文章编号:1004-0609(2009)10-1815-07
电沉积微纳米镍的组织结构与力学性能
许伟长,戴品强
(福州大学 材料科学与工程学院,福州 350108)
摘 要:在氨基磺酸镍体系的镀液中通过直流、脉冲电沉积分别制备了不同晶粒尺寸的块体镍。通过室温单向拉伸实验比较了这些镍的力学性能。 结果表明:拓宽电沉积纳米镍的晶粒尺寸分布可显著提高其塑性,同时,保留较高的强度。所制备的具有宽晶粒尺寸分布(5~120 nm)的平均晶粒尺寸为27.2 nm的纳米镍,抗拉强度为1 162~ 1 211 MPa,断裂伸长率为10.4%~11.4%。与平均晶粒尺寸为22.4 nm的窄晶粒尺寸分布(5~60 nm)的纳米镍相比,抗拉强度降低约200 MPa,但断裂伸长率提高了3.4%。通过对纳米镍微观组织的TEM观察,揭示了宽晶粒尺寸分布纳米镍中塑性的显著提高源于塑性变形中大晶粒(100 nm以上)内存在类似传统粗晶材料中的晶内位错滑移。
关键词:纳米镍;力学性能;变形机制;电沉积
中图分类号:TG 174.441 文献标识码: A
Microstructures and mechanical properties of
electrodeposited microcrystalline and nanocrystalline Ni
XU Wei-chang, DAI Pin-qiang
(College of Materials Science and Engineering, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou 350108, China)
Abstract: The bulk Ni with various grain sizes were prepared by direct current or pulse electrodeposition, respectively, in the nickel sulfamate electrolyte. The uniaxial tensile tests were performed at room temperature to compare the mechanical properties among these Ni samples. The results show that the ductility in electrodeposited nanocrystalline (NC) Ni can be significantly enhanced with a higher strength by extending the grain size distribution. The NC Ni samples with a broad grain size distribution (5-120 nm) and an average grain size of 27.2 nm have an ultimate tensile strength (σUTS) of 1 162-1211 MPa and an elongation to failure (δETF) of 10.4%-11.4%. Compared with the NC Ni samples that have a narrow grain size distribution (5-60 nm) and an average grain size of 22.4 nm, the σUTS of NC Ni with a broad grain size distribution decreases by 200 MPa, but the δETF increases by 3.4%. By the TEM observations of the microstructures in NC Ni, it is revealed that the apparent enhancement of ductility in NC Ni with a broad grain size distribution results from the presence of intragranular dislocation sliding in the large grains (above 100 nm) during plastic deformation, similar to that in conventional coarse-grained materials.
