微焊点中金属原子的热迁移及其对界面反应影响的研究进展
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报2015年第8期
论文作者:赵宁 钟毅 黄明亮 马海涛
文章页码:2157 - 2167
关键词:电子封装;互连焊点;钎料;热迁移;界面反应;金属间化合物
Key words:electronic packaging; interconnect solder joint; solder; thermomigration; interfacial reaction; intermetallic compound
摘 要:电子产品的日益发展要求更高的封装密度、更好的性能和更小的尺寸,使得电子器件所承载的功率密度显著升高,由此产生严重的焦耳热问题,导致作为主要散热通道的微互连焊点内将产生较高的温度梯度,这将诱发金属原子的热迁移,并引起严重的可靠性问题。对近年来有关Sn-Pb、Sn-Ag、Sn-Ag-Cu、Sn-Bi和Sn-Zn等微互连焊点中金属原子的热迁移行为和关键问题进行综合分析,总结热迁移对微互连界面反应的影响,阐述金属原子热迁移的机理和驱动力,并归纳传递热Q*的计算方法及微互连焊点中主要金属元素的Q*值。最后,指出微互连焊点热迁移研究存在的主要问题,并对其未来研究发展趋势进行了展望。
Abstract: The electronic products are increasingly demanding for higher packing density, better performance and smaller size, resulting in significant increase of power density applied on devices. The issue of Joule heating becomes more severe and a temperature gradient will form in the solder joints which act as the main heat dissipation channel. As a result, thermomigration of metal atoms will occur, which causes serious reliability problems of the solder joints. The thermomigration of metal atoms in Sn-Pb, Sn-Ag, Sn-Ag-Cu, Sn-Bi, Sn-Zn micro interconnect solder joints as well as the key issues were analyzed synthetically. The effect of thermomigration on interfacial reaction was included. The mechanism and the driving force of thermomigration of metal atoms were explained. The calculation methods for heat transport (Q*) and the values of Q* of main metal elements in solder joints were summarized. The main issues and trends of the studies on thermomigration in micro interconnect solder joints were finally proposed.
文章编号:1004-0609(2015)08-2157-10
赵 宁,钟 毅,黄明亮,马海涛
(大连理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,大连 116024)
摘 要:电子产品的日益发展要求更高的封装密度、更好的性能和更小的尺寸,使得电子器件所承载的功率密度显著升高,由此产生严重的焦耳热问题,导致作为主要散热通道的微互连焊点内将产生较高的温度梯度,这将诱发金属原子的热迁移,并引起严重的可靠性问题。对近年来有关Sn-Pb、Sn-Ag、Sn-Ag-Cu、Sn-Bi和Sn-Zn等微互连焊点中金属原子的热迁移行为和关键问题进行综合分析,总结热迁移对微互连界面反应的影响,阐述金属原子热迁移的机理和驱动力,并归纳传递热Q*的计算方法及微互连焊点中主要金属元素的Q*值。最后,指出微互连焊点热迁移研究存在的主要问题,并对其未来研究发展趋势进行了展望。
关键词:电子封装;互连焊点;钎料;热迁移;界面反应;金属间化合物
中图分类号:TG111.6 文献标志码:A
ZHAO Ning, ZHONG Yi, HUANG Ming-liang, MA Hai-tao
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China)
Abstract: The electronic products are increasingly demanding for higher packing density, better performance and smaller size, resulting in significant increase of power density applied on devices. The issue of Joule heating becomes more severe and a temperature gradient will form in the solder joints which act as the main heat dissipation channel. As a result, thermomigration of metal atoms will occur, which causes serious reliability problems of the solder joints. The thermomigration of metal atoms in Sn-Pb, Sn-Ag, Sn-Ag-Cu, Sn-Bi, Sn-Zn micro interconnect solder joints as well as the key issues were analyzed synthetically. The effect of thermomigration on interfacial reaction was included. The mechanism and the driving force of thermomigration of metal atoms were explained. The calculation methods for heat transport (Q*) and the values of Q* of main metal elements in solder joints were summarized. The main issues and trends of the studies on thermomigration in micro interconnect solder joints were finally proposed.
