Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 1791-1799
Thermal-mechanical response of microscale functional film for infrared window
Xing LIU1, Xin-zhi WANG2, Jia-qi ZHU1, Jie-cai HAN1
1. Center for Composite Materials, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China;
2. School of Energy Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Received 6 December 2013; accepted 22 May 2014
Abstract: Infrared window in hypersonic missile usually suffers complex aerodynamic force/heat during high-speed flight. A finite element method was adopted to simulate the thermal and stress response of microscale functional film for infrared window under different aerodynamic heats/forces conditions. Temperature and stress distribution were obtained with different heat fluxes. There is almost constant stress distribution along the film thickness except a sudden decrease near the substrate. The maximum stresses are located at the points which are 0.5 mm away from the edges. Different film materials result in different stress values. The temperature and stress in ZrN are larger than those in Y2O3. Besides the numerical simulation, an oxygen propane flame jet impingement test was performed to investigate thermal shock failure of the infrared window. Some place of the window surface has spots damage and some place has line crack damage after thermal shock.
Key words: infrared window; thin films; finite element method; thermal stress; aerodynamic heating
1 Introduction
Infrared window is a key component of a hypersonic missile’s integration of structure and function. There is no doubt that infrared window has great effects on transferring the targets’ infrared signal, maintaining the aerodynamic shape and protecting imaging systems. Hypersonic missile usually suffers strong aerodynamic forces and serious aerodynamic heating, which will cause coupling effects of heat, force and light on the infrared window. This will lead the whole infrared detection system paralysis. Infrared window is composed of substrate materials and functional films. Polycrystalline ZnS is a common infrared substrate material, but it still has some drawbacks, such as soft texture, low mechanical strength and big brittleness [1]. Because of those drawbacks, polycrystalline ZnS cannot resist natural condition of the erosion of the raindrops and sandstone in the atmospheric environment. Moreover, it cannot resist the intensity aerodynamic heat/force. [2] Due to its high refractive index, it has large reflecting loss. Therefore, it is badly in need of an antireflective and protective film. Commonly used film materials include diamond-like carbon (DLC) [3-5], carbon germanium (GexC1-x), zirconium nitride (ZrN), yttria (Y2O3), yttrium fluoride (YF3) and boron phosphide (BP) [6-10].
It is very important to do research on failure of infrared window, so many organizations and scholars have studied it for a long period [11-15]. Because of the aerodynamic heats/forces, infrared window materials suffer complex three-dimensional heat/stress conditions. Window’ rupture, film delamination, light distortion and other failure phenomenon carry out when the macro/ micro structure and thermodynamic state of materials have tremendous changes. RUSSELL et al [16] used the ATAC3D aerothermal analysis code to provide convective and pressure boundary conditions coupled with the ANSYS finite element analysis code to solve the three dimensional finite element problem to analyze the thermal shock on infrared windows. KARAKSINA et al [17] studied the effect of hot isostatic pressing conditions on the microstructure of CVD ZnS and analyzed the mechanisms of zinc sulfide recrystallization at high temperatures and pressures. TOMBA and CAVALIERI [18] developed an elasto-dynamic solution for thermal shock due to heat convection at a constant temperature in a thick orthotropic cylindrical shell and presented the complete dynamic response of thermal shock stresses.
LIU and HUANG [19] established a model of coupled heat transfer of radiation and condition on infrared window and investigated the effects of material properties and thermal boundary condition on temperature distribution.
In order to study the mechanisms of function film delamination in infrared window materials, obtaining the thermal stress distribution of thin films is the primary work. A finite element analysis method is carried out to simulate the thermal response of microscale functional film for infrared window under the conditions with different aerodynamic heats/forces. Two kinds of films (Y2O3 and ZrN) were investigated as comparison. Thermal stress distributions of the films are obtained. Additionally, oxygen propane flame jet impingement test is performed to investigate the thermal shock failure of the infrared window. Microscope pictures are taken to evaluate the damage on the infrared window.
