利用生物质从黄铜矿和辉铜矿混合矿中可持续提取铜
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2019年第10期
论文作者:David Lukumu BAMPOLE Patricia LUIS Antoine. F. MULABA-BAFUBIANDI
文章页码:2170 - 2182
关键词:可持续提铜;黄铜矿-辉铜矿混合矿;铜形态;三价铁浸出;中温生物浸出机理;氧化还原电位
Key words:sustainable copper extraction; mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite; copper speciation; ferric leaching; mesophilic bioleaching mechanism; redox potential
摘 要:本文阐述提铜工艺的可持续性。实际上,针对混合硫化矿(黄铜矿和辉铜矿),尝试在33.3 ℃下使用中温混合菌群的提铜工艺和三价铁浸出过程。其中,生物浸出实验是在矿石粒径-75+53 μm范围内完成的。采用细菌作为催化剂,铜收率达65.50%。另一方面,在三价铁浸出过程中,矿石粒径为-53+38 μm,温度升高至70 ℃时,铜收率提高到78.52%。与高温浸出过程相比,中温生物浸出过程在铜的提取中显示出明显的优势。通过SEM-EDS、FTIR和XRD表征,结合各种热力学分析,可以认为间接机理是主要的浸出机理。对于黄铜矿-辉铜矿混合矿而言,浸出机理分为三种过渡产物机理,即多硫化物机理、硫代硫酸盐机理和元素硫机理。铜形态转变为Cu2S-CuS-Cu5FeS4-Cu2S,最后转变为CuSO4。在发生亚铁氧化和硫酸铁生成反应的同时,细菌消耗掉硫化矿物,形成强酸,最后在低温下形成CuSO4,这种铜生产方案要求室温下氧化还原电位高于550 mV,以便有效地提取铜。
Abstract: This paper elaborated on the sustainability of the copper extraction process. In fact, an alternative copper extraction route from mixed sulphide ores, chalcopyrite and chalcocite using mesophilic biomass consortium at 33.3 °C and ferric leaching process were attempted. Bioleaching experiments were settled with a fraction size of -75+53 μm. Bacteria were used as the catalyst. A copper yield of 65.50% was obtained. On the other hand, in ferric leaching process, with a fraction size of -53+38 μm, when the temperature was increased to 70 °C, the copper leaching rate increased to 78.52%. Thus, comparatively, the mesophilic bioleaching process showed a more obvious advantage in copper extraction than leaching process with a high temperature. However, it has been resolved from the characterization performed using SEM-EDS, FTIR and XRD observations coupled with different thermodynamic approaches that, the indirect mechanism is the main leaching mechanism, with three transitory mechanisms (polysulphide, thiosulphate and elemental sulphur mechanisms) for the mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite ore. Meanwhile, the speciation turns into Cu2S-CuS-Cu5FeS4-Cu2S before turning into CuSO4. While ferrous oxidation and the formation of ferric sulphate occur, and there is a formation of strong acid as bacteria digest sulphide minerals into copper sulphate at low temperature, which is why this copper production scenario requires a redox potential more than 550 mV at room temperature for high copper leaching rate.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29(2019) 2170-2182
David Lukumu BAMPOLE1,3, Patricia LUIS2, Antoine. F. MULABA-BAFUBIANDI1
1. Mineral Processing and Technology Research Centre, Department of Metallurgy, School of Mining, Metallurgy and Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering and the Built Environment, University of Johannesburg, Doornfontein Campus, P. O. Box 17911, South Africa;
2. Materials & Process Engineering (iMMC-IMAP), UC Louvain, Place Sainte Barbe 2, 1348 Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium;
3. Department of Industrial Chemistry, Faculty of Polytechnique, University of Likasi, 177, Shituru Campus, P. O. Box 1946, Likasi, Democratic Republic of the Congo
Received 25 November 2018; accepted 28 August 2019
Abstract: This paper elaborated on the sustainability of the copper extraction process. In fact, an alternative copper extraction route from mixed sulphide ores, chalcopyrite and chalcocite using mesophilic biomass consortium at 33.3 °C and ferric leaching process were attempted. Bioleaching experiments were settled with a fraction size of -75+53 μm. Bacteria were used as the catalyst. A copper yield of 65.50% was obtained. On the other hand, in ferric leaching process, with a fraction size of -53+38 μm, when the temperature was increased to 70 °C, the copper leaching rate increased to 78.52%. Thus, comparatively, the mesophilic bioleaching process showed a more obvious advantage in copper extraction than leaching process with a high temperature. However, it has been resolved from the characterization performed using SEM-EDS, FTIR and XRD observations coupled with different thermodynamic approaches that, the indirect mechanism is the main leaching mechanism, with three transitory mechanisms (polysulphide, thiosulphate and elemental sulphur mechanisms) for the mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite ore. Meanwhile, the speciation turns into Cu2S-CuS-Cu5FeS4-Cu2S before turning into CuSO4. While ferrous oxidation and the formation of ferric sulphate occur, and there is a formation of strong acid as bacteria digest sulphide minerals into copper sulphate at low temperature, which is why this copper production scenario requires a redox potential more than 550 mV at room temperature for high copper leaching rate.
Key words: sustainable copper extraction; mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite; copper speciation; ferric leaching; mesophilic bioleaching mechanism; redox potential
1 Introduction
Bio-hydrometallurgy is presented nowadays as an alternative route for hydrometallurgical and pyro- metallurgical processing [1,2]. Hydrometallurgy is a successful process in the primary production and recycling of metal components. In hydrometallurgical as well as bio-hydrometallurgical processes, the leaching process is a key step that consists of dissolving a solid phase in an aqueous medium to subsequently separate the compounds of interest. Chalcopyrite is the most abundant copper sulphide and it is widely spread in the ecosystem [3,4]. It is typically found in the environment embedded in rich pyritic-siliceous ore [5].
However, many studies proposed mechanisms for the dissolution of chalcopyrite and chalcocite using thermophilic bacteria or conventional ferric leaching method but there are not conclusions on mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite [6-9]. In the meantime, the termination and limitation of chalcopyrite and chalcocite mechanisms are still a subject of discussion owing to the diversified and large number of outcomes showing different assumptions, which could be attributed to the diversity of the mineralogical composition of the sulphide minerals.
The challenge in determining the sustainable copper extraction and precise mechanism in a mixed chalcopyrite–chalcocite in the presence or absence of mesophilic bacterial strains becomes evident. Hence, it turns out to be very important to make a comparison between conventional ferric leaching and mixed pyritic siliceous chalcopyrite-chalcocite bioleaching using indigenous mesophilic bacterial strains originated from the same bulk samples as well as the characterization of the bioleachate solution, copper sulphide minerals speciation and solid bioleachate residues by means of new analytical techniques as mentioned below coupled with some thermodynamic considerations. On the other hand, there is a hope that indigenous mesophilic microorganisms could be useful in future industrial applications, keeping into consideration their availability and other advantages over moderately and extremely thermophilic strains. This work used indigenous mesophilic strains originated from the same copper rock sample for biotic experiments. In addition, scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (SEM-EDS), Fourier- transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) were used by coupling with thermodynamic simulation approaches in order to determine the dissolution mechanisms and limitations of this green and sustainable copper extraction method.
