文章编号:1004-0609(2008)10-1825-06
钙对镁合金表面锰系转化膜的影响
刘 锋1, 2,单大勇1,韩恩厚1,刘常升2
(1. 中国科学院金属研究所 环境腐蚀中心,沈阳 110016;
2. 东北大学 材料与冶金学院,沈阳 110016)
摘 要:将钙离子作为添加剂,加入到镁合金锰系转化膜成膜溶液中。应用粗糙度仪和电化学方法研究钙离子对膜层粗糙度和膜层耐蚀性的影响规律;应用SEM和XPS分析钙离子对膜层表面形貌影响、膜层的元素组成和钙离子的存在形式。结果表明:Ca(NO3)2浓度大于2 g/L后,膜层粗糙度较未添加前有所降低,膜层表面组织变得平整,膜层裂纹变得窄小;Ca(NO3)2浓度为5 g/L时,膜层的耐蚀性最好。XPS结果表明,膜层主要由Mn、P、O、Mg、Ca和Al元素组成,钙离子在膜层中以CaCO3、CaO和一种无定形态磷酸钙盐存在。
关键词:钙离子;镁合金;锰系磷酸盐转化膜;裂纹
中图分类号:TG 174 文献标识码: A
Effect of Ca2+ on phosphate conversion coating on magnesium alloy
LIU Feng1, 2, SHAN Da-yong1, HAN En-hou1, LIU Chang-sheng2
(1. Environment Corrosion Center, Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China;
2. School of Material and Metallurgy, Northeast University, Shenyang 110016, China)
Abstract: Ca2+ was added into the phosphate conversion solution of magnesium alloy as an additive. Roughness tester and electrochemical test were used to analyze the effect of Ca2+ on the roughness and corrosion resistance of coating; SEM was used to observe effect of Ca2+ on the morphology of coating. XPS was used to investigate the composition of coating and what kind of Ca salts existing in the coating. The results show that the surface of coating turns to smooth and the crack of the coating becomes narrow when the concentration of Ca(NO3)2 in conversion solution exceeds 2 g/L. The corrosion resistance of coating is the best at 5 g/L of Ca(NO3)2. XPS results show that the coating is composed of Mn, P, O, Mg, Ca and Al, and Ca2+ exists in the coating in the form of CaCO3, CaO and a kind of amorphous calcium phosphate salt.
