

结霜工况下水蒸气在冷表面上冷凝成核的理论与实验研究
洪天顺,梁彩华,吕宁
(东南大学 能源与环境学院,江苏 南京,210096)
摘要:为了揭示结霜初期冷表面上冷凝成核过程的发展规律及其影响因素,针对结霜工况下冷表面在凝结初期的冷凝成核过程,建立基于吉布斯自由能理论与分子动力学理论的理论模型,并对结霜工况下低温铝表面的凝结过程进行可视化实验研究。研究结果表明:通过理论模型所得成核能障系数变化特征与实验结果有良好的一致性;成核位点的凝结成核能障系数越低,越容易形成初始液核;在凝结开始后50 s内,初始液核的位点的成核能障系数随时间呈线性递增;在冷凝成核阶段,由于水蒸气在凹结构上形成液核的成核能障较小,初始液滴会优先出现在表面上存在划痕、凹槽的区域;水蒸气冷凝形成初始液核的困难程度随着基底材料表面能降低而增加,随着冷表面温度升高而增加,随着空气露点温度降低而增加。
关键词:结霜;凝结成核;成核能障
中图分类号:TK124 文献标志码:A 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID)
文章编号:1672-7207(2021)06-1865-11
Theory and experimental study of water vapour nucleation process on a cold surface in frosting condition
HONG Tianshun, LIANG Caihua, LU Ning
(School of Energy and Environment, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China)
Abstract: In order to study the condensation nucleation process on a cold surface at the initial stage of frosting, a theoretical model based on Gibbs free energy and molecular dynamics theory was established. A visual experiment of condensation on cold aluminum surface in frosting conditions was carried out. The results show that the variation characteristies of the nucleation energy barrier coefficient obtained by the theoretical model are in good agreement with those of the experiment. The priority of forming the initial liquid nucleus for a nucleation site decreases with the increase of the nucleation barrier coefficient. Within 50 s after the start of condensation, the nucleation barrier coefficient of the nucleation site where the initial liquid nucleus appears increases linearly with the increase of time. The difficulty of water vapor nucelate to form the initial liquid core increases with the decrease of the surface energy of the substrate material, increases with the increase of the cold surface temperature, and increases with the decrease of the air dew point temperature.
Key words: frosting; condensation nucleation; nucleation barrier
空气源热泵在冬季制热工况下运行时容易结霜,霜层的存在增加了换热器与空气之间的换热热阻,降低了换热过程的效率,对机组性能产生不良影响[1]。水蒸气在-20 ℃以下的低温表面上凝结生成液核的活化率远高于凝华生成霜核的活化率,因此,结霜通常要经历液滴凝结、液滴冻结、霜层生长等过程[2-3]。其中,成核过程作为凝结的初始阶段,在凝结过程中起着关键性作用[4]。凝结液滴的分布对结霜过程有重要影响,稀疏的液滴分布能够有效延缓液滴的冻结,抑制霜层的生长[5-6],因此,研究水蒸气在冷表面上的冷凝成核过程对全面揭示霜层的形成与生长具有重要意义。根据有无基底诱导,凝结成核可以分为均相成核和非均相成核,冷表面上的冷凝成核现象属于非均相成核。TAMMANN等[7]提出了冷凝成核的发生机制,认为当表面达到一定过冷度后,凝结液核将随机地出现在冷表面的任意位置。MCCORMICK等[8]通过实验研究了镀苄硫醇的铜表面冷凝过程,实验结果证明了TAMMANN等[7]提出的机制。自此,不少学者针对纯蒸汽中的冷凝成核过程开展了一系列理论研究[9-15]。LIU等[16-17]运用可用能极值模型分析了液核内部的温度分布对非均相成核的影响。GUAN等[18]通过理论分析了电场作用对成核过程的影响,认为电场可以减小水蒸气中液滴凝结的临界半径,促进液滴凝结过程。AILI等[19]对超疏水表面纳米结构对成核过程的影响进行了研究,发现材料的本征润湿性和成核位点的形状对液滴成核有显著影响。IWAMASTSU[20]研究了液滴在球形表面上的成核情况,构建了液滴在球面上成核的理论模型,考虑了线张力对成核位垒的影响。XU等[21]运用分子动力学模拟研究了水蒸气在V型纳米阵列上凝结成核过程的润湿模式。目前关于冷凝成核的理论与实验研究主要集中于纯蒸汽工况下的凝结过程,而针对湿空气中冷凝成核过程的研究较少。为此,本文作者基于吉布斯自由能理论和分子动力学理论,考虑湿空气中不凝性气体的影响,构建结霜工况下过冷表面上水蒸气冷凝成核的理论模型,对结霜工况下过冷铝表面水蒸气凝结初期的冷凝成核特性进行可视化实验研究,分析水蒸气冷凝成核过程的影响因素,以便揭示冷表面水蒸气冷凝成核特性的发展规律。
1 理论模型
考虑水蒸气在光滑水平表面上的冷凝成核过程,凝结形成的初始液核在水平表面上呈球缺状,液核半径为r,液核与表面的接触角为 ,如图1所示。液核所处的环境条件如下:冷表面的温度为
,如图1所示。液核所处的环境条件如下:冷表面的温度为 ,湿空气的露点温度(饱和温度)为
,湿空气的露点温度(饱和温度)为 ,相对湿度为HR,液相温度为
,相对湿度为HR,液相温度为 ,气相温度为
,气相温度为 。
。

