Negative effect of dissolved organic compounds on settling behavior of synthetic monominerals in red mud
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2016年第7期
论文作者:胡慧萍 王梦 刘锦伟 陈启元
文章页码:1591 - 1602
Key words:hydration grossular; hematite; dissolved organic compounds; settling performance; simulated bayer digestion
Abstract: Hydration grossular and hematite monominerals were synthesized. The effects of dissolved organic compounds (including sodium formate, sodium acetate, sodium oxalate, sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate) on the settling performance of hydration grossular or hematite slurries were studied. The settling of the slurries was also investigated with the addition of sodium polyacrylate (PAAS) or hydroxamated polyacrylamide flocculant (HCPAM). The adsorption mechanism of organic compounds on monominerals surfaces was studied by FT-IR and XPS, respectively. A deterioration in settling is observed in order of disodium phthalate>sodium salicylate>sodium oxalate>sodium formate (or sodium acetate). Moreover, PAAS can efficiently eliminate the negative effects of organic compounds on the settling performance of the hydration grossular slurry. HCPAM can efficiently eliminate the negative effects of sodium formate, sodium acetate and sodium oxalate on the settling performance of the hematite slurry, but it only partially improves the settling performance of hematite slurry containing sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate. FT-IR and XPS results show that organic compounds are physically adsorbed on hydration grossular surface, and chemisorptions of organic compounds occur on hematite surface with a bidentate chelating complex.
J. Cent. South Univ. (2016) 23: 1591-1602
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-016-3213-y
WANG Meng(王梦), HU Hui-ping(胡慧萍), LIU Jin-wei(刘锦伟), CHEN Qi-yuan(陈启元)
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Abstract: Hydration grossular and hematite monominerals were synthesized. The effects of dissolved organic compounds (including sodium formate, sodium acetate, sodium oxalate, sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate) on the settling performance of hydration grossular or hematite slurries were studied. The settling of the slurries was also investigated with the addition of sodium polyacrylate (PAAS) or hydroxamated polyacrylamide flocculant (HCPAM). The adsorption mechanism of organic compounds on monominerals surfaces was studied by FT-IR and XPS, respectively. A deterioration in settling is observed in order of disodium phthalate>sodium salicylate>sodium oxalate>sodium formate (or sodium acetate). Moreover, PAAS can efficiently eliminate the negative effects of organic compounds on the settling performance of the hydration grossular slurry. HCPAM can efficiently eliminate the negative effects of sodium formate, sodium acetate and sodium oxalate on the settling performance of the hematite slurry, but it only partially improves the settling performance of hematite slurry containing sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate. FT-IR and XPS results show that organic compounds are physically adsorbed on hydration grossular surface, and chemisorptions of organic compounds occur on hematite surface with a bidentate chelating complex.
Key words: hydration grossular; hematite; dissolved organic compounds; settling performance; simulated bayer digestion
1 Introduction
The alumina industry in China has developed rapidly in the last decades, and the Bayer process is still the principal industrial process in the production of alumina all over the world. China has abundant bauxite reserves mainly in the form of diaspore. The production of alumina from bauxite requires an effective solid- liquid separation in gravity thickeners to generate Bayer liquors containing low amounts of suspended solids. As the quality of bauxite in China continues to deteriorate (with mass ratio of Al and Si lower than 5), this solid- liquid separation becomes more difficult due to the higher solid content of red mud in the Bayer liquor.
In general, the bauxite ores contain from 0.1% to 0.4% (mass fraction) organic compounds and occasionally as high as 0.6% (mass fraction) [1]. The organic compounds are comprised of a complex mixture of humates, lignin and cellulose [2]. On digestion of this bauxite in the Bayer process, 50%-90% of the organic compounds may be extracted into the Bayer liquor as dissolved organic compounds. The dissolved organic compounds may be classified into three distinct groups [1]: humic acids, freshly extracted high relative molecular mass material and its initial degradation products with relative molecular mass greater than 500 u (e.g. fulvic acid); intermediate degradation products which constitute the building “blocks” of the large humic molecules (e.g. aromatic carboxylic acids and phenolic acids); the lower relative molecular mass degradation products (sodium formate, sodium acetate, sodium oxalate and so on). Dissolved organic compounds build up in the recirculating process liquor to concentrations determined by a complex interaction of inputs, outputs and reactions in a dynamic steady-state, and the organic concentrations range from 0 g/L to 40 g/L [3].
DOMINICUS and KEVORK [1], JOHN and MORRIS [4] and BERNHARD et al [5] have proposed that organic compounds in general dissolved in the Bayer process result in poorer settling of red mud. L et al [6-9] have found that the deterioration in settling of red mud containing dissolved organic compounds was observed without flocculants. The order of the deterioration in the settling is humic acid (or fulvic acid)>disodium terephthalate>phenol>sodium oxalate> sodium formate (or sodium acetate). The negative effects of some organic compounds (including fulvic or humic acids with the concentration below 1.0 g/L) and the others (including sodium formate, sodium acetate,sodium oxalate, phenol or disodium terephthalate) can be mitigated by the addition of flocculants, and the deterioration of the settling of red mud cannot be apparently eliminated by flocculants when concentrations of fulvic or humic acid increased to 3.5 g/L. However, in L
et al [6-9] have found that the deterioration in settling of red mud containing dissolved organic compounds was observed without flocculants. The order of the deterioration in the settling is humic acid (or fulvic acid)>disodium terephthalate>phenol>sodium oxalate> sodium formate (or sodium acetate). The negative effects of some organic compounds (including fulvic or humic acids with the concentration below 1.0 g/L) and the others (including sodium formate, sodium acetate,sodium oxalate, phenol or disodium terephthalate) can be mitigated by the addition of flocculants, and the deterioration of the settling of red mud cannot be apparently eliminated by flocculants when concentrations of fulvic or humic acid increased to 3.5 g/L. However, in L ’s work, the lack of settling data of red mud in the absence of organic compounds with the addition of flocculants results in inaccuracy to estimate the elimination of negative effects of organic compounds on the settling performance of red mud by flocculants. Meanwhile, the wide variations in the species of red mud and dissolved organic compounds in Bayer liquors result in difficulties to identify the main influencing factors of the settling performance of red mud.
