DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.01.024
基于蒙特卡罗法的纳米颗粒悬浮液的太阳能吸收性能
陈星宇,伍东玲,周萍,庞丹,陈梅洁
(中南大学 能源科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:基于蒙特卡罗法,研究考虑纳米颗粒散射作用下其悬浮液的太阳能吸收性能。研究结果表明:当纳米颗粒粒径较大时,颗粒散射作用对其悬浮液吸收性能的影响不能忽略;随着颗粒粒径增大,悬浮液的太阳能吸收效率先增大后减小,半径为55 nm的Cu@SiO2颗粒获得最优的太阳能吸收性能;随着悬浮液颗粒体积分数和厚度增大,悬浮液的太阳能吸收效率逐渐增大,但进一步增大悬浮液颗粒体积分数和厚度,其太阳能吸收效率逐渐达到饱和,且未能完全吸收太阳辐射,体积分数为0.21%(高度为1 mm)和高度为21 mm(体积分数为0.01%)的悬浮液获得的太阳能吸收效率分别为71.55%和76.79%;基于此,通过设计多层SiO2@Cu@SiO2颗粒调控悬浮液在太阳光谱上的吸收性能,达到了太阳能全光谱吸收。
关键词:纳米颗粒;散射;吸收;蒙特卡罗;太阳能
中图分类号:TK519 文献标志码:A
文章编号:1672-7207(2021)01-0239-10
Solar absorption performance of nanoparticle suspensions based on Monte Carlo method
CHEN Xingyu, WU Dongling, ZHOU Ping, PANG Dan, CHEN Meijie
(School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Based on the Monte Carlo method(MC), the solar absorption performance of the suspension under the influence of nanoparticle(NP) scattering was studied. The results show that when the size of nanoparticles is large, the effect of particle scattering on the absorption performance of the suspension cannot be ignored. As the NP size increases, the solar absorption efficiency of the suspension first increases and then decreases. Cu@SiO2 nanoparticles with a radius of 55 nm obtain the best solar absorption performance. As the volume fraction and thickness of the suspension increase, the solar absorption efficiency of the suspension gradually increases, but if the volume fraction and thickness of the suspension further increase, the solar absorption efficiency gradually reaches saturation and fails to fully absorb solar