Key words: nanocrystalline Ni; mechanical property; deformation mechanism; electrodeposition
自上世纪德国科学家Gleiter等[1]首次提出纳米材料的概念以来,其优异的电、磁、力学等性能一直是当代科学界研究的热点。在力学性能方面,已经发现纳米金属材料较其粗晶同类材料在屈服强度上有数倍的提高,现已报道的纳米金属材料的拉伸强度最高可达2.4~2.5 GPa[2-3]。目前,可制备纳米块体材料的方法主要有剧烈塑性变形、纳米粉末低温合成、电沉积等等[4]。这些方法各有优缺点。由电沉积技术制备的纳米金属材料具有界面清洁、晶粒尺寸分布窄、致密度高等优点,但缺点是容易因添加剂引入杂质而掩盖了材料固有力学性能的表征[5]。近10年里,电沉积纳米镍、纳米铜被广泛作为模型材料用于研究纳米晶的力学行为与变形机制,其中具有代表性的工作成果见文献[6-9]。用电沉积法制备的纳米镍,主要是一种窄晶粒尺寸分布的纳米镍(下文中简称为窄晶纳米镍)[10-11],晶粒尺寸分布在10~50 nm之间,平均晶粒尺寸为20~30 nm。这种纳米镍的抗拉强度可达1 GPa以上,但塑性(断裂伸长率)通常小于5%。
研究发现,窄晶纳米镍经过200 ℃低温退火获得双峰晶粒尺寸分布(bimodal grain size distribution)的基体后可提高塑性[10]。双峰晶粒尺寸分布是相对于单峰晶粒尺寸而言的。单峰晶粒尺寸分布指由统计获得的晶粒尺寸分布图类似正态分布,具有单峰形状。双峰晶粒尺寸分布是在晶粒尺寸分布图上出现两个单峰形状,即数量上大部分晶粒被分别集中在两个峰所对应的尺寸上。此外,在含大尺寸晶粒团簇的镀态纳米镍中,也获得了较高的塑性[12]。从广义上讲,双峰晶粒尺寸分布与大晶粒团簇都可被认为是属于一种宽晶粒尺寸分布的范畴,这表明拓宽纳米材料的晶粒尺寸分布是获得高塑性的一种途径。
本文作者在氨基磺酸镍体系的镀液中通过改变工艺参数分别制备了晶粒尺寸在1 ?m以上的粗晶镍、普通的窄晶纳米镍以及一种新颖的宽晶粒尺寸分布(10~120 nm)纳米镍(下文中简称为宽晶纳米镍)。通过对比实验,研究了这3种镍镀层材料的显微组织结构与宏观力学性能之间的关系,分析了晶粒尺寸分布的宽、窄对纳米镍塑性的影响及它们的变形机制。
1 实验
本研究使用的基础镀液成分上包括氨基磺酸镍、氯化镍、硼酸和十二烷基硫酸钠。通过改变pH值、电流密度和添加剂这3种因素,在直流或方波脉冲条件下分别制备了微米镍、窄晶纳米镍和宽晶纳米镍。阳极选用高纯低硫镍板(纯度>99.9%,质量分数),阴极选用电解抛光的不绣钢片,浸液阴阳面积比为1?4。电沉积过程中使用氨基磺酸溶液和碱式碳酸镍溶液调节镀液的pH值。制备的镀层厚度为160~180 μm。镀层与不锈钢基底结合力差,可通过机械法剥离。
用线切割机从镀层上切割拉伸试样。试样总长40 mm,标距区长10 mm,宽6 mm。在微机控制的电子万能试验机(CMT-6104)上进行室温下的单向拉伸试验,应变速率为10-4 s-1。采用日本岛津的XD-SA型X射线衍射仪对镀层结构进行分析,衍射条件为铜靶,电子加速电压为35 kV,电流为20 mA。运用Jade 5.0软件计算微纳米镍的晶粒尺寸与晶格应变,计算前采用经退火处理的标准粗晶硅样品的谱图扣除衍射仪的仪器宽化。采用Tecnai G2 F20型场发射电子显微透射电镜对镀层的微观结构进行观察,电子加速电压为200 kV。透镜试样采用双喷电解仪进行减薄,所用的电解液为15 mL高氯酸+285 mL乙醇,电解电压为50 V,电解温度为-20~-30 ℃。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 组织结构分析
