文章编号:1004-0609(2015)10-2656-10
Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金搅拌摩擦焊接接头的显微组织、力学性能及局部腐蚀性能
叶 锐1,杨继东1,彭小燕1,徐国富1, 2, 3,尹志民1, 2
(1.中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2.中南大学 材料科学与工程学院 有色金属材料科学与工程教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083;
3.中南大学 粉末冶金研究院 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083)
摘 要:通过硬度测试、极化曲线测试、腐蚀浸泡和慢应变速率拉伸方法研究Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金板材搅拌摩擦焊接接头的力学性能和局部腐蚀性能,并利用金相显微镜和透射电镜对焊接接头的显微组织进行分析。结果表明:焊接接头的硬度曲线呈现W型,硬度最低值出现在热影响区与热机影响区的交界处;和母材相比,焊接接头的局部抗腐蚀性能降低,应力腐蚀敏感性增大。热机影响区的腐蚀电位最低,腐蚀电流密度最高,晶间腐蚀深度最大,抗腐蚀性能最差。热机影响区的硬度和腐蚀性能的降低,主要是由于该区的晶粒发生变形,大部分η′沉淀强化相溶解,晶界上分布着大量的η相。
关键词:Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金;搅拌摩擦焊接;显微组织;力学性能;局部腐蚀
中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
Microstructure, mechanical properties and localized corrosion property of friction stir welded joint of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy
YE Rui1, YANG Ji-dong1, PENG Xiao-yan1, XU Guo-fu1, 2, 3, YIN Zhi-min1, 2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Nonferrous Materials Science and Engineering, Ministry of Education,
School of Material Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Research Institute of Powder Metallurgy,
Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The mechanical properties and localized corrosion of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy friction stir welded joint were investigated by hardness testing, polarization curve testing, corrosion immersion testing and slow strain rate tensile testing. Moreover, the microstructure of the welded joint was characterized by optical microscopy and the transmission electron microscopy. The results show that the hardness curve of the welded joint exhibits “W” shape, and the lowest hardness appears in the transition zone between heat affected zone(HAZ) and thermo-mechanical affected zone (TMAZ). Compared with the base material, the localized corrosion resistance of the welded joint decreases, and the stress corrosion