文章编号:1004-0609(2009)02-0201-07
Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金热压缩变形的流变应力行为和显微组织
刘晓艳1,潘清林1, 2,何运斌1,李文斌1,梁文杰1,尹志民1, 2
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院, 长沙410083;
2. 中南大学 有色金属材料科学与工程教育部重点实验室, 长沙410083)
摘 要:采用热模拟实验对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag耐热铝合金进行热压缩实验,研究合金在热压缩变形中的流变应力行为和变形组织。结果表明:Al-Cu-Mg-Ag耐热铝合金在热压缩变形中的流变应力随着温度的升高而减小,随着应变速率的增大而增大;该合金的热压缩变形流变应力行为可用双曲正弦形式的本构方程来描述,其变形激活能为196.27 kJ/mol;在变形温度较高或应变速率较低的合金中发生部分再结晶,并且在合金组织中存在大量的位错和亚晶;随着温度的升高和应变速率的降低,合金中拉长的晶粒发生粗化,亚晶尺寸增大,位错密度减小,合金的主要软化机制逐步由动态回复转变为动态再结晶。
关键词:Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金;耐热铝合金;热压缩变形;流变应力
中图分类号:TG 146.21 文献标识码:A
Flow stress behavior and microstructure of
Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy during hot compression deformation
LIU Xiao-yan1, PAN Qing-lin1, 2, HE Yun-bin1, LI Wen-bin1, LIANG Wen-jie1, YIN Zhi-min1, 2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. The Key Laboratory of Nonferrous Materials Science and Engineering of Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The behavior of the flow stress and the deformation microstructure of heat-resistant aluminum alloy Al-Cu-Mg-Ag during hot compression deformation were studied by thermal simulation test. The results show that the flow stress decreases with increasing deforming temperature and increases with increasing strain rate. The flow stress of the alloy during hot compression deformation can be described by constitutive equation in hyperbolic sine function with a hot deformation activation energy of 196.27 kJ/mol. Partial recystallization takes place in the alloys deformed at a high temperature or at a low strain rate, and large number of dislocations and subgrains are observed in the alloy. The elongated grains observed in the samples coarsen with increasing temperature and decreasing strain rate. Correspondingly, the subgrain size increases and the dislocation density decreases. The main soften mechanism of the alloy transforms from dynamic recovery to dynamic recrystallization.
