文章编号:1004-0609(2009)06-1087-06
温度对Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料吸放氢过程
相转变行为的影响
张文丛,贾彬彬,于元春
(哈尔滨工业大学 (威海) 材料科学与工程学院,威海264209)
摘 要:利用充氢反应球磨工艺制备氢化态Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢复合材料,测试材料的吸放氢动力性能,并利用Avrami指数研究储氢材料吸放氢过程中相转变行为特征。结果表明:在研究的温度范围内,温度越高,越有利于提高Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢复合材料的吸放氢速度;在150~200 ℃范围内吸氢时,其Avrami指数由初始阶段的1.0~1.5很快变为0.5,即储氢材料很快进入已形成相的增厚阶段;在150~200 ℃范围内,温度变化对吸氢相转变影响不大,但影响相转变速率;放氢过程中,根据Avrami 指数的变化,相转变基本过程为形核长大阶段和新相继续稳定长大阶段(无新的晶核形成),温度变化同样影响其放氢速率,但对其放氢过程的相转变规律影响不大。
关键词:储氢材料;吸放氢;Avrami指数;形核长大;动力学
中图分类号:TG.139 文献标识码: A
Effect of temperature on phase transformation behaviors of Mg-3Ni-2MnO2 hydrogen storage materials during hydrogenation and dehydrogenation process
ZHANG Wen-cong, JIA Bin-bin, YU Yuan-chun
(School of Materials Science and Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology (Weihai), Weihai 264209, China)
Abstract: The hydrided Mg-3Ni-2MnO2 hydrogen storage materials were fabricated through ball-milling under hydrogen atmosphere. The hydrogenation and dehydrogenation dynamic properties were measured. The Avrami index was used to study the phase transformation behavior character. The results show that in the range of temperatures selected, the higher the temperature is, the faster the hydrogenation and dehydrogenation velocities of the fabricated Mg-3Ni-2MnO2 hydrogen storage materials are. When the materials is absorbed in the range of 150?200 ℃, the value of Avrami index can change quickly from 1.0?1.5 in the initial period to about 0.5, indicating that this period is for the new phase to increase thickness quickly. The change of temperature has no obvious effect on the phase transformation behavior character whereas affects the phase transformation velocity. During the dehydrogenation process, its phase transformation period includes nucleation and growth, and steady growth of the new phase with no new crystal nucleus appearing, according to the change of Avrami index. The change of temperature also affects the dehydrogenation velocity and has no obvious effect on the phase transformation behavior character.
Key words: hydrogen storage materials; hydrogenation and dehydrogenation; Avrami index; nucleation and growth; dynamics
镁基储氢材料在氢能安全高效存储方面具有广阔的应用前景[1?2],其理论储氢量为7.6%,是一种大容量的储氢材料。随着材料制备手段[3?5]以及材料配方设计[6?8]的日趋完善,利用机械合金化材料制备工艺[9?10],可获得具有优异吸放氢动力学性能的镁基储氢材料[11?13]。
本文作者利用充氢反应球磨技术制备Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢复合材料,充分发挥Ni、MnO的催化功能,实现对材料吸放氢动力学性能的改善,并利用Johnson-Mahl-Avrami(J-M-A)方程求解Avrami指数,对储氢材料吸放氢过程的相转变行为特征进行研究。
1 实验
