文章编号:1004-0609(2011)11-2763-06
抽拉速率对定向凝固Ni-45Ti-5Al合金微观组织的影响
杨春雷, 郑立静, 李 岩, 周 磊, 张 虎
(北京航空航天大学 材料科学与工程学院,北京 100191)
摘 要:采用Bridgman型液态金属冷却定向凝固方法,研究Ni-45Ti-5Al(摩尔分数,%)合金在不同抽拉速率(20、100和200 μm/s)下定向凝固后的相组成及其形态特征。结果表明:Ni-45Ti-5Al合金定向凝固生长区呈现明显的柱状晶生长形态,定向效果良好,NiTi基体以[100]方向为择优取向,Ti2Ni析出相沿[111]晶向择优生长。随着抽拉速率的提高,Ti2Ni相更加细小、分散,由在胞晶界上几乎连续分布改变为断续分布。在20~200 μm/s的宽生长速率范围内,均以胞状晶形态生长,固/液界面形态没有发生显著变化;随着抽拉速率从20 μm/s增加到200 μm/s,定向胞晶组织明显细化,平均胞晶间距由85 μm减小到25 μm。
关键词:Ni-45Ti-5Al合金;定向凝固;微观组织;固/液界面
中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
Effect of withdrawal rate on microstructure of directionally solidified Ni-45Ti-5Al alloys
YANG Chun-lei, ZHENG Li-jing, LI Yan, ZHOU Lei, ZHANG Hu
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Beijing 100191, China)
Abstract: The phase compositions and shapes of directionally solidified (DS) Ni-45Ti-5Al (mole fraction, %) alloys were investigated in the Bridgman liquid-metal-cooling directional-solidification process at withdrawal rates of 20, 100 and 200 μm/s. The results show that the columnar grain growth is observed in the DS specimens. The preferred crystal orientation of NiTi matrix is [100] direction and that of Ti2Ni phase precipitated on the matrix is [111] direction. With the increase of withdrawal rate, the Ti2Ni phase becomes finer and distributes from continuously to discontinuously in the intercellular region. When the withdrawal rate varies from 20 μm/s to 200 μm/s, all the solid/liquid interface morphologies are cellular, the DS microstructure is refined obviously and the cellular spacing decreases from 85 μm to 25 μm.
Key words: Ni-45Ti-5Al alloy; directional solidification; microstructure; solid/liquid interface