radiation. The solar energy absorption efficiency of the suspension with the volume fraction of 0.21% (height of 1 mm) and the height of 21 mm (volume fraction of 0.01%) is 71.55% and 76.79%, respectively. Based on it, the full solar spectrum absorption is achieved by designing multiple layers of SiO2@Cu@SiO2 particles to control the absorption performance of the suspension in the solar spectrum.
Key words: nanoparticle; scattering; absorption; Monte Carlo; solar energy
太阳能作为一种清洁可持续能源,为解决传统化石能源短缺问题,缓解环境危机提供了可能,其相关研究得到了广泛关注。目前,太阳能的利用方式主要为光-热转换利用和光-电转换利用,其中,光-热转换是一种简单有效的利用方式。在通过工作介质吸收太阳辐射并将其转化为热量的光-热转换利用中,提高工作介质对太阳辐射的吸收性能是太阳能高效利用的前提。针对纯水、醇类、油类等常用工质对太阳辐射吸收能力有限,导致光热转换能力有限的问题,学者们提出将纳米颗粒分散在基液中形成纳米颗粒悬浮液,以强化工质对太阳辐射的吸收性能[1-3]。针对纳米颗粒悬浮液的太阳能光-热转换特性,研究学者展开了大量相关实验研究和数值模拟。实验研究发现,在基液中添加较低体积分数的纳米颗粒,可以提高工质的吸收率,进而大幅度提高工质的最大温升和光热转换效率[4-6]。其具体温升和转换效率受纳米颗粒悬浮液类型和浓度的影响[7-10]。数值模拟表明,与基液相比纳米颗粒悬浮液具有更强的太阳能光-热转换性能[11-13]。其光-热转换性能受纳米颗粒材料、粒径、形状、结构、颗粒体积分数、悬浮液厚度及基液介电常数的影响[14-18]。通过前人的实验研究和数值模拟发现,颗粒的物化特性是影响悬浮液吸收性能的主要因素。而在数值计算中,颗粒的物化特性主要通过颗粒的吸收系数和散射系数来表现其对悬浮液吸收性能的影响。在现有的多数研究中,通常假设颗粒粒径较小,符合瑞利散射定律的条件,进而根据瑞利散射的计算方程,以悬浮液的吸收或消光系数来计算纳米颗粒悬浮液的吸收性能[19-21]。然而,对金属纳米颗粒悬浮液而言,颗粒的散射截面积随粒径的增大而增大,当粒径超过一定范围时,颗粒的散射截面积将超过吸收截面积[22],此时颗粒的散射特性对悬浮液体系吸收性能的影响将不能被忽略。因此,对于金属纳米颗粒悬浮液,准确评估其悬浮液体系吸收性能具有重要意义。本文作者基于蒙特卡罗(MC)法,计算不同粒径下纳米颗粒悬浮液太阳能吸收性能,分析纳米颗粒散射作用对其悬浮液体系太阳能吸收性能作用规律;讨论颗粒浓度及悬浮液厚度对其太阳能吸收性能的影响;最后,设计多层核壳颗粒达到了太阳能全光谱吸收。
1 理论与模型
由于悬浮液中纳米颗粒数量巨大,直接求解纳米颗粒悬浮液光学性能计算量巨大。对于低浓度纳米颗粒悬浮液,可以先求解单个纳米颗粒的光学性能,然后,基于相关假设和修正模型求解悬浮液体系的光学性能。在本文中,首先,基于有限元法(FEM)对单个纳米颗粒的光学特性进行计算;然后,基于独立散射条件得到纳米颗粒悬浮液的吸收、散射系数;最后,通过MC法计算纳米颗粒悬浮液的吸收特性。
1.1 纳米颗粒吸收、散射系数计算模型