2 Models
2.1 Heat transfer model
According to energy balance principle, the wall temperature can be described by using the thermal conduction differential equation. For three-dimensional unsteady problem in Cartesian coordinate system, heat conduction differential equation is
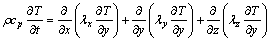 (1)
(1)
where ρ is the density; cp is the specific heat capacity; T is the temperature; t is the time; λx, λy, and λz are the thermal conductivities in x-, y- and z-direction, respectively. Additionally, the inner heat source is ignored.
Boundary conditions are as follows.
Inner surface of the solid wall is natural convection:
 (2)
(2)
Thermal flux of the outside surface is given by flow field calculation:
 (3)
(3)
where n means the outer normal of the surface; h is the convective heat transfer coefficient; Te and Ts represent the gas temperature and surface temperature, respectively; k is the thermal conductivity in outer normal of the surface; q is the heat flux; Γ is the area of the surface.
Meanwhile, the solid wall is also transferred by radiation. When the Mach number is small, the impact of radiation heat transfer can be ignored.
2.2 Thermal stress model
The stress and strain must satisfy the following equations.
The balance equation is
 (4)
(4)
where σ is the normal stress; τ is the shearing stress; Fx, Fy, Fz are the body forces of x-, y-, z-coordinate component, respectively;  ,
,  ,
, 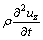 are dynamic terms.
are dynamic terms.
The physical equation is given as follows:
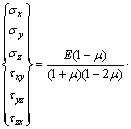
 (5)
(5)
where ε is the extension strain; γ is the shear strain; A1=μ/(1-μ); A2=(1-2μ)/[2(1-μ)]; E is the elastic modulus; μ is the Poisson ratio; α is the thermal expansion coefficient; ΔT is the variation of temperature.
2.3 Calculation model and mesh
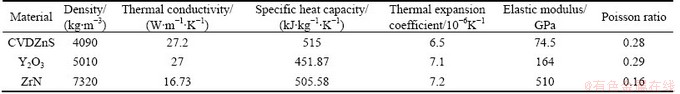
The material parameters in the simulation are listed in Table 1. Taking the actual computing capability of the computer into account, the dimensions of the calculating window are 6 mm × 5 mm × 1 mm, and the film thickness is 1 μm [16].
Table 1 Thermal and mechanical properties
Following assumptions are made to simplify the numerical cases: 1) Substrate material and functional film are both isotropic elastic materials; 2) Substrate material is fixed to the aircraft, so the displacement of its side is limited; 3) Environment does not affect the material properties; 4) Radiation heat transfer is ignored.
Directly coupling method was applied to simulating the thermal and stress distribution with coupling element SOLID5. Also structured grids were employed to build the calculating model. There are totally 54016 nodes and 47250 meshes in the model. As the window surface is exposed to the complex aerodynamic force/heat, these gradually varied grids are applied in the simulation. These grids get dense gradually from the backside to the surface. The grids of the model are shown in Fig. 1.
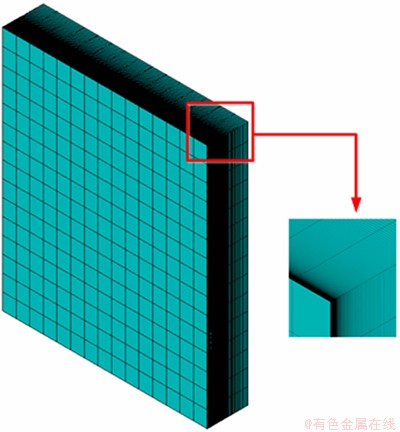
Fig. 1 Model of infrared window and its film
Thermal boundary condition on the out surface is a constant heat flux. And adiabatic boundary conditions are applied to the other surface. All surfaces are free to deform.
As infrared window usually suffers heat fluxes of 1×105-1×106 W/m2 [15], 4 different heat fluxes were chosen for the numerical simulation (see Table 2).
Table 2 Heat fluxes used in simulation
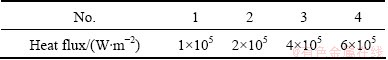
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Numerical results and analysis
As the missile system is a terminal guidance, so the infrared window will suffer inclement aerothermo- dynamic environment only a few seconds. Finally, the simulation time was set as 10 s.
