文章编号:1004-0609(2013)11-3211-07
Mg含量对Ti-Mg复合脱氧钢中夹杂物与组织的影响
胡春林1, 2,宋 波1, 2,宋高阳1, 2,辛文彬1, 2,毛璟红3
(1. 北京科技大学 钢铁冶金新技术国家重点实验室,北京 100083;
2. 北京科技大学 冶金与生态工程学院,北京 100083;
3. 北京科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,北京 100083)
摘 要:采用高温实验和光学显微镜、扫描电子显微镜等研究Mg含量对1 873 K下Ti-Mg复合脱氧后铸锭样品中夹杂物组成、大小分布以及实验钢中晶内铁素体形核的影响。结果表明:当Mg含量(质量分数)为0.001 5%~0.002 6%时,实验钢中夹杂物的分布最为细小弥散,晶内铁素体形核效果较好。当奥氏体化温度为1 200 ℃时,钢中晶内铁素体的比例较高,有利于晶内铁素体形核的最佳奥氏体晶粒大小为120 μm左右。
关键词:Ti-Mg合金;脱氧;夹杂物;晶内铁素体;奥氏体晶粒
中图分类号:TF03 文献标志码:A
Effect of Mg content on inclusions and microstructure of steel by Ti-Mg complex deoxidation
HU Chun-lin1, 2, SONG Bo1, 2, SONG Gao-yang1, 2, XIN Wen-bing1, 2, MAO Jing-hong3
(1. State Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallurgy, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China;
2. School of Metallurgical and Ecological Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China;
3. School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China)
Abstract: The effects of Mg content on the composition, size distribution of inclusions and microstructure of ingot samples deoxided by Ti-Mg at 1 873 K were investigated by high temperature tests, SEM-EDS and optical microscopy (OM). The results show that when the Mg content (mass fraction) varies from 0.001 5% to 0.002 6%, the inclusions in experimental steel are fine-distributed, and the effectiveness of intragranular ferrite nucleation is better. At austenitizing temperature of 1 200 ℃, the proportion of intragranular ferrite in steel is higher, and the optimized austenite grain size that is beneficial to intragranular ferrite nucleation is about 120 μm.
