Hydrogeochemical modelling of corrosive environment contributing to premature failure of anchor bolts in underground coal mines
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2020年第5期
论文作者:彭亚 Wendy TIMMS
文章页码:1599 - 1610
Key words:anchor bolts; hydrogeochemical modelling; rock bolts and cable bolts; stress corrosion cracking; water chemistry analysis
Abstract: Anchor bolts are commonly used throughout underground mining and tunnelling operations to improve roof stability. However, premature failures of anchor bolts are significant safety risks in underground excavations around the world due to susceptible bolt materials, a moist and corrosive environment and tensile stress. In this paper, laboratory experiments and hydrogeochemical models were combined to investigate anchor bolt corrosion and failure associated with aqueous environments in underground coal mines. Experimental data and collated mine water chemistry data were used to simulate bolt corrosion reactions with groundwater and rock materials with the PHREEQC code. A series of models quantified reactions involving iron and carbon under aerobic and anaerobic conditions in comparison with ion, pH and pE trends in experimental data. The models showed that corrosion processes are inhibited by some natural environmental factors, because dissolved oxygen would cause more iron from the bolts to oxidize into solution. These interdisciplinary insights into corrosion failure of underground anchor bolts confirm that environmental factors are important contributors to stress corrosion cracking.
Cite this article as: PENG Ya, Wendy TIMMS. Hydrogeochemical modelling of corrosive environment contributing to premature failure of anchor bolts in underground coal mines [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(5): 1599-1610. DOI: https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s11771-020-4393-z.

J. Cent. South Univ. (2020) 27: 1599-1610
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4393-z
PENG Ya(彭亚)1, 2, Wendy TIMMS3
1. School of Civil and Resource Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing,Beijing 100083, China;
2. School of Minerals and Energy Resources Engineering, UNSW Sydney, Sydney 2052, Australia;
3. Faculty of Science Engineering & Built Environment, Deakin University, Geelong 3216, Australia
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2020
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2020
Abstract: Anchor bolts are commonly used throughout underground mining and tunnelling operations to improve roof stability. However, premature failures of anchor bolts are significant safety risks in underground excavations around the world due to susceptible bolt materials, a moist and corrosive environment and tensile stress. In this paper, laboratory experiments and hydrogeochemical models were combined to investigate anchor bolt corrosion and failure associated with aqueous environments in underground coal mines. Experimental data and collated mine water chemistry data were used to simulate bolt corrosion reactions with groundwater and rock materials with the PHREEQC code. A series of models quantified reactions involving iron and carbon under aerobic and anaerobic conditions in comparison with ion, pH and pE trends in experimental data. The models showed that corrosion processes are inhibited by some natural environmental factors, because dissolved oxygen would cause more iron from the bolts to oxidize into solution. These interdisciplinary insights into corrosion failure of underground anchor bolts confirm that environmental factors are important contributors to stress corrosion cracking.
Key words: anchor bolts; hydrogeochemical modelling; rock bolts and cable bolts; stress corrosion cracking; water chemistry analysis
Cite this article as: PENG Ya, Wendy TIMMS. Hydrogeochemical modelling of corrosive environment contributing to premature failure of anchor bolts in underground coal mines [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(5): 1599-1610. DOI: https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s11771-020-4393-z.
1 Introduction
Anchor bolts including rock bolts and cable bolts are predominant components of the supporting system in underground mining projects [1-3]. However, frequent premature failures of these anchor systems in rock strata saturated with groundwater have been observed as a significant safety risk in mine operations around the world. These failures were not only restricted to rock bolts or cable bolts that had been in service for a long time. Bolts installed within one year or even less have also been suffering from premature failures [4-6]. Increasing interest has been shown in identifying these premature failures by considering stress corrosion cracking (SCC) mechanism [4, 7-13], which has also been widely recognized in other applications such as marine corrosion and petroleum pipeline corrosion [14-17]. According to the SCC mechanism, there are three dominant factors that induce premature failures which include susceptible material, a corrosive environment and tensile stress. Mining-induced stress, the presence of groundwater and mineral environments are reported to be contributing factors to SCC failures of rock bolts and cable bolts [18]. There have been numerous laboratorial experiment studies investigating the influence of these factors on SCC of rock bolts and cable bolts by simulating underground in-situ conditions. Some experiments drew attention to the possible groundwater influence on inducing SCC of bolts under load conditions. Bolts were immersed in mine water alone, and these experiments found no SCC phenomena after one year [4] or after 3.5 years [19]. Other experiments were conducted focusing on the influence of both groundwater and surrounding mineral materials, and then SCC failures were identified during the test period [20], indicating that more complex factors might be involved in the SCC process. Additionally, to simulate SCC failures, accelerated methods were adopted in laboratory testing by using more aggressive solutions or introducing microorganisms such as sulphate reducing bacteria (SRB), and SCC failures were also observed in the experiment [10, 21].
In addition to the experimental study on SCC of rock bolts and cable bolts, there has already been some modelling work performed on SCC in other regions by using microstructural peridynamic models and finite element models [22, 23]. However, these models only focused on the mechanical behavior of the material during the stress cracking process. There would have been a relatively long period of corrosion process prior to the onset of stress cracking. To clarify the relation between these two processes, hydrogeochemical methods can be a useful way to throw light on the research gap. Hydrogeochemical methods have been adopted for research on a wide range of topics, such as mine drainage and water pollution [24, 25], aquifers and aquitards [26-28], and deep formation water [29, 30]. Only a few studies have applied hydrogeochemical knowledge to corrosion processes underground and including diffusion [30, 31]. However, they were dealing with corrosion problems under different circumstances than anchor bolt corrosion and failure. For example, PENA et al [31] built hydrogeochemical models to study the corrosion rate of carbon steel canisters used for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. KLAPPER et al [30] focused on modelling the corrosion rate of scaling and corrosion influencing technical facilities during geothermal energy production. Considering this history, the current study is a valuable initial attempt to apply hydrogeochemical modelling in studying anchor bolt corrosion and failure issues.
