文章编号:1004-0609(2015)-09-2453-11
热镀锌铝镁镀层的切边保护性能和耐腐蚀机理
袁训华1,林 源2,张启富1
(1. 新冶高科技集团有限公司 先进金属材料涂镀国家工程实验室, 北京 100081;
2. 国家知识产权局专利局 专利审查协作广东中心,广州 510530)
摘 要:采用SEM观察了成分不同热镀锌合金镀层的微观结构和镀层腐蚀后的表面形貌,用电化学和循环腐蚀试验分析镀层钢板的腐蚀行为和耐蚀性能,并用XRD分析镀层表面腐蚀产物的相组成。结果表明:热镀锌铝镁镀层中Al、Mg及Zn2Mg相的存在可以使镀层表面形成稳定的化合物,降低电化学试验时镀层的电流密度和溶解速度;镀层中的共晶相可以使Mg元素在镀层中均匀分布,从而抑制阴极反应;镀层腐蚀后形成的Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O和Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O是不溶性的胶状腐蚀产物,可以有效隔断镀层与外界物质间的电子传输。腐蚀初期,Zn2Mg优先溶解,为腐蚀产物提供足够的Mg元素,部分Mg元素进入Zn的腐蚀产物中,形成Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O和Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O。而Al3+和Mg2+的存在可以降低镀层中Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O脱水形成无保护作用ZnO的趋势,增加Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O和Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O等腐蚀产物的量,且Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O和Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O填充于腐蚀缝隙中可以进一步阻止腐蚀的发生,使得镀层表面获得更低的电位,因而对阳极的分层扩散驱动力变小,降低切边部位在长期腐蚀中的溶解情况,提高镀层的耐蚀性能和切边保护性能。
关键词:热镀锌铝镁镀层;显微组织;电化学;循环腐蚀试验;切边保护性能;耐腐蚀机理
中图分类号:TG174.44 文献标志码:A
Cut-edge protection performance and corrosion resistance mechanisms of galvanized Zn-Al-Mg alloy coating
YUAN Xun-hua1, LIN Yuan2, ZHANG Qi-fu1
(1. National Engineering Laboratory of Advanced Coating Technology for Metals,
New Metallurgy Hi-Tech Group Co., Ltd., Beijing 100081, China;
2. Patent Examination Cooperation Center, Patent Office, SIPO, Guangdong, Guangzhou 510530, China)
Abstract: The microstructure and surface morphology after corrosion of the hot-dip galvanizing alloy coating with different components were observed by scanning electron microscopy, the corrosion performance and corrosion resistance of coating were analyzed by the electrochemistry and cyclic corrosion test, and the phase composition of corrosion product on the coating surface was analyzed by X-ray diffractometry. The results show that the corrosion current density of galvanized Zn-Al-Mg alloy coating is lower than that of zinc coated steel in electrochemical test, which proves that the existing of aluminum, magnesium and Zn2Mg phase can make the stable compounds form on the surface of coating and reduce the dissolution rate of zinc. The eutectic phase can make the Mg element uniformly distribute in the galvanized Zn-Al-Mg alloy coating, and inhibit the cathode reaction. Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O and Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O are insoluble colloidal corrosion products of galvanized Zn-Al-Mg alloy coating after corroded, which can cut off the electronic transmission between coating and external substance, effectively. Zn2Mg is dissolved preferentially in the initial corrosion, which provides enough Mg elements for the corrosion products, part of Mg elements dissolve from the surface of coating, get into the corrosion products of zinc, and form Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O and Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O. However, the exist of Al3+ and Mg2+ can reduce the trend that Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O dehydrated to from zinc oxide without protective effect, and increase the amount of Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O and Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O in galvanized Zn-Al-Mg alloy coating. And the chemical compound of Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O and Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O can be full in the corrosion cracks that furthermore prevent corrosion occurring in the coating, so, the lower potential is obtained on surface of coating, thus, the hierarchical diffusion driving force of anode becomes small, which can reduce the dissolution of cut-edge part of galvanized Zn-Al-Mg alloy coating in the long-term corrosion and improve the corrosion resistance and cut-edge protection performance of galvanized Zn-Al-Mg alloy coating.
