文章编号: 1004-0609(2006)03-0550-05
结晶器含钛无氟保护渣的粘度和熔化特性
刘永庆, 唐 萍, 文光华, 张明熹
(重庆大学 材料科学与工程学院, 重庆 400044)
摘 要: 以CaO-SiO2-TiO2渣系为基础配制了含钛无氟结晶器保护渣, 为建立和优化配置规律, 通过实验测定熔渣的粘度和熔点, 研究了含钛无氟保护渣熔化特性与助熔剂、 TiO2含量及二元碱度之间的关系。 结果表明: B2O3和碱金属Na2O、 Li2O均能有效降低粘度和熔点,其中以B2O3作用最为明显; TiO2含量为6%时, 粘度和熔点均呈最小值。 在4%~10%范围内, MgO可降低粘度, 但会使熔点升高; 含量〈3%时, MnO可降低粘度, 含量超过5%则会同时使粘度和熔点增加。
关键词: 二氧化钛; 无氟结晶器保护渣; 粘度; 熔点 中图分类号: TF777.1
文献标识码: A
Viscosity and melting properties of fluoride-free and titanium-bearing mold fluxes
LIU Yong-qing, TANG Ping, WEN Guang-hua, ZHANG Ming-xi
(College of Materials Science and Engineering, Chongqing University,
Chongqing 400044, China)
Abstract: Fluorine mostly comes from mold powders during the continuous casting process. Developing and using fluoride-free mold powders is of importance to the environmental protection. Fluoride fluxes were confected based on the CaO-SiO2-TiO2 slag system. In order to establish and optimize the confect rule of fluoride-free fluxes, the relationship between the melting properties of fluoride-free mold fluxes and fusing reagents, binary basicity and TiO2 content was investigated by measuring the viscosity and melting point of the melted slag. The experimental result indicates that the effective compositions in lowering the viscosity and melting point are B2O3, Na2O and Li2O, in which the effect of B2O3 is the most remarkable; When the content of titanium is 6% in mass, both the viscosity and melting point show the minimum, If the content of MgO is 4%-10%, it can reduce the viscosity but increase the melting point. MnO can help to reduce the viscosity when the content of MnO〈3%, but to increase the viscosity and melting point when the content of MnO>5%.