Key words: Ti-Mg alloy; deoxidation; inclusions; intragranular ferrite; austenite grain
晶粒细化是一种可同时提高钢材强度和韧性的技术。作为一种有效细化晶粒的方法,氧化物冶金技术从一开始提出就得到了广泛的关注[1],其关键原理是利用钢中细小弥散析出的非金属夹杂物作为钢液冷却过程中晶内铁素体的异质形核核心促进形核,同时通过钉扎高温下晶界的移动,抑制奥氏体晶粒的长大来细化晶粒[2-6]。
在过去的研究中,人们利用TiN质点或TiN-MnS 复合化合物控制焊接热影响区(Heat affected zone,HAZ)奥氏体晶粒长大和促进针状铁素体大量形成,改善HAZ的韧性[7]。但随着焊接技术的不断进步和大线能量焊接技术的广泛应用,焊接热影响区峰值温度越来越高,在高温(1 350 ℃)的条件下TiN 或TiN-MnS 复合化合物质点往往发生固溶,起不到钉扎奥氏体晶粒的作用。近年研究发现[8-9],高温下氧化物比氮化物和碳氮化物更稳定,能有效阻止奥氏体晶粒长大,而且可有效地提供晶内针状铁素体形核地点,促进针状铁素体大量形成,细化HAZ组织,明显改善HAZ韧性。
近年来,在使用含Mg合金脱氧和使夹杂物变性等方面也进行了一定的研究,结果表明:含Mg合金脱氧可以使钢液中氧含量降到极低,夹杂物呈细小颗粒状并在钢中均匀分布;含Mg合金可以使簇状Al2O3夹杂变成细小的、随机弥散的尖晶石型(MgO·Al2O3)夹杂物[10]。研究表明,钢液中细小、弥散分布的含Mg夹杂物可作为钢凝固过程中析出相理想的形核核心,从而促进钢中针状铁素体组织的转变,细化钢的组织[11-14]。目前,关于Ti-Mg复合脱氧钢中夹杂物形貌组成、大小分布以及奥氏体晶粒尺寸对针状铁素体形核的影响的详细报道较少。
本文作者在实验室条件下对低碳钢进行Ti-Mg复合脱氧处理,研究Mg含量对Ti-Mg复合脱氧后钢中夹杂物成分、大小以及实验钢组织的影响,并考察奥氏体化温度对晶内铁素体形核的影响以及有利于晶内铁素体形核的最佳奥氏体晶粒尺寸,为Ti-Mg复合脱氧在氧化物冶金中的应用提供相关依据。
1 实验
冶炼实验在高温钼丝炉内进行,炉内通氩气保护,用PtRh30-PtRh6热电偶配合FP93系列自动程序控温仪控制炉温,控温精度为±2 ℃。将盛有实验钢的氧化铝坩埚(d 45 mm×100 mm)放入高温炉内,通电加热升温。原料加热至1 600 ℃熔化,保温5 min,待钢液完全熔清后用插入法先后将FeTi合金(含Ti 30%,质量分数)、SiMg合金(含Mg 20%)加入钢液深处进行脱氧处理,脱氧后的钢液在1 600 ℃下保温5 min后断电随炉冷却到1 200 ℃,取出淬火,实验钢成分如表1所列。
试样经线切割、预磨、抛光后利用带能谱仪的JSM-6480LV型扫描电子显微镜(SEM-EDS)对夹杂物的形貌与组成进行分析,夹杂物大小分布统计在扫描电镜随机取30个视场的照片后,利用图像处理软件Image J计算夹杂物的当量直径。试样经3%硝酸酒精侵蚀后利用XJZ-6型光学显微镜(OM)观察试样的显微组织形貌。
热处理实验在高温电阻炉上进行,将试样3分别在不同奥氏体化温度(900、1 000、1 100和1 200 ℃)下保温20 min后分别进行空冷和淬火;空冷试样用于观察奥氏体化温度对实验钢组织的影响,淬火试样用于研究不同奥氏体化温度下奥氏体晶粒的大小。空冷试样经3%硝酸酒精侵蚀后利用光学显微镜观察显微组织形貌,淬火试样采用饱和苦味酸水溶液+洗涤剂+盐酸2滴组成的侵蚀剂加热到60℃下进行侵蚀后用光学显微镜观察晶粒大小。
表1 实验钢化学成分
Table 1 Chemical compositions of samples (mass fraction, %)
2 结果与讨论
