开挖过程中隧洞围岩应力主轴旋转及其对围岩破坏模式的影响
崔溦,王宁
(天津大学 水利工程仿真与安全国家重点实验室,天津,300072)
摘要:采用扩展有限元法(XFEM),通过模拟岩体初始裂隙,研究应力主轴旋转变化下的岩体裂隙扩展模式;以某地下隧洞工程为例,分析隧洞开挖过程中不同部位围岩主应力旋转变化情况;结合应力旋转下岩体裂隙扩展模式,研究这种变化对围岩破坏的影响。研究结果表明:应力方向的旋转会造成围岩中初始裂隙在扩展深度和扩展方向上发生明显变化;在隧洞开挖过程中,洞顶附近岩体的应力方向则在旋转一定角度后即恢复初始方向,边墙附近岩体主应力最大旋转角度接近90°;受应力主轴旋转影响,不同类型岩体宏观上表现为不同的破坏模式,在实际工程中应予以关注。
关键词:岩石破坏;裂隙扩展;应力主轴旋转;扩展有限元(XFEM)
中图分类号:TU452 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2014)06-2062-09
Principal stress axis rotation and effect on failure model of surrounding rock during tunnelling
CUI Wei, WANG Ning
(State Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Engineering Simulation and Safety, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China)
Abstract: By means of extended finite element method (XFEM), the crack propagation mode on condition of principal stress axis rotation based on the simulation of initial crack was studied. An underground tunnel project was studied as an example, and the changes of principal stress axis rotation in different parts of the surrounding rock during the excavation process of the tunnel were studied. Then the influence of stress axis rotation on failure modes of surrounding rock was studied combined with the crack propagation mode in the rotation process. The results show that the rotation of principal stress axis can lead to significant change on the depth and direction of the propagation of initial crack. During the excavation process, the principal stress of rock mass near hanging wall returns to the initial direction after the maximum rotation angle appears, while the maximum rotation angle of principal stress of rock mass near sidewall is close to 90°. Affected by the axis rotation of principal stress, different types of rocks have different macroscopic failure modes, which means enough attention should be paid to this problem in practical project.