cracking susceptibility increases. The TMAZ exhibits the lowest corrosion potential, the highest current density, the largest intergranular corrosion depth and the lowest corrosion resistance. During welding, most η′ phase dissolves and a number of η phase is located at grain boundaries in the grains of TMAZ, which leads to the decrease of hardness and corrosion resistance.
Key words: Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy; friction stir welding; microstructure; mechanical property; localized corrosion
Al-Zn-Mg系合金经过热处理后强度大大提高,同时具有良好的焊接性能和耐蚀性,广泛用作航空航天、交通运输等行业的结构材料[1-3]。微合金化是进一步提升Al-Zn-Mg系合金综合性能的重要且有效途径之一。20世纪70年代,全俄轻合金研究院研究发现向Al-Zn-Mg系合金中添加微量Sc元素可显著提高其力学性能、抗应力腐蚀性性能,并改善焊接性能[3],因为Sc元素与Al元素形成的Al3Sc颗粒可细化晶粒、抑制再结晶[4-5]。但Sc元素的价格高,在一定程度上限制其的广泛应用。Sc、Zr的复合添加能够形成Al3(Sc,Zr)弥散相,能够更有效地细化晶粒、抑制再结晶、提高Al-Zn-Mg系合金的综合性能[3-4, 6],还可减少Sc元素的添加量,从而引起了广泛的关注。
作为结构材料,良好的焊接性能通常必不可少,因为在实际应用中往往需要对Al-Zn-Mg系合金进行连接。搅拌摩擦焊(Friction stir welding,简称 FSW)是由英国焊接研究所 TWI 于 1991 年研发的一种新型固态连接技术,相对于传统熔焊焊接方式其具有诸多优势,如连接温度低、焊后残余应力小、接头性能高等[1, 7-11],可实现Al-Zn-Mg系合金的高效连接。国内外对搅拌摩擦焊工艺也已经做了大量的研究,例如搅拌针旋转速度、焊接速度、焊接热等对接头组织的影响[11-12]。Al-Zn-Mg系合金搅拌摩擦焊焊接头常常可分为焊核区(WNZ)、热机影响区(TMAZ)和热影响区(HAZ) 3个区域,每个区域的显微组织往往不同,从而造成力学性能及局部腐蚀性能的不均匀[7, 9]。诸多研究表明,其搅拌摩擦焊焊接头腐蚀最严重的区域也不尽相同,对于合金AA2024-T351搅拌摩擦焊接接头,当搅拌针旋转速度低时,最严重的区域为焊核区,而当速度较高时,腐蚀最严重的区域就变为热影响区[13];对于合金AA7108 T79搅拌摩擦焊接接头[14],腐蚀最为严重的区域为热机影响区。
但是纵观国内外的研究,对新型Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr搅拌摩擦焊接接头中各区域的显微组织及其腐蚀性能的影响却鲜有研究。因此,为了提升Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金搅拌摩擦焊的综合性能,必须进一步分析Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金搅拌摩擦焊接接头中显微组织对性能影响的机理。本文作者对一种含钪锆的Al-Zn-Mg合金搅拌摩擦焊接接头的显微组织、力学性能与局部腐蚀性能进行了全面的研究和分析,力求为该合金在航空航天的应用提供理论基础。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料
实验材料是由东北轻合金有限公司提供的2mm厚T6态Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金板材,其化学成分为Al-5.7Zn-1.98Mg-0.33Cu-0.25Sc-0.10Zr-0.18Fe-0.11Si-0.32Mn(质量分数,%)。搅拌摩擦焊接选用螺旋形搅拌针,其直径与母材(BM)的相同,都是2 mm,旋转速度为600 r/min,焊接方向平行于母材的轧向,采用单面焊,焊速为20 mm/min。
1.2 实验方法
焊接接头的硬度测试在HB-3000型布氏硬度计上进行,压头直径为2.5 mm,负荷为612.9 N,加载时间为30 s,沿垂直焊接方向在焊缝上表面测量硬度,获得焊接接头区域不同部位的硬度。
