J. Cent. South Univ. (2016) 23: 669-676
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-016-3112-2
Geochemistry of lower Silurian shale of Longmaxi Formation, southeastern Sichuan Basin, China: implications for provenance and source weathering
GUO Ling(郭岭)1, 2, JIA Chao-chao(贾超超)2, DU Wei(杜伟)3
1. State Key Laboratory of Continental Dynamics (Northwest University), Xi’an 710069, China;
2. Department of Geology, Northwest University, Xi’an 710069, China;
3. Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development of Sinopec, Beijing 100083, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Abstract: Lower Silurian Longmaxi Shale (SLS) in southeastern Sichuan Basin, China, was analyzed for major and selected trace elements, and their provenance, intensity of palaeoweathering of the source rocks were analyzed based on these elements. The results show that SiO2, Al2O3 and Fe2O3, are dominant major elements with average contents of 60.59%, 15.91% and 5.87% in Upper Silurian Longmaxi Shale (USLS), and 65.14%, 13.24% and 4.68% in Lower Silurian Longmaxi Shale (LSLS). The TiO2-Zr plot, Hf (ppm) versus La/Th discriminant diagram, and abundance of Cr and Ni suggest a dominantly felsic source for the Longmaxi sediments. Average chemical index of alteration (CIA), plagioclase index of alteration (PIA) values (64.05% and 72.86%, respectively) imply low-degree chemical weathering of the source material in early Longmaxi time, and average CIA, PIA values (68.44% and 80.35%, respectively) imply moderate chemical weathering of the source material in late Longmaxi time.
Key words: trace elements; black shale; provenance; weathering; discriminant diagrams; Sichuan Basin
1 Introduction
Black shales cover only a small percentage of continental land area but are economically and environmentally important [1-3]. Specifically, these shales often host significant amounts of hydrocarbon, such as oil and gas that can be exploited profitably [4]. The geochemistry of shales, especially trace elements are believed to represent the average composition of the upper continental crust than other sedimentary rocks [5], since they preserve the original signature of the provenance and diagenetic history [6]. Many studies have utilized the geochemical composition of clastic sediments, and successfully inferred the source-area weathering conditions [7-9] and the provenance [10-16].
Fine-grained siliciclastic rocks are suitable for provenance studies. For example, Sc and Co are quantitatively transferred from the catchment to the sedimentary basin. In contrast, coarse-grained sediments may show sorting effects [16]. Most siliciclasitic units internal to Archean greenstone terrenes are first cycle volcanogenic turbidities. Proterozoic and younger basins have detritus with a large component of K-rich granites from intracrustal melting [16].
There are relatively few papers with comprehensive major and trace element data for shales in lower Silurian series shales in southeastern Sichuan Basin. The southeastern Sichuan Basin has excellent preservation of shales, especially in lower Silurian series (e.g., Longmaxi Formation shale). Accordingly, in this study we report geochemical data for shales from lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in southeastern Sichuan Basin to address: 1) source rock composition of the Silurian Longmaxi Shales (SLS); and 2) source area weathering intensity of the SLS.
2 Geological setting
The study area is located in the southeastern part of the Sichuan Basin (Fig. 1(a)), which is a foreland basin formed during the Late Triassic [12]. The southeastern Sichuan Basin features relatively high uplift rates with strong tectonic compression. The tectonic stresses of folds formed in the Cretaceous underwent relaxation or release in the Cenozoic, leading to the creation of a series of large-scale NNE-trending faults along anticlinal axes and wings. These processes ultimately created the modern tectonic landscape of the study area (Fig. 1(b)). The SLS, with 250 m in thickness in the northern part of the study area and 15 m in its southern part, was deposited during the early Silurian Longmaxi stage. Deposition occurred in a foreland basin that had generally a restricted circulation with the open ocean, and detrital materials came primarily from the Chuandian Uplift which was located in the southeastern part of the study area [13].