Key words: Ca2+; magnesium alloy; phosphate conversion solution; crack
耐蚀性差是镁合金应用的瓶颈之一[1-2]。目前应用在镁合金的表面防护方法主要包括:化学转化膜、微弧氧化技术,有机涂层和金属镀层等[3],其中化学转化膜具有廉价、操作简单等优点。目前研究较多的化学转化膜体系包括:磷酸盐转化膜[4]、锡酸盐转化膜[5]、稀土转化膜[6]和有机酸转化膜[7]等。
镁合金锰系转化膜[8]已经应用到生产中,但存在成膜时间过长、膜层粗糙度逐渐上升和处理效率下降等缺点。由于钙离子具有提高膜层的耐蚀性、细化膜层结构等优点,所以在钢铁磷化中得到应用[9]。因此,针对镁合金磷酸锰系转化膜在生产中遇到的问题,本文作者将钙离子作为添加剂加入到成膜溶液中,并研究钙离子对膜层的粗糙度、表层结构和耐蚀性等指标的影响规律,以便确定最佳添加量,为镁合金锰系磷酸盐转化膜性能改进提供了一种有效的途径。
1 实验
实验材料为AZ91D压铸镁合金,试样的加工尺寸为:3 cm×2 cm×0.2 cm。
试样处理步骤为:800#水砂纸打磨→水洗→碱洗除油→水洗→酸洗→水洗→成膜处理→水洗→干燥。
碱洗液成分为25 g/L的NaOH溶液,处理温度为70 ℃,时间1 min;酸洗液为20 g/L的NH4H2PO4溶液,处理温度为常温,时间0.5 min;成膜溶液成分为基础液[10]和一定浓度的Ca(NO3)2,其中Ca(NO3)2依次按0、1.0、2.0、3.0、4.0、5.0、6.0、7.0 g/L添加到基础液中,处理温度为60 ℃,pH为2.75,时间10 min。
应用精度为十万分之一的电子天平对成膜前后试样进行称重;利用MITUTOYO表面粗度计,对膜层的粗糙度进行测量。
将不同工艺条件下获得的试样经过硅胶封闭,分别留有1 cm×1 cm的端面。电化学测试采用三电极体系,将试样作为工作电极放入到3.5%NaCl溶液中,饱和甘汞电极(SCE)为参比电极,铂片为辅助电极。应用M398/M263系统进行电化学交流阻抗(EIS)测量,仪器为EG&G公司生产的273型恒电位仪和5210型锁相放大器,激励信号为幅值5 mV的正弦波,频率范围为0.01 Hz-100 kHz,初始延迟时间为300 s;应用EG&G公司的M352/M273系统测试动电位极化曲线,初始延迟时间为600 s,扫描速度为0.5 mV/s,从自腐蚀电位-0.1 V开始极化扫描。
采用 XL30 FEG ESEM 型环境扫描电子显微镜,对膜层表面形貌进行观察。加速电压10~25 kV,束斑直径2~3 μm,探测深度2~3 μm;应用ESCALAB250光电子能谱仪(XPS)对膜层进行分析[11-12],X射线源为MgKa,功率为300 W,分析面积为2 mm×2 mm,真空度为1×10-5 Pa。
2 结果及分析
2.1 钙离子对成膜前后增重和粗糙度的影响
转化膜是一种沉积膜,即难溶磷酸盐在镁合金表面沉积的过程,然而由于成膜溶液为酸性溶液,对膜层有一定的侵蚀作用,因此膜的形成可以看成是一种难溶磷酸盐沉积和溶解的动态过程;试样在成膜过程中,也受到了溶液的侵蚀作用,因此在试样表面存在着基体的溶解、膜的沉积和膜的溶解3个过程,因此试样质量的变化在一定程度上反映了成膜速度的快慢,即可以认为当试样增质较大时,成膜速度较快[13]。图1所示为Ca(NO3)2添加浓度对试样增质随的影响规律,从图中可以看出,试样增质随着钙离子浓度增加而增加,因此与钢铁磷化相同,钙离子对成膜过程有加速作用。图2所示钙离子对膜层粗糙度影响规律。从图中可以看出,当Ca(NO3)2的浓度小于2 g/L时,膜层粗糙度单调减小;当Ca(NO3)2的浓度大于2 g/L后,膜层粗糙度基本不变。因此钙离子的加入可以达到降低膜层粗糙度的目的。
