活性炭孔隙结构在其丙酮吸附中的作用
刘伟,李立清,姚小龙,孙政,刘峥
(中南大学 能源科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:为了探讨活性炭孔结构对其吸附的影响,分别用氮气绝热吸附、扫描电镜(SEM)和傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR),对活性炭表面物化性质进行表征。并以丙酮为吸附质,在温度为298.15 K下进行静态和动态吸附实验,研究丙酮在活性炭上的吸附平衡、吸附动力学与吸附能。结果表明:活性炭样品的丙酮饱和吸附容量与活性炭的比表面积、总孔容有正相关关系。孔径在1.67~2.22 nm之间的孔容和丙酮吸附量之间存在较好的线性关系,且线性斜率随丙酮浓度增加而变大。丙酮吸附行为符合Langmuir吸附等温模型和准二级动力学方程式。活性炭的孔是丙酮吸附速率主要制约因素,各吸附阶段吸附速率主要制约因素分别为:快速吸附阶段为微孔、中孔,颗粒内扩散阶段为微孔,吸附末尾阶段为中孔。丙酮在活性炭表面的覆盖率是丙酮分子与吸附剂内吸附位的作用结果,孔结构不同,吸附位分布不同,丙酮表面覆盖率小的活性炭吸附能大,表明活性炭孔结构对其吸附能产生影响。
关键词:活性炭;丙酮;孔结构;相关性;吸附动力学
中图分类号:O647.31 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2012)04-1574-10
Role of pore structure of activated carbon in adsorption for acetone
LIU Wei, LI Li-qing , YAO Xiao-long, SUN Zheng, LIU Zheng
(School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: To explore the effects of activated carbon pore structure on its adsorption performance, the chosen activated carbon samples were characterized by nitrogen adsorption isotherms, scanning electron microscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Acetone as adsorbate, the static and dynamic adsorption experiments were made at 298.15 K. The adsorption equilibrium, adsorption kinetics and adsorption energy of acetone on activated carbon were discussed. The results show that the adsorption capacity for acetone is positive correlation to both total pore volume and specific surface area of activated carbon. Pore volume and acetone adsorptive capacity show a good linear relation when pore diameter is between 1.67-2.22 nm, and linear slope increases with the increase of acetone concentration. The adsorption behavior obeys Langmuir adsorption isotherm model and pseudo-second-order kinetic model. Pore is the major constraints of adsorption rate, specifically, at fast adsorption stage, adsorption rate is mainly restricted by micropore and mesopore, while at