NiTi金属间化合物材料具有优良的力学性能、良好的形状记忆效应以及生物相容性,在航空航天和医疗等领域得到了广泛应用[1]。近年来,KOIZUMI等[2-3]发现, 将Al作为合金化元素加入到近等摩尔比的NiTi基合金中可以大幅提高NiTi合金的强度,其室温压缩强度达到2 300 MPa,超过镍基高温合金Rene95的室温压缩强度,1 000 ℃的压缩屈服强度达到200 MPa,而合金的密度基本保持在6.0 g/cm3左右,比镍基高温合金低25%左右,有望成为一类新型轻质高温结构金属间化合物材料。孟令杰等[4-7]对不同摩尔比的NiTi-Al基合金的合金化、组织结构及力学性能等进行了广泛的研究,发现Al元素的添加能促进高温强化相的析出,显著改善合金的室温及高温强度,但同时也损害NiTi合金优良的室温塑性。初步的研究结果表明,典型的NiTi-Al合金在800~900 ℃具有良好的高 温持久性能和高温抗氧化性能,室温断裂韧性大于30 MPa·m1/2,而室温伸长率小于1%。定向凝固态合金可以发挥某些晶向具有优异性能的优势,从而具有更优的高温力学性能和更大室温伸长率[8]。因此,在定向凝固条件下如何控制和改善NiTi-Al基合金中高温强化相的形态特征,减少高温强化相对NiTi基合金优良室温塑性的损害,成为NiTi-Al基合金作为一类在800~900 ℃使用的新型高温结构用金属间化合物基材料发展的关键。
为此,本文作者采用液态金属冷却定向凝固方法,研究Ni-45Ti-5Al(摩尔分数,%)合金组织形态随定向凝固抽拉速率的演变规律,为NiTi-Al基合金凝固组织的控制与性能优化提供依据。
1 实验
合金的名义成分为Ni-45Ti-5Al,由纯度为99.76%的海绵钛、99.98%的镍块和99.99%的铝锭,采用水冷铜坩埚磁悬浮真空感应熔炼炉反复熔炼4次后浇铸成质量约为6 kg的母合金锭。 线切割切取直径为14 mm、长为230 mm的试棒,车削掉表层氧化皮后用丙酮清洗、 烘干, 装入内径d14.5 mm×240 mm的Al2O3/Y2O3双层结构陶瓷管[9]中。使用Bridgman型液态金属冷却定向凝固炉,将炉膛抽真空至6.0×10-3 Pa后再充入高纯Ar至0.5×105 Pa,采用钨筒电阻加热到1 550 ℃ (炉膛隔热板之上约100 mm处W-Re热电偶测温)、保温20 min后进行定向凝固实验,分别以20、100和200 μm/s的速率抽拉150 mm,淬入Ga-In-Sn合金液。
将定向凝固试棒沿抽拉方向从中间对剖,一半用于观察纵截面组织,另一半用于观察不同凝固位置处的横截面组织。采用D/max2200pc型X射线衍射仪(XRD)进行物相测定,所用射线为Cu Kα,电压为40 kV,电流为40 mA,扫描速度为6(°)/min,扫描范围为20°~90°;采用JXA-8100型电子探针(EPMA)附带的INCA能谱仪(EDS)、OlympusBX51M型金相显微镜(OM)和Cambridge3400型扫描电镜(SEM)分析合金相的组成和微观组织;采用Image-Tool专业图像分析软件统计微观组织的尺寸大小和体积分数。腐蚀剂配比为V(HF):V(HNO3):V(H2O)=1:4:5。
2 结果
2.1 定向凝固试样的宏观组织
加热温度为1 550 ℃,抽拉速率分别为20、100和200 μm/s的定向凝固试棒的宏观组织如图1所示。由图1可见,试棒均存在两个界面:一个是定向凝固初始界面,即未熔区与定向生长区的界面(如实线箭头所示);另一个是淬火固/液界面(如虚线箭头所示)。在两个界面之间,定向凝固生长区呈现明显的柱状晶生长形态,定向效果良好。随着抽拉速率的提高,柱状晶宽度逐渐减小。
2.2 定向凝固试样稳态生长区的微观组织
2.2.1 合金的相组成及择优取向
图2所示为磁悬浮真空感应熔炼的铸态试样与不同抽拉速率下定向凝固态试样横截面(图1所示定向凝固初始界面之上约100 mm处,下同)的XRD谱。可见,该合金主要由两相组成:具有B2结构的NiTi相的基体和Ti2Ni相。经过定向凝固后,组织具有高度择优取向,NiTi基体以[100]方向为择优取向;同时,Ti2Ni相在2θ为30°附近的特征峰强度明显增强,说明Ti2Ni相在定向凝固过程中沿[111]晶向择优生长,铸态试样组成相的择优取向不明显。
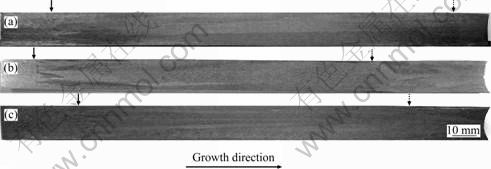
图1 不同抽拉速率下定向凝固试棒的纵剖面宏观组织
