高Zn含量Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金中应力腐蚀开裂、晶界微化学成分及Zn含量之间的关系
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2021年第8期
论文作者:袁丁玲 陈送义 陈康华 黄兰萍 昌江郁 周亮 丁云峰
文章页码:2220 - 2231
关键词:Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金;应力腐蚀开裂;锌含量;晶界微化学成分
Key words:Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy; stress corrosion cracking; Zn content; grain-boundary microchemistry
摘 要:通过应力腐蚀开裂测试、晶间腐蚀测试实验结合扫描电镜以及高角度环形暗场像扫描透射电镜观测,研究Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金中腐蚀行为、晶界中微化学成分以及合金Zn含量之间的关系。结果表明,高Zn含量Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金抗拉强度的提高主要归因于基体中形成的高密度纳米析出相。含11.0% Zn合金比含7.9% Zn (质量分数)合金的应力腐蚀平台速率高大约一个数量级,其主要原因是形成高Zn含量的晶界析出相和较宽的无沉淀析出带。基于合金的腐蚀断裂形貌、晶界微化学成分以及电化学性能,讨论不同Zn含量合金的应力腐蚀开裂机制。
Abstract: The correlations among the corrosion behaviour, grain-boundary microchemistry, and Zn content in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys were studied using stress corrosion cracking (SCC) and intergranular corrosion (IGC) tests, combined with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and high-angle angular dark field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM) microstructural examinations. The results showed that the tensile strength enhancement of high Zn-containing Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys was mainly attributed to the high density nano-scale matrix precipitates. The SCC plateau velocity for the alloy with 11.0 wt.% Zn was about an order of magnitude greater than that of the alloy with 7.9 wt.% Zn, which was mainly associated with Zn enrichment in grain boundary precipitates and wide precipitates-free zones. The SCC mechanisms of different Zn-containing alloys were discussed based on fracture features, grain-boundary microchemistry, and electrochemical properties.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 31(2021) 2220-2231
 among stress corrosion cracking, grain-boundary microchemistry, and Zn content in high Zn-containing Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys
among stress corrosion cracking, grain-boundary microchemistry, and Zn content in high Zn-containing Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloysDing-ling YUAN1,2, Song-yi CHEN1,2, Kang-hua CHEN1,2,3, Lan-ping HUANG1,2, Jiang-yu CHANG1,2, Liang ZHOU1,2, Yun-feng DING2,3
1. Light Alloy Research Institute, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Nonferrous Structural Materials and Manufacturing, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology for National Defence on High-Strength Lightweight Structural Materials, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 17 August 2020; accepted 27 May 2021
Abstract: The correlations among the corrosion behaviour, grain-boundary microchemistry, and Zn content in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys were studied using stress corrosion cracking (SCC) and intergranular corrosion (IGC) tests, combined with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and high-angle angular dark field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM) microstructural examinations. The results showed that the tensile strength enhancement of high Zn-containing Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys was mainly attributed to the high density nano-scale matrix precipitates. The SCC plateau velocity for the alloy with 11.0 wt.% Zn was about an order of magnitude greater than that of the alloy with 7.9 wt.% Zn, which was mainly associated with Zn enrichment in grain boundary precipitates and wide precipitates-free zones. The SCC mechanisms of different Zn-containing alloys were discussed based on fracture features, grain-boundary microchemistry, and electrochemical properties.
Key words: Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy; stress corrosion cracking; Zn content; grain-boundary microchemistry
1 Introduction
High-strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys have been widely used as structural materials in aerospace industry based on their desirable mechanical properties [1-3]. In the development of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys in recent decades, the total alloy element content (Zn, Mg, and Cu), particularly the (Zn + Mg) content, has been significantly increased to enhance strength. Recently, compared with traditional alloys, the high Zn combined with low Cu composition design has been crucial for developing new generation high-hardenability super-strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy thick plate. However, these new generation Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys are more susceptible to stress corrosion cracking (SCC) than traditional alloys. The SCC resistance of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys is closely correlated to the alloy composition, microstructure, and corrosion environment. For example, Cu enrichment in grain boundary precipitates (GBPs) can effectively improve the SCC resistance due to noble potential GBPs with respect to the matrix [4,5]. Adding trace elements Sc, Er, and Yb to 7xxx aluminum alloys exhibited lower corrosion susceptibility because of inhibiting matrix recrystallization behaviour and stabilizing deformation substructure [6-9]. In addition, over- aging heat treatment and slow quenching rate can significantly reduce the corrosion susceptibility but at the expense of strength [10-16]. Air humidity and experimental temperature can drastically promote crack growth rate [17].