Key words: Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy; heat-resistant aluminum alloy; hot compression deformation; flow stress
Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金是一种新型高温耐热铝合金材料。与现有的2×××系耐热铝合金相比,Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金不仅具有较高的室温强度和耐损伤性能,还具有优良的高温性能。因此,Al-Cu-Mg-Ag新型合金有望满足超音速飞机的经济性要求及耐热性能要求,是超音速飞机备选材料的一个发展方向。
目前,Al-Cu-Mg-Ag耐热铝合金的研究主要集中在合金成分设计[1?2]、热处理工艺[3]以及复合添加[4?6]等方面,对这类合金在热变形条件下的流变应力行为的研究相对较少。肖代红等[7]在研究Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg- 0.6Ag合金板材的超塑性时发现,合金在变形温度为500 ℃,应变速率为5×10?4 s?1的条件下塑性最好,最大伸长率为320%,应变速率敏感系数达到0.58。余日成等[8]在研究Al-Cu-Mg-Ag耐热铝合金的热加工工艺时发现,在温度为470 ℃、变形量为50%的条件下热轧,轧出的板材效果最好,其室温抗拉强度达到470 MPa,对应的伸长率达到8%~10%。因此,研究该类合金在高温变形时的流变应力变化规律,建立有关的流变应力模型,可为该类材料的热加工工艺提供理论与实验依据。为此,本文作者对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag耐热铝合金进行热压缩实验,研究该合金在热变形条件下的流变应力行为及微观组织的变化。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料
实验所采用的原材料为工业纯铝、纯镁和纯银以及A1-Cu、A1-Mn和A1-Zr中间合金。采用铸锭冶金方法制备Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.5Ag-0.3Mn-0.15Zr(质量分数,%)合金铸锭。铸锭于500 ℃均匀化处理24 h,然后切取小块试样,加工成d10 mm×15 mm的圆柱形压缩试样。为了减小试样与压头之间的摩擦,压缩试样两端各加工出厚度为0.2 mm的凹槽,在压缩过程中,将槽内均匀填充润滑剂。
1.2 实验方法
压缩实验在Gleeble-1500热力模拟实验机上进行。应变速率为0.001、0.01、0.1、1.0和10 s?1,变形温度为340、380、420、460和500 ℃,总压缩变形量为60%。利用自身电阻进行加热,加热速率为 1 ℃/s,变形前保温5 min。压缩实验结束后立即对试样进行水淬处理,以保留合金压缩结束后的变形组织。
1.3 微观组织观察
将试样沿压缩方向切开,采用金相显微镜和透射电镜观察合金的微观组织。金相显微分析在POLYVER-MET金相显微镜上进行。透射电镜样品经机械预减薄后双喷穿孔而成。电解液为硝酸+甲醇(体积比为1?3),温度低于?20 ℃。TEM组织观察在TECNAI G2 20电镜上进行,加速电压为200 kV。
2 实验结果
2.1 合金热压缩变形的真应力-真应变曲线
图1所示为Al-Cu-Mg-Ag耐热铝合金在高温压缩变形时的真应力-真应变曲线。在热变形初期,流变应力随应变的增加而迅速增大至峰值。在相同应变速率下,随变形温度的升高,峰值应力明显下降;在相同变形温度下,随应变速率的增加,峰值应力升高,说明Al-Cu-Mg-Ag耐热铝合金在该试验条件下具有正的应变速率敏感性。
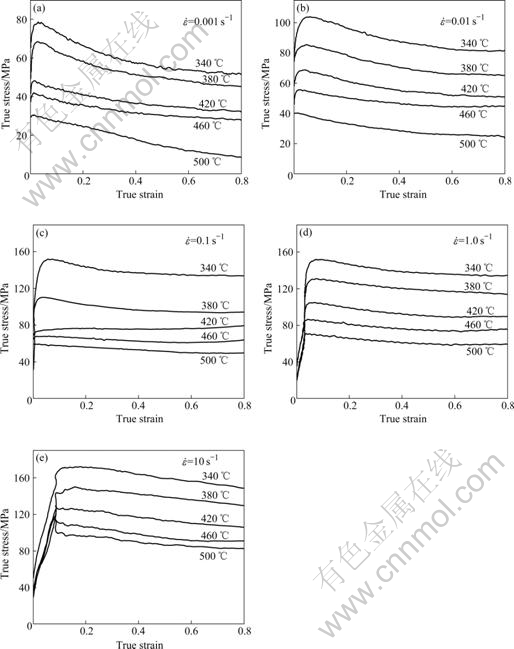
图1 Al-Cu-Mg-Ag耐热铝合金热压缩变形的真应力—真应变曲线
Fig.1 True stress—true strain curves of heat- resistant aluminum alloy Al-Cu-Mg-Ag during hot compression deformation: (a) = 0.001 s?1; (b)
= 0.001 s?1; (b)  = 0.01 s?1; (c)
= 0.01 s?1; (c)  = 0.1 s?1; (d)
= 0.1 s?1; (d)  = 1.0 s?1; (e)
= 1.0 s?1; (e)  = 10 s?1
= 10 s?1
金属和合金的热变形是一个受热激活控制的过程,其流变行为可用应变速率 、温度T和流变应力σ之间的关系来描述。对不同热加工数据的研究表明,
、温度T和流变应力σ之间的关系来描述。对不同热加工数据的研究表明, 、T和σ之间的数学关系表达式主要有以下3种情况[9?12]。
、T和σ之间的数学关系表达式主要有以下3种情况[9?12]。

