文章编号:1004-0609(2009)04-0708-06
Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu(0.1RE)/Cu焊点界面区微观组织与Cu6Sn5的生长动力学
王要利1, 2,张柯柯1, 2,韩丽娟1,温洪洪1
(1. 河南科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,洛阳 471003;
2. 河南省有色金属材料科学与加工技术重点实验室,洛阳 471003)
摘 要:利用X射线衍射分析仪、JSM-5610LV扫描电镜及能谱分析研究钎焊和时效过程中低银Sn-2.5Ag- 0.7Cu(0.1RE)/Cu焊点界面区显微组织和Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的生长行为。结果表明:钎焊过程中焊点界面区Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的厚度是溶解和生长两方面共同作用的结果;随着时效时间的延长,焊点界面区Cu6Sn5的形貌由扇贝状转变为层状,其长大动力学符合抛物线规律,由扩散机制控制;添加0.1%稀土元素能有效减慢界面Cu6Sn5金属间化合物在钎焊及时效过程中的长大速度,可改变焊点裂纹的起源位置,提高其可靠性。
关键词:Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu(0.1RE)钎料;Cu6Sn5;钎焊;时效;微观组织;长大动力学⊙
中图分类号:TG 42 文献标识码: A
Microstructure and growth behavior of Cu6Sn5 forSn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu(0.1RE)/Cu solder joint interface
WANG Yao-li1, 2, ZHANG Ke-ke1, 2, HAN Li-juan1, WEN Hong-hong1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471003, China;
2. The Key Laboratory of Non-ferrous Materials Science and Processing Technic of Henan Province,
Luoyang 471003, China)
Abstract: The microstructure and growth behavior of Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compound (IMC) of low Ag content Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu(0.1RE)/Cu solder joint interface were investigated by using the X-ray diffraction, JSM-5610LV scanning electronic microscope and energy spectrum analysis. The results show that the Cu6Sn5 thickness of the solder joint interface is decided by its diffraction and growing during the soldering. With the aging time increasing, the Cu6Sn5 micrograph of the solder joint interface can be changed from the scallop-like to the shape-layer, and the growing dynamics is coincidence with the law of parabola and its growing behavior is controlled by diffusion. With adding tiny rare earth(0.1RE) in the Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu solder alloy, the Cu6Sn5 growing rate of the solder joint can be effectively reduced during the soldering and aging period, and the crack initiation place can be changed, so the reliability of the solder joint can be greatly improved.
Key words: Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu(0.1 RE) solder alloy; Cu6Sn5; soldering; aging; microstructure; growing dynamics