In this paper, a series of thermodynamic equilibrium models combined with laboratory experiments were developed for investigating factors that contribute to anchor bolt corrosion both in the laboratory experiment and underground coal mines. Water chemistry data of groundwater released by dripping rock bolts were used to simulate anchor bolt corrosion. Reactions under aerobic and anaerobic conditions were discussed, and pH and pE trends were analyzed in comparison with experimental data. In addition, it was identified that microbial activities could influence corrosion process that may further lead to SCC failures. This research is an interdisciplinary study with regard to the underground bolt corrosion environment under aerobic and anaerobic conditions, which ultimately aims to develop corrosion inhibitor strategies to prevent SCC failures of anchor bolts, and hence improving both mining safety and productivity.
2 Methods and setup
2.1 Rock and cable bolts corrosion experimental methods and setup
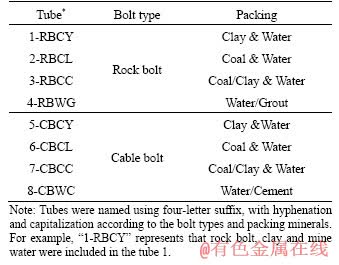
Testing of rock and cable bolts was conducted within a variety of material packings (as shown in Table 1 and Figure 1) including saturated clay, saturated coal, mine water and grout/cement. Rock bolts and cable bolts used in these experiments were the same types utilized at a longwall underground coal mine in the Sydney Basin, Australia. The mill scale layer from every bolt was removed prior to the experiments. This mill scale, which is usually only 0.1 mm in thickness, is designed to act as a cathodic protection layer to provide an initial barrier to atmospheric corrosion. The work to remove it was performed by professionals at the Jennmar factory in Sydney using industrial sanding equipment. The type of rock bolt used was HSAC 840 ribbed bolt with a core diameter of 21.7 mm and a total diameter of 23.6 mm including ribbing. The type of cable bolt used in the experiment was Plain Superstrand cable bolt with a total stand diameter of 21.8 mm. These types were chosen as they are well represented in the broken bolts database [20, 32]. The length of both rock bolt specimens and cable bolt specimens was limited to 1 m, in contrast to lengths of 2 m and 4-8 m within coal mines, respectively. This length was chosen to be suitable for testing in the laboratory. Strands were removed (8 inner and 8 outer) from every Plain Superstrand cable bolt, so that the cable bolt specimen was comprised of a centre strand encircled by one inner strand and one outer strand. Mine water, coal and clay were collected near the location where premature SCC failures had occurred in the same longwall underground coal mine in the Sydney Basin, Australia. Because the test column diameter was 60 mm, it was necessary to reconstitute the rock materials by tightly packing around the bolts, using a stiff rod to compact the materials by hand. The materials were therefore expected to be of reduced strength compared with in situ rock mass. However, this would not affect chemical reactions.
Table 1 Experimental design with different material packings
Water samples were taken every 8-10 d from crucial sections of the packings, and analyzed for pH, electrical conductivity (EC) and dissolved oxygen (DO) by using HACH HQ40d Portable Meters, as shown in Figure 2. After a period of 76 d, the experiment was disassembled and the materials were visually evaluated. Water chemistry trends were further analysed through anion and cation testing by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) techniques.
2.2 Batch-reaction modelling methods and setup
The PHREEQC program developed by the US Geological Survey was used for hydrogeochemical modelling. It is capable of performing aqueous speciation and solubility, reaction path, inverse mass balance modelling, and one-dimensional advective-dispersive-reactive transport calculations [33]. With this software, speciation and equilibrium reactions and the dissolution of mineral phases during corrosion process can be calculated by assuming mass balance, complete mixing of water and thermodynamic equilibrium. The PHREEQC program is suitable for all environments where chemical reactions are occurring between water and materials to reach chemical equilibrium. This applies to environments without oxygen (eg. fully sealed rock bolts in grout without oxygenated groundwater), and environments with air (eg. interface of rock bolt with roadway tunnel roof). Batch-reaction models were developed and run with the default thermodynamic PHREEQC.DAT database, which includes essential thermodynamic data for aqueous species, gas and mineral phases.
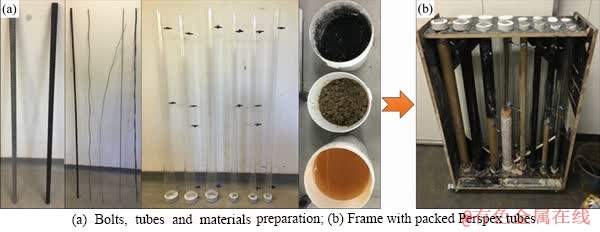
Figure 1 Experiment preparation and holding frame with packed Perspex tubes:

Figure 2 Water sampling and testing methods:
Microbial activity also contributes to SCC failures of anchor bolts, according to previous research showing the presence of microbial species including SRB such as Desulfovibrio in the bolt environment [20, 34]. In fact, SCC of anchor bolts may also be a special type of microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC), which is a process of electrochemical reactions [35-37]. Electron transfer must occur during the corrosion process. To achieve this electron transfer process, organic carbon and iron solid were represented by stepwise addition of carbon and iron elements with zero valences in the modelling, both of which were defined in the REACTION block. The ratio of carbon and iron addition was 3:1 (by moles) in each step, determined by a trial of different ratios. The input value of elemental iron was set to approximate the mass loss of the bolts during experiments, and the distribution of total iron over Fe2+ and Fe3+ was calculated from pE values [38]. The redox reactions in the anaerobic condition would be driven by the input of organic carbon and iron. The organic carbon was oxidized to inorganic carbon, increasing the electron activity in the solution, and then the electrons were utilized by other components such as sulphate. Iron was oxidized during corrosion of bolts, with the electrons available to reduce other species such as hydrogen ions. As oxygen was observed throughout the experiment, aerobic conditions (positive DO) were considered in the modelling. However, local anaerobic conditions could develop around the bolt surface due to biofilms and clay materials surrounding bolts.
