文章编号: 1004-0609(2005)05-0746-05
(Cr-Si-Ni)/Si薄膜的微观结构和电阻率
张玉勤, 董显平, 吴建生
(上海交通大学 材料科学与工程学院 教育部高温材料及测试重点实验室, 上海 200030)
摘 要: 采用磁控溅射方法在Si(100)基底上制备了Cr-Si-Ni电阻薄膜, 研究了不同温度退火时薄膜微观结构的转变过程以及对电阻率的影响。 结果表明: 薄膜在溅射态和低于300℃热处理时为非晶态; 退火温度高于300℃以后, 薄膜中析出CrSi2晶化相; 当退火温度达到600℃时, 薄膜中还有少量多晶Si相析出, 同时在薄膜与基底界面处还发生了原子的相互扩散; CrSi2晶化相成“岛”状结构, 弥散分布在非晶绝缘基底上; 薄膜室温电阻率随着退火温度的上升, 呈先上升、 后下降趋势; 薄膜电阻率随退火温度的变化行为与薄膜微观结构的变化以及界面扩散有关。
关键词: 电阻薄膜; Si基底; 微观结构; 界面扩散; 电阻率 中图分类号: TM241.1
文献标识码: A
Microstructure and electrical resistivity of Cr-Si-Ni films deposited on Si substrates
ZHANG Yu-qin, DONG Xian-ping, WU Jian-sheng
(Key Laboratory for High Temperature Materials and Tests of Ministry of Education,
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiaotong University,
Shanghai 200030, China)
Abstract: Cr-Si-Ni resistive films were prepared on n-type Si (100) substrates by magnetron sputtering. The microstructure evolution and electrical resistivity of the films as a function of annealing temperatures were investigated. The results reveal that the microstructure of the films at as-deposited state and annealed at temperature lower than 300℃ are amorphous state. With the annealing temperature increases to higher than 300℃, the nanocrystalline CrSi2 begins to appear. A few polycrystalline Si phase is separated at the films, and an atomic interdiffusion at the interface between the films and Si substrates can be observed, when the annealing temperature reaches 600℃. Cr-Si-Ni films consist of the nanocrystalline phase as an island dispersed in amorphous insulating matrix. With the annealing temperatures increasing, the room temperature resistivity of the films rises at the beginning, then goes down. The annealing behavior of the resistivity is correlated with the microstructure and interfacial diffusion of the films.
Key words: resistive film; Si substrates; microstructure; interfacial diffusion; electrical resistivity