2.1 钢中夹杂物形貌与组成
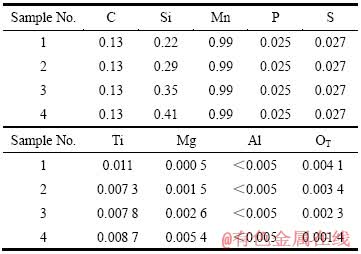
图1所示为利用SEM-EDS观察分析得到的各试样中夹杂物形貌与组成随着Mg含量的增加而变化的情况。从图1(a)~1(c)可以看出,钢中Mg含量为0.000 5%~0.002 6%时,经Ti-Mg复合处理后钢中夹杂物主要为由内部Ti-Mg氧化物和外层包覆MnS+TiN组成的复合夹杂物。随着Mg含量的增加,Ti-Mg氧化物中Mg含量明显增加。当钢中Mg含量达到0.005 4%时,氧化物夹杂主要成分为MgO,同时有MgS生成(见图1(d))。CHANG等[14]研究Mg含量对Si/MnTi脱氧钢中夹杂物的影响时发现,随着Mg含量从0.000 4%增加至0.005 2%,实验钢中复合夹杂物内部氧化物相的变化为ilmenite(MnTiO3+MgTiO3+ Ti2O3)→spinel(Mg2TiO4+MgTi2O4+Mn2TiO4+MnTi2O4)→spinel(Mg2TiO4+MgTi2O4+Mn2TiO4+MnTi2O4)+MgO→MgO。从EDS能谱可以看出,本实验体系下Ti-Mg氧化物夹杂的成分变化规律趋势与前人的研究结果基本相同。KIM等[12]研究发现,向Mn/Si/Ti脱氧低碳钢中加入Mg后,细小弥散分布的含Mg夹杂物能够诱导晶内铁素体形核,可以明显细化钢的组织。
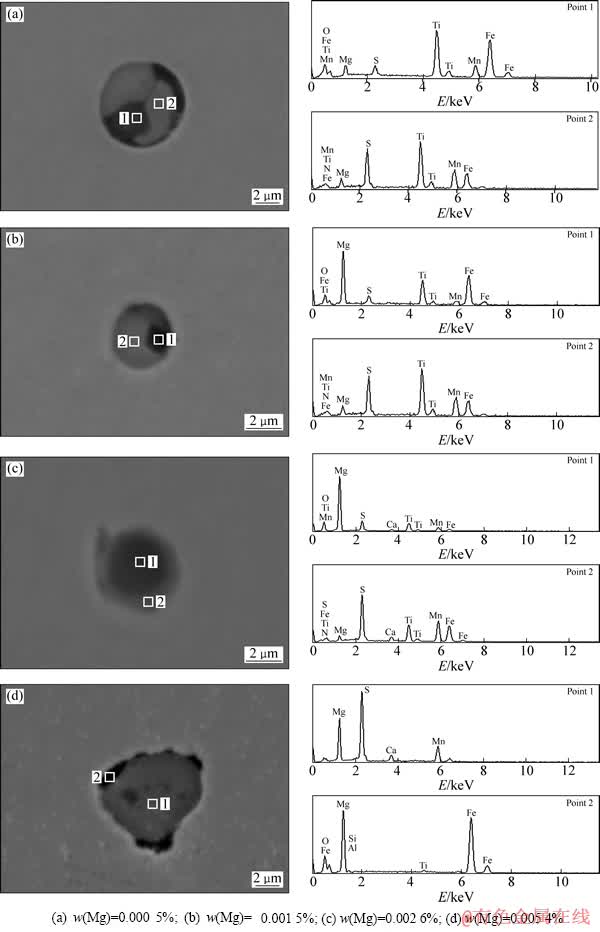
图1 随着Mg含量变化时实验钢中夹杂物形貌与组成
Fig. 1 Morphologies and chemical compositions of inclusions with Mg content changing
2.2 Mg含量对夹杂物尺寸分布的影响
非金属夹杂物能否在钢中诱发晶内铁素体形核,不仅与非金属夹杂物的化学成分有关,夹杂物的尺寸和分布也是重要的影响因素。本实验4组试样抛光后利用扫描电镜在800倍视场下随机拍摄30张图片,利用图像处理软件image J 统计得到的实验钢夹杂物尺寸分布的结果见图2。从图2可以看出,Mg含量为0.000 5%时,钢中尺寸小于3 μm的夹杂物占夹杂物总数的71%(样品1),Mg含量增加至0.001 5%时,钢中小于3 μm的夹杂物比例增加至82%(样品2);Mg含量为0.002 6%时,小于3 μm的夹杂物比例进一步增加,占夹杂物总量的88%(样品3);但Mg含量为 0.005 4%时,钢中小于3 μm的夹杂物减少,仅占钢中夹杂物总量的66%(样品4)。由此可见,随着Mg含量的增加,钢中小于3 μm的夹杂物比例先增加后减少;当Mg含量在0.001 5%~0.002 6%范围时,钢中小于3 μm的夹杂物比例最高,实验钢夹杂物分布最细小弥散。
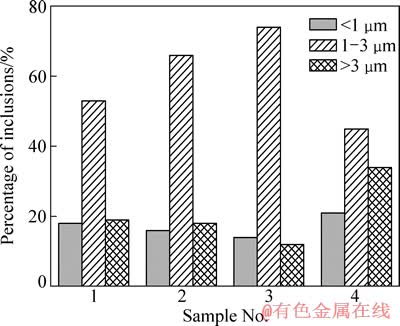
图2 实验钢中夹杂物的尺寸分布
Fig. 2 Size distribution of inclusions in steels
关于有利于晶内针状铁素体形核的合理夹杂物的尺寸的报道很多,LEE[15]计算表明,有利于晶内铁素体形核的夹杂物尺寸为0.25~0.8 μm;BARBARO等[16]发现针状铁素体易于在尺寸为0.4~0.6 μm的氧化物颗粒上形成;而YAMAMOTO等[17]通过能谱分析也表明,IGF有效核心是直径0.4~2 μm的夹杂物颗粒。LEE等[18]通过研究认为,当夹杂物大小在1~1.1 μm时其形核能力达到最大。虽然关于晶内铁素体形核夹杂物尺寸报道不一,但是一般认为钢中夹杂物的分布越细小弥散,其晶内铁素体形核效果越强。因此,从图2可以看出,当Mg含量为0.001 5%~0.002 6%时夹杂物最为细小,其晶内铁素体形核能力最强。
2.3 实验钢组织随Mg含量的变化
