不同碳材料辅助下混合中度嗜热微生物浸出黄铜矿的比较研究
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2019年第6期
论文作者:朱萍 刘学端 陈爱佳 刘宏伟 尹华群 邱冠周 郝晓东 梁伊丽
文章页码:1294 - 1303
关键词:黄铜矿;浸出;碳材料;混合中度嗜热微生物;微生物群落结构
Key words:chalcopyrite; leaching; carbon material; mixed moderate thermophiles; microbial community structure
摘 要:采用混合中度嗜热微生物研究4种碳材料(人造石墨、炭黑、活性炭和碳纳米管)对黄铜矿浸出的催化作用。结果表明,添加人造石墨和活性炭能使溶液pH值降低,氧化还原电位维持在合适的范围,使浸出液中总铁、三价铁浓度和矿渣表面吸附微生物的数量增加,最终提高黄铜矿中铜的浸出率;而添加炭黑和碳纳米管能抑制浸矿微生物的生长,最终导致浸出效率降低。X射线衍射分析表明,在添加人造石墨和活性炭实验组中,黄钾铁矾和硫膜是钝化层的主要成分,但钝化层的形成不会影响黄铜矿的进一步分解。此外,人造石墨和活性炭的添加使浸出体系中游离微生物和吸附微生物的群落结构发生改变。在黄铜矿浸出末期,硫氧化菌A. caldus S1(丰度为93%~98%)成为优势菌种,而铁氧化菌L. ferriphilum YSK所占比例仅为1%~2%。
Abstract: The catalysis of four carbon materials including artificial graphite (AG), carbon black (CB), activated carbon (AC) and carbon nanotube (CN) on chalcopyrite bioleaching by mixed moderate thermophiles was comparatively investigated. In AC and AG added bioleaching groups, low solution pH and suitable redox potential values, high total iron and ferric iron concentrations, and large number of adsorbed bacteria were obtained, resulting in high copper extractions. CB and CN inhibited the growth of bioleaching bacteria and led to the low bioleaching efficiency. X-ray diffraction analysis showed that jarosite and sulfur film were the main components of passivation layer with the addition of AG and AC, but did not hinder the dissolution of chalcopyrite. Microbial community structures of free and attached cells in AC and AG added groups changed dramatically compared with mixed moderate thermophiles. The sulfur-oxidizing bacteria of A. caldus S1 strain dominated the microbial community (93%-98%) at the end of bioleaching. The iron-oxidizing bacteria of L. ferriphilum YSK only accounted for low percentage (1%-2%).
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29(2019) 1294-1303
Ping ZHU1,3, Xue-duan LIU1,3, Ai-jia CHEN1,3, Hong-wei LIU1,3, Hua-qun YIN1,3, Guan-zhou QIU1,3, Xiao-dong HAO1,2, Yi-li LIANG1,3
1. School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Soil Conservation and Environmental Protection, College of Resources and Enviroment, Linyi University, Linyi 276000, China;
3. Key Laboratory of Biometallurgy of Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 11 September 2018; accepted 15 March 2019
Abstract: The catalysis of four carbon materials including artificial graphite (AG), carbon black (CB), activated carbon (AC) and carbon nanotube (CN) on chalcopyrite bioleaching by mixed moderate thermophiles was comparatively investigated. In AC and AG added bioleaching groups, low solution pH and suitable redox potential values, high total iron and ferric iron concentrations, and large number of adsorbed bacteria were obtained, resulting in high copper extractions. CB and CN inhibited the growth of bioleaching bacteria and led to the low bioleaching efficiency. X-ray diffraction analysis showed that jarosite and sulfur film were the main components of passivation layer with the addition of AG and AC, but did not hinder the dissolution of chalcopyrite. Microbial community structures of free and attached cells in AC and AG added groups changed dramatically compared with mixed moderate thermophiles. The sulfur-oxidizing bacteria of A. caldus S1 strain dominated the microbial community (93%-98%) at the end of bioleaching. The iron-oxidizing bacteria of L. ferriphilum YSK only accounted for low percentage (1%-2%).
Key words: chalcopyrite; leaching; carbon material; mixed moderate thermophiles; microbial community structure
1 Introduction
Chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) is the most abundant copper sulfide resource; however, CuFeS2 is refractory to be chemically leached due to its high lattice energy and stable structural configuration [1]. As an economical and eco-friendly method, bioleaching technology has attracted much more attention and has been used in the copper extraction of CuFeS2 [2]. In recent years, many studies have indicated that mixed moderate thermophiles including A. caldus, L. ferriphilum, S. thermosulfidooxidans and F. thermophilum can greatly accelerate reaction kinetics and reduce the formation of passivation layer accumulated on the surface of ore particles, thus enhance the Cu recovery of chalco-pyrite [3,4]. Therefore, the moderate thermophiles have the superiority for the application in chalcopyrite bioleaching compared to mesophilic [5] and extremely thermophilic microbial consortia [6].