intra-particle diffusion stage and the end stage, micropore and mesopore is the main constraint of adsorption rate, respectively. Acetone surface coverage on activated carbon is the interaction results between acetone molecules and adsorption site. The activated carbon, pore structure different, adsorption site distribution will be different, the smaller the surface coverage, the higher the adsorption energy is, indicating that activated carbon pore structure can influence adsorption energy.
Key words: activated carbon(AC); acetone; pore structure; correlation; adsorption kinetics
活性炭已广泛应用于净化(如制糖、食品加工、水生产)、污染控制(如水/废水处理、工业废气中有机气体的去除)、催化、电能储存、黄金提取和多成分有机气体分离[1-2]等领域。活性炭巨大的表面积和孔体积保证其吸附处理能力。而在吸附处理工艺中,成本是制约其应用的关键因素,活性炭对被处理化合物的吸附能力是吸附处理工艺成本控制的一个重要因素[3-4]。活性炭的吸附性能与活性炭本身的性质、吸附质性质[5]、吸附条件[6]都有关系。其中,影响吸附的最主要因素是活性炭的孔隙结构[7-9]和吸附剂分子尺寸。因此,对于吸附处理工艺,选择合适的活性炭吸附剂用于吸附去除指定的化合物是非常重要。从微观角度,探讨有机气体吸附与活性炭孔隙结构、吸附剂分子尺寸相互作用机制,为多孔炭功能设计及性能的开发和特定物质吸附处理中活性炭的选择提供理论依据。丙酮是挥发性有机气体(VOCs)中酮类具有代表性的化合物[10]。因此,活性炭对丙酮的吸附能力可作为活性炭对VOCs中极性分子吸附的一个重要的指标。本文作者借助比表面积分析仪表征活性炭的比表面积、微孔容和孔径分布;关联分析活性炭的比表面积、孔容与丙酮吸附量,并通过动力学和吸附能研究活性炭吸附行为与孔结构的关系。
1 实验部分
1.1 样品
实验所用4种活性炭样品分别来源于:河南长葛利民活性炭有限公司(AC-1)、山西新华活性炭有限公司(AC-2)、宁夏华辉股份有限公司(AC-3)、广州金骏龙碳业化工有限公司(AC-4)。样品使用前用去离子水清洗3次,去掉表面灰分等杂质,然后在423.15 K下真空干燥5 h。
1.2 物性测试
活性炭样品的比表面积和孔隙分布由气体吸附法测定,采用美国贝克曼库尔特有限公司SA3100型快速比表面积及孔隙分析仪,以N2为吸附质,各活性炭样品在高纯液氮温度下进行吸附。样品总孔容(V)由相对压力为0.981 4时的液氮吸附量换算成液氮体积得到;样品比表面积由标准BET方法计算得到;微孔孔容和外表面积由BJH法获得;孔径分布用HK方程和密度函数理论(DFT-Density Functional Theory)正则化方法计算。同时,利用场发射扫描电镜(HITACHI-S4800)观察活性炭的表面结构。活性炭的表面基团用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(NEXUS670,美国Nicolet 公司)测试。
1.3 等温吸附量测定
实验以丙酮为吸附质,吸附温度298.15 K。实验测试4种活性炭在不同浓度下对丙酮的吸附量。实验装置如图1所示。抽取的室内空气经过装有硅胶的干燥器(2个干燥器交替使用)干燥水分后,一部分直接进入混合器;另一部分穿过微型喷淋器(用一个微型泵将有机气体发生器里的丙酮溶剂泵入喷淋器)。调节混合器前的2个气阀,使2股气流在混合器中的混合浓度达到一定值,用真空泵将该混合气送入恒温器中以维持恒定的丙酮气体浓度。
1.4 动态吸附量测定
由图1所示装置产生的一定浓度的丙酮气体通入图2所示装置(置于298.15 K恒温室),活性炭质量随时间变化通过分析天平(岛津,AUW120)测试。尾气利用活性炭处理后排出。