Key words: hot dip galvanized Zn-Al-Mg alloy coating; microstructure; electrochemistry; cyclic corrosion test; cut-edge protection performance; corrosion resistance mechanism
随着锌资源的不断消耗和环境污染的日益严重,热镀锌镀层在耐蚀性能和力学性能等方面已不能满足要求,耐蚀性能更高、经济性能更好的新型合金镀层成为研究和开发的重点[1-2]。在热镀锌镀层中添加适量的镁和铝可以有效提高镀层的耐腐蚀性能和力学性能,从而既可以延长镀层的使用寿命,又能通过降低镀层质量减少锌的消耗。因热镀锌铝镁合金镀层具有良好的耐蚀性、耐损伤性和切边保护性而成为研究的重点,为此,日本和欧洲的钢铁公司相继开发了多种成分不同的热镀锌铝镁合金镀层钢板[3]。部分热镀锌铝镁镀层钢板进行了商业化生产,主要包括Super Zinc(Zn-4.5%A1-0.1%Mg(质量分数))、Super Dyma线(Zn-11%Al-3%Mg-0.2%Si(质量分数))、Dyma Zinc (Zn- 0.5%Mg(质量分数))和ZAM(Zn-11%Al-3%Mg(质量分数))等[4-5]。许多研究者对锌液中添加镁对提高镀层耐蚀性能的影响进行了研究,KOMASTSU等[6]的研究结果表明,镁的加入改变了镀层的组织结构,在腐蚀环境下,Mg能长期抑制碳酸锌及氧化锌等非保护性腐蚀产物的形成,且含镁镀层的腐蚀产物具有优异的抑制阴极反应的效果。KIMATA等[7]研究热镀Zn-11%Al-3%Mg-0.2%Si镀层钢板的大气腐蚀性能,结果表明热镀锌铝镁镀层无论是直接使用还是涂漆后使用均具有良好的耐蚀性能。SOHN等[8]通过SEM观察了腐蚀后热镀锌铝镁镀层的断面形貌,利用XRD、TEM等分析了镀层中二元共晶的腐蚀行为。ISHIKAWA等[9]研究了热镀锌铝镁镀层的腐蚀产物,发现在水溶液中可以分离出ZnCl2、AlCl3以及MgCl2等化合物,并认为腐蚀产物是由Zn(Ⅱ)、Al(Ⅲ)和Mg(Ⅱ)[Zn(Ⅱ)wAl(Ⅲ)xMg(Ⅱ)y](2w+3x+2y)(OH)(2w+3x+2y)-z-Clz·nH2O组成,它们凝聚在一起,形成致密的氧化膜,阻碍了镀层的进一步腐蚀。李锋等[10-11]研究热镀Zn-11%Al-3%Mg-0.2%Si(质量分数)合金镀层在NaCl体系中的腐蚀行为及铝、镁对锌镀层显微组织和物相组成的影响。上述研究成果只对热镀锌铝镁镀层的耐蚀性能进行了评价,没有从腐蚀产物的形成机理、损伤后镀层的防护机理和镀层的切边防护性能等方面给出热镀锌铝镁镀层具有良好耐蚀性能的原因。为此,本文作者通过调整镀液化学成分制备了成分不同的4种热镀锌合金镀层钢板,通过组织结构的观察,循环腐蚀试验和XRD分析,对比了纯锌镀层、铝锌硅镀层和锌铝镁镀层的组织特征、腐蚀产物的形成机理和耐蚀性能,根据镀层的腐蚀产物从理论上解释热镀锌铝镁镀层切边保护性能和耐腐蚀机理。
1 实验
1.1 试验材料
试验用基板材料为普通冷轧低碳钢(0.08%C、0.4%Mn、0.006%Si、0.021%P、0.02%Cu(质量分数)),4种热镀锌合金的镀液成分如表1所示。热镀锌实验在连续热镀锌模拟机上进行,钢板经过酸洗、清洗、烘干处理后放入热镀锌模拟机,钢板退火温度为800 ℃,采用体积分数为5%(H2+N2)的气体还原钢板表面的氧化物,退火时间60 s,GI、ZAM和SD镀层钢板入锌锅温度490 ℃,锌液温度480 ℃,GL镀层钢板入锌锅温度610 ℃,锌液温度590 ℃,浸镀时间3 s,镀层厚度控制在15 μm左右。
1.2 镀层显微组织与物相
用QUANTA-650型环境扫描电镜观察镀层的表面和断面形貌,加速电压为20 kV。用Philips Analytical X′Pert PRO MPD型X射线衍射仪(XRD)分析了热镀锌铝镁镀层的相组成,XRD的靶材为Cu Kα,加速电压35 kV,电流40 mA,λ=0.154 nm,衍射角度2θ的范围20°~90°,扫描速度2 (°)/min。