采用FEM方法求解纳米颗粒的光学特性时,电磁波在颗粒中的传播过程可以通过Helmholtz方程进行描述[23]:
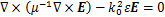 (1)
(1)
式中:E为电场,V/m;μ为磁导率,H/m;k0为波数,m-1;ε为介电常数,水的介电常数取1.33;铜的光学常数来自JOHNSON等[24]的研究结果。
通过求解上述Helmholtz方程可以获得颗粒的电磁场分布。基于电磁场分布,纳米颗粒的热损耗功率密度可通过如下方程进行描述[25]:
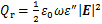 (2)
(2)
式中:ε0为真空介电常数;ω为入射光的频率,Hz;ε″为材料介电常数的虚部。通过如下方程可以对颗粒的吸收、散射功率进行计算:
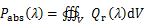 (3)
(3)
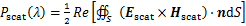 (4)
(4)
式中:V为纳米颗粒体积,m3;S为闭合曲面,m2。基于如上吸收与散射功率结合光的入射功率Iin,可以得到颗粒的吸收、散射和消光截面积:
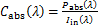 (5)
(5)
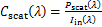 (6)
(6)
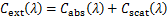 (7)
(7)
式中:Cabs,Cscat及Cext分别为颗粒的吸收、散射和消光截面积,m2。将吸收、散射和消光截面积除以颗粒几何面积,可以得到颗粒的吸收、散射和消光系数:
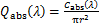 (8)
(8)
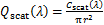 (9)
(9)
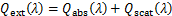 (10)
(10)
1.2 纳米颗粒悬浮液光学特性计算模型
根据上述纳米颗粒的光学特性,可以得到纳米颗粒悬浮液的光学特性。为保证悬浮液的工作稳定性,基液中加入的纳米颗粒的体积分数通常很小。在低浓度和小颗粒条件下,光子与颗粒之间的相互作用可以视为独立散射[19]。因此,可以通过独立散射来近似获得纳米颗粒悬浮液的光学特性。而纳米颗粒悬浮液的吸收系数主要由颗粒的吸收系数和基液的吸收系数构成,可将其描述为[26]
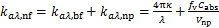 (11)
(11)
式中:kaλ, nf,kaλ, bf和kaλ, np分别为悬浮液、基础流体和纳米颗粒的吸收系数,m-1;κ为基液的吸收系数,m-1;fv为颗粒体积分数;Vnp为单个纳米颗粒的体积,m3;本文所采用基液为水。
由于基液水几乎不存在散射,因此纳米颗粒悬浮液的散射系数近似等于颗粒的散射系数,其可描述为
 (12)
(12)
式中:ksλ, nf,ksλ, bf和ksλ, np分别为悬浮液、基础流体和纳米颗粒的散射系数,m-1。由此,可将纳米颗粒悬浮液的消光系数描述为
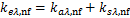 (13)
(13)
基于所求得的纳米颗粒悬浮液的吸收、散射系数,采用MC法可以对悬浮液中光子的传播过程进行模拟。MC法是指以概率论和数理统计为基础的一种统计计算方法,其基于被模拟系统的概率模型,通过计算机进行随机试验,对系统的随机特性进行模拟。对于本文的研究,需要对大量光子的传播路径进行模拟并将结果平均来获得体系反射率和吸收率的近似值。