采用慢应变速率拉伸(SSRT)试验来评价母材和焊接接头的抗应力腐蚀能力,试验根据GB/T 15970.7—2000在LETRY公司生产的应力腐蚀试验机上进行,拉伸方向垂直于焊接方向,试样标距为15 mm,拉伸应变速率为 9×10-4 mm/min。试验在室温下进行,介质环境分别为干燥空气和3.5% NaCl溶液(质量分数)。并利用FEI Sirion200型扫描电镜对应力腐蚀试样断口进行观察和分析。
根据GB/T 7998—2005进行晶间腐蚀(IGC)实验,腐蚀介质为57 g NaCl+10 mL H2O2(ρ=1.01 g/mL),加入蒸馏水制备1 L的腐蚀溶液,试验温度保持在(35±2) ℃,浸泡时间24 h。整个焊接接头(50 mm×5 mm×2 mm)经30% HNO3溶液浸泡,蒸馏水冲洗后吹干,截取其横断面,制成金相试样,在Leica公司生产的DMIL LED型倒置金相显微镜下观察其横截面晶间腐蚀情况。极化曲线测试是在Im6ex型电化学工作站上进行,采用的三电极体系,工作电极为接头各个区域的样品裸露面,辅助电极为铂电极,参比电极为饱和甘汞电极[7],实验溶液为剥落腐蚀溶液,扫描速率为1 mV/s。
焊接接头试样经粗磨、细磨和机械抛光后,用Keller试剂进行浸蚀,干燥后在倒置金相显微镜下观察各个区域的晶粒大小、形貌等。在母材以及焊接接头不同区域取透射电镜(TEM)试样,机械减薄至约100 μm后,在V(HNO3):V(CH3OH)=1:3的混合溶液中双喷电解减薄,利用液氮将温度控制在-10 ℃以下。在FEI公司生产的TECNAI G220型透射电镜下观察试样,加速电压为 200 kV,主要观察母材以及焊接接头不同区域的晶粒和晶界以及其析出相的大小、形貌、分布等。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 显微组织
图1所示为Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金焊接接头的金相照片。由图1(a)所示,整个焊缝区呈碗状,热机影响区的组织在前进侧(AS)和后退侧(RS)有所不同,前进侧分区界限明显而窄(见图1(c)),而后退侧的分区界限不明显,靠近前进侧的更加明显。焊核区由于搅拌针的强烈搅拌作用,为细小的等轴状晶粒,如图1(b)所示;热机影响区由于受到剧烈的塑性变形和焊接循环热的双重作用,包含了大量的变形晶粒,如图1(c)所示;在热影响区,由于只受到少量焊接热循环的作用,因此晶粒组织与母材的类似,为纤维状组织,如图1(d)和(e)所示。此外,从图1中还能看到许多黑色的初生相粒子,这些粒子在母材区和热影响区中大都沿轧向呈链状分布。在热机影响区和焊核区中,这些粒子由于搅拌针的搅拌作用而被破碎,尺寸变小;在热机影响区中粒子分布显示出金属塑性流动的特征,而在焊核区中分布较弥散、均匀。
图2所示为Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金母材的TEM像。由于合金中添加了Sc、Zr元素,形成的高密度的Al3(Sc,Zr)弥散粒子可钉扎位错及晶界[15],强烈地抑制再结晶,得到几乎完全的未再结晶组织或强烈的回复组织(见图1(e))。因此,在图2(a)中,可观察到大量细小的亚晶粒,尺寸大都小于1 μm,并且一些亚晶内部还能观察到大量的位错。由于经过时效处理,基体中被大量细小的沉淀强化相所覆盖,如图2(b)所示。大部分的晶界上的第二相较粗大,尺寸约为20 nm,呈不连续分布状态,晶界附近有较明显的无沉淀析出带(PFZ),宽度约为16 nm。

图1 Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金焊接接头不同区域的金相照片
Fig. 1 OM images of friction stir welded joint of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy at different zones

图2 Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金母材的TEM像
Fig. 2 TEM images of base materials