随着电子产品向小型化、轻量化和多功能化的发展及人们环保意识的增强,Sn-Ag-Cu系钎料合金由于具有优良的润湿和力学性能[1-2],被认为是Sn-Pb钎料最有潜力的替代品之一[3]。在无铅钎料中添加微量稀土(RE)以改善或提高钎焊焊点的综合性能已取得了较好的试验结果[4-6]。GUO等[7]和SONG等[8]研究表明,钎焊焊点界面区Cu6Sn5金属间化合物(Intermetallic compound)的厚度及形态对焊点的可靠性有很大影响,特别是形成很厚的反应层时,其与基板及钎料之间的热膨胀系数等差别较大,易产生龟裂。但迄今为止,针对焊点界面Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的系统研究尚未见文献报道。为此,本文作者选择Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu(0.1RE)/Cu焊盘的界面反应为研究对象,重点研究钎焊及时效过程中钎焊焊点界面区微观组织和金属间化合物Cu6Sn5的长大行为,这对焊点可靠性预测、高可靠性软钎焊材料尤其是当前环保型无铅钎料的开发均有着重要的理论和实用价值。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料
实验原材料采用99.9%的Sn、Ag、Cu及富Ce和La的混合稀土。在真空度为5×10-3Pa的非自耗电炉ZHW-600A中制备Cu-RE中间合金及Sn-2.5Ag- 0.7Cu钎料合金,在相同条件下适量中间合金与Sn、Ag和Cu制备所需的Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu-0.1RE钎料合金。采用IRIS Intrepid全谱直读等离子体发射光谱仪测定Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu-0.1RE钎料合金中稀土元素残余量。
1.2 钎焊实验与时效处理
钎焊焊点形貌及尺寸如图1所示。母材为紫铜板,钎料合金在轧辊机上轧制成厚0.1 mm的薄带,钎剂为22%ZnCl2+2%NH4Cl,钎焊温度为270 ℃。
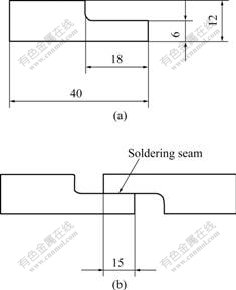
图1 钎焊焊点试样示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagrams of test specimen for solder joint: (a) Specimen before soldering; (b) Test sample of solder joint
将钎焊后的试样置于干燥箱里进行时效处理,为了保证钎焊焊点不受氧化等问题的干扰,将钎焊焊点试样放在二硫化钼中进行时效处理[5],为了缩短时效时间,时效温度选取微电子连接的最高服役温度为150 ℃[6-10]。
采用4%和15%的硝酸酒精溶液腐蚀钎料合金及钎焊焊点,在JSM-5610LV扫描电镜上观察焊点的显微组织和Cu6Sn5的表面形貌,并进行成分分析。金属间化合物厚度的测量是将JSM-5610LV扫描电镜上所得的照片导入AutoCAD中采用相关软件测量不同照片中Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的面积再除以其长度后求平均值得到的。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 界面区金属间化合物的显微结构
图2所示为Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu-0.1RE/Cu焊点界面区的XRD谱。由图2可知,Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu-0.1RE钎焊焊点界面区的金属间化合物主要由靠近钎料一侧厚度不均匀的脆硬Cu6Sn5相和靠近基体Cu一侧的Cu3Sn相组成。图3(a)所示为界面区金属间化合物的截面形貌。由图3(a)可知,钎焊后钎料合金界面区靠近钎料合金侧的Cu6Sn5金属间化合物呈扇贝状分布,并且较薄。通过对近界面区的能谱分析可知界面附近Sn和Cu元素的质量分数,如图3(b)所示。图3(c)所示为Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的切面形貌。由图3(c)可以看出,该区由许多圆形或抛物面形的金属间化合物小颗粒组成,大多数的颗粒周围都有5~7个颗粒紧挨着。通过能谱分析的原子个数比推测及文献[9-10]可知,这些颗粒为Cu6Sn5金属间化合物,且在Cu6Sn5金属间化合物颗粒之间存在较深的沟槽,在三点交合处沟槽最深,这可能是由于初生相β-Sn在扩散过程中与基板扩散过来的Cu元素发生反应生成了Cu6Sn5金属间化合物而形成了显微的Kirkendall孔洞[11]。这对钎料合金焊点的可靠性有很大的影响。
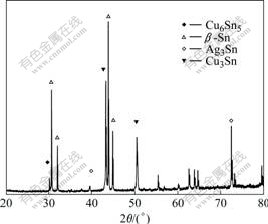
图2 Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu-0.1RE/Cu焊点界面区的XRD谱
Fig.2 XRD pattern of Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu-0.1RE/Cu solder joint interface

图3 Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu-0.1RE焊点界面区Cu、Sn元素含量及Cu6Sn5的形貌
Fig.3 Cu6Sn5 cross-section micrograph (a), contents of elements Cu and Sn at different points near solder joint interface (b) and Cu6Sn5 section micrograph (c) of Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu- 0.1RE solder joint interface
2.2 界面区裂纹萌生