利用行星式球磨机QM-1SP制备Mg-3Ni-2MnO2复合材料。试验中所选用的原材料产地及基本性质如表1所列。利用自行设计的测试装置(如图1所示)进行吸放氢过程动力学性能测试。本试验所选取的样品成分为95Mg-3Ni-2MnO2(质量分数)。将混合充分的样品放入不锈钢球磨罐中充氢球磨,氢气的压力为0.5 MPa,球料比为20?1,球磨罐的转速为300 r/min。利用日本日立公司生产的设备型号为S?570的扫描电镜对经球磨80 h制备的储氢材料进行形貌观察。相转变分数为实际的吸放氢量(H/M)与理论储氢量(7.6%,质量分数)的比值,是吸放氢过程进程的标志。
表1 试验用原材料
Table 1 Raw materials used in experiments


图1 吸放氢测试装置示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of apparatus for measuring hydrogenation and dehydrogenation dynamics of metal hydride: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 12, 13, 14—Valves; 4—Hydrogen storage container; 7—Pressure gauge; 8—Reactor and heater; 9—Pressure sensor; 11—Vacuum meter; 15—Bellows sealed value; 8—Equilibrium container; 17—Measure cylinder; 18—Displacement sensor; 19—Computer digital record system; 20—Cooling pipe
2 结果与讨论
2.1 Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料的吸放氢动力学性能
图2所示为制备的Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料的SEM像。由图2可知,其平均颗粒尺寸小于2 μm。在2.5 MPa、150℃~200 ℃温度范围内该储氢材料的吸氢相转变动力学曲线如图3所示。由图3可知,Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料具有良好的吸氢动力学性能,吸氢过程的最大相转变分数为0.82,即最大吸氢量为6.23%(质量分数)。吸氢温度对相转变速度有影响,在选定的温度范围内,初始吸氢温度越高,越有利于吸氢。张文丛等[14]利用J-M-A方程建立了该配方储氢材料的本征吸放氢动力学方程并进行了数值模拟,模拟结果表明,Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料吸氢过程存在一个临界吸氢温度,临界温度以下吸氢时,温度越高,吸氢动力学性能越优异;而在临界温度以上时,吸氢温度越高,则吸氢速度越慢。本文作者从实验的角度部分验证了该结论的合理性。

图2 Mg-3Ni-2MnO2的SEM像
Fig.2 SEM image of Mg-3Ni-2MnO2
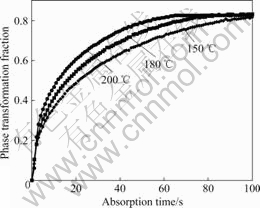
图3 不同温度下Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料吸氢过程的相转变动力学曲线
Fig.3 Phase transformation kinetics curves of Mg-3Ni-2MnO2 hydrogen storage materials under different temperatures during hydrogenation process
图4所示为Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料在0.1 MPa、不同温度条件下放氢相转变动力学曲线。由图4可知,储氢材料同样具有良好的放氢动力学曲线,温度对放氢动力学曲线有影响,其基本规律为:放氢温度越高,放氢动力学性能越优异。该储氢材料放氢过程最终的相转变分数约为0.8。
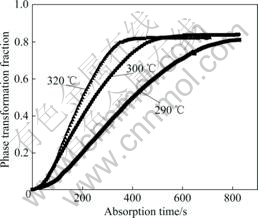
图4 不同温度下Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料放氢相转变动力学曲线
Fig.4 Phase transformation kinetics curves of Mg-3Ni-2MnO2 hydrogen storage materials at different temperatures during dehydrogenation process
2.2 Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料吸氢过程相转变行为特征
储氢材料吸氢过程是MgH2的形核、长大过程,研究晶体形核长大动力学性能,较传统的方法是利用Johnson-Mehl-Avrami公式:
 (1)
(1)
式中 F为相转变分数;k为速率常数,与温度和压力有关;t为相变时间;η为Avrami指数,指数的数值反映材料相变行为的特征,通过对J-M-A方程进行合理的变形处理可求解Avrami指数。
图5所示为根据图3所示的储氢材料吸氢动力学曲线,按照J-M-A方程进行数学处理所获得的lnln[1/(1?F)]—lnt关系曲线。通常情况下认为:金属储氢材料粉体的吸氢过程包括表面过程(氢气在颗粒表面的化学吸附、分解并形核)、扩散过程(MgH2形成后氢原子在形成的MgH2相中的扩散)和界面反应过程(氢原子从β相进入α相)。在吸氢初始阶段,相转变速率较大(见图3),而由图5可知,该阶段的Avrami指数在1.0~1.5范围内变化,结合储氢材料颗粒尺寸较小、表面积大的特点,可以认为此时表面效应发挥重要作用。而后的整个阶段,其Avrami指数约为0.5,表明已形成的新相不断增厚[15]。
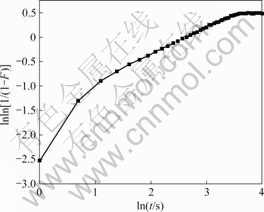