图1 水蒸气在水平表面上冷凝成核示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of nucleation on a smooth surface
对模型进行如下假设:
1) 湿空气为理想气体,满足理想气体状态方程;
2) 液滴凝结开始前,局部湿空气中水蒸气的温度等于液滴凝结发生后液体的温度,即Tv=Tl。
根据吉布斯自由能判据,系统的自发过程总是向着自由能减少的方向进行,当气液之间的相变转化时,比吉布斯自由能的变化量为
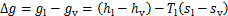 (1)
(1)
式中: 为相变过程的吉布斯自由能变化量;
为相变过程的吉布斯自由能变化量; 为液相比吉布斯自由能;
为液相比吉布斯自由能; 为气相比吉布斯自由能;
为气相比吉布斯自由能; 为液相比焓;
为液相比焓; 为气相比焓;
为气相比焓; 为液相比熵;
为液相比熵; 为气相比熵。
为气相比熵。
考虑湿空气中的水蒸气分子从未饱和状态变化至饱和状态,从饱和状态变化至过饱和状态,最终发生凝结相变的过程,式(1)右端的两项可以根据以下公式进行计算:

 (2)
(2)

 (3)
(3)
式中: 为水从气态变为液态的相变潜热;
为水从气态变为液态的相变潜热; 为液态水的比热容;
为液态水的比热容; 为气态水蒸气的比热容;
为气态水蒸气的比热容;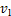 为液态水的比体积;
为液态水的比体积; 为液态水的压力;
为液态水的压力; 和
和 分别为环境温度
分别为环境温度 和
和 时湿空气的饱和水蒸气分压力;
时湿空气的饱和水蒸气分压力; 为湿空气的相对湿度;
为湿空气的相对湿度; 为理想气体常数。
为理想气体常数。
将式(2)和式(3)代入式(1)可得


 (4)
(4)
对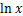 在
在 处泰勒展开,并略去二阶小项,有
处泰勒展开,并略去二阶小项,有 ,代入式(4)得
,代入式(4)得

 (5)
(5)
当环境温度为-30~20 ℃,空气流速为0.2~5.0 m/s时,可以估算温度边界层的厚度大约为 量级,而凝结液核的半径为
量级,而凝结液核的半径为 量级,可知凝结液核的特征尺度r远小于温度边界层的厚度
量级,可知凝结液核的特征尺度r远小于温度边界层的厚度 ,即
,即 ,据此可以认为,在水蒸气冷凝成核过程中,液核周围湿空气温度近似等于冷表面温度,即
,据此可以认为,在水蒸气冷凝成核过程中,液核周围湿空气温度近似等于冷表面温度,即 。因此,液滴凝结成初始液核过程中产生的体积自由能变化量为
。因此,液滴凝结成初始液核过程中产生的体积自由能变化量为