Cr-Si系硅化物薄膜由于具有较高的片层电阻率、 较小的电阻温度系数(TCR)以及良好的热稳定性和化学稳定性, 成为集成电路和微电子设备中非常有吸引力的电阻薄膜材料[1-4]。 迄今为止, 使用在集成电路中的硅化物电阻薄膜大多采用金属沉积在Si基底上经扩散反应方法形成, 例如外延生长法[5-8]。 但是采用扩散法制备的电阻元件除了存在界面平整度差、 基底消耗量大、 热稳定性差、 重复制造性不好、 损耗非线性等缺点外, 更主要的缺点是很难获得高的电阻值。 对于一些需要较高阻值薄膜元件的低功率设备, 比如心脏起搏器、 便携式电子设备等, 扩散法制备的元件就很难满足该要求。 针对这些缺点, 可以通过在基底上预先制备绝缘中间层, 然后再将薄膜沉积在中间层上的方法来克服或者减轻[9, 10]。 然而中间层的加入不仅会导致成本的增加, 而且由于薄膜电阻器对基底非常敏感, 这样中间层本身又会带来新的缺点, 从而引出新的问题。 因此, 研究将硅化物薄膜直接沉积在硅基底上, 作为电阻薄膜应用于集成电路和微电子设备引起了越来越多的兴趣。
近年来, 采用扩散法制备硅化物电阻薄膜的研究较多[5-8], 但采用将Cr-Si系硅化物薄膜直接沉积在Si基底上, 并研究其微观结构和电性能的文献比较少。 根据前期研究结果, 在Cr-Si合金靶材中加入3%~6%Ni(摩尔分数)可以改善薄膜的电性能和靶材的制备加工性能[11, 12]。 本文作者采用Cr17Si80Ni3合金靶材通过射频磁控溅射方法在n型Si(100)基底上制备了Cr-Si-Ni薄膜, 研究了热处理过程中薄膜微观结构的转变过程和界面扩散情况, 分析了微观结构及界面扩散对薄膜电阻率的影响。
1 实验
采用真空熔炼法制备了Cr-Si-Ni合金靶材, 成分为Cr17Si80Ni3, 然后使用CEVP-1000C型射频磁控溅射仪制备薄膜。 薄膜沉积在单晶抛光n型Si(100)基底上, 溅射前基底经过预处理。 溅射室本底真空度为1×10-4Pa, 沉积过程中, 持续通入氩气, 使压力始终保持在0.4Pa, 溅射功率固定在300W, 薄膜厚度控制在300nm和1μm, 基片在沉积过程中处于室温状态。 制备的薄膜在箱式电阻炉进行热处理, 氩气氛保护, 退火温度范围250~600℃, 间隔50℃热处理, 保温180min。
薄膜厚度由ALPHA-STEP 500表面轮廓仪测量, 厚度为1μm的薄膜用于能谱仪成分分析, 其它测试都在厚度300nm的薄膜上进行。 微观结构分析分别在DMAX-111型X射线衍射仪(XRD)和Hitachi H800 型透射电镜(TEM)上进行, 成分深度分析利用PHI 550 ESCA/SAM 俄歇能谱仪(AES)进行, 利用四探针测试仪(SDY-5型)测量不同温度处理后薄膜的室温电阻率。 纵断面 TEM 试样通过SEIKO FIB-SMI2200聚焦离子束系统(FIB)来制备(图1), 其具体步骤见文献[13]。 制备出的试样尺寸为10μm ×5μm×160nm。 采用AES分析时, 一次电子束电压3keV, 电流1μA, Ar+离子刻蚀电流密度100μA/cm2, 电压3kV, 刻蚀剥离速度约为12nm/min。
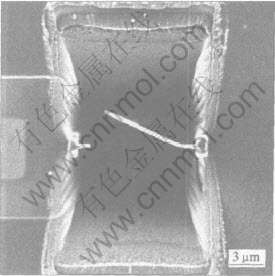
图1 聚焦离子束系统制备的Cr-Si-Ni薄膜纵断面TEM像
Fig.1 Cross-sectional TEM image of Cr-Si-Ni films prepared by
using focused ion beam system (FIB)
2 分析与讨论
2.1 薄膜微观结构分析
由于择优溅射, 溅射薄膜的化学成分与靶材的化学成分存在一定的偏差, 经EDX多点分析, Cr-Si-Ni溅射薄膜的平均化学成分(摩尔分数)为: Cr 21.66%, Si 74.47%和Ni 3.88%。 图2 所示为溅射态和不同温度退火处理180min的Si基底Cr-Si-Ni 薄膜的X射线衍射谱(由于衍射峰太弱, 布拉格角在25°以下和60°以上的衍射图谱可以忽略)。 从图中可以明显看出, 薄膜在溅射态及低于300℃热处理时呈非晶态; 热处理温度高于300℃以后, 图谱中出现了CrSi2(111)晶化相衍射峰, 说明薄膜中有CrSi2晶化相析出; 随着热处理温度的进一步升高, CrSi2的衍射峰强度增大; 在450℃时同时出现了CrSi2(112)衍射峰; 而且当退火温度达到600℃时, 图谱中不仅出现了更多晶面的CrSi2相衍射峰, 并且发现有多晶Si的衍射峰出现。 通过对600℃处理的单晶Si基底XRD分析表明, 证明在薄膜中确实有多晶Si相析出。 另外, 根据图2还可以看出随着热处理温度的升高, CrSi2晶粒的尺寸逐渐增大。 由于薄膜中Ni含量较少, X射线衍射没有检测到与Ni相关相(如NiSi或NiSi2相)的谱线。