’s work, the lack of settling data of red mud in the absence of organic compounds with the addition of flocculants results in inaccuracy to estimate the elimination of negative effects of organic compounds on the settling performance of red mud by flocculants. Meanwhile, the wide variations in the species of red mud and dissolved organic compounds in Bayer liquors result in difficulties to identify the main influencing factors of the settling performance of red mud.
According to previous studies [10-11]][, the digestion of bauxite in the form of diaspore leaves behind red mud, containing predominant amount of hydration grossular and hematite, and a bit of perovskite. The typical silicon-containing and iron-containing monominerals in red mud are hydration grossular and hematite, respectively. Although the wide variations exist in the species and amounts of dissolved organic compounds between different Bayer liquors, there are fundamental similarities of the functional groups (such as carboxylic groups and hydroxyl groups), and the organic compounds presented in Bayer liquors are aliphatic and aromatic compounds with carboxylic groups and hydroxyl groups. On the other hand, LIU et al [12] found that the flocculation of hydration grossular using commercially available sodium polyacrylate (PAAS) occurred by a polymer bridging mechanism, and an improvement in clarity of the supernatant in the hematite slurry using self-made hydroxamated polyacrylamide flocculant (HCPAM) was achieved by a chemisorption mechanism.
In this work, monocarboxylate (sodium formate and sodium acetate), dicarboxylate (sodium oxalate), phenol containing carboxylate groups (sodium salicylate) and aromatic carboxylate (disodium phthalate) are chosen as typical dissolved organic compounds in Bayer liquors. Monominerals in red mud, hydration grossular and hematite, were correspondingly synthesized under the simulated Bayer digestion in alumina production. The effects of dissolved organic compounds in Bayer liquors on the settling behavior of the hydration grossular slurry or hematite slurry were studied. The settling performance of the hydration grossular slurry or hematite slurry in the presence or the absence of organic compounds was also investigated with the addition of PAAS or HCPAM. The adsorption mechanism of organic compounds on the surfaces of monominerals of red mud was studied by FT-IR and XPS, respectively.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials and reagents
Monomineral kaolinite was friendly supplied by Zhengzhou Light Metals Research Institute of Aluminum Corporation of China. Synthetic goethite was prepared according to the procedure of LEKKERKERKER et al [13], then dried at 60 °C for 10 h and characterized by X-ray powder diffraction pattern on X-ray diffractometer (D/max 2500, Rigaku Corporation, Cu Kα radiation, Japan) (Fig. 1(a)). Industrial grade aluminum hydroxide (ω(Al(OH)3)≥99.2%, mass fraction) was purchased from Zhengzhou Light Metals Institute of Aluminum Corporation of China. Other reagents were of analytical grade.
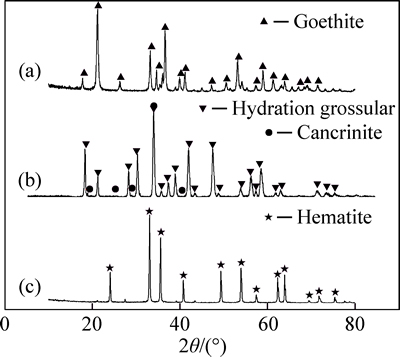
Fig. 1 XRD of synthetic goethite (a), hydration grossular (b) and hematite (c)
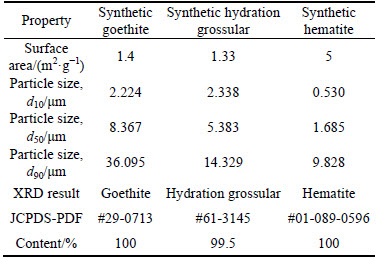
Synthetic hydration grossular (Ca3Al2(SiO4)(OH)8) and hematite (α-Fe2O3) were prepared by a simulated Bayer digestion as follows: the simulative circulating mother liquor was prepared by NaOH and Al(OH)3, with 212 g/L of alkali concentration (Nk) and 3.2 of caustic molar ratio (ak, Na2O to Al2O3). Synthetic hydration grossular suspension was prepared by digesting the mixture of 10.34 g monomineral kaolinite, 9.66 g calcium oxide and 600 mL simulated circulating mother liquor (Nk=212 g/L, ak=1.50) in an autoclave at 245- 255 °C for 90 min. Synthetic hematite suspension was prepared by digesting the mixture of 30 g synthetic goethite and 600 mL simulated circulating mother liquor (Nk=212 g/L, ak=1.50) in an autoclave at 245-255 °C for 90 min. These suspensions were filtered, subsequently washed with 10% NaOH solution for several times, and then dried in a vacuum oven at 60 °C for 24 h to obtain dry muds (abbreviated as synthetic hydration grossular and synthetic hematite, respectively). The main minerals of the dry muds were characterized by semi-quantitative analysis of XRD (Figs. 1(b) and (c)). Synthetic goethite, hydration grossular and hematite were characterized by the surface area using nitrogen (Monosorb Autosorb, Quantachrome Instruments Ltd., USA) and the particle size distribution (Mastersizer2000, Malvern Instruments Ltd., UK), respectively. All the results are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Properties of synthetic goethite, hydration grossular and hematite
Sodium polyacrylate (PAAS, Zhongsheng Biological Technology Co., Ltd., China) with intrinsic viscosity of 1765 mL/g was dried in a vacuum oven at 50 °C for 20 h.
Self-made hydroxamated flocculant HCPAM was prepared by a method described by LIU et al [14] (HCPAM, with the intrinsic viscosity of 737 mL/g, 53% (molar fraction) hydroxamate groups and 15% (molar fraction) carboxyl groups. The contents of hydroxamate and carboxyl groups of HCPAM were measured by elemental analysis).
2.2 Red mud settling tests
2.2.1 Preparation of flocculant solution
The flocculant solution of PAAS or HCPAM was prepared as a solution of 0.5% (mass fraction) polymer solids in 10 g/L NaOH solution, and further diluted to a 0.1% (mass fraction) flocculant solution with de-ionized water just before use.
