壁厚AlSi10MnMg铝合金压铸流动试样充型流动临界长度随浇注温度的升高而增加,且临界长度均大于530 mm。
2) 气孔随浇注温度的升高而增多,随充型沿程流动长度的增加先减少后增加。
3) α(Al)枝晶随浇注温度的升高而变细,随充型沿程流动长度的增加变化不大。
4) 试样抗拉强度和断后伸长率随浇注温度的升高先增加后降低,当温度为650 ℃、680 ℃时,试样抗拉强度、断后伸长率随充型沿程流动长度的增加而减小;当温度为710 ℃和740 ℃时,试样抗拉强度、断后伸长率随充型沿程流动长度的增加变化不大。
ReferenceS
[1] TAUB A I, KRAJEWSKI P E, LUO A A, OWENS J N. The evolution of technology for materials processing over the last 50 years: The automotive example[J]. Journal of the Minerals Metals and Materials Society, 2007, 2: 48-57.
[2] ZHANG Tie-jun, GUO Jing-jie, SU Yan-qing. Effect of traveling magnetic on mould-filling length of the A357 melt during casting thin walled plate[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2003, 19(1): 43-46.
[3] Kulasegaram S, Bonet J, Lewis J. High pressure die casting simulation using a Lagrangian particle method[J]. Communicationg in Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2003, 19(9): 679-687.
[4] ZHANG Li-qiang, LI Luo-xing, ZHU Bi-wu. Simulation study on the low pressure die casting (LPDC) process for thin-walled aluminum alloy casting with permanent mold[J]. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 2009, 24: 1349-1353.
[5] 谭建波, 刑书明, 李立新. 半固态A356合金流变充型的极限长度[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(9): 1500-1509.
TAN Jian-bo, XING Shu-ming, LI Li-xin. Limiting length of semi-solidA356alloy rheological filling[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(9): 1500-1509.
[6] FRANKE R, DRAGULIN D, ZOVI A, CASAROTTO F. Progress in ductile aluminum high pressure die casting alloys for the automotive industry[J]. Metallurgia Italiana, 2007, 5: 21-26.
[7] RAVI K R, PILLAI R M, AMARANATHAN K R, PAI B C, CHAKRABORTY M. Fluidity of aluminum alloys and composite: A review[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 456: 201-210.
[8] HAN Qing-you, XU Han-bing. Fluidity of alloys under high pressure die casting condition[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 53: 7-10.
[9] KWON Y D, LEE Z Y. The effect of grain refining and oxide inclusion on the fluidity of Al-4.5Cu-0.6Mn and A356 alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 360: 372-376.
[10] SABATINO M D, AMBERG L, RORVIK S. The influence of oxide inclusions on the fluidity of Al-7wt.%Si alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 413/414: 272-276.
[11] VERRAN G O, MENDES R P K, VALENTINA L V O D. DOE applied to optimization of aluminum alloy die castings[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2008, 200: 120-125.
[12] 赵 鑫, 曾小勤, 陈 彬, 丁文江. 压铸工艺参数对铝合金汽缸体孔隙率的影响[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2009, 29(1): 36-38.
ZHAO Xin, ZENG Xiao-qin, CHEN bin, DING Wen-jiang. Influences of die casting parameters on the porosity in aluminum alloy air-conditioning compressor cylinder[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2009, 29(1): 36-38.
[13] 传海军, 黄晓峰, 毛祖莉, 田载友. 压铸工艺对铝合金组织性能影响的研究进展[J]. 新技术新工艺, 2007, 10: 21-24.
CHUAN Hai-jun, HUANG Xiao-feng, MAO Zu-li, TIAN Zai-you. Research progress on the influence of die casting process on structure and performance of aluminium alloy[J].New Technology & New Process, 2007, 10: 21-24.
[14] 纪莲清, 郭长江, 熊守美. 超低速压铸慢压射速度下ADC12铝合金的显微组织和性能[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 41(3): 977-981.
JI Lian-qing, GUO Chang-jiang, XIONG Shou-mei. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ADC12 aluminum alloy under super slow speed die castings with low shot speed[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2010, 41(3): 977-981.
[15] 朱爱民. 流体力学基础[M]. 北京: 中国计量出版社, 2004: 111-113.
ZHU Ai-ming. Basic fluid mechanics[M]. Beijing: China Metrology Publishing House, 2004: 111-113.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金面上项目(51075132);湖南省杰出青年基金(09JJ1007);高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金(20090161110027)
收稿日期:2011-08-01;修订日期:2011-11-11
通信作者:李落星,教授,博士;电话:0731-88821950;E-mail: llxly2000@163.com