Recent research has shown that Zn content significantly affects the mechanical and corrosion properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys. However, these studies mainly focused on traditional alloys with low Zn or high Cu contents (~6 wt.% Zn, ~2.0 wt.% Cu) [18-21]. FRANCISCO et al [18] reported that the initiation and propagation of intergranular cracks in the AA7449-T7651 alloy were much more rapid than those in AA7075-T651. HOLROYD and SCAMANS [19] proposed that over-aging heat treatment was less effective in improving the SCC resistance at a Zn content exceeding 7 wt.%, irrespective of the Cu content. CHEN et al [22] found that a high Zn content increased the strength of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys but produced lower fracture toughness compared with low Zn content. In particular, the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) [23] stated that there was a potential risk from the new generation Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys used in service due to the environment-assisted cracking. SCHWAR- ZENBOCK et al [20] compared the SCC behaviour of new generation 7000-T7x alloys with that of the traditional 7050 alloy. They reported that, in humid air, the crack growth rates of the new generation 7000-T7x alloys were 6-20 times higher than those of the AA7050-T7651 alloy. It was also indicated that a strong association between the crack growth rate and Zn content was presented in these alloys. However, the Cu content of different new generation thick-plate 7000-T7x alloys was varied significantly, and the aging heat treatment parameters were not described in detail. Notably, these parameters (Cu content and aging heat treatment condition) significantly influenced the SCC performance. In addition, the microchemistry of GBPs was only obtained using JMatPro software. Further, no systematic study between SCC and microchemistry in GBPs of high Zn-containing Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys with low Cu content has been reported.
The aim of the present study is to investigate the effect of Zn content on the microstructure, GBPs microchemistry, and SCC properties of high Zn-containing Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys. The characteristics of SCC crack propagation in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys with different Zn contents under three stages of artificial aging heat treatment were analyzed in detail. The correlations among Zn content, corrosion behaviour and microstructure of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys were studied by SCC, IGC, and electrochemical corrosion tests together with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and high- angle angular dark field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM) micro- structural examinations. The results provided a new insight for the composition design of new generation Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys.
2 Experimental
2.1 Composition and heat treatment of materials
The materials used in this investigation were prepared by conventional casting metallurgy method. The measured chemical compositions of high Zn-containing Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys are given in Table 1. The ingots were homogenized at (410 °C, 8 h) + (465 °C, 6 h) + (470 °C, 36 h) and subsequently hot-rolled into 13-mm-thick plates at a rolling temperature of 430 °C, and the total rolling reduction was 87%. All specimens were subjected to a solution heat treatment of (470 °C, 1 h) + (475 °C, 1 h) in a vertical air furnace and then quenched using room temperature water, followed by a three-stage artificial aging heat treatment (120 °C, 6 h) + (155 °C, 10 h) (cooling by cold water) + (120 °C, 24 h) (cooling by air)) [24,25]. The specimens used for observing the micro- structures and testing the corrosion properties were obtained from the central layer of the hot-rolled alloy thick plate.
Table 1 Compositions of high Zn-containing Al-Zn- Mg-Cu alloys (wt.%)

2.2 Microstructure observation
To elucidate the crack propagation mode, the crack tip regions of the SCC-tested specimens were observed via scanning electron spectroscopy (SEM, Nova Nano SEM230). A scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM, Titan G2 60—300) with an energy disperse X-ray spectroscopy (EDXS) system was used to analyze the size, distribution, and microchemistry of GBPs. The mean width of precipitation free zone (PFZ) and the sizes of matrix precipitates (MPs) and GBPs were measured using ImageJ analysis software. The thin foils for STEM were prepared by mechanically grinding with SiC paper with a grit size from 600 to 2500, then, the foils were thinned by a twin-jet electropolishing in a mixture solution (30 vol.% HNO3 and 70 vol.% CH3OH) at -25 °C and a current of 90-100 mA.
2.3 Mechanical tests
The specimens used for mechanical tests were cut along the rolling direction of the rolled plates. The mechanical data were obtained using an Instron-8082 electronic tensile machine at room temperature with a tensile speed of 2 mm/min. The gauge length, width and thickness of the tensile samples were 25, 6 and 2 mm, respectively. The tensile data here represented the average of three tests.