图1 固定床吸附装置
Fig.1 Experimental device

图2 动态吸附量测量装置
Fig.2 Scheme of measurement
2 结果与讨论
2.1 活性炭物性测试结果
活性炭样品绝热吸附N2,用于表征其表面特性,包括BET比表面积、微孔孔容、中孔孔容以及总孔容等孔结构参数,活性炭样品孔结构参数测试结果见表1。由表1可知,AC-1,AC-2,AC-3和AC-4活性炭的总比表面积由大到小的顺序为AC-1,AC-3,AC-2,AC-4。其中,AC-1,AC-2和AC-3的比表面积为930~960 m2/g,AC-4的比表面积为237.4 m2/g;但是AC-1,AC-2和AC-3之间的孔容差异较大,说明3种样品的孔隙分布不同。4种样品中,AC-3样品微孔比例最大,为85%,AC-1样品中孔比例最大,为25%。
图3所示为4种活性炭样品的电镜扫描图。由图3可见,各种大小不一的孔分布在活性炭表面。AC-1和AC-2样品表面的孔大于其他2种样品表面的孔,这表明AC-1和AC-2样品的大、中孔含量可能多于其他2种样品。AC-4样品表面孔隙明显少于其他3种样品的表面孔隙,并且主要为中孔、大孔级别。
图4所示为4种活性炭孔径分布。从图4可知:孔径为0.4~200 nm,各样品孔径范围基本集中在微孔和较小的中孔范围,孔的分布遵循常规活化样品的规律,在孔径分布曲线上,4种活性炭样品均出现4个明显峰值(0.4~0.55 nm,0.6~0.8 nm,1.4~1.5 nm,2.0~2.2 nm),4个峰值大致对应石墨层间距(0.335 nm)的整数倍。这说明,上述4种活性炭孔径体系的形成是由于类石墨微晶碳层面的刻蚀。但仔细分析,各活性炭样品的孔径分布仍有一定程度的区别。AC-1的孔径分布主要集中在0.4~0.55 nm,0.6~0.8 nm,1.4~1.6 nm,2.1~3.3 nm;AC-2的孔径分布主要集中在0.4~0.55 nm,0.6~0.8 nm,1.5~1.6 nm,1.6~4.5 nm;AC-3的孔径分布主要集中在0.4~0.6 nm,0.69~0.7 nm,1.4~1.5 nm,1.5~4.0 nm;AC-4的整体微孔孔容要明显小于其他活性炭,其孔径主要集中在0.5~3.9 nm。
表1 活性炭样品的孔结构参数
Table 1 Parameters of activated carbons