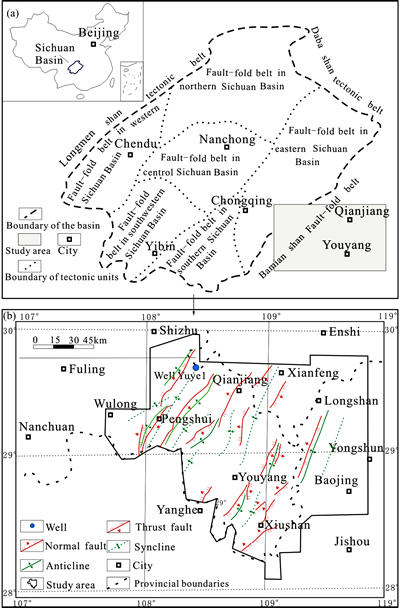
Fig. 1 Sketch tectonic map of Sichuan Basin (a) and detailed tectonic map and well location in study area (b)
3 Material and methods
The samples analyzed in the present study were collected from cores of well Yuye1, which were wrapped in plastic, transported to Beijing and stored at approximately 25 °C. 31 drillcore samples cross the entire stratigraphic succession of the Longmaxi Formation from well Yuye 1. Samples were crushed and powdered (200 mesh) in pollution-free vibration grinding machine P9 in the analytical laboratory at the Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology. Power samples are dried at 102 °C for 3 h, and then placed in the drier for analysis.
Major element compositions of whole rocks were analyzed using a Philips PW2404 X-ray fluorescence spectrometer at the same laboratory, with analytical uncertainties better than 3% for all major elements, and the analytical procedures were similar to those described by Jin et al [14]. Trace elements determination was performed using Finnigan-MAT ElementⅠHR-ICP-MS at the same laboratory, with analytical uncertainties better than 4%, and the analytical procedures were similar to those described by Jin et al [14].
4 Results
4.1 Major element geochemistry
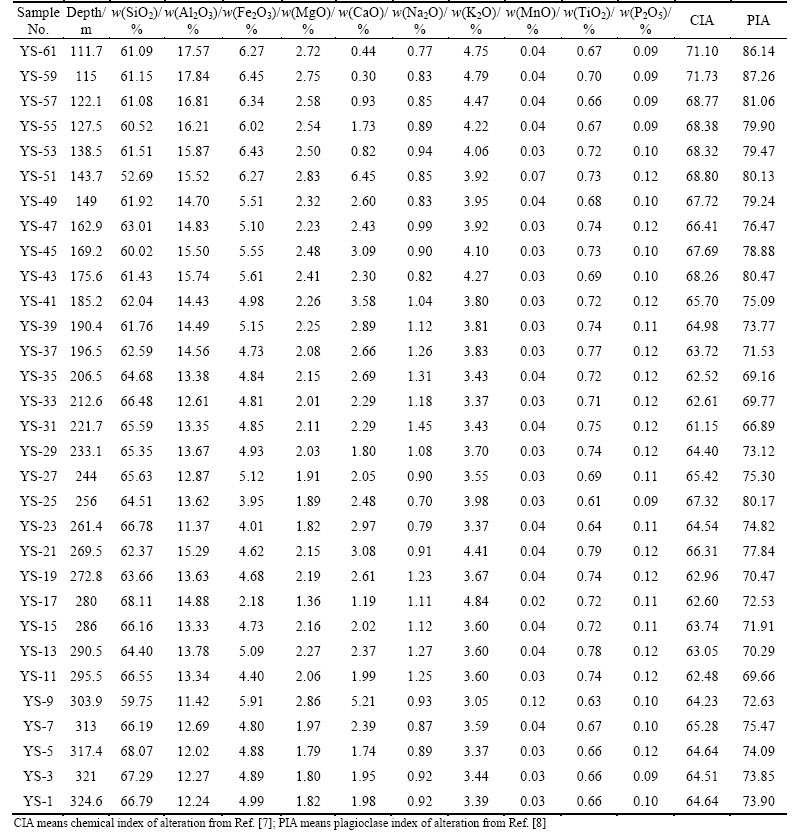
Major element concentrations of shales are presented in Table 1. The SiO2 content is lower in the upper part of the Silurian Longmaxi Shale (USLS, from 190 m to 110 m) (52.69%-63.01% in mass fraction; average content 60.59%; number of samples n=11), than in the lower part of the Silurian Longmaxi Shale (LSLS, from 190 m to 324.4 m) (59.75%-68.11%; average content 65.14%; number of samples n=20). The Al2O3 content is greater in ULSL than in the LSLS (Table 1), as a result of the dilution effect of quartz [15]. The average MnO, TiO2 and P2O5 contents are almost similar between the USLS and LSLS (Table 1). The USLS is higher in Fe2O3 (4.98%-6.45%), MgO (2.23%-2.83%) and K2O (3.80%-4.79%) contents than the LSLS (Fe2O3, 2.18%- 5.91%; MgO, 1.36%-2.86%; K2O, 3.05%-4.84%).The average CaO (2.24%) and Na2O (0.88%) contents in USLS are lower than those in the LSLS (CaO, 2.43%; Na2O, 1.06%).
Table 1 Major element concentrations for shales of Longmaxi Formation
4.2 Trace element geochemistry
Trace element concentrations of the shale samples collected from 31 stratigraphic units belonging to the Longmaxi Formation are presented in Table 2. The values of each shale sample are compared with trace elements values of upper continental crust (UCC) [16]. The upper part of the SLS is higher in elements Sc, Co, Cu, Rb, Y, Nb, Ba, and Th, and lower in Cr, Ni, Sr, Zr and U than that in lower part of the SLS. In comparison to upper continental crust (UCC) [16], the SLS shows large variations in trace elements concentrations. Except for Sr, Zr, Nb and Hf, the rest of the trace elements in the SLS is higher than that in the UCC (Figs. 2(a), (b) and (c); Table 2).
5 Discussion
5.1 Provenance