表1 热镀锌合金镀层的镀液成分
Table 1 Composition of Zn-Al-Mg liquid

1.3 腐蚀试验
阻抗谱和动电位极化在3.5%NaCl(质量分数)溶液中进行,实验温度(25±1) ℃,暴露在大气的静态电解液中。试验前,先将工作电极固定在3.5%NaCl(质量分数)电解液中浸泡40 min,以获得稳定的开路电势。电化学试验在Gamry Reference 600恒电位仪上进行,参比电极为饱和甘汞电极,辅助电极为铂电极,测试试样面积为1 cm2,非工作面用环氧树脂封装,极化测试的扫描电位范围为-0.20~0.50 V,扫描速率为0.5 mV/s;EIS测量在开路电位下进行,测量频率范围为0.1~1×105 Hz,施加幅度为10 mV的正弦扰动。
切边腐蚀试验在循环盐雾实验箱中进行,将尺寸为200 mm×300 mm的试样在不封边的情况下直接放入Ascott CC 1000XP循环腐蚀实验箱,按照GB/T 24195-2009中的方法B进行加速腐蚀实验。试验条件如下:酸性盐雾1 h (35 ℃,pH值为2.5,盐浓度为6 g/L),干燥4 h ((60±1) ℃,20%~30%RH),湿热试验3 h ((80±1) ℃,95%RH),耐蚀性用循环腐蚀试验试样表面出现红锈面积达5%的时间评价,切边腐蚀性能用产生红锈距切边的距离衡量。
2 实验结果
2.1 镀层表面及断面形貌
图1所示为ZAM镀层、SD镀层和GL镀层表面SEM像。从图1中可以看出,ZAM镀层表面由不同相构成的复杂组织(见图1(a)),主要物相为富锌相以及锌和硬的金属间化合物Zn2Mg组成的二元共晶相,同时包含前两项以及富铝相的三元共晶相和富铝相的枝晶结构。SD镀层由典型的共晶相、块状相和针状相成(见图1(b)),共晶相是树枝状Zn-Al-Zn2Mg三元共晶体为主的结晶组织,由两相间隔组成,占据了镀层表面的大部分面积。镁在镀层表面呈均匀而微细的分布,镀层表面除此三元共晶体外还有大量Zn-Al二元共晶体存在。GL镀层组织主要由灰黑色和灰白色的两相组成(见图1(c)),灰黑色相为铝优先结晶形成的富铝相,其形貌为细小的树枝状组织,构成整个镀层的网络骨架;灰白色的相为分布在树枝状晶空隙内的伪共晶富锌相。

图1 镀液成分不同的镀层表面SEM像
Fig. 1 SEM images of surfaces of different coatings
图2所示为ZAM镀层、SD镀层和GL镀层断面SEM像。从图2中可以看出,ZAM镀层的断面存在两种明显的不同组织(见图2(a)),一种是粗大的灰色状组织,一种为细小密布的组织。其中粗大的块状相是Zn-HCP初生相,而细小的块状相是Al-FCC初生相,网状共晶相是Zn-Zn2Mg二元共晶体和Zn-Al-Zn2Mg三元共晶体。而SD镀层断面的细密组织分布更为广泛(见图2(b)),镀层断面主要由几种比较典型的相组成,粒状组织、针状组织和共晶组织。粒状组织和针状组织中Mg和Si的含量较高,镀层主要由细小的初晶Mg相和Zn2Mg相,Zn-Al-Zn2Mg三元共晶体及针状Zn-Al二元共晶体组成。共晶相主要分布在块状相的周围,由两相间隔组成,间距约1 μm,呈放射状向外扩散;块状相点缀于共晶相中,直径约为几个微米;针状相呈典型针状结构,割裂了正常树枝晶的生长,不均匀地分布于共晶相中,宽度约为1 μm,长度一般小于10 μm。Si元素的存在使合金镀层明显细化,镀层结构更加致密,而镀层断面则是由枝晶状组织和合金层组成,枝晶分布于镀层的整个截面上,合金层比较薄,约1 μm。GL镀层中的富铝树枝晶构成了镀层的主体(见图2(c)),其次为填充于树枝晶间隙的Al-Zn共析相,其形状大致为球团状。
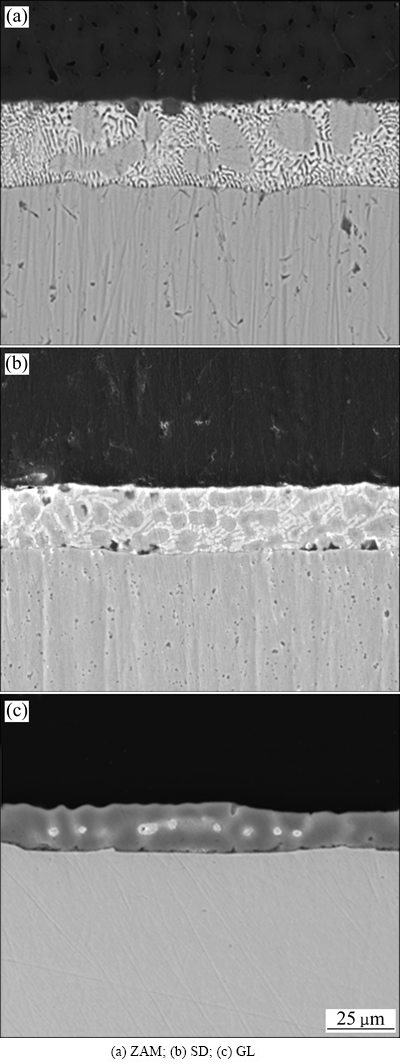
图2 镀液成分不同的镀层截面SEM像
Fig. 2 SEM images of cross-section of different coatings
2.2 镀层的电化学阻抗分析