Key words: titanium; fluoride-free mold fluxes; viscosity; melting point
连铸过程中, 保护渣对于保证连铸顺利进行和提高铸坯表面质量扮演着十分重要的角色。 保护渣在钢液面上吸收钢水热量熔化后流入结晶器壁与凝固坯壳之间, 起到改善润滑与控制传热的作用[1]。 传统保护渣中均加入5%~15%的氟化物如萤石、 冰晶石等以降低粘度和熔化温度, 来保证有效的润滑。 高碱度下, CaF2可促使保护渣析出枪晶石(3CaO·2SiO2·CaF2)晶体, 进而控制结晶器与凝固坯壳间的传热热阻, 这一作用在浇注板坯及裂纹敏感性钢种时尤为重要[2, 3]。 但渣中氟化物有20%~30%会溶入二冷水中, 使其呈酸性, 造成水质污染, 加剧铸机腐蚀和水口侵蚀。 因此, 有必要研制新型的环保无氟保护渣[4-9]。
无氟保护渣以CaO-SiO2-TiO2三元渣系为基础, 配以多种助熔剂及炭质材料制成。 TiO2在一定碱度下能够与CaO作用析出钙钛矿(CaO·TiO2)晶体, 可以替代含氟保护渣中的枪晶石, 控制结晶器铜壁和凝固坯壳间的传热[10, 11]。 由于保护渣必须具有适当的粘度和熔化温度, 以保证良好的润滑和绝热保温性能[12, 13]。 因此, 为获得含TiO2无氟保护渣的配制规律, 通过实验研究了含TiO2无氟保护渣中Na2O、 Li2O、 MgO、 MnO、 B2O3和TiO2等成分及二元碱度(R=CaO/SiO2)对粘度和熔化温度的影响规律。
1 实验
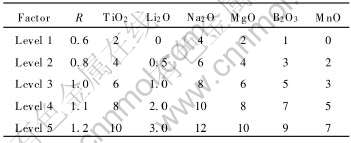
保护渣实验样以含钛高炉渣、 水泥熟料、 硅灰石为基本原料, 配加了苏打(Na2CO3)、 硼砂(B2O3)、 镁砂(MgO)、 碳酸锂(Li2CO3)、 锰矿粉(MnO)等熔剂。 实验通过正交设计方法研究CaO-SiO2-TiO2渣系中5种助熔剂(Li2O, Na2O, B2O3, MgO, MnO)、 二元碱度(R)和二氧化钛含量对无氟保护渣粘度和熔化温度的影响规律, 设计了七因素五水平的正交表[14], 各因素及水平列于表1。
表1 正交实验因素水平表
Table 1 Factor and level of orthogonal test (mass fraction, %)
实验采用旋转粘度计测定熔渣的粘度, 过程在MoSi2高温炉内进行。 炉膛温度恒定在1300℃。 实验时, 温度升至1200℃左右时开始将250g粉状保护渣样分批加入石墨坩埚内熔化。 待完全熔化后将温度稳定在1300℃, 开始测定粘度, 记录20个粘度数据取平均值, 即为保护渣在1300℃时的粘度值, 绝对误差为±0.005Pa·s。 保护渣的熔点用半球点法测定, 被测试样用样模及制样锤打结为d3mm×3mm的渣柱, 放置于送样管中的刚玉载片上, 送入铂丝炉加热, 升温速度控制在20℃/min左右, 当临近熔点约50℃内时, 升温速度降至约5℃/min。 以半球点温度定义保护渣的熔化温度。
2 结果与分析
通过正交实验对实验结果进行直观分析, 得出各因素对保护渣粘度和熔化温度的影响规律, 分析结果列于表2。 从表2可知, 对含钛无氟保护渣粘度影响的主次因素顺序为: B2O3>R>MnO>TiO2>MgO>Li2O>Na2O; 对熔化温度的主次因素顺序为: B2O3>Li2O>Na2O>TiO2>MgO>R>MnO。
2.1 碱度和TiO2与保护渣粘度和熔化温度的关系
碱度对粘度和熔点的影响如图1所示。 可见, 随二元碱度R在0.6~1.2范围内增大, 无氟熔渣于1300℃的粘度值呈先降后升趋势, 在R为0.9左右时, 达到极小值, 约为0.18Pa·s; 熔化温度则随碱度增加而升高。 碱度升高意味着CaO含量增加或SiO2含量降低, 连铸保护渣的氧硅比增大, 使渣中非桥氧增多, 硅氧复杂阴离子团被离解, 结构趋于简单, 熔渣粘度减小。 可以解释R小于0.90时随R增加无氟熔渣粘度降低。 而当R大于0.90时, 在测试温度下, 随碱度增大CaO含量增加, CaO与渣中TiO2作用形成早期析出的钙钛矿(熔点, 1970℃), 导致形成树枝状和网状结构的固溶体, 恶化渣的流动性, 增大熔渣的表观粘度。 因此, 从获得低的粘度和熔化温度角度考虑, 含钛无氟渣中R值应控制在0.8~1.1之间。 超出该范围会使粘度和熔化温度大幅增加, R增加0.1可使无氟熔渣粘度升高约0.3Pa·s, 使熔化温度升高约10℃。