Key words: electronic packaging; interconnect solder joint; solder; thermomigration; interfacial reaction; intermetallic compound
金属原子的热迁移是在一定驱动力作用下发生的由扩散控制的质量迁移过程。较为详细的热迁移相关研究始于1879年,研究发现,试管两端温度差异会使盐溶液浓度不均匀,热端的盐溶液浓度低于冷端的,并推断温度梯度引了起盐的迁移通量[1]。类似地,成分均匀的合金在一定温度梯度下将变得不均匀。这种热交换和原子扩散交互作用而去合金化的现象称为SORET效应,也称为热迁移或温度梯度驱动的原子扩散。电子封装微互连焊点钎料主要为Sn基二元或多元合金,在一定温度梯度下也会发生热迁移现象[2-3]。
当前,电子产品不断追求高密度、高性能、多功能和微型化,电子器件在服役时产生的焦耳热已成为微电子技术面临的主要问题之一[4-5]。图1所示为典 型的电子封装微互连焊点结构示意图。电子器件在工作时,芯片侧晶体管及其间连线产生的焦耳热远大于基板产生的焦耳热[6]。承载供电和散热等作用的焊点必然成为热量传递的主要通道,这就在焊点内形成温度梯度[7]。随着微电子工业逐步进入集成电路(IC)的后摩尔定律时代,3D IC封装成为解决超大规模IC物理极限的出路之一。3D IC封装中芯片的堆叠使焦耳热问题更加严重,需要引入热沉进行散热,因此,产生的温度梯度显著增大。3D IC封装广泛采用微凸点(μ-bump)和硅通孔(TSV)进行芯片互连,微凸点的尺寸仅10 μm左右,比倒装焊点尺寸小一个数量级。若10 μm的微凸点两端温度相差1 ℃,则形成1000 ℃/cm的温度梯度,足以诱发金属原子的热迁移,引起严重的可靠性问题[4]。
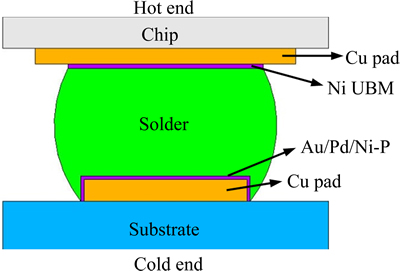
图1 电子封装微互连焊点结构示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of micro-electronic packaging interconnect solder joint
钎料与凸点下金属层(UBM)之间的界面反应是影响封装互连可靠性的关键。界面反应形成金属间化合物(IMC)是实现焊点冶金连接的必要条件,但界面IMC的脆性本质使得其厚度及形貌必须得到有效控 制[8-9]。焊点的尺寸持续减小,导致界面IMC占整个焊点的比例将明显提高[10]。界面IMC的生长、演化受钎料和基体金属原子扩散的影响,微焊点中温度梯度使钎料中金属原子的定向扩散能力增强而引起热迁移,并使元素重新分布,将显著影响界面IMC的生长,进而影响微互连的可靠性[2, 11]。
近年来,国内外诸多学者对微互连焊点内的热迁移现象进行了报道,从早期的Sn-Pb钎料到目前的无铅钎料,取得了较为丰硕的成果,但仍有一些问题悬而未解。本文作者对近年来国内外有关Sn-Pb、Sn-Ag、Sn-Ag-Cu、Sn-Bi及Sn-Zn等钎料焊点的热迁移行为及其对互连界面反应的影响以及热迁移研究中所涉及的关键问题进行了综合分析和概括评述,并结合本文作者所在课题组最近在微焊点热迁移及界面反应方面的一些研究结果,对未来的研究趋势进行了展望。
1 互连焊点中的热迁移行为
1.1 Sn-Pb焊点
Sn-Pb钎料的应用具有悠久的历史,其热迁移行为的研究较为丰富,研究方案和思路具有代表性。在对Sn-37Pb倒装焊点进行直流加载时钎料向冷端迁移,当焊点的热端与阴极一致时,热迁移可增强电迁移效应,当它们不一致时,热迁移将减弱电迁移效应[7]。通过改进实验设计消除电迁移的影响,对热迁移进行独立研究,采用直径为100 μm的Sn-Pb复合微焊点,芯片侧钎料成分为Sn-97Pb,基板侧钎料成分为Sn-37Pb,焊点内温度梯度达到1000 ℃/cm时,引起Sn原子向热端芯片侧迁移,Pb原子向冷端基板侧迁移[12]。OUYANG等[13]在Cu/95Pb5Sn-37Pb63Sn/Cu复合线性焊点的两端分别接入热源和热沉,在焊点中形成约2500 ℃/cm的温度梯度,观察到焊点成分发生再分布,认为这是由Sn向热端迁移而Pb向冷端迁移导致的,并指出引起热迁移的温度梯度门槛值约为1000 ℃/cm。对共晶Sn-37Pb倒装焊点热迁移的进一步研究,发现钎料中的层片结构相在热迁移后组织细化,由于层片结构相的界面不规则,表明热迁移是一个熵增过程,组织细化就是熵生成在微观上的行为表现[14]。沿着焊点进行成分分析,元素浓度呈阶梯式分布,热迁移后Pb在焊点冷端附近浓度急剧升高,远离冷端的平均浓度,从初始的37%(质量分数)下降到25%左右;而远离冷端的Sn几乎留在原位置,平均浓度从初始的63%升高到70%左右[2]。这证明Sn-Pb焊点热迁移中Pb是主导成分。
但是,在室温下对Sn-Pb焊点的热迁移研究却得到不同的实验现象。TAO等[15]研究了25 ℃下Sn-Pb复合焊点的热迁移,其中芯片侧钎料成分为Sn-97Pb,基板侧钎料成分为Sn-37Pb,观察到冷端出现大量富Sn相,因此,在较高的温度梯度和较低的环境温度下,Sn为主要的热迁移元素,并向冷端迁移。随后,基于温度梯度的原子热力学理论,进一步分析了Sn和Pb的热迁移行为,指出钎料中所有元素均由热端向冷端迁移,但在不同温度条件下元素的扩散速率不同,导致热迁移的主导元素存在差异[16]。
1.2 Sn-Ag焊点
Sn-Ag钎料共晶成分为Sn-3.5Ag,熔点为221 ℃,在再流焊和微凸点中得到较为广泛的应用。倒装焊点Cu/Sn-3.5Ag/Cu在150 ℃下热迁移时,热端Cu原子通过间隙扩散方式快速进入Sn基体,芯片侧Cu UBM和IMC之间形成孔洞[17]。理论计算得到,Cu在温度梯度高于400 ℃/cm时的热迁移驱动力将大于电流密度为9.7×103 A/cm2时的电迁移驱动力。热迁移引起的孔洞会导致焊点电阻升高或开路等可靠性问题。