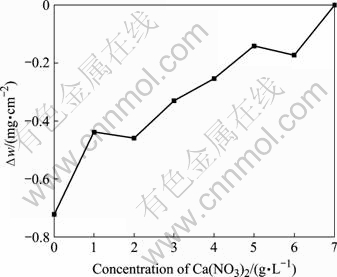
图1 Ca(NO3)2浓度对试样增重的影响
Fig.1 Influence of concentration of Ca(NO3)2 on mass gain of samples
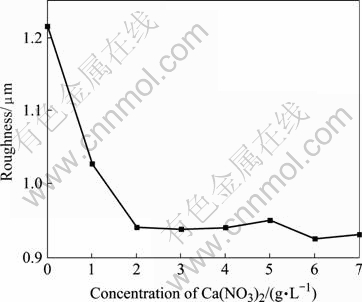
图2 Ca(NO3)2浓度对膜层粗糙度的影响
Fig.2 Influence of concentration of Ca(NO3)2 on roughness of coatings
2.2 钙离子对膜层耐蚀性的影响
图3所示为3.5%NaCl溶液中膜层的EIS谱Nyquist图,Nyquist图均由两个容抗弧组成,在Nyquist图中高频部分反映的是膜层阻挡层的特征,中低频反映膜层的多孔性特征[14-15]。应用Zsimpwin3.0软件对阻抗谱进行模拟, 图4所示为模拟电路图。由于膜层的微观不均匀性,所以采用CPE(常相位角元件)代替电容元件C进行拟合,Rs为溶液电阻,R1为多孔层电阻,CPE1表示多孔层电容特征,R2为转化膜阻挡层电阻,CPE2表示膜层阻挡层的电容性特征。一般认为,膜层电阻值越大,表示CPE值的Y0值越小,膜层的耐蚀性越好,同时,CPE值越小,膜层致密性越好。表1所列为拟合参数值,可以看出,在Ca(NO3)2浓度为5 g/L时,多孔层电阻R1最大,表示CPE值大小的Y0最小,阻挡层的阻值R2最大,因此此时膜层的耐蚀性最好。
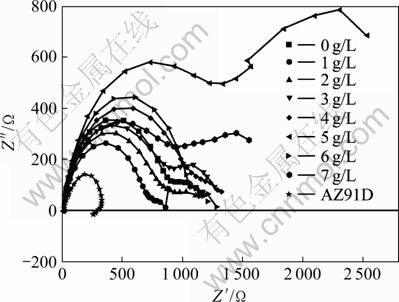
图3 Ca(NO3)2浓度不同时膜层的交流阻抗谱
Fig.3 EIS result of coatings when concentration of Ca(NO3)2 were different
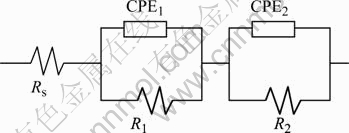
图4 膜层模拟电路
Fig.4 Equivalent circuit for phosphate conversion coating
表 1 膜层阻抗拟合参数值
Table 1 Impedance parameters of conversion coating
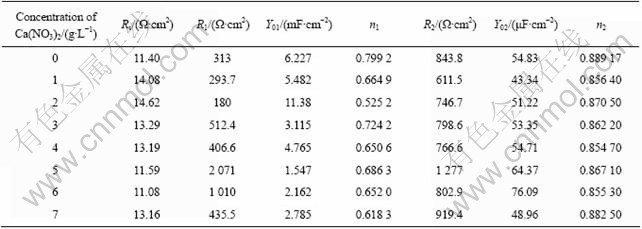
图5所示为膜层在3.5%NaCl溶液中的极化曲线结果。表2所列为极化曲线的拟合参数值,可以看出,膜层的自腐蚀电位在-1.4901和-1.5446之间变化,随着钙离子浓度增加,自腐蚀电位有向负转移的趋势;而Icorr的变化趋势为先减后增,即当Ca(NO3)2浓度小于5 g/L时,随着Ca(NO3)2浓度增加,Icorr逐渐减小,当Ca(NO3)2浓度大于5 g/L后,Icorr有增大趋势,在Ca(NO3)2浓度为5 g/L时,Icorr最小,此条件下膜层耐性最好。
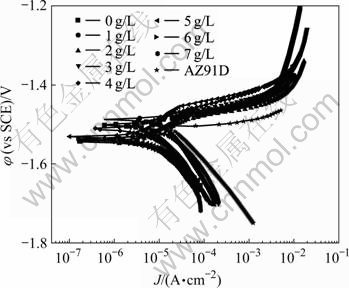
图5 膜层极化曲线结果
Fig.5 Potentiodynamic polarization curves
表 2 极化曲线拟合参数值
Table 2 Electrochemical parameters related to polarization curves