Fig.1 Macrostructures of longitudinal section of DS ingots grown at different withdrawal rates: (a) 20 μm/s; (b) 100 μm/s; (c) 200 μm/s
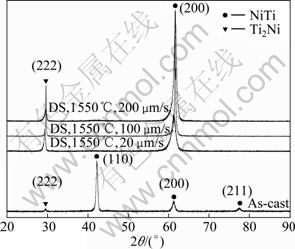
图2 Ni-45Ti-5Al合金铸态与定向凝固态的XRD谱
Fig.2 XRD patterns of as-cast and DS Ni-45Ti-5Al alloys
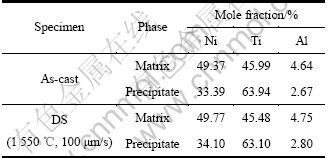
铸态与定向凝固稳态生长区试样典型微观组织的电子探针背散射电子图像如图3所示,各相EDS分析结果如表1所列。由图3(a)可见,铸态试样的微观组织为不规则等轴晶,等轴晶内是灰色的基体相,晶界处是黑色的析出相。EDS分析表明,灰色基体相为固溶了Al元素近等摩尔比的NiTi相,黑色析出相摩尔比n(Ti+Al):n(Ni)≈2:1,为固溶了Al元素的Ti2Ni相,呈块状或条状分布于胞晶界。由图3(b)可见,定向凝固态试样的纵截面微观组织形态与铸态组织有明显区别,呈胞状晶形态定向生长。EDS分析表明,定向组织也由NiTi基体相和Ti2Ni析出相组成,Ti2Ni相也呈块状或条状分布于胞晶界。铸态和定向凝固态试样的基体中固溶的Al元素含量高于Ti2Ni析出相中的Al元素含量。
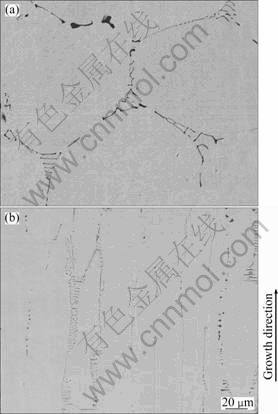
图3 铸态与抽拉速率为100 μm/s时定向凝固态Ni-45Ti-5Al合金试样纵截面的EPMA背散射电子图像
Fig.3 Backscattered EPMA images of Ni-45Ti-5Al alloys: (a) As-cast specimen; (b) Longitudinal section of steady state zone of DS specimen at withdrawal rate of 100 μm/s
表1 铸态与定向凝固稳态生长区试样中各相(见图3)的EDS分析结果
Table 1 Compositions of constituent phases in both as-cast and DS specimens shown in Fig.3 analyzed by EDS
已有研究表明,Al原子进入合金基体的晶格中,主要占据Ti原子的位置[10-14]。由于Al元素在NiTi基体中相对富集、在Ti2Ni中相对贫乏,因此,合金基体总体处于富Ti状态。
2.2.2 稳态生长区组织
图4所示为不同抽拉速率下定向凝固试棒稳态生长区纵截面和横截面的微观组织。从纵截面微观组织(见图4(a)、(c)和(e))可以看出,在3种抽拉速率条件下,定向凝固试样稳态生长区形貌基本相同,均以胞状晶形态生长。随着抽拉速率的提高,胞晶间距逐渐减小,定向胞晶组织明显细化。
从横截面组织(见图4(b)、(d)和(f))可以看出,与铸态组织(见图3(a))相比,定向凝固后晶粒尺寸变得细小,组织得到一定程度的细化。当抽拉速率为20 μm/s时,Ti2Ni相几乎连续分布在胞晶界上(见图4(b));随着抽拉速率的提高,Ti2Ni相更加细小、分散,断续分布在胞晶界上(见图4(d)和(f))。
2.3 固/液界面形貌
图5所示为不同抽拉速率下定向凝固试样的固/液界面形貌。由图5可以看出,当抽拉速率为20 μm/s时,淬火界面处胞状晶形态发生了明显变化,粗大的胞状晶尖端发生分叉,沿着生长方向向液相中延伸,变成细长的胞状晶,可以观察到由于分叉产生的侧向分枝(见图5(a));当抽拉速率为100 μm/s时,在快淬部位很难观察到固/液共存的糊状凝固区,但淬火界面上、下组织形貌差别明显,界面之下为较粗大的胞状晶组织,界面之上为细小的胞状晶组织(见图5(b));而当抽拉速率为200 μm/s时,淬火界面不明显,淬火界面上下部位均为细小的胞状晶组织(见图5(c))。
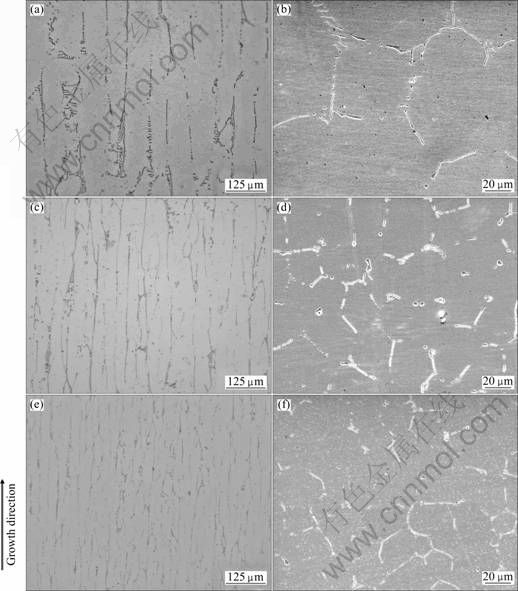
图4 不同拉速率下定向凝固稳态生长区纵截面的金相组织和横截面的SEM像