将焊点Ni/Sn-2.5Ag/Ni两端分别连接热沉和热源形成7380 ℃/cm的温度梯度,观察到反常的界面Ni3Sn4生长现象,即热端Ni层被大量溶解且Ni3Sn4生长被抑制,而冷端Ni层消耗较少且Ni3Sn4快速生长。分析认为,温度梯度驱使热端Ni原子向冷端迁 移,导致热端Ni层被大量消耗,同时Ni原子在冷端积累,促进了冷端界面反应[18]。此外,Ag3Sn趋于在冷端分布,故认为Ag向冷端迁移。热迁移严重影响界面IMC的生长和UBM的溶解行为。GUO等[19]在钎焊下焊点热迁移的实验中也发现类似的现象,将Cu/Sn-2.5Ag/Cu焊点在260 ℃的热台上回流40 min后,观察到热端界面Cu6Sn5 IMC厚度为3.5 μm,而冷端Cu6Sn5 IMC厚度则达到12.3 μm,即两端界面IMC发生不对称生长。同时发现,冷端Cu UBM的消耗少于热端的。分析认为,热迁移驱动热端Cu原子快速向冷端迁移,一方面促进了热端Cu UBM向液态钎料中的溶解,另一方面迁移到冷端的Cu原子参与界面反应,以Cu6Sn5的形式析出,促进了冷端界面IMC的生长。通过有限元模拟得到焊点内的温度梯度仅为51 ℃/cm。可见,由于原子在液体中的扩散速率远大于在固体中的,钎焊条件下产生热迁移所需要的温度梯度或驱动力则明显降低。
1.3 Sn-Ag-Cu焊点
Sn-Ag-Cu钎料具有良好的力学性能、润湿性和 可靠性,是目前最具代表性的无铅钎料。焊点Cu/Sn-4.0Ag-0.5Cu/Cu在1000 ℃/cm的温度梯度作用下,Cu向冷端迁移促使热端界面Cu6Sn5溶解,其厚度随时间逐渐减小[20]。由于空位迁移方向和Sn晶粒粗化方向相同,以及背应力效应,焊点表面硬度从冷端到热端逐渐减小[21]。在原位观察Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu倒装焊点中Sn原子的热迁移现象时,发现热端出现凸起,而冷端出现孔洞,纳米压痕扩散标示向冷端迁移与空位通量方向一致,说明空位迁移是热迁移的主导因素[22]。Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu焊点在环境温度为150 ℃ 时,一定温度梯度下保持62 h后观察到Sn原子明显向热端迁移的现象,当环境温度为125 ℃而其他条件不变时,即使保持341 h,仍然没有Sn原子的迁移现象,说明125~150 ℃之间存在触发Sn原子热迁移的温度门槛值。这可能是由背应力效应造成的,由于Sn从冷端向热端迁移,在冷端形成拉应力而在热端形成压应力,Sn受到指向冷端的背应力作用,热迁移力受到背应力的反制效应[2]。
热迁移的门槛参数是热迁移研究的一个关键问题,参数在低于某一特定值时,热迁移将不会发生。对门槛参数作进一步分析,对比倒装芯片封装和3D IC封装无铅钎料焊点Sn原子的热迁移[4]。热迁移力和背应力作用下Sn原子的净通量(Jnet)计算式如下:
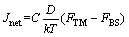 (1)
(1)
式中:C为原子浓度,即单位体积原子个数;D为扩散系数;k为玻尔兹曼常数;T为绝对温度;FTM和FBS分别为温度梯度和背应力引起原子迁移的驱动力。对于尺寸为100 μm的倒装焊点,工作温度约为150 ℃、温度梯度为2829 ℃/cm,26 h后观察到焊点热端出现Sn凸起、冷端出现孔洞。计算得FTM=8.25×10-18 N,FBS=3.52×10-18 N,由此可知,FTM远大于FBS,背应力不足以抵消热迁移力。因此,Sn热迁移是Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu倒装焊点失效的重要原因。对于3D IC封装焊点,尺寸为5.8 μm,工作温度约为134 ℃、温度梯度为5345 ℃/cm,644 h后,未观察到明显的Sn迁移现象。计算得FTM=1.62×10-17 N,FBS=6.08×10-17 N。FTM小于FBS,因此,背应力足以抵消热迁移力,Sn原子迁移不明显。因此,焊点中Sn原子出现热迁移的临界条件可表示为FTM+FBS=0,即
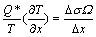 (2)
(2)
或
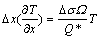 (3)
(3)
式中:Ω为原子体积;Q*为元素传递热;σ为弹性极限;Δx为焊点高度;可认为Δx(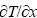 )是Sn原子热迁移的门槛参数。由式(3)可知,其他条件一定时,触发Sn热迁移温度梯度门槛值随着焊点高度的增加而减小,温度门槛值随焊点高度的增加而增大。即触发Sn原子热迁移的驱动力随焊点高度的减小而增大。由此可见,微互连焊点的热迁移行为表现出体积(尺寸)效应。
)是Sn原子热迁移的门槛参数。由式(3)可知,其他条件一定时,触发Sn热迁移温度梯度门槛值随着焊点高度的增加而减小,温度门槛值随焊点高度的增加而增大。即触发Sn原子热迁移的驱动力随焊点高度的减小而增大。由此可见,微互连焊点的热迁移行为表现出体积(尺寸)效应。
微焊点中热迁移行为的产生通常伴随着电迁移,热-电耦合作用下金属原子的迁移行为对分析微焊点的微观组织结构演化和可靠性研究更具实际意义。GU等[23]研究了Cu/Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu/Ni焊点在5×103 A/cm2直流电作用下电迁移和热迁移的耦合效应。发现,Ni和Cu向冷端迁移,Sn向热端迁移。分析指出:在Cu原子的迁移过程中热迁移占主导;在Ni原子的迁移过程中电迁移效应占主导,但热迁移效应也具有相同量级,不可忽略;热迁移对Sn迁移通量的作用可以忽略不计。LI等[24]研究发现,Cu/Sn-3.0Ag- 0.5Cu/Cu焊点在通电时,阴极区界面大部分Cu焊盘和界面IMC化合物层显著变薄,但在阴极界面附近的钎料中出现大块Cu6Sn5化合物堆积。模拟得到焊点阴极区的温度梯度为2250 ℃/cm,阴极区热迁移驱动力超过电迁移驱动力,热迁移控制阴极区的原子扩散过程,导致阴极区界面附近IMC的异常堆积。SA等[25]通过实验观察到Cu/Sn-3.5Ag-0.7Cu/Cu焊点经2×104 A/cm2的电流密度作用后,在焊点阴极侧表面出现Cu6Sn5 IMC异常堆积。分析认为,焊点存在的温度梯度导致界面IMC异常长大,热迁移和电迁移驱使阴极侧IMC挤出在表面堆积。热-电耦合作用下微互连焊点的可靠性分析与评价是3D IC封装技术研究的一个难点和关键。