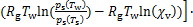
 (6)
(6)
式中: 为体积自由能变化量;
为体积自由能变化量; 为液态水的密度。
为液态水的密度。
水蒸气凝结形成初始液核过程中的系统自由焓变化量由两部分组成,其中,一部分是水蒸气由气态转化为液态所需的体积自由能变化量,另一部分为液核形成过程中的表面自由能变化量 ,可以用如下公式进行计算:
,可以用如下公式进行计算:


 (7)
(7)
水蒸气凝结形成稳定的液核需要跨越一个成核势垒,其值等于系统自由焓变化量的极大值,反映水蒸气从气态向液态转化的过程中,由亚稳态转变为稳态所需要的功。通过求取 关于r的极值点,可以获得形成临界液核时的临界成核半径
关于r的极值点,可以获得形成临界液核时的临界成核半径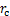 以及所需成核位垒
以及所需成核位垒 。
。
 (8)
(8)
 (9)
(9)


 (10)
(10)
凝结液核的内部压力可以由Laplace方程计算获得:
 (11)
(11)
定义水平表面上的成核能障系数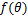 为
为
 (12)
(12)
水平表面上的凝结成核能障仅受表面能影响,由本征接触角θ决定,表面能越低,本征接触角越大。当θ=180°时,相当于均相凝结成核,将θ=180°代入式(12),可得f (θ)=1;当θ<180°时,为非均相凝结相成核,f (θ)<1。凝结成核能障系数f (θ)表征固体表面对凝结成核的诱导作用,成核能障系数越小,即凝结成核能障越小,凝结成核越容易发生。
当水蒸气在非光滑水平表面上凝结形成初始液核时,成核能障系数f还与表面的结构参数有关,f =f (θ,x1,x2,…,xi,α1,α2,…,αj),其中,x1,x2,…,xi,α1,α2,…,αj为表面的结构参数[15, 20, 22]。由此可知,当表面材料确定时,成核能障系数能够反映成核位点的结构特性。液核在凸球面、凹球面、凸锥面、完全浸润的凹锥面和未完全浸润的凹锥面上形成的形态示意图如图2所示[23]。当材料的本征接触角为95°时,4种理想表面结构(凸锥面、凹锥面、凸锥侧、凹锥侧)上的成核能障系数分别为0.960 9,0.104 8,0.572 6和0.562 7[23]。

图2 不同表面结构上凝结成核示意图[23]
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of nucleation on different surface structures
由于对临界成核半径、成核能障等参数进行实验测量有较大困难,本研究针对水蒸气在冷表面上形成液核的速率进行实验研究。根据分子动力学理论可以推导出纯蒸汽在水平表面上的非均相成核速率[24-25]。本研究在此基础上,考虑湿空气中不凝性气体的影响,认为

 (13)
(13)
式中:p为湿空气中水蒸气的分压力;k为玻尔兹曼常数; 为阿伏伽德罗常数;M为水的摩尔质量;m为单个水分子的质量;
为阿伏伽德罗常数;M为水的摩尔质量;m为单个水分子的质量; 和
和 分别为单位体积湿空气中的水蒸气分子数与空气分子数。
分别为单位体积湿空气中的水蒸气分子数与空气分子数。
2 实验装置及方法
本研究所采用的可视化研究实验平台如图3所示

图3 可视化研究实验平台示意图
Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of experiment setup
冷台系统采用TPC150温度控制单元,采用半导体温差电制冷获得低温,半导体制冷的热端热量被低温恒温槽制取的冷却水带走。冷台有内置温度传感器,便于实现对冷台温度进行测量,冷台的温度设定通过手动操作实现。在设定完成冷台温度后,冷台将以0.5 ℃/s的温度变化速率从初始温度变化至设定温度。采用型号为MER-310-12UC-L的CCD显微摄像仪对凝结过程中的细微观图像进行记录,并将图像传输至计算机。在图像采集过程中,使用黄色冷光源对实验表面进行照明。
本研究采用的实验表面为裸铝表面,使用型号为科诺SL150的接触角测量仪对实验表面的静态接触角、前进角、后退角等参数进行测量,运用Rafael-Tadmor方法计算获取表面的本征接触角。选取实验表面上任意5个位置测量静态接触角、前进角、后退角,并计算实验表面的本征接触角,结果如表1所示。翅片表面使用高导热硅脂粘贴在冷台表面上。使用型号为精创RC-4HA/C的温湿度测量仪对环境温湿度进行监测,其温度测量精度为±0.5 ℃,相对湿度测量精度为±2.5%。在实验过程中,各实验组的温度和湿度测量值如表2所示。
表1 裸铝表面接触角测量值
Table 1 Contact angle of naked aluminum surface measured with SEM (°)