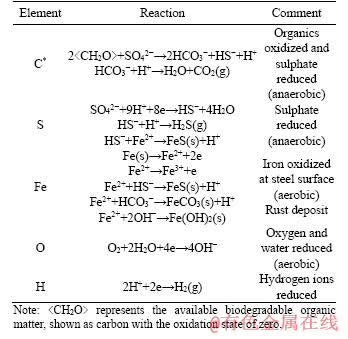
The initial chemical compositions in the models were specified based on water chemistry measurement of the initial mine water used in the experiment. To increase the reliability of water analytical data, the alkalinity value was calculated to achieve a zero-charge balance of ions in water. These data are shown in Table 2. The initial O2 value for mine water was 8.5 mg/L. However, to identify possible anaerobic process, it was also set as 0 or 3 mg/L in some models. The major elements involved in the bolt corrosion process, C, S, Fe, O and H, are affected by redox processes, dissolution equilibrium, and corrosion rust deposition [27, 31, 39-41]. In Table 3, equations of primary reactions that may occur during bolt corrosion process were listed, representing reaction types of organic matter degradation, sulphate reduction, iron oxidation, precipitation equilibrium, and cathodic reaction under aerobic or anaerobic conditions. The specific reaction process would be decided by thermodynamic calculations based on the PHREEQC.DAT database.
Table 2 Initial chemistry of mine water from a dripping bolt
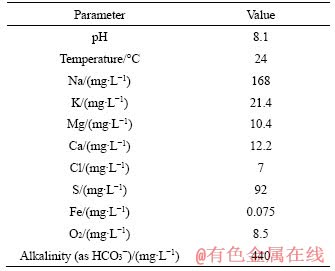
Table 3 Dominant reactions for main elements in solution
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Experimental results and discussion
After 76 d of testing, visual evaluation showed general corrosion on almost all the bolt specimens. Corrosion was more obvious in the upper regions where more atmospheric oxygen could diffuse into the water of the packed sample. Pitting corrosion was found on bolt specimens surrounded by coal or coal and clay. Cable bolt specimens in particular showed crevice corrosion, which was probably as a result of the cable bolt specimen being composed of multiple cable bolt strands. It should be noted that no cracks were visible on any bolt specimens, which was attributed to the absence of tensile stress and the short period of testing. In other experiments as part of the broader ARCL research program, the influence of tensile stress on SCC has been identified and cracks have been identified [10, 42].
Water chemistry varied between each experimental sample, and over time during experiments. Water chemistry of the initial mine water and six final water samples are shown in Table 4. A piper diagram was plotted to show the relative abundance of major ions present and also to group the water samples (Figure 3). Six samples were Na-HCO3 type water, while the sample 2-RBCL-b was Na-Cl type. The sulphate values declined in most of the samples, except the one in 2-RBCL-b showing an obvious increase in concentration. Concentrations of other ions including Ca2+, Na+, Mg2+, Fe2+ and Cl- in 2-RBCL-b were also higher than those from other measured samples. Additionally, the final pH of this sample was 8.0, being the lowest value among all seven water samples, while the EC value at 2.67 mS/cm was the highest. This water sample was collected from the lower region about 100 mm above the tube bottom, where coal was tightly packed around the bolt. The notable difference between the water chemistry of this sample and the others could result from the heterogeneous composition of coal, leading to substance dissolution including sulphur compounds and chlorides from coal material into limited amount of water [43]. There might also be more complex redox reactions here because of the lowered pH value and higher sulphate concentration. Concentration of iron ions in water samples from those tubes filled with coal or grout showed a decrease, while in contrast, iron ions clearly increased in clay filled samples. In tube 2-RBCL-a and tube 3-RBCC-a, distinct increases of nitrate occurred from below detection to 4.7 and 109 mg/L, respectively. These increases were probably attributable to dissolution and degradation of organic matter [27].