Bioleaching of chalcopyrite on an industrial scale is still limited. Several strategies have been proposed to increase the bioleaching efficiency, such as using the photocatalysis through increasing the reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+ which was used as the substrate for microbes [7], controlling the solution redox potentials to improve bioleaching efficiency [8] or inventing novel technique to remove the passivation layer by BACFOX bio-reactor [9]. However, these methods are hardly to be utilized in practice of chalcopyrite bioleaching, especially in heap bioleaching. The addition of catalysts (e.g., Ag+, polyethylene glycol and chloride) is beneficial to increasing the dissolution rates and final copper extraction of chalcopyrite. HU et al [10] found that a complexly porous Ag2S-Ag layer can be formed on the surface of chalcopyrite particles with the Ag+ addition rather than the formation of tenacious sulfur membrane, which can improve electrical conductivity and promote the electronic transfer through ferric ion. Polyethylene glycol added into chalcopyrite leaching system can increase the biosorption of bioleaching bacteria and intensify the sulfur layer oxidation wrapped on bioleached residual surfaces to improve the dissolving rate [11]. Chloride can reduce the activation energy to enhance dissolution kinetics of chalcopyrite. However, the microbial activity and growth can be restricted by Cl- even at low concentration (0.1%) [12]. Therefore, the leaching agents mentioned above are rarely available on account of high price or toxic effect to bioleaching microbes.
Carbon materials are produced and gained relatively effortless. MA et al [13] indicated that the artificial graphite prepared from nickel nanoparticles doped pitch and natural graphite flakes by hot-pressing sintering method exhibited high specific capacity and excellent rate capability. This synthetic graphite is a promising anode for lithium-ion battery. The fibrous shape of carbon nanotube owned the properties of high aspect ratio, large accessible external surface area and well developed mesopore, contributing the superior removal capacity of contaminants in drinking water [14]. Carbon black served as carriers of platinum nanocrystals and LiFePO4 offered excellent electrochemical properties of the new synthesized materials [15,16]. Activated carbon was applied in the biometallurgy of chalcopyrite. The aggregates of chalcopyrite and activated carbon formed galvanic interaction and changed electrical conductivity of the reaction product layer, further increased chalcopyrite dissolution by ferric sulfate [17]. However, previous studies concerning the carbon-aided bioleaching technology mostly focused on the effects of activated carbon load on chalcopyrite dissolution. It is necessary to search the efficient, cheap and easily obtained carbon material to improve copper extraction and lower the production cost of chalcopyrite bioleaching on industrial scale.
Therefore, four carbon materials of artificial graphite, carbon black, activated carbon and carbon nanotube were used for the chalcopyrite bioleaching by mixed moderate thermophiles. The objectives of this study are to determine the effects of four carbon materials on copper bioleaching efficiencies, bioleaching behaviors and the microbial community structures. We expect that this study will be valuable for better understanding the carbon material-aided bioleaching technology.
2 Experimental
2.1 Chalcopyrite and carbon material samples
The original mineral sample used in this study was achieved from Chambishi Copper Mine of Zambia. XRD analysis showed that chalcopyrite (87.4%) and quartz (4.5%) were the main compositions of this sample. The chemical element analysis showed that this chalcopyrite sample contained 30.7% Cu, 29.6% Fe, 25.7% S, 1.1% Ca and 12.9% other elements. Chalcopyrite was milled to power with sizes <75 μm for subsequent bioleaching experiments.
Four kinds of carbon materials, including artificial graphite (AG), carbon black (CB), activated carbon (AC) and carbon nanotube (CN) used in this study were purchased from Shengshi Carbon Material Co., Ltd., in Hubei Province of China. The particle sizes of all samples were <75 μm. The properties of carbon materials are presented in Table 1.
Table 1 Properties of carbon materials used in present study

2.2 Mixed moderate thermophiles
Four moderately thermophilic strains of Leptospirillum ferriphilum YSK, Acidithiobacillus caldus S1, Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST and Ferroplasma thermophilum L1 were provided by the Key Laboratory of Biometallurgy of Ministry of Education, Central South University in Changsha of China. They were grown in basal salt medium consisting of (NH4)2SO4 (3 g/L), K2HPO4 (0.5 g/L), KCl (0.1 g/L), Ca(NO3)2 (0.01 g/L) and MgSO4·7H2O (0.5 g/L). The culture conditions of each strain are presented in Table 2.
Table 2 Parameters of culture media of four strains

Each strain was harvested by centrifuging at 10000 r/min for 15 min when the bacterial density reached (1-2)×108 cell/mL. Finally, equal bacterial density of each of four strains was pooled, resulting in the final mixed moderate thermophiles for subsequent experiments.
2.3 Bioleaching experiments
Bioleaching experiments with the assistance of four carbon materials were performed in 500 mL of shake flasks containing 200 mL sterilized basal salt medium over a period of 21 d. Each of four carbon materials was mixed with chalcopyrite concentrate (10%) in a porcelain mortar, and pestled for 10 min before being added into each bioleaching group [18]. The final pulp densities of chalcopyrite and each carbon material were 2% and 0.2%, respectively. The initial solution pH was adjusted to 2.0 with 10 mol/L sulfuric acid. The mixed moderate thermophiles were added into bioleaching systems, and the initial bacterial density was 4.4×107 cell/mL. Shake flasks were incubated at 175 r/min and 45 °C in a temperature-controlled rotary shaker. Biotic control group (CuFeS2+B, B represented the mixed moderate thermophiles) was conducted in parallel without the addition of carbon materials. The abiotic control groups (CuFeS2, CuFeS2+AG, CuFeS2+CB, CuFeS2+AC, and CuFeS2+CN) were also carried out without adding the bacteria and/or carbon materials. The solution losses due to samples for the physicochemical analysis of solution were compensated with sterilized fresh basal salt medium. The experiments were performed in triplicate.