Key words: rock damage; crack propagation; principal stress axis rotation; extended finite element method (XFEM)
隧洞开挖造成的围岩应力状态的改变是影响隧洞安全的主要因素。围岩应力状态的改变引起岩体内部裂隙的产生和扩展,进而有可能造成围岩失稳破坏。这种应力状态的改变包含应力的方向和大小2个方面的变化,通常应力大小的变化控制着裂隙的深度,应力方向的改变控制着裂隙的密度,岩体的破坏是这2个因素相互作用的结果[1],但现有研究成果中大多仅关注应力的变化对围岩破坏的影响。对于岩体中的初始裂隙,应力方向的旋转过程可能造成裂隙扩展模式的改变,从而引发不同的岩体破坏。因此,隧洞开挖过程中应力方向的旋转对隧洞安全性的影响不容小觑,有必要对其内在作用机制进行研究。目前,许多学者已经注意到这一问题并进行了相应的研究。郑颖人等[2]就“考虑应力主轴旋转的广义塑性力学”问题进行了探讨,分解出了旋转应力分量,推导出了旋转应力分量引起的塑性变形增量的理论公式,认为应力主轴旋转可以引起塑性变形增量;Eberhardt[3]通过对隧洞开挖过程的三维数值模拟,研究了围岩主应力方向旋转变化的过程;张社荣等[4]研究了掌子面推进过程中隧道顶部和侧墙应力状态的变化,其结果表明:随着隧道挖掘的深入,其顶部岩体的第三主应力方向由竖直向下旋转至沿洞壁的切线方向,隧道边墙岩体的第三主应力方向一直维持不变。Kaiser等[5]以Winston Lake Mine中回采巷道为实例,通过三维边界元计算预测了巷道顶壁的应力旋转过程,其结果与实测十分吻合,并通过研究应力路径指出了巷道顶壁层离塌方的成因。Diederichs等[6]通过数值模拟方法研究了应力旋转对裂隙的扩展影响以及岩石开挖过程中花岗岩及花岗闪长岩的破坏问题。Derek [7]的研究表明受应力大小变化和应力旋转影响,实际脆性岩体在较小应力水平下即发生破坏。本文作者考虑平面问题,采用XFEM法,验证应力主轴旋转对岩体初始裂隙的扩展影响,说明应力旋转可以改变裂隙扩展方向,增大裂隙扩展深度。基于以上研究,采用有限元数值模拟方法对某地下隧洞开挖过程中不同部位应力主轴旋转情况进行研究分析,得到洞顶和边墙部位应力大小和主轴变化规律,并通过引用岩石破坏阈值研究开挖过程中2类围岩(灰色花岗岩和花岗闪长岩)的破坏机理,以便为类似地质隧洞开挖的支护设计和时机选择提供理论参考。
1 基本理论
1.1 扩展有限元(XFEM)
应力主轴旋转下围岩裂隙扩展方式采用扩展有限元进行分析。扩展有限元方法[8-9](XFEM)的基本思想是用一些附加函数来改进传统有限元,使得裂缝几何独立于计算网格,扩展函数通常包括裂隙尖端附近渐进函数(用于模拟裂隙尖端附近的应力奇异性)及间断函数(用于表示裂隙面处位移跳跃)。图1所示为XFEM富集模式。
扩展有限元法中,通过附加函数加强常规有限元逼近模拟裂纹的扩展,其位移逼近可用下式表示:
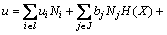
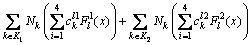 (1)
(1)
式中:I为所有节点的集合,即右端第1项;J为裂纹完全贯穿单元节点的集合(图1中“□”表示的节点),即右端第2项;K1和K2分别为裂纹两端和影响域被裂纹嵌入的单元节点的集合,即右端第3项和第4项;Ni为节点i的形函数;ui为节点i位移向量的连续部分;bi为结点i与阶跃函数相关的节点加强自由度;cil1和cil2分别为2个裂尖处于弹性渐进裂尖函数有关的节点加强自由度;H(x)为沿裂纹面的间断阶跃函数;F1l(x)和F2l(x)(l=1,…,4)为裂纹尖端应力裂尖函数。
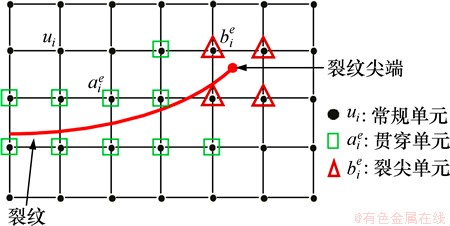
图1 XFEM富集模式
Fig. 1 Enrichment mode of XFEM
图2所示为局部坐标系下的Heaviside函数。沿裂纹面的间断阶跃函数H(x),在局部坐标系(见图2)下由以下公式给出:
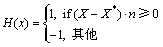 (2)
(2)