图1所示为纳米颗粒悬浮液中光子传播示意图。从图1可知:光子在纳米颗粒悬浮液中传播时,有被吸收、散射和透射3种可能。当光子被吸收或透过时光子将消失;而当光子被散射时,被散射的光子将继续运动且运动方向可能被改变,当光子方向改变时,光子的新方向可以借助Henyey-Greenstein散射相函数来确定[27]。对悬浮液体系而言,每个光子在其间的传播过程都是独立随机事件,根据Beer-Lambert定律得到光子被吸收或散射随光子移动距离s变化的概率密度函数为
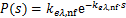 (14)
(14)
式中:keλ, nf表示悬浮液消光系数,m-1;s表示光子移动距离,m。
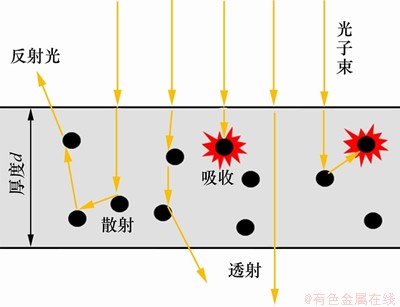
图1 纳米颗粒悬浮液中光子传播示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of photon propagation in NP suspension
2 模型验证
为保证数值模拟的准确性,在计算前需要对模型进行验证。对于颗粒光学特性的计算,Mie理论计算出的解析解被认为是精确解,通常用于FEM模型的验证。图2(a)所示为FEM和Mie理论计算的半径为50 nm的铜球纳米颗粒的吸收系数和散射系数,其中离散区最大网格尺寸为2 nm。从图2(a)可知:有限元的计算结果与Mie理论的计算结果吻合度良好,2种计算方法得到的吸收系数和散射系数之间的相对误差分别为3.0%和3.3%,表明FEM可以获得有效的计算结果。
对于颗粒悬浮液吸收特性的计算,在低浓度小颗粒的条件下可以利用Beer-Lambert定律对MC法的计算结果进行验证。图2(b)所示为MC法和Beer-Lambert定律计算的颗粒半径为10 nm,颗粒体积分数为0.02%,悬浮液厚度为1 mm的Cu纳米颗粒悬浮液的太阳光谱吸收效率,其中通过光子数无关性检验,本文模拟的光子数为3 000万。从图2(b)可知:MC法的计算结果与Beer-Lambert定律的计算结果吻合度很好,2种方法得到的光谱吸收率之间的相对误差为1.2%,结果表明MC法的计算结果具有良好的准确性。
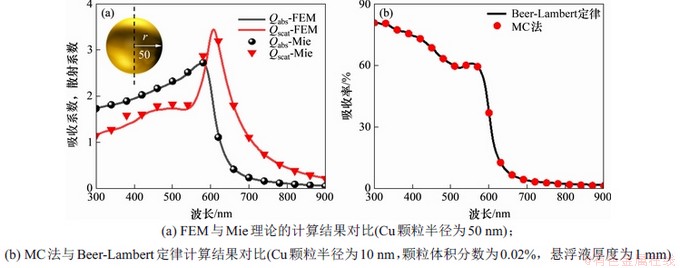
图2 FEM与Mie理论的计算结果对比和MC法与Beer-Lambert定律计算结果对比
Fig. 2 Comparison of calculation results between FEM and Mie theory and comparison of calculation results between MC method and Beer-Lambert law
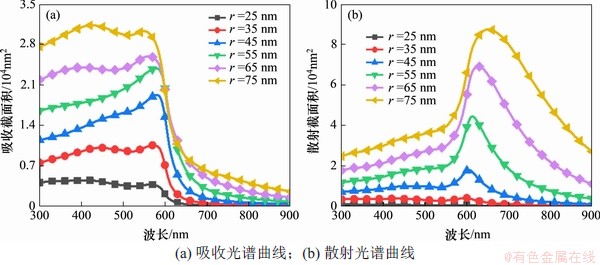
图3 不同粒径Cu@SiO2颗粒光学特性
Fig. 3 Optical properties of Cu@SiO2 particles with different particle size
3 结果与讨论
3.1 粒径对颗粒光学特性的影响
由于分散在基液水中的Cu纳米颗粒容易被氧化,为此,本文在Cu纳米颗粒表面添加一层固定厚度为5 nm的SiO2壳组成Cu@SiO2结构来防止Cu核氧化。由于本研究中的外层SiO2壳层主要用来保护Cu颗粒,因此下文讨论的所有半径均只考虑铜核半径。图3所示为不同粒径的Cu@SiO2纳米颗粒的吸收和散射光谱曲线。从图3(a)可知:Cu@SiO2纳米颗粒的吸收截面积随粒径的增大而增大,且随着粒径的进一步增大吸收截面积开始出现2个峰值,另外吸收截面积对应的峰值波长将随粒径的增大而发生轻微的蓝移。从图3(b)可以看出:Cu@SiO2纳米颗粒的散射截面积随粒径的增大而增大,且散射截面积随波长的变化规律相同,而散射截面积对应的峰值波长将随粒径的增大而发生轻微的红移。同时,对比图3(a)和3(b)可知,随着粒径的增大颗粒散射截面积将逐渐超过吸收截面积,此时,颗粒的散射特性对其悬浮液体系光学性能的影响将不能被忽略。