ZENER等[13]于1944年提出并验证了应变速率和温度的关系可用一项参数Z表示为
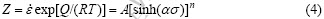
图2所示为本实验条件下的峰值应力σ与应变速率、变形温度和参数Z与流变应力之间的关系曲线。可以看出ln sinh(ασ)与ln 、T ?1和lnZ满足线性关系。
、T ?1和lnZ满足线性关系。
由式(1)~(4)及图2可以得出Al-Cu-Mg-Ag的几个参数值和Q值,结果列于表1。
表1 Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的参数及Q值
Table 1 Parameters and Q value of Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy

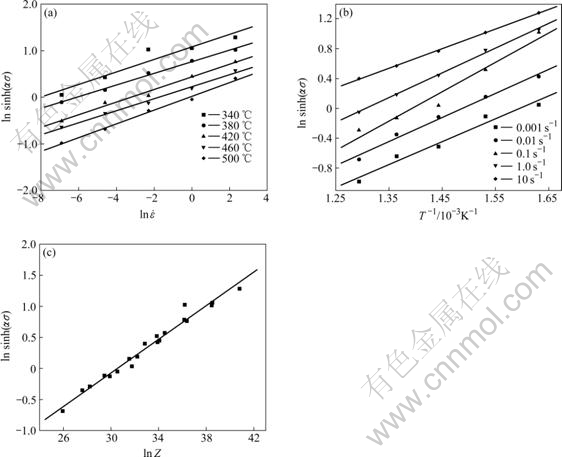
图2 lnsinh(ασ)与ln 、T ?1和lnZ的关系
、T ?1和lnZ的关系
Fig.2 Relationships among lnsinh(ασ), ln( ), T ?1 and lnZ: (a) lnsinh(ασ) vs ln
), T ?1 and lnZ: (a) lnsinh(ασ) vs ln ; (b) lnsinh(ασ) vs T ?1; (c) lnsinh(ασ) vs lnZ
; (b) lnsinh(ασ) vs T ?1; (c) lnsinh(ασ) vs lnZ
由表1可知,Al-Cu-Mg-Ag耐热铝合金的变形激活能为196.27 kJ/mol。将表1中各参数代入式(3),可得Al-Cu-Mg-Ag耐热铝合金的热压缩变形时的流变本构方程:
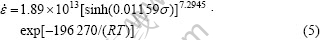
2.2 合金的热压缩变形组织
图3所示为不同变形条件下合金的金相显微组织。由图3可知,在合金组织中均存在沿垂直于压缩方向拉长的变形晶粒,部分合金中出现再结晶晶粒,合金变形组织随着变形条件的改变而发生改变。在变形温度为420 ℃,应变速率为0.1 s?1的合金组织中只有拉长的变形晶粒(见图3(b))。随着应变速率的减小,晶粒发生粗化,当应变速率减小到0.001 s?1时,合金组织中出现少量细小的再结晶晶粒(见图3(a));同样是在应变速率为0.1 s?1的条件下,随着变形温度的升高,拉长的变形晶粒也发生粗化,当温度升高到500 ℃时,合金组织中也出现少量细小的再结晶晶粒(见图3(d))。这表明在应变速率较小和变形温度较高的条件下,合金发生部分动态再结晶,并且再结晶晶粒的体积分数和晶粒尺寸均随变形温度的升高和应变速率的减小而增大(见图3(a)、(c)和(d))。

图3 在不同热变形条件下合金的金相显微组织
Fig.3 Optical microstructures of specimens compressed under different conditions: (a) t = 420 ℃,  =0.001 s?1; (b) t = 420 ℃,
=0.001 s?1; (b) t = 420 ℃,  =0.1 s?1; (c) t = 500 ℃,
=0.1 s?1; (c) t = 500 ℃,  =0.001 s?1; (d) t = 500 ℃,
=0.001 s?1; (d) t = 500 ℃,  =0.1 s?1
=0.1 s?1
图4所示为不同变形条件下合金的TEM照片。变形组织中存在大量的亚晶及位错。当变形温度为420 ℃,应变速率为0.1 s?1时,合金组织中亚晶尺寸较小,晶界及晶内存在大量的位错(见图4(a))。随着热变形温度的升高,合金中亚晶晶粒尺寸逐渐增大,亚晶晶内及晶界位错密度逐渐减小(见图4(b))。当变形温度升高到500 ℃时,合金组织中位错密度进一步减小,晶界逐渐变得平直、清晰,出现少量再结晶晶粒(见图4(c)和(d)),图(d)所示为图(c)中箭头所示位置的放大像,表明合金组织由动态回复转向动态再结晶。
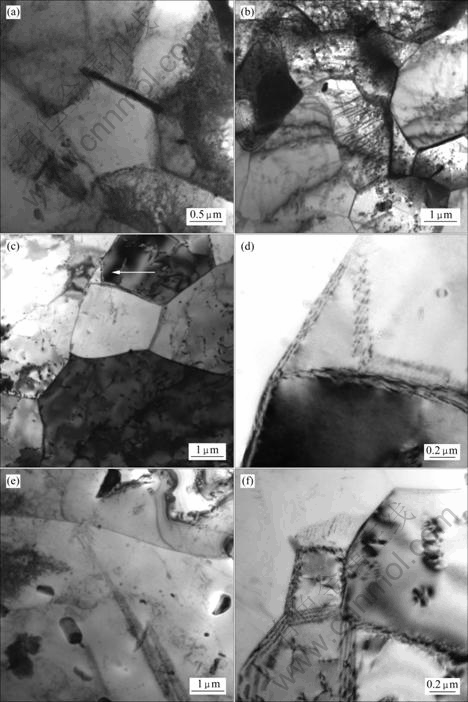
图4 不同热变形条件下合金的TEM照片
Fig.4 TEM images of specimens compressed under different conditions: (a) t = 420 ℃,  =0.1 s?1; (b) t = 460 ℃,
=0.1 s?1; (b) t = 460 ℃,  =0.1 s?1; (c), (d) t = 500 ℃,
=0.1 s?1; (c), (d) t = 500 ℃,  =0.1 s?1; (e) t = 460 ℃,
=0.1 s?1; (e) t = 460 ℃,  =0.001 s?1; (f) t = 460 ℃,
=0.001 s?1; (f) t = 460 ℃,  =10 s?1