2 Experimental
2.1 Chemicals
All reagents and solvents employed in this investigation were of analytical grade for making sure that all experiments are well done. Distilled water, absolute ethanol and hydrochloric acid for bacterial DNA identification were purchased from Johannesburg, South Africa.
2.2 Sample collection and methodology
The bulk samples used in this work were collected in the DR Congo, and the mixed chalcopyrite–chalcocite ore was collected from Kamoa orebody, one of the largest copper high-grade deposit in the world. However, the crushed ore was sieved with particle sizes from -150 to -38 μm for liberating and facilitating copper.
The bioleaching experiment was carried out as indicated elsewhere [10]. Meanwhile, the redox potential was ranged between 350 and 550 mA. The solid bioleachate residues were obtained after a leaching experiment in the presence of native mesophilic strains originated from the same sample. The solid bioleachate residues were analyzed using SEM-EDS, XRD and FTIR spectrometry for displaying a clear understanding of the exact mechanism of the mixed chalcopyrite- chalcocite.
2.3 Analytical techniques
Samples underwent chemical composition analysis using XRF spectrometry. The Cu, Co, Fe, Ni, Ca, Mg, K, Mn, Al and Si contents of the samples were analyzed using an X-ray tube and two crystal analysis materials made by Rigaku Tokyo, Japan.
Crystalline structures were evaluated using several analytical techniques employed in mineralogical studies. XRD tomography of the bulk samples was performed using the ULTIMA IV diffractometer with the following measurement conditions: scan speed, 2 (°)/min; radiation generated at 40 kV; λ=1.5406 nm at 30 mA; scan axis at 2θ. XRD data were collected employing a computer- controlled XRD. Crystal elements were characterized using a FTIR spectrometer in a range of 4000-500 cm-1. The stretching vibrations (spectra) of bulk samples were then identified.
The analysis of solid bioleachate residues that were mounted in polished sections, was made using TESCAN SEM-EDS devices with the backscattering electron mode and the detector employing a beam voltage of 20 kV.
2.4 Bacterial identification
The next generation sequencing of 16S rRNA was performed from the synthetic bacterial consortium for allowing the assessment of microbiota diversity and detection of microorganisms. This technique combined with the method called interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) coupled with polymerise chain reaction (PCR) amplification. Those methods confirmed the presence of five DNA classes identified, which are Gammaproteobacteria, beta proteobacteria, Alphaproteobacteria, Bacilli, and Acidobacteria. They were greatly identified and numbered from the designed synthetic bacterial consortium, which were used as inoculum. Among them, Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans species are the most known for their biotechnological interest.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Characterization of bulk sample
The XRF, XRD and FTIR data (referring to Table 1 as well as Figs. 1 and 2, respectively) confirmed that the rock sample was made up of a silica matrix bearing copper in the form of chalcopyrite–chalcocite and with a huge amount of silica. However, the XRF analysis shows the presence of Si, Fe, Al, Mg and Ca as major components in the recalcitrant ore. The contents of the major components were 46.70% Si, 17.09% Fe, 12.16% Al, 11.34% S, 4.26% Mg, 4.55% Cu and 2.97% Ca. Other elements that existed as minor substances were K, As, Se, Pb, Sr and Mn. The isotopic signature of cobalt was noticed to be quite trivial with 0.0095%, and this was observed in the chemical characterization results related to different fraction sizes of the sample used as provided in Table 2.
Table 1 Main chemical composition of mixed chalcopyrite- chalcocite ore (wt.%)


Fig. 1 XRD pattern of dolomitic-siliceous matrix bearing copper sulphides, mainly chalcopyrite and chalcocite

Fig. 2 FTIR spectrum of mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite ore
The XRD analysis was utilized for the qualitative examination of the bulk sample. The identification of minerals in the bulk sample was achieved regarding the peak position and intensity in comparison with the spectra from drafted powder diffraction data for minerals. The FTIR analysis (see Fig. 2) shows the evolution of transmittance as a function of wavenumber. Thus, it is first indicated that Al—OH and Si—O turned out to be the main functional groups observable in the ranges around 500 and 1000 cm-1, respectively. Intensive peak at 1000.20 cm-1 was due to the Al—O—S stretching vibration bond [11]. The bands at 100.40-100.60 cm-1 corresponded to the Al—OH vibrations. The functional groups were related to inter-Si—O—Si tetrahedral bands stretching with SiO2 and the hydroxyl band of gibbsite [12] caused the bands at 796.83-777.83 cm-1. On the other hand, the same combination fundamental absorption band was observed in the region of 796.83-694.52 cm-1. It is almost in this region, where the bonding of some silica with the sulphur atom or molecule or ion occurred (730-690 cm-1). Iron existed in the form of Fe—O and Fe2O3 close to 500 cm-1, almost below 694.52 cm-1 [13]. A carbonate structure was also detected at around 1423.12 cm-1. This structure isolate was usually the radical 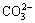 group bearing the symmetric stretch (ν3). The hydroxyl linkage group (—OH) and/or H2O strong bands also showed absorption bands at 3388.51 and 1714.33 cm-1 in the matrix spectrum. This revealed the presence of water (H—O—H) stretching vibrations in a relative absorbance caused by the hydroxyl-linkage nature of the diamictite materials. The SEM-EDS observations in Fig. 3 and Table 3 are in agreement with the XRF, XRD, and FTIR results as indicated above and helpful to investigate the tomography related to the sample and different copper grain sizes as shown in Fig. 4.
group bearing the symmetric stretch (ν3). The hydroxyl linkage group (—OH) and/or H2O strong bands also showed absorption bands at 3388.51 and 1714.33 cm-1 in the matrix spectrum. This revealed the presence of water (H—O—H) stretching vibrations in a relative absorbance caused by the hydroxyl-linkage nature of the diamictite materials. The SEM-EDS observations in Fig. 3 and Table 3 are in agreement with the XRF, XRD, and FTIR results as indicated above and helpful to investigate the tomography related to the sample and different copper grain sizes as shown in Fig. 4.
3.2 Effect of particle size on copper extraction from mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite ore
A ferric leaching experiment was carried out by varying particle size in the range from +150 to -38 μm at pulp density of 2% (w/v) and with 4 g of Fe2(SO4)3 over 2 h, at pH 1.5 and 120 r/min. There was a weaker extraction of 28% of copper because of possible chemical reactions and the mineralogical lattice of the composite sample. However, the effect of particle size on the leaching rate of copper is clearly shown in Fig. 4(a).