2.4 Physicochemical analysis
The chalcopyrite samples were digested by an acid mixture of HF, HNO3 and HClO4 on an electric heating plate (XJS20-42, Labotery Instruments Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China), and the elemental contents were measured with an inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES, Optima 5300 DV, Baird Instruments Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The total iron and copper concentrations in the solution during chalcopyrite bioleaching process were also determined by ICP-OES. The ferrous iron concentration was detected by the phenanthroline spectrophotometry method, and ferric iron concentration was the difference between the concentrations of total iron and ferrous iron. The solution pH values were measured with a digital pH meter (PHS-3C, Leici Analytical Instruments Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), and redox potentials were determined by a platinum electrode with an Ag/AgCl electrode as reference (BPH-221, Bell Analytical Instruments Co., Ltd., Dalian, China). The bacterial density in solution was counted directly using a hemocytometer with an optical microscope (BX41, Olympus Instruments, Tokyo, Japan). Residue samples were collected and dried at regular intervals as the bioleaching process continued for the X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis (DX-2700, Dandong Instrument Equipment Co., Ltd., Dandong, China).
2.5 Microbial community structure analysis
2.5.1 Total genomic DNA extraction
The free and attached cells from the CuFeS2+B, CuFeS2+AG+B and CuFeS2+AC+B groups on day 21 were withdrawn. Samples (100 mL, containing residues and solution) in three groups were centrifuged at 2000 r/min for 3 min for separating the supernatant and precipitate. The supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm millipore filter membrane to obtain the free cells. The genomic DNA of free cells and initial mixed moderate thermophiles was extracted using the TIANamp Bacteria DNA kit (Tiangen Biotech Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The genomic DNA of attached cells from bioleached residues was extracted using the E.Z.N.A. Soil DNA kit (Omega Bio-Tek Inc., Newark, NJ, USA) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instruction. The crude genomic DNA was purified by 1.0% agarose gel and stored at -20 °C until it was used. The experiments were performed in triplicate.
2.5.2 Real-time quantification polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
RT-qPCR was used to analyze the microbial community of free and attached cells. The primers of four species were designed using Primer Premier 5.0 on-line design system and synthesized by BioSune Biotech Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. Details of primer sequence were summarized in Ref. [19]. The quality of amplified specific DNA fragments was checked through 1.2% agarose gel electrophoresis and purified using E.Z.N.A. Gel extraction kit (Omega Bio-Tek Inc., Newark, NJ, USA). DNA sequencing was conducted by BioSune, and BLAST analysis was conducted in GenBank (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/) to ensure the primers specificity. Before RT-qPCR, standard curves of four strains were constructed by diluting the conventional PCR products (102-109 copy/mL). The RT-qPCR was performed with iCycler iQ Real-time PCR detection system (Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Hercules, USA). The reaction procedures were as follows: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, and then 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, 55 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s. After each run ended, melting curves for the amplicons were measured by increasing the temperature from 59 to 99 °C at intervals of 0.5 °C. The negative controls were also designed and all experiments were run in triplicate.
RT-qPCR data were analyzed using iCycler MyiQ software v1.0 (Bio-Rad). Copy numbers of each conserved gene were quantified based on the standard curves, which resulted from known concentrations of PCR products. The correlation coefficients for the standard curves for each gene were greater than 0.995. The PCR amplification efficiencies were between 88.0% and 110%. Cell number of each strain was calculated according to the total cell numbers and percentage of each type of strains.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effects of different carbon materials on copper extraction
The copper extractions with leaching time from chalcopyrite in the presence of four carbon materials are shown in Fig. 1. The copper extractions were significantly enhanced by AC and AG compared with CB and CN with the addition of mixed moderate thermophiles. The bioleaching efficiencies increased slightly in the first 9 days, and subsequently began to accelerate from day 9 to day 15, then kept stable. The final copper extractions reached up to 69.9% (CuFeS2+ B+AC) (B is the mixed moderate thermophiles), 53.8% (CuFeS2+B+AG) and 43.9% (CuFeS2+B) on day 21, respectively. The copper yields increased by 26.0% and 9.9% compared to CuFeS2 + B group. However, in CB and CN added bioleaching groups, the leaching efficiencies of copper were only 12.2% and 18.4%, respectively. Meanwhile, the copper extractions in all abiotic groups were lower than 12%.

Fig. 1 Variation of copper extractions during chalcopyrite bioleaching
The highest copper extraction was obtained in the AC added bioleaching group, indicating that AC could greatly enhance chalcopyrite dissolution, which was in accordance with previous studies [20-22], which indicated that the improved dissolution rates were mainly attributed to galvanic interaction between activated carbon and chalcopyrite. As shown in Table 1, specific surface area (SSA) of AC ((800.4±5.9) m2/g) was higher than those of the other three carbon materials, but electrical conductivity value was the lowest. HAO et al [23] showed that SSA was the key factor improving the bioleaching efficiency of the copper sulfide ores by means of better galvanic interaction, biofilm formation, direct contact and lower redox potentials. The copper extraction in AG added bioleaching group was higher than that in CuFeS2+B group. The great electrical conductivity ((0.52±0.11) S/m) of AG endowed a more electropositive (anodic) character to the bioelectrode (moderate thermophiles), finally enhanced the biooxidation of chalcopyrite concentrate by acidophilic bacteria [24]. Meanwhile, previous study also showed that graphite could increase copper sulfide ores bioleaching via rising the microbial population and galvanic interaction [25]. Notably, the copper yields in CuFeS2+B, CuFeS2+B+AG and CuFeS2+B+AC groups increased by 40.7%, 42.6% and 52.8%, respectively compared to the corresponding abiotic control groups, demonstrating that the presence of moderate thermophiles played an important role in chalcopyrite dissolution. However, no obvious difference of copper extractions was observed in bioleaching and chemical leaching groups of CB and CN, which might indicate that the bacterial growth was inhibited by CB and CN.