ZAM镀层、SD镀层和GL镀层阻抗谱的Nyquist图如图3所示,从图3中可以看出,ZAM镀层和SD镀层的阻抗弧半径相近,比GL镀层的容抗弧半径大。由于阻抗图的容抗弧半径越大,其电化学反应阻力越大,腐蚀过程中电荷转移阻力大,耐蚀性就越好[12],说明镀层添加镁元素后可以有效提高镀层的耐蚀性能。GL镀层的Nyquist图有明显的一个高频容抗弧和中频容抗弧,从Bode图中可以明显看出两个的时间常数(见图3),而ZAM镀层和SD镀层的阻抗图谱只是有高频容抗弧组成,是单一的容抗弧,没有感抗弧的存在,说明添加Mg元素后,镀层在腐蚀发生反应的初期主要由电荷迁移控制反应,镀层在电解液中没有出现点蚀行为,也就没有蚀孔存在[13]。
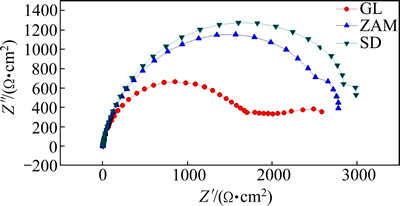
图3 镀液成分不同的镀层阻抗谱的Nyquist图
Fig. 3 Nyquist plots of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of different coatings
根据阻抗谱图的特点可以得出不同镀层钢板的腐蚀等效电路图如图4所示。从而可以利用数据分析软件ZSimpWin计算出不同镀层的阻抗。GL镀层采用的等效电路为Rs(Q1R1)(Q2R2)。其中,Rs表示NaCl溶液的溶液电阻;Q1表示镀层电容;Q2表示双电层电容;R1表示镀层电阻;R2表示基体腐蚀反应的极化电阻。
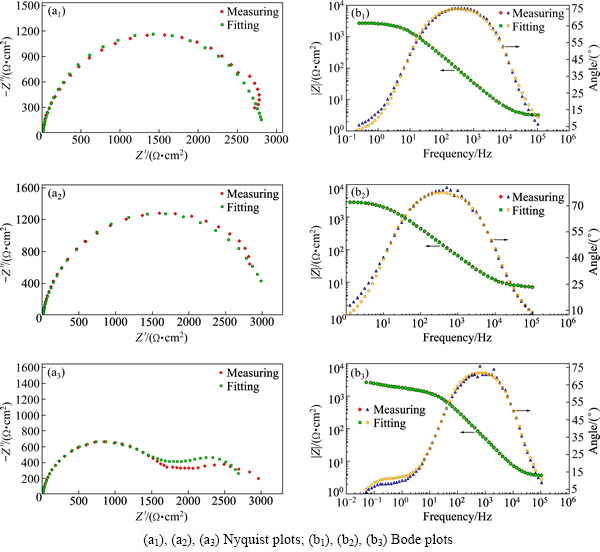
图4 拟合所得ZAM、SD和GL镀层的交流阻抗谱
Fig. 4 Fitting results of GL coatings through using ZSimpWin soft
ZAM和SD镀层采用等效电路为Rs(Q1R1),Q1表示金属合金镀层/溶液双电层电容;R1表示镀层电阻,拟合结果如图5所示。从等效电路模拟结果可知,GL镀层、ZAM镀层和SD镀层在3.5%NaCl(质量分数)溶液中的极化电阻分别为1274、2845和3144 Ω,ZAM和SD镀层的极化阻力均高于GL镀层的,说明镀层中添加镁、铝后,腐蚀过程中更容易在镀层表面形成稳定的腐蚀产物从而避免腐蚀的进一步发生,降低腐蚀电极的有效面积,提高镀层的耐腐蚀性能。
2.3 镀层的电化学极化曲线

图5 镀层钢板在3.5%NaCl溶液中腐蚀的等效电路图
Fig. 5 Equivalent circuit of different coatings in 3.5%NaCl solution
图6所示为成分不同的镀层在3.5%NaCl溶液中的极化曲线。由图6可以看出,GL镀层、ZAM镀层和SD镀层的腐蚀电位φcorr分别为-1.07、-1.03、-0.95 V,其腐蚀电流密度与腐蚀电位成反比。ZAM镀层和SD镀层的腐蚀电位与Zn的腐蚀电位比较接近,说明镀层中的铝、镁离子更倾向于形成化合物,难以在双电层中稳定存在。阳极极化曲线均存在钝化区,电流的增加受到阻碍,阳极过程受到阻滞。这是由于浓差极化和试样表面腐蚀产物的阻抗极化而造成的。随着极化的进行,阳极极化在-0.63 V左右时电流减小。因此,阳极极化在-0.63 V处,镀层已经基本完全溶解,电流减小,达到一种暂时的钝化状态。说明热镀锌铝镁镀层阳极极化曲线的活化钝化区不明显,整个阳极过程基本处于活化状态,电极反应受阴极氧化反应控制[14]。

图6 镀液中成分不同的镀层在3.5%NaCl溶液中的极化曲线
Fig. 6 Potentiodynamic polarization plots of different coatings in 3.5% NaCl solution
2.4 镀层表面腐蚀产物的相组成分析
为了确定ZAM镀层和SD镀层腐蚀前后镀层中相组成,分别对循环腐蚀前、循环腐蚀90次和循环腐蚀150次的镀层进行XRD实验,其结果如图7所示。
ZAM镀层和SD镀层未腐蚀时,镀层中的相组成为Al、Zn和Zn2Mg,其中SD镀层中Zn2Mg的峰值较高。结合Zn-Al-Mg三元合金相图可以确定,共晶相为Zn-Zn2Mg的二元共晶和Zn-Al-Zn2Mg的三元共晶,富铝相主要是以粒状、针状组织组成的树枝晶。腐蚀后ZAM镀层和SD镀层的XRD分析结果显示其腐蚀产物主要由氧化锌(ZnO)、碱性氧化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)和碱性碳酸锌铝(Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·