Table 2 Particle size distribution of mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite ore

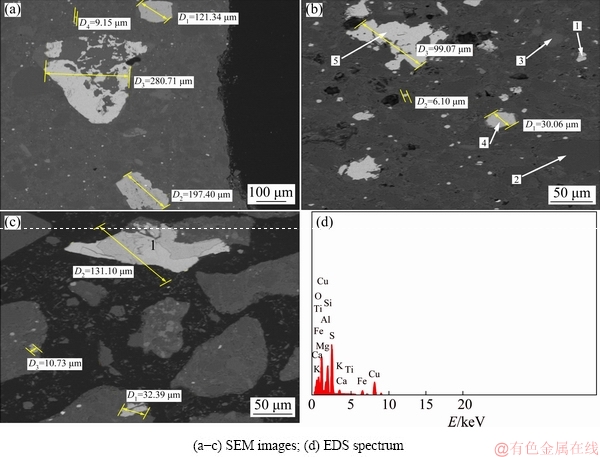
Fig. 3 SEM-EDS micrographs showing morphology of mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite ore
Table 3 EDS results related to one of spectra of mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite ore

Theoretically, the ore particles with fine sizes were easily leached owing to the mass transfer and higher leaching rate.
Indeed, in the presence of fine sizes, metal liberation is very casual, and dissolution is affected. Figure 4(a) shows that when the size is decreased, the copper leaching rate increases relatively quickly. The lower extraction rate was noted to be more substantial in the coarser sized ranges than that in finer sized ranges. In addition, it has been observed that the leaching rates of Cu and Co increase slowly when the particle size is increased from +150-106 to -75+53 μm. When the size is decreased to -53+38 and -38 μm, the leaching rate is increased relatively fast even if less recovery was reported. This might be assigned to substantial oxidation of Fe2+ in the minerals into Fe3+ ions in the fraction sizes from -53 to +38 μm, and -38 μm particles affecting the copper leaching rate present in the pyritic siliceous phase. On the other hand, another explanation could be attributed to the composition of the overall crystal lattice of the matrix used as well as the microbiota activity and growth, which have participated in better liberation of Fe3+ in the finer sizes as mentioned above. These approaches are in agreement with results in Refs. [14,15]. It might be assumed that mixed fractions of finer particles with sizes >38 μm and -53+38 μm of mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite could allow better liberation of copper during abiotic leaching process but more exposure time is required to achieve better results.
Conversely, the lower extraction rate was noted to be much substantial in the coarser size ranges than finer size. That is why the choice was a particle size of -53+38 μm, since grinding would not be required due to the high operation cost at -38 μm. Compared with biotic leaching as shown in Fig. 4(b), at first, metal recovery increased after a slight increase during the first 4 d of biotic leaching corresponding with the bacterial activity. Thus, these scenarios correspond to the phases of bacterial growth i.e. the lag phase, the phase of exponential growth and the stationary phase. Different states, according to different particle sizes, were observed in each phase, and a difference occurred during the lag phase, 4-7 d, with particle sizes of -53, +53-75 and +75-106 μm, respectively. 42.4% of copper extraction was obtained at a particle size of -75 μm, without shaking, and under incubation at 33.3 °C. The results show that abiotic leaching is more energy demanding than biotic leaching. On the other hand, the great bio-solubilization at particle sizes <75 μm could be vindicated through distribution and mineralogy, including weaker acid consumption from silica and the nature of generated residues, which are dolomitic gangue, and aided by a substantial amount of Fe within the overall matrix with particle sizes <75 μm [16,17].

Fig. 4 Abiotic leaching results using ferric sulphate with pulp density 2% (w/v) at 30 °C, 2 h and pH 1.5 (a) and biotic leaching results with pulp density of 2% (w/v) at 33.3 °C, and redox potential of 350-550 mV over 16 d
The decrease of the particle size to -75 μm could be explained through acid consumption by the gangue, owing to the reduced exposition of the mineral surface [18]. This is contributed to the narrowing of the particle sizes during the leaching process due to mineralogy and biomass activity, which is based on the control in the activity of iron. In contrast, NEMATI and HARRISON [19] believed that the range of particle sizes below +150 μm did not influence the morphology and growth kinetics of the cells. Nevertheless, HEDRICH et al [20] believed that a significant bio-dissolution occurred at a particle size of -75 μm, compared with other particle sizes that revealed the lowest extraction rate. This could be explained by the morphology of mineral phases and the chemical composition of bio-leached residues by using SEM and XRD analysis at a particle size of -75 μm.
3.3 Effect of leaching temperature on copper recovery from mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite ore
Figure 5(a) shows that the effect of temperature is more evident on metal extraction compared with that obtained under preceding conditions. As a result, the leaching rate of Cu was noted to be an average of 78.52% at 70 °C, while a decrease was noted at 90 °C with 65.48%. This is due to the increase of jarosite and elemental sulphur accumulation, which hindered the dissolution action at high temperature at 50% of copper recovery. On the other hand, this means that the diffusion control is less accelerated despite an increase in temperature. Conversely, considering the obtained results compared with the biotic experiment results at 33.3 °C mentioned in Fig. 5(b), all the results obtained in the presence of indigenous bacterial strains were more suitable and flexible than results obtained in the abiotic process (technically suitable, economically and environmentally friendly). Indeed, as illustrated in Fig. 5(a) at 70 °C and 90 °C with pulp density of 12% (w/v), the copper leaching rates in the abiotic experiment were only about 78% and 65%, respectively. However, in the biotic experiment with a pulp density of 12% (w/v) at 33.3 °C, the recovery yield was 65.2%. What confirms the assumption of the bioleaching process as an alternative route to the conventional method, is energy saving. The copper behaviour in bacterial leaching and the abiotic experiment is therefore different. It was noted that there was almost significant copper leachable, 78.52% at 70 °C and 38.57% at 30 °C, respectively in abiotic leaching, while the biotic experiment recorded 65.2% of copper yield at only 33.3°C as mentioned in Fig. 5(b). Meanwhile, the copper concentrations of the solution tended to decrease at the end of the tests. This phenomenon is less important since it is observed in every test.