表2 实验结果直观分析
Table 2 Visual analysis of experimental results
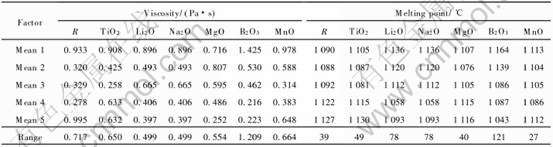
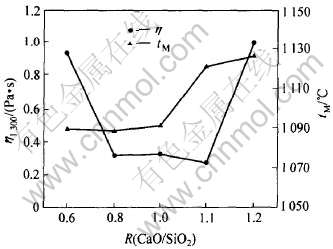
图1 碱度对粘度和熔点的影响
Fig.1 Effect of basicity on viscosity and melting point
图2所示为TiO2含量对粘度和熔点的影响。 由图2可知, 当TiO2的含量小于6%时, TiO2含量增加可降低无氟渣粘度, 当TiO2含量大于6%时, 粘度则随着TiO2含量的增加而增加。 TiO2对无氟渣熔点的影响规律与其对粘度的影响相似, TiO2含量为6%时熔点得到最小值。 中性条件下,
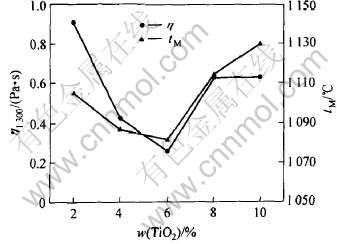
图2 TiO2含量对粘度和熔点的影响
Fig.2 Effect of TiO2 content on viscosity and melting point
TiO2含量较低时对熔渣具有稀释作用, TiO2进入液渣中, 由于钛离子(Ti4+, 1.85nm-3)场强明显小于硅离子场强(Si4+, 2.44nm-3), 对氧离子的束缚能力较小, 从而表现出氧离子部分解离的倾向, 并且Ti4+不会象Si4+那样构成复杂的阴离子团, 因而有利于渣中复杂硅氧离子团趋向简单结构, 促使熔渣粘度降低[8]。 当TiO2含量大于6%时, 保护渣早期析出钙钛矿的趋势增大[15], 作为高熔点矿物离散在无氟熔渣中, 致使粘度升高。 因此含钛无氟渣中TiO2含量应在4%~8%范围内, 能够获得好的理化性能。
2.2 Na2O和Li2O与保护渣粘度和熔化温度的关系
图3所示为Na2O含量对粘度和熔点的影响。 可以看出, 随Na2O含量的升高无氟渣的粘度值减小, 平均增加1%的Na2O可使粘度降低约0.05Pa·s。 在含量小于10%时, Na2O也可使熔化温度降低。 Na2O为网链结构限制体, Na+和O2-均可以破坏硅酸盐复杂网链结构, 增加熔渣的流动性, 降低粘度。
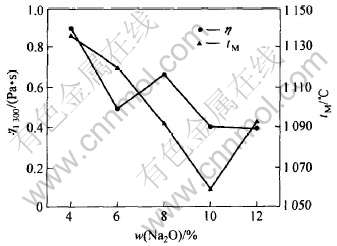
图3 Na2O含量对粘度和熔点的影响
Fig.3 Effect of Na2O content on viscosity and melting point
图4所示为Li2O含量对粘度和熔点的影响。 图4表明, 随Li2O含量的提高, 无氟保护渣粘度降低。 Li2O与Na2O均为碱金属氧化物, 因此在熔渣中的作用机理相似, 加入Li2O可提供非桥氧, 破坏硅氧四面体结构, 降低粘度。 Li2O能和保护渣中的大部分组分形成低熔点相, 大幅度降低保护渣的熔化温度, 0.5%的Li2O可使无氟渣熔点降低约22℃。 适宜加入量为Li2O小于2%。
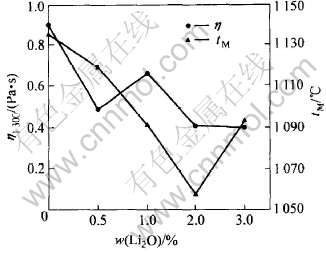
图4 Li2O含量对粘度和熔点的影响
Fig.4 Effect of Li2O content on viscosity and melting point
2.3 MgO和MnO与保护渣粘度和熔化温度的关系
图5所示为MgO含量对粘度和熔点的影响。 可见, MgO含量小于4%时对含钛无氟渣粘度影响较小。 在4%~10%范围内, 每1%的MgO可使粘度降低约0.1Pa·s。 MgO加入量从2%升至4%, 保护渣的熔点降低了约24℃。 但继续增加又使熔点大幅升高。 MgO对粘度的影响分两方面: 一方面Mg2+和Na+、 K+、 Li+等碱金属离子一样能使硅氧负离子团解聚使粘度降低; 另一方面, Mg2+的电价数较大而半径又不大, 因此, 其离子势较Na+、 K+、 Li+大, 能夺取硅氧负离子团中的O2-来包围自己, 导致硅氧负离子团聚合如2[SiO4]4-[FY][Si2O7]6-+O2-, 使硅氧负离子团网络结构复杂, 粘度增大。