式中:X为高斯点,X*为位于裂纹上距X最近点,n为单位外法线向量。
裂纹尖端位移场可用水平集函数构造的裂尖函数Fi(r, θ)来表达:
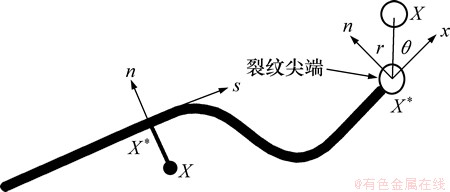
图2 局部坐标系下的Heaviside函数
Fig. 2 Heaviside function at local coordinate system
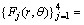
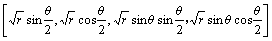 (3)
(3)
式中:r和θ为裂纹尖端为坐标原点、裂纹外切线为极轴的局部极坐标;(r, θ)为极坐标系,裂纹尖端切线方向对应θ=0。
在有限元计算中,虚功方程为
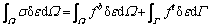 (4)
(4)
由式(4)以及有限元近似位移表达式(1)可以得到XFEM的支配方程:
Ku=F (5)
式中:u为结点位移列向量;K为整体刚度矩阵,由单元刚度矩阵集合而成:
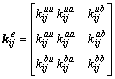 (6)
(6)
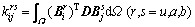 (7)
(7)
式中:D为弹性本构矩阵;u,a和b分别代表单元位移向量的连续部分、贯穿单元和裂纹尖端所在单元的结点改进自由度;i和j代表单元结点数目;Biu,Bia和Bib分别为常规应变矩阵、贯穿单元以及裂尖单元的附加应变矩阵。
F为整体荷载列阵,由单元荷载列阵集合而成:
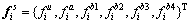 (8)
(8)
式中:fiu为常规单元的荷载列阵向量;fia,{fib1,fib2,fib3,fib4}T分别由贯穿单元和裂尖单元的荷载附加列阵。
1.2 应力旋转下的岩体裂隙扩展机制
图3所示为主应力旋转导致的岩体裂隙扩展机制。由图3可见:当应力达到岩体破坏强度时,岩体中出现沿应力方向的微裂缝;随着应力的旋转,不断出现沿新的应力方向的微裂隙,从而使裂隙密度逐渐增加并最终造成新旧裂隙的交叉、贯通[3],这对岩体的稳定极为不利。
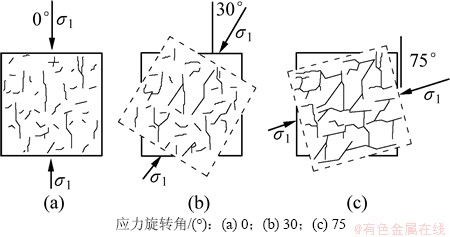
图3 主应力旋转导致的岩体裂隙扩展机制[3]
Fig. 3 Fracture extension mechanism induced by principal stress rotation
除了对裂隙网络产生影响外,应力主轴旋转还会对裂隙的扩展方式产生影响。图4所示为主应力旋转下的初始裂隙扩展模式。由图4可见:在初始状态下,主应力方向与初始裂隙主方向斜交,裂隙尖端萌生沿主应力方向的翼裂纹[10],但由于主应力在垂直裂隙方向上的分力的影响,初始裂隙尖端的拉裂破坏受到限制,翼裂纹扩展深度较小;随着主应力的方向旋转至接近平行于初始裂隙的方向,翼裂纹尖端扩展方向出现同角度旋转、仍平行于旋转后的主应力方向,且翼裂纹扩展深度大幅度增大;而随主应力方向恢复至原始状态,裂隙尖端进一步扩展,其发展过程基本为上一过程的重复。在主应力的旋转变化过程中,裂隙尖端的扩展方向始终与主应力方向平行,即裂隙尖端旋转角与主应力旋转角相同;与此同时,裂隙扩展深度不断增大。
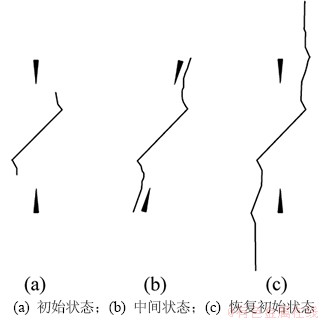
图4 主应力旋转下的初始裂隙扩展模式
Fig. 4 Initial crack propagation through principal stress rotation
对于主应力方向在旋转后又回复初始方向的情况,极易与主应力未发生旋转的情况混淆。通常,在应力未旋转的情况下(图3(a)),各裂隙扩展方向基本相互平行,裂隙间不易出现贯通的现象;但鉴于图4中的单条裂隙在主应力旋转下的扩展模式,应力旋转可能使相邻裂隙间出现贯通(图3(b),(c)),从而对围岩稳定产生不利影响。
2 应力主轴旋转对岩体初始裂隙扩展的影响
在应力主轴旋转情况下,岩体初始裂隙的扩展模式与未旋转的情况有重要差别。对于两者的区别,本节通过模拟不含应力主轴旋转和包含应力主轴旋转两条应力路径下岩体初始裂隙的扩展模式来加以说明。算例计算采用XFEM方法,2条应力路径以围压的形式加载于岩体模型。计算过程中取岩体模型物理力学参数为:弹性模量40.0 GPa,泊松比0.25,重度2 760 kN/m3,抗拉强度3.5 MPa,断裂能200 N/m。