图3 活性炭SEM像
Fig.3 SEM photographs of activated carbons

图4 由DFT方法计算的活性炭孔径分布
Fig.4 Pore size distribution of activated carbons by density functional theory
为了考察活性炭表面基团的含量,对4种活性炭样品进行了红外光谱分析,测试结果如图5所示。由图5可见:AC-1,AC-2,AC-3和AC-4活性炭的红外光谱图上均没有出现明显的峰值波动,只在1 600 cm-1处出现对应于内酯基或羧基中C=O伸缩振动的吸收带,但波动幅度极小。由此可知,4种原始活性炭样品的表面化学性质类似,原始活性炭样品几乎不含表面官能团或含量甚微。

图5 活性炭FTIR谱
Fig.5 FTIR spectrum of activated carbons
2.2 吸附性能
在298.15 K下,调节图1混合器前的2个气阀,使丙酮质量浓度分别稳定于4.0 g/m3(ρ1),7.2 g/m3(ρ2),12.0 g/m3(ρ3),23.5 g/m3(ρ4)和58.6 g/m3(ρ5),进行吸附实验。实验得到各活性炭样品的吸附等温线如图6所示。由图6可知:AC-1,AC-2和AC-3活性炭在不同质量浓度下的丙酮吸附量变化基本相同,且吸附量为AC-4丙酮吸附量的3~4倍,这与4种活性炭之间比表面积及孔容的比例关系相同,说明活性炭吸附容量与活性炭的比表面积和孔容有正相关关系,其是影响活性炭丙酮吸附性能的主要因素。但是,由表1、图4和图6知:AC-1与AC-3比表面积基本相同,孔结构不同,而在23.5 g/m3以下时,2种活性炭的丙酮吸附量相差较大,这说明孔径分布的差异将对吸附过程产生不同的影响,因而活性炭AC-1和AC-3即使有表面积相差不大的情况,也会因孔径分布的细微差异而表现出不同的吸附效果。
根据图6数据,分别用Langmuir和Freundlich方程式进行拟合,拟合所得参数见表2。从表2可知,在所研究的浓度范围内,Langmuir吸附等温线方程的相关系数R2均明显比由Freundlich方程得到的大,表明丙酮在活性炭样品上的吸附等温线能较好地用Langmuir吸附等温线模型来表示。它表示丙酮在4种活性炭上的吸附主要为单分子层吸附。同时,随着吸附剂比表面积和孔容的增大,拟合所得到的常数KF逐渐增大,其中AC-1的KF最大,表明,活性炭的吸附性能与其比表面积、孔容有直接关系,但具体相互作用需要进一步研究。4种活性炭Freundlich方程拟合常数n均大于1,说明在研究浓度范围内均为优惠吸附过程[11]。