图3所示为Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金焊接接头不同区域的TEM像。对比图2和图3可以发现,经过搅拌摩擦焊接后,母材的显微组织发生了变化。热影响区在焊接时只受到热循环的作用,虽然在金相显微镜下观察到与母材类似的纤维状组织,但其中的亚晶粒发生了一定程度的长大,与焊核区越近,温度越高,因此亚晶尺寸越大,如图3(a)所示。对比图2(a)和图3(a)可知,热影响区的亚晶粒尺寸明显更大,可达2.5 μm左右。基体中的沉淀强化相出现粗化,如图3(b)所示,一些晶界上的第二相也发生了粗化,尺寸变大(约50 nm);第二相之间的距离增加,晶界无沉淀析出带的宽度为25 nm。焊接时热机影响区受到机械力和热的双重作用,发生了一定程度的塑性变形;由于在较高温度下,发生了动态回复,很多的亚晶界不是很清晰,如图3(c)所示。基体中η′沉淀强化相大部分被溶解[7],少数残留的强化相尺寸也变大,如图3(d)所示。大部分晶界上析出了第二相,但尺寸较小,在23 nm左右,且多呈不连续分布状态;由于基体中基本没有η′沉淀强化相,晶界附近也观察不到无沉淀析出带。焊核区在焊接时受到搅拌针强烈的搅拌作用并且温度很高,不仅发生强烈的塑性变形,而且观察到大量细小的等轴晶粒,尺寸约为1 μm,如图3(e)所示。这些细等轴晶是由于焊核区在焊接时发生了动态再结晶形成的。在一些晶粒内部可看到一些较大的黑色第二相粒子,尺寸大约为150 nm,可能是一些初生相在搅拌针高速旋转的作用下被破碎而形成的。晶内的η′沉淀强化相和晶界的第二相几乎完全溶解,如图3(f)所示,但晶内仍可看到许多马蹄状Al3(Sc,Zr)粒子,这说明这些粒子的热稳定性非常好;另外一些粒子位于晶界而阻碍其迁移,起到细化晶粒的作用。
2.2 硬度分布
图4所示为Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金搅拌摩擦焊接接头中的硬度分布曲线。由图4可知,焊接接头的硬度曲线呈典型的“W”形状[16-17]。母材的硬度值最高,并从母材向焊接接头中心方向(即热影响区)硬度逐渐下降;而且在距离中心7mm左右时,热机影响区的硬度达到最低值,约为141HB;但是焊核区的硬度又会升高,大约为155HB。
焊接接头的硬度分布与其中不同区域的显微组织特征密切相关。Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金是可热处理强化合金,时效后基体中形成大量的纳米级GP区η′沉淀强化相可显著提高其强度和硬度;并且细小GP区η′沉淀强化相的数量越多,强化效果越好。母材为T6态,基体中析出了高密度的η′沉淀强化相(见图2),显然具有良好的强化作用,另外其中的亚晶粒也十分细小,也对硬度有一定的贡献,因此此区域硬度最高。热影响区中基体的η′沉淀强化相粗化(见图3),亚晶也粗化,因此硬度必然降低;而且离焊核区越近,温度越高,这种粗化现象越严重;并且逐渐远离焊缝中心,加工硬化逐渐减弱,因此硬度呈现出不断下降的趋势,到达热机影响区与热影响区分界处,硬度值最低。热机影响区大部分的η′沉淀强化相溶解,残留的少量强化相尺寸大,显然强化效果低,另外是由于在晶界上析出了一些第二相(见图3(d)),基体中的过饱和度降低,在后续室温停放过程中能形成的GP区少。焊核区的晶粒细小,焊接时η′沉淀强化相基本都溶解至基体中,可形成高过饱和度的固溶体,后续室温停放时能析出更多的GP区,因此和热机影响区相比,焊核区的硬度值更高。

图3 Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金焊接接头中不同区域的TEM像
Fig. 3 Low magnification((a), (c), (e)) and high magnification((b), (d), (f)) TEM images of friction stir welded joints at different zones
2.3 局部腐蚀性能
2.3.1 极化曲线和晶间腐蚀浸泡结果

图4 Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金搅拌摩擦焊接接头的硬度分布
Fig. 4 Hardness distribution in friction stir welded joint of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy

图5 Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金搅拌摩擦焊接接头不同区域的极化曲线
Fig. 5 Polarization curves of friction stir welded joint of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy at different zones
表1 Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金搅拌摩擦焊接接头不同区域的极化参数