3.2 不同方法计算纳米颗粒悬浮液体系吸收率的对比
通过计算不同粒径颗粒的吸收、散射系数可知,当颗粒粒径增大到一定值时,悬浮液中颗粒散射特性的作用将不能被忽略。而现有的多数研究,一般以悬浮液的吸收或消光系数来计算纳米颗粒悬浮液的吸收性能。当以吸收系数来计算悬浮液的吸收率时,忽略了系统中颗粒的散射特性;而当以消光系数来计算悬浮液的吸收率时,则认为系统中的散射光子将会被完全吸收。显然,随着粒径的增大,这2种计算方法都无法准确计算悬浮液的吸收特性。为此,本文采用同时考虑吸收和散射特性的MC法来计算悬浮液的吸收特性。
在纳米颗粒体积分数为0.01%,悬浮液厚度为1 mm的不同粒径的纳米颗粒悬浮液体系中,分别采用3种不同方法对悬浮液体系的吸收率进行计算。方法A,考虑吸收和散射系数的MC法;方法B,基于吸收系数的Beer-Lambert定律;方法C,基于消光系数的Beer-Lambert定律,得到吸收率随光谱分布情况如图4所示。由图4(a)可知:当颗粒半径为15 nm时,3种不同计算方法得到的悬浮液吸收率在整个计算波长范围内基本吻合。这主要是因为,当颗粒粒径较小时,颗粒的散射系数较小,悬浮液系统的吸收系数与消光系数近似相等,散射对悬浮液系统的作用可以忽略不计,因而3种计算方法结果吻合。然而,随着颗粒半径的增大,悬浮液中颗粒散射特性的作用逐渐增强,3种方法得到的计算结果间的差值也逐渐增大,如图4(b)~ 4(d)所示。当颗粒半径为75 nm时,MC法得到的悬浮液吸收效率比基于吸收系数计算结果高10.7%,比基于消光系数计算结果低60.1%。
由图4(b)可知:当颗粒半径为50 nm时,MC法的计算结果并不总是介于基于吸收系数和基于消光系数得到的结果之间。造成该现象主要是因为,随着Cu@SiO2纳米颗粒粒径的增大其不对称因子的波长依赖性逐渐增强,且颗粒的不对称因子随波长的增加而减小,如图4(e)所示。由图4(f)可知:对于半径为50 nm的颗粒而言,当波长为300 nm时,颗粒的散射主要以较小的锥角向前传播;当波长为700 nm时,颗粒在各个方向上的散射概率基本相等。而研究的悬浮液颗粒浓度较低厚度较小,向前散射的光子并不能被完全吸收,因此在短波段由MC法计算的吸收率略低。以上结果表明,随着颗粒粒径的增大,采用综合考虑吸收和散射系数的MC法来代替单纯采用吸收系数或消光系数来计算吸收率的方法具有重要意义。
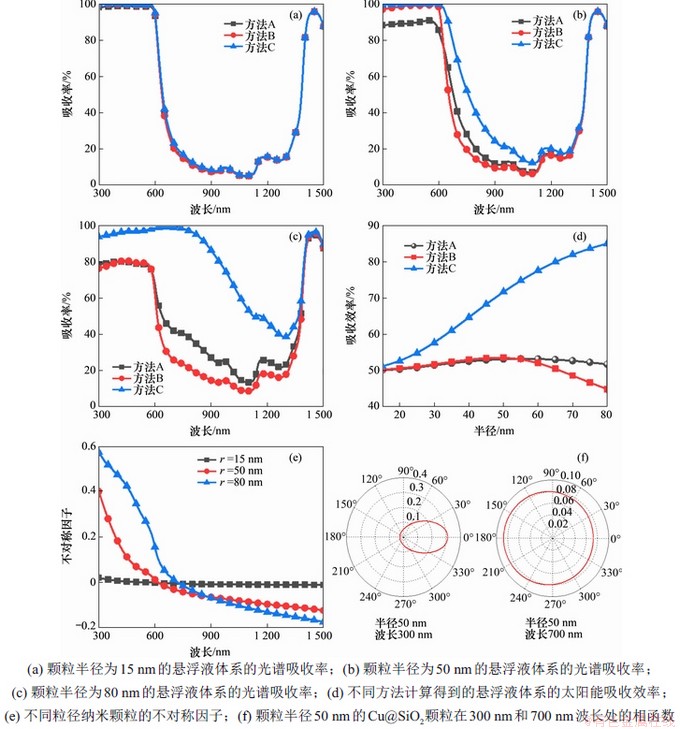
图4 计算方法A,B和C所得不同粒径的Cu@SiO2纳米颗粒悬浮液体系吸收性能曲线
Fig. 4 Absorption performance curves of Cu@SiO2 NP suspension systems with different particle sizes under calculation methods A, B and C
3.3 纳米颗粒粒径、体积分数及悬浮液厚度对悬浮液体系吸收性能的影响
光谱吸收率是评价纳米颗粒悬浮液体系太阳能吸收性能的重要参数,基于以上分析发现,在确定组分的悬浮液中,纳米颗粒粒径、体积分数及悬浮液厚度是影响悬浮液吸收率的重要因素。图5所示分别为纳米颗粒粒径、体积分数及悬浮液厚度对悬浮液吸收率和悬浮液体系太阳能吸收效率的影响。由图5(a)可知:当固定颗粒体积分数为0.01%,悬浮液厚度为1 mm时,在波长小于600 nm的范围内,光谱吸收率随粒径的增大而降低,当波长大于600 nm时,光谱吸收率随粒径的增大而增大。进一步计算得到悬浮液体系在整个太阳光谱内对太阳能吸收效率随粒径的变化如图5(b)所示,太阳能吸收效率先随粒径的增大而增大,在达到最大值之后,吸收效率将随粒径的增大而减小。由于体系中颗粒体积分数较小、悬浮液厚度较薄,因此,当颗粒半径为55 nm时,悬浮液获得的最大吸收效率仅为53.2%。