In basic simulation, a window with CVD ZnS substrate and Y2O3 film was studied under different heat fluxes. Temperature and stress distributions were obtained.
Temperature distributions of the infrared window at 10 s with different heat fluxes are shown in Fig. 2. From Fig. 2 we can see that the temperature is almost the same and uniform on the film surface when the heat flux is 1×105 W/m2. The maximum temperature is in the outer surface and it is 536 K; the minimum temperature is in the inner surface and it is 534 K. No obvious differences reveal in temperatures. With the increasing of heat fluxes, the temperature of the window increases gradually. When the heat flux is 6×105 W/m2, the maximum temperature is also in the outer surface and reaches 1728 K; the minimum temperature is also in the inner surface and reaches 1717 K. This indicates that different heat fluxes have the same effects on temperature distribution law of the infrared window. The temperature is almost the same and uniform along the film surface.
Temperature variation with time at different heat fluxes at the center of the film surface is shown in Fig 3. It can be seen from Fig. 3 that the temperature at the center of the film increases with an exponential form, and the greater the heat flux is, the higher the temperature is. Meanwhile, the temperature also increases with time because of the thermal cumulating.
Stress distributions of the infrared window with different heat fluxes are shown from Fig. 4 to Fig. 7. At 10 s, the minimum stress is about 0.8 GPa and mainly occurs at the edges of the film surface when the heat flux is 1×105 W/m2. The stress increases from the surface edges to the surface center firstly. The maximum stress locates about 0.5 mm away from the edges, about 0.89 GPa. The stress is almost uniform distribution in the whole center of the film. From the figures we can see that similar stress distributions are obtained at different heat fluxes. With the increasing heat fluxed, film stress increased. Obviously, the heat flux has a great effect on the stress distribution of the film.
The stress variation with time at the center of the inner surface of the functional film and near the edge of the inner surface of the functional film is shown in Fig. 8. It can be seen from Fig. 8 that the stresses under different heat fluxes have similar distribution laws, which increase with the thermal shock time lapse. When the stress exceeds the material’s allowable stress, the film will fail.
The variation of the maximum stress along the film thickness is shown in Fig. 9, where H means the distance from the outer surface of the film to the inner surface of the film in the thickness direction. It can be seen from the figure that the maximum stress is almost constant from the outer surface to the inner surface. Near the substrate, the maximum stress has a sudden decrease, and the maximum stress decreases more as the heat flux increases more as the heat flux increases.
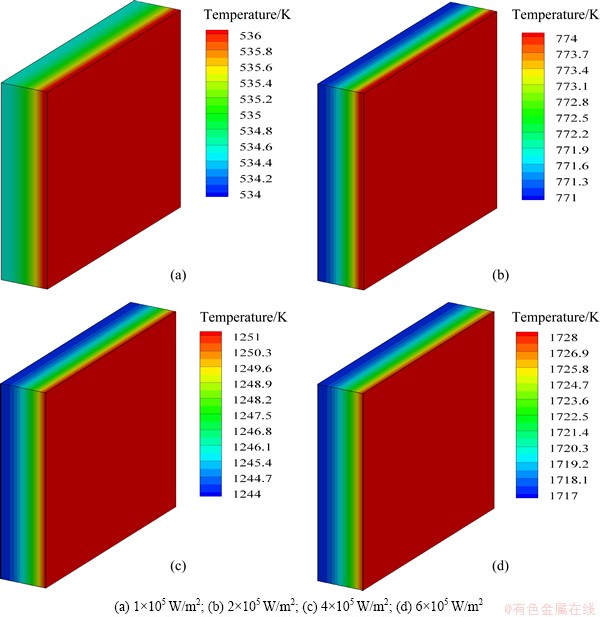
Fig. 2 Temperature distributions at 10 s with different heat fluxes
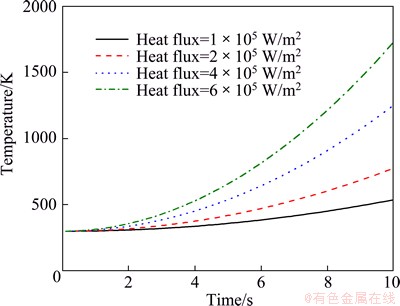
Fig. 3 Center temperature variation of outer surface with time at different heat fluxes
CVD ZnS-Y2O3 and CVD ZnS-ZrN were used as a comparison under the heat flux of 4×105 W/m2 to analyze the effect of film materials.