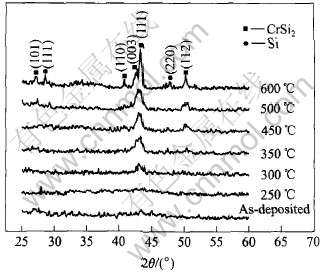
图2 溅射态和不同温度下退火处理180min的Cr-Si-Ni薄膜的X射线衍射谱
Fig.2 XRD patterns of Cr-Si-Ni films at as-deposited state and annealed at different temperatures for 180min
图3所示为薄膜在500℃和600℃热处理180min后的纵断面TEM形貌及选区电子衍射(SAED)。 从图中可以看出, 薄膜中有大量CrSi2晶化相析出, 这与XRD所得的结果是一致的。 CrSi2晶化相成“岛”状结构, 弥散分布在非晶绝缘基底上。 在退火温度为600℃时, 可以观察到更多的晶化相析出, 而且晶粒长大速度快, 很多晶粒开始团聚在一起, 晶粒间距明显比500℃时下降很多, 这对薄膜的电阻率将产生很大的影响。 同时根据图3还可以看出, 薄膜与基底的界面平整, 说明热处理过程中薄膜界面处没有显著的扩散。
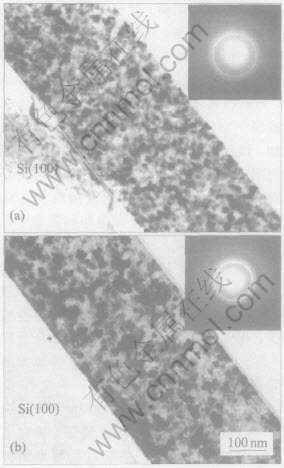
图3 (Cr-Si-Ni)/Si薄膜于500℃(a)和600℃(b)热处理180min后纵断面的TEM形貌及选区电子衍射花样
Fig.3 Cross-sectional TEM micrographs and SAED patterns of Cr-Si-Ni films deposited on Si substrates annealed at 500℃(a) and
600℃(b) for 180min
2.2 薄膜的AES深度分析
图4所示为沉积在Si基底上的Cr-Si-Ni薄膜溅射态和600℃热处理180min后的AES深度分布曲线。 图4(a)所示为在溅射态试样中Si、 Cr、 Ni和O元素的相对原子含量。 从图中可以看出, 在薄膜层中, Si、 Cr、 Ni元素的分布比较均匀。 但是在薄膜与基底的交界处, Si、 Cr、 Ni元素的分布与薄膜层存在差异, Cr和Ni元素的含量要低于薄膜层, Si含量要稍高于薄膜层, 其原因主要是由于Si基底表面粗糙度引起的。 图4(b)所示为Si基底Cr-Si-Ni薄膜在600℃热处理180min后AES深度的分布。 可以看出, 热处理以后的薄膜与基底界面层的宽度比溅射态试样界面层宽度增大了, 这表明在薄膜和Si基底的界面上发生了元素的相互扩散。 在界面处出现了Cr向Si基底的扩散和Si的富集, 富集的Si相以多晶的形式析出。 这就说明在图2中, 薄膜在600℃热处理后出现多晶Si相的原因。 从图4还可以看出, 这个界面层的宽度较小, 说明界面扩散程度不是很大, 这与图3(b) 所获得的TEM结果相互吻合。 这表明所制备的Cr-Si-Ni薄膜在Si基底上具有较好的热稳定性。
2.3 微观结构和界面扩散对薄膜电性能的影响
图5所示为Si基底Cr-Si-Ni薄膜在溅射态和不同温度退火处理180min后的室温电阻率。 从图中可以看出, 薄膜室温电阻率随着退火温度的上升, 呈先上升、 后下降趋势。 当退火温度低于300℃时, 薄膜电阻率随着温度的上升缓慢的增大; 当退火温度高于300℃以后, 薄膜电阻率的增大速度加快; 特别是退火温度500℃时, 薄膜电阻率发生跃变, 达到最大值; 而后随着温度的进一步升高, 电阻率反而快速下降。 薄膜电阻率随退火温度的变化行为与薄膜热处理过程中微观结构的变化以及界面扩散有非常大的关系, 其影响机理可以用Neugebauer和Webb所提出的不连续金属薄膜的活化隧道理论[14]来解释。 活化隧道理论的本质是把载流子的热活化产生机理与隧道效应相互结合起来。 该理论认为由于热活化的结果, 电子从一个中性小岛移至另一个中性小岛, 从而使原来中性的一些小岛带上了电荷。 在带电小岛和中性小岛间的电子传输则是一个隧道过程。