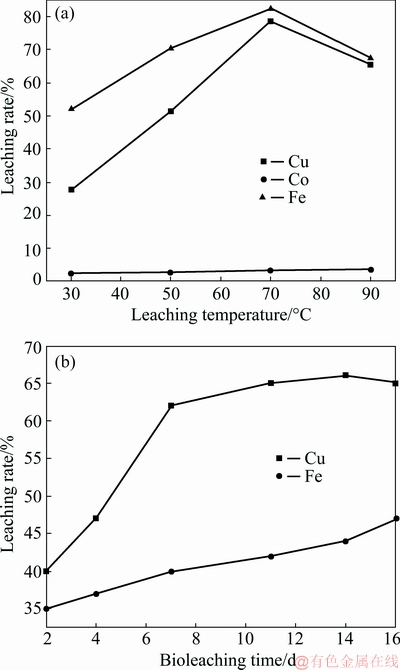
Fig. 5 Influence of temperature on leaching rate in abiotic experiment at pH 1.5, pulp density of 12% (w/v) during 2 h in the presence of 1.5 mol/L H2O2 (a) and bioleaching time on leaching rate in biotic experiment at 33.3 °C, pulp density of 2% (w/v), fraction size of -75 μm, 16 d and redox potential of 350-550 mV (b)
The highest total iron reached was about 45% of oxidation in biotic leaching, which was more than copper oxidation in abiotic experiment at 30 °C. In the meantime, it was observed that the iron oxidation in the abiotic experiment was more substantial than the copper oxidation. This phenomenon could be attributed to the mineralogical composition of the ore used and observed working conditions in both experiments. Furthermore, the compromise between the temperature and redox potential could also contribute to explaining the iron behaviour in the biotic experiment, which was why various iron oxidation values were recorded in a redox potential range between 350 and 550 mV. Much more attention is needed in the prospect studies with respect to abiotic leaching, nevertheless, it is of interest to mention that the difference in terms of copper extraction yield, which has been observed between 70 and 90 °C in the abiotic leaching, confirms the importance of serious control of temperature with other parameters as well as the compromise to be taken with redox potential in order to enhance the copper efficiency. This explains the need to break out the limitation of activation energy for getting higher copper extraction in abiotic testing than in biotic experiment. Yet, the better iron extraction performance in abiotic system than in biotic experiment could be explained by the thermodynamic frameworks, which have been established during the respective experiments and based on the mineralogical nature of head sample used and the medium conditions [21]. In addition, the difference could be attributed to the fast kinetic of Fe2+ and slow Fe3+ reduction and biodegradation of sulphur coupled with the delay in the accumulation of hydroxide ions in biotic experiment generating the jarosite, which is known as inhibitor agent of bacterial activity and growth until a certain level is well defined [22].
The dynamic interactions of ferric and ferrous iron, which form the total iron as observed in Figs. 6(a) and (b), can influence the decaying streams of the increased copper leaching rate and reduce the final redox potential with the effect of the iron-copper extraction in chemical leaching compared with the bioleaching process based on the influence of bacterial activity. This observation is in accordance with the earlier studies carried out by KHOSHKHOO et al [23] as well as the SEM-EDS outcomes of the solid bioleachate residues. On the other hand, in abiotic experiment, the feature system requires temperature higher than 90 °C with 65% of leaching rate, to reach 80% of copper oxidation [24]. The findings confirmed that the abiotic leaching or conventional method is very energy demanding compared with biotic leaching with 65.2% of copper extraction at 33.3 °C with 12% (w/v) of solid loading. Our biotic experiment outcomes are efficient compared to those obtained by BEHERA et al [25] at 25 °C. Conversely, PETERSEN and DIXON [26] believed that the temperature did not have an effect during the chalcopyrite bioleaching time but, the redox potential played a critical role in copper extraction yield.
Nevertheless, there is a link electrochemically between redox potential and temperature as per the Nernst Law [27]. In our case, it can be therefore confirmed that the increased redox potential has to be promoted for efficient mesophilic bioleaching. This phenomenon was confirmed by the XRD observations of solid bioleachate residues during bioleaching time (Fig. 6). In contrast, some studies on the chalcopyrite and chalcocite bioleaching process with the same conditions but redox potential >650 mV showed substantial copper extraction compared to the findings obtained in Ref. [26], despite the presence of chalcocite in the used sample. This may be attributed to the decreased redox potential used in this research (350-550 mV) and the earlier Jarosite accumulation rate originated from the pyrite oxidation, which has been reported. However, the chemical and mineralogical compositions of the overall matrix highlighted the better ponderation of iron and silica originated from pyrite and quartz, respectively, which have been reported as antibacterial agents in their increased oxidation. Additionally, the increased rate of some by-products and the copper speciation as well as the behavior of bacterial activity and growth occurring during biotic experiment can provide much more revelations to the decreased copper yield. Hence, it may be concluded that the redox potential should be increased at redox potential >650 mV without reaching the critical redox potential >750 mV.

Fig. 6 XRD patterns of samples in biotic experiment at 33.3 °C, -75 μm, 2-11 d, and redox potential of 350-550 mV
3.4 Characterization of solid state of bioleachate residues-induced metamorphic transformation of mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite ore
From the XRD analysis in Fig. 6, it can be observed that covellite, bornite and chalcocite appeared in the bioleachate residues at days 2, 4 and 6 respectively and chalcocite disappeared from the 11th day. Covellite appeared at day 2 (Fig. 6(a)) and then increased and disappeared. The bornite phase took place as observed in Fig. 6(b). The chalcocite phase was observed after the disappearance of the bornite phase (Fig. 6(c)) during the bioleaching process; jarosite formation increased with the evolution of time and turned out to be the key composition with time. In addition, the anatase phase and elemental sulphur were identified in the full experiment. Indeed, in this work the Cu microparticles on TiO2 surface were enclosed in the bioleachate solid residues and those present in the pregnant leach solution (PLS) led to bacterial inactivity. The FTIR analysis was helpful to display a better understanding of the copper sulphide disappearance time (11th day and 14th day). Based on the obtained results, it can be reported that the exothermic reaction at working temperature of 33.3 °C generated a copper oxidation and then a precipitated covellite (CuS) occurred a bit late because of the low rates of redox potential and Fe2+ oxidation as observed in Figs. 7(a) and (b). It is of interest to mention that the substantial increased Fe2+ was directly accredited to the steady decrease of the pH in the system as observed in Fig. 7(b). These observations are in agreement with the investigations carried out in Ref. [28-30].
In this respect, this research mentioned the existence of three copper speciations (steps) before the formation of copper sulphate at required Fe2+ concentration, which involves literally the increase of redox potential [31]. Similar findings have been provided in Refs. [32,33]. The latter might be formed in two copper sulphates (Cu2SO4 and CuSO4) depending on the redox potential rate and the formation of by-products (jarosite and elemental sulphur). Nevertheless, the formation of copper sulphate (CuSO4) requires an elevated redox potential (0.5 or 1 V) in the system.