根据晶内铁素体形核的贫锰区机制[18-19],处于夹杂物附近钢基体中较强的奥氏体稳定元素Mn被吸附至夹杂物周围或者内部。由于Mn在奥氏体和铁素体中的扩散系数都很小,距离夹杂物较远的基体中的Mn不能及时补充到夹杂物邻近区域,因此在夹杂物周围形成一个贫Mn区。而贫Mn区的存在使奥氏体的稳定性下降,增大了铁素体形核的驱动力,即有利于IGF形核。从前面的研究可以看出,Ti-Mg复合脱氧的夹杂物可以作为MnS的形核核心,有利于诱导晶内铁素体形核。
图3所示为不同Mg含量时实验钢的显微组织。

图3 不同Mg含量下实验钢的显微组织
Fig. 3 Microstructures of steels with different Mg contents
从图3可以看出,当钢中Mg含量为0.000 5%时,钢的显微组织主要由大量块状铁素体、部分晶内针状铁素体和少量粒状贝氏体组成,晶内铁素体的比例在50%左右(见图3(a))。当Mg含量为0.001 5%时,钢的显微组织由大量晶内铁素体、少量块状铁素体和贝氏体组成,晶内铁素体的比例为80%左右(见图3(b))。Mg含量为0.002 6%时,钢的显微组织主要为晶内针状铁素体和少量块状铁素体,晶内铁素体比例为85%左右(见图3(c))。而当Mg含量为0.005 4%时,钢中的显微组织为大量的粒状贝氏体、少量快状铁素体和晶内铁素体,晶内铁素体含量较低,低于10%(见图3(d))。结果表明:Ti-Mg复合处理有利于钢中晶内铁素体形核,随着Mg含量在一定范围内增加,钢中晶内铁素体比例相应增加;当Mg含量较高时,由于生成的夹杂物尺寸较大,晶内铁素体比例降低。本实验条件下有利于晶内铁素体形核的Mg含量范围为0.001 5%~ 0.002 6%。
2.4 奥氏体化温度对晶粒和组织的影响
为研究不同奥氏体化温度对晶内铁素体形核的影响,本实验将晶内铁素体形核效果较好的试样3作为研究对象,在箱式电阻炉中分别于900、1 000、1 100和1 200 ℃下保温20 min空冷至室温,观察各试样的显微组织。
图4所示为不同奥氏体化温度下试样3的显微组织。从图4可以看出,当奥氏体化温度为900 ℃时,实验钢的显微组织主要由大量块状铁素体、珠光体和少量渗碳体组成(见图4(a)),当奥氏体化温度上升至 1 000 ℃时,渗碳体和珠光体含量降低,开始出现少量晶内铁素体(见图4(b)),当奥氏体化温度为1 100 ℃时,渗碳体和珠光体基本消失,钢的显微组织主要由少量晶内铁素体和大量块状铁素体组成,晶内铁素体含量明显增加(见图4(c));当奥氏体化温度为1 200 ℃时,实验钢的显微组织由大量晶内铁素体和少量块状铁素体组成(见图4(d))。实验结果表明,奥氏体化温度为1 200 ℃时,实验钢的晶内铁素体比例最高。由此可见,有利于晶内铁素体形核的奥氏体化温度为1 200 ℃左右。
钢中晶内铁素体的形成受多方面的影响,不仅与夹杂物类型有关,还与夹杂物的数量和尺寸、冷却速率以及原奥氏体晶粒大小等因素有关。有报道指出,当奥氏体晶粒大小达到某一最佳尺寸时,可实现晶内铁素体的体积最大化,在钛脱氧的钢中,针状铁素体相对形核能力与奥氏体晶粒大小之间基本上符合C曲线关系,认为最佳的奥氏体晶粒尺寸在180~190 μm左右[16]。LEE等[20]的研究也表明,原奥氏体晶粒大于100 μm时有利于针状铁素体的稳定形成。可见,对于不同钢种成分,适合晶内铁素体形核的原奥氏体晶粒尺寸不同。
图4 试样3在不同奥氏体温度下保温20 min空冷的显微组织
Fig. 4 Microstructures of sample 3 holding at different austenitizing temperatures for 20 min
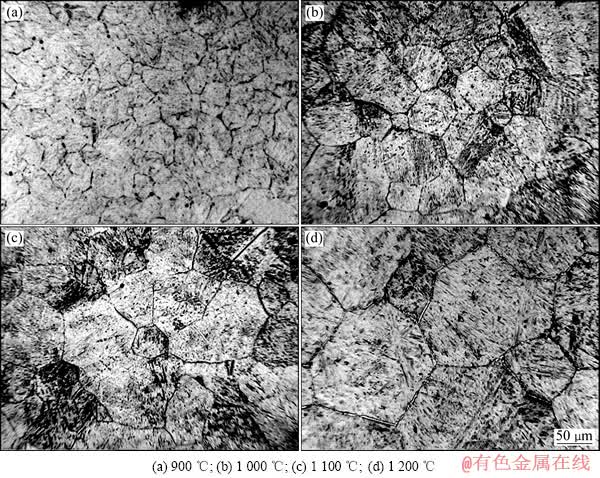