图6 在298.15 K下活性炭对丙酮的平衡等温吸附线
Fig.6 Activated carbons adsorption isotherms for acetone at 298.15 K
2.3 孔结构对吸附性能的影响
孔是吸附质分子在吸附剂中吸附驻留的场所。吸附质分子能否进驻吸附剂孔中,受吸附剂孔大小、吸附质分子大小、吸附势强弱等影响;吸附质分子大而孔小,则分子不能进驻孔中;吸附质分子尺寸远小于孔尺寸时,由于吸附势强度不足的制约,孔内只能驻留数层吸附质分子,孔容无法完全利用。为此,结合吸附质分子大小、孔容分布,利用线性回归法,探讨活性炭的孔径结构与其丙酮吸附容量的关系。
丙酮的相对分子质量为58.08,分子直径为0.556 nm[12],结合丙酮分子大小,根据吸附质分子是按单层分子或多层分子吸附于吸附剂孔中的原理(BET),将孔径按丙酮分子直径倍数划分,由DFT法所得各样品孔径分别在0.48~0.56 nm,0.8~1.11 nm,1.11~1.67 nm,1.67~2.22 nm,2.22~2.78 nm,2.78~3.34 nm,0.56~1.67 nm,0.56~2.22 nm和1.11~2.22 nm之间的孔容如表3所示。使用线性回归法对样品上述各孔径范围内的孔容及丙酮吸附量进行线性拟合。
表2 Langmuir和Freundlich吸附等温线模型拟合参数
Table 2 Parameter of Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms equations

表3 活性炭孔容分布
Table 3 Pore volume distribution of activated carbons mL/g

表4 活性炭孔容与丙酮吸附量的线性相关度
Table 4 Linear correlation between pore volume of activated carbons and adsorption capacity of acetone mL/g

依据线性回归分析,得出各孔径范围孔容的线性相关度R2,见表4。从表4可以看出,孔径1.67~2.22 nm之间的孔容与不同浓度下丙酮吸附量的线性相关度R2均大于0.96,即其线性度远较其他孔径范围的好,图7所示为其线性拟合结果。从图7可以看出:在其他吸附条件相同的条件下,拟合直线斜率随丙酮浓度增加而变大,直线截距呈减小趋势,代表了丙酮浓度趋势对活性炭吸附性能的影响。对样品活性炭孔径在1.67~2.22 nm之间的线性回归方程做显著性检验。

图7 孔径 1.67~2.22 nm之间孔容和丙酮吸附量关系
Fig.7 Relationship between adsorption capacity for acetone and pore volumes of 1.67-2.22 nm
在质量浓度ρ1下,线性方程Y1=1 270x+4.77,检验此线性回归是否显著,取α=5 %


查表得拟合系数检验临界值t0.025(2)=4.30,而拟合系数检验值T=7.20,所以线性回归显著。依照上述方法分别对其他质量浓度下的线性回归方程式做显著性检验,结果表明其线性回归均显著,因此说明活性炭孔径在1.67~2.22 nm之间的孔容与丙酮吸附量存在较好的线性关系。
2.4 孔结构对吸附行为的影响
图8所示为样品AC-1,AC-2,AC-3和AC-4在吸附质量浓度ρ5下4种样品的吸附量与吸附接触时间的关系。在前40 min,4种样品吸附量迅速增加,在100 min内基本实现吸附平衡。此外,在相同的实验条件下,样品AC-1,AC-2,AC-3和AC-4的吸附能力明显不同,样品AC-1和AC-3具有最高的吸附容量和吸附速率,其次是样品AC-2,最后是样品AC-4。丙酮的快速吸附,显示了丙酮分子和吸附剂之间高的结合速率,这是因为本实验所用活性炭含有一定的中孔(见表1),而丙酮在中孔中的扩散比微孔中扩散的速度快。上述结果还表明,活性炭一定量的中孔保证了吸附质在孔中的扩散速率,而更大的微孔容,又使吸附速率更快。