Table 1 Polarization parameters of friction stir welded joint of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy at different zones
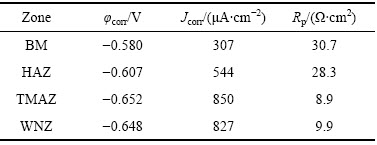
图5所示为焊接接头不同区域的极化曲线。通过CView 2.0软件对这些曲线进行分析,可以得到腐蚀电位(φcorr)、腐蚀电流密度(Jcorr)和极化电阻(Rp),结果列于表1。据这些结果可知,母材的φcorr和Rp最大,Jcorr最小;热影响区的φcorr和Rp减小,Jcorr升高;热机影响区和焊核区的φcorr和Rp显著减小,而Jcorr显著升高。一般而言,φcorr越高,腐蚀倾向越小,Rp越大,Jcorr越小,腐蚀速度越小。因此,据表1中的结果,可以认为不同区域耐蚀性能的高低顺序应为:母材、热影响区、焊核区、热机影响区。
焊接接头试样放入晶间腐蚀溶液时,表面很快就有气泡产生,且随着时间的延长反应更加剧烈,浸泡2 h后气泡数量增多,试样表面也发生变化,逐渐由金属原色变为黄褐色,尤其是在焊核区和热机影响区。浸泡6 h后拿出试样,观察到焊接接头试样不同区域的腐蚀情况不同,焊核区和热机影响区的腐蚀程度较热影响区和母材区更为严重。图6所示为Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金焊接接头不同区域以及母材晶间腐蚀浸泡后截面的显微组织。由图6(a)和(b)可知,焊核区和热机影响区基本上都发生了腐蚀,焊核区的最大腐蚀深度约为42.1 μm,热机影响区的最大腐蚀深度达72.9 μm。在热影响区,只有极少数的位置发生了腐蚀,最大深度约12.5 μm,如图6(c)所示。而在母材区基本上观察不到明显的腐蚀,如图6(d)所示。这些结果与前述极化曲线测试的结果具有较好的一致性。
2.3.2 慢应变速率拉伸结果
图7所示为母材及搅拌摩擦焊接接头在空气及3.5% NaCl溶液中的慢应变速率拉伸曲线。表2所列为慢应变速率拉伸试验结果。应力腐蚀敏感因子可通过式(1)计算[18]:
 (1)
(1)
式中:ISSRT为应力腐蚀敏感因子,数值越大则应力腐蚀敏感性越大,数值越小则应力腐蚀敏感性越小。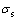 、
、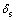 分别为腐蚀介质下的抗拉强度和伸长率;
分别为腐蚀介质下的抗拉强度和伸长率; 、
、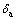 分别为空气中的抗拉强度和伸长率。
分别为空气中的抗拉强度和伸长率。
由图7和表2中的结果可知,无论是在空气中还是在NaCl溶液中,母材的强度和伸长率均比焊接接头的要高。在NaCl溶液浸泡时,晶界上η相极易被腐蚀,而与此同时外力的作用又会加速η相粒子的溶解,导致腐蚀裂纹沿着晶界快速扩展而使材料提前发生断裂,强度和塑性下降。相比于在空气中拉伸,母材及其搅拌摩擦焊接接头在3.5% NaCl溶液中拉伸的拉伸强度、屈服强度和伸长率均有不同程度的下降;其中伸长率的下降程度较大,母材的约为16.4%,而焊接接头的达到了35.5%。就断裂时间而言,母材的从空气中的70.3 h降至3.5% NaCl溶液中的59.1 h,降幅约为16%;而焊接接头的从64.1 h降至30.7 h,降幅达到了52%。母材的ISSRT为0.049,而焊接接头的为0.079。因此,综合上述结果可认为,经过搅拌摩擦焊接后Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金板材的应力腐蚀敏感性增加。

图6 Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金焊接接头不同区域以及母材晶间腐蚀浸泡后截面的显微组织
Fig. 6 Cross-sectional microstructures of friction stir weld joints and parent metals of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloys at different zones

图7 Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金母材及搅拌摩擦焊接接头的慢应变速率拉伸曲线
Fig. 7 Slow strain rate tensile curves of base metal(BM) and friction stir weld(FSW) of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy
图8所示为拉伸断口的SEM像及OM像。从图8(a)和(b)可知,母材在空气和NaCl溶液中拉伸断口上都可看到许多穿晶韧窝,一些大韧窝中有破碎状的第二相粒子,推测为初生相粒子(见图1),NaCl溶液中的拉伸断口中沿晶断裂的比例更高。相对于空气中的断口,焊接接头在NaCl溶液中的拉伸断口可以看到同样的变化趋势,而且由图8(d)可知,沿晶断裂的比例更高。由图8(e)可知,在空气中焊接接头拉伸后断裂位置在焊核区中心,是因为余高致使焊缝中心变为最薄的微区(见图1),板材厚度为2 mm,而焊缝中心的厚度只有1.85 mm。由图8(f)可知,在盐溶液中焊接接头拉伸后断裂位置在热机影响区与焊核区的分界处[19],在焊接过程中,此过渡区速度梯度比较大,组织缺乏平滑过渡[8]。此外,与合金母材相比,焊核区仍然是一个软化区,硬度仅略高于最小值。
表2 慢应变速率拉伸试验结果
Table 2 Results of slow strain rate tensile testing

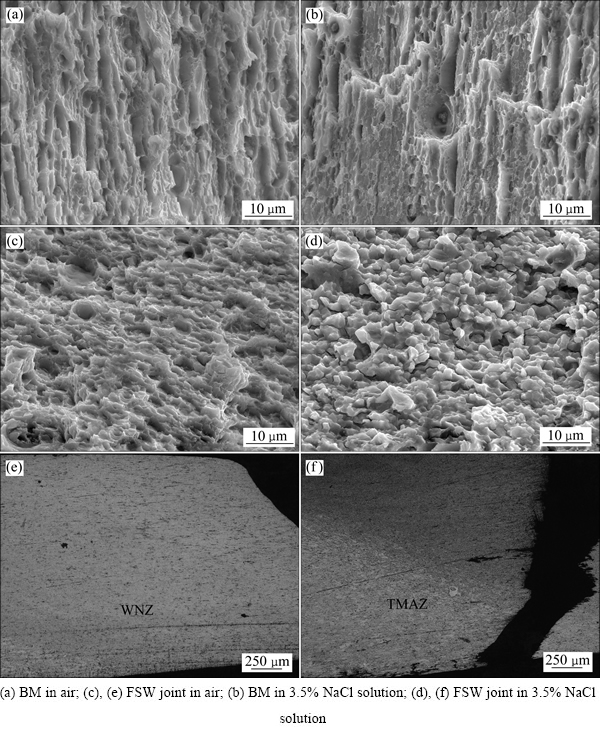
图8 Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金母材和搅拌摩擦焊接接头拉伸断口的SEM像以及搅拌摩擦焊接接头拉伸断口侧面的金相照片
Fig. 8 SEM images of fracture surface of BM and FSW joint of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy((a), (b), (c), (d)) and cross-sectional OM images of FSW joint((e), (f))
综合极化曲线测试、晶间腐蚀浸泡及慢应变速率拉伸结果可知,所研究的Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金板材经过搅拌摩擦焊接后局部腐蚀性能变差,腐蚀性能最差的位置应在热机影响区。晶间腐蚀及慢应变速率拉伸时裂纹扩展一般都沿着晶界萌生和扩展,因为晶界上分布的η相粒子常常为阳极相[20, 23],在NaCl溶液中极易被腐蚀(见图2)。显然,搅拌摩擦焊接接头的局部腐蚀性能变化主要与其中晶粒组织和晶界析出状态密切相关。由图1和图2可知,母材中包含了大量的亚晶组织,有研究表明[24],亚晶界往往较大角度晶界有更好的腐蚀抗力;另外,母材中大部分晶界上的第二相尺寸较大且分布不连续,无沉淀析出带较窄,这就有利于阻碍腐蚀沿晶界的快速扩展,减小腐蚀速率。因此,母材具有良好的耐蚀性能。其焊接接头中,无论是焊核区,还是热影响区和热机影响区,大角度晶界的数量增加,一定程度上降低了腐蚀抗力。在热机影响区中,大部分晶界上形成了更多的η相粒子,显然会降低该区域的耐蚀性能。另外,有研究表明[19],由于焊接时搅拌针的强烈搅拌和轴肩的摩擦导致的热机作用,会导致在焊接接头中合金元素分布和显微组织很不均匀,这不仅增加了晶界和晶内的电极电位差别,还导致不同区域之间的差别更大,尤其是热机影响区和焊核区分界处,如图1所示,组织突变明显。因此,此过渡区域耐蚀性能变差,而且导致Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金在搅拌摩擦焊接后应力腐蚀敏感性较母材的更高。
3 结论
1) Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金板材焊接接头中热影响区的一些亚晶发生长大,晶内沉淀强化相和晶界第二相粗化;热机影响区晶内大部分沉淀强化相发生溶解,而晶界析出大量第二相;焊核区为细小等轴晶粒,晶内可见明显的Al3(Sc,Zr)粒子,GP区起强化作用。
2) Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金板材焊接接头的硬度较母材有明显的下降,呈现W型,硬度最低值出现在热机影响区与热影响区的交界处,约为141 HB。硬度降低的主要原因是:晶内η′沉淀强化相的大量溶解,并随着远离焊缝中心距离增大其加工硬化逐渐弱化。
3) Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金板材焊接接头母材区的腐蚀电位最高,热机影响区的最低;热机影响区的腐蚀电流密度最大,母材区的最小;热机影响区的晶间腐蚀深度最大,为72.9 μm,母材区未见明显的晶间腐蚀;焊接接头慢应变速率拉伸的ISSRT值为0.079,高于母材区的0.049,焊接接头的应力腐蚀敏感性更高。
REFERENCES