3.2 Effects of different carbon materials on physico- chemical parameters in solution
The changes in pH, redox potential, total iron and ferric iron concentrations in solution with leaching time in the presence of four carbon materials are shown in Fig. 2. In the bioleaching run of CB and CN added groups, the solution pH values were higher than those of chemical leaching groups (Fig. 2(a)). However, the solution pH decreased rapidly from the 6th day and finally declined to 1.48 (CuFeS2+B), 1.48 (CuFeS2+AG+ B) and 1.61 (CuFeS2+AC+B) on day 21, respectively. In the corresponding chemical leaching groups, the solution pH increased slowly in the first 4 days and remained stable in the later leaching stage, and in CuFeS2 group, the lowest pH value was obtained. The pH values were the integrated results of acid consumption and acid generation in leaching process. Carbon materials could promote the dissolution of chalcopyrite both in chemical and bioleaching experiments, and more alkaline substances (e.g., alkaline oxide and acid oxide) were released and neutralized by protons, resulting in the high solution pH. In CuFeS2+B, CuFeS2+AG+B and CuFeS2+ AC+B groups having inoculum, sulfur oxidizing organisms of A. caldus S1 and S. thermosulfidooxidans ST were able to oxidize S0 and reduced inorganic sulfur compounds (RISCs) dissolved from chalcopyrite, resulting in the decrease of pH even in the presence of carbon materials, which was responsible for the increase of copper extractions.

Fig. 2 Variation of pH (a), redox potential (b), concentrations of total iron (c) and ferric iron (d) in solution during chalcopyrite bioleaching
As shown in Fig. 2(b), different carbon materials induced different solution redox potential values. In the bioleaching operation of CuFeS2, AG and AC added groups, the redox potentials increased sharply from the 9th day and reached up to 689.7, 608.3 and 499.0 mV on day 21, respectively. However, the redox potentials were lower in other groups maintaining at 330-400 mV throughout the leaching process. The iron oxidizing microbes (e.g., L. ferriphilum DX) in mixed moderate thermophiles could oxidize ferrous iron into ferric iron, resulting in high solution redox potential values of CuFeS2+B, CuFeS2+AG+B and CuFeS2+AC+B groups, and facilitated the Cu bioleaching. Notably, the CuFeS2+ B and CuFeS2+AG+B groups stayed at the high redox potential values of above 600 mV compared to CuFeS2+ AC+B. However, the extremely high copper extraction was obtained in CuFeS2+AC+B. It was indicated that carbon material-aided bioleaching performance could accelerate the dissolution of chalcopyrite at the appropriate redox potential values. The redox potential was a key factor affecting the chalcopyrite dissolution. Former studies proved that minerals sulfide dissolution could be improved by controlling redox potential at relatively low values. THIRD et al [26] indicated that low redox potentials of 380-420 mV (vs Ag/AgCl) controlled by oxygen limitation could enhance the final copper recovery of chalcopyrite. ZHAO et al [8] also showed that decreasing solution redox potential and maintaining it in an appropriate range (380-480 mV (vs Ag/AgCl)) using the bornite could increase the chalcopyrite dissolution. In this study, AC caused relatively low solution redox potential (330-500 mV) compared with CuFeS2+B and CuFeS2+AG+B bioleaching groups (600-650 mV), which was beneficial to the final copper extraction.
The variations of total iron and ferric iron concentrations presented the similar trends with the redox potentials in CuFeS2+B, CuFeS2+AG+B and CuFeS2+AC+B groups (Figs. 2(c) and (d)). The total iron and ferric iron concentrations increased rapidly from the 9th day and reached maxima on days 12 or 15. Ferric ion acted as an efficient oxidant and was found to be beneficial to dissolving chalcopyrite in both chemical leaching and bioleaching [27]. Compared to CuFeS2+B, the high total iron concentrations dissolved from chalcopyrite and high ferric iron concentrations generated from ferrous iron oxidation were obtained in AG and AC added bioleaching groups, greatly improved the bioleaching efficiency. At later stage of bioleaching, ferric iron concentration decreased to 930, 1130 and 1430 mg/L in the three groups, respectively. It was probably due to the fact that the passivation layer of jarosite and sulfur was mainly formed, and slightly affected the chalcopyrite dissolution, resulting in the stable copper extractions (Fig. 1).