表2 温度和湿度测量值
Table 2 Measured results of temperature and humidity

实验前,使用型号为德图Testo830-S1的红外测温仪对实验表面温度进行多次测量。经测量,在实验设定的温度范围内,实验表面与冷台间有0.5 ℃的温差。在实验过程中,设定表面初始温度为10 ℃,设定表面最终温度为-10 ℃。冷台温度设定完成后,以1 帧/s的频率进行图像采集。采用标尺网格法对液滴尺寸进行标定,即在相同放大倍率下对标尺上的网格进行拍摄。
利用Photoshop对采集的图像进行手动计数处理,以获取特定时刻下的液滴数量以及不同时段间由于合并所减少的液滴数量。当初始液滴粒径长大至1 μm左右时,能清晰分辨。根据ROSE理论[10]以及本文实验结果,认为粒径在2 μm以下的液滴不发生合并,因此,可以认为液滴在生长至能清晰分辨前未发生合并。
3 结果及讨论
当实验表面的温度降低至露点温度时,凝结开始发生。为方便将实验过程中的冷表面温度纳入理论模型中进行考虑,将实验表面温度降低至环境露点温度时刻作为初始时刻,根据冷台温度的变化规律,在实验过程中,实验表面的温度随时间的变化关系可以用下式表示:
 (14)
(14)
式中: 为冷表面的温度;
为冷表面的温度; 为所处实验工况下的露点温度;
为所处实验工况下的露点温度; 为时间。
为时间。

图4 实验一的凝结过程可视化实验图像
Fig. 4 Visual images of condensation process of Experiment 1
观察实验图像发现:液滴的成核过程主要发生在0~50 s之间,50 s后几乎没有新的液滴形成。这是因为实验所处工况下的有效成核位点均被液滴所覆盖,而其余区域由于成核能障过高无法形成初始液核。选择10,20,30,40和50 s时图像对液滴数量进行统计,并且统计(0,10],(10,20],(20,30],(30,40]和(40,50] s时段内由于合并减少的液滴数量。(0, ]的成核数量
]的成核数量 可以由
可以由 时刻的液滴数量
时刻的液滴数量 以及(0,
以及(0, ]内因合并减少的液滴数量
]内因合并减少的液滴数量 相加获得,即
相加获得,即
 (15)
(15)
图4和图5所示为0~50 s时结霜工况下冷表面凝结初期的可视化图像,视野面积约为6.91×10-8 m2。

图5 实验二的凝结过程可视化实验图像
Fig. 5 Visual images of condensation process of Experiment 2
液滴成核数量的统计结果如图6所示。将各时间段内液滴成核数量的变化量除以视野面积可以获得该时间段内的平均成核速率,将该值代入所构建的理论模型中,获得各个时间段内成核能障系数f。成核能障系数由基底材料的表面能以及成核位点的结构特征所决定,对于某一个确定的成核位点,其表面能以及结构特征不随时间的变化而变化,因此,成核位点的成核能障系数亦不随时间的变化而发生改变。然而,在整个冷凝成核过程中,在不同时刻下出现初始液核的位点是不同的,因此,不同时刻的成核能障系数f反映的是该时刻下出现初始液滴的位点特性。
模型中,各个时间段内冷表面温度的取值及通过模型获得的成核能障系数f如表3和表4所示,其余参数的取值参见表1和表2。

图6 成核数量统计结果
Fig. 6 Results of nucleation number
表3 实验一中的参数取值
Table 3 Numerical values in Experiment 1