在实验的基础上,研究者们又试图从理论上分析热迁移过程并建立材料的损伤模型,BASARAN等[26-29]对此过程做了系列研究,采用各向同性硬化黏塑性模型和晶粒粗化模型,得到钎料强度受到黏塑性和微结构演化的影响,当热迁移产生的应力超过材料的屈服极限,钎料强度将会降低[26]。基于热力学、连续介质力学方程、物质迁移规律和热传导方程,提出热迁移过程中材料损伤的力学模型并用有限元方法进行模拟仿真[27]。在分析Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu焊点电迁移和热迁移损伤实验和计算模型时,提出电迁移和热迁移导致材料损伤的表达公式,对材料的劣化程度进行表征,计算出电流拥挤区域形成的温度梯度高达1000 ℃/cm,认为大多数焊点的失效是由电迁移和热迁移的耦合作用造成。在电流拥挤区域和焊点表层出现热斑点,形成的温度梯度使得物质趋于向中心迁移,致使这两个区域出现孔洞[28-29]。
1.4 Sn-Bi焊点
共晶Sn-58Bi钎料因为具有较低的熔点(139 ℃)而受到关注。DING等[30]通过实验设计,在常温环境 (20 ℃)下单独研究Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu焊点中金属原子的热迁移,发现在约3500 ℃/cm的温度梯度下作用100 h后,焊点热端富Bi相逐渐分散并且远离界面,而冷端富Bi相更集中并且靠近界面。因此,Bi原子向冷端迁移。热迁移200 h后富Bi相向冷端集聚更加明显,发现热端IMC中柯肯达尔空洞数量要比冷端的大得多。GU等[31-33]对Sn-Bi焊点的热迁移行为做了系列研究,发现Sn-58Bi焊点在电流密度5×103 A/cm2、50 ℃条件下,形成527 ℃/cm的温度梯度,指出Sn-58Bi的热迁移过程与Sn-37Pb钎料的热迁移过程相似,当热迁移与电迁移同向时则促进界面反应进行,反之则抑制界面反应[31]。又设计菊花链结构,在110 ℃下通电2.5 A,研究Sn-58Bi球珊阵列焊点的纯热迁移效应及与电迁移的耦合效 应[32]。在电流作用下Bi向阳极迁移形成富Bi相;在温度梯度下,Bi趋于冷端累积。故当热迁移与电迁移方向相同时,它们相互促进Bi的迁移,反之则抑制Bi的迁移。其后,采用Au/Ni-P/Cu/Sn-8Zn-3Bi/Ni/Ni-P/Au线性焊点研究纯热迁移效应及与电迁移的耦合效应,在110 ℃下施加5×103 A/cm2交流或直流电时,焊点形成196 ℃/cm的温度梯度[33]。直流通电时,估算单个Zn原子电迁移和热迁移的能量变化分别为3.2×10-28和2.2×10-28 J,数值相近,这说明热迁移效应和电迁移效应同样不可忽略。交流通电时,只有热迁移效应,因Cu的电阻率比Ni的小,Cu侧为冷端,通电384 h后冷端界面形成厚5.2 μm的富Zn层,故认为Zn原子从热端向冷端迁移。
1.5 Sn-Zn焊点
Sn-Zn钎料的共晶熔点(198.5 ℃)与Sn-37Pb的接近,成为具有潜在应用价值的无铅钎料合金。本文作者所在课题组关于Cu/Sn-1Zn/Cu焊点热迁移对钎焊界面反应影响的最新研究结果如图2所示。焊点在 250 ℃热台上钎焊,上界面为冷端,下界面为热端。有限元分析得到钎料中形成了约35 ℃/cm的温度梯度,实验中可以明显观察到热端和冷端IMC生长的差异。反应5 min时,冷端、热端界面处均生成连续的层状Cu5Zn8 IMC,热端IMC的厚度略大于冷端的。钎焊15 min以后,热端原本粘附于基板上的Cu5Zn8 IMC逐渐脱落,同时,在基板上形成Cu6Sn5 IMC,且Cu5Zn8和Cu6Sn5厚度均不断增大;冷端界面Cu5Zn8 IMC逐渐溶解,并转变为Cu6Sn5相(固溶微量Zn原子)。黄明亮等[34]研究电迁移对焊点界面反应的影响时同样观察到了类似的IMC脱落现象。可见,随着反应的进行,冷端界面Cu5Zn8 IMC逐渐溶解、消失,而热端界面Cu5Zn8 IMC不断增厚,说明液态钎料中Zn原子在温度梯度作用下不断向热端迁移。这是微互连焊点热迁移行为研究的新发现。
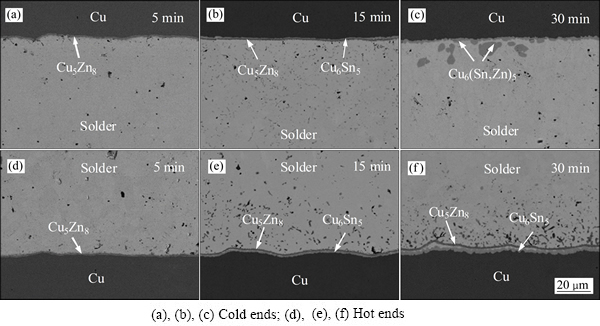
图2 Cu/Sn-1Zn/Cu焊点在250 ℃热台钎焊不同时间后的SEM像
Fig. 2 SEM images of Cu/Sn-1Zn/Cu solder joints after reflow on hotplate at 250 ℃ for different time
1.6 其他焊点
包括UBM、IMC和其他钎料的热迁移行为。CHEN等[35]在150 ℃下研究IMC的热迁移,发现由于Cu-Sn IMC向冷端迁移,同时,在焊点热端形成孔洞严重影响焊点可靠性。但是Ni-Sn IMC即使在1400 ℃/cm温度梯度下依然未发生迁移,通过类比电迁移驱动力,计算得到Ni热迁移需要的温度梯度至少为8050 ℃/cm。
热迁移可导致焊点UBM过度溶解。Ti被广泛用作Al线和UBM之间扩散阻挡层,其传递热为768 kJ/mol[36]。CHEN等[37]研究倒装焊点中Ti原子的热迁移,Al线和Sn-3.5Ag钎料之间为5 μm Cu UBM/0.12 μm Ti,有限元分析得到实验时在Ti层中形成了5800 ℃/cm的温度梯度,Ti原子获得很大的热迁移驱动力,约为1.75×10-17 N,并从热端向冷端迁移,导致Ti层溶解失效,随后Al原子开始向冷端迁移进入Cu UBM形成Al-Cu IMC,导致Al线中形成大量的孔洞。
本文作者所在课题组利用同步辐射实时原位成像技术在线研究热迁移效应对Cu/Sn/Cu焊点钎焊界面反应的影响[38]。有限元模拟显示焊点内形成了82.2 ℃/cm的温度梯度。通过同步辐射原位观察到冷、热端IMC的非对称性生长和Cu基体的非对称性溶解,其结果如图3所示[38]。冷端形成Cu6Sn5和Cu3Sn两层IMC且Cu6Sn5快速生长,而热端只形成Cu6Sn5 IMC,且缓慢生长到一定厚度后停止生长;热迁移显著抑制了冷端Cu基体的溶解,而加速了热端Cu基体的溶解,并且被溶解的Cu原子向冷端迁移,为冷端界面IMC的快速生长提供原子通量。此外,热迁移还导致界面IMC在钎焊冷却阶段形成不对称形貌,冷端Cu6Sn5 IMC由扇贝状转变为小平面结构,而热端仍保持为扇贝状。从IMC生长动力学分析可知,热迁移效应作用下焊点冷端界面Cu浓度高于热端,则根据Sn-Cu相图可知,冷端液态金属凝固温度高于热端的,故冷端的过冷度将远大于热端的,因此,小平面状IMC更容易在冷端形成,而热端易形成扇贝状IMC。同时,由于Cu原子在温度梯度作用下由热端向冷端迁移,更加不利于热端Cu原子在界面上沉积,导致热端只形成扇贝状IMC。小平面状IMC生长速度(S)可由S≈2ΔTr/G表示(式中:r为IMC晶粒曲率半径;G为温度梯度;ΔT为相对过冷度)。由于焊点冷端G方向与IMC生长方向相同,故S为正值,因此冷端可形成小平面状IMC;而热端S为负值,无法形成小平面状IMC。