2.2.2 Preparation of hydration grossular or hematite slurry for settling tests
Several series of hydration grossular or hematite slurries with dissolved organic compounds for settling tests were prepared as follows: the simulative circulating mother liquor was prepared by NaOH and Al(OH)3 (Nk=240 g/L, ak=1.5). The dissolved organic compound (sodium formate, sodium acetate, sodium oxalate, sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate) was dissolved in boiled de-ionized water to obtain the corresponding organic compound solution. 100 mL boiled simulative circulating mother liquor, 8 g hydration grossular or 6 g hematite and a suitable amount of de-ionized water along with varying amounts of the organic compound solution were added into a 250 mL graduated cylinder (f30 mm× 260 mm) to yield 200 mL suspensions. The addition of each organic compound to the suspension is based on a series of fixed molar ratios for carboxylate group of each organic compound to calcium ion of hydration grossular or ferric ion of hematite, for example, the molar ratios for carboxylate group of each organic compound to calcium ion of hydration grossular were correspondingly 0.33, 0.26, 0.20, 0.13 and 0.07, and the molar ratios for carboxylate group of each organic compound to ferric ion of hematite were correspondingly 0.26, 0.21, 0.16, 0.10 and 0.05. The addition amount of the organic compound was based on the mass of the organic compound per volume of the suspension (g/L). The suspensions were stirred at (95±1) °C to obtain hydration grossular slurries with solid content of 40 g/L or hematite slurries with solid content of 30 g/L (Nk= 120 g/L, ak=1.5) at different organic concentrations, respectively.
The hydration grossular or hematite slurry in the absence of organic compounds was prepared similar to the slurries in the presence of organic compounds except that organic compounds were not added to the slurries.
2.2.3 Settling tests
200 mL boiled hydration grossular or hematite slurry in the presence or the absence of organic compounds was placed in a 250 mL graduated cylinder (f30 mm×260 mm), and the cylinder was immediately placed into a glass water bath maintained at (95±1) °C for 30 min. Then, the slurry was mixed using a hand-operated plunger for several times to obtain well- mixed slurry. Timing was started immediately upon stopping mixing, and the height of the solid/liquid interface was recorded at a certain interval. The settling rates were calculated by timing the descent of the mud interface for the first 1 min and for the first 5 min, respectively. After the settling test lasted for 30 min, the clarity of the supernatant was determined by a WGZ-3 turbidimeter (China). After finishing the settling tests described above, the lowest settling rate for the first 1 min of the hydration grossular or hematite slurry at a certain critical concentration of organic compounds was observed. The settling test of the hydration grossular or hematite slurry which was in the presence of organic compounds at a certain critical concentration or in the absence of organic compounds was conducted through similar operation described above except that 240 g/t PAAS or HCPAM was added to the slurry. The amount of the flocculant was based on the mass of flocculant change per mass of solids of the slurry (g/t).
2.3 Adsorption mechanism research
The technique used for adsorbing sodium formate, sodium acetate, sodium oxalate, sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate on the hydration grossular or hematite surface was modified from that developed by JONES [15]. 0.25 g hydration grossular or hematite was placed in an airtight conical flask with 50 mL of 0.001 moL/L sodium hydroxide solution and sonicated at 60 °C for 10 h to obtain a suspension, and the suspension was centrifuged for 30 min at 4000 r/min to separate the supernatant and the solid. The supernatant was decanted to obtain a fresh, carbonate-free hydration grossular or hematite solid placed in an airtight conical flask. 50 mL of a certain concentration of organic compounds in 2 mol/L sodium hydroxide solution was added to the conical flask with 0.25 g of carbonate-free hydration grossular or hematite solid, and the molar ratio for carboxylate groups of organic compounds to calcium ions of hydration grossular or ferric ions of hematite is 10:1. After the mixture was sonicated at 60 °C for 10 h and equilibrated for 24 h, the mixture was centrifuged at 4000 r/min to obtain a solid, and the solid was washed with de-ionized water for one time and dried in a vacuum oven at 60 °C for 24 h. The samples of hydration grossular or hematite after the treatment of sodium formate, sodium acetate, sodium oxalate, sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate were obtained.
Hydration grossular or hematite before the treatment of organic compounds (untreated hydration grossular or untreated hematite) was prepared in the same manner except that organic compounds were not added to the carbonate-free hydration grossular or hematite solid.
The infrared spectra of the samples were measured by a Nicolet-6700 FT-IR spectrometer. Samples were intimately mixed with previously dried KBr by gentle grinding, and a resolution of 4 cm-1 was used and 16 scans accumulated. The samples were analyzed on X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (ESCALAB 250XI, Thermo Scientific Co., USA) utilizing Al Kα X-ray at 1486.6 eV. All measurements were carried out at the pressure below 10-8 Pa with the automatic charge neutralization device. All spectra were charge-referenced so that the unfunctionalized aliphatic C 1s component occurred at 284.8 eV.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Settling performance of different monomineral slurries in presence or absence of different dissolved organic compounds without flocculants
3.1.1 Settling performance of hydration grossular slurries
Settling tests were conducted on 40 g/L hydration grossular slurries to illustrate the effects of dissolved organic compounds (including sodium formate, sodium acetate, sodium oxalate, sodium salicylate and disodium phthalate) on the settling performance without flocculants. The results presented in Fig. 2 were generated by altering the organic species and increasing the concentration of organic compounds in the hydration grossular slurry.