图4所示为Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu(0.1RE)钎料合金钎焊焊点萌生的裂纹。由图4可知,Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu钎料合金焊点界面区的Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的厚度很不均匀,在焊点服役过程中,大部分裂纹在界面区Cu6Sn5金属间化合物内沿Cu基板方向萌生,这是由于硬 脆[12-14]的Cu6Sn5与钎料合金和基板Cu之间的热膨胀系数差别较大,在焊点服役过程中,导致焊点的断裂韧性下降而出现裂纹。当添加0.1%RE后,焊点界面区Cu6Sn5变得相对较为均匀,此时裂纹在钎料合金内部萌生,此时Cu6Sn5主要起到连接钎料合金与基板Cu的作用。这说明界面区Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的几何尺寸及形态对焊点的裂纹萌生有很大的影响,这与文献[12]中的结果一致。

图4 不同钎料合金的焊点裂纹萌生区
Fig.4 Solder joint crack initiation areas of Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu-xRE solder joints: (a) Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu; (b) Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu-0.1RE
2.3 钎焊过程中Cu6Sn5的界面反应
Cu在270 ℃的液态Sn-2.5Ag钎料中的溶解度为1.40%(质量分数)[13]。因此,在钎焊过程中,只要液态钎料中Cu未达到饱和状态,金属间化合物就会通过晶界或晶粒表面向液态钎料中溶解[14],所以在钎焊过程中Cu6Sn5的生长和溶解过程同时存在。MA等[15]对固态物质向液态物质中溶解动力学的研究表明,化合物在钎焊过程中的溶解速度可表示为

式(1)表明金属间化合物的溶解速度与Cu在液态钎料中浓度和固溶限差成正比。
图5所示为钎焊时间对界面区Cu6Sn5厚度的影响。由图5可知,钎焊时间较短时,钎料合金钎焊焊点界面区Cu6Sn5的长大速度相对较快,随着钎焊时间的延长,界面区Cu6Sn5的长大速度变慢。这是由于钎焊时间较短时,虽然Cu6Sn5金属间化合物在钎料合金中的固溶度较大,其溶解速度也较大,但界面区还没有形成连续的金属间化合物层,Cu6Sn5金属间化物的生成是液态金属与Cu直接反应形成的,因此,其长大速度也大;随着钎焊时间的延长,虽然界面Cu6Sn5金属间化物的溶解速度减慢,但界面区形成了连续的Cu6Sn5金属间化合物,其生长受扩散机制控制,故生长速度减慢。
由图5还可以看出,在相同条件下,添加微量稀土元素的Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu-0.1RE钎料合金钎焊焊点的Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的长大速度明显小于Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu,说明添加微量稀土元素能有效地阻止钎焊过程中Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的长大,这可能是由于微量富Ce和La的混合稀土不溶于Sn基体但具有亲Sn性的缘故,易与Sn发生反应生成化合物而降低Sn的活度,有利于抑制界面Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的生长。这与钎焊过程中Cu-Sn在扩散过程中形成金属间化合物不仅取决于元素的浓度梯度而且取决于元素的活度相一致[15]。
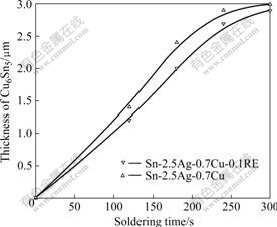
图5 钎焊时间对Cu6Sn5厚度的影响
Fig.5 Effects of soldering time on thickness of Cu6Sn5
2.4 时效过程中焊点界面区的显微结构
在时效过程中,外界为钎料和基体Cu提供了足够的能量,合金内部及界面区的金属间化合物经历了析出、扩散与重新组合,因而合金内部的形貌与界面区的形貌将相应地发生变化。图6所示为Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的厚度与时效时间的关系,由图6可知,Cu6Sn5金属间化合物层随着时效时间的延长而生长,形貌由扇贝状转变为较平整的层状,而焊点中的钎料合金也由时效0 h时较为均匀的共晶组织长大成较大颗粒状的Cu6Sn5金属间化合物。且在Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu钎料合金焊点界面区的Cu6Sn5金属间化合物内出现了较为明显的Kirkendall现象;而添加0.1%的富Ce和La的混合稀土元素对钎料合金在时效过程中共晶组织的均匀化及界面区Cu6Sn5的生长有一定的阻碍作用,这与文献[13]中的研究结果相一致。

图6 时效时间对Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu(0.1RE)焊点界面区Cu6Sn5的影响
Fig.6 Effect of aging time on Cu6Sn5 of Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu solder joints (a), (b) and Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu-0.1RE solder joints (c), (d): (a) 0 h; (b) 96 h; (c) 0 h; (d) 96 h;
2.5 时效过程中Cu6Sn5的长大动力学
钎焊后钎料与Cu基板界面的金属间化合物在时效过程中的生长速度,可用以下经验方程来描述[6,16]:

将两种钎料焊点界面区Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的厚度与时效时间的关系进行线形拟合可得图7。由图7可以看出,Cu6Sn5的厚度与时效时间之间的关系大致呈抛物线规律,这表明界面区Cu6Sn5的生长受扩散机制控制。
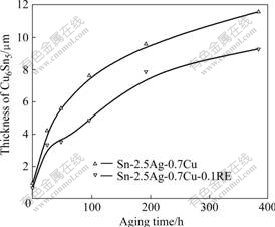
图7 Cu6Sn5厚度与时效时间的关系
Fig.7 Relationship between thickness of Cu6Sn5 and aging time
图8所示为钎料合金钎焊焊点界面区Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的厚度与时效时间的平方根之间的关系。通过对图中曲线进行线形拟合可知,对于Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu(0.1RE)/Cu钎焊焊点界面区Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的生长由扩散机制控制,这与文献[6,16]中的研究结果一致,即焊点界面区金属间化合物的生长可简化为


图8 Cu6Sn5厚度与时效时间平方根的关系
Fig.8 Relationship between thickness of Cu6Sn5 and square root of aging time
由图7和8可知,添加微量稀土元素的Sn-2.5Ag- 0.7Cu-0.1RE焊点界面区的Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的生长速率小于Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu的,这可能与RE的包覆作用有关。
3 结论
1) 钎焊过程中Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu(0.1RE)/Cu焊点界面区Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的厚度是由溶解和生长共同作用的结果;时效过程中焊点界面区Cu6Sn5由扇贝状转变为层状,其生长动力学与时效时间的平方根呈线性关系,生长受扩散机制控制。
2) 添加微量的稀土元素能减慢焊点界面区Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的生长速度、几何尺寸及形态,从而改变焊点裂纹起源的位置,提高焊点可靠性。
REFERENCES
[1] 张柯柯, 王要利, 樊艳丽, 祝要民, 张 鑫, 阎焉服. 微量RE及环境条件对Sn-Ag-Cu钎焊接头蠕变断裂寿命的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2007, 36(8): 1473-1476.
ZHANG Ke-ke, WANG Yao-li, FAN Yan-li, ZHU Yao-min, ZHANG Xin, YAN Yan-fu. Effect of Ce-La mixed rare earth content and environment condition on the creep rupture life of Sn-Ag-Cu solder joints[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2007, 36(8): 1473-1476.
[2] 樊艳丽, 张柯柯, 王双其, 程光辉, 王要利, 余阳春. 水洗钎剂下Sn-Ag-Cu系钎料对不同基板的润湿特性[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2006, 26(9): 604-606.
FAN Yan-li, ZHANG Ke-ke, WANG Shuang-qi, CHENG Guang-hui, WANG Yao-li, YU Yang-chun. Wettability of Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder containing low Ag for different substrate with water-soluble flux[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2006, 26(9): 604-606.
[3] 许天旱, 赵麦群, 刘新华. Sn-Ag-Cu系无铅焊锡成分的优化研究[J]. 电子元件与材料, 2004, 23(8): 14-21.
XU Tian-han, ZHAO Mai-qun, ZHAO Xin-hua. Study on the optimal free-lead solder alloy of Sn-Ag-Cu system[J]. Electronic Components & Materials, 2004, 23(8): 14-21.
[4] 张柯柯, 王双其, 余阳春, 王要利, 樊艳丽. Sn-Ag-Cu-RE系无铅钎料与表面贴装元器件的润湿适配性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(11): 1908-1912.
ZHANG Ke-ke, WANG Shuang-qi, YU Yang-chun, WANG Yao-li, FAN Yan-li. Wetting match performance of Sn-Ag-Cu-RE lead-free solder for surface mount component[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(11): 1908-1912.