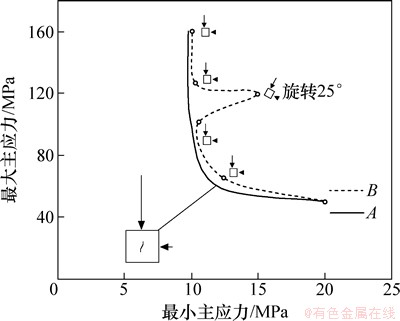
图5 加载应力路径示意图
Fig. 5 Stress paths loading in model
加载的2条应力路径如图5所示,图中应力加载曲线起点(假定为隧洞开挖前)位于右下侧、终点(假定为隧洞开挖完成)为左侧上部顶点;路径B中的应力发展过程与路径A的基本一致,但在其发展过程中增加了25°的应力方向旋转。需要指出的是:上述应力加载曲线未考虑中主应力的作用。
图6(a)和(b)所示分别为应力路径A和B下的初始裂缝扩展情况及其竖向变形云图。由图6(a)可知:在应力路径A下,大主应力方向始终为竖直方向,裂隙尖端由于受到拉伸作用而产生翼裂纹;随着大主应力的增加,翼裂纹继续扩展,且其扩展方向大致平行于大主应力的方向[11]。由图6(b)可知在应力路径B下,裂隙发展过程主要分为3个阶段;初期大主应力方向为竖直方向,裂隙扩展情况与图6(a)的相同;当主应力方向旋转25°时,上一阶段萌生的翼裂纹尖端出现新的翼裂纹,新的翼裂纹沿平行于旋转25°后的大主应力方向扩展;随着主应力方向回复初始状态,大主应力方向回复竖直方向,与竖直方向夹角为25°的翼裂纹尖端萌生新的平行于竖直方向的翼裂纹。除上述裂隙扩展方向上的变化外,对比图6(a)和(b)可知:应力旋转下的初始裂隙扩展深度要明显大于无应力旋转的深度,同时,裂隙附近岩体的不均匀变形的情况也更明显。假设图6(a)中裂隙扩展被岩块边界约束,则图6(b)中所示的裂缝扩展深度势必会超出岩块边界,导致裂缝在低应力下的贯通和相互作用。
由以上计算结果可知:对于工程岩体,应力主轴旋转可加剧和改变初始裂隙扩展深度和扩展形式从而在岩体内部形成破碎带,导致岩体承载力下降,造成塌方等围岩失稳现象。

图6 岩体初始裂隙扩展模式计算结果(单位:m)
Fig. 6 Calculation results of initial crack propagation in rock
3 应力主轴旋转及其对围岩破坏的影响
某水利工程地下隧洞埋深约为420 m,开挖断面为圆形,开挖洞径D=3.5 m,围岩中灰色花岗岩和花岗闪长岩混杂,为研究简便,将岩体模型看作各向同性材料,其材料参数取2类岩石的加权平均值,见表1。隧洞轴线方向与现场原岩应力中的中主应力σ2方向平行。原岩应力中沿洞轴线方向水平应力为45.0 MPa,垂直洞轴线方向水平应力为60.0 MPa,竖向应力大小为11.0 MPa[11]。以此实际工程为例,基于有限元软件ABAQUS,采用岩石最常用的摩尔库伦本构模型,研究隧洞开挖过程中的应力旋转及围岩破坏模式。计算模型在垂直洞轴线的竖向及水平向均由洞轴线向两侧延伸10倍洞径,沿隧洞轴线开挖方向取模型长度为8倍洞径。为提高计算精度同时缩短计算时间,采用由内及外逐渐增大的规则六面体网格,并在隧洞轴线中间监测断面附近加密网格,最终模型单元总数为69 836,有限元模型见图7。数值模拟计算过程中,模型底部施加全约束,四周施加法向约束。
表1 数值模型参数
Table 1 Parameters for numerical model
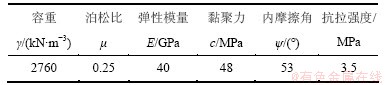
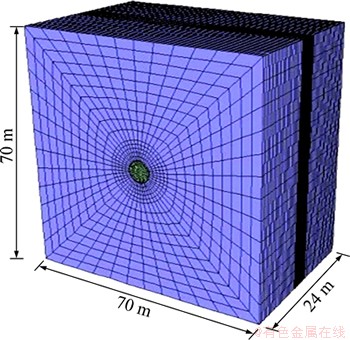
图7 三维有限元模型及尺寸示意图
Fig. 7 Three-dimensional finite-element mesh and model geometry
3.1 隧洞开挖引起的应力主轴旋转
利用软件计算出各监测点所有应力值,基于MATLAB软件编写相应的计算主应力大小和方向的程序代码,从而可以求得计算监测点各主应力值及其与初始方向的夹角,以此为基础进行下一步的深入研究分析。