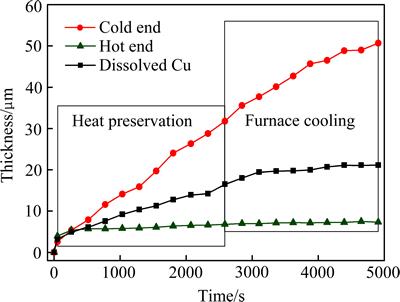
图3 钎焊过程中焊点冷、热端界面IMC厚度和热端Cu溶解厚度随时间变化[38]
Fig. 3 Thicknesses of interfacial IMCs at cold and hot ends and dissolved Cu at hot end during soldering[38]
2 热迁移驱动力及元素传递热
2.1 热迁移驱动力
热迁移是温度梯度驱动的热流和扩散原子交互作用结果,温度梯度可以驱动电子运动,电子在高温区有较高的能量,并与扩散原子交互作用,进而驱动原子热迁移。根据菲克第一定律,原子扩散的驱动力和原子通量由化学势梯度决定
 (4)
(4)
式中:J为原子通量;x为位移;μ为化学势[39]。不同于相互扩散过程中两种组分的浓度梯度方向相反,热迁移时组分经历的温度梯度相同,因此,化学势变化均为正值。以温度梯度作为驱动力,并定义Q*为传递热,则μ是T和Q*的函数,故热迁移原子通量J又可表示为
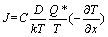 (5)
(5)
由式(4)和(5)可知,Q*具有与μ相同的量纲,代表每个原子能量或热能。此外,Q*的符号也可以由式(5)定义,如果原子从热端向冷端扩散,Q*为正;原子从冷端向热端扩散,Q*为负[2]。根据式(4)和(5),热迁移驱动力FTM可表示为
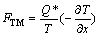 (6)
(6)
对热迁移驱动力的量级进行评估[12]。设温度梯度为1000 ℃/cm,单个原子跳跃距离a = 3×10-8 cm,则原子迁移距离的温度变化为3×10-5 ℃,热能变化ΔQ≈1.3×10-27 J,可得FTM≈0.4×10-17 N。对比电迁移驱动力FEM,据报道焊点中电流密度1×104 A/cm2将引起钎料中元素电迁移[40]。电迁移驱动力可表示为[39]
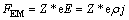 (7)
(7)
式中:取电子电荷e=1.6×10-19 C;电阻率ρ=1×10-7 Ω·m,有效电荷数Z*=10,则FEM=1.6×10-17 N。可见,热迁移驱动力比电迁移力要小,但相差较小,若1×104 A/cm2的电流密度可以诱发焊点的电迁移,则1000 ℃/cm的温度梯度将引起焊点的热迁移。
从唯象的观点,将温度梯度对元素扩散通量的影响与浓度梯度的影响做类似的处理,对菲克定律进行修订。焊点元素在温度梯度作用下,根据菲克第一定律则有扩散通量
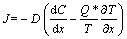 (8)
(8)
类似地,也可以根据菲克第二定律的扩散通量
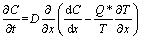 (9)
(9)
通过式(8)或(9)可得到特定情况下焊点中溶质元素的分布和时间的关系。
2.2 热迁移元素传递热Q*计算
原子通量JTM的定义
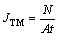 (10)
(10)
式中:A为焊点横截面积;t为反应时间;N为原子个数。
由式(5)和(10)可得
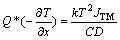 (11)
(11)
可见,若已知扩散系数D、平均温度T、温度梯度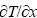 和原子通量JTM,则可以通过式(11)确定Q*。实验中可通过直接测量和有限元分析等方法获得平均温度和温度梯度,因此,确定JTM对Q*的计算至关重要。传递热Q*计算的实验方法总结如下。
和原子通量JTM,则可以通过式(11)确定Q*。实验中可通过直接测量和有限元分析等方法获得平均温度和温度梯度,因此,确定JTM对Q*的计算至关重要。传递热Q*计算的实验方法总结如下。
2.2.1 富集相原子含量的测量
OUYANG等[14]采用Sn-37Pb倒装焊点,测量冷端富铅相的Pb浓度与初始浓度差ΔCPb=0.32和富铅相厚度X=12.5 μm。根据Sn-73Pb的密度ρ=10.25 g/cm3,摩尔质量M=183.3 g/mol,作用时间t=27 h+20 min,实验温度为180 ℃、温度梯度为1000 ℃/cm,则有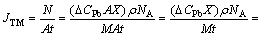 1.36× 1014 atom/(cm2·s)。由式(11)可得Pb的传递热Q*=+25.3 kJ/mol。
1.36× 1014 atom/(cm2·s)。由式(11)可得Pb的传递热Q*=+25.3 kJ/mol。
2.2.2 纳米压痕迁移量的测量
OUYANG等[41]在实验前使用聚焦离子束在共晶Sn-37Pb焊球表面蚀刻直径0.1 μm、深200 nm的纳米压痕作为标示。在2143 ℃/cm的温度梯度下保持96 h,由于JSn+JPb=-JV(其中JV为空位迁移通量,Pb为迁移主导元素),伴随着Pb向冷端迁移,标示压痕向相反方向移动的平均距离Δx = 3.2 μm。
共晶Sn-37Pb密度ρ=8.11 g/cm3,摩尔质量M=136.39 g/mol,则热迁移通量为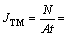
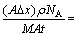 3.3×1013 atom/(cm2·s)。利用式(11)计算得Pb的传递热Q*=+26.8 kJ/mol。
3.3×1013 atom/(cm2·s)。利用式(11)计算得Pb的传递热Q*=+26.8 kJ/mol。
2.2.3 UBM消耗量的测量