Many investigators have demonstrated that chemical composition of siliciclastic sedimentary rocks is related to that of their source regions and this principle has been used to characterize the source rocks from which the investigated siliciclastic sedimentary rocks were derived [10-11, 17-18]. The abundance of Cr and Ni in clastic sedimentary rocks can be considered a proxy in provenance studies. A high content of Cr and Ni is predominantly found in sediments derived from ultramafic rocks, whereas a low concentration of Cr and Ni indicates a felsic provenance [10, 19]. Garver et al [10]. have demonstrated that elevated Cr and Ni abundances (w(Cr)>150×10-6 and w(Ni)>100×10-6), low Cr/Ni ratios (1.3-1.5) and a high correlation coefficient between these two elements (r=0.90) are indicative of ultramafic rocks in the source region. The Cr (78.5-125)×10-6 and Ni (42.2-86.9) concentrations (Table 2) in most of the studied samples are relatively low, with a less significant correlation coefficient (r=0.22) and variable Cr/Ni ratios (1.1-2.3). These low Cr and Ni concentrations in the studied samples may be showing a felsic provenance of the SLS. Furthermore, a binary diagram (Fig. 3(a)) of Hf versus La/Th ratios has also been used to discriminate the source area [17]. In this source discrimination diagram, most of the shales (27 samples, 87% of total samples) of the present study plot in the field of felsic source, and only 4 samples plot near the filed of felsic source (Fig. 3(a)). In the provenance discrimination diagram of Roser and Korsch [20], the discriminant functions are based on contents of both immobile and variably mobile major elements, and on this diagram (Fig. 3(b)), most of the shales of the present study plot in the field of quartzose sedimentary provenance and only one sample plot in the field of felsic igneous provenance. Concentration of zircon (Zr) is also used for characterizing the nature and composition of source rocks [21]. The average concentrations of Zr and Ti do not show a significantly wide variation (Table 1 and Table 2), and it may be possible that significant fractionation of Zr and Ti might not have acquired during transportation and deposition of SLS. This interpretation is corroborated by the total absence of any horizon containing either megascopic or microscopic zircon or titanium concentration within the shale horizons [11]. Average zircon content of the SLS varies from 118×10-6 to 222×10-6 (Table 2), which is similar to the average value for granite. A TiO2 versus Zr plot distinguishes three different source rock types, i.e., felsic, intermediate and mafic; the TiO2/Zr weight ratio generally decreases with increasing SiO2 content, from >200 for mafic igneous rocks, 195-55 for intermediate igneous rocks, to <55 for felsic rocks [21]. The TiO2/Zr weight ratio of the SLS ranges from 29.8 to 59.3 with average value 42.0. The TiO2 versus Zr plot of the SLS (Fig. 4) represents predominantly felsic source rocks for the Silurain Longmaxi shales, which corroborates the interpretations from the TiO2/Zr ratio, discrimination diagram of La/Th ratio and Hf abundance.