2.4 Corrosion tests
In accordance with GB12445.1—90 [26], the SCC velocities and critical stress intensity factors were measured by applying a constant displacement on double-cantilever beam (DCB) specimens in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution at (35±1) °C. Each specimen was polished perpendicularly to the rolling direction, and the pre-cracking with 2-3 mm was performed before the specimen was immersed in the corrosion environment. To ensure the accuracy of the experimental data, the crack length was examined using a OLYMPUS DSX500 optical microscope (OM). Accelerated IGC tests were performed according to the GB/T 7998—2005 standard [27]. The maximum corrosion depths were also measured using the OM. The open-circuit and potentiodynamic polarization tests were performed to evaluate electrochemical corrosion resistance using a CHI660C electrochemical workstation. In these tests, a standard three-electrode cell configuration comprising saturated calomel reference electrode, Pt counter electrode, and specimens with exposed surface area of 1 cm2 as a working electrode, was used. The scan rate was 0.005 V/s. The electrochemical measurements were conducted in the 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution at room temperature, and the specimens used for these measurements were mechanically ground to a grit size of 2500 and cleaned with ethanol. CHI660C software was used to analyze and fit the data from Tafel-type, and the pitting potential (φpit), pit transition potential (φptp), repassivation potential (φrep), current density (Jcorr), anodic Tafel constant (ba) and cathode Tafel constant (bc) were obtained using CHI660C software. In addition, the corrosion resistance (Rcorr) was calculated using the following equation [28]:
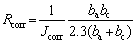 (1)
(1)
3 Results
3.1 Mechanical properties
The mechanical properties of the investigated alloys with different Zn contents are shown in Table 2. The ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and yield strength (YS) increased with the increase of Zn content, whereas a reverse trend for elongation. The UTS and YS of Alloy 1 were (603±6) and (590±4) MPa, respectively, which were 10.0% and 7.1% lower than the corresponding values for Alloy 3. The elongation value of Alloy 1 was 22.5% higher than that of Alloy 3. However, no significant differences were found between the tensile properties of Alloy 1 and Alloy 2, indicating that the effect of the Zn content on strength was limited.
Table 2 Mechanical properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys with different Zn contents

3.2 SCC properties
The dependence of the SCC crack propagation velocity on the stress intensity factor for the alloys in a 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution is shown in Fig. 1. The SCC plateau velocities, (da/dt)II, and threshold stress intensity factor, KISCC, were used to evaluate the susceptibility of SCC. The crack propagation velocity decreased with decreasing Zn content. Alloy 1 had the slowest crack propagation velocity at all testing stages. The value of (da/dt)II decreased by about one order of magnitude as the Zn content decreased from 11.0 to 7.9 wt.%. KISCC increased with decreasing the Zn content as follows: Alloy 3 (KISCC≈2.19 MPa·m1/2) < Alloy 2 (KISCC≈ 3.97 MPa·m1/2) < Alloy 1 (KISCC≈8.58 MPa·m1/2). The SCC macrofracture surface morphologies of the investigated alloys are shown in the insert in Fig. 1(a). The propagation lengths of the SCC cracks on the fracture surface (dark region) of the studied alloys indicated a combined effect of corrosion medium and stress. The SCC-tip regions are highlighted by the red dashed line. These results demonstrated that the alloy containing a higher Zn content was more sensitive to SCC.

Fig. 1 DCB results of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys with various Zn contents
3.3 SEM and OM images
High magnification fractographs of DCB SCC-tip regions are shown in Fig. 2. Prominent intergranular fractures were visible in all alloys, and more corrosion cracks can be observed along the grain boundaries in the alloys with high Zn content than those with low Zn content. Further, extensive corrosion sludges were observed on the fractured surface (Figs. 2(a, c, e)). For the alloy with the highest Zn content (11.0 wt.% Zn), numerous cleavage facets and parts of microvoids were observed on the fracture surface. Notably, the corrosion cracks propagated not only along the grain boundaries but also around the intermetallics. Some spherical intermetallics can also be easily observed in the microvoids shown in Fig. 2(e), implying that microcracks propagated through these microvoids and coalesced with each other until the specimens failed under the external load. The crack-propagation paths were predominately distributed along the grain boundaries (Figs. 2(b, d, f)). Moreover, “chicken claw” fringes and intergranular cracks can be observed in the alloy with the highest Zn content (Fig. 2(f)). These features of the SCC morphology are a further evidence that alloys with high Zn content were more sensitive to SCC than those with low Zn content.