图5 在2.5 MPa和200 ℃条件下Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料的lnln[1/(1?F)]—lnt曲线
Fig.5 Curve of lnln[1/(1?F)]—lnt for Mg-3Ni-2MnO2 hydrogen storage materials under conditions of 2.5 MPa and 200 ℃
图6所示为Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料不同吸氢温度下的lnln[1/(1?F)]—lnt曲线。由图6可知,不同温度下储氢材料吸氢的lnln[1/(1?F)]—lnt曲线近似平行,曲线斜率相同,即Avrami指数相同,这说明在不同温度下吸氢,储氢材料有着相似的相转变行为规律,温度变化只改变吸氢过程的相转变速率。

图6 在不同温度下Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料吸氢过程的lnln[1/(1?F)]—lnt曲线
Fig.6 Curves of lnln[1/(1?F)—lnt for Mg-3Ni-2MnO2 hydrogen storage materials under different temperatures during hydrogenation process
2.3 Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料放氢过程相转变行为特征
放氢过程是Mg的形核、长大过程。图7所示为根据图4中氢化态储氢材料在300 ℃、0.1 MPa条件下放氢相转变动力学曲线按照J-M-A方程进行合理的数学处理所获得的lnln[1/(1?F)]—lnt曲线。由图7可知,曲线并非是一条直线,考虑到放氢过程所需时间相对较长,为了准确描述Mg-3Ni-2MnO2材料放氢过程相转变的基本规律,本文作者引入了区域Avrami指数η的概念。

图7 在300 ℃和0.1 MPa条件下Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料的lnln[1/(1?F)]—lnt曲线
Fig.7 Curve of lnln[1/(1?F)]—lnt for Mg-3Ni-2MnO2 hydrogen storage materials under conditions of 300 ℃ and 0.1 MPa
图8所示为氢化态储氢材料在300 ℃放氢时的区域Avrami指数变化曲线。由图8可知,在相变初始阶段,即相转变分数小于0.1时,区域Avrami指数由较小值很快达到2.0,因此,此阶段是镁的形核以及晶核长大的过程,由图4可知,该阶段所用的时间约为70 s。随着相转变的进行,区域Avrami指数开始降低,当相转变分数为0.3时,其值为1.5,这个阶段仍为新相的长大过程。在随后的阶段,考虑误差因素的影响,此时的储氢材料区域Avrami指数基本保持在1.5左右,该阶段的相转变分数处于0.3~0.75范围内,主要发生已有晶核的稳定长大,没有新的晶核形成。其放氢相转变行为如表2所列。
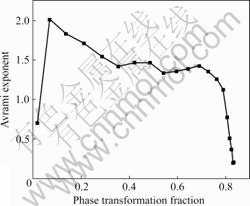
图8 Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料300 ℃等温放氢过程的区域Avrami指数
Fig.8 Local Avrami exponent of Mg-3Ni -2MnO2 hydrogen storage materials during isothermal dehydrogenation process at 300 ℃
表2 氢化态Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料放氢相转变行为
Table 2 Phase transformation behavior of hydrided Mg-3Ni- 2MnO2 during dehydrogenation process

图9所示为不同温度下氢化态Mg-3Ni-2MnO2材料放氢过程的lnln[1/(1?F)]—lnt曲线。由图9可知,氢化态储氢材料在不同温度下放氢时,其lnln[1/(1?F)]—lnt曲线形状在反应的大多数时间内基本相似,即曲线斜率近似一致,这说明温度对储氢材料放氢过程相转变影响也不大,只对其相转变速率有影响。

图9 在不同温度下氢化态Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料放氢过程的lnln[1/(1?F)]—lnt曲线
Fig.9 Curves of lnln[1/(1?F)]—lnt for Mg-3Ni-2MnO2 hydrogen storage materials at different temperatures during dehydrogenation process
3 结论
1) 在所研究的温度范围内,温度越高,越有利于提高Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢复合材料吸放氢速度,其吸放氢相转变动力学性能越优异。
2) 在150~200 ℃范围内吸氢时,储氢材料Avrami数值由初始阶段的1.0~1.5很快变为0.5左右,即储氢材料很快进入已形成相的增厚阶段;在150 ℃~ 200 ℃范围内,温度变化对其吸氢相转变行为影响不大,而对相转变速率有影响。
3) Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料放氢过程中,Avrami指数数值随反应分数的变化而不同,根据数值的变化范围,其放氢过程的相转变阶段分为:形核长大阶段、新相稳定长大阶段(无新的晶核形成);温度变化同样对放氢相转变速率有影响,而对其相转变影响不大。
REFERENCES
[1] 柳东明, 巴志新, 李李泉. 镁基储氢合金制备新方法—氢化燃烧合成法[J]. 粉末冶金技术, 2005, 23(3): 224?228.