Fig. 7 Evolution of bioleaching process as functions of copper leaching rate and redox potential (φ) (a) and evolution of pH and Fe2+ leaching rate during bioleaching process (b) at 33.3 °C, pulp density of 2% (w/v) and particle size of -75 μm

Fig. 8 FTIR spectra from bioleachate residues at 33.3 °C, fraction size of -75+53 μm and redox potential of 450-550 mV
The FTIR spectra (Figs. 8(a) and (b)) support the increased jarosite by the crystal lattice theoretical bands occurring near 470, 650, 700 cm-1 and 900-925 cm-1; this is observed based on the generated data for both transmittance modes. An intensive band assigned to ν1 ( ) is reported for a large number of sulphates with inaccurate configuration at 950-1000 cm-1 [34]. A strong doublet stretching vibration at 700 and 760 cm-1 correlates with ν4 (
) is reported for a large number of sulphates with inaccurate configuration at 950-1000 cm-1 [34]. A strong doublet stretching vibration at 700 and 760 cm-1 correlates with ν4 ( ), and the strong doublet band is reinforced by the intensive peak closer to the wide band between 3550 and 3200 cm–1 and a weak band occurring from 1750 to 1000 cm–1, which are assigned to differential linkage of —OH distending vibrations of water. Hence, by coupling the bands related to
), and the strong doublet band is reinforced by the intensive peak closer to the wide band between 3550 and 3200 cm–1 and a weak band occurring from 1750 to 1000 cm–1, which are assigned to differential linkage of —OH distending vibrations of water. Hence, by coupling the bands related to  and —OH some observable AlOOH and FeOOH phases display a γ-OH linkage near 750 cm-1 as well as a δ-OH doublet adjacent to 1030 cm-1 [35]. The intensive peaks at 2800 and 2900 cm-1 are also attributed to the jarosite occurring with amalgamation to stretching vibrations mentioned above. Hence, the jarosite accumulation is very substantial on the 14th day, which is observable when comparing with Figs. 8(a) and (b)). The jarosite formation occurred at the main components on day 14. This jarosite accumulation affects the copper leaching rate and decreases the dissolution together with sulphur degradation, H2S and FeOOH, because of hydrogenation reaction, increased sulphuric acid and Caro’s reaction. These observations are in contract with the studies carried out by LIU et al [36-38] who observed the jarosite and chalcocite formation at day 4 with thermophilic and mesophilic bacterial strains, while in this work we observed the same phases at day 6. Meanwhile, the findings obtained in this work are not in agreement with the studies of LIU et al [36] who argued that there was no evident passivation influence on copper leaching rate through jarosite and S precipitation. Nevertheless, the difference could be attributed to the mineralogical composition of the ore used; the iron and sulphur concentrations in the overall matrix, the operating conditions over time, and the delay in the reduction of Fe3+ ions can be attributed to the jarosite accumulation. Hence, it is of interest to mention that the fast jarosite formation in our studies could be explained by the rapid pyrite oxidation beyond mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite bioleaching process in the second stage of pyrite oxidation, which depends upon the dynamic interaction between microbiota activity and growth as well as Fe2+ oxidation affecting the passivation of the copper grains. As a result, the copper leaching rate is therefore undesirably affected as well. This evidence could be observed by SEM-EDS results of bioleachate residues (Fig. 9). The EDS results, which have been observed in Fig. 9(d) were assigned to Point 1 in Fig. 9(c). The chemical compositions of Point 1 are observed in Table 4.
and —OH some observable AlOOH and FeOOH phases display a γ-OH linkage near 750 cm-1 as well as a δ-OH doublet adjacent to 1030 cm-1 [35]. The intensive peaks at 2800 and 2900 cm-1 are also attributed to the jarosite occurring with amalgamation to stretching vibrations mentioned above. Hence, the jarosite accumulation is very substantial on the 14th day, which is observable when comparing with Figs. 8(a) and (b)). The jarosite formation occurred at the main components on day 14. This jarosite accumulation affects the copper leaching rate and decreases the dissolution together with sulphur degradation, H2S and FeOOH, because of hydrogenation reaction, increased sulphuric acid and Caro’s reaction. These observations are in contract with the studies carried out by LIU et al [36-38] who observed the jarosite and chalcocite formation at day 4 with thermophilic and mesophilic bacterial strains, while in this work we observed the same phases at day 6. Meanwhile, the findings obtained in this work are not in agreement with the studies of LIU et al [36] who argued that there was no evident passivation influence on copper leaching rate through jarosite and S precipitation. Nevertheless, the difference could be attributed to the mineralogical composition of the ore used; the iron and sulphur concentrations in the overall matrix, the operating conditions over time, and the delay in the reduction of Fe3+ ions can be attributed to the jarosite accumulation. Hence, it is of interest to mention that the fast jarosite formation in our studies could be explained by the rapid pyrite oxidation beyond mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite bioleaching process in the second stage of pyrite oxidation, which depends upon the dynamic interaction between microbiota activity and growth as well as Fe2+ oxidation affecting the passivation of the copper grains. As a result, the copper leaching rate is therefore undesirably affected as well. This evidence could be observed by SEM-EDS results of bioleachate residues (Fig. 9). The EDS results, which have been observed in Fig. 9(d) were assigned to Point 1 in Fig. 9(c). The chemical compositions of Point 1 are observed in Table 4.
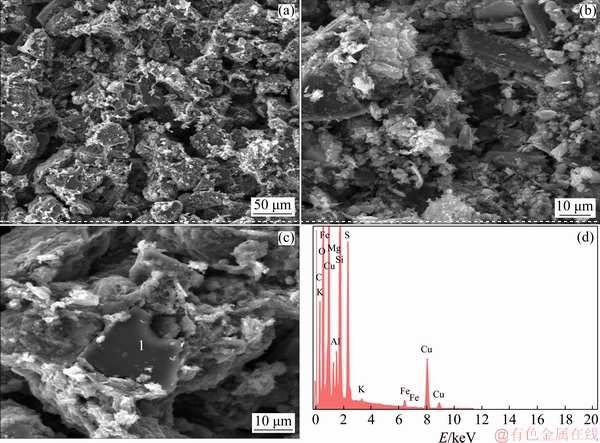
Fig. 9 SEM images (a-c) showing effective alteration of mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite ore at 33.3 °C, fraction size of -75+53 μm on day 16, and EDS spectrum of Point 1 in Fig. 1(c) (d)
Table 4 EDS analysis of chemical compositions in bioleachate residues at Point 1 in Fig. 9(c)

From the results in Tables 2 and 3 correlated to the chemical characterization of the head sample and the EDS results of the bioleachate residues in Table 4 respectively, an effective alteration of the recalcitrant ore used as overall feed is observed based on the recorded values in terms of comparison. The analysis results of bioleachate residues after bioleaching time confirmed the presence of the jarosite as a candidate of passivation during mesophilic bioleaching time. Indeed, it can be seen that the morphologies (Figs. 9(a-c)) and chemical compositions (Fig. 9(d) and Table 4: EDS results) shed some light on the bioleachate residue properties. Furthermore, all the micrographs showed that they were made up of Cu, P, Fe, S, O, K and C. These chemical compositions are provided in the precipitates in different proportions. These precipitates can be predicted as an iron oxide which is combined to an amalgamation of potassium, alteration of silica and elemental sulphur, especially when the medium is rich in sulphate and contains elements such as Na, P and N, and K originated from the 9K culture medium is in favor of jarosite formation. Sulphur, copper and iron are originated from the dissolution of mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite ore. The presence of C in several spectra is assigned to microorganisms because it has been originated from non-polished sections of the solid bioleachate residues as observed in Figs. 9(a-c). Table 4 shows a carbon component that could be attributed to an organic component matter, probably due to the presence of bacteria in these precipitates. These observations show that most bacteria would be encrusted by these precipitates. The SEM-EDS results of the bioleachate residues confirmed the similar trends that the copper oxidation with native mesophilic strains is governed by two stages (dissolution and non-dissolution).