Table 4 Water chemistry of water samples
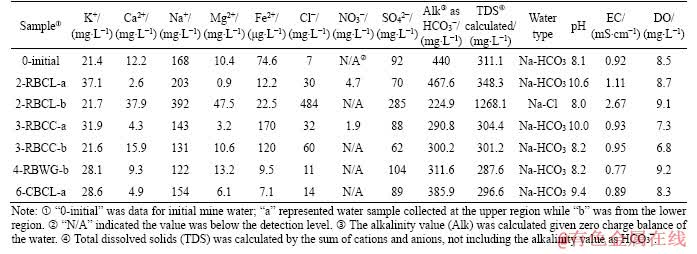
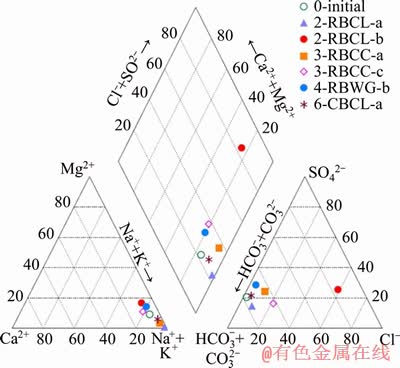
Figure 3 Piper diagram of water samples
Continuous measurements showed pH of water samples from the upper tube generally increased during the experiment. For example, the pH of sample 2-RBCL-a increased up to 10.6, while water samples from the lower tube changed slightly around the initial pH of 8.1 of mine water. Continuous DO measurements showed that there was plentiful dissolved oxygen in all solutions. An overall downward trend to around 7.5 mg/L was investigated during the first 40 d, followed by an increase to over the initial DO value of 8.5 mg/L for upper water samples, and a relatively steady status for lower water samples. EC data presented an overall gradual downward trend during the first 40 d after an initial increase from the initial value of 0.92 mS/cm of only mine water, with the lower water samples recording a notably higher EC value. After about 40 d, EC values of almost all samples tended to be steady. Higher EC level would suggest a greater corrosion rate and vice versa, so it is apparent that the corrosion rate gradually decreased and then stabilized during the experiments.
In summary, it was observed that oxygen was not exhausted during the experiments. The upper region of every tube was exposed to the atmosphere during each water sampling contributing to relatively severe corrosion in the upper regions. Both distinct general corrosion and pitting corrosion were found on the surface of bolt specimens. However, no cracks were visible, probably due to the lack of tensile stress and short experimental period. Sulphate reduction and pitting corrosion tended to appear where the bolt environment was tightly packed by geological materials or possibly microbial activity forming a biofilm with reaction products to inhibit oxygen movement.
3.2 Modelling results and discussion
A series of hydrogeochemical models were developed as listed in Table 5, according to the specific methods presented in Section 2.2. These models were designed to evaluate factors influencing bolt corrosion due to interaction of bolts and rock materials with groundwater, assuming thermodynamic equilibrium.
Table 5 List of models and independent variables
3.2.1 DO influence
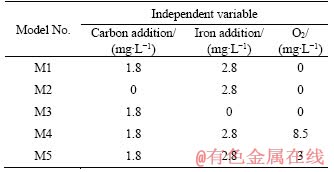
It was observed that oxygen was not exhausted during experiments, therefore oxygen was included in some of the models to evaluate the influence of DO. According to model M4 (as shown in Figure 4), when O2 value was set as 8.5 mg/L, the dominant redox couple in the solution was C/O2 and Fe/O2, indicating an excess amount of O2. In this case, more CO2 and Fe3+ were produced, without any sulphate reducing reaction. The pE value was consequently higher than 12, restricting sulphate reduction.
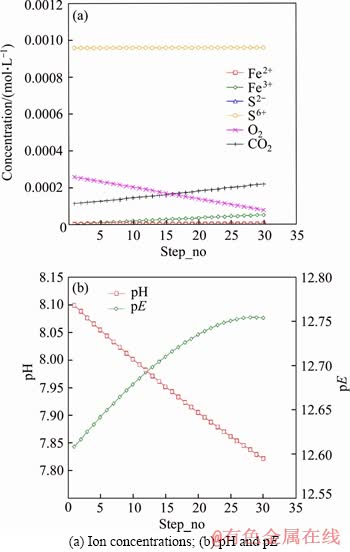
Figure 4 Trend of ion concentrations, pH and pE in model M4:
In another model M5 (as shown in Figure 5), carbon and iron were added in 30 steps, with the alkalinity as 440 mg/L and O2 as 3 mg/L. It took 27 steps to reach a sulphate value of 88.99 mg/L (9.270×10-4 mol/L), close to the concentration of 89 mg/L (9.271×10-4 mol/L) measured in the experiment 6-CBCL-a. In this model, during the first 15 steps, oxygen was present in the solution. During this period, both oxygen and carbon were reduced, while iron was oxidized to Fe2+ and Fe3+. More Fe3+ prior to Fe2+ existed in this period as a result of the strong oxidizing conditions. More CO2 was produced than in later period. In this model, O2 was exhausted in the solution over 15 steps. Then Fe3+ was reduced to Fe2+, followed by sulphate reduction. Overall, the pH of the solution showed a decrease during the presence of oxygen, and tended to increase during the reduction of Fe3+ and sulphate. The pE value was in the range of 12 to 13 with oxygen present, and stayed in the range of -5 to -4 when oxygen was exhausted.
It can be concluded from these models that the presence of sufficient oxygen would have a negative effect on sulphate reduction and could additionally slow pitting corrosion. The fact that oxygen is reduced before other possible species including Fe3+, SO42-, CO2, HCO3- was confirmed by modelling. There are many examples of sulphate reduction associated with low redox conditions [44], such as was demonstrated in our modelling. High concentration of O2 leads to high redox potential, which would restrict SRB catabolism to reduce sulphate.
