文章编号:1004-0609(2010)S1-s0011-05
显微组织对近α型TG6钛合金高温蠕变变形行为的影响
段 锐1, 张 华2, 蔡建明1, 黄 旭1, 曹春晓1
(1. 北京航空材料研究院,北京 100095;
2. 贵州安大航空锻造有限责任公司,安顺 561005)
摘 要:研究TG6钛合金在3种显微组织条件下的600 ℃蠕变变形行为,在600 ℃,200 MPa的测试条件下,粗晶的网篮组织具有最强的蠕变抗力,而细晶的等轴组织具有最弱的蠕变抗力,双态组织介于中间。经过600 ℃长期热暴露后,TG6钛合金网篮组织的蠕变抗力有所下降,而双态组织和等轴组织的蠕变抗力反而得以提高,这归因于α2相和硅化物沉淀析出对蠕变抗力的作用,均匀析出的α2相可以提高合金的蠕变抗力,而硅化物的析出会使得α基体贫Si,减弱了Si原子气团对位错攀移的阻碍作用,从而导致蠕变抗力的下降。TG6钛合金在600 ℃,200 MPa下的稳态蠕变变形主要受位错攀移机制的控制。
关键词:高温钛合金;蠕变行为;位错攀移
中图分类号:TG146 文献标志码:A
Effect of microstructure on creep deformation behavior of near-alpha titanium alloy TG6
DUAN Rui1, ZHANG Hua2, CAI Jian-ming1, HUANG Xu1, CAO Chun-xiao1
(1. Beijing Institute of Aeronautical Materials, Beijing 100095, China;
2. Guizhou Anda Aviation Forging Co., Ltd., Anshun 561005, China)
Abstract: The creep behaviors of three microstructures of TG6 titanium alloy disc forgings at 600 ℃ were studied. Under the condition of 600 ℃ and 200 MPa, the coarse-grain basketweave structure has the highest creep resistance, fine-grain equiaxed structure has the lowest creep resistance, and the duplex structure has a moderate creep resistance. After a long thermal exposure at 600 ℃, the creep resistance of basketweave structure reduces. On the contrary, the creep resistances of duplex and equiaxed structures improve, which may be due to the different roles of α2 phase and silicide precipitation on the creep resistance. The homogeneous precipitated α2 phase may improve the resistance, while the silicide precipitation may result in reduction of creep resistance due to the depletion of Si in α matrix. The steady state creep deformation of TG6 titanium under 600 ℃ and 200 MPa is mainly controlled by dislocation climbing.
Key words: high temperature titanium alloy; creep behavior; dislocation climbing