图8和图9所示分别为隧洞开挖过程中的隧洞顶部及边墙监测点(监测点距洞壁约25 mm)的主应力及其方向变化曲线。图中σ1,σ2和σ3分别表示最大主应力、中主应力和最小主应力,以压为正值;横坐标表示掌子面与计算点的距离,纵坐标表示主应力,曲线上的向量表示主应力的方向;标识上的竖线表示竖直方向,“×”线表示垂直洞轴线的水平方向,横线表示平行洞轴线方向。为便于说明,规定掌子面未超过监测点的一侧为监测点后方,超过监测点的一侧为监测点前方。由图8可知:从主应力的变化来看,对于洞顶围岩,在掌子面推进至监测点后方约1.5倍洞径时,主应力开始变化;随着掌子面向前推进,σ1和σ2处于逐渐增大的状态,σ3则逐渐减小;在掌子面通过监测点断面时各主应力突然增大,随后σ1仍继续增长且在掌子面推进至监测点前方约1.5倍洞径时达到稳定,σ2和σ3则出现回降并在掌子面推进至监测点前方约0.5倍洞径后即达到稳定。从主应力方向的变化来看,当掌子面推进至监测点后方约1倍洞径时,顶部监测点σ2和σ3方向开始出现明显变化,σ2和σ3方向主要在沿洞轴线的竖直平面内旋转;顶部监测点σ1的方向旋转出现在掌子面通过监测点断面前后,主要在沿洞轴线的水平面内旋转;各主应力方向最大旋转角度出现在掌子面通过断面时,并在掌子面通过监测点断面后即基本回复至初始状态(旋转角度为0°)。
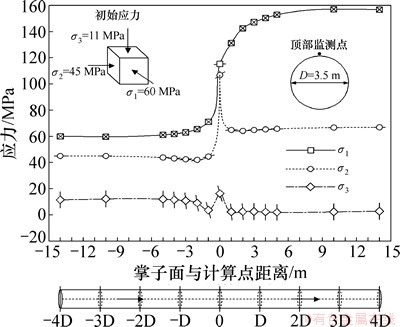
图8 隧洞顶部监测点主应力变化曲线
Fig. 8 Stress path plots of principal stress magnitudes and orientations at monitoring points in tunnel roof
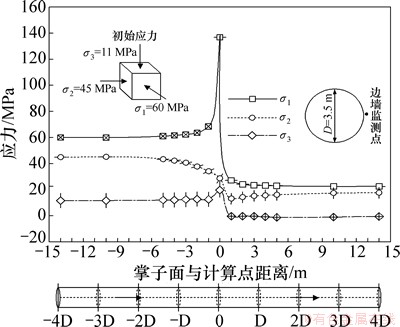
图9 隧洞边墙监测点主应力变化曲线
Fig. 9 Stress path plots of principal stress magnitudes and orientations at monitoring points in tunnel wall
由图9可知:对于边墙处围岩,从主应力大小的变化上来看,随着掌子面向前推进,边墙监测点的主应力处于不断降低的状态,仅σ1和σ3在掌子面通过监测点断面时出现的短暂的增长;且主应力变化自掌子面推进至监测点后方约1倍洞径时开始,至掌子面推进至监测点前方约1倍洞径时结束。从主应力的方向变化来看,当掌子面推进至监测点后方约1倍洞径时,边墙监测点σ2方向开始出现明显的变化;σ2和σ3方向旋转出现在掌子面通过监测点断面时;在掌子面通过监测点断面后,边墙监测点各主应力方向旋转基本结束;相较于初始状态,各主应力方向均出现了约90°的旋转,σ1的方向由最初的与洞轴线垂直的水平方向旋转至与洞轴线平行的水平方向,σ2由与洞轴线平行的水平方向旋转至竖直方向,σ3则由竖直方向旋转至与洞轴线垂直的水平方向。
由计算可知:在开挖过程中,隧洞顶部和边墙附近岩体应力主轴都有一定角度的旋转。洞顶围岩应力主轴旋转一定角度后随即恢复初始方向,而边墙附近岩体应力主轴旋转角接近90°。
3.2 应力旋转对围岩破坏的影响
理论研究表明[6, 12]:对于花岗闪长岩,当应力偏量σ1-σ3或σ2-σ3超出110 MPa时,岩体产生初始破坏,即认为此时开始产生初始裂隙;而对于灰色花岗岩,这一应力阈值稍小,约为80 MPa。作者参照该破坏阈值规律,结合数值模拟结果说明该实际工程开挖过程中岩石破坏情况。
图10所示为隧洞顶部距洞壁25 mm处岩体的应力路径及σ1旋转角的变化曲线。图中左侧实线描述了隧洞开挖过程σ1的旋转角与大小变化的过程;右侧实线描述隧洞开挖过程此处岩体σ1与σ3大小变化的过程,虚线则为σ2与σ3大小变化的过程;右侧2条倾斜直线分别为灰色花岗岩和花岗闪长岩产生初始破坏的阈值界限,当应力差曲线达到岩石破坏阈值界限时,相应岩性的岩体即出现初始破坏,岩体内产生初始裂隙。
分析图10可知:在隧洞开挖过程中,在掌子面推进至断面后方约0.2 m时,σ1-σ3达到灰色花岗岩的初始破坏阈值(80 MPa),灰色花岗岩产生初始破坏,并形成初始裂隙,之后σ1-σ3大小持续增加且σ1出现约35°的旋转后基本回复初始方向,应力的方向旋转作用于前期产生的初始裂隙,导致岩体的裂隙扩展机制类似于图6(b),裂隙扩展增大幅度较大;而花岗闪长岩的初始破坏主要出现在掌子面通过断面约0.2 m的距离后,此时σ1-σ3已超出花岗闪长岩的初始破坏阈值(110 MPa),且σ1-σ3的大小仍处于增大的状态,但此时σ1方向已基本恢复至初始状态,此后应力方向变化几乎无变化,其对初始裂隙扩展方向的影响也较小,裂隙扩展主要受主应力变化的影响,故围岩中花岗闪长岩的裂隙扩展机制类似于图6(a),相对于花岗岩其裂缝扩展幅度较小。同时,由图10给出的σ2的变化过程,可见σ2的变化同样可能造成隧洞围岩的破坏与初始裂隙扩展形式的变化。但由于σ2-σ3未达到花岗闪长岩的破坏阈值,隧洞围岩σ2变化仅可能对灰色花岗岩产生上述影响。