表4 实验二中的参数取值
Table 4 Numerical values in Experiment 2

凝结成核能障系数f随时间的变化规律如图7所示,可见f可以近似为时间的线性函数。对f随时间的变化规律进行线性拟合,在实验一和实验二所示工况下(见表2),当时间分别为16.7 s和22.1 s时,f取0.131 9,该值为当材料的本征接触角为57°(即实验表面的本征接触角)时,水蒸气在水平表面结构上形成临界液核的成核能障系数。实验一中16~24 s内凝结过程的可视化图像见图8。从图8可见:在16 s前,液滴出现的位置主要集中分布在表面上的划痕、凹槽处;16 s后,液滴出现的位置开始均匀地分布在表面的任意位置。实验二中20~28 s内的可视化图像见图9。从图9可见:在21 s前,液滴出现的位置主要集中分布在表面上的划痕凹槽处;在21 s后,液滴出现的位置开始均匀地分布在表面的任意位置。图8和图9中的红色框线显示部分时刻下初始液滴出现的位置。通过理论分析可知,表面材料确定时,成核能障系数能够反映成核位点的结构特性。当成核能障系数f大于光滑水平表面上的成核能障系数时,水蒸气分子开始在水平表面结构的成核位点上凝结形成初始液核。微观下的凹锥面、凹球面等容易形成初始液核的表面结构位点分布在表面上存在凹槽、划痕的区域,而水平表面结构位点则能相对均匀地分布在表面上(不集中于凹槽、划痕附近),因此,当液滴出现的位置开始均匀地分布在表面的任意位置时,可以认为该时间点是水蒸气分子开始在水平表面结构上形成初始液核的时刻,可见,通过理论模型计算获得的成核能障系数与实验结果相吻合。

图7 凝结成核能障系数随时间的变化规律
Fig. 7 Variation of condensation barrier coefficients with time

图8 实验一中16~24 s时凝结过程的可视化图像
Fig. 8 Visual images of condensation process of Experiment 1 from 16 s to 24 s
从图7可以看出f随着时间不断增大,这表明在凝结初期,水蒸气会先在成核能障系数低的位点形成临界液核;当成核能障系数相对低的成核位点被液滴覆盖后,成核能障系数相对高的成核位点开始出现液滴,因此,可以认为成核位点的成核能障系数越低,在该成核位点形成初始液核的优先度越高。从所采集的实验图像也可以看出:在成核初期,液滴主要集中出现在表面存在划痕、凹槽的区域,直至f大于液滴在光滑表面上的成核能障系数时,才开始均匀地出现在表面的任意位置。这是由于液滴在凹面上的成核能障系数较小,形成初始液核所需的成核能障较小,因此,更容易形成初始液核。在凝结开始50 s后,视野范围内几乎不再出现新的液滴,其原因在于实验工况下的有效成核位点均被液滴所覆盖,而其余区域由于成核能障过高无法形成初始液核。根据所统计的实验结果(见图6),在实验一工况下(露点温度为5.1 ℃),液滴的成核位点密度约为2.67×1010 m-2,而在实验二工况下(露点温度为3.2 ℃),液滴的成核位点密度约为1.34×1010 m-2,可见湿空气中含湿量的变化对表面成核位点密度也有显著影响。

图9 实验二中20~28 s时凝结过程的可视化图像
Fig. 9 Visual images of condensation process of Experiment 2 from 20 s to 28 s
4 水蒸气在冷表面上冷凝成核特性
临界成核半径、成核能障可以反映水蒸气冷凝形成初始液核的难易程度,成核速率反映水蒸气冷凝形成初始液核程度,本研究针对以上3个参数的变化规律进行探究与讨论,分析水蒸气在冷表面冷凝成核的特性。
当本征接触角为60°,环境露点温度为5 ℃,湿空气相对湿度为60%时,临界成核半径随冷面温度的变化如图10(a)所示。从图10(a)可见:临界成核半径随着冷面温度的升高而增大;冷表面的温度影响凝结过程中的相变驱动力,冷表面温度越高,相变驱动力越小,初始液核越难以形成。当本征接触角为60°,冷表面温度为-10 ℃,湿空气相对湿度为60%时,临界成核半径随露点温度的变化如图10(b)所示。从图10(b)可以看出:临界成核半径随着露点温度的升高而减小;露点温度越高,表明湿空气的含湿量越大,空气越潮湿,初始液核越容易形成。
冷表面温度和露点温度对成核能障的影响分别如图11(a)和图11(b)所示,可见冷表面温度越低、露点温度越高,成核能障越小,初始液核越容易形成,这与图10所示结果相同。当露点温度为5 ℃,冷面温度为-10 ℃,空气相对湿度为60%时,成核能障随本征接触角变化规律如图11(c)所示。从图11(c)可见:成核能障随本征接触角的增大而增大。本征接触角反映了基底材料的表面能,表面能越低,本征接触角越大,因此,基底材料的表面能越低,初始液核越难以形成。当露点温度为5 ℃,冷表面温度为-10 ℃,空气相对湿度为60%时,成核能障系数对成核能障的影响如图11(d)所示。理论结果表明,成核位点的成核能障系数越大,形成初始液核所需的成核能障越高,初始液核越难以形成。

