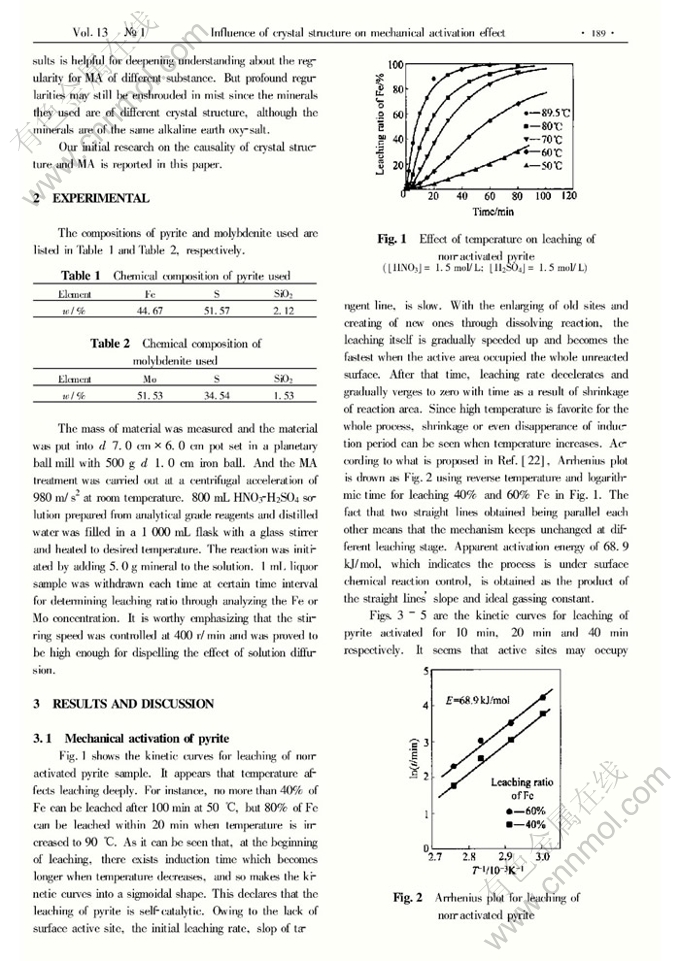
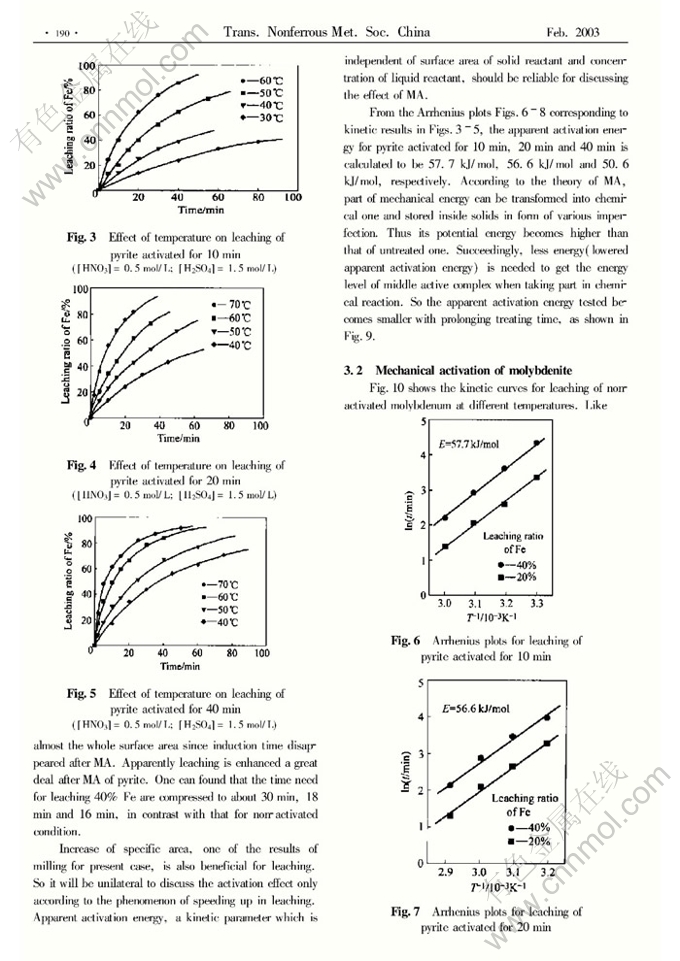
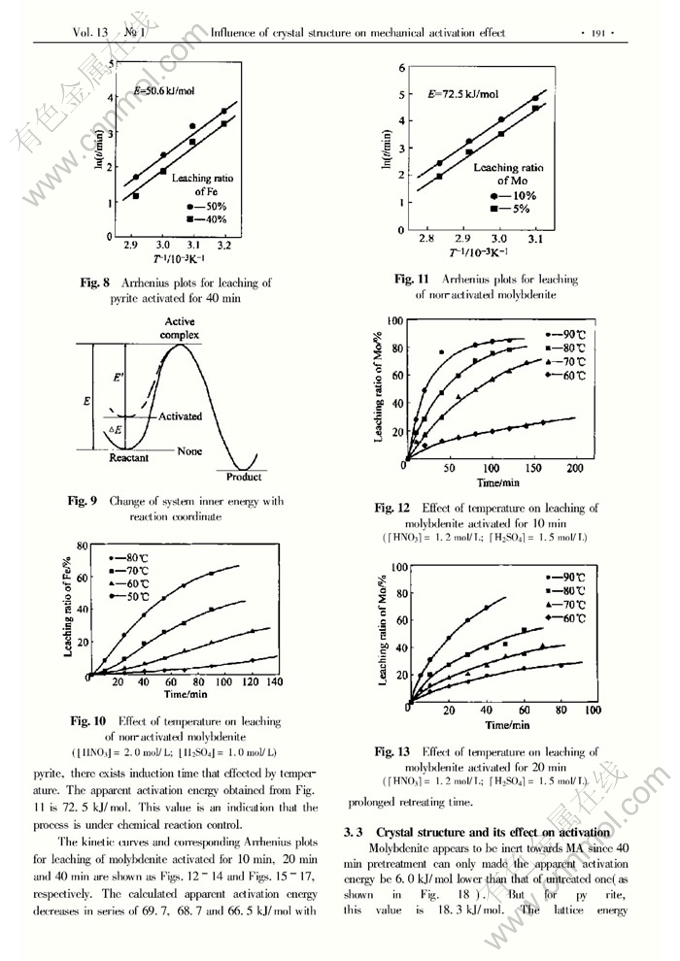
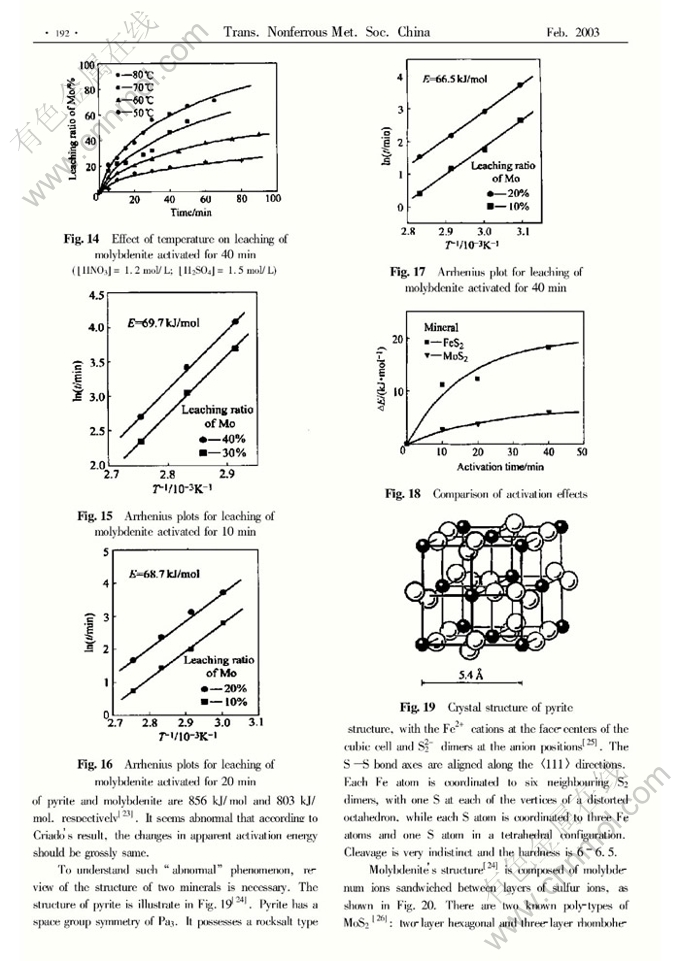
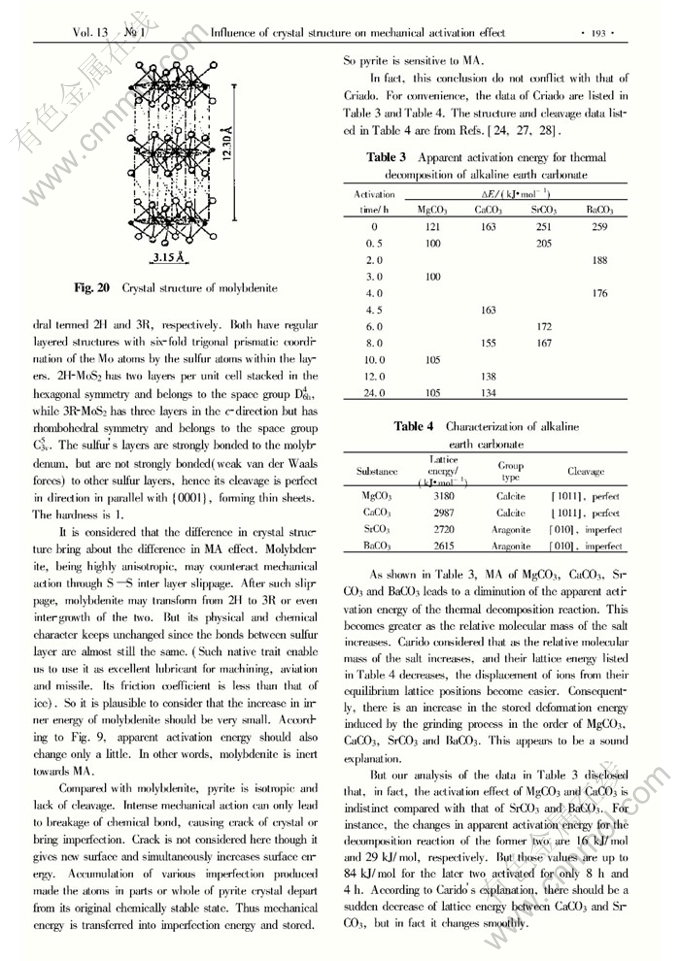
Influence of crystal structure on mechanical activation effect
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2003年第1期
论文作者:赵中伟 李洪桂 孙培梅 李运姣 霍广生
文章页码:188 - 194
Key words:mechanical activation; crystal structure; apparent activation energy
Abstract: The effect of mechanical treatment on pyrite and molybdenite was studied. After mechanically activated for 40min under the same condition, the apparent activation energy for leaching reaction of layer-structured molybdenite in HNO3-H2SO4 solution becomes 6.0kJ/mol lower than that for untreated one; while for isotropic pyrite, this value is 18.3kJ/mol. Pyrite seems to be more sensitive towards mechanical activation. Resorting to the difference in crystal structure, it is considered that anisotropic molybdenite may obviate violate mechanical action through inter-layer slippage, while isotropic pyrie can not. So the action may damage pyrite crystal and produce large amount of lattice imperfection. Consequently, more mechanical energy is absorbed by pyrite crystal. So it is one-sighted to consider the mechanical activation effect according to only crystal lattice energy. Crystal structure, isotropy or anisotropy, is an important parameter which affects a lot.