2.3 钙离子对膜层微观组织的影响
图6所示为膜层的SEM照片,可以看出,当没有加入钙离子的时候,膜层表面裂纹较宽;当钙离子浓度大于2 g/L后,膜层的表面裂纹变得窄小,但是当Ca(NO3)2浓度达到7 g/L时,膜层表面裂纹又有变宽趋势,但较未添加前仍有改善。将膜层的SEM照片与图2相对应,可以看出,钙离子浓度达到2 g/L后,膜层裂纹数量减少,进而使膜层的粗糙度降低照片的结果也与电化学结果相对应,即当钙离子浓度增加到一定浓度后,膜层致密性增加,表面裂纹变得细小,膜层的耐蚀性得到提高。
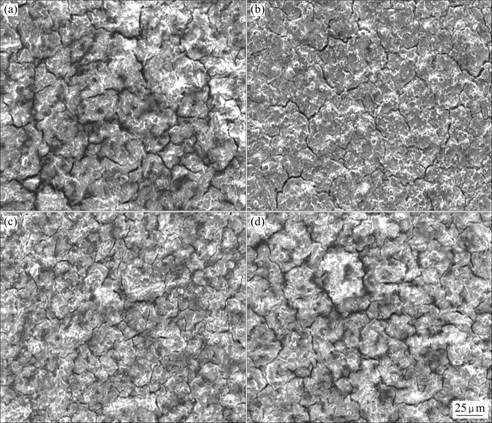
图6 Ca(NO3)2浓度对膜层形貌的影响
Fig.6 Influence of concentration of Ca(NO3)2 on coating morphology: (a) 0 g/L; (b) 2 g/L , (c) 5 g/L; (d) 7g/L
2.4 膜层的成分及存在形式
图7所示为Ca(NO3)2浓度为5g/L时,所成膜层表面的全元素扫描结果,表3所列为膜层中各种元素的含量,可以看出膜层主要由Al、P、Ca、O、Mn和Mg组成。图8所示为Ca 2p峰的窄幅扫描谱,应用XPS数据处理软件XPSPEAK4.1对Ca 2p进行分峰,数据和文献分析[16],Ca2p3/2峰对应的化合物为CaCO3和CaO,Ca2p1/2峰对应的化合物可能为一种无定形态磷酸钙盐。
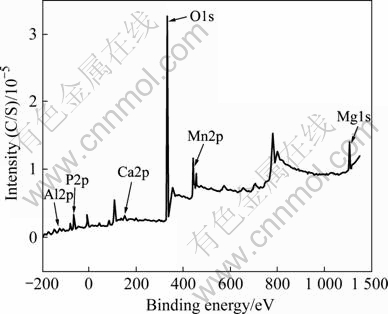
图7 全元素扫描结果
Fig.7 XPS survey spectra of conversion coating
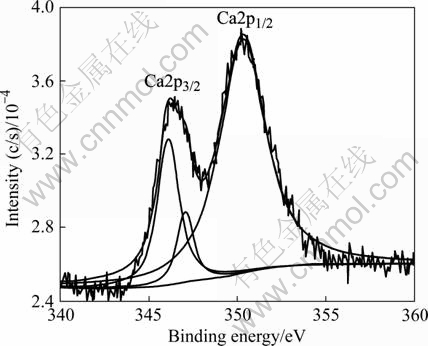
图8 Ca2p峰的窄幅扫描谱结果
Fig.8 Narrow scanning XPS survey spectra for Ca2p
表3 膜层元素含量
Table 3 Element concentration of conversion coating

3 结论
1) 钙离子的添加使成膜速度有所增加。当Ca(NO3)2的浓度小于2 g/L时,膜层粗糙度单调减小;当Ca(NO3)2的浓度大于2 g/L后,膜层粗糙度基本不变。
2) 当Ca(NO3)2 浓度达到5 g/L时,转化膜膜层自腐蚀电流密度最小,膜层耐蚀性最好。
3) Ca(NO3)2浓度大于2 g/L后,膜层表面组织变得平整,膜层裂纹变得窄小。
4) 膜层主要由Mn、P、O、Mg、Ca和Al元素组成,钙离子在膜层中以CaCO3、CaO和一种无定形态磷酸钙盐存在。
REFERENCES
[1] BALLERINI G, BARDI U, BIGNUCOLOR, CERAOLO G. About some corrosion mechanisms of AZ91D magnesium alloy. Corrosion Science[J]. 2005, 47(9): 2173-2184.
[2] SONG Guang-ling, HAPUGODA S. Degradation of the surface appearance of magnesium and its alloys in simulated atmospheric environments[J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(3): 1245-1265.