Table 2 Trace element concentrations in ppm for shales of Longmaxi Formation
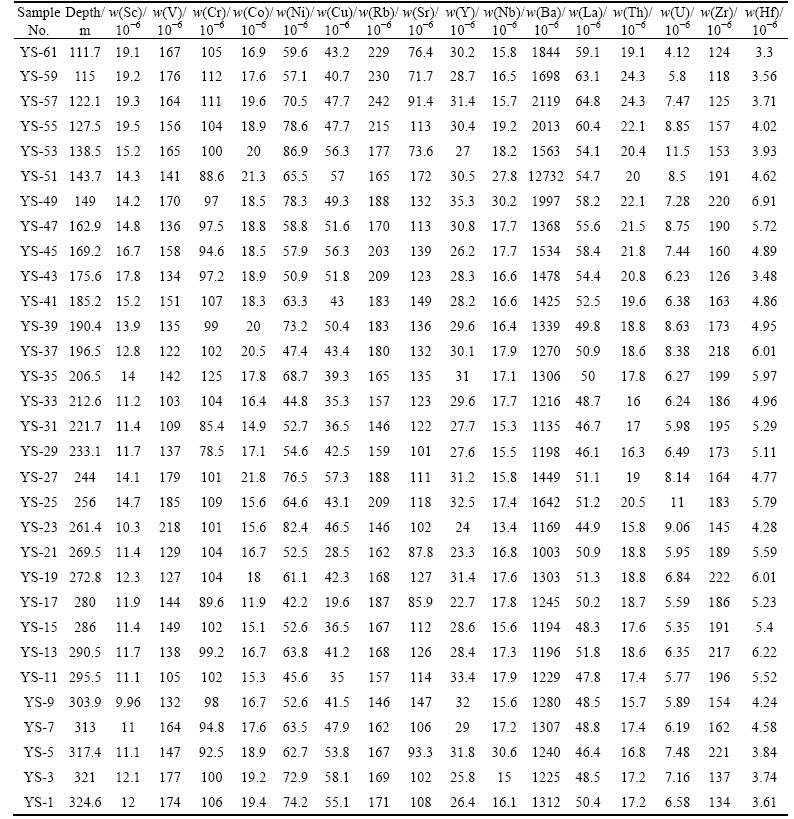
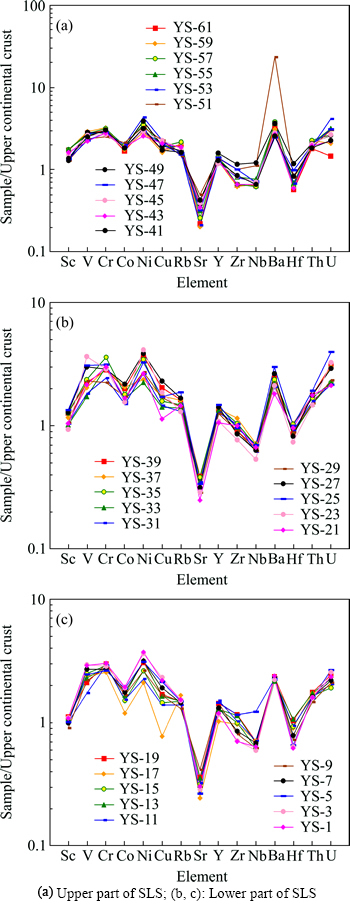
Fig. 2 Multi-element normalized diagram for shale samples, normalized against average upper continental crust [16]:
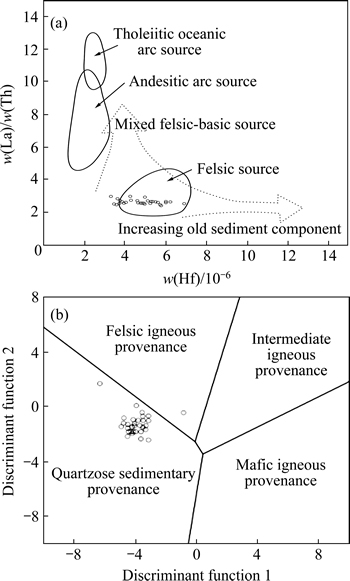
Fig. 3 Source discrimination for shales of Longmaxi Formation in terms of La/Th mass ratio and Hf abundance (fileds from ref. [17]) (a), and provenance discrimination diagram for shales of Longmaxi Formation (b) (fileds from ref. [20]. Discriminant function 1=(-1.773×TiO2%)+(0.607×Al2O3%)+ (0.76×Fe2O3T%)+(-1.5×MgO%)+(0.616×CaO%)+(0.509× Na2O%)+(-1.22×K2O%)+(-9.09). Discriminant Function 2= (0.445×TiO2%)+(0.07×Al2O3%)+(-0.25×Fe2O3T%)+(-1.142×MgO%)+(0.438×CaO%)+1.475×Na2O%+(1.426×K2O%)+(-6.861))
5.2 Source area weathering
Intensity of chemical weathering of source rocks is controlled mainly by source rock composition, duration of weathering and rates of tectonic uplift of source region [22]. About 75% of the labile material of the upper crust is composed of feldspars and volcanic glass, and chemical weathering of these materials ultimately results in the formation of clay minerals [8, 23]. Elements such as Ca, Na and K are largely removed from source rocks during chemical weathering. The amount of these elements surviving in soil profiles and in sediments derived from them is a sensitive index of the intensity of chemical weathering [24-25].