As shown in Fig. 2, the organic compounds have small effects on the settling performance of the hydration grossular slurry. This is accompanied by a slight decrease of the settling rate for the first 1 min and almost no decrease for the first 5 min compared with that in the absence of organic compounds. The settling rate for the first 1 min in the absence of organic compounds is 0.6 m/h. In general, minimal or no effect on the settling rate is seen by the addition of sodium formate to the hydration grossular slurry, and its settling rate for the first 1 min is close to that in the absence of organic compounds. As less than 2.7 g/L of sodium acetate is added to the hydration grossular slurry, no decrease of settling rate for the first 1 min is observed. Increasing the concentration of sodium acetate from 5.3 g/L to 13.3 g/L results in 0.36 m/h of the settling rate for the first 1 min. The presence of sodium oxalate causes a remarkable decrease in the settling rate for the first 1 min, and the settling rate for the first 1 min is 0.18 m/h with the concentration of sodium oxalate ranging from 1.31 g/L to 6.56 g/L. Increasing the concentration of sodium salicylate from 3.10 g/L to 15.68 g/L or disodium phthalate from 2 g/L to 10 g/L results in a gradual decrease of the settling rate for the first 1 min, and the lowest settling rates for the first 1 min of the slurry are 0.15 m/h and 0.18 m/h when the critical concentrations of sodium salicylate and disodium phthalate are 15.68 g/L and 10.00 g/L, respectively. After allowing the slurries to settle for 30 min, the clarity of the supernatant in the presence of sodium oxalate, sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate is poorer than that in the absence of organic compounds. All the results show that the deterioration in settling performance is observed in the presence of organic compounds. The order of the deterioration in settling performance is disodium phthalate>sodium salicylate>sodium oxalate> sodium formate (or sodium acetate).
3.1.2 Settling performance of hematite slurries
The effects of dissolved organic compounds on the settling performance of 30 g/L hematite slurries were investigated without flocculants.
As shown in Fig. 3, the organic compounds have notable effects on the settling performance of the hematite slurry. This is accompanied by a remarkable decrease of the settling rate for the first 1 min and first 5 min compared with that in the absence of organic compounds. The settling rates for the first 1 min and first 5 min of the hematite slurry in the absence of organic compounds are 4.68 m/h and 2.22 m/h, respectively. In general, the minimal effects on the settling rate are seen by the addition of sodium formate or sodium acetate to hematite slurries. The settling rates for the first 5 min in the presence of sodium formate and sodium acetate are close to that in the absence of organic compounds, and the lowest settling rates for the first 1 min are correspondingly 3.66 m/h and 3.6 m/h at 6.7 g/L of the critical concentration of sodium formate and at 13.3 g/L of the critical concentration of sodium acetate, respectively. When the concentration of sodium oxalate in the hematite slurry increases, the settling rate decreases at first, and then increases. The lowest settling rate for the first 1 min and first 5 min are correspondingly 1.2 m/h and 1.75 m/h, respectively, at 5.25 g/L of the critical concentration of sodium oxalate. As the concentrations of sodium salicylate range from 3.1 g/L to 15.68 g/L and disodium phthalate from 2 g/L to 10 g/L in the hematite slurry, a gradual decrease of the settling rate occurs. When the concentration of sodium salicylate increases to 15.68 g/L, the lowest settling rates for the first 1 min and first 5 min are correspondingly 0.90 m/h and 1.70 m/h, respectively. When the concentration of disodium phthalate increases to 10 g/L, the lowest settling rates for the first 1 min and first 5 min are correspondingly 0.48 m/h and 1.50 m/h, respectively. The clarity of the supernatant in the presence of organic compounds (especially disodium phthalate) is poorer than that in the absence of organic compounds. These results indicate that the deterioration in settling performance is observed in the presence of organic compounds. The order of the deterioration in settling performance is disodium phthalate>sodium salicylate> sodium oxalate>sodium formate (or sodium acetate).
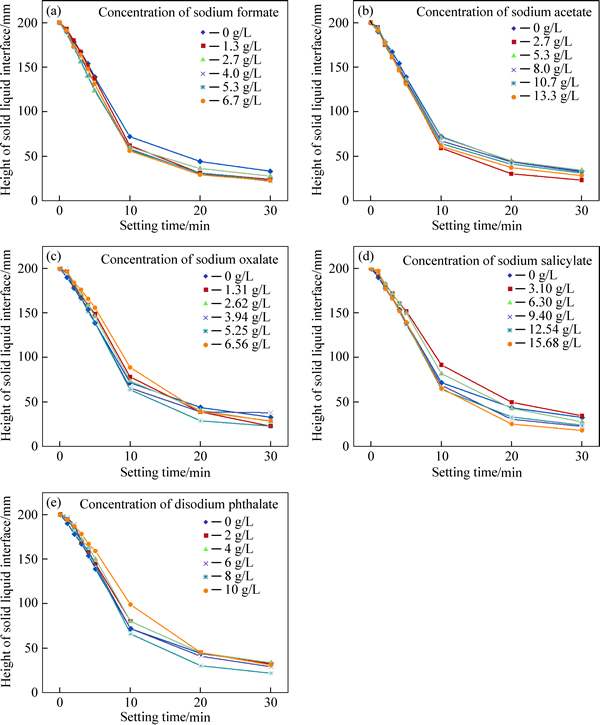
Fig. 2 Settlement performance of 40 g/L hydration grossular slurries as a function of different concentrations of sodium formate (a), sodium acetate (b), sodium oxalate (c), sodium salicylate (d) and disodium phthalate (e)
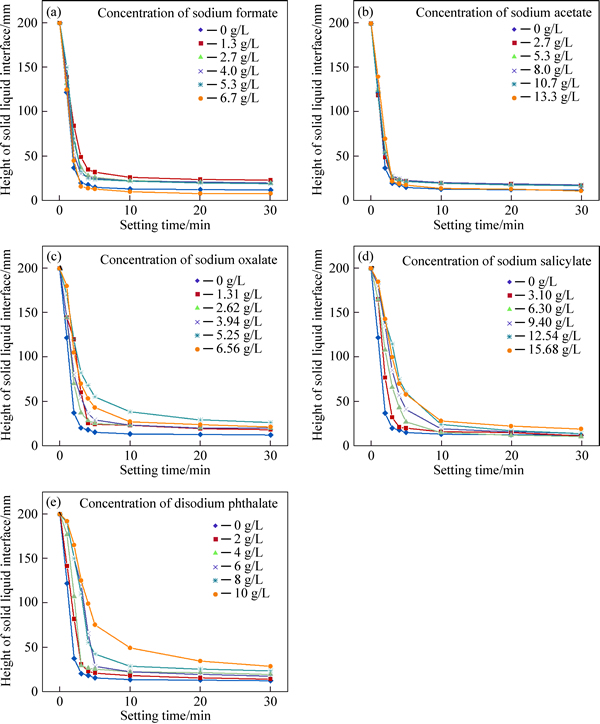
Fig. 3 Settlement performance of hematite slurries with solid content of 30 g/L as function of different concentrations of sodium formate (a), sodium acetate (b), sodium oxalate (c), sodium salicylate (d) and disodium phthalate (e)
3.2 Effects of flocculants on settling performance of different monomineral slurries in presence or absence of different dissolved organic compounds
3.2.1 Settling performance of hydration grossular slurries with addition of PAAS
Focused on 40 g/L hydration grossular slurries in the presence of organic compounds at the critical concentration (i.e., the lowest settling rate occurred at this critical concentration of organic compounds without flocculants) or in the absence of organic compounds, PAAS at dosage of 240 g/t was introduced in order to eliminate the negative effects of the organic compounds on the settling behaviors of the slurries. The results are present in Fig. 4.