4H2O)等构成。Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O和Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O是不溶性的胶状腐蚀产物,它的存在可以有效隔断镀层与外界物质间电子的传输,提高热镀锌铝镁镀层的耐蚀性能[15]。
2.5 镀层的切边腐蚀性能
热镀锌合金钢板实际应用前一般须剪裁成形,这样就会使钢基体在切边部位出现裸露,从而在此处优先发生腐蚀。据已知研究结论[16-17],热镀锌铝镁镀层钢板表现出良好的切边耐腐蚀性能,然而切边腐蚀机理尚不明确。图8所示为GI镀层、GL镀层、ZAM镀层和SD镀层钢板循环腐蚀试验次数与红锈距切边距离之间的关系,这里用镀层表面产生红锈距切边的宽度来衡量镀层的切边保护性能。从图8中可以看出,随着循环腐蚀试验次数的增加,GI和GL镀层切边部位产生的红锈宽度逐渐增加,而ZAM和SD镀层随着循环腐蚀次数的增加,切边部位只出现白锈而未出现红锈。GI在循环次数为30次时,红锈产生的宽度已达到9 mm,随时间的延长,红锈的宽度越来越大,从边缘至整块镀层钢板逐渐腐蚀失效。为了深入研究SD镀层钢板切边的腐蚀行为,对循环腐蚀试验后GI镀层和SD镀层的切边腐蚀产物类型、形貌和稳定性进行分析比较。
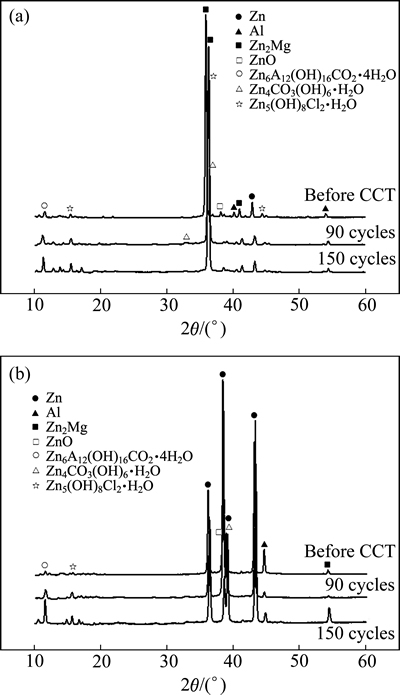
图7 ZAM镀层和SD镀层腐蚀产物的XRD谱
Fig. 7 XRD patterns of ZAM (a) and SD (b) coating
图9所示为循环腐蚀后GI镀层与SD镀层钢板切边部位的形貌。从图9中可以看出,当循环次数为4次时,GI镀层的切边部位腐蚀初期覆盖着白锈,并在切边部位出现了大量的点状红锈;而SD镀层的切边部位在腐蚀初期只出现少量白锈。随着循环腐蚀周期的延长,GI镀层切边部位出现大面积红锈,且向内部扩展;而SD镀层切边部位仅被白锈覆盖,完全没有红锈产生。
图10所示为循环腐蚀试验后GI镀层和SD镀层切边部位腐蚀产物的形貌。从图10中可以看出,GI镀层腐蚀产物呈粗大疏松的结构(见图10(a)),而SD镀层切边部位腐蚀产物外观呈细小致密的结构(见图10(b)),致密的腐蚀产物能够减缓腐蚀的进一步发生,这也是SD镀层具有良好切边耐蚀性能的原因。
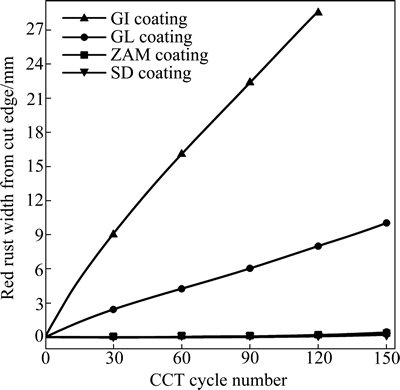
图8 镀层循环腐蚀试验次数与切边红锈宽度的关系
Fig. 8 Relationship between red rust from cut-edge of exposed sheet type specimens and CCT cycle number
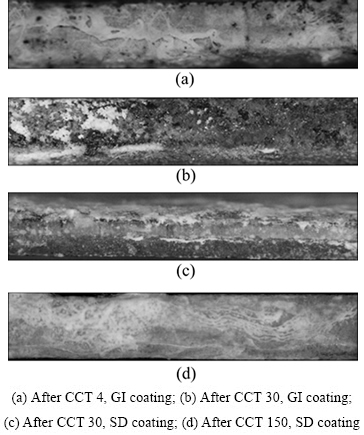
图9 GI镀层与SD镀层循环腐蚀试验后切边部位的腐蚀 形貌
Fig. 9 Corrosion morphologies of cut-edge areas after CCT test
图11所示为GI镀层与SD镀层切边部位腐蚀产物的XRD谱。从图11中可以看出,SD镀层的切边腐蚀产物由氧化锌(ZnO)、碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)、碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)和碱性碳酸锌铝(Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O)构成;而GI镀层的切边腐蚀产物由主要由氧化锌(ZnO)、碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)及少量的碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)构成,腐蚀产物中没有碱性碳酸锌铝(Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O)。