The IGC cross-section images of specimens with different Zn contents are shown in Fig. 3. It can be observed that many corrosion pits in the alloys with relatively low Zn content displayed a “spoon” shape, whereas the 11.0 wt.% Zn- containing alloy exhibited “cylindrical” corrosion tip. The maximum IGC depths of the samples with Zn contents of 7.9, 9.0 and 11.0 wt.% were 69.1, 125.9 and 230.8 μm, respectively. Thus, the 11.0 wt.% Zn-containing alloy exhibited the highest susceptibility to IGC.
3.4 TEM images
Typical microstructures of aging precipitation for the three alloys are shown in Fig. 4. Relatively small, elliptical precipitates can be observed in the case of Alloy 1 (Figs. 4(a, d)). However, both elliptical and elongated precipitates are presented in the case of alloys (Alloy 2) with high Zn content (Figs. 4(b, e)). In Alloy 3, large elliptical and elongated precipitates and some fine elliptical and elongated precipitates are presented in Fig. 4(c, f)).

Fig. 2 DCB fracture analysis results of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys with different Zn contents

Fig. 3 Optical micrographs of maximum depth for Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys with different Zn contents after 12 h IGC
The statistic parameters for the mean size of GBPs, MPs, and PFZs are summarized in Table 3. The alloys with higher Zn content exhibited wider PFZs and larger GBPs and MPs. The GBPs diameters were the largest for the alloy with 11.0 wt.% Zn ((103.7±18.2) nm), intermediate for the alloy with a Zn content of 9.0 wt.% ((66.5±9.6) nm), and the least for the alloy with the Zn content of 7.9 wt.% ((39.8±7.1) nm). Corresponding selected area diffraction patterns (SADPs) along the <110>Al zone axes and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images are presented in Fig. 5. Two types of η and η' precipitates were formed in the three alloys (Figs. 5(a-c)). Based on the fast Fourier transformation (FFT) patterns and inverse FFT analysis, large incoherent η precipitates (labeled A and enclosed by the orange rectangles in Fig. 5(d)) and relatively small semi-coherent elongated η' precipitates (labeled B and enclosed by the blue rectangles in Fig. 5(d)) with thicknesses of 3.8 and 2.2 nm and diameters of 17.8 and 7.5 nm, respectively, can be observed for Alloy 3. These results indicated that the Zn content of the alloys significantly influenced the size of precipitates, however, its influence was insignificant on the type of the precipitates.
HADDF-STEM images and microchemistry of GBPs for investigated alloys are presented in Fig. 6.

Fig. 4 TEM images of typical grain boundaries precipitates (a-c) and matrix precipitates (d-f) in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys
Table 3 Statistical parameters of grain boundary precipitates size, matrix precipitates size and PFZ width for various Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys

The width of PFZs increased as the Zn content increased from 7.9 to 11.0 wt.%. Moreover, the composition profile across GBPs clearly revealed the Zn enrichment in GBPs, indicating contents of ~28.1, ~37.9, ~52.8 at.% Zn for alloys with Zn contents of 7.9, 9.0, and 11.0 wt.%, respectively. However, notably, according to the results of the EDX analysis, there was little difference in the Mg and Cu contents of the GBPs among the three alloys. In addition, a high Zn-containing alloy was responsible for Zn enrichment in GBPs and PFZs.
3.5 Electrochemical corrosion properties
Figure 7 shows the open circuit potential as a function of immersion time for the alloys with different Zn contents. For all samples, the open circuit potentials of the investigated alloys first decreased and remained almost constant after being tested for ~1000 s. The alloy with the 11 wt.% Zn exhibited a more negative potential than the other two alloys. The value of the open circuit potential decreased from -0.784 to -0.859 V (vs SCE) as the Zn content increased from 7.9 to 11.0 wt.%.

