
Effects of crystallization on low-temperature specific heat capacity of Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 bulk metallic glass
WANG Zhi-xin, SUN Bin, LU Jin-bin
School of Materials and Chemical Engineering, Zhongyuan Institute of Technology, Zhengzhou 450007, China
Received 17 May 2010; accepted 24 March 2011
Abstract: The specific heat capacities of Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 bulk metallic glass (BMG) and crystallized alloys were measured from 2 to 101 K. The effect of crystallization on the specific heat capacity of the BMG was studied. The effects of crystallization and the relationship between local modes and boson peak in the BMG were discussed. The specific heat capacity deviates from the simple Debye behaviors, showing the presence of local harmonic modes (Einstein oscillator) in the BMG and the crystallized alloy. Model calculation includes the contribution of one Debye mode and two Einstein modes for the BMG, one Debye mode and one Einstein mode for the crystallized alloy, showing an adequate description of the experimental data.
Key words: Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG; specific heat capacity; crystallization
1 Introduction
The low temperature specific heat capacity is important for understanding the low-energy excitation in bulk metallic glasses (BMGs). At low temperature, typically T <1 K, the specific heat capacity, cp, of glasses depends approximately linear on temperature [1-3]. At T>1 K, the specific heat capacity deviates from the expected T3 dependence, presenting a broad maximum in curve of cp/T3 [4]. The low temperature specific heat capacity varying linearly with temperature and the anomalous thermal conductivity, was well accounted by the tunneling model [1]. For some BMGs, such as Zr46.75Ti8.25Cu7.5Ni10Be27.5, (Cu50Zr50)92Al8 and Cu50Zr50, their low temperature specific heat capacities were well fitted by the Debye mode and the Einstein mode [5-8]. The thermal properties of alloys directly related to its atomic structure, or its vibrational and configurational entropy which is significantly affected by the nearest- neighbor configuration [8-9]. BMGs are usually metastable at room temperature and will form crystalline or quasicrystalline phases when the temperature increases to the phase transition temperature [10-12]. Crystallization of BMGs makes changes in structure and physical properties [13-14]. Amorphous solids exhibit unusual thermal properties at low temperature, which are in turn very different from those of crystalline solids [1]. Recently, some works have shown the low temperature thermal properties of the Zr-, Cu-, and La-based BMGs, and the effects of composition or heat treatment (no crystallization) on the low temperature specific heat capacity of the BMGs [6, 8, 15]. However, there is little information about effects of crystallization on the low-temperature specific heat capacity of BMGs. In this work, we report the observation of Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG which has excellent glass-forming ability and mechanical properties [16] and the crystallized alloys by measuring the specific heat capacity from 2 to 101 K. The effect of crystallization on the low- temperature specific heat capacity of Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG was discussed.
2 Experimental
Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG was prepared by melting highly pure elements and by suction casting the melt into a copper mold under pure argon atmosphere. The glass transition temperature Tg, onset crystallization temperature Tx, and the melting temperature Tm of the Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG are 734, 782, and 1 189 K, respectively [17]. The crystallized alloy was got by annealing the BMG at 873 K for 2 h. The structure of the samples was identified to be amorphous by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and differential scanning calorimeter (DSC). Specific heat capacity measurements were carried out between 2 and 101 K with the heat capacity option of the commercial physical property measurement system (PPMS, Quantum Design, USA). According to the specifications, the relative error on the specific heat capacity measurements on this instrument is less than 2%. The masses of the samples of the Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG and crystallized alloys, which are used for the measurements, were 15.19 and 13.46 mg, respectively.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Structure of Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG at different states
Figure 1 shows the XRD patterns of the Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG at different states. The XRD pattern of the as-cast alloy shows a broad diffused peak without any detectable crystallized peaks, indicating a glass structure within the examining limit of the XRD. After being annealed at 873 K for 2 h, the BMG contains Cu8Zr3, Cu10Zr7 and some unknown crystalline phases, as shown in Fig. 1.