[1] HEINZ A, HASZLER A, KEIDEL C, MOLDENHAUER S, BENEDICTUS R, MILLER W S. Recent development in aluminium alloys for aerospace applications[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 280(1): 102-107.
[2] LI J F, BIRBILIS N, LI C X, JIA Z Q, CAI B, ZHENG Z Q. Influence of retrogression temperature and time on the mechanical properties and exfoliation corrosion behavior of aluminium alloy AA7150[J]. Materials Characterization, 2009, 60: 1334-1341.
[3] 彭小燕, 曹晓武, 段雨露, 陈举飞, 徐国富, 尹志民. 7020铝合金 MIG焊焊接接头的组织与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(4): 912-918.
PENG Xiao-yan, CAO Xiao-wu, DUAN Yu-lu, CHEN Ju-fei, XU Guo-fu, YIN Zhi-min. Microstructures and properties of MIG welded joint of 7020 aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(4): 912-918.
[4] 姜 峰. Al-Mg-Sc中间合金制备及其应用研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2002: 1-95.
JIANG Feng. Study on the manufacture of AI-Mg-Sc master alloy and its application[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2002: 1-95.
[5] 尹志民, 潘清林, 姜 峰, 李汉广.钪和含钪合金[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2007: 1-581.
YIN Zhi-min, PAN Qing-lin, JIANG Feng, LI Han-guang. Scandium and its alloys[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2007: 1-581.
[6] SENKOV O N, SHAGIEV M R, SENKOVA S V, MIRACLE D B. Precipitation of Al3(Sc,Zr) particles in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Sc-Zr alloy during conventional solution heat treatment and its effect on tensile properties[J]. Acta Materialia, 2008, 56(15): 3723-3738.
[7] DENG Ying, YE Rui, XU Guo-fu, YANG Ji-dong, PAN Qin-lin, PENG Bing, CAO Xiao-wu, DUAN Yu-lu, WANG Ying-jun, LU Li-ying, YIN Zhi-min. Corrosion behaviour and mechanism of new aerospace Al-Zn-Mg alloy friction stir welded joints and the effects of secondary Al3ScxZr1-x nanoparticles[J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 90: 359-374.
[8] THOMAS W M, NICHOLAS E D, NEEDHAM J C, MURCH M G, TEMPLE S P, DAWES C J. Friction stir butt welding: China, 91259788[P]. 1991.
[9] 王国庆, 赵衍华. 铝合金的摩擦搅拌焊接[M]. 北京: 中国宇航出版社, 2010: 1-321.