Fig. 5 Selected area diffraction patterns (SADPs) in <110>Al zone axes for Alloy 1 (a), Alloy 2 (b) and Alloy 3 (c), inverse FFT image of Alloy 3 (d), FFT patterns (e, g) of precipitates in frames B and A in (d) and inverse FFT images (f, h) corresponding to (e, g), respectively

Fig. 6 HADDF-STEM images (a-c) and corresponding EDX line scan curves (d-f) of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys with different Zn contents

Fig. 7 Open circuit potential curves of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys with different Zn contents
Figure 8 shows the effect of Zn content on expressive local corrosion from cyclic polarization curves. The curves for all alloys had a similar shape, and there was no apparent difference in the electrochemical reaction mechanism among the three alloys. A summary of the corresponding data from the potentiodynamic polarization measurement is presented in Table 4. Generally, higher φcorr, φpit, and φptp or lower Jcorr suggest lower corrosion susceptibility in a corrosive environment. The value of φcorr became more negative as the Zn content increased, and the value of Jcorr for the alloy with the highest Zn content was about 3 times as high as that of the lowest one, implying that alloys with lower Zn content had a better resistance to electrochemical corrosion. As the applied potential increased toward φpit, pit formation rate within alloys rapidly increased. Obviously, the pitting potential was sensitive to the change of Zn content in alloys. φpit changed from -0.698 to -0.771 V (vs SCE) as the Zn content increased from 7.9 to 11.0 wt.%. This trend was consistent with that of φcorr. Moreover, the polarization resistance (Rcorr) decreased as the Zn content increased, which can be ascribed to the superposition effect of the resistance of the passive film and charge-transfer resistance. The corresponding decrease in Rcorr from 43305.8 to 19816.6 Ω·cm2 indicated that the stability of the passive film decreased as the anodic dissolution reaction on the metal surface became more rapid. All electrochemical test results implied that a high Zn accumulation in GBPs resulted in low resistance to electrochemical corrosion.
4 Discussion
The strength of age-hardenable Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys is closely correlated with the density of MPs. Herein, the UTS and YS were found to increase with the increase of Zn content, mainly because high Zn-containing alloys provided a high number density of η' MPs (Table 2). Moreover, super- saturated solid solubility increased with a rise in Zn content and higher precipitation kinetics provided the necessary condition for GBPs’ growth in subsequent aging process, resulting in large GBPs and wide PFZ [22].

Fig. 8 Cyclic polarization curves of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys with different Zn contents in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution
The SCC plateau velocity (da/dt)II for the 11.0 wt.% Zn-containing alloy was about an order of magnitude higher than that of the 7.9 wt.% Zn-containing alloy (Fig. 1). The SCC behaviour can be divided into two stages: crack initiation and crack propagation. Typically, the crack initiation and propagation of SCC were associated with cathode intermetallic particles and anodic GBPs. Less intermetallic particles, such as Al7Cu2Fe, Mg2Si, and Al2CuMg, were found to be present in the new generation alloys with high Zn content than in traditional alloys with low Zn content, such as AA7050 (~ 6.2 wt.% Zn, ~2.2 wt.% Cu) and 7150 (~6.3 wt.% Zn, ~2.3 wt.% Cu) [19,29-31]. The decrease in the number of intermetallic particles helps to decrease crack initiation sites. Previous researches [29,32-35] have established that the SCC process was controlled by the anodic dissolution and the hydrogen embrittlement mechanisms, and the results of the present study confirmed the same. The two main factors should be considered when analyzing the SCC behaviour of the investigated alloys.
Table 4 Electrochemical data of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys with various Zn contents

(1) Anodic dissolution
According to the results of the electrochemical corrosion resistance (Fig. 8 and Table 4), the electrochemical activity of the alloy increased with the increase of Zn content. Generally, hydrogen generation was accompanied by anodic dissolution due to galvanic reaction among the GBPs, PFZ and adjacent alloy matrix. In aluminium alloy, the MgZn2 electrode potential was -1.0 V, the electrode potential of Zn (-0.8 V) was lower than that of Al (-0.68 V). The higher Zn accumulation in Mg(Zn,Al)2 increased the potential differences between the GBPs and the surrounding matrix, resulting in a more active breakdown potential of Mg(Zn,Al)2 than that for the matrix [34]. Therefore, for the PFZ and GBPs with high Zn content, electrochemical corrosion was promoted owing to their low potentials, which was consistent with the results of electrochemical corrosion analysis. In addition, Zn or Mg enrichment in intermetallics was preferentially corroded owing to their negative potentials [36]. Moreover, corrosion pits were associated with the local anodic dissolution of GBPs and intermetallic phases easily acted as crack initiation sites, and micro-cracks surrounding the coarse intermetallics accelerated crack propagation. Generally, the ratio of pit depth (d) to pit width (D) was greater than 10, indicating crack initiation sites, whereas an aspect ratio of 1 was associated with uniform corrosion [29,37]. As shown in Fig. 3, the higher the Zn content is, the greater the number of corrosion pits with d/D>10 is. The SCC susceptibility caused by high Zn content can also be explained by SCC fracture morphology (Fig. 2). The higher the Zn content of the alloy is, the greater the number of microcracks is. And evident intergranular fracture occurred along the grain boundaries.