=10 s?1
从图4中还可以看出,应变速率对合金的变形组织也有很大影响。当变形温度为460 ℃,应变速率为10 s-1时,合金中存在大量的位错墙,并且能够观察到由位错墙组成的尺寸较小的亚晶(见图4(f)),此时,合金中主要发生动态回复。当应变速率减小到0.001 s?1时,晶界位错几乎消失,晶内位错密度也明显减小,亚晶晶界变得平直、清晰(见图4(e)),说明合金中已经发生再结晶,这与金相组织观察的结果一致。
3 分析与讨论
合金在较高温度下的塑性变形,是加工硬化和动态软化的动态平衡过程。加工硬化是由于在外加应力下,位错密度增加,但位错的运动被合金中晶界、杂质、位错缠结或第二相粒子阻碍引起的[14]。动态软化则使位错密度降低和位错重新排列成低能量状态的组织。在热变形过程中,主要的软化机制是动态回复和动态再结晶。上述分析表明,Al-Cu-Mg-Ag耐热铝合金在热压缩变形时,其流变应力和微观组织的变化均强烈地依赖于应变、变形温度和应变速率。
3.1 应变的影响
在热变形初期,合金内位错密度陡然增加,而合金中的晶界、杂质、位错缠结及第二相粒子都能阻碍位错运动,位错运动到这些位置就会被阻止,从而产生位错塞积群,使合金产生加工硬化。变形抗力的增加,使得流变应力在热变形初期随应变的增加几乎呈直线迅速增大至峰值(见图1)。随着应变的增加,位错塞积数目不断增多,在塞积处产生很大的应力集中,当应力大到足以启动位错时,位错开始运动,此时,合金组织中由动态回复或动态再结晶所引起的软化能够消除部分由位错增多所引起的硬化,从而使加工硬化程度下降,流变应力随应变的增加而不同程度的减小(见图1)。
3.2 变形温度的影响
在较高温度(≥340 ℃)的热变形过程中,位错通过攀移和交滑移,使处于同一滑移面上的异号位错相互吸引而抵消,位错密度降低;同号位错相互排斥,并按照某种规律排列成位错墙,构成小角度亚晶界(见图4(f)),位错由高能态的混乱排列转向低能态的规则排列[15]。此时,合金中主要发生动态回复。随着变形温度的升高,原子的动能增大,原子间的结合力减弱,临界切应力降低,滑移系增加,位错的活动能力增强,位错之间的相互抵消和重排使得位错密度进一步降低,亚晶发生转动,取向差较小的亚晶发生合并,形成大角度晶界的再结晶晶核(见图4(c)和(d))。随着热变形的进行,大角度晶界发生迁移,晶界变得清晰、平直,逐渐形成完整的再结晶晶粒。动态再结晶的发生,使得热变形中的加工硬化得到消除或部分消除,在真应力—真应变曲线上的表现是随着温度的升高,流变应力减小。
3.3 应变速率的影响
如图3(a)和(b)所示,虽然是在相同的变形温度下,在应变速率为0.001 s?1的合金组织中已经发生部分再结晶,而在应变速率为10 s?1的合金组织中没有发生再结晶,这说明应变速率对合金组织的影响也很大。本实验中,应变速率为0.001 s?1的合金热变形时间为600 s,而应变速率最高的合金热变形时间仅为0.06 s。因此,在较高的应变速率下,合金组织中动态回复和再结晶不能够充分进行,亚晶尺寸较小,位错密度较大(见图4(f))。随着应变速率的减小,位错有足够的时间进行攀移和交滑移,它们之间的相互抵消和重排进行得更充分,位错密度减小(见图4(e)),取向差较小的亚晶发生合并,亚晶尺寸增大,逐渐形成完整的再结晶晶粒,加工硬化得到消除或部分消除,使得流变应力随着应变速率的减小而减小。
无论是热变形温度的升高还是热变形时间的延长(即应变速率的减小)都有利于位错的运动。随着热变形温度的升高和应变速率的减小,位错之间的相互抵消和重组更加彻底和完善,位错向低密度方向变化,亚晶尺寸增大,逐步发生再结晶,流变应力减小,合金中的主要软化机制逐步由动态回复转变为动态再 结晶。
4 结论
1) 在热压缩初期,合金的流变应力均随应变的增加而迅速增大至峰值。在较低的应变速率下,应力达到峰值后随应变的增加而迅速下降;随着应变速率的增大,应力达到峰值后随应变的增加下降幅度减小。
2) 在应变速率一定的条件下,合金的流变应力随变形温度的升高而减小;在变形温度一定的条件下,合金的流变应力随应变速率的增大而增大。Al-Cu- Mg-Ag合金热压缩变形的流变应力行为可用双曲正弦形式的本构方程来描述:
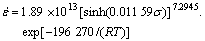
3) 随着热变形温度的升高和应变速率的减小,位错向低密度方向变化,亚晶尺寸增大,合金中的主要软化机制逐步由动态回复转变为动态再结晶。
REFERENCES
[1] CHANG C H, LEE S L, LIN J C, YEH M S, JENG R R. Effect of Ag content and heat treatment on the stress corrosion cracking of Al-4.6Cu-0.3Mg alloy[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2005, 91(2/3): 454?462.