图1(a)所示为电沉积微米镍镀态下的TEM明场像,显示微米镍的晶粒尺寸在1 ?m以上,晶粒内部存在少量的生长孪晶,同时晶粒内部还存在较高密度的位错,如图中白色矩形框中所示。图1(b)所示为图1(a)中白色矩形区域的放大,清晰地显示了出现在晶粒内部的位错线。

图1 镀态微米镍的TEM明场相和聚集在晶粒内部的位错
Fig.1 TEM bright field image (a) and dislocations accumulated in grain interior (b) (Fig.1(b) corresponding to magnifying area marked by white rectangular frame in Fig.1(a), for as-deposited microcrystalline Ni)
图2所示为窄晶纳米镍镀态下的TEM明场相与晶粒尺寸分布。从图2(a)中可见,镀态下窄晶纳米镍的晶粒大小均匀,约20~30 nm,大部分晶粒之间的晶界无法清晰地被辨认出。图2(a)左上角的选区电子衍射花样呈连续的环状,具有晶粒尺寸细小的纳米晶材料所共有的特征。图2(b)所示为晶粒数量分数随晶粒尺寸变化的统计分布图。由图2(b)可见,该纳米镍的晶粒尺寸分布范围为5~60 nm之间,其中超过70%的晶粒的大小分布在10~30 nm之间,属于典型的窄尺寸纳米镍。由被统计晶粒计算出的TEM平均晶粒大小为22.4 nm。

图2 镀态窄晶纳米镍的TEM明场像与晶粒尺寸分布
Fig.2 TEM bright field image (a) and grain size distribution (b) for as-deposited nanocrystalline Ni with narrow grain size distribution
图3所示为宽晶纳米镍镀态下的TEM明起像与晶粒尺寸分布。从图3(a)中可见,镀态宽晶纳米镍的晶粒尺寸不均匀,小晶粒的尺寸约10~20 nm,大晶粒的尺寸约100~120 nm。图3(a)左上角的选区电子衍射花样呈现连续的环状,进一步表明尽管宽晶纳米镍中存在一些晶粒尺寸接近或稍超过纳米材料定义界限(100 nm)的晶粒,但是它的整体晶粒尺寸仍然足够细小。图3(b)所示为晶粒数量分数随晶粒尺寸变化的统计分布图,表明晶粒尺寸连续分布在5~120 nm之间,其中超过80%的晶粒的尺寸分布在10~50 nm之间,晶粒尺寸分布在50~120 nm之间的晶粒个数仅占 约10%。由被统计的晶粒计算出的平均晶粒大小为27.2 nm。

图3 镀态宽晶纳米镍的TEM明场像与晶粒尺寸分布
Fig.3 TEM bright field image (a) and grain size distribution (b) for as-deposited nanocrystalline Ni with broad grain size distribution
图4所示为3种电沉积镍的XRD谱。由图4可知,与标准的纯镍粉末(标准镍)相比,微米镍(MC Ni, microcrystalline Ni)几乎表现出完全的(200)晶面织构;窄晶纳米镍(N-NC Ni, narrow nanocrystalline Ni)的XRD谱与标准镍的XRD谱比较接近;而宽晶纳米镍(B-NC Ni, broad nanocrystalline Ni)则表现出较强的(200)晶面织构。

图4 镀态微米镍、窄晶纳米镍和宽晶纳米镍的XRD谱
Fig.4 XRD patterns for as-deposited coarse-grained Ni and nanocrystalline Ni with narrow and broad grain size distribution, respectively: (a) MC Ni; (b) N-NC Ni; (c) B-NC Ni; (d) Standard Ni powder