(2) Hydrogen embrittlement
MARLAUD et al [38] found that the Zn content in MPs was shown to increase with increasing Zn content of the alloys. Additionally, high Zn content in a solid solution tended to cause hydrogen embrittlement owing to the adsorption of H [39]. Remarkably, in this study, a clear relationship was detected between quasi-cleavage cracks with “chicken claw” fringes (Figs. 2(e, f)) and hydrogen embrittlement [32,40]. Similar observations were reported by OGER et al [41,42] and HARDWICK et al [43], giving support to the validity of these results. They reported that the role of hydrogen embrittlement on SCC performance can be explained in terms of brittle transgranular (quasi-cleavage) fracture areas. Parts of hydrogen accumulation in alloys with high Zn content originated from anodic dissolution of GBPs and intermetallic particles, resulting in an increase in anodic dissolution rate accompanied with considerable H-emission. Once the local H content reaches a critical value, greater hydrogen accumulation and more pronounced hydrogen embrittlement will occur. Based on a combination of the above analysis and results shown in Figs. 2(e, f) and Figs. 6(d-f), it can be deduced that a high Zn content in GBPs may promote the absorption of H in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys and give rise to hydrogen embrittlement.
In summary, the complex process of SCC for high Zn-containing Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys resulted from the interdependence of many factors. Based on a comparison and analysis of the effect of different Zn contents on corrosion susceptibility of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys, it was indicated that the SCC mechanism for the investigated alloys in NaCl solution was probably the combination of anodic dissolution and hydrogen embrittlement. Moreover, the roles of anodic dissolution and hydrogen embrittlement in SCC were more obvious for the higher Zn-containing Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys.
5 Conclusions
(1) The MPs density, GBPs size, and PFZs width increased with the increase of Zn content. The tensile strength of the alloy with high Zn content was enhanced compared to that with low Zn content owing to the formation of more MPs in the former.
(2) The Zn content in GBPs obviously increased as the Zn content of alloys increased. The SCC plateau velocity (da/dt)II for alloy containing 11.0 wt.% Zn was about an order of magnitude higher than that of alloy containing 7.9 wt.% Zn mainly because of high Zn content in the GBPs and wide PFZ.
(3) Low Zn content inhibited SCC propagation and other types of local corrosion due to the positive potential of GBPs and less SCC cracking initiation sites.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial supports from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016- YFB0300801), the State Key Laboratory of High Performance Complex Manufacturing of Central South University, China (No. ZZYJKT2020-03), and the National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology for National Defence on High-strength Lightweight Structural Materials of China (No. 20190104).
References
[1] WILLIAMS J C, STARKE E A. Progress in structural materials for aerospace systems [J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51: 5775-5799.
[2] DURSUN T, SOUTIS C. Recent developments in advanced aircraft aluminium alloys [J]. Materials and Design, 2014, 56: 862-871.
[3] TANG Jian-guo, CHEN Hui, ZHANG Xin-ming, LIU Sheng-dan, LIU Wen-jun, OUYANG Hui, LI Hong-ping. Influence of quench-induced precipitation on aging behavior of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 1255-1263.
[4] YUAN Ding-ling, CHEN Kang-hua, CHEN Song-yi, ZHOU Liang, CHANG Jiang-yu, HUANG Lan-ping, YI You-ping. Enhancing stress corrosion cracking resistance of low Cu-containing Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys by slow quench rate [J]. Materials and Design, 2019, 164: 1-11.
[5] KNIGHT S P, BIRBILIS N, MUDDLE B C, TRUEMAN A R, LYNCH S P. Correlations between intergranular stress corrosion cracking, grain-boundary microchemistry, and grain-boundary electrochemistry for Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52: 4073-4080.
[6] XIAO Quan-feng, HUANG Ji-wu, JIANG Ying-ge, JIANG Fu-qin, WU Yun-feng, XU Guo-fu. Effects of minor Sc and Zr additions on mechanical properties and microstructure evolution of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30: 1429-1438.
[7] FANG H C, CHEN K H, CHEN X, CHAO H, PENG G S. Effect of Cr, Yb and Zr additions on localized corrosion of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy [J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51: 2872-2877.
[8] ZOU Liang, PAN Qing-lin, HE Yun-bin, WANG Chang-zhen, LIANG Wen-jie. Effect of minor Sc and Zr addition on microstructures and mechanical properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17: 340-345.
[9] WANG Yi-chang, WU Xiao-dong, CAO Ling-fei, TONG Xin, MALCOLM J C, LIU Qing. Effect of trace Er on the microstructure and properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloys during heat treatments [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2020, 792: 139807.
