
Hydrogen behavior in titanium aluminide alloys
PAN Bao-wu(潘保武)1, 2, CHU Wu-yang(褚武扬)2
1. Key Laboratory on Instrumentation Science and Dynamic Measurement, Ministry of Education,
North University of China, Taiyuan 030051, China;
2. Department of Material Physics, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China
Received 20 April 2006; accepted 30 June 2006
Abstract: This is a synthetical report about hydrogen behavior in titanium aluminide alloys in our group. There are two kinds of hydrogen solubility in titanium aluminides, one is the overall solubility at high temperature in the matrix without hydride and the other is the terminal solubility at low temperature in the matrix in equilibrium with the hydride. The former decreases but the later increases with increasing temperature. Hydrogen as a temporary β stabilizer clearly decreases the size of the α2 phase, and increases greatly the amount of β phase, and then increases evidently the mechanical properties of Ti3Al+Nb. The cathodic corrosion of TiAl during charging is due to hydride on the surface. The decrease of the strength, the strain to fracture and fracture toughness for hydrogenated samples is due to hydride. The enrichment of atomic hydrogen at the crack tip during charging under sustained load can enhance localized plastic deformation and cause hydrogen-induced delayed cracking.
Key words: titanium aluminide alloys; hydrogen; hydride; delayed cracking
1 Introduction
Titanium aluminide alloys based on Ti3Al and TiAl have received sufficient attention showing that they may be legitimate candidate materials of construction for aerospace systems, and then undergone extensive investi- gations[1]. Hydrogen behaviors in titanium aluminide alloys have been widely studied in our group since 1991 [2-23]. The main results are as follows.
2 Two kinds of hydrogen solubility in titani- um aluminides
All hydrogen entered into Ti-24Al-11Nb alloy (Ti3Al+Nb) at high temperature T1 is solutionized in the matrix without hydride, and the solubility of hydrogen in the matrix without hydride at T1 is called as the overall solubility of hydrogen. Hydrides begin to precipitate when temperature is cooled to a critical value of T2<T1, the solubility of hydrogen in equilibrium with the hydride phase at T2 is called as the terminal solubility of hydrogen.
A Sieverts apparatus was used to measure the decomposition pressure of hydrogenated Ti-24Al-11Nb samples with various hydrogen concentrations during heating. The result is shown in Fig.1. Fig.1 shows that for the sample with xH=2.3% (mole fraction), no hydride precipitates in high temperature region of CB, therefore, the curve of CB is the solubility equation of hydrogen in the matrix without hydride, i.e. p(H2) vs 1/T corres- ponding to xH=2.3%. The slope of CB is the partial molar heat of solution for the matrix, which is 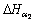 =-21 kJ/mol. When the sample is cooled to B=447 ℃, hydride begins to precipitate, thus B is the highest temperature of hydride existing and the curve of AB is the solubility equation of hydrogen in the two phase region (matrix and hydride). As soon as hydrogen precipitates, almost all of hydrogen become hydride, and then the slope of AB is the partial molar heat of solution in the hydride, i.e. ΔHγ=-74.9 kJ/mol. The intersection B gives the temperature at which the hydrogen concentration of 2.3% represents the terminal solubility, which is 447 ℃. Fig.1 shows that the larger the hydrogen concentration of the hydrogenated sample, the higher the temperature of the intersection, therefore, the terminal solubility of hydrogen in the matrix in equilibrium with the hydride increases with increasing temperature. Based on Fig.1, the equation of the terminal solubility at 1.013 25×105 Pa is
=-21 kJ/mol. When the sample is cooled to B=447 ℃, hydride begins to precipitate, thus B is the highest temperature of hydride existing and the curve of AB is the solubility equation of hydrogen in the two phase region (matrix and hydride). As soon as hydrogen precipitates, almost all of hydrogen become hydride, and then the slope of AB is the partial molar heat of solution in the hydride, i.e. ΔHγ=-74.9 kJ/mol. The intersection B gives the temperature at which the hydrogen concentration of 2.3% represents the terminal solubility, which is 447 ℃. Fig.1 shows that the larger the hydrogen concentration of the hydrogenated sample, the higher the temperature of the intersection, therefore, the terminal solubility of hydrogen in the matrix in equilibrium with the hydride increases with increasing temperature. Based on Fig.1, the equation of the terminal solubility at 1.013 25×105 Pa is
x*=6.8×103exp(-5750/T ) (1)
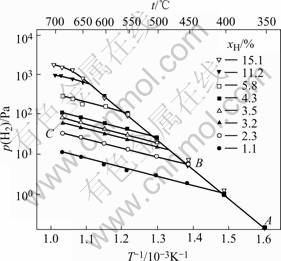
Fig.1 Summary plot of lg p(H2) vs 1/T (AB line is for matrix and hydride phases, and the other lines parallel to BC represent hydrogen concentration in matrix without hydride)
The slope of 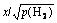 at various temperatures can be obtained based on the data of the CB line, and then the equation of the overall solubility of hydrogen in the matrix without the hydride is
at various temperatures can be obtained based on the data of the CB line, and then the equation of the overall solubility of hydrogen in the matrix without the hydride is
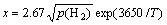 (2)
(2)
The overall solubility of hydrogen in the matrix without the hydride decreases with increasing temperature.