As shown in Fig. 4, with the addition of PAAS, the settling rate of the hydration grossular slurry in the presence of sodium formate, sodium acetate, sodium oxalate, sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate is almost equal to that in the absence of organic compounds, and the clarity of the supernatant is significantly improved. The result indicates that PAAS can efficiently eliminate the negative effects of organic compounds on the settling of the hydration grossular slurry.
3.2.2 Settling performance of hematite slurries with addition of HCPAM
As for 30 g/L hematite slurries in the presence of organic compounds at the critical concentration or in the absence of organic compounds, 240 g/t dosage of HCPAM was added to the slurries. The results are present in Fig. 5.

Fig. 4 Settlement performance of 40 g/L hydration grossular slurries in presence of organic compounds at critical concentration or in absence of organic compounds with or without addition of PAAS:
As shown in Fig. 5, with the addition of HCPAM, the settling rate of the hematite slurry in the presence of sodium formate, sodium acetate or sodium oxalate is close to that in the absence of organic compounds. The addition of HCPAM can improve the settling rate of the hematite slurry in the presence of sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate. Whereas with the addition of HCPAM to the slurries, the setting rate of the hematite slurry in the presence of sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate is still smaller than that in the absence of organic compounds. With the addition of HCPAM, the clarity of the supernatant is significantly improved except for that in the presence of sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate. Therefore, the negative effects of sodium formate, sodium acetate and sodium oxalate on the settling of the hematite slurry can be efficiently eliminated by HCPAM, and HCPAM just partially improves the settling of the hematite slurry in the presence of sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate.
3.3 Adsorption mechanism of dissolved organic compounds on synthetic monominerals in red mud
The structural changes of hydration grossular and hematite before and after the treatment of organic compounds were investigated by FT-IR and XPS, respectively.

Fig. 5 Settlement performance of 30 g/L hematite slurries in presence of organic compounds at critical concentration or in absence of organic compounds with or without addition of HCPAM:
3.3.1 Adsorption mechanism of organic compounds on hydration grossular surface
1) FT-IR analysis
FT-IR spectra of unadsorbed sodium formate, sodium oxalate, sodium salicylate and disodium phthalate are depicted in Fig. 6. FT-IR spectra of hydration grossular before and after the treatment of sodium formate, sodium oxalate, sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate are depicted in Fig. 7.
In the FT-IR spectrum of unadsorbed sodium formate (Fig. 6(a)), the asymmetric (νasym) and symmetric (νsym) stretches of the carboxylate group in unadsorbed sodium formate are located at 1598 cm-1 and 1363 cm-1, respectively. Furthermore, the weak band at 1448 cm-1 is assigned to the C—H bending vibration of sodium formate.
In the FT-IR spectrum of unadsorbed sodium oxalate (Fig. 6(b)), the asymmetric (νasym) and symmetric (νsym) stretches of the carboxylate group in sodium oxalate are located at 1641 cm-1 and 1321 cm-1, respectively. Furthermore, the weak band at 1417 cm-1 is assigned to the △(O—C—O) vibration of sodium oxalate.
In the FT-IR spectrum of unadsorbed sodium salicylate (Fig. 6(c)), the asymmetric (νasym) and symmetric (νsym) stretches of the carboxylate group can be identified as the bands at 1587 cm-1 and 1378 cm-1, respectively. The bands at 1623 cm-1, 1486 cm-1 and 1469 cm-1 are assigned to the C—C ring stretching modes of benzene. The band at 1295 cm-1 is assigned to the bending mode of the phenolic (Ph—O—H) group.The phenolic Ph—O stretching vibration is represented by the band at 1250 cm-1 in sodium salicylate [16].

Fig. 6 FT-IR spectra of sodium formate (a), sodium oxalate (b), sodium salicylate (c) and disodium phthalate (d)
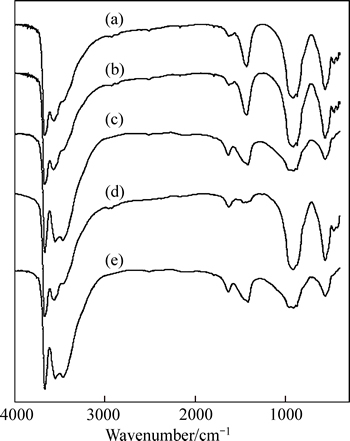
Fig. 7 FT-IR spectra of untreated hydration grossular (a) and hydration grossular after the treatment of sodium formate (b), sodium oxalate (c), sodium salicylate (d) and disodium phthalate (e)
In the FT-IR spectrum of unadsorbed disodium phthalate (Fig. 6(d)), the asymmetric (νasym) and symmetric (νsym) stretches of the carboxylate group can be identified as the bands at 1563 cm-1 and 1382 cm-1, respectively. The band corresponding to the C=O stretching vibration in carboxylate group is located at 1673 cm-1. And the C—C ring stretching mode of benzene occurs at 1484 cm-1 [17].
As shown in Fig. 7, no obvious changes are observed and the characteristic adsorption peaks of organic compounds can be barely found in the spectra of the hydration grossular after the treatment of organic compounds. The results show that no chemisorption occurs between the organic compounds and hydration grossular, but a physisorption of organic compounds might occur on the hydration grossular surface.