LIU Dong-ming, BA Zhi-xin, LI Li-quan. Effect and using of magnesium hydriding reaction in hydriding combustion synthesis of Mg2NiH4[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2005, 23(3): 224?228.
[2] 房文斌, 张文丛, 于振兴, 王尔德. 镁基储氢材料研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(5): 853?862.
FANG Wen-bin, ZHANG Wen-cong, YU Zheng-xing, WANG Er-de. Recent development of Mg-based hydrogen storage material[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(5): 853?862.
[3] LI Chuan-jian, WANG Xin-lin. Investigations on the cycle stability and the structure of the MmNi3.6Co0.75Mn 0.55Al0.1 hydrogen storage alloy(Ⅰ). Measurements and analysis of the cycle stability and the phase structure[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1999, 284: 270?273.
[4] LI Li-quan, AKIYAMA T, YAGI J I, Hydrogen storage alloy of Mg2NiH4 hydride produced by hydriding combustion synthesis from powder of mixture metal[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2000, 308: 98?103.
[5] 赵显久, 李 谦, 林根文, 周国治, 张捷宇, 鲁雄刚. Mg-Mg2Ni1?xMex的氢化反应动力学[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(5): 973?978.
ZHAO Xian-jiu, LI Qian, LIN Gen-wen, ZHOU Guo-zhi, ZHANG Jie-yu, LU Xiong-gang. Hydriding reaction kinetics of Mg-Mg2Ni1?xMex compositions[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(5): 973?978.
[6] OELERICH W, KLASSEN T, BORMANN R. Metal oxide as catalysts for improved hydrogen sorption in nanocrystalline Mg-based material[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2001, 315: 237?233.
[7] 李法兵, 蒋利军. 机械合金化直接合成镁基复合储氢材料研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2005, 34(5): 750?753.
LI Fa-bing, JIANG Li-jun. Research for direct synthesis of Mg-Based hydrogen storage composite material[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2005, 34(5): 750?753.
[8] YU Zhen-xing, LIU Zu-yan, WANG Er-de. Hydrogen storage properties of the Mg-Ni-CrCl3 nanocomposite[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 2002, 333: 207?211.
[9] ZALUS K L, ZALUSKA A, TESSIER P. Catalytic effect of Pd on hydrogen absorption in mechanically alloyed Mg2Ni, LaNi5 and FeTi [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compound, 1995, 217(2): 295?300.
[10] 朱文辉, 高 岩, 朱 敏. 镁含量对MmNi5?x(CoAlMn)x/Mg复合储氢合金吸氢性能影响[J]. 材料工程, 2000, 5: 9?11.
ZHU Wen-hui, GAO Yan, ZHU Min. The influence of Mg content on the hydrogen absorption properties of MmNi(5?x) (CoAlMn)x/Mg nanocrystalline composite[J]. Journal of Material Engineering, 2000, 5: 9?11.
[11] WANG Er-de, YU Zheng-xing, LIU Zu-yan. Hydrogen storage properties of nano-composite Mg-Ni-MnO2(wt%) made by mechanically milling[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2002, 12(2): 227?232.
[12] ZALUSKA A, ZALUSKA L, STROM-OLSEN J O. Nanocrystalline magnesium for hydrogen storage[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compound, 1999, 288(1/2): 217?225.
[13] LIANG G, HUOT J, BOILY S, van NESTE A, SCHULZ R. Hydrogen storage properties of the mechanically milled MgH2-V nanocomposite[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1999, 291: 295?301.
[14] 张文丛, 刘鲁生, 王召友, 王尔德. Mg-3Ni-2MnO2储氢材料本征吸放氢动力学性能研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2007, 36(2): 226?230.
ZHANG Wen-cong, LIU Lu-sheng, WANG Zhao-you, WANG Er-de. Numerical simulation of intrinsic absorption and desorption kinetics for Mg-3Ni-2MnO2 hydrogen storage materials[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2007, 36(2): 226?230.
[15] 徐祖耀. 相变原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000.
XU Zu-yao. Phase transformation theory[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2000.
基金项目:山东省科技攻关计划资助项目(2008GG10007004, 2008GG10003005);山东省中青年科学家奖励计划资助项目(2006130)
收稿日期:2008-10-22;修订日期:2009-02-11
通讯作者:张文丛,副教授,博士;电话:0631-5687209;E-mail: zhangwencong@yahoo.com.cn
(编辑 李向群)