WANG Guo-qing, ZHAO Yan-hua. Friction stir welding of aluminum[M]. Beijing: China Aerospace Press, 2010: 1-321.
[10] 陈 杰, 张 海, 刘德佳, 王小明. 我国搅拌摩擦焊接技术的研究现状和热点分析[J]. 电焊机, 2011, 41(10): 92-97.
CHEN Jie, ZHANG Hai, LIU De-jia, WANG Xiao-ming. Research progress and focus of friction stir welding in China[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2011, 41(10): 92-97.
[11] PARK J C, HAN S M, JANG S K, KIM S J. Optimum traveling and rotation speeds in friction stir welding for dissimilar Al alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(7): 1486-1490.
[12] RADISAVLJEVIC I, ZIVKOVIC A, RADOVIC N, GRABULOV V. Influence of FSW parameters on formation quality and mechanical properties of Al 2024-T351 butt welded joints[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(2): 3525-3539.
[13] JARIYABOON M, DAVENPORT A J, AMBAT R, CONNOLLY B J, WILLIAMS S W, PRICE D A. The effect of welding parameters on the corrosion behaviour of friction stir welded AA2024-T351[J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(2): 877-909.
[14] WADESON D A, ZHOU X, THOMPSON G E, SKELDON P, OOSTERKAMP L D, SCAMANS G. Corrosion behaviour of friction stir welded AA7108 T79 aluminium alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(4): 887-897.
[15] ZHANG Wei, XING Yuan, JIA Zhi-hong, YANG Xiao-fang, LIU Qing, ZHU Chang-luo. Effect of minor Sc and Zr addition on microstructure and properties of ultra-high strength aluminum alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(12): 3866-3871.
[16] POUGET G, REYNOLDS A P. Residual stress and microstructure effects on fatigue crack growth in AA2050 friction stir welds[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2008, 30(3): 463-472.
[17] HATAMLEH O, SINGH P M, GARMESTANI H. Corrosion susceptibility of peened friction stir welded 7075 aluminium alloy joints[J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51(1): 135-143.
[18] LI B, PAN Q L, ZHANG Z Y, LI C. Research on intercrystalline corrosion, exfoliation corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy[J]. Materials and Corrosion, 2013, 64(7): 592-598.
[19] LUMSDEN J B, MAHONEY M W, RHODES C G, POLLOCK G A. Corrosion behavior of friction stir welded AA7050- T7651[J]. Corrosion, 2003, 59(3): 426-432.
[20] TSAI T C, CHUANG T H. Role of grain size on the stress aluminum corrosion cracking of 7475 alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1997, 225(1): 135-144.
[21] NAJJAR D, MAGNIN T, WARNER T J. Influence of critical surface defects and localized competition between anodic dissolution and hydrogen effects during stress corrosion cracking of a 7050 aluminium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1997, 238(1): 293-302.
[22] 邓 英. 微量钪锆对高强耐蚀可焊铝锌镁合金组织和性能的影响[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012: 1-141.
DENG Ying. Effects of minor Sc and Zr additions on the microstructures and properties of high-strength, corrosion- resistant and weldable Al-Zn-Mg alloys[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012: 1-141.
[23] WADESON A, ZHOU X, THOMPSON G E, SKELDONA P, DJAPIC O L, SCAMANS G. Corrosion behavior of friction stir welded AA7108-T79 aluminium alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(4): 887-897.
[24] 张 茁, 陈康华, 方华婵. 微量Cr和Nb对Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金力学性能和应力腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(6): 985-990.
ZHANG Zhuo, CHEN Kang-hua, FANG Hua-chan. Effects of trace Cr and Nb additions on mechanical properties and stress corroded cracking of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr aluminium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(6): 985-990.
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(G2005CB623705);中南大学粉末冶金国家重点实验室开放基金资助课题
收稿日期:2015-03-03;修订日期:2015-06-08
通信作者:徐国富,教授,博士;电话:0731-88877217;E-mail: csuxgf66@csu.edu.cn