From Fig. 10 we can see that the law of temperature distributions in the thin film is the same with different film materials. The temperature is higher in the outer face and lower in the inner face. Temperature is almost the same and uniform along the film surface. Meanwhile, the temperature is almost unchanged at the same heat flux.
Temperature variation with time for different film materials at the center of the film surface is shown in Fig. 11. It can be seen from the figure that the temperature at the center of the film increases in the form of exponent, and the temperature is almost unchanged for different film materials.
Stress variations with time for different film materials at the center of the inner surface of the functional film and near the edge of the inner surface of the functional film are shown in Fig. 12. It can be seen from the figure that the stresses for different film materials have similar distribution laws. Stresses increase with the lapse of thermal shock time. Obviously, the stress in ZrN film is larger than that in Y2O3 film.
The variations of the maximum stress along the film thickness for different film materials are shown in Fig. 13. It can be seen from the figure that the maximum stress in ZrN is much larger than that in Y2O3, and there is a LARGE sudden change in the ZrN.
By comparing the temperature and stress distributions with different materials, we can see that film material’s properties have little effect on the temperature and stress distribution, but they have great effects on the stress variation. They have the same temperature distribution and variation under the same condition, but the stress in ZrN is much larger than that in Y2O3.
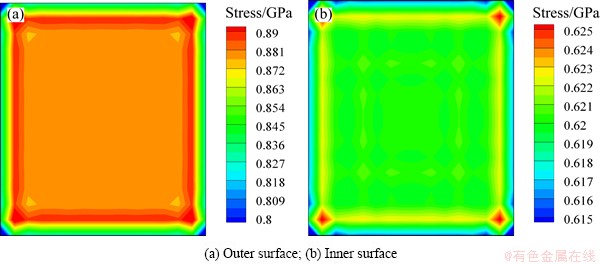
Fig. 4 Stress response at 10 s (Heat flux=1×105 W/m2)
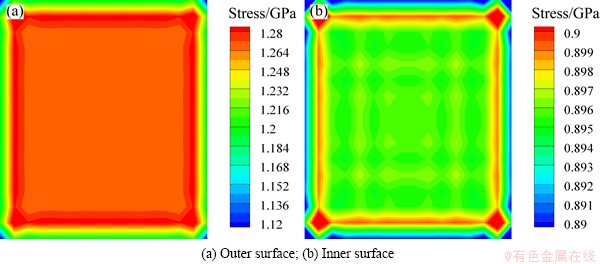
Fig. 5 Stress response at 10 s (Heat flux=2×105 W/m2)
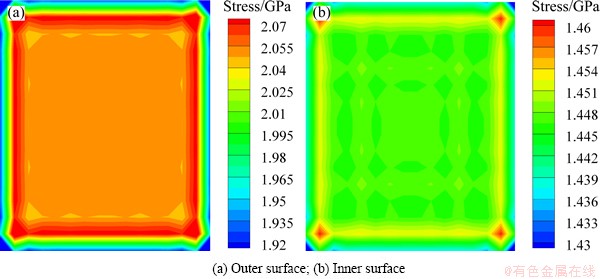
Fig. 6 Stress response at 10 s (Heat flux=4×105 W/m2)

Fig. 7 Stress response at 10 s (Heat flux=6×105 W/m2)
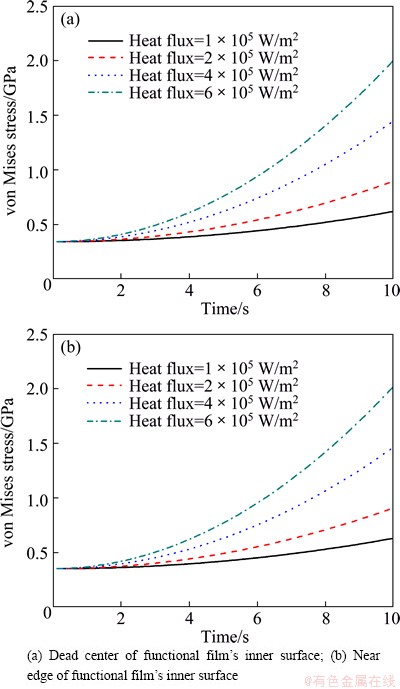
Fig. 8 Stress variation with time at different heat fluxes
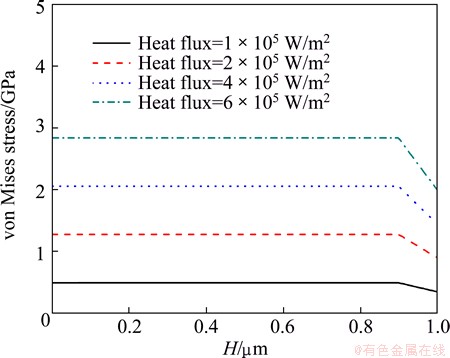
Fig. 9 Stress variation along film thickness (H) at 10 s
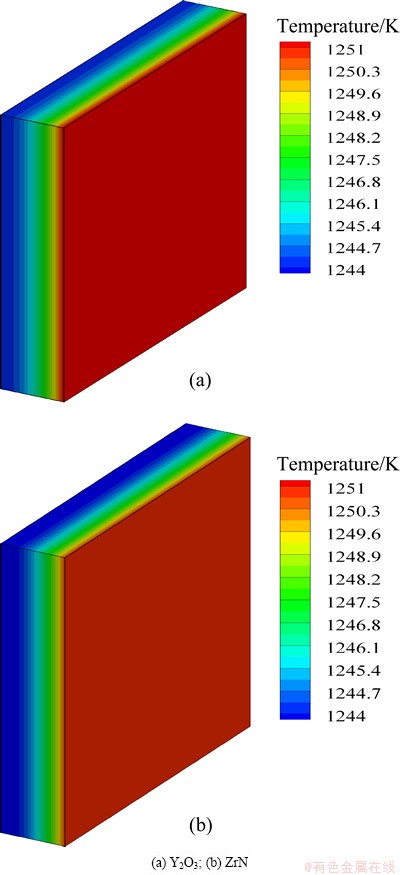
Fig. 10 Temperature distribution at 10 s with heat flux of 4×105 W/m2 for different film materials
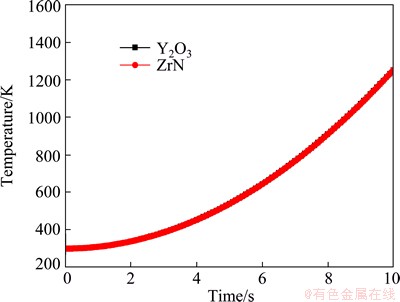
Fig. 11 Center temperature variation of outer surface with time for different film materials
3.2 Experimental results
In order to study the surface damage, a thermal shock experiment was carried out. The skeleton drawing of oxygen-propane experiment is shown in Fig. 14. The specimen (ZnS-Y2O3, d30 mm × 8 mm) is limited in the center of a graphite plate, and a high-temperature oxygen-propane flame jet is towards the specimen center. The experiment conditions are listed in Table 3.