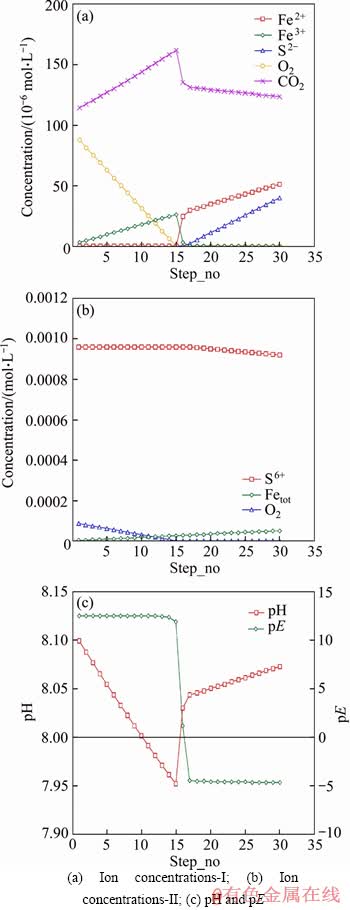
Figure 5 Trend of ion concentrations, pH and pE in model M5:
3.2.2 Carbon source
Though there have been different views about the role of organic carbon in metabolic activities of SRB [45, 46], it is generally accepted that SRB can use organic carbon both as a reductant for sulphate and as a source of carbon for growth, which in turn will also accelerate the rate of sulphate reduction. Energy can be obtained from sulphate reduction for growth and other energy consuming metabolic activities. The role of SRB using organic carbon and sulphate during corrosion of anchor bolts was modelled by focusing on the redox reactions where carbon and iron were electron donors and sulphate was the main terminal electron acceptor. Also, a small number of electrons were accepted by hydrogen ions to form hydrogen gas.
Inorganic carbon usually exists with +4 valence in chemical compounds, and thus cannot serve as an electron donor to promote sulphate reduction, as shown in models M1 and M2. In model M2, iron addition and alkalinity were specified although no carbon was added. The model showed that almost no sulphate reduction occurred during all 30 steps of the model as shown in Figure 6. By contrast, sulphate reduction occurred in model M1 as shown in Figure 6. This is consistent with SRB metabolic activities that utilise organic carbon rather than inorganic carbon for growth and energy. Underground mine water and coal sediment may contain carbon as small organic molecules, such as formate, acetate, lactate, propionate, butyrate, and also macromolecules [27]. This provides carbon sources that can be consumed by SRB, thereby supporting the existence of SRB in the surrounding environment of anchor bolts.
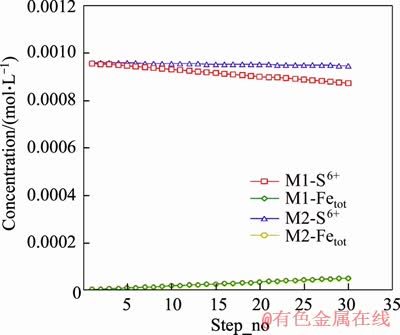
Figure 6 Trend of sulphate and iron concentrations in models M1 and M2
3.2.3 pH and pE trends
In model M3, carbon addition and alkalinity values were specified, while no iron was added. Without adding iron into the solution, a sulphate value of 88.93 mg/L (9.264×10-4 mol/L) was obtained after 13 steps, similar to the final sulphate concentration of 89 mg/L (9.271×10-4 mol/L) measured in experiment 6-CBCL-a. As shown in Figure 7, the pH trend was reducing, while the pE value declined during the first 9 steps and then increased slightly. At the 13th step, pE was -4.66, still lower than the initial pE of -4.59. This model indicated that the reaction between carbon and sulphate would lower the pH of the solution, which was consistent with existing research showing that SRB utilize organic carbon and sulphate to produce CO2 and H2S, leading to local acidic conditions. This would change the local electrochemical nature at the bolt surface, not only intensifying the pitting corrosion, but also facilitating the entry of absorbed hydrogen atoms into bolts. The absorbed hydrogen atoms in bolts could probably lead to initiation and propagation of cracks [16, 21, 39].
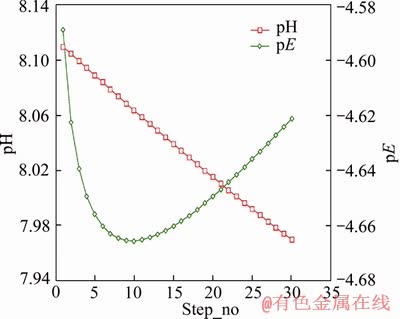
Figure 7 Trend of pH and pE in model M3
In contrast with model M3, iron addition was also specified in model M1, while other values remained the same as model M3. After 11 steps, sulphate in this model reached 88.97 mg/L (9.268×10-4 mol/L), which was close to the previous experimental value. The pH increased linearly while the pE value tended to decrease from -4.61 to -4.76 during the 11 steps as shown in Figure 8. Based on model M3, sufficient O2(8.5 mg/L) was included in model M4. This model showed that pH would decrease and pE would increase to over 12 (as shown in Figure 4(b)), while during the experiment, pH of both upper and lower samples declined sometimes, and the pH in lower regions changed slightly around the initial pH of 8.1. However, most upper water samples presented an obvious pH increase, the exact reason for which was unclear, but it was probably related to the complex compositions of both mine water and packing mineral materials.
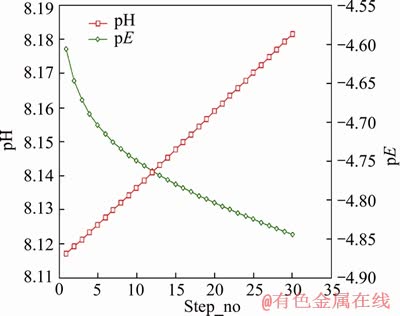
Figure 8 Trend of pH and pE in model M1
These modelling results indicate that during the bolt corrosion process, the interaction among organic carbon, sulphate and iron in anaerobic conditions would probably lead to pH increase and pE decrease. Reactions by SRB that utilize organic carbon and sulphate to produce CO2 and H2S would probably lead to local acidic conditions, and this in turn would accelerate the local corrosion rate, particularly with a biofilm that restricted water interactions but retained reaction products. A local electrochemical change at the bolt surface would also facilitate absorbed hydrogen atoms to enter into bolts, contributing to the appearance of cracks. The modelling also demonstrated that the pE range for sulphate reduction was generally between -5 to -4. If sufficient oxygen occurred to oxidize organic carbon and iron, pH would be likely to reduce while pE would increase.