2) XPS analysis
Figure 8 shows the binding energies of Ca 2p of hydration grossular before and after the treatment of organic compounds. As shown in Fig. 8, there are no changes of binding energies of Ca 2p for hydration grossular before and after the treatment of organic compounds (with Ca 2p3/2 at 346.78 eV and Ca 2p1/2 at 350.28 eV). Combined with the results from FT-IR spectra, it can be concluded that organic compounds are not chemically but physically adsorbed on the hydration grossular surface.
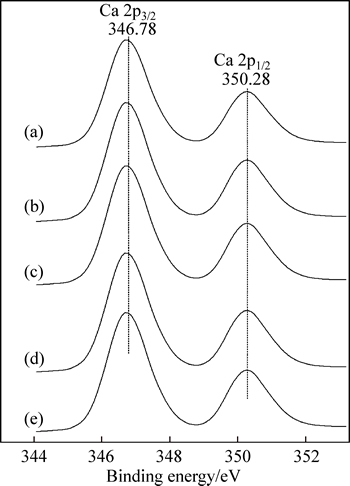
Fig. 8 XPS spectra of Ca 2p of untreated hydration grossular (a) and hydration grossular after treatment of sodium formate (b), sodium oxalate (c), sodium salicylate (d) and disodium phthalate (e)
3.3.2 Adsorption mechanism of dissolved organic compounds on hematite surface
1) FT-IR analysis
FT-IR spectra of hematite before and after the treatment of sodium formate, sodium oxalate, sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate are depicted in Fig. 9.
The FT-IR spectrum of untreated hematite is depicted in Fig. 9(a). There are no characteristic vibrational bands in the zone between 1200 cm-1 and 1700 cm-1, and the band at 1627 cm-1 is assigned to the vibration of adsorbed water.
Early study [18] has demonstrated that the expected frequency shifts occurred when carboxylic acids or their salts were adsorbed as carboxylates on inorganic (oxide) surfaces. When the carboxyl group of carboxylic acids or their salts is directly involved in the adsorption, it is possible to identify the structures on the basis of the carboxylate asymmetric (νasym) and symmetric (νsym) stretches, and their separation (△ν=νasym-νsym). △ν(adsorbed) and △ν(salt) are correspondingly the separation of the symmetric and asymmetric stretches of the carboxylate group of the adsorbed carboxylate salt and the unadsorbed carboxylate salt. They can be used to identify the adsorbed structures: when the value of △ν(adsorbed) is smaller than △ν(salt), a bidentate chelating complex is observed (two oxygen atoms of the carboxylate group form two bonds with one metal atom on the solid surface). However, when △ν(adsorbed) is greater than △ν(salt), a monodentate mononuclear complex is seen (only one oxygen atom of the carboxylate group binds with one metal atom on the solid surface). In binuclear bridging complexes (two oxygen atoms of the carboxylate group bind with two metal atoms on the solid surface), △ν(adsorbed) is almost equal to △ν(salt).
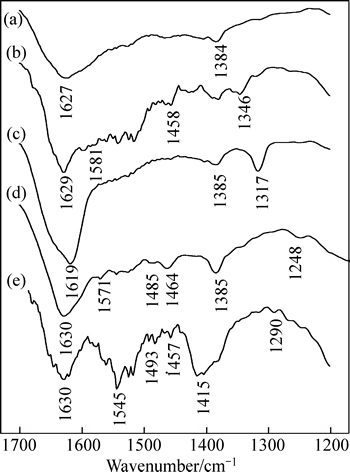
Fig. 9 FT-IR spectra of untreated hematite and hematite (a) after treatment of sodium formate (b), sodium oxalate (c), sodium salicylate (d) and disodium phthalate (e)
For hematite after the treatment of sodium formate, spectral bands at 1581 cm-1 and 1346 cm-1 are indicative of the asymmetric (νasym) and symmetric (νsym) stretches of carboxylate group, respectively (Fig. 9(b)). The asymmetric (νasym) and symmetric (νsym) stretches of carboxylate group of adsorbed sodium oxalate are correspondingly at 1619 cm-1 and 1317 cm-1, respectively (Fig. 9(c)). △ν(salt) for unadsorbed sodium formate and sodium oxalate are correspondingly 235 cm-1 and 320 cm-1, while △ν(adsorbed) of adsorbed sodium formate and sodium oxalate are correspondingly 235 cm-1 and 302 cm-1. This suggests that a bidentate chelating complex may be formed between two oxygen atoms of carboxylate group in sodium formate or sodium oxalate and one surface iron atom of hematite.
FT-IR spectrum of hematite after the treatment of sodium salicylate (Fig. 9(d)) shows that the asymmetric (νasym) and symmetric (νsym) stretch frequencies of carboxylate group of adsorbed sodium salicylate are at 1571 cm-1 and 1385 cm-1, respectively. The △ν(adsorbed) value (187 cm-1) of adsorbed sodium salicylate is slightly smaller than the △ν(salt) value (208 cm-1) of unadsorbed sodium salicylate. Besides, the C—C stretching of benzene ring undergoes significant shifts upon forming a complex with hematite surface because the substituent of the benzene ring affects the charge density and the charge distribution on the benzene ring. In addition, the absence of the bending frequency of the Ph—O—H in adsorbed sodium salicylate indicates the deprotonation and coordination of the phenolic group with the surface iron atom of hematite. This suggests that the adsorbed sodium salicylate can form a bidentate chelating complex in which one oxygen atom of the carboxylate group and the oxygen atom of phenolic group bind with one surface iron atom of hematite.
For hematite after the treatment of disodium phthalate, the bands at 1545 cm-1 and 1415 cm-1 are correspondingly the asymmetric (νasym) and symmetric (νsym) stretches of carboxylate group of adsorbed disodium phthalate. The △ν(adsorbed) value (129 cm-1) of adsorbed disodium phthalate is slightly smaller than the △ν(salt) value (181 cm-1) of unadsorbed disodium phthalate. And the band corresponding to the C=O stretching vibration in carboxylate group located at 1673 cm-1 disappeared after adsorption (Fig. 9(e)). The results assume that a bidentate chelating complex between two carboxylate groups of disodium phthalate and one surface iron atom of hematite may be formed.