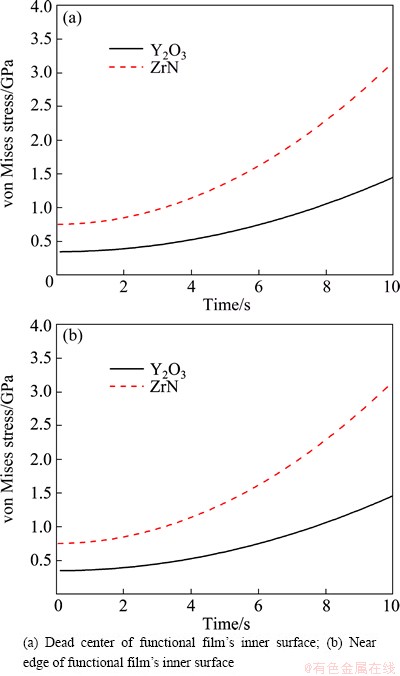
Fig. 12 Stress variation with time for different film materials
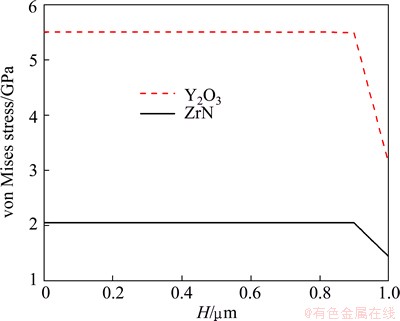
Fig. 13 Stress variation along film thickness at 10 s for different film materials
After 10 s thermal shock, the surface of the infrared window was damaged. The macroscopically photo of the damaged window is shown in Fig. 15. From Fig. 15 we can see that the specimen has many cracks. During the experiment, these cracks broke out while thermal shock stopped suddenly. The specimen suffered the greatest temperature difference and greatest thermal stress when the thermal shock stopped. When the thermal stress is larger than the materials’ allowable stress, the cracks break out.
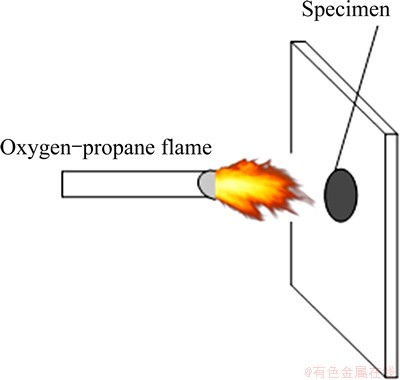
Fig. 14 Skeleton drawing of oxygen-propane experiment
Table 3 Experimental conditions

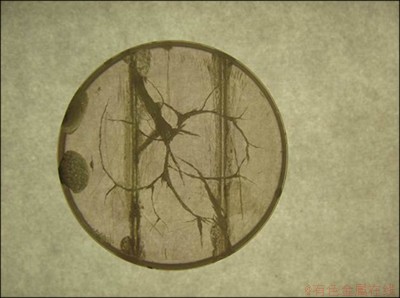
Fig. 15 Picture of infrared window surface after thermal shock
The metallographic microscope images of the infrared window surface after 10 s thermal shock is shown in Fig. 16, where the four pictures were taken from different places of the window. It shows that some of the window surface has spots damage, and some has line crack damage.
SEM images of the infrared window surface after 10 s thermal shock is shown in Fig. 17. The four pictures show the boundary and the center damage conditions with two different scales respectively. From the figure we can see that the damage mainly occurred in the center of the window. There are little small spot damages at the boundary of the window. Line cracks and big spot damage happened in the center of the window.