[3] 周婉秋, 单大勇, 曾荣昌. 镁合金的腐蚀行为与表面防护方法[J]. 材料保护, 2002, 35(7): 1-3.
ZHOU Wan-qiu, SHAN Da-yong, ZENG Rong-chang. Corrosion behavior and surface protection of magnesium alloys [J]. Materials Protection, 2002, 35(7): 1-3.
[4] LI G Y, LIAN J S, NIU L Y. Growth of zinc phosphate coatings on AZ91D magnesium alloy[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2006, 201(3): 1814-182.
[5] LIN C S, LIN H C, LIN K M, LAI W C. Formation and properties of stannate conversion coatings on AZ61 magnesium alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(1): 93-109.
[6] RUDD A L, BRESLIN C, MANSFELD F. The corrosion protection afforded by rare earth conversion coatings applied to magnesium[J]. Corrosion Science, 2000, 42(2): 275-288.
[7] LIU Jian-rui, GUO Yi-na, HUANG Wei-dong. Study on the corrosion resistance of phytic acid conversion coating for magnesium alloys[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2006, 201(3): 1536-1541.
[8] 周婉秋, 单大勇, 韩恩厚, 柯 伟. 镁合金无铬化学转化膜的耐蚀性研究[J]. 材料保护, 2002, 35(2): 12-14.
ZHOU Wan-qiu, SHAN Da-yong, HAN En-hou, KE Wei. Studies on corrosion resistance of a non-chromate conversion coating for magnesium alloys[J]. Materials Protection, 2002, 35(2): 12-14.
[9] 唐 林, 张 涛, 郑 岷. 钙离子在锌系磷化中的作用研究[J]. 电镀与精饰, 2003, 25(5): 5-8.
TANG Lin, ZHANG Tao, ZHENG Min. Investigation on the effect of calcium ion in zinc series phosphating[J]. Plating and Finishing, 2003, 25(5): 5-8.
[10] 周婉秋, 单大勇, 韩恩厚, 柯 伟. 镁合金无铬化学转化膜制备方法及所用成膜溶液. 中国ZL02132772.6[P]. 2002.
ZHOU Wan-qiu, SHAN Da-yong, HAN En-hou, KE Wei. Preparation method of non-chromate conversion coating for magnesium alloys and the solution. ZL02132772.6[P]. 2002.
[11] 文美兰. X射线光电子能谱的应用介绍[J]. 化工时刊, 2006, 20(8): 54-56.
WEN Mei-lan. Introduction of X-ray Photoelectron spectroscopy application[J]. Chemical Industry Times, 2006, 20(8): 54-56.
[12] 刘世宏, 王当憨, 潘承璜. X 射线光电子能谱分析[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 1988.
LIU Shi-hong, WANG Dang-han, PAN Cheng-huang. XPS survey spectra[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1988.
[13] ZHAO Ming, WU Shu-sen, ANA Ping, FUKUDA Y, NAKAE H. Growth of multi-elements complex coating on AZ91D magnesium alloy through conversion treatment[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 427(1): 310-315.
[14] 赵旭辉, 左 禹, 赵景茂. 铝阳极氧化膜在NaCl溶液中的电化学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(4): 562-567.
ZHAO Xu-hui, ZUO Yu, ZHAO Jing-mao. Electrochemical properties of anodized aluminum films in sodium chloride solution[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(4): 562-567.
[15] 曹楚南, 张鉴清. 电化学阻抗谱导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002.
CAO Chu-nan, ZHANG Jian-qing. An introduction to electrochemical impedance spectroscopy[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002.
[16] TAKADAMA H, KIM H M, KOKUBO T, et al. XPS study of the process of apatite formation on bioactive Ti-6Al-4V alloy in simulated body fluid[J]. Science and technology of advanced material, 2001, 2(2): 389-396.
基金项目:国家“十一五”科技支撑计划(2006BAE04B05-2);国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2007CB613705)
收稿日期:2008-02-27;修订日期:2008-07-04
通讯作者:韩恩厚,研究员,博士;电话:02483685772;E-mail: ehhan@imr.ac.cn
(编辑 何学锋)