表1所列为根据图4中XRD衍射峰宽化计算出的晶粒尺寸和晶格应变。微米镍的XRD晶粒尺寸为64.1 nm,与图1中TEM观察到的结果不相符合。这是由于粗晶晶内位错同样会造成衍射峰的宽化,与BUDROVIC等[6]在粗晶铜的循环拉伸变形过程中所观察到的相同。对于窄、宽晶纳米镍,TEM统计出的平均晶粒尺寸与XRD计算出的结果非常接近。这是因为,在纳米晶粒内部的位错数量极少或难以存在。因此,在研究晶粒尺寸位于纳米尺度的材料时,XRD峰宽化可放心地作为一种准确的晶粒尺寸表征方法。
表1 微纳米镍XRD、TEM平均晶粒尺寸与XRD晶格应变
Table 1 XRD and TEM average grain sizes and XRD lattice strain for microcrystalline and nanocrystalline Ni
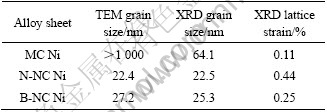
对于晶格应变,表中数据显示微米镍的低至0.11%,窄晶纳米镍的晶格应变高达0.44%,宽晶纳米镍的介于两者之间。电沉积镍的晶格应变随晶界体积分数的增加而增大。微米镍中晶粒粗大,晶界体积分数低。对于平均晶粒尺寸为22.5 nm的窄晶纳米镍,晶界体积分数显著地高于微米镍,由此造成的不可忽视的晶界附近原子的无序排列增加了晶粒的微观应变。而宽晶纳米镍,通过在纳米基体中形成一定比例(5%)的大晶粒,拓宽晶粒尺寸分布,晶界体积分数较窄尺寸纳米镍有所减少,从而减少了晶界附近无序原子的含量,使得微观应变低于窄尺寸纳米镍。
2.2 力学性能分析
图5所示为电沉积微纳米镍的工程应力—应变曲线。从图5可见,3种块体镍的屈服强度随晶粒尺寸的减小而升高,与Hall-Petch关系所预测的结果一致。3种块体镍的屈服强度数值及其他力学性能参数详见表2。表2中σ0.2、σUTS、δEOF、δ、εU 和n分别表示工程应变为0.2%时的工程应力、极限拉伸强度、断裂伸长率、塑性应变、均匀应变和应变硬化指数。
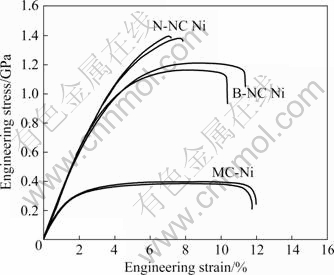
图5 电沉积微纳米镍的工程应力—应变曲线
Fig.5 Curves of engineering stress versus engineering strain for electrodeposited microcrystalline and nanocrystalline Ni
表2 电沉积微纳米镍的力学性能参数
Table 2 Mechanical properties for electrodeposited microcry- stalline and nanocrystalline Ni
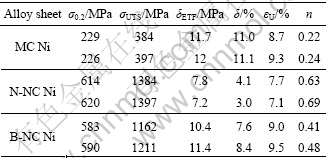
微米镍虽然强度低,但具有较好的塑性,断裂伸长率接近12%,塑性约11%,弹性应变量约1%,均匀塑性变形量达8.7%~9.3%。微米镍强度达到屈服点后,在小应变(1%~4%)范围内出现强应变硬化,之后在应力应变曲线上出现很长得一段平台。这被认为是位错增殖与湮灭过程达到动态平衡,故应变硬化消 失[13]。对于窄晶纳米镍,其屈服强度较微米镍提高约2倍,抗拉强度提高约2.5倍,弹性应变高达3%,显著高于微米镍。窄晶纳米镍在应变硬化过程中断裂,塑性较微米镍大幅度降低。对于宽晶纳米镍,屈服强度稍低于窄晶纳米镍,抗拉强度比窄晶纳米镍低了200~300 MPa,这符合Hall-Petch关系(宽晶纳米镍的平均晶粒尺寸略大于窄晶纳米镍)。宽晶纳米镍在屈服之后(应变范围4%~6%)出现明显的强烈应变硬化,但应变硬化能力随应变的增加而减弱,在拉伸曲线上出现与微晶镍拉伸曲线上相似的平台,只是平台阶段持续的塑性变形量减小了,表明宽晶纳米镍在变形过程中也存在位错增值与湮灭的动态平衡过程。