与钢、铝合金、镍基高温合金相比,高温钛合金在比强度、比蠕变强度等方面具有显著优势,因此,广泛应用于先进航空发动机压气机轮盘、叶片等部件,可显著减轻发动机的质量,从而提高发动机的推重比和使用性能[1-2]。随着合金化理论的发展及制造工艺技术水平的提高,高温钛合金的使用温度得以提高,目前,最高长时耐热温度可达600 ℃的典型合金有IMI834等[3],进一步提高钛合金的使用温度主要受到高温蠕变抗力和抗氧化能力的限制[4]。
在航空发动机的设计中,一般将转动部件的蠕变应变控制在0.4%以下[5],以保证在规定的工作状态和寿命期内,发动机的静止和转动部件的蠕变变形不影响外场正常使用,也不影响发动机的分解和再装配。更大的蠕变变形会导致叶片与机匣之间的相互摩擦,容易引发“钛火”等故障。因此,蠕变性能是航空发动机零部件,特别是转动部件用高温钛合金最重要的设计准则之一,来提高航空发动机安全使用性能和延长使用寿命[6]。研究钛合金在高温服役状态下的蠕变变形行为具有重要意义。
TG6(Ti-Al-Sn-Zr-Nb-Ta-Si-C)是设计用于航空发动机压气机在600 ℃以下环境使用的近α型高温钛合金,通过多元复杂合金化的固溶强化和适当利用第二相的沉淀强化作用,以提高合金的高温蠕变抗力。本文作者研究显微组织对TG6钛合金600 ℃蠕变性能的影响,分析蠕变变形行为及机制,为设计和寿命评估提供所需的实验数据和参考。
1 实验
经金相法测定,TG6钛合金的α+β/β转变温度(θβ)为1 050 ℃。采用两种不同工艺生产发动机盘锻件,一种采用β模锻和(1 000 ℃, 2 h, AC)+(750 ℃, 2 h, AC)的固溶时效处理,以得到网篮组织;另一种采用α+β模锻,也采用固溶时效处理,为了得到不同的初生α相含量,固溶处理温度分别为1 030 ℃和1 000 ℃,均保温2 h后空冷,时效均采用(750 ℃, 2 h)+AC。为了评估600 ℃长期热暴露对TG6钛合金蠕变性能的影响,同时也测试热处理并经600 ℃, 100 h热暴露后合金相应组织的蠕变性能。
在RDW30100型电子式蠕变持久试验机上测试了TG6钛合金在600 ℃, 200 MPa条件下的蠕变性能,试验采用圆柱试样,工作部分直径为16 mm,标距长50 mm,采用自动数据采集系统记录应变与时间的关系曲线,根据曲线的斜率计算出稳态蠕变速率(最小蠕变速率)。在Philip Quanta-600型扫描电镜上进行TG6钛合金显微组织的观察和分析。
2 结果
2.1 显微组织
图1所示为TG6钛合金盘模锻件热处理状态的显微组织。其中:图1(a)为β模锻并两相区固溶时效处理得到的网篮组织,可以看到原始β晶界,α相呈片层状,这种组织具有最佳的蠕变强度、断裂韧度和疲劳扩展抗力,但塑性较低。图1(b)所示为α+β模锻并经1 030 ℃固溶和750 ℃时效处理得到的双态组织,在β转变组织的基体上分布着等轴的初生α晶粒,初生α晶粒大部分分布在原始β晶界上或者在三叉晶界上,初生α相(αp)含量在10%左右,平均尺寸为14.05 μm,双态组织具有适中的综合力学性能,是航空钛合金锻件最为常用的组织状态;图1(c)所示为α+β锻并经1 000 ℃固溶和750 ℃时效处理得到的等轴组织,初生α相含量高于50%,因固溶温度较低,没有完全发生等轴化,初生α呈现出一定的方向性,这种组织具有最佳的塑性,但热强性较低。

图1 TG6钛合金盘锻件热处理状态的显微组织
Fig.1 Microstructures of TG6 titanium alloy disc forgings in STA state: (a) Basket structure; (b) Duplex structure; (c) Equiaxed structure
2.2 TG6钛合金在600 ℃, 200 MPa下的蠕变性能
表1给出了TG6钛合金不同组织盘锻件在600 ℃,200 MPa,100 h条件下的蠕变性能,其中包括初始应变、总应变、塑性蠕变应变和稳态蠕变速率。图2所示为相应的蠕变过程应变—时间曲线。因限于蠕变测试时间,蠕变曲线上只给出了初始蠕变阶段和稳态蠕变阶段的一部分。