图5(c)所示为悬浮液吸收率随颗粒体积分数的变化规律。从图5(c)可以看出:吸收率随颗粒体积分数的增大而增大,与基液相比,在基液中加入小体积分数的纳米颗粒即可大幅提高工质的吸收率。如图5(d)所示,当固定颗粒半径为55 nm,悬浮液厚度为1 mm,在基液中加入体积分数分别为0.01%和0.02%的纳米颗粒时,悬浮液体系的吸收效率由9.3%分别提高到53.2%和59.2%。同时,悬浮液的吸收效率将随颗粒体积分数的增加而进一步增大,且其增长速率将随体积分数的增加而逐渐变缓趋于饱和。
图5(e)和5(f)所示分别为悬浮液吸收率和吸收效率随悬浮液厚度的变化规律。从图5(e)可以看出:不同厚度的悬浮液体系的吸收率随波长的变化规律相似,悬浮液吸收率随厚度的增加而增大。从图5(f)可知:悬浮液体系的吸收效率随悬浮液厚度的增加先快速增大然后增长速率逐渐变缓,当固定颗粒半径为55 nm,体积分数为0.01%,将悬浮液厚度由1 mm增加至3 mm时,悬浮液体系的吸收效率由53.2%增加到67.1%,进一步增加悬浮液厚度至21 mm时悬浮液的吸收效率增大到76.8%。
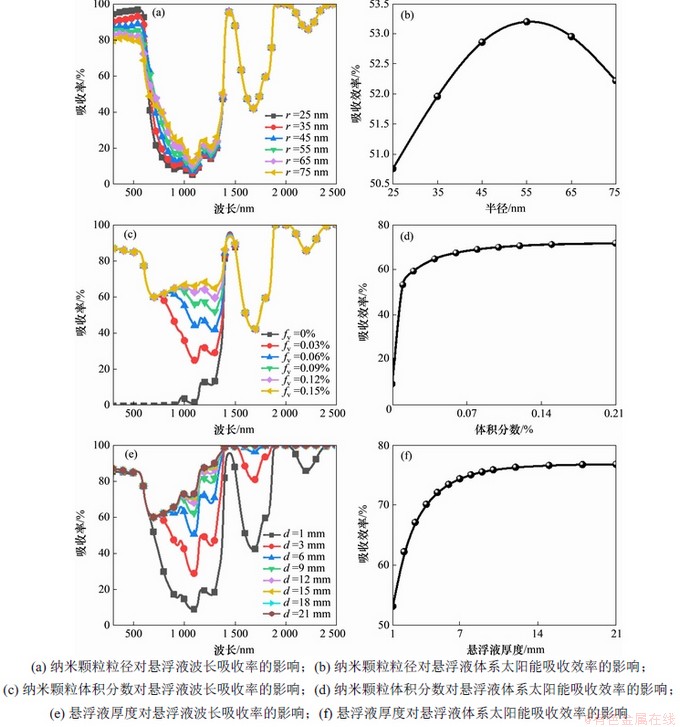
图5 Cu@SiO2纳米颗粒悬浮液体系太阳能吸收性能
Fig. 5 Solar absorption performance of Cu@SiO2 NP suspension system
3.4 悬浮液体系吸收性能优化
由以上研究可知,悬浮液体系受到光谱本身的限制,调节颗粒粒径、体积分数和悬浮液厚度均无法高效的吸收太阳光。金属纳米颗粒的光学性质对其周围的介质的介电性质十分敏感,为此设计了SiO2@Cu@SiO2核壳纳米颗粒,多层纳米颗粒结构的中间层Cu与其两侧的SiO2核和SiO2壳之间由于材料间介电性质的不同,会增强Cu的局部表面等离子共振强度,使得颗粒的吸收能力得到了提高。进而提高了悬浮液在太阳光谱上的吸收效率,强化纳米流体对太阳能吸收性能。在本研究中保持颗粒总粒径不变,分析核壳比对吸收性能的影响,其中核壳比的定义为Φ=ts/Rsum(ts表示壳层厚度,Rsum表示颗粒总粒径)。图6(a)所示为不同核壳比颗粒对应的吸收光谱曲线。从图6(a)可以看出:颗粒吸收截面积的峰值随核壳比的减小而增大,其峰值波长随核壳比的减小而出现明显的红移。而峰值波长的红移可以弥补光谱吸收上的缺口,强化悬浮液的吸收性能如图6(b)和6(c)所示。图6(d)所示为悬浮液体系吸收效率随核壳比及悬浮液厚度的变化情况。从图6(d)可知:悬浮液体系的吸收效率随核壳比的减小而增大,随悬浮液厚度的增加而增大。当固定颗粒总半径为30 nm,核壳比为0.5,体积分数为0.01%,将悬浮液厚度由1 mm增加至21 mm时,悬浮液体系的吸收效率由52.2%增加到89.5%;当固定颗粒总半径为30 nm,悬浮液厚度为1 mm,体积分数为0.01%,将核壳比由0.5减小至0.1时,悬浮液体系的吸收效率将由52.2%增加到71.1%。
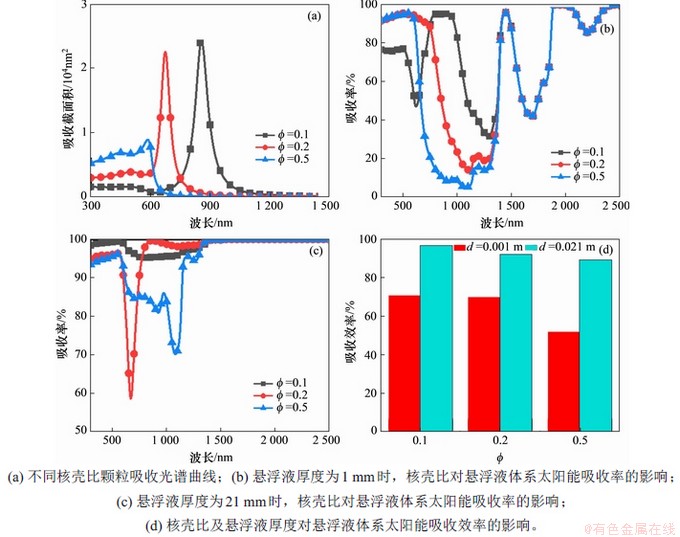
图6 核壳颗粒悬浮液体系太阳能吸收性能(核壳颗粒总半径为30 nm)
Fig. 6 Solar absorption performance of the core-shell particle suspension system (total radius of core-shell particles is 30 nm).