GUO等[19]测量了Cu/Sn-Ag/Cu焊点在钎焊前两端Cu UBM的平均厚度均为X0=(20±1.0) μm。焊点在260 ℃热台上钎焊40 min后,冷端Cu UBM减少到(17.9±0.2) μm,热端Cu UBM则减少到(15.1±0.1) μm。热端UBM消耗厚度Δx=4.9 μm,Cu的密度ρ=8.92 g/cm3和摩尔质量M=63.5 g/mol,则有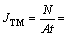
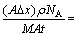 1.49×1016 atom/(cm2·s)。利用式(11)计算得Cu的传递热Q* =20 kJ/mol。
1.49×1016 atom/(cm2·s)。利用式(11)计算得Cu的传递热Q* =20 kJ/mol。
2.2.4 元素浓度分布的测量
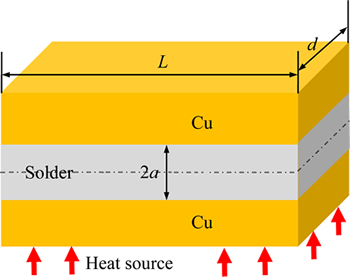
图4 热迁移实验试样示意图
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of tested sample for thermomigration
本文作者提出了一种新的传递热计算方法。如图4所示,以Sn-Bi钎料为例,假设焊点高度为2a,沿水平中心面可将焊点分为热端和冷端,则可认为JTM是冷端Bi含量在热迁移前后的差值。已知钎料的密度和摩尔质量,分别对热迁移和正常钎焊(无温度梯度) 时间t后的焊点进行元素浓度分布检测,可得到温度梯度下处理后Bi浓度分布f(x)及正常钎焊处理后的Bi浓度分布g(x)。设x为距冷端界面的距离,钎料的密度和摩尔质量分别为ρ与M。为确定JTM,可取长度L、宽度d的焊点单元,其微元体积:V=Lddx。令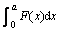
为f(x)与g(x)在焊点冷端界面到焊点中心[0, a]所围的面积,则有
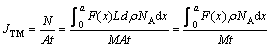 (12)
(12)
最后,利用式(11)可计算出Bi的传递热。由于考虑了正常条件(无温度梯度)下金属原子因界面反应等因素的消耗,与上述几种方法相比,浓度分布积分法无疑更为准确和全面。
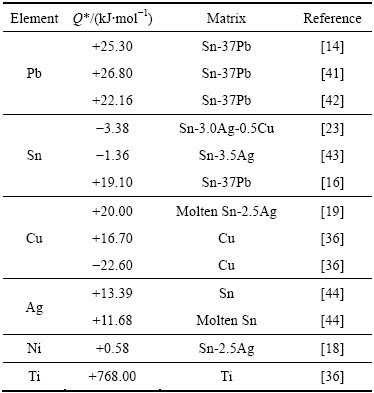
传递热Q*是热迁移的关键参数之一,通过Q*和温度梯度可以计算出元素当前条件下的驱动力,获得元素的迁移机制与规律。本文作者将文献报道的微互连焊点中主要金属元素的传递热Q*总结列于表1中。
表1 微互连焊点金属元素热迁移传递热(Q*)
Table 1 Transport heat (Q*) of metal element in micro solder joints
3 金属原子热迁移对焊点界面反应的影响
钎料与UBM之间的界面反应是影响封装互连可靠性的关键,界面反应形成IMC是实现焊点冶金连接的必要条件,但界面IMC的脆性本质使得其厚度及形貌必须得到有效控制,而界面IMC的生长、演化受钎料和基体金属原子扩散的影响,微焊点中温度梯度使钎料中金属原子的定向扩散能力增强而引起热迁移,并使元素重新分布,将影响界面IMC的生长和UBM的溶解,进而影响微互连的可靠性。温度梯度作用下焊点中原子迁移示意图如图5所示,焊点两侧界面处由浓度梯度引起的原子迁移(Jchem)均可表示为[38] Jchem=JGB+JB(式中JB为体扩散通量,JGB为晶界扩散通量)。若焊点中的原子向冷端进行热迁移,则冷端参与形成界面IMC的原子通量JIMC1=Jchem+JTM-Jsolder= JGB+JB+JTM-Jsolder(式中Jsolder为从IMC中扩散进入钎料的通量;而热端参与形成界面IMC的原子通量JIMC2=Jchem-JTM-Jsolder=JGB+JB-JTM-Jsolder)。由于微焊点高度较小,在初始阶段冷端和热端的Jchem、Jsolder的差异可忽略,故JIMC1>JIMC2。由以上分析可知,随着原子向冷端进行热迁移,冷端溶质浓度的升高将快于热端的,促进冷端IMC快速生长,逐渐增厚的IMC和较高的溶质浓度将抑制冷端UBM基体的溶解,冷端的浓度梯度逐渐小于热端的,使得JIMC1>JIMC2得到维持;而热端溶质浓度较低,IMC生长缓慢,同时,热端基体也加速溶解。同理,若焊点原子在温度梯度作用下向热端迁移,热迁移促进热端IMC快速生长,抑制热端UBM基体的溶解,而加速冷端基体的溶解。由此可见,微焊点中金属原子热迁移使钎料中元素重新分布,可显著影响界面IMC的生长和UBM的溶解。
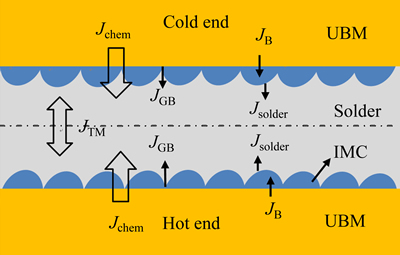
图5 焊点中原子通量示意图
Fig. 5 Schematic diagram of atomic fluxes in solder joint
4 展望
随着3D IC封装技术的兴起与快速发展,微凸点中的热迁移现象将更加凸显,由其引起的可靠性问题应引起关注。目前,关于微焊点热迁移行为及其对互连界面反应影响的报道,主要集中在原子的迁移规律与机制、界面IMC的非对称生长、UBM的过度溶解消耗和微焊点损伤模型等,但仍存在诸多问题需深入研究,主要包括如下几个方面。
1) 钎料体系众多,各元素的热迁移行为差别较大,一些研究结果之间存在矛盾,需进一步研究加以验证,明确主迁移元素及其迁移方向。
2) 实验条件较为单一,只涉及某一种或两种因素,而实际焊点通常受热迁移、电迁移、背应力和电流拥挤效应等综合作用,需要在实验和理论上加以分析和表征。
3) 对于钎焊条件下钎料为液态的热迁移行为研究较少,相应的元素传递热和热迁移门槛参数数据较为匮乏,相关研究亟需开展。
4) 由于热迁移导致界面反应的不对称性,并可能使焊点中形成凸起和孔洞,使得焊点对机械加载或冲击更敏感,甚至导致连接的开路。因此,迫切需要评价热迁移作用下微互连焊点的可靠性,并进行寿命预测,为微电子产业发展消除后顾之忧。
REFERENCES
[1] PLATTEN J K. The soret effect: A review of recent experimental results[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2006, 73(1): 5-15.
[2] CHEN C, HSIAO H Y, CHANG Y W, OUYANG F Y, TU K N. Thermomigration in solder joints[J]. Materials Science and Engineering R: Reports, 2012, 73(9): 85-100.
[3] 张金松, 吴懿平, 王永国, 陶 媛. 集成电路微互连结构中的热迁移[J]. 物理学报, 2010, 59(6): 4395-4402.