3.3 Implications for measures preventing bolt corrosion
There are three primary methods for preventing steel corrosion to address known corrosion mechanisms: use of coating systems, improvement of corrosion-resistant steel materials and avoidance of corrosive environments.
For bolts in underground coal mines, traditional measures to prevent bolt corrosion mainly apply the first two methods. Bolts of high strength and corrosion-resistant properties are primarily selected. Also, engineers have used protective coatings to effectively insulate bolts from the impact of the anchoring environment. However, premature failures were still found in underground coal mines. Developing steel bolts that have higher resistance to corrosion and SCC may be prohibitively expensive. Therefore, it is necessary to develop other effective ways to ameliorate this problem.
According to this research, hydrogeochemical and microbial activities should be considered as important contributory factors to corrosion and failure of anchor bolts, although complex conditions such as aerobic and anaerobic are expected in underground environments. Hydrogeochemical modelling can indicate, in a quantitative manner, effective strategies to inhibit corrosion by modifying aspects of the bolt environment, for example, limiting oxygen exposure, limiting or absorbing organic carbon sources of microbial grown, enhancing growth of protective biofilms composition, and similar environmental inhibitor strategies.
With the knowledge developed during ongoing research, the composition of bolt coatings could be improved with various inhibitors. Alternatively, there could be effective ways to add inhibitors to the grout or resin when encapsulate the bolts in roadways. To achieve this, local scale hydrogeochemical models that better represent the dynamics of microbial processes could be developed to quantify inhibiting mechanisms.
4 Conclusions
This paper evaluated hydrogeochemical aspects of corrosion processes that can lead to bolt failure in underground excavations. A unique combination of site data, experimental data and hydrogeochemical modelling was used to quantitatively evaluate aspects of water-rock-bolt interactions in the environment surrounding the bolts.
Experiments over a period of 76 d showed that general corrosion and pitting corrosion were the primary corrosion types at the bolt surface. However, no cracks were visible, probably on account of the lack of tensile stress and short experimental period. Oxygen was not exhausted in the mine water solution, such that while aerobic conditions dominated, anaerobic processes were possible only at the bolt surface where microbial activity, reaction products and geological materials impeded oxygen supply. Periodic exposure to the atmosphere during water sampling may have accelerated the corrosion in the upper regions of these experiments. Sulphate reduction tended to appear in localised surfaces of the bolt, along with obvious pitting corrosion.
Based on the water chemistry data collected from these experiments, batch-reaction models were built to investigate influences in the corrosion process. It can be deduced from the modelling results that, during the bolt corrosion process in anaerobic conditions, organic carbon degradation rather than inorganic carbon promoted the sulphate reduction process, acting as electron donor and a source for growth of microbes. Catabolism activities of microbes such as SRB utilizing organic carbon and sulphate may lead to a localized acidity near the bolt surface, which would accelerate the rate of corrosion. The change of the local electrochemical nature at the bolt surface would also facilitate absorbed hydrogen atoms to enter into bolts, contributing to the development of cracks. The suitable pE range for sulphate reduction was between -5 to -4, but the increased dissolved oxygen raised the redox potential. Oxygen was reduced prior to other species including Fe3+, SO42-, CO2, HCO3-. This would also slow down sulphate reduction and SRB catabolism activities. In this case, anaerobic corrosion of bolts might be inhibited. However, bolt corrosion could also be accelerated with more iron oxidized by oxygen to form iron oxides and hydroxide oxides.
Further research is ongoing to identify sensitivity of corrosion to components such as Na2S and H2S. Additionally, kinetic models could be developed by including specific energy yields for the microbial redox processes. It is recommended that local scale hydrogeochemical models could be developed to quantify inhibiting mechanisms such as biofilms and other barriers between the bolt surface and the surrounding environment.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express sincere gratitude to Patrick Moore for his contributions throughout the experiment part. Many thanks to Prof. Serkan Saydam, Mark Whelan, WU Sai-sai, and CHEN Hong-hao for their helpful discussion and advice.
References
[1] YAN Hong, HE Fu-lian, LI Lin-yue, FENG Rui-min, XING Peng-fei. Control mechanism of a cable truss system for stability of roadways within thick coal seams [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(5): 1098-1110. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-017-3513-x.
[2] WANG Qi, LUAN Ying-cheng, JIANG Bei, LI Shu-cai, YU Heng-chang. Mechanical behaviour analysis and support system field experiment of confined concrete arches [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(4): 970-983. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-019-4064-0.
[3] ZHAO Zeng-hui, GAO Xiao-jie, TAN Yun-liang, MA Qing. Theoretical and numerical study on reinforcing effect of rock-bolt through composite soft rock-mass [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(10): 2512-2522. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-018-3932-3.
[4] VANDERMAAT D, SAYDAM S, HAGAN P C, CROSKY A. Examination of rockbolt stress corrosion cracking utilising full size rockbolts in a controlled mine environment [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2016, 81: 86-95. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015. 11.007.
[5] LI Shu-cai, WANG Hong-tao, WANG Qi, JIANG Bei, WANG Fu-qi, GUO Nian-bo, LIU Wen-jiang, REN Yao-xi. Failure mechanism of bolting support and high-strength bolt-grouting technology for deep and soft surrounding rock with high stress [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23(2): 440-448. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-016-3089-x.