3.3 Effects of different carbon materials on bacterial densities of free and attached cells
The amount of bacterial density in solution via direct count with an optical microscope is shown in Fig. 3(a). The variation of the number of microorganisms was in accordance with the trend of copper extraction (Fig. 1). The bacterial density in CuFeS2, CuFeS2+AG+B and CuFeS2+AC+B groups increased hardly in the first 9 days, then rapidly increased to peaks of 10.4×108 cell/mL (day 15), 9.1×108 cell/mL (day 18) and 7.32×108 cell/mL (day 18), respectively. After that, the bacterial concentrations of the three experiments began to decline slightly (CuFeS2) or kept relatively stable (CuFeS2+AG+B and CuFeS2+AC+B). However, there was no obvious growth of microbes in CB and CN added groups, and the bacterial densities were near zero since the bioleaching process began. The results indicated that the addition of CB and CN restrained the growth of mixed moderate thermophiles. ZHANG et al [28] showed that the metals (e.g., copper and silver) loaded on carbon black had the antibacterial activity to the microorganisms via the adsorption of microbes on carbon black surface. UPADHYAYULA et al [14] also indicated that the inherent cytotoxic nature of pristine CN played an indirect role in improving the microbial sorption efficiency but prohibited the growth of pathogens including bacteria [29] and bacteria endospores [30] on CN surface. The inhibitory effect on microbes scarcely caused the profitable changes of leaching parameters (e.g., low pH, high redox potential and ferric iron concentration) (Fig. 2), thus hardly increased copper extractions in CuFeS2+CB+B and CuFeS2+CN+B groups.

Fig. 3 Variation of cell density in solution via direct count during chalcopyrite bioleaching (a), and densities of free and attached cells via RT-qPCR in CuFeS2+B, CuFeS2+AG+B and CuFeS2+AC+B groups at end of chalcopyrite bioleaching (b)
Figure 3(b) shows the densities of free cell in solu- tion and attached cell on bioleached residual surface via RT-qPCR in CuFeS2+B, CuFeS2+AG+B and CuFeS2+ AC+B groups at the end of bioleaching. The results showed the variations of free cell density via RT-qPCR were similar with those determined by direct count (Fig. 3(a)). However, there was a significant difference between the densities of free cell and attached cell in three experiments on day 21. In CuFeS2 group, the density of attached cell was lower than that of free cell. While the attached cell densities, especially in CuFeS2+AC+B group, were higher than free cell densities, which might benefited from the large SSA and strong adsorption capacity of activated carbon. The bacterial adsorption quantity was determined by the interfacial property of the adsorbent [31]. The characteristics of high surface area with high surface reactivity and microporous structure made the activated carbon to be the versatile adsorbents for both bioleaching bacteria and chalcopyrite particles [32]. Microbial colonization and subsequent biofilm formation on the surface of mineral particles were crucial to dissolve the chalcopyrite, and the numbers of attached cells had significantly positive correlation with the corresponding copper extractions [33]. The biofilm including the attached bacteria and metabolites on the interface developed many independent and protective microenvironments against the adverse bioleaching conditions such as possibly infertile bulk-solution composition and dynamic force (e.g., solution flows and abrasion) [34]. Moreover, the bioleaching bacteria existed in biofilm could enhance electron transfer through ferric iron and intensify galvanic interaction between activated carbon and chalcopyrite, further accelerated copper extraction efficiency by direct contact [35].
3.4 XRD analysis of solid residues
The components of raw mineral and bioleached residues collected at the end of chalcopyrite bioleaching were analyzed by XRD. As seen in Table 3, the contents of chalcopyrite in raw mineral accounted for (87.4± 1.5)%, while they declined to (55.7±1.2)%, (50.6±0.8)% and (44.1±0.7)% in CuFeS2+B, CuFeS2+AG+B and CuFeS2+ AC+B groups on day 21, respectively. Meanwhile, the components of jarosite and sulfur were detected. The contents of jarosite were (16.4±0.4)% (CuFeS2+B), (21.5±0.3)% (CuFeS2+AG+B) and (35.6±0.9)% (CuFeS2+AC+B), which also explained the decrease trend of ferric iron concentration shown in Fig. 2(d). However, the variations of sulfur content in bioleached residues presented the opposite trend, and the low percentage was observed in CuFeS2+AC+B group. As the bioleaching process continued, Fe3+ and S0 were released from chalcopyrite dissolution (Eq. (1)). S0 could be oxidized into H2SO4 by sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. H+ and Fe3+ as leaching agents could improve the CuFeS2 bioleaching efficiency (Eqs. (2) and (3)). The generated Fe2+ could be oxidized into Fe3+ by iron-oxidizing bacteria. In the later bioleaching stage, Fe3+ and S0 contents increased gradually with the decrease of the CuFeS2 content, which could accelerate the passivation layer formation of jarosite (Eq. (4)) and S0 film.
CuFeS2→Cu2++Fe3++2S0+5e (1)
CuFeS2+4H++O2→Cu2++2S0+Fe2++2H2O (2)
CuFeS2+4Fe3+→Cu2++5Fe2++2S0 (3)
M++3Fe3++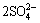 +6H2O→ MFe3(SO4)2(OH)6+6H+
+6H2O→ MFe3(SO4)2(OH)6+6H+
(M+ is monovalent cation of K+, Na+ and NH4+) (4)
In the process of chalcopyrite bioleaching, jarosite and sulfur membranes were the main components of passivation layer, which greatly slowed down the bioleaching performance [36]. The yield and structure of the passivation layer were significantly influenced by microbes, ferric iron, pH and redox potential [37,38]. In CuFeS2+AC+B group, relatively low solution pH and redox potential values were observed, while the highest jarosite content was still detected at the final stage of bioleaching, which might be attributed to the highest ferric iron concentration in solution. But even so, the maximum bioleaching efficiency of copper was obtained with the addition of AC, suggesting that the AC greatly promoted the dissolution of chalcopyrite. In addition, the attached cells of sulfur oxidizing bacteria could effectively eliminate the sulfur membrane and promote chalcopyrite dissolution with the assistance of AG and AC. Therefore, the S0 contents in AG and AC added bioleaching groups were lower than that in biotic control [39].