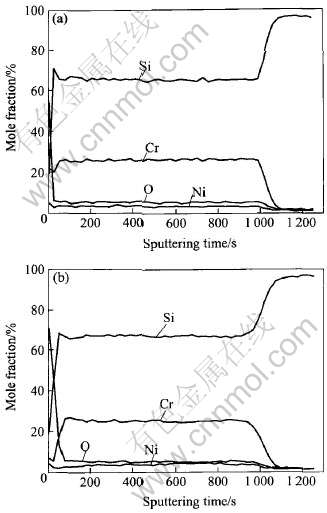
图4 (Cr-Si-Ni)/Si薄膜溅射态和600℃退火处理180min后AES深度的分布
Fig.4 Auger depth profiles of Cr-Si-Ni films
deposited on Si substrates at as-deposited
state(a) and annealed at 600℃ for 180min(b)
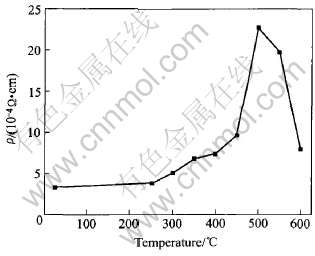
图5 (Cr-Si-Ni)/Si薄膜在溅射态和不同温度下退火处理180min后的室温电阻率
Fig.5 Room temperature resistivity of Cr-Si-Ni films deposited on Si substrates at
as-deposited state and annealed at various temperatures for 180min
根据活化隧道理论, 在一定温度下的薄膜电阻R可以近似表示为[9, 15]

式中 C和A为常数; k为波耳兹曼常数; r为小岛半径; s为岛间距离; q为电子电荷量; ε为有效绝缘常数; 为小岛之间有效势垒高度, 与岛的表面位垒有关。 在薄膜厚度和表面积确定的情况下, 式(1)反映了薄膜电阻率与小岛尺寸和岛间距离之间的关系。
根据式(1)和(2), 薄膜电阻率随着岛半径的增大而减小、 随着岛间距的增大而增大, 但是岛间距对电阻率的影响要比岛半径的影响大得多, 因此薄膜电阻率的变化更多的依赖于岛间距的变化。 根据前面的分析, 生长阶段薄膜由很多独立的小岛组成, 由于基底在沉积过程中一直保持低温状态, 因而这些小岛保留在原始位置; 随着沉积的不断进行, 更多的溅射粒子沉积在基底上, 从而形成了一个相对连续的薄膜。 当退火温度低于300℃时, 薄膜呈非晶态结构。 由于升温的作用, 薄膜中的小岛互相移动, 形成了弥散的小岛群, 而且尺寸和间距也在缓慢增大, 因而薄膜电阻率缓慢提高。 退火温度在300~500℃之间时, 岛获得的能量更多, 薄膜晶化析出了纳米CrSi2晶粒, 而且其晶粒大小和间距也不断增大, CrSi2晶化相团聚成较大的小岛群弥散分布在非晶绝缘基底上。 因而在这个温度范围内, 晶粒间距比晶粒大小的增加要快一些, 薄膜电阻率随之迅速增大。 但温度超过500℃以后, 析出的CrSi2晶粒的体积分数和尺寸急剧增大, 导致晶粒间距迅速减小(图3), 最终使得薄膜电阻率反而快速下降。
对于Si基底Cr-Si-Ni薄膜, 其电阻率随退火温度的变化行为主要与微观结构有关。 但是在较高温度退火时薄膜与基底的界面扩散对电阻率也有一定的影响。 由图4可知, 随着退火温度的升高, 在薄膜与Si基底界面上发生了原子的相互扩散, 形成了一个较小的界面扩散层。 尽管这个界面扩散层的宽度非常的小, 然而其在导电过程中与薄膜层可能会形成“并联”电路, 起了电阻的“并联”作用, 从而会导致薄膜的电阻率有一定的减小。 对于本文实验所制备的薄膜, 由于扩散层的宽度非常小, 因而对电阻率的没有显著的影响。 因此, 从以上分析可以看出, 将Cr-Si-Ni薄膜直接沉积在单晶Si基底上可以在较低的热处理温度下获得较高的电阻率, 可以克服扩散法制备薄膜电阻带来的一些问题。
3 结论
采用磁控溅射法制备在Si(100)基底上的Cr-Si-Ni电阻薄膜在溅射态及低于300℃热处理时呈非晶态结构; 退火温度高于300℃以后, 薄膜中析出CrSi2晶化相; 当退火温度达到600℃时, 薄膜中有少量多晶Si相析出。 CrSi2晶化相成“岛”状结构, 弥散分布在非晶绝缘基底上。 随着热处理温度的升高, 薄膜中晶化相尺寸不断增大。 在高温退火时, 薄膜与Si基底的界面处发生了原子的相互扩散, 但界面扩散层的宽度非常小, 说明薄膜具有较好的热稳定性。 薄膜室温电阻率随着退火温度的上升, 呈先上升、 后下降趋势。 薄膜电阻率随退火温度的变化行为与薄膜热处理过程中微观结构的变化以及界面扩散有关。
REFERENCES
[1]Brückner W, Griemann H, Schreiber H, et al. Degradation of CrSi(W)-O resistive films[J]. Thin Solid Films, 1992, 214: 84-91.