Quantitative measures, such as the chemical index of alteration (CIA) [7] and the plagioclase index of alteration (PIA) [8], are potentially useful to evaluate the degree of chemical weathering. High CIA values (greater than 80) reflect the removal of labile cations (e.g., Ca2+, Na+, K+) relative to stable residual constituents (Al3+, Ti4+) during weathering, and indicate high chemical weathering. Low CIA (less than 60) values indicate the near absence of chemical alteration [7-8, 26]. PIA monitors and quantifies progressive weathering of feldspars and volcanic glass to clay minerals [8]. PIA values of shales suggest intense destruction of feldspars during the course of source weathering, fluvial transport, sedimentation and diagenesis [27]. With increasing weathering, the PIA values increases with decrease in total alkali content (K2O+Na2O). This is due to destruction of feldspars among which plagioclase is preferentially removed than K-feldspars [23]. The equations of CIA and PIA indices mentioned above are:
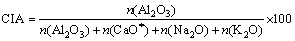
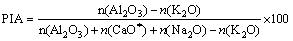
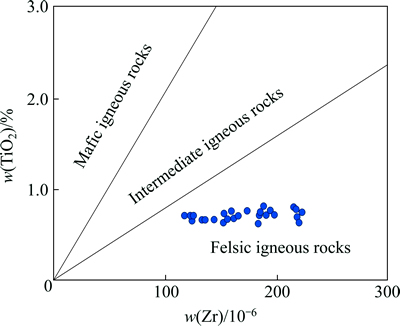
Fig. 4 TiO2-Zr plot for SLS after Hayashi et al [21]
In the above equations CaO* represents CaO from the silicate fraction, and all major oxides are expressed in molar proportions.