SD镀层钢板中的碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)的峰值要比GI镀层中碱性氯化锌的峰值要高出许多,氧化锌(ZnO)的峰值则相对较低,说明SD镀层的切边腐蚀产物中存在较多的碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)。碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)和碱性碳酸锌铝(Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O)是不溶性的胶状腐蚀产物,可以有效隔断镀层与外界物质间电子的传输。因此,SD镀层中Mg、Al、Si等合金元素的存在有效地抑制了阴极反应,切边部位在长期腐蚀中发生较少的溶解,其原因是完整的端面在空间上抑制了产生阴极和阳极之间反应的条件,使得表面获得更低的电位从而对阳极的分层扩散驱动力变小,使得SD镀层表现出了良好的切边耐腐蚀性能。
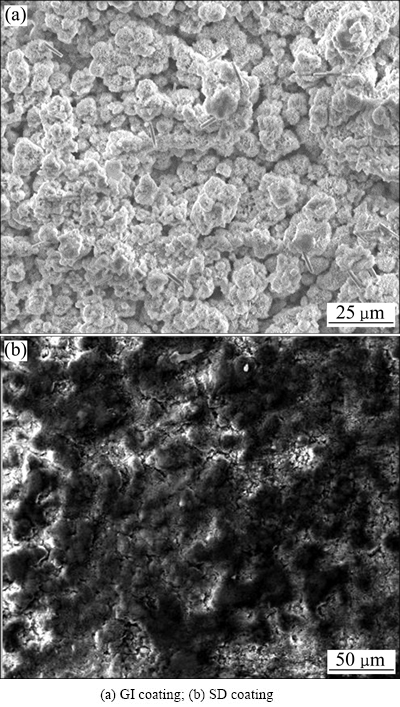
图10 循环腐蚀试验后GI镀层和SD镀层切边部位腐蚀产物形貌
Fig. 10 Corrosion product morphologies of cut-edge areas after CCT test
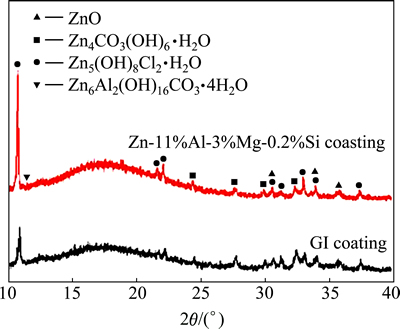
图11 GI镀层和SD镀层钢板切边腐蚀产物XRD谱
Fig. 11 XRD patterns of corrosion products on steel sheet part of cut-edge area after CCT test
为了比较GI镀层和SD镀层腐蚀产物的稳定性,在0.5%NaCl(质量分数)中性溶液中进行恒电势测试,试验在室温下进行。图12所示为两种镀层切边腐蚀后恒电势的测试结果。切边腐蚀后试验恒电势的测试数据显示,阳极电流密度在SD镀层钢板切边的一端低于GI镀层钢板。由此可知,SD镀层钢板的腐蚀产物比GI镀层钢板更稳定。
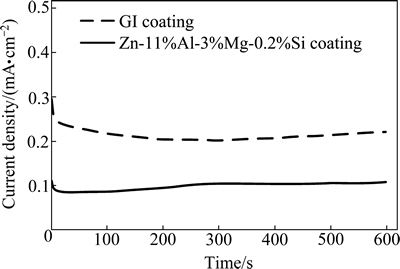
图12 GI镀层和SD镀层钢板切边腐蚀后的恒电势测试结果
Fig. 12 Potentiostatic test results of GI and SD coatings after CCT test
3 分析与讨论
3.1 SD镀层的切边保护性能
SD镀层在循环腐蚀过程中切边部位镀层与钢基体发生腐蚀反应的过程如图13所示。从图13(a)可以看出,在循环腐蚀试验初期,镀层中的Mg和Zn元素首先发生阳极反应变成离子状态,由于循环腐蚀溶液中水分子的加入,与Mg2+和Zn2+反应生成氢氧化镁(Mg(OH)2)和氢氧化锌(Zn(OH)2)的沉淀,反应的动力为镀层与钢基体之间的电位差。图13(b)所示为循环 腐蚀试验后期SD镀层发生的反应。随着腐蚀溶液中Cl-的加入,由于镀层中金属化合物间存在电位差,在阴极生成了碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)腐蚀产物。Mg2+首先溶解并沉积在切边部位,作为反应的阴极;Mg2+同时也溶解在距切边一定距离的地方作为反应的阳极,从而加强了切边腐蚀过程中阴极的保护作用。从SD镀层钢板切边腐蚀产物的成分分析来看(见图11),在切边处形成了一层致密保护的膜,其主要成分为碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)、碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)、碱性碳酸锌铝(Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O)及少量氢氧化锌(Zn(OH)2)和氢氧化镁(Mg(OH)2)等,这些化合物在一定时间内就会覆盖满切边部位(见图13(b))。循环腐蚀后形成于断面的保护膜由于具有较差的导电性能,可以对切边部位的腐蚀起到良好的抑制作用,此外,SD镀层内所含有的少量Si也能够促进切边部位保护膜的形成。