Fig.4 Longitudinal OM images ((a), (c), (e)) and transverse SEM images ((b), (d), (f)) of steady state zone of DS samples at different withdrawal rates: (a), (b) 20 μm/s; (c), (d) 100 μm/s; (e), (f) 200 μm/s
可见,由于该成分合金的固液两相线温度区间很窄[2],所以,在过热温度下(约250 ℃)及20~200 μm/s的宽生长速率范围内,甚至在快淬区都是以胞状晶形态生长,合金的固/液界面形貌没有发生显著变化。
3 讨论
由于Ni-45Ti-5Al合金的固液两相线温度区间很窄,在20~200 μm/s的宽生长速率范围内,合金的固/液界面形态没有发生显著变化,NiTi均以胞状晶形态生长;随着抽拉速率的提高,NiTi胞晶间距逐渐减小,定向胞晶组织明显细化。抽拉速率对NiTi胞晶间距和Ti2Ni析出相含量(体积分数)的影响如图6所示。由图6可见,随着抽拉速率从20 μm/s增加到200 μm/s,平均胞晶间距明显减小,由85 μm减小到25 μm,合金中析出相Ti2Ni的含量逐渐由3.4%增加到6.3%(体积分数)。
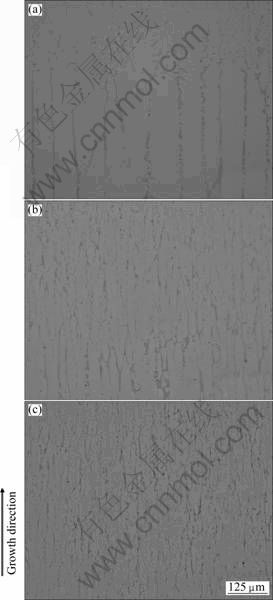
图5 不同抽拉速率下定向凝固试样的固/液界面形貌
Fig.5 Morphologies of solid/liquid interfaces of DS samples at different withdrawal rates: (a) 20 μm/s; (b) 100 μm/s; (c) 200 μm/s
合金在单向凝固条件下,胞/枝晶一次臂间距λ1与生长速率(v)和温度梯度(G)之间的关系符合下式[15]:
λ1=αG-1/2v-1/4 (1)
式中:α为材料的物性参数。
图7所示为本实验条件下稳态区定向胞晶间距λ1与凝固参量G-1/2v-1/4的关系。可以看出,二者近似于线性关系,实验结果与理论模型较为吻合。
定向排列的NiTi细胞晶组织和细小的断续分布在胞晶间的Ti2Ni析出相有利于合金高温强度和室温塑性的提高。从凝固组织和工艺控制角度出发,Ni-45Ti-5Al合金定向凝固生长时,选择200 μm/s以内较高的生长速率是有益的。
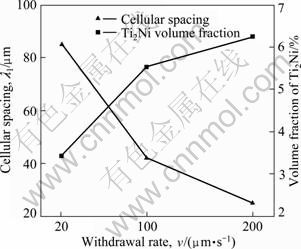
图6 稳态区胞晶间距λ1和析出相Ti2Ni体积分数随抽拉速率的变化
Fig.6 Variation of cellular spacing and volume fraction of Ti2Ni with withdrawal rate in steady state zone of DS ingots
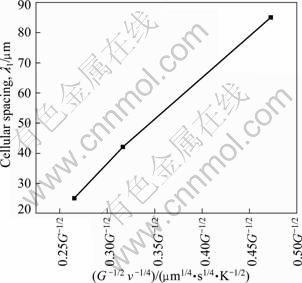
图7 稳态区胞晶间距λ1与凝固参量G-1/2v-1/4的关系
Fig.7 Dependence of cellular spacing on G-1/2v-1/4
4 结论
1) Ni-45Ti-5Al合金定向凝固生长区呈现明显的柱状晶生长形态,定向效果良好。定向凝固没有改变合金的相组成,但改变了组成相的形态。经过定向凝固后,组织具有高度择优取向并细化,NiTi基体以[100]方向为择优取向,Ti2Ni析出相沿[111]晶向择优生长;随着抽拉速率提高,Ti2Ni相更加细小、分散,由在胞晶界上几乎连续分布改变为断续分布。
2) Ni-45Ti-5Al合金在20~200 μm/s的宽生长速率范围内均以胞状晶形态生长,固/液界面形态没有发生显著变化。随着抽拉速率从20 μm/s增加到200 μm/s,定向胞晶组织明显细化,平均胞晶间距由85μm减小到25 μm。胞晶间距λ1与凝固参量G-1/2v-1/4之间呈近似线性关系。
REFERENCES
[1] 徐祖耀, 江伯鸿. 形状记忆材料[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 2000: 350-351.