3 Hydrogen as temporary alloy element im- proving mechanical properties
Hydrogen like Nb is the β stabilizer in α2+β alloy (e.g. Ti3Al+Nb). The hydrogen concentration after solu- tionizing in H2 at 1 147 ℃ are 12.6% for thin tensile sample and 5% to 7% for thick WOL sample. During air cooling, hydrogen as a temporary β stabilizer clearly decreases the size of α2 phase and increases greatly the retained or transformed β phase content, as shown in Fig.2. Because the microstructure becomes fine, the ductile β phase content increases and hydrogen as hydride has been outgassed, the mechanical properties increase greatly, for example, the yield strength, the ultimate tensile strength and the strain to fracture increase by about 60%, the notch fracture strength increases by 100% and the fracture toughness increases by 60%.
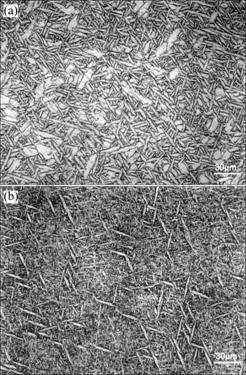
Fig.2 Microstructures resulting from β solution treatment at 1 147 ℃ in vacuum (a) and in H2 (b), followed by air cooling and outgassing at 800 ℃ (The white is α2 phase and the black is β phase)
4 Hydride-induced cathodic corrosion of TiAl alloy
It is well known that the anode is corroded and cathode undergoes protection. TiAl alloy as a cathode, however, undergoes corrosion during cathodic charging in the solution and molten salt. The rate of cathodic corrosion at cathodic constant potential is much higher than that of anodic dissolution at the same anodic constant potential, as shown in Fig.3[16]. The rate of cathodic corrosion increases linearly with current density during charging at constant current and is 10 times higher in the acid solution than in the salt solution under the same current. Experiment shows that cathodic corrosion increases with increasing hydrogen concentration in precharged sample and through adding As2O3 in the charging solution, therefore hydrogen can promote the cathodic corrosion of TiAl.
The disruption of the surface film by local hydride formation during cathodic charging causes the reaction of fresh metal with H+ and the formation of Ti3+ and TiO2+, resulting the dissolution of TiAl during cathodic charging [9,10].
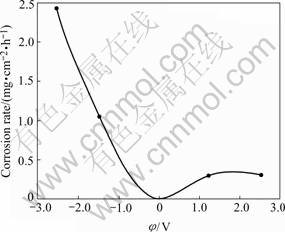
Fig.3 Variation of cathodic corrosion and anodic dissolution of TiAl with applied constant potential (0.5 mol/LNa2SO4+H2SO4, pH=2, 24 h.)
5 Role of hydride and atomic hydrogen in hydrogen embrittlement
Eqn.(1) shows that the terminal solubility of hydrogen in the matrix (Ti3Al+Nb) in equilibrium with the hydride at room temperature is 3×10-5% (mole fraction), which can be ignored. Therefore, all hydrogen in precharged sample becomes hydride, and the effect of hydrogen on mechanical properties of precharged sample is due to hydride instead of atomic hydrogen. The variation of properties in Ti3Al+Nb alloy with hydrogen concentration or hydride content is shown in Fig.4[4]. Fig.4 shows that the yield strength under compression increases, but the ultimate tensile strength(UTS), the strain to fracture εf or the plastic strain to fracture εP, notch fracture strength σF and the fracture toughness KIC decrease with increasing the hydride content.
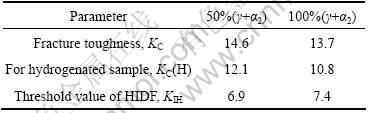
For TiAl alloy, the decrease of mechanical properties in precharged sample is also due to hydride[7, 9]. For TiAl with an electroless NiP coatings, cathodic corrosion during charging can be avoided, and hydrogen can enter the sample. The fracture toughness of precharged sample decreases by 20%, as listed in Table 1. This is all due to hydride[9]. Hydrogen-induced delayed cracking of a precharged sample does not occur under sustained load of KI/KC=0.9 to 0.95 because of no atomic hydrogen in the TiAl matrix. However, atomic hydrogen can continuously enter into the TiAl during charging under sustained load, and the enrichment of atomic hydrogen at the crack tip through stress-induced diffusion causes delayed fracture. The threshold stress intensity factor of delayed fracture, KIH, is listed in Table 1. Table 1 shows that atomic hydrogen causes the fracture toughness of precharged sample, KC(H), which is due to the hydride, to decrease further by 30%.