从图6可看出,随着晶粒尺寸减小,金属镍的应变硬化率显著增加,应变硬化率随晶粒尺寸的变化规律与表1中应变硬化指数随晶粒尺寸的变化规律一致。根据Considère拉伸失稳判据,当拉伸过程中dσ/dε<σ时,材料发生塑性失稳。据此,微米镍与宽晶纳米镍均发生了理论塑性失稳(塑性失稳点如图6中★所示),宽晶纳米镍的失稳应变值高于微米镍的。但微米镍在流变应力达到失稳点后,断裂前所持续的塑性应变超过5%。而纳米镍在流变应力达到失稳点后,断裂前持续的塑性应变不到3%。这与应变硬化率随应变增加而减小的速度有关,在纳米镍中,在应变增加过程中应变硬化率减小的速度快,因此,在大应变下的应变硬化率无法补偿当时的高应力,于是失稳发生后便较快地发生断裂。窄晶纳米镍在拉伸过程中未达到失稳点就已发生断裂,这与纳米镍缺乏晶内位错活动(滑移)有关。
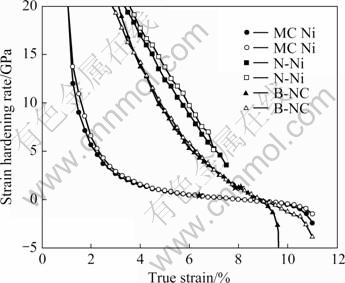
图6 电沉积微纳米镍的应变硬化率与真实应变的关系曲线
Fig.6 Curves of strain hardening rate versus true strain for electrodeposited microcrystalline and nanocrystalline Ni
2.3 变形机制讨论
电沉积窄晶纳米镍相对于微米镍而言,抗拉强度得到了数倍的提高,可达1.2 GPa以上,但是塑性较低,仅有3%~4%[10-11]。分子动力学模拟预测结果表明:尺寸为15~50 nm的晶粒可通过晶界发射不全位错的方式来协调塑性[14-15]。WU等[16]在TEM下观察到了这一现象,从实验上证实了纳米晶中存在这种特殊的变形机制。本研究制备的窄尺寸纳米镍力学性能与文献[10-11]报道的结果很相似。WANG等[14]发现,利用纳米晶粒存在低温异常长大的特点,在特定温度退火可让部分纳米晶粒异常长大至几百纳米,形成一种具有双峰晶粒尺寸分布特点的组织。这种方法可使原来的纳米材料在保持高强度的同时显著提高塑性。纳米材料塑性的提高可归因于退火后基体中形成的超细晶(晶粒尺寸位于100~500 nm)。超细晶晶粒通过以全位错滑移为主导的方式产生大塑性变形;同时大部分先前未长大的纳米级小晶粒(基体晶粒)又起了主要的细晶强化作用,平均晶粒尺寸遵循Hall-Petch关系,从而保持纳米材料强度不降低[17]。本实验中制备了一种宽晶纳米镍,它在塑性上显著地高于窄晶纳米镍,其工程应力-应变曲线在塑性变形阶段所表现出的力学行为与电沉积粗晶镍的相似,即初期具有强应变硬化,之后应变硬化随应变增加而下降,达到一种位错增殖与湮灭的动态平衡。图7(a)所示为宽晶纳米镍拉伸断口附近的TEM明场像。由图7(a)可见,变形后晶粒较镀态下发生了显著的长大,在大晶粒内部、晶界上有高密度位错塞积,但在小晶粒内未观察到位错。这表明了宽晶纳米镍在变形中大晶粒内部引发了较为明显的以全位错滑移为主导的塑性变形,这是它获得窄晶纳米镍无法具备的高塑性的主要原因。

图7 宽晶纳米镍和窄晶纳米镍拉伸断口附近的TEM明 场像
Fig.7 TEM bright field images in proximity of tension fracture for nanocrystalline Ni with broad grain size distribution (a) and narrow grain size distribution (b)
图7(b)所示为窄晶纳米镍拉伸断口附近的TEM明场像。图7(b)中未观察到任何的位错,但通过与该镍镀态下的TEM组织(图2(a))对比,发现变形后窄晶纳米镍的晶粒发生了长大,50 nm左右的晶粒数显著增多,晶界变得清晰可见,在大部分晶粒群中10~20 nm的小晶粒消失了。由于图7(b)中未观察到变形后残留在晶粒内部的位错残骸,因此,对于窄晶纳米镍而言,塑性变形过程中传统的全位错滑移机制不再占主导。当纳米晶粒的尺寸小到临界尺寸以下时,晶粒内部位错不能存在,变形过程中也不能期望能开动Frank-Read源进行位错增殖[18],这样就不存在类似于在粗晶中以位错滑移方式提供的塑性。因此,纳米晶粒无法获得类似于粗晶金属的优异塑性。窄晶纳米镍在变形过程中相当数量的小晶粒合并成了大晶粒,使小角度晶界的比例减小了,大角度晶界比例增加以及变形后微观应变的减小共同导致变形后出现清晰的晶界。小晶粒合并的过程可通过晶界滑移或晶粒转动来实现[8, 19]。以上这些表明纳米晶粒在塑性变形过程中同时存在着多种变形机制如晶界发射不全位错、晶粒转动、晶界滑移等以协调塑性。对于窄晶纳米镍,由于未观察到变形过程中的位错痕迹,变形初期(应变小于4%)的应变硬化行为的起因目前尚无清楚的认识。