The two stages could be shed light trough the thermodynamic framework based on the effect of the temperature and equilibrium potentials. Furthermore, these copper intermediate phases can be approached thermodynamically as well (HSC Chemistry 5.0 for simulation).
3.5 Approach on thermodynamic speciation of mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite ore during mesophilic bioleaching in atmospheric conditions
It can be highlighted that CuS, Cu5FeS4 and Cu2S phases, which have been observed by XRD spectrometry as mentioned above, are the main solid phases of chalcopyrite metamorphic transformation in the indirect mechanism, hence, the couple (Fe3+, Fe2+) and the elemental sulphur (S) are by-products before the Cu2+ final phase [39]. As a result, the CuFeS2 oxidative dissolution reactions are facilitated by means of forming sulphuric acid by H+ reactions, which are summarized in Tables 5 and 6 (originated from the previously reported transitory mechanisms). This approach in accordance with the Pourbaix diagram revealed below in Fig. 10.
As mentioned in Table 5 and Fig. 10, both potentials are correlated with the expected dissolution reactions as functions of the Cu2+ and Fe2+ concentrations. The different cryptograms in φ (description) are correlated with the redox potentials in Table 5, which have been designed from the HSC Chemistry database [40].
Table 5 Equilibrium potentials of CuFeS2 eventual oxidative solubilization reaction routes in H2SO4

Table 6 Standard Gibbs free energy of formation related to Cu1+xS at 25 °C (kJ/mol)
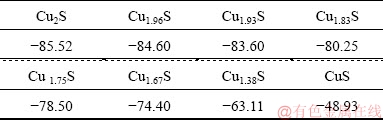

Fig. 10 Pourbaix diagram of S-Cu-Fe-H2O system at 33 °C and pH 0.5-2.5 (HSC Chemistry 5.0)
The analysis from the HSC Chemistry database [41,42], considers the following speciation sequence order:
CuS
Different potentials in Table 5 are correlated with different transitory phases in Eq. (1). Increased potentials are a function of the concentration of Fe2+ and the potential sequence order. φo4-1, is the CuFeS2 redox potential in favor of being converted directly into CuSO4 (see Tables 5 and 6) because the dissolution is reported to be in an acidic system. That is why the oxidative reactions take place in the mixed chalcopyrite- chalcocite surface layers, with a tendency to form intermediate phases, keeping the three expected routes into consideration. This can be observed in a Pourbaix diagram (Fig. 10). CuS is the most likely phase; Cu5FeS4 is the second most likely one. Nevertheless, it could also be reported that the chalcocite has only the intermediate phase before forming a large amount of Cu2+ or CuSO4, as per the following reaction:
Cu2S+2H+=Cu2++CuS+H2S (2)
According to the available literature [43,44], the diffusion channel of chalcocite transitory phases as shown in Eq. (2), the H2S diffusion is not rapid, and the subsequent elemental sulphur biodegradation stops the diffusion of bornite as an intermediate phase [43,44]. This could be explained in the CuS termination through direct oxidation of Fe3+, even in the presence of Fe3+ accumulation.
Based on thermodynamic approaches, different standard Gibbs free energy values in Table 6 confirm the assumption.
The Cu1+xS is provided as an equation, considering different standard Gibbs free energy values and their formation expresses their linear relation:  = -49.947-36.30×0.99=-85.884 kJ/mol (determination coefficient is 0.9962).
= -49.947-36.30×0.99=-85.884 kJ/mol (determination coefficient is 0.9962).
Thus, the value -49.947 kJ/mol is assumed to be the value of the standard free energy of CuS from Table 6. It is between the values described in Ref. [45], corresponding closely to the value of metals of 48.929 kJ/mol.
Once CuFeS2 is attacked by H+ reactions, the decomposition state can occur, and then Cu5FeS4, CuS and Cu2S generate as transitory phases before CuFeS2 completes decomposition into Cu2+, with Fe2+ and elemental sulphur as a by-product into the solution according to these reactions.
CuFeS2+2H+=CuS2+H2S+Fe2+ =-2.303×8.314×298lg{[Fe2+][H2S]/[H+]2}=20421 J/mol (3)
=-2.303×8.314×298lg{[Fe2+][H2S]/[H+]2}=20421 J/mol (3)
2CuFeS2+4H+=CuS2+2H2S+S+Fe2+ =-2.303×8.314×298lg{[Fe2+]2[H2S]2/[H+]4}=54513 J/mol (4)
=-2.303×8.314×298lg{[Fe2+]2[H2S]2/[H+]4}=54513 J/mol (4)
5CuFeS2+8H+=Cu5FeS4+4H2S+2S+4Fe2+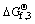 =-2.303×8.314×298lg{[Fe2+]4[H2S]4/[H+]8}=79406 J/mol (5)
=-2.303×8.314×298lg{[Fe2+]4[H2S]4/[H+]8}=79406 J/mol (5)
It can be observed that Reactions (3-5) are accompanies by the H2S liberation during the dissolution route from the solution. This observation is in accordance with the result in Ref. [45]. Indeed, the resulting H2S concentration with different transitory phases assumes the sequence Cu5FeS4→CuS>Cu2S. Both H2S concentrations are reduced at the same time with the increase of pH and Fe2+ concentration which turn out to be more stable with the similar amount of concentration.
4 Conclusions
(1) The biotic experiment using indigenous mesophilic strains which were originated from the same rock sample was proven to be a sustainable copper extraction method and an alternative route to conventional ferric leaching process. Bioleaching process was settled at 33.3 °C, a pulp density of 2% (v/w) and a fraction size of -75+53 μm, which gave a copper extraction rate of 65.50% in 16 d. Compared to ferric leaching process at 70 °C with addition of 1.5% H2O2, a fraction size of -53+38 μm and a pulp density of 2% (v/w), the copper leaching rate upgraded to 78.52%, which demonstrated that the bioleaching process is lower energy demanding and cost and more environmentally friendly than ferric leaching process of the mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite ore.