表1 TG6钛合金在600 ℃, 200 MPa, 100 h条件下的蠕变性能
Table 1 Creep properties of TG6 titanium alloy tested under 600 ℃, 200 MPa, 100 h
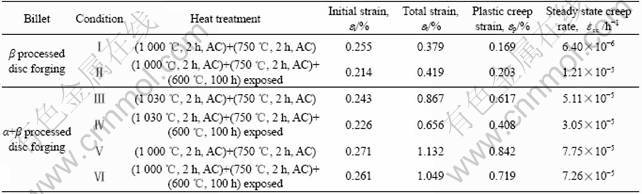

图2 TG6钛合金盘锻件的蠕变变形曲线
Fig.2 Creep deformation curves of TG6 titanium alloy disc forgings: (a) Basket structure; (b) Duplex structure; (c) Equiaxed structure
从表1可以看出,采用β锻获得的盘锻件,其对应的网篮组织具有最小的蠕变应变和蠕变速率,表明网篮组织具有最佳的高温蠕变抗力;而采用α+β锻获得的盘锻件,其对应双态组织和等轴组织具有较高的蠕变应变和蠕变速率,其蠕变应变是网篮组织的两倍以上,且随着初生α相含量的增加,蠕变抗力下降。从图2可以看到,3种组织状态对应的蠕变速率均随时间的增加而逐步减小,网篮组织到30 h左右进入稳态蠕变阶段,而双态组织和等轴组织到10~15 h就进入了稳态蠕变阶段,明显少于网篮组织进入稳态蠕变阶段所需要的时间。
从表1还可以看到,在这3种组织状态下,经过600 ℃,100 h热暴露后,网篮组织对应的蠕变应变提高了,而双态组织和等轴组织对应的蠕变应变反而降低了,这与在高温蠕变过程中微观组织中第二相(主要是α2相和硅化物)析出对蠕变起了作用有关。
3 分析与讨论
在所有的钛合金的显微组织类型中,片层组织和网篮组织具有优异的高温蠕变抗力,双态组织次之,而等轴组织最差,本蠕变测试结果与其他作者的研究结果一致[7],符合高温钛合金组织与蠕变性能关系的一般规律。对于TG6钛合金来说,造成不同显微组织对应蠕变性能之间的差异主要有以下4个原因:
1) 金属的高温蠕变变形主要由晶界的滑动和晶内的位错攀移和滑移组成,对于双态组织和等轴组织,初生α相周围为β转变组织,围绕等轴α提供了快速扩散通道,有利于晶界滑动和沿晶扩散,随着初生α相含量的减少,β转变组织中的α和β片层变长,使得晶界滑动对总的蠕变变形起的作用相应减小。
2) 网篮组织中形成的片层α相与β相遵守Burgers取向关系,α与β相为半共格关系,扩散速率小,因此回复造成的位错攀移速率低,而双态组织和等轴组织,初生α相与临近的β相没有取向关系,界面是非共格的,位错回复更快,位错攀移速率高,导致高的蠕变变形速率[8]。
3) 不同组织之间蠕变性能的差异也与合金元素的再分配有关。对于双态组织,在相变点以下固溶处理时,根据相平衡规律,α稳定化元素,如Al、O在初生α中富集,而固溶冷却时形成的β转变组织中的片层α含有相对较少的α稳定化元素,因此会产生软化,造成总体蠕变抗力的降低。
4) 网篮组织在高温蠕变测试过程中,容易在片层α中析出共格有序的α2相,α2相的析出将显著提高蠕变抗力,而双态组织和等轴组织中析出的α2相相对较少,且分布不均匀,因此,总的蠕变抗力要低于网篮组织的。
尽管片层组织和网篮组织具有最佳的高温蠕变抗力,但在实际生产和使用过程中,高温钛合金往往采用双态组织作为使用状态的组织。对于航空发动机用高温钛合金部件来说,在设计时除了考虑高温蠕变性能的因素外,更为重要的是长期使用的疲劳性能问题,不论轮盘和叶片,疲劳破坏是其主要的失效模式,而双态组织具有比片层组织和网篮组织更好的疲劳性能。
从图2的蠕变曲线可知,在初始蠕变阶段,TG6钛合金具有较高的蠕变速率,随着时间的延长,逐步下降到一个稳定的值,代表着稳态蠕变阶段的开始。在初始蠕变阶段,可动位错多,容易出现位错滑移运动,从而产生快速变形。在施加的应力作用下,伴随着内应力的堆积,可动位错的减少导致蠕变速率的衰减[9],随着应变硬化程度的增加,蠕变速率逐步减小,直到达到一个稳定的值,表明进入了稳态蠕变阶段。在稳态蠕变阶段,被认为是位错运动的应变强化和由热激活回复软化达到了动态平衡,导致了近乎不变的蠕变速率。