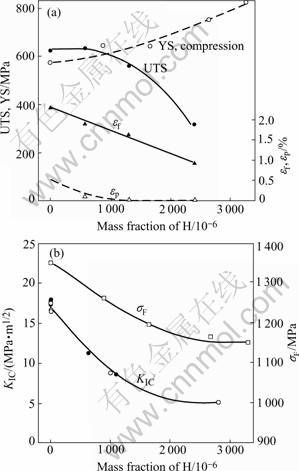
Fig.4 Dependence of mechanical properties on hydrogen con- centration: (a) YS, UTS and εf; (b) σF and KIC
Table 1 KC, KC(H) and KIH in TiAl alloy (MPa?m1/2)
6 Hydrogen enhanced local plasticity re- sulting in hydrogen-induced delayed cracking
Hydrogenated WOL sample with wH=2 880×10-6 is polished after loading to cracking, and then keeps constant displacement in air. Slip bands appear at the crack tip after keeping the constant displacement for 4 min and increase with time. Hydrogen-induced cracks initiate discontinuously along the slip bands after keeping the constant displacement for 12 min.
The other loaded and polished WOL is put in H2 at 400 ℃ for 0.5 min, slip bands appear ahead of crack tip, as shown in Fig.5(a). Put again the sample in H2 at 400 ℃ for 0.5 min, the slip bands increase, as shown in Fig.5(b). Charging further in H2 at 400 ℃ for 0.5 min, microcracks of A and B initiate along the slip bands, as shown in Fig.5(c). The hydrogen-induced crack propagates during charging continuously, as shown in Fig.5(d). The results show that atomic hydrogen at crack tip can promote local plastic deformation and hydrogen- induced crack initiates when the hydrogen-enhanced local plasticity develops into a certain condition. In-situ observation in TEM shows that hydrogen could enhance emission and motion of dislocation under constant load, i.e. local plastic deformation, and a dislocation-free zone forms. When the stress concentration within the dislocation-free zone or ahead of a pile-up of dislocations increases to equate the cohesive strength, which has been decreased by hydrogen, atomic bonds will break down, resulting in the initiation of hydrogen- induced crack[24].

Fig.5 Initiation of hydrogen induced cracking in H2 gas at 400℃ (A, B, C-hydrogen induced cracking): (a) 0.5 min; (b) 1 min; (c) 1.5 min; (d) 2 min
7 Conclusions
There are two kids of hydrogen solubility in titanium aluminides, one is the overall solubility at high temperature in the matrix without hydride, and the other is the terminal solubility at low temperature in the matrix in equilibrium with the hydride. The former decreases but the later increases with increasing temperature. Hydrogen as a temporary β stabilizer clearly decreases the size of the α2 phase in the two-phase alloy of Ti3Al+Nb and increases greatly the β phase content, resulting in increasing evidently the mechanical properties. Forming hydride on the surface can induce cathodic corrosion of TiAl during cathodic charging. For precharged titanium aluminides, the effect of hydrogen on mechanical properties is all due to hydride. Enrichment of atomic hydrogen at the crack tip, however, during charging under sustained load can enhance localized plastic deformation, resulting in hydrogen- induced cracking.
References
[1] ZHANG Yong-gang, HAN Ya-fang, CHEN Guo-liang, GUO Jian-ting. Intermetallic Structure Materials [M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 2001. 686-831.(in Chinese)
[2] CHU Wu-Yang, THOMPSON A W, WILLIAMS J C, et al. Hydrogen solubility in a titanium aluminide alloy [J]. Acta Metall Mater, 1992, 40(3): 455-462.
[3] CHU Wu-yang, THOMPSON A W. Effect of hydrogen as a temporary β stabilizer on microstructure and brittle fracture behavior in a titanium aluminide alloy [J]. Metall Trans A, 1991, 22A(1): 71-81.
[4] CHU Wu-yang, THOMPSON A W. Hydrogen effects on brittle fracture of the titanium aluminide alloy Ti-24Al-11Nb [J]. Metall Trans A, 1992, 23A(4): 1299-1312.
[5] GAO Jia, WANG Yan-bin, CHU Wu-yang, HSIAO Chi-mei. Study of hydride in TiAl after cathodic charging [J]. Scr Metall Mater, 1992, 27(9): 1219-1222.
[6] CHU Wu-yang, XIAO Ji-me, THOMPSON A W. Mechanism of hydrogen facilitated cleavage in titanium aluminide [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1992, 5(4): 286-291.