图8 不同活性炭在298.15 K下的丙酮吸附量
Fig.8 Activated carbons adsorption capacity for acetone at 298.15 K
利用3个已知的动力学模型,探讨孔结构对吸附行为的影响。首先,吸附动力学准一阶模型主要用于描述物理吸附过程,可以用下面方程描述:
 (1)
(1)
其中,qt和qe,exp分别为吸附时间为t时和吸附平衡时的丙酮吸附量,mg/g;qe,cal为预测平衡吸附量,mg/g;k1为准一阶吸附速率常数,min-1。用式(1)对4个活性炭样品在298.15 K下的丙酮吸附数据作ln(qe,exp-qt)~t线性关系图,吸附动力学速率常数k1的拟合计算结果列于表5。
其次,基于平衡状态的准二阶动力学模型主要用于描述物理和化学复合吸附过程,其形式如下:
 (2)
(2)
其中:k2为准二阶吸附速率常数,min-1。用式(2)对4个活性炭样品在298.15 K下的丙酮吸附数据作t/qt与t的线性关系图,吸附动力学速率常数k2的拟合计算结果列于表5。
归一化标准差Δq,是用来寻找可以描述对样品吸附的最适用吸附动力学模型,可由如下公式计算:
 (3)
(3)
其中,N为实验测试点数目;Δq为吸附量归一化标准差,%。准一、准二吸附动力学模型检验结果见表5。
从表5可以看出,AC-1,AC-2和AC-3样品用准一阶方程和准二阶方程拟合的线性相关系数均大于0.95,Δq均较小,说明3种样品均可以用这2种模型模拟吸附动力学。但是,用准二阶方程拟合的相关系数更接近于1,这说明准二阶动力学模型结果相关性更好,更能真实地反映活性炭吸附丙酮的反应机理,同时表明,AC-1,AC-2和AC-3活性炭均受吸附剂表面官能团的影响,但是影响很小,在吸附过程中不起主导作用。而AC-4样品主要适用准二阶模型模拟吸附动力学,说明样品受化学吸附影响较AC-1,AC-2,AC-3要大。FTIR谱线(图5)中,同一峰值点AC-4波动大于其他3种活性炭也可证明这一点。
由于上述2个动力学模型不能解释扩散机理,依据以上2个方程,Weber等[13]提出粒间扩散模型,这是一个经验函数关系式,吸附质吸附在吸附剂上的量与t1/2成比例而不是吸附时间t,Weber-Morris方程如下:
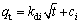 (4)
(4)
其中:kdi为i阶段的速率常数,mg/(g·h1/2);ci为i阶段截距。对于颗粒内扩散,qt与t1/2将是线性关系,如果点通过原点,那么速率的限制就只受颗粒内扩散影响[14]。
颗粒内扩散模型拟合参数见表6,4种活性炭吸附丙酮的拟合曲线如图9所示。由表6可知,颗粒内扩散模型均能很好地拟合4种活性炭。从图9可知:线性拟合图呈现出多线性类型,表明吸附有3个或更多的吸附阶段。第1阶段,吸附质分子在实验装置中扩散,吸附质浓度由小变大的外部表面吸附阶段。吸附速率受吸附质浓度和表面孔大小影响。第2阶段是瞬间吸附或外部表面吸附阶段;这是吸附力场叠加效应作用的结果。第3个阶段是渐进或缓慢的吸附阶段,颗粒内扩散是吸附速率的控制因素,该阶段吸附力场叠加效应减弱或消失。第4阶段是最终平衡阶段,由于大部分的微孔和部分中孔被吸附质填充,内颗粒扩散进一步减缓,吸附速率进一步减小。很明显,4种样品第1吸附阶段吸附速率相差不大,并且与总孔容、BET比表面积没有关联性,这个阶段主要速率限制因素为边界层条件,即吸附质浓度,表面孔径。第1阶段在约1 min内迅速完成,继而进入瞬间吸附阶段(第2阶段),该阶段吸附速率常数kd2从大到小依次为:AC-1,AC-3,AC-2,AC-4,这与表1中4种样品微孔容排序基本相同(样品AC-1和AC-3除外)。但是由于AC-1中孔容和微孔容都较大,所以综合吸附速率就大,因此,该阶段吸附速率受制因素主要为微孔容和中孔容,且主要为微孔容。4种样品第2阶段基本在20 min内完成,接着进入颗粒内扩散阶段(第3阶段),该阶段吸附更加深入孔隙,微孔发达程度成为唯一受制因素,因此,吸附速率常数kd3与微孔所占比例顺序相同,从大到小为AC-3,AC-2,AC-1,AC-4。吸附进入第4阶段,微孔基本填充完毕,开始以多层吸附为主,利于多层吸附的中孔成为吸附速率主要的限制因素,吸附速率常数kd4与中孔容顺序基本相同,从大到小顺序为AC-2,AC-1,AC-3,AC-4。
综上所述,丙酮吸附满足气体吸附一般过程,即吸附质分子扩散到吸附剂外表面,再通过颗粒内扩散到吸附剂内表面,最后到达吸附位而被吸附。从表6还可知:4种活性炭样品的吸附速率常数有下列关系:kd2,kd3,kd1,kd4,因为较大的可利用孔容和充足的吸附质传递通道是保证吸附速率的主要因素。
2.5 表面覆盖率
由Langmuir方程模拟可知,丙酮在4种活性炭上的吸附主要为单分子层吸附。基于上述分析和吸附量、吸附质分子的投影面积,吸附剂在每克活性炭上的覆盖面积可由下列公式得到:
 (5)
(5)
式中,SCx为覆盖面积,m2/g;Am为一个分子的投影面积(按分子直径计算,m2);qx为吸附量(可为实测吸附量也可为模型预测吸附量),mg/g;MW为摩尔质量,g/mol;此外,表面覆盖率定义为SCx与BET比表面积的比值,计算结果如表7所列。
表5 298 K时不同活性炭吸附丙酮的动力学方程及速率常数
Table 5 Dynamics equations and speed constant of activated carbons adsorption for acetone at 298 K