[10] SONG Feng-xuan, ZHANG Xin-ming, LIU Sheng-dan, TAN Qi, LI Dong-feng. The effect of quench rate and overageing temper on the corrosion behaviour of AA7050 [J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 78: 276-286.
[11] QI Xin, JIN Ji-rong, DAI Chun-li, QI Wen-juan, HE Wang-zhao, SONG Ren-guo. A study on the susceptibility to SCC of 7050 aluminum alloy by DCB specimen [J]. Materials, 2016, 9: 1-10.
[12] CHEN Song-yi, CHEN Kang-hua, PENG Guo-sheng, LIANG Xin, CHEN Xue-hai. Effect of quenching rate on microstructure and stress corrosion cracking of 7085 aluminum alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 47-52.
[13] DITTA A, WEI Lin-jun, XU Yan-jin, WU Su-jun. Microstructural characteristics and properties of spray formed Zn-rich Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy under various aging conditions [J]. Materials Characterization, 2020, 161: 1-10.
[14] XIAO Quan-feng, XU Yuan-ming, HUANG Ji-wu, LI Bo, WANG Bao-feng, LIU Shi-chao, FU Le. Effects of quenching agents, two-step aging and microalloying on tensile properties and stress corrosion cracking of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9: 10198-10208.
[15] WANG Yi-chang, CAO Ling-fei, WU Xiao-dong, TONG Xin, LIAO Bin, HUANG Guang-jie, WANG Zhen-gan. Effect of retrogression treatments on microstructure, hardness and corrosion behaviors of aluminum alloy 7085 [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 814: 152264.
[16] WANG Shuai, LUO Bing-hui, BAI Zhen-hai, ZHENG Ya-ya, HE Chuan, GEN Jiang. Revealing the aging time on the precipitation process and stress corrosion properties of 7N01 aluminium alloy [J]. Vacuum, 2020, 176: 1-10.
[17] YOUNG G A, SCULLY J R. The effects of test temperature, temper, and alloyed copper on the hydrogen-controlled crack growth rate of an Al-Zn-Mg-(Cu) alloy [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2002, 33: 101-115.
[18] FRANCISCO U D, LARROSA N O, PEEL M J. Hydrogen environmentally assisted cracking during static loading of AA7075 and AA7449 [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2020, 772: 1-11.
[19] HOLROYD N J H, SCAMANS G M. Stress corrosion cracking in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu aluminum alloys in saline environment [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2013, 44: 1230-1253.
[20] SCHWARZENBOCK E, OLLIVIER E, GARNER A, CASSELL A, HACK T, BARRETT Z, ENGEL C, BURNETT T L, HOLROYD N J H, ROBSON J D. Environmental cracking performance of new generation thick plate 7000-T7x series alloys in humid air [J]. Corrosion Science, 2020, 171: 1-19.
[21] YANG X B, CHEN J H, HUANG L P, FAN T W, DING Y, YU X W. A transmission electron microscopy study of microscopic causes for localized-corrosion morphology variations in the AA7055 Al alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2018, 34: 1719-1729.
[22] CHEN Zi-yong, MO Yuan-ke, NIE Zuo-ren. Effect of Zn content on the microstructure and properties of super-high strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2013, 44: 3901-3920.
[23] EASA. Environmentally assisted cracking in certain aluminium alloys [R]. European Aviation Safety Agency, Safety Information Bulletin 2018–04R1. 2018. https://ad. easa.europa.eu/ad/2018-04R1.
[24] ZHOU Liang, CHEN Kang-hua, CHEN Song-yi, ZHANG Xing-lin, FAN Shu-min, HUANG Lan-ping. Comparison of hardenability and over-aging precipitation behaviour of three 7xxx aluminium alloys [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2019, 35: 637-644.
[25] FAN Shu-min, CHEN Song-yi, ZHANG Xing-lin, ZHOU Liang, HUANG Lan-ping, CHEN Kang-hua. Influence of muti-stage aging heat treatment on precipitation microstructure and corrosion resistance of 7056 aluminum alloy [J]. Journal of Materials engineering, 2019, 47: 136-143.
[26] GB12445.1—90. High strength alloys—Method of stress corrosion test for double cantilever beam (DCB) specimens [S].
[27] GB/T 7998—2005. Test method for inter-granular corrosion of aluminum alloys [S].
[28] CHEN Song-yi, LI Ji-yu, HU Gui-yun, CHEN Kang-hua, HUANG Lan-ping. Effect of Zn/Mg ratios on SCC, electrochemical corrosion properties and microstructure of Al-Zn-Mg alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 757: 259-264.