[6] WANG Hui, ZHENG Peng-qiang, ZHAO Wen-juan, TIAN Hong-ming. Application of a combined supporting technology with U-shaped steel support and anchor-grouting to surrounding soft rock reinforcement in roadway [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(5): 1240-1250. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-018-3821-9.
[7] KANG Hong-pu, WU Yong-zheng, GAO Fu-qiang, LIN Jian, JIANG Peng-fei. Fracture characteristics in rock bolts in underground coal mine roadways [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2013, 62: 105-112. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2013.04.006.
[8] HADJIGEORGIOU J, DORION J, GHALI E. Support system performance under different corrosion conditions [J]. Journal of the Southern African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 2008, 108(6): 359-365. http://www.scielo.org. za/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2225-62532008000600007/.
[9] VANDERMAAT D, SAYDAM S, HAGAN P C, CROSKY A. Back-calculation of failure stress of rockbolts affected by stress corrosion cracking in underground coal mines [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2017, 100: 310-317. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017. 10.029.
[10] WU Sai-sai, CHEN Hong-hao, CRAIG P, RAMANDI H, TIMMS W, HAGAN P C, CROSKY A, HEBBLEWHITE B, SAYDAM S. An experimental framework for simulating stress corrosion cracking in cable bolts [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2018, 76: 121-132. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2018.03.004.
[11] KOVAC J, ALAUX C, MARROW T J, GOVEKAR E, LEGAT A. Correlations of electrochemical noise, acoustic emission and complementary monitoring techniques during intergranular stress-corrosion cracking of austenitic stainless steel [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(6): 2015-2025. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2010.02.035.
[12] TORIBIO J, VALIENTE A. Failure analysis of cold drawn eutectoid steel wires for prestressed concrete [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2006, 13(3): 301-311. DOI: 10.1016/ j.engfailanal.2005.03.003.
[13] GRAY P. Stress corrosion cracking of rock bolts [C]// Coal 1998: Coal Operator’ conference. University of Wollongong & the Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 1998. https://ro.uow.edu.au/coal/ 258/.
[14] WINZER N, ATRENS A, SONG G, GHALI E, DIETZEL W, KAINER K U, HORT N, BLAWERT C. A critical review of the stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of magnesium alloys [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2005, 7(8): 659-693. DOI: 10.1002/adem.200500071.
[15] MA H, LIU Z, DU C, WANG H, LI X, ZHANG D, CUI Z. Stress corrosion cracking of E690 steel as a welded joint in a simulated marine atmosphere containing sulphur dioxide [J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 100: 627-641. DOI: 10.1016/ j.corsci.2015.08.039.
[16] WAN Hong-xia, DU Cui-wei, LIU Zhi-yong, SONG Dong-dong, LI Xiao-gang. The effect of hydrogen on stress corrosion behavior of X65 steel welded joint in simulated deep sea environment [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2016, 114: 216-223. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2016.01.020.
[17] HAASE R J, HANKE L D. Alkaline carbonate SCC failures at a refinery [J]. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2018, 18(1): 153-161. DOI: 10.1007/s11668-018-0391-y.
[18] CROSKY A, FABJANCZYK M, GRAY P, HEBBLEWHITE B. Premature rock bolt failure: Stage 2 [R]. Sydney, ACARP Project, 2004.
[19] AZIZ N, CRAIG P, NEMCIK J, HAI F. Rock bolt corrosion– An experimental study [J]. Mining Technology, 2014, 123(2): 69-77. DOI: 10.1179/1743286314Y.0000000060.
[20] CRAIG P, SERKAN S, HAGAN P C, HEBBLEWHITE B, VANDERMAAT D, CROSKY A, ELIAS E. Investigations into the corrosive environments contributing to premature failure of Australian coal mine rock bolts [J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2016, 26(1): 59-64. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2015.11.011.
[21] VILLALBA E, ATRENS A. Hydrogen embrittlement and rock bolt stress corrosion cracking [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2009, 16(1): 164-175. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfailanal. 2008.01.004.
[22] DE MEO D, DIYAROGLU C, ZHU N, OTERKUS E, SIDDIQ M A. Modelling of stress-corrosion cracking by using peridynamics [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(15): 6593-6609. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene. 2016.02.154.
[23] ZHU Long-kui K, YAN Yu, LI Jin-xu, QIAO Li-jie, VOLINSKY A A. Stress corrosion cracking under low stress: Continuous or discontinuous cracks? [J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 80: 350-358. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2013.11.057.
[24] EQUEENUDDIN S M, TRIPATHY S, SAHOO P K, PANIGRAHI M K. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of acid mine drainage and water pollution at Makum Coalfield, India [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2010, 105(3): 75-82. DOI: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2010.04.006.
[25] BANWART S A, MALMSTRoM M E. Hydrochemical modelling for preliminary assessment of minewater pollution [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2001, 74(1): 73-97. DOI: 10.1016/S0375-6742(01)00176-5.
[26] van STEMPVOORT D R, van der KAMP G. Modeling the hydrogeochemistry of aquitards using minimally disturbed samples in radial diffusion cells [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2003, 18(4): 551-565. DOI: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02) 00152-X.
[27] JAKOBSEN R, COLD L. Geochemistry at the sulfate reduction–methanogenesis transition zone in an anoxic aquifer—A partial equilibrium interpretation using 2D reactive transport modeling [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(8): 1949-1966. DOI: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.01.013.
[28] TIMMS W, HENDRY M. Quantifying the impact of cation exchange on long-term solute transport in a clay-rich aquitard [J]. Journal of hydrology, 2007, 332(1, 2): 110-122. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.06.025.