表6 粒子内扩散模型拟合参数
Table 6 Parameters obtained by fitting of intra-particle diffusion model


图9 不同活性炭吸附丙酮的颗粒内扩散模型拟合曲线
Fig.9 Intra-particle diffusion model fitting of activated carbons adsorption for acetone
由表7可知:在实验浓度范围内,丙酮在AC-1,AC-2,AC-3和AC-4上的表面覆盖率,分别为27%~66%,21%~63%,22%~66%和33%~72%。4种活性炭中,在相同浓度下,丙酮在AC-4上的表面覆盖率最高,在AC-2上的表面覆盖率最低。假设能实现有效吸附的吸附位为有效吸附位,由表7可知,当丙酮浓度由4 g/m3变到58.6 g/m3时,丙酮在4种活性炭上的表面覆盖率均有明显增大,说明吸附剂的有效吸附位变多,可知,吸附质浓度增大对有效吸附位起正相关作用。由Langmuir模型预测的最大吸附量可知,AC-1,AC-2,AC-3,AC-4的最大覆盖面积分别为:705,684,736,187 m2/g。
吸附剂的吸附力源于吸附剂内/外表面未释放的表面力,并且孔径越小的孔其未释放的表面力越大,当发生吸附作用时,吸附最先发生在吸附力强的微孔处。同时,吸附质分子的性质、吸附质分子与吸附剂表面的距离也对吸附力产生影响。但吸附温度、浓度一定时,发生吸附所需的吸附力就主要受孔径大小制约。吸附质在吸附剂表面的覆盖面积被认为是立体/平面因素对吸附剂内吸附位分布的作用。基于上述分析,丙酮质量浓度为4 g/m3时,其在吸附剂上的覆盖面积小,微孔容可以满足该浓度下丙酮在活性炭上的覆盖面积,该浓度下的覆盖面积是深度较深的微孔吸附的结果,即吸附深度和厚度作用的结果。58.6 g/m3的丙酮在4种吸附剂上的覆盖率均大于63 %,微孔容已经不能满足,故丙酮质量浓度为58.6 g/m3时,丙酮在吸附剂上的覆盖面积是微孔、中孔、大孔吸附共同作用的结果,即是吸附宽度和厚度作用的结果。则丙酮在吸附剂在上的覆盖面积是由吸附深度向吸附宽度发展的。
2.6 孔结构对吸附能的影响
活性炭吸附剂表面分子形成吸附力场,在对吸附质进行吸附时,产生吸附能。吸附能的大小既取决于吸附剂的表面性质,又取决于吸附质分子的性质,同时还取决于吸附质分子与吸附剂表面的距离。吸附能在一定程度上综合反应了活性炭及吸附质物性参数对吸附行为的影响功效。D-R方程[15]可以很好地描述化合物在炭材料上的吸附行为,通过D-R方程对吸附等温线进行线性拟合,可得出活性炭的特征吸附能E0。D-R方程的形式为:
 (6)
(6)
 (7)
(7)
式中:W为相对压力p/p0下孔中吸附质的平衡吸附容量,mL/g;W0为微孔极限吸附容积,mL/g;A为吸附势,A=R0Tln(p0/p);β为吸附亲和系数;E0和E分别为标准吸附质氮和所用吸附质的特征吸附能;p0和p分别为饱和蒸汽压和平衡压力;R0为摩尔气体常数;T为热力学温度。
将AC-1,AC-2,AC-3和AC-4氮吸附等温线按照D-R方程进行线性关联,得到转化为分压ln2(p0/p)与吸附容积对数lnW的关系,结果如图10所示。根据D-R方程线性拟合得到的直线斜率为-2.303(RT/βE0)2,由此求得AC-1,AC-2,AC-3和AC-4对氮的特征吸附能分别为18.00,22.66,21.47和16.93 kJ/mol。丙酮的亲和系数β为0.88[16],则可计算AC-1,AC-2,AC-3和AC-4对丙酮的吸附能分别为15.84,19.94,18.90和14.90 kJ/mol。4种活性炭的吸附能从大到小依次为AC-2,AC-3,AC-1,AC-4,与表7中表面覆盖率排序相反,说明吸附能大的活性炭表面覆盖率小。而丙酮在活性炭表面的覆盖率是丙酮分子与吸附剂内吸附位的作用结果。孔结构不同,吸附位分布不同,因此,表明活性炭孔结构对其吸附特定物质的吸附能产生影响。
表7 298 K时丙酮在活性炭上的覆盖面积和表面覆盖率
Table 7 Coverage area and surface coverage of acetone on activated carbons at 298 K m2/g