There is no direct method to distinguish and quantify the contents of CaO belonging to silicate fraction and non-silicate fraction [27], and McLennan et al [28] proposed an indirect method for quantifying CaO content of silicate fraction assuming reasonable values of Ca/Na ratios of silicate material [28]. Following this procedure, the CIA and PIA values of the shales have been determined and the results are provided in Table 1. The CIA values in the studied shales vary from 61.15% to 71.73% (average 65.61%). PIA value indicating the intensity of alteration of source material varies from 66.89% to 87.26% (average 75.53%). Moreover, the CIA and PIA values of the SLS generally can also be divided into two sections, i.e. LSLS (from190 m to 324.4 m) and USLS (from 190 m to 110 m). The CIA and PIA values are relatively consistent in lower part of the SLS sequence, besides an influx of more weathered detritus in the section from 240 m to 260 m of the SLS sequence (Fig. 5). The average values of CIA and PIA in this section are 64.05% and 72.86%, respectively, which are indexes of a relatively low- degree of chemical weathering [7-8]. In the USLS sequence, the average CIA is 68.44%, which is an index of a moderate chemical weathering [7]. The average PIA in this section is 80.35%, which shows more feldspar being intensely destructed deposited than that in the LSLS. The CIA and PIA values increased steadily, which shows that an influx of more and more weathered detritus in this section (Fig. 5). The CIA values from 65% to 75% reflected a warm and humid climate conditions, and a moderate chemical weathering, and CIA values from 60% to 65% reflected a cold and arid climate conditions, and a low-degree chemical weathering [7]. Relying on CIA and PIA values, it can be contended that the source rock of the SLS was subjected to low-degree to moderate chemical weathering in the Longmaxi period in study area.
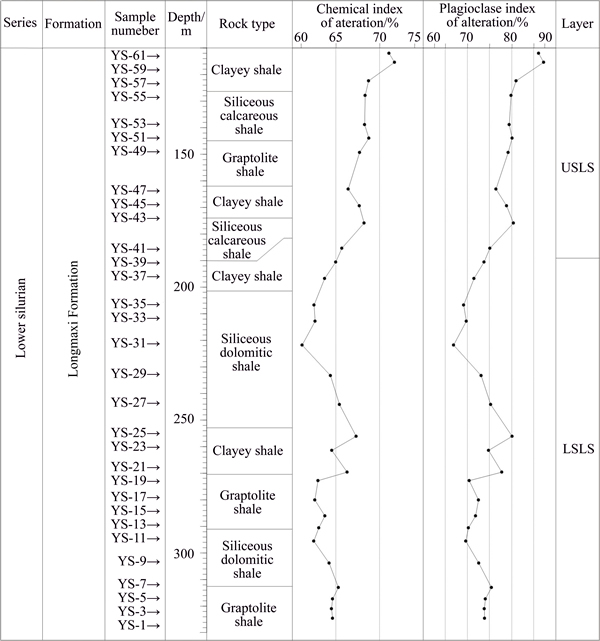
Fig. 5 CIA and PIA variations in SLS sequence from well Yuye 1 (USLS: upper part of Silurian Longmaxi Shale; LSLS: Lower part of Silurian Longmaxi Shale)
6 Conclusions
1) The average SiO2, CaO and Na2O contents in the upper part of the Silurian Longmaxi Shale (ULSL) are 60.59%, 2.24% and 0.88%, respectively, while 65.14%, 2.43% and 1.06%, respectively in the lower part of the Silurian Longmaxi Shale (LSLS). The average Al2O3, Fe2O3, MgO and K2O contents are 15.91%, 5.87%, 2.51% and 4.20%, respectively, in ULSL, and 13.24%, 4.68%, 2.03% and 3.65%, respectively, in the LSLS.