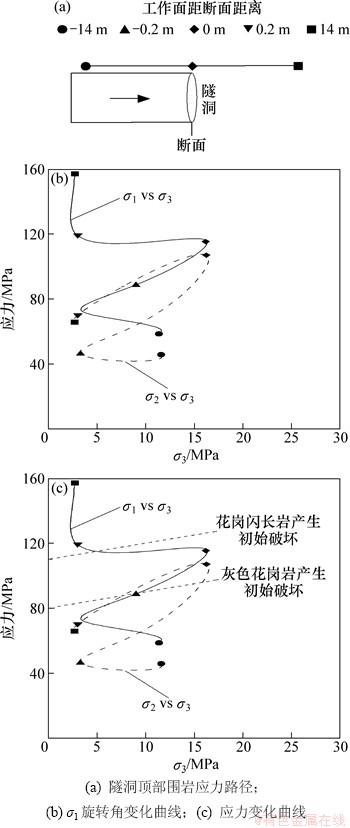
图10 隧洞顶部围岩应力路径及σ1旋转角变化曲线
Fig. 10 Plot of stress paths and rotation angle of σ1 for a point at tunnel crown during excavation
隧洞开挖数值模拟过程中,通过在洞顶及沿隧洞环向1/4圆周不同部位设置相应监测点,更加详尽地说明围岩不同部位应力主轴旋转及其对围岩破坏的影响情况。
图11所示为隧洞开挖过程中顶部围岩主应力及旋转角变化曲线。对于洞顶以上围岩的应力变化情况,选取5个距洞顶不同距离的监测点加以说明,代表点示意图见图11(d)。图11(a),(b)和(c)分别描述了隧洞开挖过程中围岩σ1,σ2和σ3的大小及旋转角变化情况,同时在图(a)和图(b)的右侧分别给出了σ1-σ3和σ2-σ3的变化曲线。
由图11可知:在开挖过程中,洞顶以上2 m范围内岩体三向主应力都有旋转一定角度后恢复初始方向的现象发生,且最大旋转角出现在掌子面通过监测断面时。同一时刻,越靠近顶壁的围岩主应力旋转角越大,且σ1和σ2的旋转角明显大于σ3的旋转角。由图11(a) 及图(b)右侧曲线可知:围岩σ1的变化是导致顶部围岩破坏的主要因素,主要影响距顶壁0.15 m范围内的围岩破坏,对灰色花岗岩来说该距离可以达到1.0 m左右,且与图10中规律一致;当灰色花岗岩出现初始裂缝时,岩体围岩应力仍处于旋转过程中,对花岗岩中初始裂缝的扩展将起到较大的促进作用,且其发生初始破坏在开挖面到达之前,而花岗闪长岩发生破坏在掌子面经过之后;σ2的大小和方向变化仅对洞壁处(约25 mm范围内)灰色花岗岩的破坏产生影响;由于σ3的大小远未达到造成围岩破坏的程度且其旋转角较小,对两类围岩破坏基本无影响。
图12所示为隧洞开挖过程中环向围岩主应力大小及旋转角变化曲线。对于断面内自起拱线至顶点处隧洞环向范围内的围岩应力的变化情况,选取沿环向局洞壁25 mm的4个监测点加以说明,监测点示意图见图12(d)。图12(a),(b)和(c)分别描述了隧洞开挖过程中各监测点σ1,σ2和σ3及旋转角变化,同时在图(a)和图(b)的右侧分别给出了σ1-σ3和σ2-σ3的变化曲线。
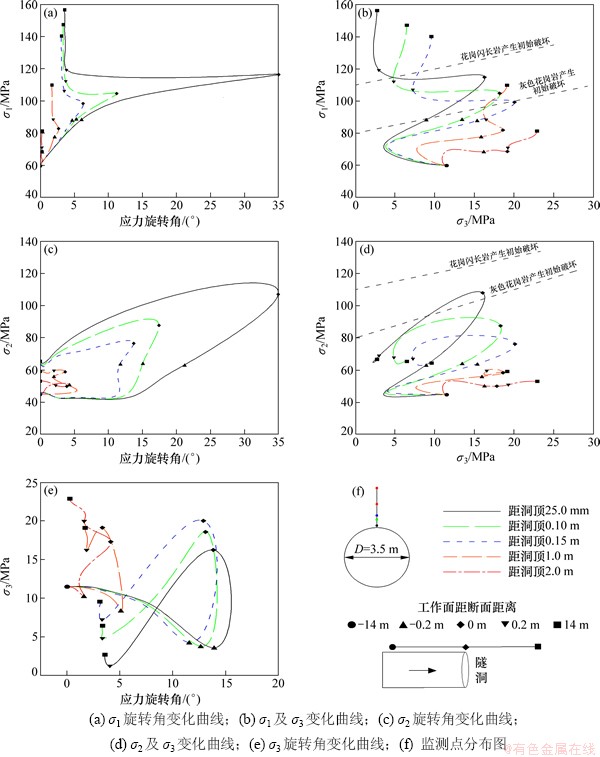
图11 隧洞开挖过程中顶部围岩主应力及旋转角变化曲线
Fig. 11 Plot of principal stress magnitudes and rotation angle of surrounding rock in tunnel during excavation
由图12可知:在隧洞开挖过程中,环向上越靠近洞顶的围岩主应力最大旋转角越小,且洞顶附近围岩σ1和σ2的同期旋转角大于σ3;越靠近边墙处的围岩主应力最大旋转角越接近90°,σ1的大小及方向变化对围岩破坏的影响程度最大。对于与水平面夹角30°以内的隧洞围岩,σ1和σ2的旋转角度随掌子面的推进而逐渐增大,其最大旋转角为90°左右。对于与水平面夹角大于30°的隧洞围岩,σ1和σ2的旋转角在达到峰值后即逐渐降低,其旋转角度在掌子面通过监测断面时达到峰值。环向洞壁附近围岩破坏主要受σ1大小和方向变化的影响,σ1的旋转主要影响此处岩性接近灰色花岗岩的围岩的破坏;σ2的大小及方向变化仅可能影响与水平面夹角接近90°的围岩破坏。σ3的数值较小,对围岩破坏基本无影响。
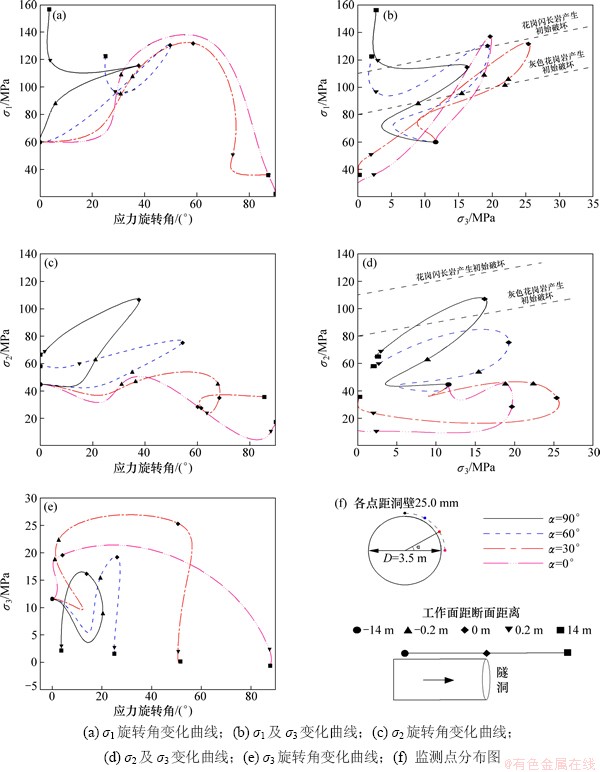
图12 隧洞开挖过程中环向围岩主应力及旋转角变化曲线
Fig. 12 Plot of principal stress magnitudes and rotation angle of surrounding rock in tunnel wall from crown to springline during excavation