[5] YAN Yan-fu, FENG Li-fang, ZHANG Ke-ke, WEN Jiu-ba. Influence of temperature on creep behavior of Ag particle enhancement Sn-Cu based composite solder[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2007, 12(3): 296-301.
[6] AHAT S, 杜黎光, 孙志国, 盛 玫, 罗 乐. Sn-Ag-Cu表面贴装焊点在时效和热循环过程中的组织及剪切强度变化[J]. 金属学报, 2001, 37(4): 439-444.
AHAT S, DU Li-guang, SUN Zhi-guo, SHENG Mei, LUOLe. Effects of aging and thermal cycling on the microstructure and shear strength of Sn-Ag-Cu surface mount solder joint[J]. Acta Metallrugica Sinica, 2001, 37(4): 439-444.
[7] GUO F, LUCAS J P, SUBRAMANLIAN K N. Creep behavior in Cu and Ag particles-reinforced composite and eutectic Sn3.5Ag and Sn-4.0Ag-0.5Cu non-composite solder joints [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2001, 12: 27-35.
[8] SONG H G, MORRIS J W, HUA F. The creep properties of lead-free solder joints[J]. Journal of Minerals, Metals and Materials, 2002, 6: 30-32.
[9] WANG Yin-hui, NISIDA K, HUTTER M. Surface activation process of lead-free solder bumps for low temperature bonding[C]// 2005 6th International Conference On Electronics Packing Technology, Shenzhen: China Electronics Packing Society, 2005: 404-407.
[10] SUGANUMA K. 无铅焊接技术[M]. 宁晓山, 译. 北京: 北京科学出版社, 2004: 62-66.
SUGANUMA K. Welding Technology of Lead-free Solder [M]. NING Xiao-shan, transl. Beijing: Beijing Science Press, 2004: 62-66.
[11] YOON J W, JUNG S B. Effect of isothermal aging on intermetallic compound layer growth at the interface between Sn-3.5Ag-0.75Cu solder and Cu substrate[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2004, 39(13): 4211-4217.
[12] VIANCO P T, REJENT J A, HLAVA P F. Solid-state intermetallic compound layer growth between copper and Sn-3.9Ag-0.6Cu solder[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2004, 33(9): 990-1004.
[13] ZHANG Ke-ke, WANG Yao-li, FAN Yan-li, YANG Jie, YAN Yan-fu, ZHANG Xin. Research on creep properties of Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu-XRE lead-free-soldered joints for surface mount technology[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2007: 353-358.
[14] 王 烨, 黄继华, 张建纲, 齐丽华. Sn-3.5Ag-0.7Cu/Cu界面的显微结构[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(11): 495-499.
WANG Ye, HUANG Ji-hua, ZHANG Jian-gang, QI Li-hua. Microstructure of Sn-3.5Ag-0.5Cu/Cu interface[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(11): 495-499.
[15] MA D, WANG W D, LAHIRI S K. Scallop formation and dissolution of Cu-Sn intermetallic compound during solder reflow[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2002, 91(5): 3312-3315.
[16] 岳译新, 谭澄宇, 郑子樵, 李世晨, 叶建军. 新型Ag-Cu-Ge钎料的性能及钎焊界面特征[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(10): 1793-1798.
YUE Yi-xin, TAN Cheng-yu, ZHENG Zi-qiao, LI Shi-chen, YE Jian-jun. Properties and interface microstructure of new type Ag-Cu-Ge solder [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(10): 1793-1798.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50774029);河南省高校创新人才基金资助项目(教高2004-294);河南省高校杰出科研人才创新工程资助项目(2004KYCX020);河南省杰出青年科学基金资助项目(074100510011);河南科技大学大学生训练计划资助项目(SRTP2008010)
收稿日期:2008-07-23;修订日期:2009-01-05
通讯作者:王要利,助理实验师;电话:13949241298;E-mail: wangyaoli001@163.com
(编辑 李向群)