需要指出的是,本研究中的宽晶纳米镍不同于双峰晶粒尺寸分布纳米镍,虽然它们都可被认为是一种广义上的宽晶粒尺寸分布纳米镍(区别于窄尺寸纳米镍),但两者不同之处在于:1) 在获取手段方面,本研究中的纳米镍是在镀态下就具备较宽的晶粒尺寸分布,不同于经过低温退火或其他方法,如低温球磨后进行热等静压合成[20],来获得较宽的晶粒尺寸分布;2) 本研究中的宽晶纳米镍的晶粒尺寸是在一个连续范围内分布(5~120 nm),不同于双峰晶粒分布的晶粒尺寸连续分布在两个分开的范围内[10],且双峰晶粒分布下的大晶粒群与小晶粒群之间的尺寸差高达几百纳米。对于电沉积纳米金属材料,我们认为镀态下宽晶粒尺寸分布的组织结构比通过退火获得的双峰晶粒尺寸分布的组织更具优越的力学性能。这是因为:1) 在退火过程中,电沉积材料基体中杂质元素的晶界偏聚不可避免地产生或重或轻的脆性[10],导致不能实现塑性的完全提高;2) 由于双峰分布的大晶粒与小晶粒尺寸差别大,可能会造成塑性变形被局限在少量大晶粒内部,而无法传递到大量的小晶粒之间,不能大幅度地提高纳米镍的塑性。
3 结论
1) 对于电沉积纳米镍,TEM统计的平均晶粒尺寸与XRD峰宽化计算出的晶粒尺寸非常接近,因此,XRD峰宽化可用于准确测定该类纳米材料的平均晶粒尺寸。
2) 拓宽电沉积纳米镍的晶粒尺寸分布,可显著提高其塑性同时保留较高的强度。本研究通过氨基磺酸镍体系的电镀液成功地制备平均晶粒尺寸为27.2 nm,晶粒尺寸分布为5~120 nm的纳米镍。该纳米镍的抗拉强度为1 162~1 211 MPa,断裂伸长率为10.4%~ 11.4%。
3) 对于宽晶粒尺寸分布的纳米镍,塑性变形过程中100 nm以上的大晶粒内可存在类似传统粗晶金属材料中的晶内位错滑移。
REFERENCES
[1] BIRRINGER R, GLEITER H, KLEIN H P, MARQUARDT P. Nanocrystalline materials an approach to a novel solid structure with gas-like disorder[J]. Physics Letters A, 1984, 102(8): 365-369.
[2] LI H Q, EBRAHIMI F. Tensile behavior of a nanocrystalline Ni-Fe alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54: 3977-3986.
[3] GU C D, LIAN J S, JIANG Q, JIANG Z H. Ductile-brittle-ductile transition in an electrodeposited 13 nanometer grain sized Ni-8.6 wt.%Co alloy[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2007, 459: 75-81.
[4] DAO M, LU L, ASARO R J, DE HOSSON J T M, MA E. Toward a quantitative understanding of mechanical behavior of nanocrystalline metals[J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55(12): 4041-4065.