2) The TiO2-Zr plot, Hf versus La/Th discriminant diagram, and abundance of Cr and Ni suggests a dominantly felsic source for the Longmaxi sediments. CIA and PIA suggest moderate climate conditions during deposition and indicate that extreme weathering conditions are probably negligible in the source area. The enhanced leaching of feldspar and relatively high CIA and PIA suggest that the weathering is relatively more severe during the late Longmaxi time. The relatively low CIA and PIA in the LSLS imply low- degree chemical weathering during early Longmaxi time.
References
[1] BANERJEE S, DUTTA S, PAIKARAY S, MANN U. Stratigraphy, sedimentology and bulk organic geochemistry of black shales from the Proterozoic Vindhyan Supergroup (central India) [J]. Journal of earth system science, 2006, 115(1): 37-47.
[2] SHPIRT M Y, PUNANOVA S A, STRIZHAKOVA Y A. Trace elements in black and oil shales [J]. Solid Fuel Chemistry, 2007, 41(2): 119-127.
[3] POLLACK G D, KROGSTAD E J, BEKKER A. U-Th-Pb-REE systematics of organic-rich shales from the ca. 2.15 Ga Sengoma Argillite Formation, Botswana: Evidence for oxidative continental weathering during the great oxidation event [J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 260(3): 172-185.
[4] CURTIS J B. Fractured shale-gas systems [J]. AAPG bulletin, 2002, 86(11): 1921-1938.
[5] LI Da-peng, CHEN Yue-long, WANG Zhong, LIN Yu, ZHOU Jian. Paleozoic sedimentary record of the Xing-Meng Orogenic Belt, Inner Mongolia: Implications for the provenances and tectonic evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(7): 776-785.
[6] MONDAL M, WANI H, MONDAL B. Geochemical signature of provenance, tectonics and chemical weathering in the Quaternary flood plain sediments of the Hindon River, Gangetic plain, India [J]. Tectonophysics 2012, 566: 87-94.
[7] NESBITT H W, YOUNG G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites [J]. Nature, 1982, 299: 715-717.
[8] FEDO C M, NESBITT H W, YOUNG G M. Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance [J]. Geology, 1995, 23(10): 921-924.
[9] RAZA M, AHAMD A, SHAMIM M K, KHAN F. Geochemistry and detrital modes of Proterozoic sedimentary rocks, Bayana Basin, north Delhi fold belt: implications for provenance and source-area weathering [J]. International Geology Review, 2012, 54(1): 111-129.
[10] GARVER J I, ROYCE P R, SMICK T A. Chromium and nickel in shale of the Taconic foreland: a case study for the provenance of fine-grained sediments with an ultramafic source [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1996, 66(1): 100-106.
[11] PAIKARAY S, BANERJEE S, MUKHERJI S. Geochemistry of shales from the Paleoproterozoic to Neoproterozoic Vindhyan Supergroup: Implications on provenance, tectonics and paleoweathering [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32(1): 34-48.
[12] JIA Qiu-peng, JIA Dong, LUO Liang, CHEN Zhu-xin, LI Yi-quan, DENG Fei, SUN Sheng-si, LI Hai-bin. Three-dimensional evolutionary models of the Qiongxi structures, southwestern Sichuan basin, China: Evidence from seismic interpretation and geomorphology [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica: English Edition, 2009, 83(2): 372-385.
[13] JIANG Zai-xing, GUO Ling, LIANG Chao. Lithofacies and sedimentary characteristics of the Silurian Longmaxi Shale in the southeastern Sichuan Basin, China [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2013, 2(3): 238-251.