Fig. 1 XRD patterns of Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG at different states: (a) As-cast; (b) Annealed at 873 K for 2 h
Figure 2 shows the DSC traces of Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG at different states. The DSC trace of the as-cast alloy shows crystallization process (exothermic). No exothermic process occurs in DSC measurement of the annealed sample, indicating that crystallization of Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG is finished completely after being annealed.
3.2 Low-temperature specific heat capacity of samples at different states
The measured specific heat capacities of the Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG and the crystallized alloy from 2 K to 101 K are shown in Fig. 3. It can be clearly seen that the temperature-dependent specific heat capacity is different for the two alloys. The BMG has larger specific heat capacity than the crystallized alloy, just like other alloys [18]. Figure 3(b) shows the specific heat capacity in the temperature range of 2-6.7 K, which is analyzed for both alloys by fitting with a polynomial form:
cp/T=g+βT2 (1)
where g is coefficient of temperature T for the electron contribution to the specific heat, and β is the coefficient of T 3 for the phonon contribution to the specific heat. So we can get that g is 2.73 mJ/(mol·K2) for the BMG and 3.15 mJ/(mol ·K 2) for the crystallized alloy.

Fig. 2 DSC traces of Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG at different states: (a) As-cast; (b) Annealed at 873 K for 2 h

Fig. 3 Specific heat capacity cp of Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG at different states in temperature range from 2 to 101 K (a), and fitting of specific heat capacity of BMG and crystallized alloy between 2-6.7 K using expression cp/T=γ+βT2 (b)
The low-temperature specific heat capacity of the BMGs could change with the heat treating. The height of peak in cp of (Cu50Zr50)92Al8 BMG decrease during the annealing process (no crystallization occurred) [6]. The peak height of the low-temperature cp of Zr46.75Ti8.25- Cu7.5Ni10Be27.5 BMG decreased in the quenched process (the quenched temperature was less than the glass transition temperature, and no crystallization occurred in quenched process) [6]. The values of g and β for the BMGs at different states were compared and listed in Table 1.
3.3 Atom state contribution to specific heat capacity for different samples
The cp of an elastic continuum normally can be explained by the Debye model in a wide temperature range. We found that the specific heat capacity of Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG and the crystallized alloy cannot be well fitted only by the Debye mode and the electron contributions and an additional of Einstein mode is required to fit cp adequately. As illustrated in Fig. 4, a model calculation includes the contribution of one Debye mode and two Einstein modes for the BMG, one Debye mode and one Einstein mode for the crystalline alloy, respectively, showing an adequate description of the experimental data. The line through the specific heat capacity data in Fig. 4 represents a fitting to the equation:
 (2)
(2)
where nD and nEi are constants, just the oscillator strengths per mole at different energies; T is temperature; CD represents contribution from Debye mode.
 (3)
(3)
where R is the gas constant and θD is the Debye temperature; CE is the contribution from Einstein mode.
 (4)
(4)
where θE is the Einstein temperature. All fitting parameters are summarized in Table 2. The strength of Einstein modes in the BMG is higher than that in the crystallized alloy.
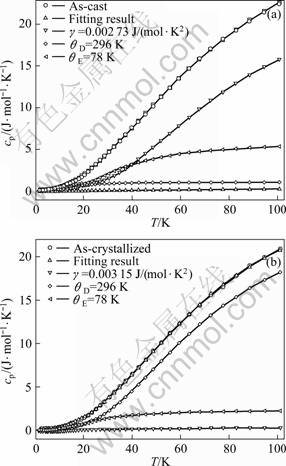
Fig. 4 Fitting results of Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG at different states between 2 K and 101 K: (a) As-cast; (b) As-crystallized
Table 1 Values of g and β for BMGs at different states

Table 2 Fitting parameters

Usually, local harmonic modes are difficultly found by measuring the specific heat capacity because of the strong interaction between the constituent atoms. But when BMGs are quickly quenched from liquid state, the icosahedral structure or large hole is kept in BMGs. There is much free volume in the oversized cage structure. There is the difference of the density between BMGs and corresponding crystalline alloys [13]. The vibrations of the loose atoms with enough large free volume are as independent local modes. So the independent local mode in the BMG shows Einstein modes by fitting of the specific heat capacity. After the BMG being crystallized, the free volume is reduced and the strength of Einstein modes is also decreased.