[5] KUMAR K S, SURESH S, CHISHOLM M F, HORTOM J A, WANG P. Deformation of electrodeposited nanocrystalline nickel[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(2): 387-405.
[6] BUDROVIC Z, van SWYGENHOVEN H, DERLET P M, van PETEGEM S, BERND S. Plastic deformation with reversible peak broadening in nanocrystalline nickel[J]. Science, 2004, 304: 273-276.
[7] Mc FADDEN S X, MISHRA R S, VALIEV R Z, ZHILYAEV A P, MUKHERJEE A K. Low-temperature superplasticity in nanostructure nickel and metal alloys[J]. Nature, 1999, 398: 684-686.
[8] SHAN Z W, STACH E A, WIEZOREK J M K, KNAPP J A, FOLLSTAEDT D M, MAO S X. Grain boundary-mediated plasticity in nanocrystalline nickel[J]. Science, 2004, 305: 654-657.
[9] LU L, SHEN Y F, CHEN X H, QIAN L H, LU K. Ultrahigh strength and high electrical conductivity in copper[J]. Science, 2004, 304: 422-425.
[10] WANG Y M, CHENG S, WEI Q M, MA E, NIEH T G, HAMZA A. Effect of annealing and impurities on tensile properties of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Ni[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 51: 1023-1028.
[11] DALLA T F, SPATIG P, SCHAUBLIN R, VICTORIA M. Deformation behaviour and microstructure of nanocrystalline electrodeposited and high pressure torsioned nickel[J]. Acta Materialia, 2005,53: 2337-2349.
[12] GU C D, LIAN J S, JIANG Z H, JIANG Q. Enhanced tensile ductility in an electrodeposited nanocrystalline Ni[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006, 54: 579-584.
[13] 谢子令, 武晓雷, 洪友士. 微纳米晶金属的应变率敏感性及应变硬化行为分析[J]. 固体力学学报, 2007, 28(1): 43-48.
XIE Zi-ling, WU Xiao-lei, HONG You-shi. Analysis of strain rate sensitivity and strain hardening behavior in ultrafine-grained and nanocrystalline metals[J]. Acta Mechanic Solid Sinica, 2007, 28(1): 43-48.
[14] van SWYGENHOVEN H, DERLET P M, FROSETH A G. Stacking fault energies and slip in nanocrystalline metals[J]. Nature Materials, 2004, 3: 399-403.
[15] SCHI?TZ J, JACOBSEN K W. A maximum in the strength of nanocrystalline copper[J]. Science, 2003, 301: 1357–1359.
[16] WU X, ZHU Y T, CHEN M W, MA E. Twinning and stacking fault formation during tensile deformation of nanocrystalline Ni[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006, 54: 1685-1690.
[17] WANG Y M, CHEN M W, ZHOU F H, MA E. High tensile ductility in a nanostructured metal[J]. Nature, 2002, 419: 912-915.
[18] LEGROS M, ELLIOTT B R, RITTNER M N, WEERTMAN J R, HEMKER K J. Microsample tensile testing of nanocrystalline metals[J]. Philosophical Magazine A, 2000, 80(4): 1017-1026.
[19] HASNAOUI A, VAN SWYGENHOVEN H, DERLET P M. On non-equilibrium grain boundaries and their effect on thermal and mechanical behavior: A molecular dynamics computer simulation [J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50: 3927-3939.
[20] LEE Z, WITKIN D B, RADMILOVIC C, LAVERNIA E J, NUTT S R. Bimodal microstructure and deformation of cryomilled bulk nanocrystalline Al-7.5Mg alloy[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 410/411: 462-467.
基金项目:福建省自然科学基金资助项目(E0810006)
收稿日期:2008-10-14;修订日期:2008-12-31
通信作者:戴品强,教授,博士;电话:0591-83734022;E-mail: pqdai@126.com
(编辑 何学锋)