总体来看,在隧洞开挖过程中,隧洞顶部和边墙附近岩体主应力都有一定角度的旋转,洞顶岩体应力主轴旋转一定角度后随即恢复初始方向,而边墙附近岩体应力主轴旋转角度接近90°。同时,由数值分析结果可知,围岩中的灰色花岗岩发生初始破坏的时间在掌子面通过之前,而花岗闪长岩初始破坏发生在掌子面经过之后。另外,由于灰色花岗岩在产生初始破坏后应力还处于旋转状态,因此,在实际工程中要特别关注洞周附近灰色花岗岩的岩体,防止由于应力大小和旋转变化导致裂隙扩展较大并产生裂缝贯穿从而引起工程岩体塌落等事故的发生。
4 结论
(1) 围岩中初始裂隙扩展方向一般与导致裂隙扩展的主应力方向平行,并随主应力方向的旋转而旋转,同时,伴随应力方向的变化,裂隙扩展深度增加,为裂隙间的贯通提供了可能性。
(2) 隧洞开挖过程中,隧洞各部位围岩主应力除数值大小随开挖过程发生变化外,应力主轴也出现不同程度旋转。洞顶附近围岩主应力则在旋转一定角度后回复初始方向,边墙附近围岩主应力的最大旋转角接近90°。
(3) 岩体破坏是围岩应力大小变化与方向旋转综合作用的结果,而一旦出现初始裂隙,应力旋转会对裂隙扩展方向和扩展深度产生重要影响。在工程实例中,灰色花岗岩产生初始破坏的时间在掌子面通过之前,而花岗闪长岩初始破坏发生在掌子面经过之后,且灰色花岗岩发生初始破坏后应力主轴旋转还在继续,在实际工程中其安全性应加以注意。
研究应力主轴旋转下不同岩体的破坏机制有助于工程人员更好地利用经验公式判断由于隧洞开挖导致围岩破坏的深度,保证支护设计的合理性,保证工程安全。
参考文献:
[1] Eberhardt E, Stead D, Stimpson B, et al. The effect of neighbouring cracks on elliptical crack initiation and propagation in uniaxial stress fields[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1998, 59(2): 103-115.
[2] 郑颖人, 沈珠江, 龚晓南. 岩土塑性力学原理[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2003: 161-169.
ZHENG Yingren, SHEN Zhujiang, GONG Xiaonan. The principles of geotechnical plastic mechanics[M]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 2003: 161-169.
[3] Eberhardt E. Numerical modelling of there-dimension stress rotation ahead of an advancing tunnel face[J]. International Journal of Rocks Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2001, 38(4): 499-518.
[4] 张社荣, 梁礼绘. 考虑三维应力旋转的隧洞衬砌支护时机研究[J]. 水利学报, 2007, 38(6): 704-709.
ZHANG Sherong, LIANG Lihui. Analysis on tunnel liner supporting time considering three-dimensional stress rotation[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2007, 38(6): 704-709.
[5] Kaiser P K, Yazici S, Maloney S. Mining induced stress change and consequences of stress path on excavation stability: A case study[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2001, 38(2): 167-180.