经过600 ℃,100 h热暴露后,不论网篮组织,还是双态和等轴组织,其在600 ℃,200 MPa下的蠕变变形行为均发生了显著变化,这与在高温蠕变测试之前原始组织状态不一样有关。为了提高TG6合金的热强性,加入了较高含量的Al、Sn、Zr,以获得最大程度的固溶强化作用,根据Rosenberg提出的铝当量经验公式[10]:
 ≤9% (1)
≤9% (1)
经计算,TG6钛合金的名义铝当量为8.8%,已接近9%的极限值,表明TG6钛合金具有α2相沉淀析出的趋势。550~650 ℃是α2相析出的热力学最佳温度区 间[11],从透射电镜观察α相的衍射斑点可以看到,热暴露后α相有超点阵衍射斑点的出现。大量的研究结果表明,超点阵衍射斑点是与α相呈共格的有序α2相,分布均匀,且当其尺寸小于120 nm时,与α相一直能保持共格关系[12]。
TG6钛合金中还含有0.4%的Si。Si是Ti的共析型β稳定化元素,当α和β相处于平衡状态时,β相中的Si含量要高于α相,因此,硅化物主要是在β相上析出。当然,当α中的Si含量超出其固溶度极限时,也会在α相内析出硅化物。
大量的研究结果表明,钛合金在600 ℃左右的温度下,其蠕变变形主要受位错攀移机制所控制。α2相和硅化物颗粒的析出强烈地影响着位错攀移速率。KOIKE等[13]的研究结果表明,α相中α2相的析出会出现显著的蠕变强化,这与α2相降低位错攀移速率具有很大关系。硅化物的析出也会明显影响蠕变性能,Si在组织中有两种存在形态,固溶于基体和以硅化物颗粒析出。Si原子容易在位错上富集,形成Cotrell气团,对位错的攀移运动具有很强的钉扎作用[14],阻碍位错的攀移和粘滞性运动。当在600 ℃长期热暴露过程中,在基体中会析出硅化物,使得基体贫Si,减弱了固溶Si原子气团阻碍位错攀移的作用,导致蠕变抗力的下降。尽管硅化物颗粒的析出可以有效抑制晶界滑 移,但晶界滑移对总的蠕变应变贡献在10%以下,因此,综合作用而言,硅化物的析出会降低合金的蠕变抗力[15]。
对于网篮组织,在600 ℃热暴露过程中,在片层的α相中,α2相析出较为均匀,且析出数量和程度较低,而硅化物的析出较为充分,比较两者对蠕变抗力的作用,硅化物析出对降低高温蠕变抗力的作用更大,表现为热暴露后高温蠕变抗力的下降。而对于双态组织和等轴组织来说,因合金元素的再分配效应,在600 ℃热暴露过程中,初生α相中α2相析出程度高,对初生α相起到显著的强化作用,α相中析出的硅化物少。而在β转变组织中,硅化物的析出尽管会引起蠕变抗力的下降,但可以被α2相析出强化而抵消。综合作用的结果是,600 ℃热暴露后微观组织的变化会改善合金的高温蠕变抗力。
4 结论
1) TG6钛合金在600 ℃,200 MPa的测试条件下,粗晶的网篮组织具有最佳的蠕变抗力,而细晶的等轴组织具有最低的蠕变抗力,双态组织介于中间。
2) TG6钛合金网篮组织的初始蠕变阶段持续30 h左右,高于双态组织和等轴组织的20 h左右。在初始蠕变阶段,蠕变变形主要受易运动的位错滑移及少量的晶界滑移所控制;当位错运动产生的应变硬化和由热激活产生的回复软化达到平衡时,进入稳态蠕变阶段。
3) 经过600 ℃长期热暴露后,TG6钛合金网篮组织的蠕变抗力有所下降,而双态组织和等轴组织的蠕变抗力反而得以提高,这与α2相和硅化物沉淀析出对蠕变抗力综合作用不一样有关。
4) TG6钛合金在600 ℃,200 MPa下的稳态蠕变变形主要受位错攀移机制所控制,均匀析出的α2相可以提高合金的蠕变抗力;而硅化物沉淀的析出使得α基体贫Si,减弱了Si原子气团对位错攀移的阻碍作用,从而导致蠕变抗力的下降。
REFERENCES
[1] WILLIAMS J C, STARKE E A. Progress in structural materials for aerospace systems[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51: 5775-5799.