[29] BOZAU E, VAN BERK W. Hydrogeochemical modeling of deep formation water applied to geothermal energy production [J]. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 2013, 7: 97-100. DOI: 10.1016/j.proeps.2013.03.006.
[30] KLAPPER H, BARTETZKO A, LEHR J. Hydrogeochemical modelling to monitor scaling and corrosion during geothermal energy production in the north german basin [C]// CORROSION 2017. NACE International, 2017.
[31] PENA J, TORRES E, TURRERO M J, ESCRIBANO A, MARTIN P L. Kinetic modelling of the attenuation of carbon steel canister corrosion due to diffusive transport through corrosion product layers [J]. Corrosion Science, 2008, 50(8): 2197-2204. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2008.06.004.
[32] CRAIG P, AZIZ N I. Shear testing of 28 mm hollow strand “TG” cable bolt [C]// 29th International Conference on Ground Control in Mining. Morgantown, West Virginia, 2010.
[33] PARKHURST D L, APPELO C A J. User’s guide to PHREEQC (Version 2): A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations [M]. 1999.
[34] VANDERMAAT D. Stress corrosion cracking of rockbolts: a laboratory based approach utilising a controlled mine envrionment [D]. Sydney, Australia: University of New South Wales, 2014.
[35] LIU Hong-wei, CHENG Y Frank. Mechanistic aspects of microbially influenced corrosion of X52 pipeline steel in a thin layer of soil solution containing sulphate-reducing bacteria under various gassing conditions [J]. Corrosion Science, 2018, 133: 178-189. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2018. 01.029.
[36] STIPANICEV M, ROSAS O, BASSEGUY R, TURCU F. Electrochemical and fractographic analysis of microbiologically assisted stress corrosion cracking of carbon steel [J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 80: 60-70. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2013.11.009.
[37] SAND W, GEHRKE T. Microbially influenced corrosion of steel in aqueous environments [J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Biotechnology, 2003, 2(2-4): 169-176. DOI: 10.1023/B:RESB.0000040468.88570.4e.
[38] APPELO C A J, POSTMA D. Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution [M]. 2nd ed. CRC Press, 2004.
[39] BIEZMA M V. The role of hydrogen in microbiologically influenced corrosion and stress corrosion cracking [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2001, 26(5): 515-520. DOI: 10.1016/S0360-3199(00)00091-4.
[40] JAKOBSEN R. Redox microniches in groundwater: A model study on the geometric and kinetic conditions required for concomitant Fe oxide reduction, sulfate reduction, and methanogenesis [J]. Water Resources Research, 2007, 43(12). DOI: 10.1029/2006WR005663.
[41] ENNING D, GARRELFS J. Corrosion of iron by sulfate-reducing bacteria: New views of an old problem [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2014, 80(4): 1226-1236. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02848-13.
[42] WU Sai-sai, CHEN Hong-hao, RAMANDI H L, HAGAN P C, CROSKY A, SAYDAM S. Effects of environmental factors on stress corrosion cracking of cold-drawn high- carbon steel wires [J]. Corrosion Science, 2017, 132: 234-243. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2017.12.014.
[43] CHOU Chen-lin. Sulfur in coals: A review of geochemistry and origins [J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2012, 100: 1-13. DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2012.05.009.
[44] STACKEBRANDT E, STAHL D A, DEVEREUX R. Taxonomic relationships. in In Sulfate-reducing bacteria [M]. Springer, 1995: 49-87. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1582-5_3.
[45] DINH H T, KUEVER J, MUβMANN M, HASSEL A W, STRATMANN M, WIDDEL F. Iron corrosion by novel anaerobic microorganisms [J]. Nature, 2004, 427(6977): 829-832. DOI: 10.1038/nature02321.
[46] GU Ting-yue. New understandings of biocorrosion mechanisms and their classifications [J]. Journal of Microbial & Biochemical Technology, 2012, 4(4): iii-vi. DOI: 10.4172/1948-5948.1000e107.
(Edited by ZHENG Yu-tong)
中文导读
地下煤矿锚杆(索)过早失效腐蚀环境的水文地球化学模拟
摘要:锚杆(索)被广泛应用于地下采矿和巷道掘进过程中以提高顶板稳定性。由于锚固材料的腐蚀敏感性、所处潮湿、腐蚀环境以及拉伸应力的影响,锚杆(索)的过早失效是地下开采工程中存在的重大安全隐患。本文将实验室实验与水文地球化学模型相结合,对地下煤矿水环境下锚杆(索)的腐蚀破坏进行了研究。根据实验数据和矿井水水化学数据,采用PHREEQC软件对锚杆(索)与矿井地下水和岩层材料间腐蚀反应进行了模拟分析。建立了一系列的模型量化铁和碳元素反应量,模拟了有氧和无氧条件下水环境中的化学反应,得到各离子浓度、pH和随反应进度的变化趋势,并与实验结果进行对比。结果表明,锚杆(索)的腐蚀受到某些自然环境因素的抑制,因为水中溶解氧可以促进更多铁氧化。通过水文地球化学模拟等手段,阐明了锚杆(索)周边环境是影响其应力腐蚀开裂过程的重要因素。
关键词:锚杆(索);水文地球化学模拟;锚杆和锚索;应力腐蚀开裂;水化学分析
Foundation item: Project(140100153) supported by Australian Research Council Linkage Grant
Received date: 2019-08-10; Accepted date: 2020-02-17
Corresponding author: Wendy TIMMS, PhD, Professor; Tel: +61-3-5227-8692; E-mail: wendy.timms@deakin.edu.au; ORCID: 0000- 0002-6114-5866