[2] XIAO D H, WANG J N, DING D Y, CHEN S P. Effect of Cu content on the mechanical properties of an Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2002, 343(1/2): 77?81.
[3] BEFFORT O, SOLENTHALER C, SPEIDEL M O. Improvement of strength and fracture toughness of a spray-deposited Al-Cu-Mg-Ag-Mn-Ti-Zr alloy by optimized heat treatments and thermomechanical treatments[J]. Mater Sci Eng A,1995, 191(1/2): 113?120.
[4] 肖代红, 陈康华, 宋 旼. 铈对Al-Cu-Mg-Mn-Ag合金时效析出与显微组织的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(5): 669?675.
XIAO Dai-hong, CHEN Kang-hua, SONG Min. Effect of cerium addition on precipitation and microstructure of Al-Cu-Mg-Mn- Ag alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(5): 669?675.
[5] XIAO Dai-hong, HUANG Bai-yun. Effect of Yb addition on precipitation and microstructure of Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China,2007, 17(6): 1181?1185.
[6] GABLE B M, SHIFLET G J, STARKE Jr E A. The effect of Si additions on Ω precipitation in Al-Cu-Mg-(Ag) alloys[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 50(1): 149?153.
[7] 肖代红, 宋 旼, 陈康华. Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag合金的超塑性变形[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2007(4): 50?54.
XIAO Dai-hong, SONG Min, CHEN Kang-hua. Superplasticity deformation of Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag alloy[J]. Aerospace Materials & Technology, 2007(4): 50?54.
[8] 余日成, 刘志义, 刘延斌, 徐 敏, 阎 宽, 马飞跃. Al-Cu-Mg-Ag系高强耐热合金的热加工工艺研究[J]. 金属热处理, 2006, 31(5): 75?79.
YU Ri-cheng, LIU Zhi-yi, LIU Yan-bin, XU Min, YAN Kuan, MA Fei-yue. Hot working process of a high strength heat resisting Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2006, 31(5): 75?79.
[9] POIRIER J P. 晶体的高温塑性变形[M]. 关德林, 译. 大连: 大连理工大学出版社, 1989.
POIRIER J P. Crystal plastic deformation at high temperature[M]. GUAN De-lin, translate. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology Press, 1989.
[10] 沈 健. 2091铝合金高温塑性变形的研究[D]. 长沙: 中南工业大学, 1996.
SHEN Jian. Study on the plastic deformation behavior of 2091 Al alloy at elevated temperatures[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Technology, 1996.
[11] JONAS J J, SELLARS C M, TEGART M W J. Strength and structure under hot working conditions[J]. International Metallurgical Reviews, 1969, 14(130): 1?24.
[12] SHEPPARD T, PARSON N C, ZAIDI M A. Dynamic recrystallization in Al-7Mg alloy[J]. Metal Science, 1983, 17(10): 481?490.
[13] ZENER C, HOLLOMON J H. Effect of strain-rate upon the plastic flow of steel[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1944, 15(1): 22?27.
[14] 陈森灿, 叶庆荣. 金属塑性成形原理[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1984.
CHEN Sen-can, YE Qing-rong. Metal plastic forming principles [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1984.
[15] 崔忠祈, 刘北兴. 金属学与热处理原理[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2004.
CUI Zhong-qi, LIU Bei-xing. Metallography and heat treatment principles[M]. Beijing: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2004.
基金项目:国防科工委军品配套研制资助项目(JPPT-115-2-948)
收稿日期:2008-06-03;修订日期:2008-08-25
通讯作者:潘清林,教授,博士;电话:0731-8830933;E-mail: pql@mail.csu.edu.cn
(编辑 杨华)