图10 活性炭氮吸附等温线D-R方程线性拟合曲线
Fig.10 D-R equation linear fitting curve based on nitrogen adsorption isotherms of activated carbons
3 结论
(1) 活性炭的比表面积、孔容是决定丙酮吸附量的重要因素。各活性炭的饱和吸附容量与活性炭的比表面积、孔容有正相关的关系,孔结构同样影响活性炭的吸附能力。
(2) 用Langmuir吸附等温线模型可较好地描述丙酮在样品活性炭上的吸附平衡。吸附动力学用准二阶模型拟合较好。
(3) 活性炭孔容和丙酮吸附量之间存在线性关系,线性相关度最大的孔径范围是1.67~2.22 nm之间。
(4) 利用颗粒内扩散模型能很好的描述丙酮在活性炭孔中的扩散,分析各个吸附阶段吸附速率的控制因素。4种活性炭样品的吸附速率常数有下列关系:kd2>kd3>kd1>kd4。
(5) 利用表面覆盖面积分析丙酮在孔中的扩散,当丙酮浓度由4 g/m3增加到58.6 g/m3时,丙酮在4种活性炭上的表面覆盖率均有明显增大。
(6) 活性炭孔结构对其吸附特定物质的吸附能产生影响,4种活性炭样品的吸附能从大到小依次为AC-2,AC-3,AC-1,AC-4,吸附能大的活性炭表面覆盖率小。
参考文献:
[1] Centeno T A, Fernandez J A, Stoeckli F. Correlation between heats of immersion and limiting capacitances in porous carbons[J]. Carbon, 2008, 46(7): 1025-1030.
[2] 黄维秋, 吕艳丽, 饶原刚. 油气回收吸附剂的再生方法[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2010, 26(3): 486-492.
HUANG Wei-qiu, LV Yan-li, RAO Yuan-gang. Regeneration technology of adsorptions for oil vapor recovery[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2010, 26(3): 486-492.
[3] LI Jun, QIU Jin, SUN Yao-Jun, LONG Ying-cai. Studies on natural STI zeolite: Modification, structure, adsorption and catalysis[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2000, 37(3): 365-378.
[4] YANG Juan, QIU Ke-qiang. Preparation of activated carbon by chemical activation under vacuum[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2009, 43(9): 3385-3390.
[5] CHIANG Yu-chun, CHIANG Pen-chi, HUANG Chin-pao. Effects of pore structure and temperature on VOC adsorption on activated carbon[J]. Carbon, 2000, 39(4): 523-534.
[6] Kolade M A, Kogebauer A, Alpay E. Adsorptive reactor technology for VOC abatement[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2009, 64(6): 1167-1177.
[7] 王贵珍, 李丽欣, 李永真, 等. 毛竹活性炭制备及其对含苯酚废水吸附的研究[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2010, 24(4): 700-704.
WANG Gui-zhen, LI Li-xin, LI Yong-zhen, et al. Study on the preparation of bamboo activated carbon and its phenol adsorption properties[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2010, 24(4): 700-704.
[8] CHEN Qing-jun, WANG Zhi, LONG Dong-hui, et al. Role of pore structure of activated carbon fibers in the catalytic oxidation of H2S[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2010, 49(7): 3152-3159.
[9] CHENG Bei, LE Yao, CAI Wei-quan, et al. Synthesis of hierarchical Ni(OH)2 and NiO nanosheets and their adsorption kinetics and isotherms to Congo red in water[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 185(2/3): 889-897.
[10] 沈永平, 陶波, 王琦. 2-甲基丙烯生产中有关体系的共沸点研究[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2005, 21(1): 63-67.
SHENG Yong-ping, TAO Bo, WANG Qi. Study on azeotropes of the binary systems concerning synthesis of 2-methoxypropene[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2005, 21(1): 63-67.
[11] 张东, 张文杰, 关欣, 等. 负载型纳米钛酸锶钡对水中Cd2+吸附行为研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2009, 29(3): 824-828.
ZHANG Dong, ZHANG Wen-jie, GUAN Xin, et al. Adsorption behavior of immobilized nanometer barium-strontium titanate for cadmium ion in water[J]. Spectrosc Spect Anal, 2009, 29(3): 824-828.
[12] HUANG Mei-Chiung, CHOU Chia-Huei, TENG Hsisheng. Pore-size effects on activated-carbon capacities for volatile organic compound adsorption[J]. AIChE J, 2002, 48(8): 1804-1810.
[13] Weber W J, Morris J C. Advance in water pollution research: Removal of biological resistant pollutions from wastewater by adsorption[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Water Pollution Symposium. London: Pergamon Oxford, 1962: 231-266.
[14] Hameed B H, Ahmad A A, Aziz N. Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics of acid dye adsorption on activated palm ash[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2007, 133(1/3): 195-203.
[15] WU Ju-fang, Str?mqvist Marianne E, Claesson Ola, et al. A systematic approach for modeling the affinity coefficient in the Dubinin-Radushkevich equation[J]. Carbon, 2002, 40(14): 2587-2596.
[16] 梁大明. 中国煤质活性炭[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008: 45-48.
LIANG Da-ming. China coal activated carbon[M].Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008: 45-48.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2011-04-25;修回日期:2011-08-16
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(20976200)
通信作者:李立清(1962-),男,湖南郴州人,博士,教授,从事大气污染物控制研究;电话:13807483619;E-mail:liqingli@hotmail.com