3.5 Effects of different carbon materials on microbial community structure
The microbial community structures of free and attached cells in CuFeS2+B, CuFeS2+AG+B and CuFeS2+AC+B groups on day 21 were characterized. As shown in Fig. 4, A. caldus S1, S. thermosulfidooxidans ST, L. ferriphilum YSK and F. thermophilum L1 accounted for 24.72%, 25.81%, 24.14% and 25.33% in mixed moderate thermophiles, respectively. Compared with the relative percentage of each species in initial inoculum, the microbial community compositions of free and attached cells changed obviously during the chalcopyrite bioleaching process. However, the variation trends of free and attached cells in the same group were similar.
In CuFeS2+B group, the L. ferriphilum YSK of free cell and attached cell decreased to 5.70% and 6.61%, respectively. While the percentages of A. caldus S1 dramatically increased and became the dominant species, accounting for 94.07% (free cell) and 93.30% (attached cell) of the cultures. Meanwhile, A. caldus S1 was also the predominant species and accounted for 93.38%- 98.72% in the AG and AC added bioleaching systems. Unexpectedly, the numbers of S. thermosulfidooxidans ST and F. thermophilum L1 declined sharply at the late stage of the three bioleaching systems. The proportions of the two species accounted for just below 1%, and F. thermophilum L1 was not even detected in AG and AC added groups.
Table 3 XRD analysis of solid residues in CuFeS2+B, CuFeS2+AG+B and CuFeS2+AC+B groups at end of chalcopyrite bioleaching
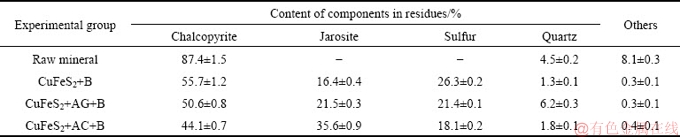
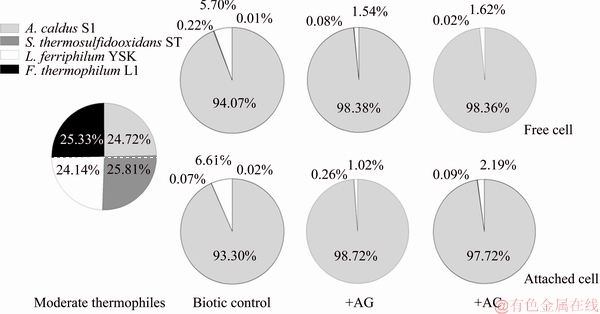
Fig. 4 Microbial community structures of free and attached cells in CuFeS2+B, CuFeS2+AG+B and CuFeS2+AC+B groups at end of chalcopyrite bioleaching
Elemental sulfur, RISCs and ferrous iron generated from chalcopyrite dissolution provided energy sources and nutrients for the growth of microorganisms. Ferrous iron was relatively effortless to be utilized by iron-oxidizing bacteria at the early and middle bioleaching stages. As shown in Fig. 2(d), ferric iron concentration from ferrous iron oxidation increased rapidly from day 9 to day 15, indicating the high activity of ferrous iron oxidizers. Ferrous iron oxidizers could oxidize chalcopyrite directly by means of the ferric iron, which were most efficient for the bioleaching performance (Fig. 1). While ferric iron concentration decreased from day 15, the energy depletion might restrict the growth and induce the low abundance of L. ferriphilum YSK in the end. RISCs were the main intermediates of chalcopyrite dissolution [40] and RISCs oxidation yielded considerably more energy than ferrous iron oxidation [41]. In the late bioleaching stage, the sulfur membrane accumulated on the chalcopyrite surface (Table 3), but could be served as energy source and benefited the growth of A. caldus S1. As shown in Fig. 2(a), the decrease trend of solution pH sustained till the end of bioleaching, suggesting the continuous sulfur oxidation process by sulfur oxidizers. All these factors accounted for the relatively high proportion of A. caldus S1 in final stage. Although two cultures of S. thermosulfidooxidans ST and F. thermophilum L1 were frequently detected in the late stage of sulfide minerals bioleaching [42], the high solution pH above 3.0 before the 6th day might inhibit the growth of these two species, resulting in the extremely low proportions.
4 Conclusions
(1) Four kinds of carbon materials including AG, CB, AC and CN were used for the chalcopyrite bioleaching by mixed moderate thermophiles. The addition of AC and AG enhanced chalcopyrite dissolution and the final copper extractions were 69.9% and 53.8%, which were improved by 26.0% and 9.9% compared with biotic control group (43.9%). CB and CN restrained the growth of mixed moderate thermophiles and led to the low bioleaching efficiencies less than 20%.
(2) In AC and AG groups, especially for AC added bioleaching group, low solution pH and redox potential values, high total iron and ferric iron concentrations, and large number of adsorbed bacteria were obtained, resulting in high copper extraction.
(3) XRD analysis showed that jarosite and S0 were detected at the late bioleaching stage. The addition of AC and AG accelerated the accumulation of jarosite, but contrary to S0 film. However, the formation of passivation layer could not significantly hinder the chalcopyrite dissolution.
(4) AC and AG dramatically changed the microbial community structures of free and attached cells. The sulfur-oxidizing bacteria of A. caldus S1 strain dominated the microbial community at the end of bioleaching.
References
[1] DUTRIZAC J E. The dissolution of chalcopyrite in ferric sulfate and ferric chloride media [J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1981, 12: 371-378.