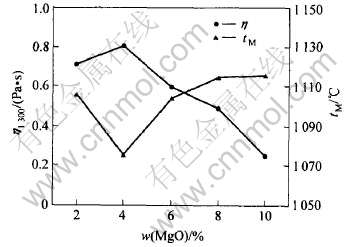
图5 MgO含量对粘度和熔点的影响
Fig.5 Effect of MgO content on viscosity and melting point
图6所示为MnO含量对粘度和熔点的影响。 由图6可知, 在MnO含量小于3%时, 降低粘度; 在大于3%时则使粘度升高。 MnO对熔化温度的影响较小, MnO其含量从0增至5%, 熔点降低了约18℃, 含量从5%增至8%, 熔点升高了约18℃。 无氟渣中MnO加入量宜在4%~6%之间。
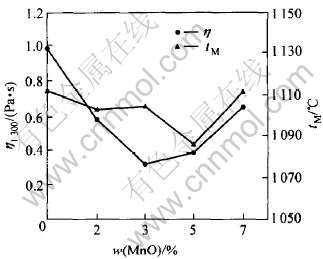
图6 MnO含量对粘度和熔点的影响
Fig.6 Effect of MnO content on viscosity and melting point
2.4 B2O3与保护渣粘度和熔化温度的关系
图7所示为B2O3含量对粘度和熔点的影响。 可见, 在0~9%的范围内, B2O3可显著降低保护渣的熔点和粘度, 平均每1% 的B2O3可降低粘度0.2Pa·s, 降低熔点约15℃。 B2O3是一种低熔点的助熔剂(450℃), 易形成低共熔物, 极大地提高保护渣的过热度, 使复合阴离子团因热振动的加剧而解体, 进而降低熔渣的粘度和熔化温度。 而

图7 B2O3 含量对粘度和熔点的影响
Fig.7 Effect of B2O3 content on viscosity and melting point
B2O3是酸性氧化物, 属于网络形成体, 因此加入量超过7%时渣的粘度略有升高。 添加适量的B2O3, 能够获得高速连铸结晶器保护渣需要的低粘度, 该结论与王新月等[16]研究结果一致。 直观分析结果显示, 在配加的助熔剂中B2O3降低粘度和熔化温度的作用均最强。 因此, 无氟保护渣中加B2O3可以代替CaF2有效降低含钛无氟渣的粘度和熔点。
REFERENCES
[1]Mills K C, Fox A B, Li Z, et al. Performance and properties of mould fluxes[J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2005, 32(1): 26-33.
[2]文光华, 迟景灏, 王谦, 等. 亚包晶钢连铸板坯表面纵裂纹的研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1999, 20(3): 1-5.
WEN Guang-hua, CHI Jing-hao, WANG Qian, et al. Investigation on surface longitudinal crack of continuous cast slab of peritectic steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1999, 20(3): 1-5.
[3]Masahito H, Masayuki K, Masashi H, et al. Mold flux for high speed continuous casting of hypo-peritectic steel slabs[J]. The Journal of the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, 2002, 88(1): 23-28.
[4]茅洪祥, 胡汉涛, 马国军. 连铸保护渣对环境的氟污染及其对策[J]. 炼钢, 1999, 15(3): 41-46.