图5 试样3在不同奥氏体温度下保温20 min后的奥氏体晶粒
Fig. 5 Austenite grains of sample 3 holding at different austenitizing temperatures for 20 min
图5所示为试样3分别在不同的奥氏体化温度下保温20 min后的奥氏体晶粒。由图5可以看出,随着奥氏体化温度的升高,奥氏体晶粒尺寸也明显增加。当奥氏体化温度为900 ℃时,实验钢的奥氏体晶粒大小在30 μm左右(见图5(a)),当奥氏体化温度升高为1 000~1 200 ℃时,奥氏体晶粒明显长大,分别为50和80 μm左右(见图5(b)和(c));当奥氏体化温度为1 200 ℃时,奥氏体晶粒的大小为120 μm左右(见图5(d))。由图4可知,奥氏体化温度为1 200 ℃时,晶内铁素体比例最高。由此可知,在本实验钢体系中,有利于晶内铁素体形核的最佳奥氏体晶粒尺寸在120 μm左右。
3 结论
1) 经Ti-Mg复合脱氧后,实验钢中主要夹杂物为由Ti-Mg氧化物和外层包覆MnS+TiN组成的复合夹杂物。随着实验钢中Mg含量的增加,氧化物中Mg含量也逐渐增加;当实验钢中Mg含量为0.005 2%时,有MgS生成。
2) 随着实验钢中Mg含量的增加,夹杂物尺寸逐渐细化;当Mg含量为0.001 5%~0.002 6%时,夹杂物分布最为细小弥散,有利于晶内铁素体形核。而当Mg含量增加到0.005 4%时,夹杂物尺寸较大,晶内铁素体形核能力下降。
3) 随着Mg含量的增加,晶内铁素体的比例先增加后减小,有利于晶内铁素体形核的Mg含量在0.001 5%~0.002 6%之间。
4) 本实验体系下有利于晶内铁素体形核的最佳奥氏体化温度为1 200 ℃,最佳奥氏体晶粒大小在120 μm左右。
REFERENCES
[1] TAKAMURA J, MIZOGUCHI S. Roles of oxides in steels performance[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Iron and Steel Congress. Nagoya: Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, 1990: 591-597.
[2] BABU S S, DAVID S A. Inclusion formation and microstructure evolution in low alloy steel welds[J]. ISIJ International, 2002, 42(12): 1344-1353.
[3] SHA Q Y, SUNZQ. Grain growth behavior of coarse-grained austenite in a Nb-V-Ti microalloyed steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 523: 77-84.
[4] FURUHARA T, SHINYOSHI T, MIYAMOTO G, YAMAGUCHI J, SUGITA N, KIMURA N, TAKEMURA N, MAKI T. Multiphase crystallography in the nucleation of intragranular ferrite on MnS+V(C, N) complex precipitate in austenite[J]. ISIJ International, 2003, 43(12): 2028-2037.
[5] 刘中柱, 桑原守. 氧化物冶金技术的最新进展及其实践[J]. 炼钢, 2007, 23(4): 1-13.