[2] BRIERLEY C L. Biohydrometallurgical prospects [J]. Hydro- metallurgy, 2010, 104: 324-328.
[3] MARHUAL N P, PRADHAN N, KAR R N, SUKLA L B, MISHRA B K. Differential bioleaching of copper by mesophilic and moderately thermophilic acidophilic consortium enriched from same copper mine water sample [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99: 8331-8336.
[4] WU A X, HU K J, WANG H J, ZHANG A Q, YANG Y. Effect of ultraviolet mutagenesis on heterotrophic strain mutation and bioleaching of low grade copper ore [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24: 2245-2252.
[5] YANG Y, LIU W, CHEN M. XANES and XRD study of the effect of ferrous and ferric ions on chalcopyrite bioleaching at 30 °C and 48 °C [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2015, 70: 99-108.
[6] ZHOU H B, ZENG W M, YANG Z F, XIE Y J, QIU G Z. Bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate by a moderately thermophilic culture in a stirred tank reactor [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2009, 99: 515-520.
[7] ZHOU S, GAN M, ZHU J Y, LI Q, JIE S Q, YANG B J, LIU X D. Catalytic effect of light illumination on bioleaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 182: 345-352.
[8] ZHAO H B, WANG J, GAN X W, ZHENG X H, TAO L, HU M H, LI Y N, QIN W Q, QIU G Z. Effects of pyrite and bornite on bioleaching of two different types of chalcopyrite in the presence of Leptospirillum ferriphilum [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 194: 28-35.
[9] PANDA S, PARHI P K, NAYAK B D, PRADHAN N, MOHAPATRA U B, SUKLA L B. Two step meso-acidophilic bioleaching of chalcopyrite containing ball mill spillage and removal of the surface passivation layer [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 130: 332-338.
[10] HU Y H, QIU G Z, WANG J, WANG D Z. The effect of silver- bearing catalysts on bioleaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2002, 64: 81-88.
[11] ZHANG R Y, WEI D Z, SHEN Y B, LIU W G, LU T, HAN C. Catalytic effect of polyethylene glycol on sulfur oxidation in chalcopyrite bioleaching by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2016, 95: 74-78.
[12] DREISINGER D, ABED N. A fundamental study of the reductive leaching of chalcopyrite using metallic iron. Part I: Kinetic analysis [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2002, 66: 37-57.
[13] MA C L, ZHAO Y, LI J, SONG Y, SHI J L, GUO Q G, LIU L. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of artificial graphite as an anode for high-performance lithium-ion batteries [J]. Carbon, 2013, 64: 553-556.
[14] UPADHYAYULA V K K, DENG S, MITCHELL M C, SMITH G B. Application of carbon nanotube technology for removal of contaminants in drinking water: A review [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2009, 408: 1-13.
[15] ZHOU Z Y, HUANG Z Z, CHEN D J, WANG Q, TIAN N, SUN S G. High-index faceted platinum nanocrystals supported on carbon black as highly efficient catalysts for ethanol electrooxidation [J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2010, 49: 411-414.
[16] SHIN H C, CHO W I, JANG H. Electrochemical properties of carbon-coated LiFePO4 cathode using graphite, carbon black, and acetylene black [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2007, 52: 1472-1476.
[17] WAN R Y, MILLER J D, FOLEY J, PONS S. Electrochemical features of the ferric sulfate leaching of CuFeS2/C aggregates [C]// RICHARDSON P E, SRINIVASAN S, WOODS R. Electrochemistry in Mineral and Metal Processing. Pennington: Electrochemical Society, 1984: 391-416.
[18] MA Y L, LIU H C, XIA J L, NIE Z Y, ZHU H R, ZHAO Y D, MA C Y, ZHENG L, HONG C H, WEN W. Relatedness between catalytic effect of activated carbon and passivation phenomenon during chalcopyrite bioleaching by mixed thermophilic Archaea culture at 65 °C [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 1374-1384.
[19] MA L Y, WANG X J, FENG X, LIANG Y L, XIAO Y H, HAO X D, YIN H Q, LIU H W, LIU X D. Co-culture microorganisms with different initial proportions reveal the mechanism of chalcopyrite bioleaching coupling with microbial community succession [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 223: 121-130.
[20] NAKAZAWA H, FUJISAWA H, SATO H. Effect of activated carbon on the bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 1998, 55: 87-94.
[21] ZHANG W M, GU S F. Catalytic effect of activated carbon on bioleaching of low-grade primary copper sulfide ores [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17: 1123-1127.
[22] LIANG C L, XIA J L, ZHAO X J, YANG Y, GONG S Q, NIE Z Y, MA C Y, ZHENG L, ZHAO Y D, QIU G Z. Effect of activated carbon on chalcopyrite bioleaching with extreme thermophile Acidianus manzaensis [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 105: 179-185.
[23] HAO X D, LIU X D, ZHU P, CHEN A J, LIU H W, YIN H Q, QIU G Z, LIANG Y L. Carbon material with high specific surface area improves complex copper ores’ bioleaching efficiency by mixed moderate thermophiles [J]. Minerals, 2018, 8: 301-315.
[24] FERNANDEZREYES J S, GARCIAMEZA J V. Bioelectrochemical system for the biooxidation of a chalcopyrite concentrate by acidophilic bacteria coupled to energy current generation and cathodic copper recovery [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2018, 40: 63-73.
[25] MEHRABANI J V, SHAFAEI S Z, NOAPARAST M, MOUSAVI S M. Bioleaching of different pyrites and sphalerite in the presence of graphite [J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2017, 34: 97-108.