[2]Brückner W, Griemann H, Monch J I, et al. High temperature stability of CrSi(W)-N films[J]. Thin Solid Films, 1992, 221: 140-146.
[3]ZHANG Yu-qin, DONG Xian-ping, WU Jian-sheng. Microstructure and electrical characteristics of Cr-Si-Ni films deposited on glass and Si(100) substrates by RF magnetron sputtering[J]. Materials Science and Engineering B, 2004, 113: 154-160.
[4]董显平, 吴建生, 毛立忠. 氮元素对Cr-Si-Al电阻薄膜晶化行为及电性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(4): 668-672.
DONG Xian-ping, WU Jian-sheng, MAO Li-zhong. Effect of nitrogen on crystallization behavior and electrical properties of Cr-Si-Al resistive films[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(4): 668-672.
[5]Mirouh K, Bouabellou A, Halimi R, et al. Microstructural study of annealed Cr/Si system using cross-sectional TEM combined with nano-analysis[J]. Materials Science and Engineering B, 2003, 102: 80-83.
[6]Mirouh K, Bouabellou A, Halimi R, et al. Cross-sectional TEM investigations of the influence of P+ ions implanted in the Si substrate on the atomic interdiffusion in the Cr-Si system[J]. Materials Science and Engineering B, 2000, 73: 116-119.
[7]Labbani R, Halimi R, Bouabellou A, et al. Elaboration of thin chromium silicide layers on P+ implanted silicon[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 2002, 480: 223-228.
[8]Zhu H N, Liu B X. Pattern evolution during the growth of CrSi layers on Si (111) upon high current pulsed Cr ion implantation[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2001, 384: 53-57.
[9]Wu F, McLaurin A W, Henson K E, et al. The effect of the process on the electrical and microstructure characteristics of the CrSi thin resistor films: partⅠ[J]. Thin Solid Films, 1998, 332: 418-422.
[10]Gong S F, Li X H, Hentzell H T G. Electrical and structural properties of thin films of sputtered CrSi2[J]. Thin Solid Films, 1992, 208: 91-95.
[11]董显平. 多元Cr-Si系硅化物薄膜微观结构和电性能的研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2003.
DONG Xian-ping. The Study of Microstructure and Electrical Properties of Cr-Si Silicide Films[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2003.
[12]Dong X P, Wu J S. Study on the crystallization of amorphous Cr-Si-Ni thin films using in situ X-ray diffraction[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2001, 17: s43-46.
[13]Longford R M, Clinton C. In situ lift-out using FIB-SEM system[J]. Micron, 2004, 35: 607-611.
[14]Neugebauer C A, Webb M B. Electrical conduction mechanism in ultrathin evaporated metal films[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1962, 33(1): 74-80.
[15]Wu F, Morris J E. The effects of hydrogen absorption on the electrical conduction in discontinuous palladium films[J]. Thin Solid Films, 1994, 246: 17-23.
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金重点资助项目(50131030); 上海市科技发展基金资助项目(02DJ14042)
收稿日期: 2004-11-22; 修订日期: 2005-03-21
作者简介: 张玉勤(1976-), 男, 博士研究生.
通讯作者: 张玉勤, 博士研究生; 电话: 021-62932440; E-mail: zyqkust@sjtu.edu.cn
(编辑龙怀中)