ZHANG Jin-song, WU Yi-ping, WANG Yong-guo, TAO Yuan. Thermomigration in micro interconnects in integrated circuits[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2010, 59(6): 4395-4402.
[4] OUYANG F Y, JHU W C. Comparison of thermomigration behaviors between Pb-free flip chip solder joints and microbumps in three dimensional integrated circuits: Bump height effect[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 113(4): 043711.
[5] HUANG M L, YE S, ZHAO N. Current-induced interfacial reactions in Ni/Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu/Au/Pd(P)/Ni-P flip chip interconnect[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2011, 26(24): 3009-3019.
[6] LAI Y S, KAO C L. Calibration of electromigration reliability of flip-chip packages by electrothermal coupling analysis[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2006, 35(5): 972-977.
[7] YE H, BASARAN C, HOPKINS D. Thermomigration in Pb–Sn solder joints under joule heating during electric current stressing[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2003, 82(7): 1045.
[8] LAURILA T, VUORINEN V, KIVILAHTI J K. Interfacial reactions between lead-free solders and common base materials[J]. Materials Science and Engineering R: Reports, 2005, 49(1): 1-60.
[9] 赵国际, 盛光敏, 邓永强. Sn-6.5Zn 钎料/Cu 基板焊点界面特征与金属间化合物的形成机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(2): 434-440.
ZHAO Guo-ji, SHENG Guang-min, DENG Yong-qiang. Formation mechanism of intermetallic compounds and interface characteristics of joint of Sn-6.5Zn solder/Cu substrate[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(2): 434-440.
[10] HSIAO H Y, LIU C M, LIN H W, LIU T C, Lu C L, HUANG Y S, CHEN C, TU K N. Unidirectional growth of microbumps on (111)-oriented and nanotwinned copper[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6084): 1007-1010.
[11] 黄明亮, 陈雷达, 赵 宁. Cu-Ni 交互作用对 Cu/Sn/Ni 焊点液-固界面反应的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(4): 1073-1078.
HUANG Ming-liang, CHEN Lei-da, ZHAO Ning. Effect of Cu-Ni cross-solder interaction on liquid-solid interfacial reaction in Cu/Sn/Ni solder joint[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(4): 1073-1078.
[12] HUANG A T, GUSAK A M, TU K N, LAI Y S. Thermomigration in SnPb composite flip chip solder joints[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88(14): 141911.
[13] OUYANG F Y, HUANG A T, TU K. N. Thermomigration in SnPb composite solder joints and wires[C]// KRUSIUS J P. Proceedings of the 56th Electronic Components and Technology Conference. San Diego: IEEE, 2006: 1974-1978.
[14] OUYANG F Y, TU K N, LAI Y S, GUSAK A M. Effect of entropy production on microstructure change in eutectic SnPb flip chip solder joints by thermomigration[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 89(22): 221906.