2) XPS analysis
Figure 10 shows the binding energies and the full widths at half maximum (FWHM) of Fe 2p of hematite before and after the treatment of dissolved organic compounds. As shown in Fig. 10, in comparison with untreated hematite, the binding energies of Fe 2p3/2 for hematite after the treatment of sodium formate, sodium oxalate, sodium salicylate and disodium phthalate are correspondingly decreased by 1.2, 1, 0.8 and 1 eV, and those of Fe 2p1/2 are correspondingly decreased by 1.4, 0.9, 1.2 and 1.1 eV. The change of chemical shift can be explained by the atomic potential model [19]. The atomic potential model assumes that the atomic core potential varies linearly with the valence charge of atoms, and the oxidation of one atom results in the increase of the atomic binding energy of the inner electron, whereas the reduction of one atom results in the decrease of the atomic binding energy of the inner electron. This indicates that partial reduction of surface iron atoms after the treatment of organic compounds may happen due to the coordination of Fe(III) of hematite surfaces with oxygen atoms of organic compounds. On the other hand, FWHM of the peaks of Fe 2p for hematite after the treatment of organic compounds is slightly smaller than that of untreated hematite, which also indicates that the partial reduction of the iron atoms may occur on the surface of hematite. This opinion is also supported by Ref. [20]: FWHM was inversely proportional to the lifetime of ion state remaining after photoemission, the electronic configuration of Fe2+ was 3d6 whilst that of Fe3+ was 3d5, and Fe2+ would have a longer lifetime than Fe3+, and then FWHM of Fe(II) 2p peaks was expected to be slightly smaller than that of Fe(III) 2p peaks. This proves that chemisorptions of organic compounds on the hematite surface in a bidentate chelating complex take place.
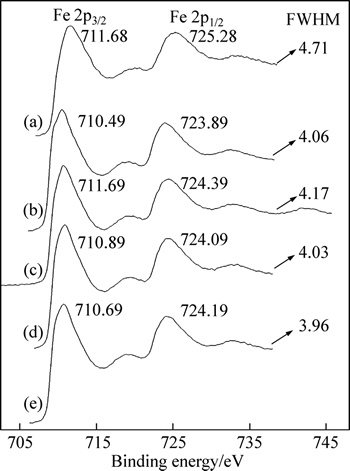
Fig. 10 XPS spectra of untreated hematite (a) and hematite after treatment of sodium formate (b), sodium oxalate (c), sodium salicylate (d) and disodium phthalate (e)
All the results show that organic compounds were not chemically but physically adsorbed on the hydration grossular surface. Therefore, organic compounds have small effects on the settling performance of the hydration grossular slurry. PAAS can efficiently eliminate the negative effects of organic compounds on the settling performance of the hydration grossular slurry because of the weak physisorption of organic compounds on the hydration grossular surface and a polymer bridging flocculation mechanism of PAAS on the hydration grossular surface.
According to our experimental results, the adsorption mechanism of organic compounds on the hematite surface is a chemisorption, which accounts for the notable effects of organic compounds on the settling performance of the hematite slurry.
The hematite slurry in the presence of sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate owns poorer settling performance than that in the presence of sodium formate or sodium acetate, which might be due to the stronger hydrophobicity of sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate than that of sodium formate or sodium acetate. The octanol-water partition coefficient (KOW) is a coefficient representing the ratio of the solubility of an organic compound in octanol to its solubility in water, and is generally used as a relative indicator of the tendency of an organic compound to adsorb to soil [21]. The higher the KOW is, the more non-polar and the more likely to adsorb on soil the organic compound is. KOW values for salicylic acid and phthalic acid are correspondingly 102.26 and 100.73, which are higher than that for formic acid (10-0.54) and acetic acid (10-0.17). This means that the adsorption of sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate on the hematite surface increases the hydrophobicity of the hematite surface and causes the hematite particles easier to float at the air/water interface. This accounts for the poorer settling performance in the presence of sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate than that in the presence of sodium formate or sodium acetate.
Furthermore, due to the difference in hydrophobicity of organic compounds, the hydrophilicity of HCPAM may weaken its adsorption on the hematite surface in the presence of sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate compared with that in the presence of sodium formate or sodium acetate. On the other hand, MANASH et al [22] and JAYANTA et al [23] studied the adsorption of benzoate and salicylate onto the natural hematite surfaces, and found that unlike benzoate, salicylate is not only chemically adsorbed at one surface iron site but also covers around three or more surface iron sites of the hematite surface. We infer that sodium formate, sodium acetate or sodium oxalate may just adsorb at one surface iron site, and sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate may not only chemically adsorb at one surface iron site but also cover around three or more surface iron sites of the hematite surface. This indicates that less active iron sites exist on the hematite surface, which makes HCPAM more difficult to be adsorbed on the hematite surface in the presence of sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate than in the presence of sodium formate or sodium acetate. Thus, HCPAM can efficiently eliminate the negative effects of sodium formate or sodium acetate on the settling performance of the hematite slurry, however, only partial improvement in the settling performance of the hematite slurry in the presence of sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate can be achieved by HCPAM.
4 Conclusions
1) The deterioration in settling performance of the hydration grossular or hematite slurry in the presence of dissolved organic compounds occurs compared with the case of the absence of organic compounds. The order of the deterioration in settling performance of the slurries is disodium phthalate>sodium salicylate>sodium oxalate> sodium formate (or sodium acetate). Moreover, dissolved organic compounds have much less negative effects on the settling performance of the hydration grossular slurry than that of hematite.
2) PAAS can efficiently eliminate the negative effects of dissolved organic compounds on the settling performance of the hydration grossular slurry. HCPAM can efficiently eliminate the negative effects of sodium formate, sodium acetate or sodium oxalate on the settling performance of the hematite slurry. But, only partial improvement in the settling performance of the hematite slurry in the presence of sodium salicylate or disodium phthalate can be achieved for by HCPAM.