3.4 Boson peak in Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG
The unusual phenomena in amorphous solids are phonon-like excitations, which exist at very high frequency (1012 Hz), and the related vibrational density of states. A universal feature of such amorphous systems is that the vibrational density of states departs from the Debye squared-frequency law, displaying an excess state, which has been named the Boson peak. The feature was mainly observed in polymeric and ceramic glasses before. In the BMG and crystallized alloys, the three-dimensional spectra are derived from the specific heat. We supposed the phonon density of states contributed from the Einstein mode is in Gaussian distribution [19]:
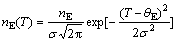 (5)
(5)
where s is the width of Gaussian (s=θE/3). The derived three-dimensional phonon spectra of both BMG and crystallized alloys are greatly different. There is higher density of states at low energy in the BMG than in crystallized alloy. So just like many other amorphous alloys [20], the excess density of states in the BMG is just reduced by the Boson peak.
There are many methods by experiments to definite boson peak, such as a peak in Raman scattering data [21], a peak in the neutron scattering data [20], a peak in the difference between the vibrational density of states of the glass and the corresponding crystal [20]. We select the third method to determine the boson peak, which is shown in Fig. 5(a). Figure 5(b) presents the total density of states of the amorphous and crystallized alloys.

Fig. 5 Rate between derived three-dimensional phonon spectrums of Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG at different states (a) and total three-dimensional phonon spectrum of both alloys (b) (ga and gc represent total density of states of glass state and crystallized state, respectively)
4 Conclusions
1) The temperature-dependent specific heat capacity of the Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 BMG is affected by crystallization and the specific heat capacity of the BMG decreases after being crystallized.
2) The specific heat capacity of the BMG and the crystallized alloy deviate from the simple Debye behaviors. Two additional Einstein modes for the BMG and one Einstein mode for the crystallized alloy are required to fit the cp results adequately.
3) The three-dimensional spectrums derived from the specific heat capacity shows boson peak in the BMG, which is associated with local harmonic modes.
References
[1] ZELLER R C, POHL R Q. Thermal conductivity and specific heat of noncrystalline solids[J]. Phys Rev B, 1971, 4: 2029-2041.
[2] ANDERSON P W, HALPERIN B I, VARMA C M. Anomalous low-temperature thermal properties of glasses and spin glasses[J]. Philos Mag, 1972, 25: 1-9.
[3] PHOLLIPS W A. Tunneling states in amorphous solids[J]. J Low Temp Phys, 1972: 351-360.
[4] GIL L, RAMOS M A, BRING A, BUCHENAU U. Low-temperature specific heat and thermal conductivity of glasses[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1993, 70(1-4): 182.
[5] TANG M B, BAI H Y, PAN M X, ZHAO D Q, WANG W H. Einstein oscillator in highly-random-packed bulk metallic glass[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 86(1-3): 021910.
[6] LI Y, YU P, BAI H Y. Study on boson peak in bulk metallic glasses[J]. J Appl Phys, 2008, 104(1-7): 013520.
[7] LI Y, BAI H Y, WANG W H. Low-temperature specific-heat anomalies associated with the boson peak in CuZr-based bulk metallic glasses[J]. Phys Rev B, 2006, 74(1-4): 052201.
[8] TANG M B, BAI H Y, WANG W H. Tunneling states and localized mode in binary bulk metallic glass[J]. Phys Rev B, 2005, 72(1-4): 012202.