图10 临界成核半径rc的影响因素及变化规律
Fig. 10 Influence factors and variation law of critical nucleation radius

图11 成核能障的影响因素及变化规律
Fig. 11 Influence factors and variation law of nucleation barrier
当本征接触角为60°,环境露点温度为5 ℃,空气相对湿度为60%时,成核速率随冷表面温度的变化规律如图12(a)所示,可见冷表面温度越低,成核速率越大。当本征接触角为60°,冷表面温度为-10 ℃,空气相对湿度为60%时,成核速率随露点温度的变化规律如图12(b)所示,可见露点温度越高,成核速率越大。当露点温度为5 ℃,冷表面温度为-10 ℃,空气相对湿度为60%时,本征接触角对水平面上成核过程中成核速率的影响如图12(c)所示,可见本征接触角越大,成核速率越低。当露点温度为5 ℃,冷表面温度为-10 ℃,空气相对湿度为60%时,成核能障系数对成核速率的影响如图12(d)所示,可见成核能障系数越低的成核位点形成初始液核的速率越快。以上分析结果与分析图11所得结果一致。

图12 成核速率J的影响因素及变化规律
Fig.12 Influencing factors and variation law of nucleation rate
5 结论
1) 针对结霜工况下过冷表面的冷凝成核过程,建立了基于吉布斯自由能理论与分子动力学理论的理论模型;对结霜工况下过冷铝表面凝结过程进行了可视化研究,理论模型结果与实验结果较一致。
2) 在凝结初期,水蒸气优先在凝结成核能障系数低的位点形成临界液核,当成核能障系数相对低的成核位点被液滴覆盖后,成核能障系数相对高的位置才开始出现液滴。成核位点的凝结成核能障系数越低,在该位点形成初始液核的优先度越高。凝结成核能障系数与基底材料的表面能以及成核位点的结构有关,基底材料表面能越低,凝结成核能障系数越高。
3) 水蒸气冷凝形成初始液核的难易程度还受冷表面的温度及空气露点温度的影响。冷表面温度及露点温度的变化影响了凝结过程中的相变驱动力,冷表面温度越高、露点温度越低,相变驱动力越小,新相越难形成。
参考文献:
[1] SONG Mengjie, DENG Shiming, DANG Chaobin, et al. Review on improvement for air source heat pump units during frosting and defrosting[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 211: 1150-1170.
[2] WU Xiaomin, DAI Wantian, XU Wangfa, et al. Mesoscale investigation of frost formation on a cold surface[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2007, 31(8): 1043-1048.
[3] SONG Mengjie, DANG Chaobin, HIGASHI T, et al. Review of experimental data associated with the solidification characteristics of water droplets on a cold plate surface at the early frosting stage[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2020, 223: 110103.
[4] FRYMYER B, VAHEDI N, NETI S, et al. Thermal modeling with diffusion for dropwise condensation of humid air[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 151: 119413.
[5] 汪峰, 梁彩华, 张友法, 等. 结霜初期超疏水表面凝结液滴的自跳跃脱落及其对结霜过程的影响[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 46(4): 757-762.
WANG Feng, LIANG Caihua, ZHANG Youfa, et al. Jumping of condensation droplets on superhydrophobic surfaces at early frosting stage and its effects on frost formation[J]. Journal of Southeast University(Natural Science Edition), 2016, 46(4): 757-762.
[6] CHU Fuqiang, LIN Yukai, YAN Xiao, et al. Quantitative relations between droplet jumping and anti-frosting effect on superhydrophobic surfaces[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2020, 225: 110315.
[7] TAMMANN G, BOEHME W. Die zahl der wassertropfchen bei der kondensation auf verschiedenen festen stoffen[J]. Annalen Der Physik, 1935, 414(1): 77-80.
TAMMANN G, BOEHME W. The process of water vapor condensation on different solids[J]. Annals of Physics, 1935, 414(1): 77.
[8] MCCORMICK J L, WESTWATER J W. Nucleation sites for dropwise condensation[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1965, 20(12): 1021-1036.
[9] GRAHAM C, GRIFFITH P. Drop size distributions and heat transfer in dropwise condensation[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1973, 16(2): 337-346.
[10] ROSE J W. Further aspects of dropwise condensation theory[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1976, 19(12): 1363-1370.
[11] FLETCHER N H. Size effect in heterogeneous nucleation[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1958, 29(3): 572-576.
[12] DILLMANN A, MEIER G E A. A refined droplet approach to the problem of homogeneous nucleation from the vapor phase[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1991, 94(5): 3872-3884.