4 结论
1) 在纳米颗粒体积分数为0.01%,悬浮液厚度为1 mm的条件下,当颗粒半径为75 nm时,MC法得到的悬浮液吸收效率比基于消光系数计算结果低60.1%,比基于吸收系数计算结果高10.7%。
2) 纳米颗粒悬浮液的吸收效率随粒径的增大先增大,在达到最大值之后逐渐减小。悬浮液吸收效率在纳米颗粒体积分数为0.01%,悬浮液厚度为1 mm,颗粒半径为55 nm的条件下获得最大值53.2%。
3) 纳米颗粒悬浮液的吸收效率随纳米颗粒体积分数和悬浮液厚度增大而增大。在颗粒半径为55 nm,悬浮液厚度为1 mm的条件下,加入体积分数为0.02%的纳米颗粒的悬浮液体系其吸收效率高于基液79.9%。在颗粒半径为55 nm,体积分数为0.01%的条件下,将悬浮液厚度由1 mm增加至3 mm,悬浮液的吸收效率由53.2%增加到67.1%。
4) SiO2@Cu@ SiO2颗粒的吸收峰值波长随核壳比的减小而出现明显的红移,悬浮液体系的吸收效率随核壳比的减小而增大,当核壳比由0.5减小至0.1时,悬浮液体系的吸收效率由52.2%增加到71.1%。
参考文献:
[1] MAHIAN O, KIANIFAR A, KALOGIROU S A, et al. A review of the applications of nanofluids in solar energy[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 57(2): 582-594.
[2] CHEN Meijie, HE Yurong, ZHU Jiaqi, et al. Investigating the collector efficiency of silver nanofluids based direct absorption solar collectors[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 181: 65-74.
[3] 何钦波, 汪双凤, 曾社铨, 等. 直接吸收式太阳能集热纳米流体辐射特性实验研究[J]. 制冷学报, 2014, 35(1): 109-113.
HE Qinbo, WANG Shuangfeng, ZENG Shequan, et al. Experimental investigation on radiation characteristic of nanofluids for direct absorption solar thermal energy systems[J]. Journal of Refrigeration, 2014, 35(1): 109-113.
[4] 陈梅洁, 唐天琪, 刘子玉, 等. 等离激元Ag纳米流体光热转换特性[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2018, 35(2): 222-226.
CHEN Meijie, TANG Tianqi, LIU Ziyu, et al. Investigating on photothermal conversion properties of plasmonic Ag nanofluids[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 35(2): 222-226.
[5] WANG Lingling, ZHU Guihua, WANG Min, et al. Dual plasmonic Au/TiN nanofluids for efficient solar photothermal conversion[J]. Solar Energy, 2019, 184: 240-248.
[6] 屈健, 田敏, 王谦, 等. 碳纳米管-水纳米流体的光热转化特性[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(S2): 113-119.
QU Jian, TIAN Min, WANG Qian, et al. Photo-thermal properties of MWCNT-H2O nanofluid[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(S2): 113-119.
[7] 徐国英, 李凌志, 张小松, 等. 添加不同纳米颗粒的导热油直接吸收集热实验性能[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(S2):293-298.
XU Guoying, LI Lingzhi, ZHANG Xiaosong, et al. Experimental performance of direct absorption collector using heat-transfer oil added with different nanoparticles[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(S2):293-298.
[8] 段慧玲, 宣益民. 等离激元纳米流体的光热特性研究[J]. 中国科学(技术科学), 2014, 44(8): 833-838.
DUAN Huiling, XUAN Yimin. Research on photo-thermal properties of plasmonic nanofluid[J]. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2014, 44(8): 833-838.
[9] ZHANG H, CHEN H J, DU Xiaoze, et al. Dependence of photothermal conversion characteristics on different nanoparticle dispersions[J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2015, 15(4): 3055-3060.
[10] 李富恒. 石墨烯纳米片-乙二醇纳米流体光热转化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(S1): 479-485.