(2) The characterization performed using SEM-EDS, FTIR and XRD tomography combined with the thermodynamic approaches confirmed that the indirect mechanism is the main leaching mechanism, with three transitory mechanisms (polysulphide, thiosulphate and elemental sulphur mechanisms) for the mixed chalcopyrite-chalcocite ore.
(3) The speciation turns into Cu2S-CuS-Cu5FeS4- Cu2S before turning into CuSO4 since the final product requires a high redox potential at room temperature for high copper leaching rate. Hence, conversely, a contact mechanism takes place when bacteria adhere to mineral surfaces. This implies that the copper suphide speciation, which occurs during bioleaching time as observed by aided XRD observations (copper sulphide metamorphic alteration), induces the metal sulphide dissolution in the zone between bacteria and mineral surface. In both cases (direct and indirect mechanisms), the bacterium contributes to the sulphide metal dissolution by the regeneration of the oxidizing agent (Fe3+).
Acknowledgements
The first author would like to acknowledge and extend his gratitude to the University of Johannesburg (UJ), South Africa, for providing the means and facilities for research – not excluding the Mineral Processing and Technology Research Centre and the Metallurgy Department.
References
[1] BAMPOLE D L, MULABA-BAFUBIANDI A F. Comparative study of simultaneous removal performance of silica and solid colloidal particles from chalcopyrite bioleachate solution by washing and coagulation methods [J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2018, 4: 470-484.
[2] BAMPOLE D L, MULABA-BAFUBIANDI A F. Removal performance of silica and solid colloidal particles from chalcopyrite bioleaching solution: Effect of coagulant (Magnafloc set #1597) for predicting an effective solvent extraction [J]. Engineering Journal, 2018, 22: 123-139.
[3] LEE K, ARCHIBALD D, MCLEAN J, REUTER M A. Flotation of mixed ore copper and sulphide minerals with xanthate and hydroxamate collectors [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2009, 22: 395-401.
[4] YIN Sheng-hua, WU Ai-xiang, HU Kai-jian, WANG Yi-ming, XUE Zhen-lin. Visualization of flow behavior during bioleaching of waste rock dumps under saturated and unsaturated conditions [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 133: 1-6.
[5] SCHMANDT D, BROUGHTON D, HITZMAN M W, PLINK-BJORKLUND P, EDWARDS D, HUMPHREY J. The Kamoa copper deposit, Democratic Republic of Congo: Stratigraphy, diagenetic and hydrothermal alteration, and mineralization [J]. Economy Geology, 2013, 108: 1301-1324.
[6] FOWLER T A, HOLMES P R, CRUNDWELL F K. On the kinetics and mechanism of the dissolution of pyrite in the presence of Thiobacillus Ferrooxidans [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 59: 257-270.
[7] HOLMES P R, CRUNDWELL F K. The kinetics of the oxidation of pyrite by ferric ions and dissolved oxygen: An electrochemical study [J]. Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64: 263-274.
[8] HUANG T, LI D. Presentation on mechanisms and applications of chalcopyrite and pyrite bioleaching in bio-hydrometallurgy— A presentation [J]. Biotechnology Reports, 2014, 4: 107-119.
[9] AI C M, WU A X, WANG Y M, HOU C L. Optimization and mechanism of surfactant accelerating leaching test [J]. Journal Central South University, 2016, 23: 1032-1039.
[10] BAMPOLE D L, LUIS P, MULAMBA E L. Effect of substrates during the adaptation of indigenous bacteria in bioleaching of sulphide ores [J]. American Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, Technology, and Sciences, 2017, 32(1): 200-214.
[11] NAYAK S, SINGH K. Instrumental characterization of clay by XRF, XRD and FTIR [J]. Journal of Bulletin of Material Science, 2007, 30: 235-238.
[12] SAIKIA B, PARTHASARATHY G. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic characterization of kaolinite from Assam and Meghalaya, Northeastern India [J]. Journal of Modern Physics, 2010, 1: 206-210.
[13] ANTOANETA ENE I V, POPESCU C S. Applications of proton-induced X-ray emission technique in materials and environmental science [J]. Annalen der Chemie, 2009, 20: 1-35.
[14] ABHILASH SINGH S, MEHTA K D, KUMAR V, PANDEY B D, PANDEY V M. Dissolution of uranium from silicate-apatite ore by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 95: 70-75.
[15] OLUBAMBI P A, NDLOVU S, POTGIETER J H, BORODE J O. Effects of ore mineralogy on the microbial leaching of low-grade complex sulphide ores [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2007, 86: 96-104.
[16] ABHILASH MEHTA K D, PANDEY B D. Bacterial leaching kinetics for copper dissolution from a low-grade Indian chalcopyrite ore [J]. REM: Revista Escola de Minas, 2013, 66(2): 245-250.
[17] ABHILASH G A, PANDEY B D. Bioleaching of low-grade granitic chalcopyrite ore by hyperthermophiles: Elucidation of kinetics- mechanism [J]. Metallurgical Research Technology, 2015, 112: 1-4.
[18] ALTINKAYA P, M?KINEN J, KINNUNEN P, KOLEHMAINEN E, HAPALAINEN M, LUNDSTR?M M. Effect of biological pre-treatment on metal extraction from flotation tailings for chloride leaching [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2018, 129: 47-53.
[19] NEMATI M, HARRISON S T L. Effect of solid loading on thermophilic bioleaching of sulphide minerals [J]. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2000, 75: 526-532.
[20] HEDRICH S, GU?ZENNEC A G, CHARRON M, SCHIPPERS A, JOULIAN C. Quantitative monitoring of microbial species during bioleaching of a copper concentrate [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2016, 7: 20-44.
[21] GERSON A R, LI Y, KAWASHIMA N, LI J, CHANDRA A P. A review of the structure, and fundamental mechanisms and kinetics of the leaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2013, 197-198: 1-32.
[22] ASSELIN E, OLVERA O G, REBOLLEDO M. Atmospheric ferric sulphate leaching of chalcopyrite: Thermodynamics, kinetics and electrochemistry [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2016, 165: 148-158.
[23] KHOSHKHOO M, DOPSON M, ENGSTROM F, SANDSTR?M A. New insights into the influence of redox potential on chalcopyrite leaching behavior [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2017, 100: 9-16.
[24] VELOSO T C, PEIXOTO J M, PEREIRA M S, LEAO V A. Kinetics of chalcopyrite leaching in either ferric sulphate or cupric sulphate media in the presence of NaCl [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2016, 148: 147-154.