LIU Zhong-zhu, KUWABARA M. Recent progress in oxide metallurgy technology and its application[J]. Steelmaking, 2007, 23(4): 1-13.
[6] SARMA D S, KARASEV A V,  P G. On the role of non-metallic inclusions in the nucleation of acicular ferrite in steels[J]. ISIJ International, 2009, 49(7): 1063-1074.
P G. On the role of non-metallic inclusions in the nucleation of acicular ferrite in steels[J]. ISIJ International, 2009, 49(7): 1063-1074.
[7] ZHANG L, LI Y J, WANG J, JIANG Q L. Effect of acicular ferrite on cracking sensibility in the weld metal of Q690+Q550 high strength steels[J]. ISIJ International, 2011, 51(7): 1132-1136.
[8] KOJIMA A, KIYOSE A, UEMORI R, MINAGAWA M, HOSHINO M, NAKASHIMA T, ISHIDA K, YASUI Y. Super high HAZ toughness technology with fine microstructure imparted by fine particles[J]. Nippon Steel Technical Report, 2004, 380: 2-5.
[9] 赵 辉, 胡水平, 武会宾, 李太全. Mg处理高钢级管线钢焊接热影响区晶内铁素体形核机制研究[J]. 钢铁, 2010, 45(2): 82-85.
ZHAO Hui, HU Shui-ping, WU Hui-bin, LI Tai-quan. Research on mechanism of nucleation of intra-granular ferrite in welding heat affected zone of magnesium treated high-grade pipeline steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2010, 45(2): 82-85.
[10] SAXENA S K. Refining reaction of magnesium in steel at steelmaking temperature[C]//Proceedings International Symposium on the Physical Chemistry of Iron and Steel making. Toronto: Conference of Metallurgists, 1982: 17-22.
[11] 文 彬, 宋 波, 毛璟红, 王福明, 潘 宁. 金属铁熔融过程中镁脱氧产物的特性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(3): 578-584.
WEN Bin, SONG Bo, MAO Jing-hong, WANG Fu-ming, PAN Ning. Characteristics of deoxidation products in molten iron treated with magnesium during melting[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(3): 578-584.
[12] KIM H S, CHANG C H, LEE H G. Evolution of inclusions and resultant microstructural change with Mg addition in Mn/Si/Ti deoxidized steels[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 53(11): 1253-1258.
[13] WEN Bin, SONG Bo, PAN Ning, HU Qing-yun, MAO Jing-hong. Effect of SiMg alloy on inclusions and microstructures of 16Mn steel[J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2011, 38(8): 577-583.
[14] CHANG C H, JUNG I H, PARK S C, KIM H S, LEE H G. Effect of Mg on the evolution of non-metallic inclusions in Mn-Si-Ti deoxidized steel during solidification: Experiments and thermodynamic calculations[J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2005, 32(3): 251-257.
[15] LEE J L. Evaluation of the nucleation potential of intragranular acicular ferrite in steel weldments[J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1994, 42(10): 3291-3298.
[16] BARBARO F J, KRAUKLIS P, EASTERLING K E. Formation of acicular ferrite at oxide particles in steels[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1989, 11(5): 1057-1068.
[17] YAMAMOTO K, KASEGAWA T, TAKAMURA J. Effect of boron on intragranular ferrite formation in Ti-oxide bearing steels[J]. ISIJ International, 1996, 36(1): 80-86.
[18] LEE T K, KIM H J, KANG B Y, HWANG S K. Effect of inclusion size on the nucleation of acicular ferrite in welds[J]. ISIJ International, 2000, 40(12): 1260-1268.
[19] MABUCHI H, UEMORI R, FUJIOKA M. The role of Mn depletion in intragranular ferrite transformation in the heat affected zone of welded joints with large heat input in structural steels[J]. ISIJ International, 1996, 36(11): 1406-1412.
[20] LEE J L, PAN Y T. The formation of intragranular acicular ferrite in simulated heat-affected zone[J]. ISIJ International, 1995, 35(8): 1027-1033.
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51274269)
收稿日期:2012-11-09;修订日期:2013-06-30
通信作者:宋 波,教授,博士;电话:010-62332271;E-mail:songbo@metall.ustb.edu.cn