3) The analyses of FTIR and XPS show that dissolved organic compounds are not chemically but physically adsorbed on the hydration grossular surface. A chemisorption of organic compounds at the hematite surface occurs, and a bidentate chelating complex may be formed between oxygen atoms of carboxylate group of sodium formate, sodium acetate or sodium oxalate and one surface iron atom of hematite. A bidentate chelating complex, in which one oxygen atom of the carboxylate group and the oxygen atom of the phenolic group of adsorbed sodium salicylate bind with one surface iron atom, may be formed. And the formation of a bidentate chelating complex between two carboxylate groups of disodium phthalate and one surface iron atom of hematite may take place.
References
[1] DOMINICUS A S, KEVORK C. Removal of organics from Bayer process streams. US 4836990 [P]. 1989-01-06.
[2] GREG P, JOANNE L. Organic compounds in the processing of lateritic bauxites to alumina. Part 1: Origins and chemistry of organics in the Bayer process [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 105: 1-29.
[3] GREG P, JOANNE S C L, CHRIS V. Organic compounds in the processing of lateritic bauxites to alumina. Part 2: Effects of organics in the Bayer process [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 127-128: 125-149.
[4] JOHN T M, MORRIS L R. Removal of high molecular weight organic compounds from Bayer process caustic liquor. US 4663133 [P]. 1987-05-05.
[5] BERNHARD S, GERHARD B, ERNST U, KLAUS S. Method for removing harmful organic compounds from aluminate liquors of the Bayer process. US 4046855 [P]. 1977-04-14.
[6] L Zi-jian, BI Shi-wen, XIE Yan-li. Effect of sodium oxalate on processes of red mud sedimentation [J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2006, 5(2): 105-108. (in Chinese)
Zi-jian, BI Shi-wen, XIE Yan-li. Effect of sodium oxalate on processes of red mud sedimentation [J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2006, 5(2): 105-108. (in Chinese)
[7] L Zi-jian, BI Shi-wen, XIE Yan-li. Effects of para-phthatlic sodium on sedimentation of red mud [J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2007, 28(1): 83-86. (in Chinese)
Zi-jian, BI Shi-wen, XIE Yan-li. Effects of para-phthatlic sodium on sedimentation of red mud [J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2007, 28(1): 83-86. (in Chinese)
[8] L Zi-jian, BI Shi-wen, XIE Yan-li. The effects of the fulvic acid on properties of mud sedimentation [J]. Light Metal, 2007, 4(2): 13-15. (in Chinese)
Zi-jian, BI Shi-wen, XIE Yan-li. The effects of the fulvic acid on properties of mud sedimentation [J]. Light Metal, 2007, 4(2): 13-15. (in Chinese)
[9] L Zi-jian, BI Shi-wen, XIE Yan-li. The effects of the humic acid on properties of mud sedimentation [J]. Journal of Molecular Science, 2006, 22(6): 413-416. (in Chinese)
Zi-jian, BI Shi-wen, XIE Yan-li. The effects of the humic acid on properties of mud sedimentation [J]. Journal of Molecular Science, 2006, 22(6): 413-416. (in Chinese)
[10] FU Wei-an. Study on behavior of silicon-containing minerals and Ti-containing minerals in high pressure digestion of bauxite [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2008: 1-71. (in Chinese)
[11] LI Xiao-bin, KONG Lian-lian, QI Tian-gui. Effect of alumogoehite in Bayer digestion process of high-iron gibbsitic bauxite [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(2): 543-548. (in Chinese)
[12] LIU Jin-wei, HU Hui-ping, WANG meng, Chen Qi-yuan. Adsorption mechanism of the simulated red mud from diaspore with high levels of silicon and iron [J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2016. ( in press)
[13] LEKKERKERKER H N W, VROEGE G J. Liquid crystal phase trasitions in suspensions of mineral colloids: New life from old roots [J]. Mathematical, Physical & Engineering Sciences, 2013, 371: 1-20.
[14] LIU Jin-wei, HU Hui-ping, WANG Meng. Synthesis of modified polyacrylamide with high content of hydroxamate groups and the settling performance of red mud [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(6): 1-8.
[15] JONES F, FARROW J B, BRONSWIJK W V. An infrared study of a polyacrylate flocculant adsorbed on hematite [J]. Langmuir, 1998, 14: 6512-6517.
[16] JYOTIRMOY S, SEKH M. Comparative adsorption involving ortho- and para-hydroxybenzonic acids in mixed-adsorbate mode onto α-alumina surface: Effect of molecular structure [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2014, 2: 90-99.
[17] MALIN L, PER P. Competitive adsorption involving phosphate and benzenecarboxylic acids on goethiteieffects of molecular structures [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 343(1): 263-270.
[18] SIMON M, ASWANI Y, PENG G, ROBIN H B. Dye-sensitized solar cells with 13% efficiency achieved through the molecular engineering of porphyrin sensitizers [J]. Nature Chemistry, 2014, 6: 242-247.
[19] MANDAL S, GHOSH C K, SARKAR D, MAITI U N. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic investigation on the elemental chemical shifts in multiferroic BiFeO3 and its valence band structure [J]. Solid State Sciences, 2010, 12: 1803-1808.
[20] YAMASHITA T, HAYES P. Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2008, 254(8): 2441-2449.
[21] LYMAN W J, REEHL W F, ROSENBLATT D H. Handbook of chemical property estimation methods: Environmental behavior of organic compounds [M]. Washington, DC, USA: American Chemical Society, 1990: 960.
[22] MANASH R D, DIPAK B, PRAKASH C B, SEKH M. Kinetics and adsorption of benzoate and salicylate at the natural hematite-water interface [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2005, 254: 49-55.
[23] JAYANTA M B, JYOTIRMOY S, SEKH M. Influence of functional groups on the adsorption behavior of substituted benzoic acids at the α-alumina/water interface [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2011, 375(1/2/3): 42-49.
(Edited by YANG Bing)
Foundation item: Project(51174231) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2015-05-06; Accepted date: 2015-08-09
Corresponding author: HU Hui-ping, Professor; Tel: +86-731-88877364; E-mail: phuhuiping@126.com