当镀层中加入镁元素后可以抑制镀层表面无保护作用的氧化锌(ZnO)形成,并且碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)和碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)填充于腐蚀裂缝中可以进一步阻止腐蚀的发生,从而提高SD镀层的耐蚀性能。另外,镀层中析出的镁与水反应形成氢氧化镁(Mg(OH)2)或羟基碳酸盐类物质,抑制阴极氧的还原反应。随后,Mg的反应物Mg(OH)2和Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O在阴极吸收空气中的二氧化碳(CO2)发生碳酸化反应后中性化,降低镀层表面的pH值,促进稳定的碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)腐蚀产物的形成,从而减缓了腐蚀的进程。且腐蚀产物中电导率较低的碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)覆盖在镀层表面,形成致密且有效的保护层,可以有效阻止Cl-的传递,从而提高SD镀层的耐蚀性能。
3.2 SD镀层的耐腐蚀机理
在循环盐雾试验中,由于Mg在NaCl溶液中呈离子状态,镀层中的Mg或Mg的化合物一部分形成为微小的阳极而有利于溶解反应。此外,Zn2Mg开路的电位(大约-1.5V (vs Ce))比GI镀层的(约1 V(vs Ce))更负,因此,腐蚀初期,Zn2Mg在共晶结构中优先溶解,最初溶解的Zn2Mg是SD镀层含镁元素腐蚀产物的来源。因此,腐蚀初期,一部分Mg从镀层表面溶解下来并进入Zn的腐蚀产物(碱性氯化锌)中。
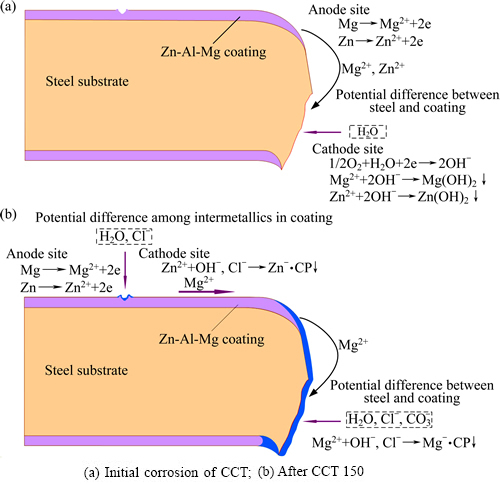
图13 SD镀层切边腐蚀过程中电子转移示意图
Fig. 13 Schematic illustration of electron transfer in SD coating during cut-edge corrosion process
从图13中GI镀层和SD镀层钢板切边部位腐蚀产物的XRD结果可以看出,循环腐蚀环境下镀层的腐蚀产物中均存在碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)。其中,GI镀层中氧化锌(ZnO)的峰值较高,说明碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)在没有Mg2+参与的情况下很容易脱水而形成氧化锌(ZnO),从而失去保护作用,导致GI镀层的耐蚀性能大大降低。而SD镀层中由于Al3+和Mg2+的存在能使碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)变得较稳定,不易形成疏松的氧化锌(ZnO),并形成碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)和碱性碳酸锌铝(Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O),说明SD镀层表面形成的腐蚀产物较稳定。
结合图11和12可以得出,腐蚀电流与腐蚀产物的形成和生长有密切联系。当腐蚀产物主要由碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)组成时,腐蚀电流密度较小;当腐蚀产物有氧化锌(ZnO)和碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)形成时,腐蚀电流密度就显著增大。据此可以推测,在此种腐蚀环境下,碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)具有较好的保护作用,说明它对溶解氧的还原反应具有较好的抑制作用。