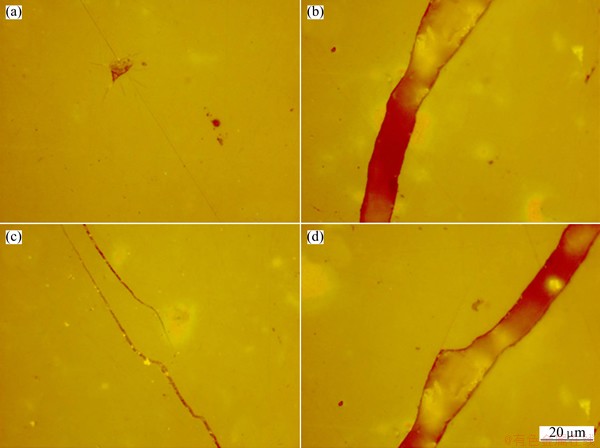
Fig. 16 Metallographic microscopy images of infrared window surface after thermal shock showing damage at different places
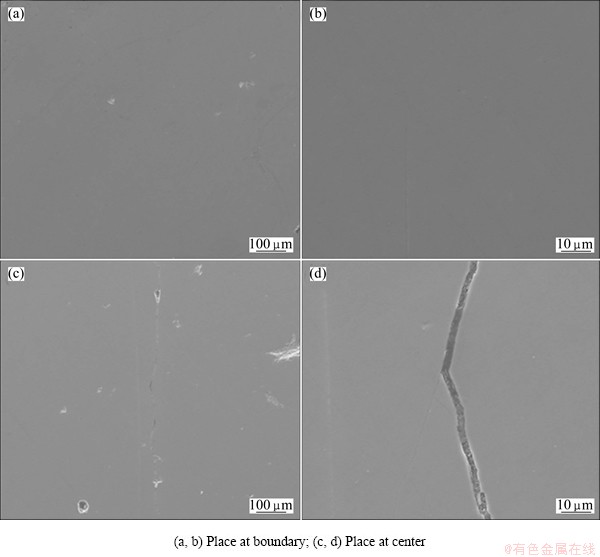
Fig. 17 SEM images of infrared window surface after thermal shock
4 Conclusions
1) An exponent increasing form was developed on the center temperature in certain heat flux. The greater the heat flux is, the more quickly the temperature increases.
2) There is almost constant stress distribution along the film thickness except a sudden decrease near the substrate. The maximum stresses are located at the points which are 0.5 mm away from the edges.
3) The same temperature and stress distribution laws bring out with different film materials in the same heat flux, but they have different values. The temperature and stress in ZrN are larger than those in Y2O3.
4) During 10 s thermal shock test, spot damages and crack damages appear in the center of the window surface.
References
[1] YASHINA E V. Preparation and properties of polycrystalline ZnS for IR applications [J]. Inorg Mater, 2003, 39(7): 663-668.
[2] LU F X, HE Q, GUO S B, ZHANG F L, TONG Y M. Sand erosion of freestanding diamond films prepared by DC arcjet [J]. Diam Relat Mat, 2010, 19(7): 936-941.
[3] HAN Jie-cai, ZHU Jia-qi. Amorphous diamond films deposited by filtered cathodic vacuum arc technology as infrared protective coatings [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals. 2005, 15(11): 1795-1799. (in Chinese)
[4] YANG P, SUNG C C, FUH Y K, CHUN C L, LO C H. Ti-containing hydrogenated carbon films fabricated by high-power plasma magnetron sputtering [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(6): 1381-1386.
[5] CHOI J, LEE S K, YOON C J, OH S E, LEE C H. Durability evaluation of DLC coating through the enhanced environmental tests[C]//Proceedings of SPIE, Optical Materials and Biomaterials in Security and Defence Systems Technology IX. Bellingham: SPIE, 2012: 85450N.
[6] HAN Jie-cai, ZHU Jia-qi, NIU Li, LU Jia, CHEN Wang-shuo. Superexcellent infrared protective coatings amorphous diamond films deposited by filtered cathodic vacuum arc technology [J]. Surf Coat Tech, 2007, 201(9-11): 5323-5325.
[7] BALABIN R M, SMIRNOV S V. Variable selection in near-infrared spectroscopy: Benchmarking of feature selection methods on biodiesel data [J]. Anal Chim Acta, 2011, 692(1): 63-72.
[8] JOSEPH S, MARCOVITCH O, YADIN Y, KLAIMAN D, KOREN N, ZIPIN H. High durability antireflection coatings for silicon and multispectral ZnS [C]//Proceeding of the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. Bellingham: SPIE, 2007: 65450T.
[9] SONG M, PARK E, HYUN M S, KIM T H, KIM H Y, LEE G. Studies on transmittance of silicon with AR coating films for IR transparent window[C]//Proceedings of SPIE, Infrared Sensors, Devices, and Applications II. Bellingham: SPIE, 2012: 85120P.