[15] TAO Y, DING L, WU Y P, SHANGGUAN D K, WU B Y. Investigation of thermomigration in composite SnPb solder joints[C]// BI K Y. Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology & High Density Packaging. Xi’an: IEEE, 2010: 1190-1194.
[16] TAO Y, DING L, WU Y P, WU B, CAI M. Theoretical analysis on the element diffusion during thermomigration[C]// BI K Y. Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology & High Density Packaging. Shanghai: IEEE, 2011: 1008-1012.
[17] CHEN H Y, CHEN C, TU K N. Failure induced by thermomigration of interstitial Cu in Pb-free flip chip solder joints[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93(12): 122103.
[18] OUYANG F Y, JHU W C, CHANG T C. Thermal-gradient induced abnormal Ni3Sn4 interfacial growth at cold side in Sn2.5Ag alloys for three-dimensional integrated circuits[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 580(15): 114-119.
[19] GUO M Y, LIN C K, CHEN C, TU K N. Asymmetrical growth of Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compounds due to rapid thermomigration of Cu in molten SnAg solder joints[J]. Intermetallics, 2012, 29(1): 155-158.
[20] ABDULHAMID M F, LI S D, BASARAN C. Thermomigration in lead-free solder joints[J]. International Journal of Materials and Structural Integrity, 2008, 2(1): 11-34.
[21] ABDULHAMID M F, BASARAN C. Influence of thermomigration on lead-free solder joint mechanical properties[J]. Journal of Electronic Packaging, 2009, 131(1): 011002.
[22] OUYANG F Y, KAO C L. In situ observation of thermomigration of Sn atoms to the hot end of 96.5Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu flip chip solder joints[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 110(12): 123525.
[23] GU X, DING K P, CAI J, KONG L W. Electromigration and thermomigration in Sn3Ag0.5Cu solder joints[C]// BI K Y. Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology & High Density Packaging. Xi’an: IEEE, 2010: 1273-1279.
[24] LI M Y, CHANG H, PANG X C, WANG L, FU Y G. Abnormal accumulation of intermetallic compound at cathode in a SnAg3.0Cu0.5lap joint during electromigration[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2011, 44(11): 115501.
[25] SA X Z, ZHOU W, WU P. Electromigration in Cu-cored Sn-3.5Ag-0.7Cu solder interconnects under current stressing[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2014, 43(4): 1144-1149.
[26] BASARAN C, LI S D, ABDULHAMID M F. Thermomigration induced degradation in solder alloys[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 103(12): 123520.
[27] LI S D, ABDULHAMID M F, BASARAN C. Simulating damage mechanics of electromigration and thermomigration[J]. Simulation, 2008, 84(8): 391-401.
[28] YAO W, BASARAN C. Computational damage mechanics of electromigration and thermomigration[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 114(10): 103708.
[29] YAO W, BASARAN C. Damage mechanics of electromigration and thermomigration in lead-free solder alloys under alternating current: An experimental study[J]. International Journal of Damage Mechanics, 2013, 23(2): 203-221.
[30] DING L, TAO Y, WU Y P. Thermomigration in Sn58Bi solder joints at low ambient temperature[C]// BI K Y. Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology & High Density Packaging. Shanghai: IEEE, 2011: 944-949.
[31] GU X, CHAN Y C. Thermomigration and electromigration in Sn58Bi solder joints[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2009, 105(9): 093537.
[32] GU X, YUNG K C, CHAN Y C. Thermomigration and electromigration in Sn58Bi ball grid array solder joints[J]. Journal of Materials Science—Materials in Electronics, 2010, 21(10): 1090-1098.
[33] GU X, YUNG K C, CHAN Y C, YANG D. Thermomigration and electromigration in Sn8Zn3Bi solder joints[J]. Journal of Materials Science—Materials in Electronics, 2011, 22(3): 217-222.
[34] 黄明亮, 陈雷达, 周少明, 赵 宁. 电迁移对Ni/Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu/Au/Pd/Ni-P倒装焊点界面反应的影响[J]. 物理学报, 2012, 61(19): 198104.
HUANG Ming-liang, CHEN Lei-da, ZHOU Shao-ming, ZHAO Ning. Effect of electromigration on interfacial reaction in Ni/Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu/Au/Pd/Ni-P flip chip solder joints[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2012, 61(19): 198104.
[35] CHEN H Y, CHEN C. Thermomigration of Cu-Sn and Ni-Sn intermetallic compounds during electromigration in Pb-free SnAg solder joints[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2011, 26(8): 983-991.
[36] CAHN R W, HAASEN P. Physical metallurgy (Vol. 1)[M]. Amsterdam: North-Holland, 1996: 616-618.
[37] CHEN H Y, LIN H W, LIU C M, CHANG Y W, HUANG A T, CHEN C. Thermomigration of Ti in flip-chip solder joints[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2012, 66(9): 694-697.
[38] QU L, ZHAO
[39] TU K N. Solder joint technology: Materials, properties and reliability[M]. New York: Springer, 2007: 338-345.
[40] ZENG K, TU K N. Six cases of reliability study of Pb-free solder joints in electronic packaging technology[J]. Materials Science and Engineering R: Reports, 2002, 38(2): 55-105.
[41] HSIAO H Y, CHEN C. Thermomigration in flip-chip SnPb solder joints under alternating current stressing[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 90(15): 152105.
[42] CHUANG Y C, LIU C Y. Thermomigration in eutectic SnPb alloy[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88(17): 174105.
[43] HSIAO H Y, CHEN C. Thermomigration in Pb-free SnAg solder joint under alternating current stressing[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 94(9): 092107.
[44] SU Y P, OUYANG F Y. The growth of Ag3Sn intermetallic compound under a temperature gradient[C]// KOZUE N. Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronic Packaging (ICEP 2014). Toyama: IEEE, 2014: 634-639.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51301030); 中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金项目(DUT14QY45)
收稿日期:2014-11-15;修订日期:2015-02-28
通信作者:赵 宁,副教授,博士;电话:0411-84708430;E-mail: zhaoning@dlut.edu.cn