LI Fuheng. Investigation on photothermal conversion characteristics of graphene nanosheets-glycol nanofluids[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(S1): 479-485.
[11] JIN X, LIN Guiping, ZEINY A, et al. Solar photothermal conversion characteristics of hybrid nanofluids: an experimental and numerical study[J]. Renewable Energy, 2019, 141: 937-949.
[12] 刘长青, 王德兵, 何燕, 等. 基于磁性纳米流体的中温太阳能吸收与光热转换性能[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(28/29): 3041-3048.
LIU Changqing, WANG Debing, HE Yan, et al. Properties of solar energy absorption and photothermal conversion at medium temperature based on magnetic nanofluids[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(28/29): 3041-3048.
[13] CAI Yaomin, NAN Yi, GUO Zhixiong. Enhanced absorption of solar energy in a daylighting louver with Ni-water nanofluid[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 158: 119921.
[14] CHEN Meijie, HE Yurong, WANG Xinzhi, et al. Numerically investigating the optical properties of plasmonic metallic nanoparticles for effective solar absorption and heating[J]. Solar Energy, 2018, 161: 17-24.
[15] WANG Zhaolong, ZHANG Z M, QUAN Xiaojun, et al. A numerical study on effects of surrounding medium, material, and geometry of nanoparticles on solar absorption efficiencies[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 116: 825-832.
[16] 段慧玲, 李强, 郑源. SiO2/Ag等离激元纳米流体的温升特性[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2017, 38(8): 1768-1771.
DUAN Huiling, LI Qiang, ZHENG Yuan. Photothermal Properties of Plasmonic Composite Nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2017, 38(8): 1768-1771.
[17] FAN Desong, LI Qiang, CHEN Weibing, et al. Graphene nanofluids containing core-shell nanoparticles with plasmon resonance effect enhanced solar energy absorption[J]. Solar Energy, 2017, 158: 1-8.
[18] QIN Caiyan, KANG K, LEE I, et al. Optimization of a direct absorption solar collector with blended plasmonic nanofluids[J]. Solar Energy, 2017, 150: 512-520.
[19] TIEN C L. Thermal radiation in packed and fluidized beds[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 1988, 110(4b): 1230-1242.
[20] QIN Caiyan, KANG K, LEE I, et al. Optimization of the spectral absorption coefficient of a plasmonic nanofluid for a direct absorption solar collector[J]. Solar Energy, 2018, 169: 231-236.
[21] CHEN Zhuo, CHEN Meijie, YAN Hongjie, et al. Enhanced solar thermal conversion performance of plasmonic gold dimer nanofluids[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, 178: 115561.
[22] CHEN Meijie, HE Yurong, WANG Xinzhi, et al. Numerically investigating the optical properties of plasmonic metallic nanoparticles for effective solar absorption and heating[J]. Solar Energy, 2018, 161: 17-24.
[23] ZHAO J, PINCHUK A O, MCMAHON J M, et al. Methods for describing the electromagnetic properties of silver and gold nanoparticles[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2008, 41(12): 1710-1720.
[24] JOHNSON P, CHRISTY R. Optical constants of transition metals: Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Pd[J]. Physical Review B, 1974, 9(12): 5056-5070.
[25] 金建铭. 电磁场有限元方法[M]. 王建国, 译. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 1998: 1-317.
JIN Jianming. Electromagnetic finite element method[M]. WANG Jianguo, trans. Xi′an: XiDian University Press, 1998: 1-317.
[26] BOHREN C F, HUFFMAN D R. Absorption and scattering of light by small particles[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1998: 326-329.
[27] MELNIKOVA I N, DLUGACH Z M, NAKAJIMA T, et al. Calculation of the reflection function of an optically thick scattering layer for a Henyey-Greenstein phase function[J]. Applied Optics, 2000, 39(24): 4195-4204.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期: 2020 -09 -27; 修回日期: 2020 -11 -16
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(52006246)(Project(52006246) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:陈梅洁,博士,副教授,从事微纳结构光-热特性调控及先进热管理技术研究;E-mail:chenmeijie@csu.edu.cn
引用格式: 陈星宇, 伍东玲, 周萍, 等. 基于蒙特卡罗法的纳米颗粒悬浮液的太阳能吸收性能[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(1): 239-248.
Citation: CHEN Xingyu, WU Dongling, ZHOU Ping, et al. Solar absorption performance of nanoparticle suspensions based on Monte Carlo method[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2021, 52(1): 239-248.