[6] Diederichs M S, Kaiser P K, Eberhardt E. Damage initiation and propagation in hard rock during tunneling and the influence of near-face stress rotation[J]. International Journal of Rocks Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2004, 41(5): 785-812.
[7] Derek Martin C. Seventeenth canadian geotechnical colloquium: The effect of cohesion loss and stress path on brittle rock strength[J]. International Journal of Can Geotech, 1997, 34(5): 698-725.
[8] 李录贤, 王铁军. 扩展有限元(XFEM)及其应用[J]. 力学进展, 2005, 35(1): 5-20.
LI Luxian WANG Tiejun. The extended finite element method and its applications[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2005, 35(1): 5-20.
[9] Stazi F L, Budyn E, Chessa J, et al. An extended finite element method with higher-order elements for curved cracks[J]. Computational Mechanics, 2003, 31(1/2): 38-48.
[10] 杨庆, 李强, 赵维, 等. 翼型裂纹扩展特性的试验和数值分析[J]. 水利学报, 2009, 40(8): 934-940.
YANG Qing, LI Qiang, ZHAO Wei, et al. Experimental study and numerical simulation on propagation characteristics of wing type cracks under compression[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2009, 40(8): 937-940.
[11] 黎立云, 黄凯珠, 韩智超, 等. 三维表面裂纹扩展试验及理论分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(2): 311-318.
LI Liyun, WONG R H C, HAN Zhichao, et al. Experimental and theoretical analyses of three-dimensional surface crack propagation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(2): 311-318.
[12] Martin C D, Read R S, Martino J B. Observations of brittle failure around a circular test tunnel[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 1997, 34(7): 1065-1073.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2013-08-24;修回日期:2013-11-15
基金项目:国家自然科学基金创新研究群体科学基金资助项目(51021004);国家自然科学基金资助项目(51279126)
通信作者:崔溦(1977-),男,山东诸城人,博士,副教授,从事岩土工程研究;电话:13920453695;E-mail:cuiwei@tju.edu.cn