[2] WINSTONE M R, PARTRIDGE A, BROOKS J W. The contribution of advanced high temperature materials to future aeroengine[C]//Proc Inst Mech Engrs, 2001, 25(1): 63-73.
[3] NEAL D F. Development of TIMETAL834[C]//ZHAO J C, FAHRMANN M, POLLOCK T M. Development of TIMETAL 834[C]//Materials Design Approaches and Experiences. Indianapolis, 2001: 199-213.
[4] WILLIAMS J C. Alternate materials choices—Some challenges to the increased use of Ti alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 263: 107-111.
[5] L?TJERING G, WILLIAMS J C. Titanium[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 2003: 238.
[6] NEAL D F. Optimization of creep and fatigue resistance in high temperature Ti alloys IMI829 and IMI834[C]//Ti’84: Science and Technology. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Metallkunde, 1984: 2419-2424.
[7] SATYANARAYANA D V V, VARMA V K, NAGALAKSHMI G, SRINIVASA RAO M K. Creep and fatigue behaviour of a near α IMI 834 titanium alloy[J]. Metals Materials and Processes, 2007, 19(1/4): 101-110.
[8] MISHRA H, GHOSAL P, NANDY T K, SAGAR P K. Influence of Fe and Ni on creep of near α-Ti alloy IMI834[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 399: 222-231.
[9] ES-SOUNI M. Primary, secondary and an elastic creep of a high temperature near α-Ti alloy Ti6242Si[J]. Materials Characterizations, 2000, 45: 153-164.
[10] ROSENBERG H W. Titanium alloying in theory and practice[C]//The Science, Technology and Application of Titanium. Oxford, UK: Pergamon Press, 1970: 851-859.
[11] ARDAKANI M G, SHOLLOCK B A, FLOWER H M. The effect of oxygen on microstructure of α and α2 phase in titanium-rich Ti-Al alloys[C]//BLENDKINSOP P A, EVANS W J, FLOWER H M. Ti’95: Science and Technology. UK, 1996: 2242-2249.
[12] BLACKBURN M J. The ordering transformation in titanium: Aluminum alloys containing up to 25 at. Pct aluminum[J]. Transactions of the Metal Society of AIME, 1967, 239: 1200-1208.
[13] KOIKE J, EGASHIRA K, MARUYAMA K, OIKAWA H. High temperature strength of α Ti-Al alloys with a locally ordered structure[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1996, 213: 98-102.
[14] XU Dong-sheng, HU Qing-miao, LU Jian-min, HAO Yu-lin, YANG Rui, KULKOVA S E, BAZHANOV D I. Point defects and mechanical behavior of titanium alloys and intermetallic compounds[C]//Third Conference of the Asian Consortium for Computational Materials Science (ACCMS-3). 2006: 220-227.
[15] PATON N E, MAHONEY M W. Creep of titanium-silicon alloys[J]. Metall Trans A, 1976, 7: 1685-1694.
(编辑 杨 华)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2007CB613803)
通信作者:段 锐,工程师;电话:010-62496623;E-mail: bj100095@126.com