XU Zu-yao, JIANG Bo-hong. Shape memory alloys[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press, 2000: 350-351.
[2] WARREN P, MURAKAMI Y, KOIZYMI Y, HARADA H. Phase separation in NiTi-Ni2TiAl alloy system[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1997, 223: 17-20.
[3] KOIZUMI Y, RO Y, NAKAZAWA S, HARADA H. NiTi-base intermetallic alloys strengthened by Al substitution[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1997, 223: 36-41.
[4] 孟令杰. NiTi-Al高温结构材料的研究[D]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2006: 51-56.
MENG Ling-jie. Study of NiTi-Al based high temperature structural materials[D]. Beijing: Beihang University, 2006: 51-56.
[5] MENG L J, LI Y, ZHAO X Q, XU H B. The mechanical properties of intermetallic Ni50-xTi50Alx alloys (x=6, 7, 8, 9)[J]. Intermetallics, 2007, 15: 814-818.
[6] XU H B, MENG L J, XU J, LI Y, ZHAO X Q. Mechanical properties and oxidation characteristics of TiNiAl(Nb) intermetallics[J]. Intermetallics, 2007, 15: 778-782.
[7] 孟令杰, 李 岩, 赵新青, 徐惠彬. Nb对富钛TiNiAl金属间化合物强化机制的影响[J]. 航空学报, 2007, 28(5): 1206-1209.
MENG Ling-jie, LI Yan, ZHAO Xin-qing, XU Hui-bin. Effect of Nb on strengthening mechanism of Ti-rich TiNiAl intermetallics[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2007, 28(5): 1206-1209.
[8] 傅恒志, 郭景杰, 苏彦庆, 刘 林, 徐达鸣, 李金山. TiAl金属间化合物的定向凝固和晶向控制[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2003, 13(4): 797-810.
FU Heng-zhi, GUO Jing-jie, SU Yan-qing, LIU Lin, XU Da-ming, LI Jin-shan. Directional solidification and lamellar orientation control of TiAl intermetallics[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13(4): 797-810.
[9] 张花蕊, 高 明, 唐晓霞, 张 虎. 定向凝固过程中Ti-47Al-2Cr-2Nb合金与Y2O3陶瓷的相互作用[J]. 金属学报, 2010, 46(7): 890-896.
ZHANG Hua-rui, GAO Ming, TANG Xiao-xia, ZHANG Hu. Interaction between Ti-47Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy and Y2O3 ceramic during directional solidification[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2010, 46(7): 890-896.
[10] HUNEAU B, ROGL P, ZENG K, SCHMID-FETZER R, BOHN M, BAUER J. The ternary system Al-Ni-Ti. Part Ⅰ: Isothermal section at 900 ℃ experimental investigation and thermodynamic calculation[J]. Intermetallics, 1999, 7: 1337-1345.
[11] ZENG K, SCHMID-FETZER R, HUNEAV B, ROGL P, BAUER J. The ternary system Al-Ni-Ti. Part Ⅱ: Thermodynamic assessment and experimental investigation of polythermal phase equilibria[J]. Intermetallics, 1999, 7: 1347-1359.
[12] KARUNARATNE M S A, CARTER P, REED R C. On the diffusion of aluminium and titanium in the Ni-rich Ni-Al-Ti system between 900 and 1 200 ℃[J]. Acta Materialia, 2001, 49(5): 861-875.
[13] BOZZOLO G H, NOEBE R D, AMADOR C. Site occupancy of ternary additions to B2 alloys[J]. Intermetallics, 2002, 10: 149-159.
[14] BOZZOLO G H, NOEBE R D, MOSCA H O. Site preference of ternary alloying additions to NiTi: Fe, Pt, Pd, Au, Al, Cu, Zr and Hf[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2005, 389: 80-94.
[15] 傅恒志, 郭景杰, 刘 林, 李金山. 先进材料定向凝固[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 566-569.
FU Heng-zhi, GUO Jing-jie, LIU Lin, LI Jin-shan. Directional solidification and processing of advanced materials[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 566-569.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
收稿日期:2010-10-09;修订日期:2011-03-25
通信作者:张 虎,教授,博士;电话:010-82316958;E-mail: zhanghu@buaa.edu.cn