[7] CHU Wu-yang, THOMPSON A W. Effect of microstructure and hydrides on fracture of TiAl [J]. Scr Metall Mater, 1991, 25(9): 2133-2138.
[8] GAO Ke-wei, WANG Yan-bin, CHU Wu-yang, HSIAO Chi-mei. Initiation and slow stable growth of brittle cracks in TiAl [J]. Scr Metall Mater, 1992, 26(5): 813-817.
[9] GAO Ke-wei, CHU Wu-yang, WANG Yan-bin, HSIAO Chi-mei, THOMPSON A W. Effects of microstructure and hydride on KIQ of TiAl [J]. Scr Metall Mater, 1992, 27(5): 555-560.
[10] GAO Jia, WANG Yan-bin, CHU Wu-yang, HSIAO Chi-mei. Study of hydride in TiAl after cathodic charging [J]. Scr Metall Mater, 1992, 27(9): 1219-1222.
[11] ZHANG Yue, WANG Yi, WANG Yan-bin, CHU Wu-yang, HSIAO Chi-mei. Hydrogen induced cracking of Ti-24Al-11Nb at room temperature [J]. Scr Metall Mater, 1993, 29(7): 975-980.
[12] ZHANG Yue, WANG Yan-bin, QIAO Li-jie, CHU Wu-gang, HSIAO Chi-mei. Investigation of fractal dimensions of hydrogen-induced brittle fracture of titanium aluminide [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1994, A177(1-2): L1-L5.
[13] ZHANG Yue, WANG Yan-bin, CHU Wu-yang, HSIAO Chi-mei. Corrosion fatigue fractography of Ti-24Al-11Nb [J]. Scr Metall Mater, 1994, 30(5): 541-546.
[14] ZHANG Yue, WANG Yan-bin, CHU Wu-yang, HSIAO Chi-mei. In-situ TEM observation of microcrack nucleation in titanium aluminide [J]. Scr Metall Mater, 1994, 31(3): 279-283.
[15] ZHANG Y, CHU W Y, HSIAO C H, WANG T. Topography of brittle fracture surfaces of titanium aluminide alloy as revealed by a scanning tunneling microscope [J]. J Vac Sci Tech B, 1994, 12(4): 2456-2458.
[16] GAO Ke-wei, WANG Yan-bin, CHU Wu-yang. Hydrogen induced delayed fracture of TiAl alloy at room temperature [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1996, 32(1): 29-32. (in Chinese)
[17] GAO K W, JIN J W, QIAO L J, CHU W Y, HSIAO C M. Effect of hydrogen on cathodic corrosion of titanium aluminide [J]. Corrosion, 1996, 52(1): 3-7.
[18] GAO Ke-wei, WANG Yan-bin, CHU Wu-yang, HSIAO Chi-mei. In-situ TEM observation of dissolution-enhanced dislocation emission, motion and the nucleation of SCC for Ti-24Al-11Nb alloy in methanol [J]. Scripta Mater, 1997, 36(2): 259-264.
[19] GAO Ke-wei, WANG Yan-bin, LIN Zhi, QIAO Li-jie, CHU Wu- yang. Fracture mechanism of TiAl intermetallics caused by hydride and atomic hydrogen [J]. Science in China Ser, 1999, 42(5): 511-520.
[20] LU Y H, ZHANG Y G, QIAO L J, WANG Y B, CHEN C Q, CHU W Y. In-situ TEM study of fracture mechanisms of polysynthetically twinned(PST) crystals of TiAl alloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2000, 289(1-2): 91-98.
[21] LU Yong-hao, QIAO Li-jie, WANG Yan-bin, CHEN C Q, CHU W Y. The twofold effects of deformation twinsof fracture behaviors of PST crystals of TiAl alloys [J]. J Mater Sci Lett, 2000, 19: 1595-1597 .
[22] LU Yong-hao, ZHANG Yong-gang, QIAO Li-jie, WANG Yan-bing, CHEN Chang-qi, CHU Wu-yang. In-situ crack propagation observation in fully lamellar Ti-49%Al alloy [J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2000, 10(5): 599-602.
[23] LU Y H , ZHANG Y G, QIAO L J, WANG Y B, CHEN C Q, CHU W Y. The fracture mechanism of a fully lamellar γ-TiAl alloy through in-situ SEM observation [J]. Intermetallics, 2000, 8(12): 1443-1445.
[24] CHU Wu-yang, QIAO Li-jie, CHEN Qi-zhi, CAO Ke-wei. Fracture and Environmental Fracture [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2000. 109-153. (in Chinese)
(Edited by YUAN Sai-qian)
Foundation item: Project(20050008031) supported by Special Foundation of Education Ministry of China about PhD
Corresponding author: PAN Bao-wu; Tel: +86-351-3921442; E-mail: pan_mail@nuc.edu.cn