[13] XU Wei, LAN Zhong, PENG Benli, et al. Evolution of transient cluster/droplet size distribution in a heterogeneous nucleation process[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(60): 31692-31699.
[14] XU Junchao, ZHANG Jun, LONG Hongming. Direct observation of heterogeneous condensation on micron particles with uniform surface[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 376: 199-208.
[15] SINGHA S K, DAS P K, MAITI B. Thermokinetics of heterogeneous droplet nucleation on conically textured substrates[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2015, 143(20): 204703.
[16] LIU Xiuliang, CHENG Ping. Dropwise condensation theory revisited: part I. droplet nucleation radius[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 83: 833-841.
[17] LIU Xiuliang, CHENG Ping. Dropwise condensation theory revisited: part II. droplet nucleation density and condensation heat flux[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 83: 842-849.
[18] GUAN Xiaojun, YANG Luhang, CHENG Ping. Effects of electric fields on onset of dropwise condensation based on Gibbs free energy and availability analyses[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2014, 58: 105-110.
[19] AILI A, GE Qiaoyu, ZHANG Tiejun. How nanostructures affect water droplet nucleation on superhydrophobic surfaces[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2017, 139(11): 112401.1-112401.10
[20] IWAMATSU M. Line-tension effects on heterogeneous nucleation on a spherical substrate and in a spherical cavity[J]. Langmuir, 2015, 31(13): 3861-3868.
[21] XU W, LAN Z, PENG B L, et al. Effect of nano structures on the nucleus wetting modes during water vapour condensation: from individual groove to nano-array surface[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(10): 7923-7932.
[22] SINGHA S K, DAS P K, MAITI B. Effect of a triple contact line on the thermokinetics of dropwise condensation on an immiscible liquid surface[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(47): 41506-41515.
[23] 罗倩妮. 超疏水翅片表面结霜初期凝结与冻结特性[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2019: 13-18.
LUO Qianni. Study on mechanism and characteristics of condensation and freeze in initial stage of frosting on superhydrophobic fin surface[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2019: 13-18.
[24] HILL P G, WITTING H, DEMETRI E P. Closure to discussions of 'condensation of metal vapors during rapid expansion'[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 1963, 85(4): 303-317.
[25] XU Wei, LAN Zhong, PENG Benli, et al. Heterogeneous nucleation capability of conical microstructures for water droplets[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(2): 812-818.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期: 2021 -03 -06; 修回日期: 2021 -04 -25
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51676033);“十三五”国家重点研发计划项目(2016YFC700304) (Project(51676033) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2016YFC700304) supported by the National Key R&D Program of China during the 13th Five-Year Plam Period)
通信作者:梁彩华,博士,教授,从事制冷空调、建筑节能及可再生能源利用研究;E-mail:caihualiang@163.com
DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.06.016
引用格式:洪天顺, 梁彩华, 吕宁. 结霜工况下水蒸气在冷表面上冷凝成核的理论与实验研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(6): 1865-1875.
Citation:HONG Tianshun, LIANG Caihua, LU Ning. Theory and experimental study of water vapour nucleation process on a cold surface in frosting condition[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2021, 52(6): 1865-1875.