[14] JIN Ye, FANG Nian-qiao, YANG Shu-ying. In situ gabbro geochemical characteristics and implications from the Southwest Indian Ocean Ridge [J]. Earth Sciece-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2012, 37(1): 57-67. (in Chinese)
[15] CULLERS R L. The geochemistry of shales, siltstones and sandstones of Pennsylvanian-Permian age, Colorado, USA: implications for provenance and metamorphic studies [J]. Lithos, 2000, 51(3): 181-203.
[16] TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S. The continental crust: Its composition and evolution [M]. Oxford, UK: Blackwell, 1985: 349.
[17] FLOYD P A, LEVERIDGE B E. Tectonic environment of the Devonian Gramscatho basin, south Cornwall: framework mode and geochemical evidence from turbiditic sandstones [J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1987, 144(4): 531-542.
[18] GHOSH P, BHATTACHARYA S K, DAYAL A M, TRIVEDI J R, EBIHARA M, SARIN M M, CHAKRABARTI A. Trace element and isotopic studies of Permo-Carboniferous carbonate nodules from Talchir sediments of peninsular India: Environmental and provenance implications [J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 2002, 111(2): 87-93.
[19] ARMSTRONG-ALTRIN J S, LEE Y I, VERMA S P, RAMASAMY S. Geochemistry of sandstones from the upper Miocene Kudankulam Formation, southern India: Implications for provenance, weathering, and tectonic setting [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2004, 74(2): 285-297.
[20] ROSER B P, KORSCH R J. Provenance signatures of sandstone-mudstone suites determined using discriminant function analysis of major-element data [J]. Chemical Geology, 1988, 67: 119-139.
[21] HAYASHI K, FUJISAWA H, HOLLAND H D, OHMOTO H. Geochemistry of ~1.9 Ga sedimentary rocks from northeastern Labrador, Canada [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(19): 4115-4137.
[22] WRONKIEWICZ D J, CONDIE K C. Geochemistry of Archean shales from the Witwatersrand Supergroup, South Africa: source-area weathering and provenance [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51(9): 2401-2416.
[23] NESBITT H W, YOUNG G M. Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(7): 1523-1534.
[24] JOHNSSON M J, STALLARD R F, MEADE R H. First-cycle quartz arenites in the Orinoco River basin, Venezuela and Colombia [J]. The Journal of Geology, 1988, 94: 263-277.
[25] NESBITT H W, FEDO C M, YOUNG G M. Quartz and feldspar stability, steady and non-steady-state weathering, and petrogenesis of siliciclastic sands and muds [J]. The Journal of Geology, 1997, 105(2): 173-192.
[26] SRIVASTAVA A K, RANDIVE K R, KHARE N. Mineralogical and geochemical studies of glacial sediments from Schirmacher Oasis, East Antarctica [J]. Quaternary International, 2013, 292: 205-216.
[27] MOOSAVIRAD S M, JANARDHANA M R, SETHUMADHAV M S, MOGHADAM M R, SHANKARA M. Geochemistry of lower Jurassic shales of the Shemshak Formation, Kerman Province, Central Iran: Provenance, source weathering and tectonic setting [J]. Chemie der Erde-Geochemistry, 2011, 71(3): 279-288.
[28] MCLENNAN S M, HEMMING S, MCDANIEL D K, HANSON G N. Geochemical approaches to sedimentation, provenance, and tectonics [J]. Special Papers-Geological Society of America, 1993, 284: 21-40.
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Foundation item: Project(41302076) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(BJ14266) supported by MOST Special Fund from the State Key Laboratory of Continental Dynamics, Northwest University, China; Project(2014JQ5191) supported by Natural Science Basic Research Plan of Shaanxi Province, China
Received date: 2015-01-21; Accepted date: 2015-07-22
Corresponding author: GUO Ling, PhD; Tel: +86-29-87613138; E-mail: guoling@nwu.edu.cn