[9] ALEINER I L, ALTSHULER B L, GALPERIN Y M. Experimental tests for the relevance of two-level systems for electron dephasing[J]. Phys Rev B, 2001, 63(1-4): 201401.
[10] LOUZGUINE-LUZGIN D V, ANTONOWICZ J, GEORGARAKIS K, VAUGHAN G, YAVARI A R, INOUE A. Real-space structural studies of Cu-Zr-Ti glassy alloy[J]. J Alloys Compd, 2008, 466: 106-110.
[11] WANIUK T, SCHROERS J, JOHNSON W L. Timescales of crystallization and viscous flow of the bulk glass-forming Zr-Ti-Ni-Cu-Be alloys[J]. Phys Rev B, 2003, 67(1-6): 184203.
[12] XIA L, DING D, SHAN S T, DONG Y D. Evaluation of the thermal stability of Nd60Al20Co20 bulk metallic glass[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90(1-4): 111903.
[13] WANG Z X, WANG R J, WANG W H. Elastic properties of Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 bulk metallic glass under high pressure[J]. Materials Letters, 2006, 60: 831-833.
[14] SCHROERS J, WU Y, BUSH R, JOHNSON W L. Transition from nucleation controlled to growth controlled crystallization in Pd43Ni10Cu27P10 melts[J]. Acta Mater, 2001, 49: 2773-2781.
[15] TANG M B, BAI H Y, PAN M X, ZHAO D Q, WANG W H. Bulk metallic superconductive La60Cu20Ni10Al10 glass[J]. J Non- crystalline Solids, 2005, 351: 2572-2575.
[16] INOUE A, ZHANG W, ZHANG T, KUROSAKA K. Cu-based bulk glassy alloy with good mechanical properities in Cu-Zr-Hf-Ti system[J]. Mater Trans JIM, 2001, 42: 1805-1812.
[17] WANG Z X, LU J B, XI Y J. Effects of quenched under high pressure on crystallization of Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10 bulk metallic glass[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2009, 499: 192-194.
[18] BAI H Y, LUO J L, ZHANG J, CHEN Z J. Low temperature specific heat of a typical glass forming alloy[J]. J Appl Phys, 2002, 91: 9123-9127.
[19] HERMANN R P, JIN R Y, SCHWEIKA W, GRANDJEAN F, MANDRUS D, SALES B C, LONG G J. Einstein oscillators in thallium filled antimony skutterudites[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2003, 90(1-4): 135505.
[20] MEYER A, WUTTKE J, PETRY W, PEKER A, BORMANN R, CODDENS G, KRANICH L, RANDL O G, SCHOBER H. Harmonic behavior of metallic glasses up to the metastable melt[J]. Phys Rev B, 1996, 53: 12107-12111.
[21] SOKOLOV A P, KISLIUK A, SOLTWISCH M, QUITMANN D. Medium-range order in glasses: Comparison of Raman and diffraction measurements[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1992, 69: 1540-1543.
晶化过程对Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10块体
金属玻璃低温比热容的影响
王志新, 孙 斌, 卢金斌
中原工学院 材料与化工学院,郑州 450007
摘 要:测量Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10块体金属玻璃和其晶化态合金在2~101 K的比热,研究晶化过程对块体金属玻璃比热的影响。讨论晶化过程对Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10块体金属玻璃低温比热和块体金属玻璃的波色峰的影响。结果表明:这两种合金的比热都与单一的德拜模型不相符,都存在着局域谐振模型(爱因斯坦模型)。分别用一个德拜模型和两个爱因斯坦模型拟合玻璃态合金,用一个德拜模型和一个爱因斯坦模型拟合晶化态合金,拟合结果与实验数据吻合得很好。
关键词:Cu60Zr20Hf10Ti10块体金属玻璃;比热;晶化
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Foundation item: Project (082102230035) supported by the Foundation of Science and Technology Department of Henan Province, China
Corresponding author: WANG Zhi-xin; Tel/Fax: +86-371-62506699; E-mail: zxwang72@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60858-3