[25] BEHERA S K, MANJAIAH M, SEKAR S, PANDA K, MAVUMENGWANA V, MULABA-BAFUBIANDI A F. Optimization of microbial leaching of base metals from a South African sulfidic nickel ore concentrate by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2017, 34: 1-13.
[26] PETERSEN J, DIXON D G. Competitive bioleaching of pyrite and chalcopyrite [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 83(1-4): 40-49.
[27] BROGAN L J. Electrochemistry of FeSO4–Na2S2O3 and CuSO4- Na2S2O3 systems for template-assisted nanowire synthesis [D]. Berkeley, USA: University of California, 2011.
[28] YU R L, ZHONG D L, MIAO L, WU F D, QIU G Z, GU G H. Relationship and effect of redox potential, jarosites and extrcellular polymeric substances in bioleaching chalcopyrite by Acidithio- bacillus ferroxidans [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(7): 1634-1640.
[29] YU R L, LIU J, CHEN A, ZHONG D L, LI Q, QIN W Q, QIU G Z, GU G H. Interaction mechanism of Cu2+, Fe2+ ions and extracellular polymeric substances during bioleaching chalcopyrite by Acidithiobacillus ferroxidans ATCC2370 [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(1): 231-234.
[30] HONG M X, WANG X X, WU L B, FANG C J, HUANG X T, LIAO R, ZHAO H B, QIU G Z, WANG J. Intermediates transformation of bornite bioleaching by Leptospirillum ferriphilum and Acidithiobacillus caldus [J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(3): 159.
[31] CHRISTEL S, HEROLD M, BELLENBERG S, BUETTI-DINH A, EL HAJJAMI M, PIVKIN I V, SAND W, WILMES P, POETSCH A, VERA M, DOPSON M. Weak iron oxidation by Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans maintains a favorable redox potential for chalcopyrite bioleaching [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 30-59.
[32] ZHU J, LI Q, JIAO W, JIANG H, SAND W, XIA J, LIU X, QIN W, QIU G, HU Y, CHAI L. Adhesion forces between cells of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans or Leptospirillum ferrooxidans and chalcopyrite [J]. Colloids Surface B: Bio-interface, 2012, 94: 95–100.
[33] ZHAO H, ZHANG Y, ZHANG X, QIAN L, SUN M, YANG Y, ZHANG Y, WANG J, KIM H, QIU G. The dissolution and passivation mechanism of chalcopyrite in bioleaching: An overview [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 136 : 140–154.
[34] OMORI K, KERR P F. Infrared studies of saline sulphate minerals [J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1963, 74: 709-734.
[35] RYSKIN Y I. The vibrations of protons in minerals: Hydroxyl, water and ammonium [C]// The Infrared Spectra of Minerals. London: The Mineralogical Society, 1974: 137-181.
[36] LIU H C, XIA J L, NIE Z Y. Relatedness of Cu and Fe speciation to chalcopyrite bioleaching by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2015, 156: 40-46.
[37] LIU H, XIA J, NIE Z, MA C, ZHENG L, HONG C, ZHAO Y, WEN W. Bioleaching of chalcopyrite by Acidianus manzaensis under different constant pH [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2016, 98: 80-89.
[38] LIU H, XIA J, NIE Z, LIU L, WANG L, MA C. Comparative study of S, Fe and Cu speciation transformation during chalcopyrite bioleaching by mixed mesophiles and mixed thermophiles [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2017, 106: 22-32.
[39] ZHAO H B, HU M H, LI Y N, ZHU S, QIN W Q, QIU G Z, WANG J. Comparison of electrochemical dissolution of chalcopyrite and bornite in acid culture medium [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 303-313.
[40] LANDOLT B. Thermodynamic properties of inorganic material [M]. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 1999.
[41] KNACKE O, KUBASCHEWSKI O, HESSELMANN K. Thermo- chemical properties of inorganic substances [M]. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer, 1991.
[42] BURKIN A R. Chemical hydrometallurgy: Theory and principles [M]. London: Imperial College Press, 2001.
[43] KOLEINI S M J, AGHAZADEH V, SANDSTR?M A. Acidic sulphate leaching of chalcopyrite concentrates in presence of pyrite [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2011, 24(5): 381–386.
[44] MAJUSTE D, CIMINELLI V, OSSEO-ASARE K, DANTAS M. MAGALH?ES-PANIAGO R. Electrochemical dissolution of chalcopyrite: Detection of bornite by synchrotron small angle X-ray diffraction and its correlation with the hindered dissolution process [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 111-112: 114-123.
[45] NKULU G, GAYDARDZHIEV S, MWEMA E, COMPERE P. SEM and EDS observations of carrollite bioleaching with a mixed culture of acidophilic bacteria [J]. Mineral Engineering, 2015, 75: 70-76.
David Lukumu BAMPOLE1,3, Patricia LUIS2, Antoine. F. MULABA-BAFUBIANDI1
1. Mineral Processing and Technology Research Centre, Department of Metallurgy, School of Mining, Metallurgy and Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering and the Built Environment, University of Johannesburg, Doornfontein Campus, P. O. Box 17911, South Africa;
2. Materials & Process Engineering (iMMC-IMAP), UC Louvain, Place Sainte Barbe 2, 1348 Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium;
3. Department of Industrial Chemistry, Faculty of Polytechnique, University of Likasi, 177, Shituru Campus, P. O. Box 1946, Likasi, Democratic Republic of the Congo
摘 要:本文阐述提铜工艺的可持续性。实际上,针对混合硫化矿(黄铜矿和辉铜矿),尝试在33.3 ℃下使用中温混合菌群的提铜工艺和三价铁浸出过程。其中,生物浸出实验是在矿石粒径-75+53 μm范围内完成的。采用细菌作为催化剂,铜收率达65.50%。另一方面,在三价铁浸出过程中,矿石粒径为-53+38 μm,温度升高至70 ℃时,铜收率提高到78.52%。与高温浸出过程相比,中温生物浸出过程在铜的提取中显示出明显的优势。通过SEM-EDS、FTIR和XRD表征,结合各种热力学分析,可以认为间接机理是主要的浸出机理。对于黄铜矿-辉铜矿混合矿而言,浸出机理分为三种过渡产物机理,即多硫化物机理、硫代硫酸盐机理和元素硫机理。铜形态转变为Cu2S-CuS-Cu5FeS4-Cu2S,最后转变为CuSO4。在发生亚铁氧化和硫酸铁生成反应的同时,细菌消耗掉硫化矿物,形成强酸,最后在低温下形成CuSO4,这种铜生产方案要求室温下氧化还原电位高于550 mV,以便有效地提取铜。
关键词:可持续提铜;黄铜矿-辉铜矿混合矿;铜形态;三价铁浸出;中温生物浸出机理;氧化还原电位
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Corresponding author: David Lukumu BAMPOLE; E-mail: davidbampole@gmail.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65123-X