[10] ZHANG Hua-yu, JIN Lei, SONG Bo, HAN Jie-cai, WANG Gui-gen, KUANG Xu-ping, SUN Rui. Enhancement in hardness and transmittance of ZnS via SiO2/Y2O3 multilayer [J]. J Alloy Compd, 2012, 539: 40-43.
[11] KLEIN C A, MILLER R P, GENTILMAN R L. Characteristic strength and Weibull modulus of selected infrared-transmitting materials [J]. Opt Eng, 2002, 41(12): 3151-3160.
[12] HAN Jie-cai, JIANG Chun-zhu, ZHU Jia-qi. Non-hydrogenated amorphous germanium carbide with adjustable microstructure and properties: a potential anti-reflection and protective coating for infrared windows [J]. Surf Interface Anal, 2013, 45(3): 685-690.
[13] BREDIKHIN V I, GAVRISHCHUK E M, IKONNIKOV V B, KARAKSINA E V, KETKOVA L A, KUZNETSOV S P, MAL’SHAKOVA O A. Optical losses in polycrystalline CVD ZnS [J]. Inorg Mater, 2009, 45(3): 235-241.
[14]  V, NEDELCU A, CARRAS M, ODILE H, XAVIER M, PHILIPPE B. Mid-wave QWIPs for the [3-4.2 μm] atmospheric window [J]. Infrared Phys Technol, 2009, 52(6): 235-240.
V, NEDELCU A, CARRAS M, ODILE H, XAVIER M, PHILIPPE B. Mid-wave QWIPs for the [3-4.2 μm] atmospheric window [J]. Infrared Phys Technol, 2009, 52(6): 235-240.
[15] de FERRI L, LOTTICI P P, LORENZI A, MONTENERO A, VEZZALINI G. Hybrid sol–gel based coatings for the protection of historical window glass [J]. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol, 2013, 66(2): 253-263.
[16] RUSSELL G W, CAYSON S C, JONES M M, CARRIGER W, MITCHELL R R, STROBEL F A, REMBERT M, GIBSON D A. Laser window design for the army hypersonic compact kinetic energy missile [J]. J Spacer Rockets, 2006, 43(5): 982-989.
[17] KARAKSINA E V, IKONNIKOV V B, GAVRISHCHUK E M. Recrystallization behavior of ZnS during hot isostatic pressing [J]. Inorg Mater, 2007, 43(5): 452-454.
[18] TOMBA M A G, CAVALIERI A L. Evaluation of the heat transfer coefficient in thermal shock of alumina disks [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2000, 276(1): 76-82.
[19] LIU Ye, HUANG Yong. Simultaneous radiation and conduction heat transfer in an infrared window [J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophys, 2012, 33(12): 2190-2193. (in Chinese).
红外窗口功能膜的热/力响应
刘 星1,汪新智2,朱嘉琦1,韩杰才1
1. 哈尔滨工业大学 复合材料与结构研究所,哈尔滨 150001;
2. 哈尔滨工业大学 能源科学与工程学院,哈尔滨 150001
摘 要:高超音速导弹在服役过程中其红外窗口承受着复杂的气动热/力环境。利用有限元方法对不同气动热/力情况下的窗口进行数值模拟,获得了不同热流密度下窗口的温度和热应力分布,应力沿膜厚方向几乎相同,但是在膜基界面附近会产生突变。在膜层表面,最大应力出现在边界旁。不同的膜层材料在相同条件下有相同的温度和应力分布规律,但是应力大不相同。比较发现,Y2O3比ZrN膜层具有更高的温度和应力。同时,进行了地面热冲击实验来观察红外窗口的破坏情况,10 s之后,发现窗口表面已经发生破坏,有些局部产生裂纹,有些局部会产生破碎的斑点。
关键词:红外窗口;薄膜;有限元方法;热应力;气动加热
(Edited by Hua YANG)
Foundation item: Projects (51222205, 51372053) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (JC201305) supported by Heilongjiang Provincial Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars, China; Project (20112302110036) supported by Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China
Corresponding author: Jia-qi ZHU; Tel/Fax: +86-451-86417970; E-mail: zhujq@hit.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63255-6