MAO Hong-xiang, HU Han-tao, MA Guo-jun. Contamination of fluorine in CC mould powder to environment and counter measures[J]. Steelmaking, 1995, 15(3): 41-46.
[5]张传兴. 连铸用无氟保护渣的研究[J]. 耐火材料, 1998, 32(2): 121.
ZHANG Chuan-xing. Study of free-fluoride mold powder for continuous casting[J]. Refractories, 1998, 32(2): 121-122.
[6]Pinheiro C A, Samarasekera I V, Brimacombe J K. Mold flux for continuous casting of steel[J]. Iron & Steelmaker (I&SM), 1995, 22(12): 43-44.
[7]韩文殿, 仇圣桃, 朱果灵. 无氟结晶器保护渣的发展[J]. 钢铁研究, 2003(2): 53-56.
HAN Wen-dian, QIU Sheng-tao, ZHU Guo-ling. Development of free-fluoride mold powder[J]. Research on Iron & Steel, 2003(2): 53-56.
[8]Chang S H, Lee I J, Kim M R, et al. Development of new mold fluxes at Pohang works[A]. Conference on Continuous Casting of Steel in Developing Countries[C]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1993. 832-841.
[9]Choi S Y, Lee D H, Shin D W, et al. Properties of F-free glass system as a mold flux: viscosity, thermal conductivity and crystallization behavior[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 345(3): 157-160.
[10]WEN Guang-hua, TANG Ping, ZHANG Li-feng, et al. Study of free-fluoride mold powder based on titanium-bearing blast furnace slag[A]. AIST/TMS Proceedings[C]. New Oreleans: Association for Iron and Steel Technology, 2004. 69-73.
[11]曲彦平, 邵桂春, 葛景岩. 含MnO高炉型钛渣粘度的研究[J]. 沈阳工业大学学报, 1997, 19(1): 78-79.
QU Yan-pin, SHAO Gui-chun, GE Jing-yan. Study on bulk viscosity of titania slag containing MnO[J]. Journal of Shenyang Polytechnic University, 1997, 19(1): 78-79.
[12]朱立光, 唐国章, 万爱珍, 等. 高速连铸保护渣粘度特性的研究. 钢铁, 2000, 35(11): 23-25.
ZHU Li-guang, TANG Guo-zhang, WAN Ai-zhen, et al. Study on viscosity of mold powders for high speed casting[J]. Iron and Steel, 2000, 35(11): 23-25.
[13]万爱珍, 朱立光, 王硕明. 连铸保护渣粘度特性及机理研究. 炼钢, 2000, 16(2): 23-25.
WAN Ai-zhen, ZHU Li-guang, WANG Shuo-ming. Study on viscosity property and mechanism of mold powder[J]. Steelmaking, 2000,16(2): 23-25.
[14]王常珍. 冶金物理化学研究方法[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2002. 458-465.
WANG Chang-zhen. Research Technique of Metallurgical Physical Chemistry[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2002. 458-465.
[15]Mukongo T, Pistorius P C, Garbers-Craig A M. Viscosity effect of titanium pickup by mould fluxes for stainless steel[J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2004, 31(2): 135-143.
[16]王新月, 黄虹, 金山同. 连铸无氟保护渣的研究[A]. 炼钢辅助材料应用技术[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2003. 132-135.
WANG Xin-yue, HUANG Hong, JIN Shan-tong. Study on continuous casting free-fluoride mold powder[A]. Applied Technology of Auxiliary Material for Steelmaking[M]. Beijing: Metallurgic Industry Press, 2003. 132-135.
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金和上海宝钢集团公司联合资助项目(50374086)
收稿日期: 2005-06-16; 修订日期: 2005-11-15
作者简介: 刘永庆(1982-), 男, 硕士研究生
通讯作者: 文光华, 教授; 电话: 023-65105202; E-mail: wengh@cqu.edu.cn
(编辑陈爱华)