[26] THIRD K A, CORD-RUWISCH R, WATLING H R. Control of the redox potential by oxygen limitation improves bacterial leaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2002, 78: 433-441.
[27] WATLING H R. Chalcopyrite hydrometallurgy at atmospheric pressure: 1. Review of acidic sulfate, sulfate–chloride and sulfate–nitrate process options [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 140: 163-180.
[28] ZHANG B, LIN Y, TANG X N, XU Y H, XIE G. Mechanism of antibacterial activity of silver and praseodymium-loaded white carbon black [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2010, 28: 442-445.
[29] NEPAL D, BALASUBRAMANIAN S, SIMONIAN A L, DAVIS V A. Strong antimicrobial coatings: Single-walled carbon nanotubes armored with biopolymers [J]. Nano Letters, 2008, 8: 1896-1901.
[30] KRISHNA V, PUMPRUEG S, LEE S H, ZHAO J, SIGMUND W, KOOPMAN B, MOUDGIL B M. Photocatalytic disinfection with titanium dioxide coated multi-wall carbon nanotubes [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2005, 83: 393-397.
[31] XIA L X, LIU X X, ZENG J, YIN C, GAO J, LIU J S, QIU G Z. Mechanism of enhanced bioleaching efficiency of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans after adaptation with chalcopyrite [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 92: 95-101.
[32] DEVASIA P, NATARAJAN K A. Adhesion of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans to mineral surfaces [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2010, 94: 135-139.
[33] DONG Y B, LIN H, XU X F, ZHANG Y, GAO Y J, ZHOU S S. Comparative study on the bioleaching, biosorption and passivation of copper sulfide minerals [J]. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 2013, 84: 29-34.
[34] FLORIAN B, NOEL N, THYSSEN C, FELSCHAU I, SAND W. Some quantitative data on bacterial attachment to pyrite [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2011, 24: 1132-1138.
[35] TANG X H, GUO K, LI H R, DU Z W, TIAN J L. Electrochemical treatment of graphite to enhance electron transfer from bacteria to electrodes [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102: 3558-3560.
[36] FENG S, YANG H, XIN Y, GAO K, YANG J, LIU T, ZHANG L, WANG W. A novel and highly efficient system for chalcopyrite bioleaching by mixed strains of Acidithiobacillus [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 129: 456-462.
[37] PLUMB J J, MCSWEENEY N J, FRANZMANN P D. Growth and activity of pure and mixed bioleaching strains on low grade chalcopyrite ore [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2008, 21: 93-99.
[38] LEAHY M J, SCHWARZ M P. Modelling jarosite precipitation in isothermal chalcopyrite bioleaching columns [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 98: 181-191.
[39] YU R L, SHI L J, GU G H, ZHOU D, YOU L, CHEN M, QIU G Z, ZENG W M. The shift of microbial community under the adjustment of initial and processing pH during bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate by moderate thermophiles [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 162: 300-307.
[40] SAND W, GEHRKE T, JOZSA P G, SCHIPPERS A. (Bio)chemistry of bacterial leaching—Direct vs. indirect bioleaching [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 59: 159-175.
[41] OKIBE N, GERICKE M, HALLBERG K B, JOHNSON D B. Enumeration and characterization of acidophilic microorganisms isolated from a pilot plant stirred-tank bioleaching operation [J]. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 2003, 69: 1936-1943.
[42] HAO X D, LIANG Y L, YIN H Q, LIU H W, ZENG W M, LIU X D. Thin-layer heap bioleaching of copper flotation tailings containing high levels of fine grains and microbial community succession analysis [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 2017, 24: 360-368.
朱 萍1,3, 刘学端1,3, 陈爱佳1,3, 刘宏伟1,3, 尹华群1,3, 邱冠周1,3,郝晓东1,2, 梁伊丽1,3
1. 中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 临沂大学 资源环境学院 山东省水土保持与环境保育重点实验室,临沂 276000;
3. 中南大学 生物冶金教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083
摘 要:采用混合中度嗜热微生物研究4种碳材料(人造石墨、炭黑、活性炭和碳纳米管)对黄铜矿浸出的催化作用。结果表明,添加人造石墨和活性炭能使溶液pH值降低,氧化还原电位维持在合适的范围,使浸出液中总铁、三价铁浓度和矿渣表面吸附微生物的数量增加,最终提高黄铜矿中铜的浸出率;而添加炭黑和碳纳米管能抑制浸矿微生物的生长,最终导致浸出效率降低。X射线衍射分析表明,在添加人造石墨和活性炭实验组中,黄钾铁矾和硫膜是钝化层的主要成分,但钝化层的形成不会影响黄铜矿的进一步分解。此外,人造石墨和活性炭的添加使浸出体系中游离微生物和吸附微生物的群落结构发生改变。在黄铜矿浸出末期,硫氧化菌A. caldus S1(丰度为93%~98%)成为优势菌种,而铁氧化菌L. ferriphilum YSK所占比例仅为1%~2%。
关键词:黄铜矿;浸出;碳材料;混合中度嗜热微生物;微生物群落结构
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (31570113) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2016YFB0101310) supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China
Corresponding author: Xiao-dong HAO, Tel: +86-731-88830546, E-mail: haoxiaodongxyz@163.com;
Yi-li LIANG, Tel: +86-731-88836943, E-mail: liangyili@hotmail.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65036-3