[29] ROUT P K, GHOSH M M, GHOSH K S. Effect of solution pH on electrochemical and stress corrosion cracking behaviour of 7150 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 604: 156-165.
[30] CHEN Jun-feng, ZHANG Xin-feng, ZOU Lin-chi, YU Yan, LI Qiang. Effect of precipitate state on the stress corrosion behavior of 7050 aluminum alloy [J]. Materials Characterization, 2016, 114: 1-8.
[31] KNIGHT S P, POHL K, HOLROYD N J H, BIRBILISI N, ROMETSCH P A, MUDDLE B C, GOSWAMI R, LYNCH S P. Some effects of alloy composition on stress corrosion cracking in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys [J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 98: 50-62.
[32] LI Long, WEI Li-jun, XU Yan-jin, MAO Ling, WU Su-jun. Study on the optimizing mechanisms of superior comprehensive properties of a hot spray formed Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2019, 742: 102-108.
[33] LIU S D, CHEN B, LI C B, DAI Y, DENG Y L, ZHANG X M. Mechanism of low exfoliation corrosion resistance due to slow quenching in high strength aluminum alloy [J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 91: 203-212.
[34] MENG Q J, FRANKEL G S. Effect of Cu content on corrosion behavior of 7xxx series aluminum alloys [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2004, 151: B271-B283.
[35] XU D K, BIRBILIS N, ROMETSCH P A. Effect of S-phase dissolution on the corrosion and stress corrosion cracking of an as-rolled Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy [J]. Corrosion, 2012, 68: 1-10.
[36] BIRBILIS N, BUCHHEIT R G. Electrochemical characteristics of intermetallic phases in aluminum alloys—An experimental survey and discussion [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2005, 152: 140-151.
[37] JONE R H. ASM Handbook 13A. Corrosion: Foundamentals, testing, and protections [M]. New York: ASM International, 2003: 349-350.
[38] MARLAUD T, DESCHAMPS A, BLEY F, LEFEBVRE W, BAROUX B. Influence of alloy composition and heat treatment on precipitate composition in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58: 248-260.
[39] KITA H. Periodic variation of exchange current density of hydrogen electrode reaction with atomic number and reaction mechanism [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1966, 113: 1095-1111.
[40] SU H, TODA H, SHIMIZU K, UESUGI K, TAKEUCHI A, WATANABE Y. Assessment of hydrogen embrittlement via image-based techniques in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu aluminum alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2019, 176: 96-108.
[41] OGER L, MALARD B, ODEMER G, PEGUET L, BLANC C. Influence of dislocation on hydrogen diffusion and trapping in an Al-Zn-Mg aluminium alloy [J]. Materials and Design, 2019, 180: 107901.
[42] OGER L, ANDRIEU E, ODEMER G, PEGUET L, BLANC C. Hydrogen-dislocation interaction in a low-copper 7xxx aluminum alloy: About the analysis of interrupted stress corrosion cracking tests [J]. Materials science and engineering A, 2020, 790: 139654.
[43] HARDWICK D A, THOMPSON A W, BERNSTEIN I M. The effect of copper content and microstructure on the hydrogen embrittlement of Al-6Zn-2Mg alloys [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1983, 14: 2517-2526.
袁丁玲1,2,陈送义1,2,陈康华1,2,3,黄兰萍1,2,昌江郁1,2,周 亮1,2,丁云峰2,3
1. 中南大学 轻合金研究院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 有色金属先进结构材料与制造协同创新中心,长沙 410083;
3. 中南大学 轻质高强结构材料国家级科技重点实验室,长沙 410083
摘 要:通过应力腐蚀开裂测试、晶间腐蚀测试实验结合扫描电镜以及高角度环形暗场像扫描透射电镜观测,研究Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金中腐蚀行为、晶界中微化学成分以及合金Zn含量之间的关系。结果表明,高Zn含量Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金抗拉强度的提高主要归因于基体中形成的高密度纳米析出相。含11.0% Zn合金比含7.9% Zn (质量分数)合金的应力腐蚀平台速率高大约一个数量级,其主要原因是形成高Zn含量的晶界析出相和较宽的无沉淀析出带。基于合金的腐蚀断裂形貌、晶界微化学成分以及电化学性能,讨论不同Zn含量合金的应力腐蚀开裂机制。
关键词:Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金;应力腐蚀开裂;锌含量;晶界微化学成分
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Corresponding author: Song-yi CHEN, Tel: +86-15874285082, E-mail: sychen08@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65650-9
1003-6326/  2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press
2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press