另外,由GI镀层循环腐蚀后镀层断面的SEM像可以看出(见图10),循环腐蚀后镀层表面生成的氧化锌(ZnO)和碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)呈疏松的碎片状或粉末状,并易于脱落。因此,可认为此种腐蚀产物的保护作用很小,几乎不能抑制溶解氧向腐蚀反应界面扩散。
因此,循环腐蚀试验过程中SD镀层钢板的腐蚀与保护的模型可以用图14所示示意图表示。从图14中可以看出,循环腐蚀试验的开始阶段,整个镀层表面均匀地形成了含Mg的碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)。由于SD镀层表面几乎全是Zn-Al-Zn2Mg三元共晶组织,因此,含Mg的碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)对镀层具有良好的保护性,且很稳定,从而抑制了非保护性的氧化锌(ZnO)和碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)的形成。另外,镀层中残余的Al可形成十分稳定的含Mg和ZnAl的腐蚀产物—碱性碳酸锌铝(Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O),它能长期保护残余镀层和钢基体免于腐蚀。这说明SD镀层中的Mg能使Zn的腐蚀产物长期稳定存在,并可抑制阴极反应,因而,SD镀层具有良好的耐蚀性能。

图14 SD镀层钢板的腐蚀过程示意图
Fig. 14 Schematic illustration of corrosion process of SD coating steel sheet
4 结论
1) 热镀锌铝镁镀层中含有纯Zn相、Zn-Zn2Mg的二元共晶相和Zn-Al-Zn2Mg三元共晶相,主要由枝晶状组织和合金层组成,枝晶状分布于镀层的整个截面上,合金层较薄,镀层的耐腐蚀性与镀层的显微组织结构具有重要的关系。
2) 热镀锌铝镁镀层中由于Al、Mg元素及Zn2Mg的存在,镀层表面纯锌相面积减小,腐蚀时镀层中的Al、Mg及Zn2Mg相更容易形成稳定的化合物,只有纯锌相发生腐蚀,镀层腐蚀的有效面积减小、从而使得电化学试验时镀层的腐蚀电流密度降低。
3) 循环腐蚀试验发现:ZAM镀层中共晶相的存在使得Mg在镀层中分布较均匀,腐蚀初期,镀层表面形成了大量的碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)等腐蚀产物,抑制腐蚀的发生,提高其镀层的耐蚀性。而在SD镀层中,Mg和Si的同时作用使碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)等腐蚀产物保持稳定,延长了镀层的耐蚀性能。
4) ZAM镀层和SD镀层的腐蚀产物主要由氧化锌(ZnO)、碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)和碱性碳酸锌铝(Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O)等构成。其中碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)和碱性碳酸锌铝(Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·
4H2O)是不溶性的胶状腐蚀产物,它的存在可以有效隔断镀层与外界物质间电子的传输,提高镀层的耐蚀性能。
5) SD镀层中的Mg、Al、Si等合金元素可以有效地抑制阴极反应。腐蚀初期,Zn2Mg在共晶结构中优先溶解,最初溶解的Zn2Mg为腐蚀产物提供了足够的镁元素,部分Mg从镀层表面溶解下来并进入Zn的腐蚀产物中,形成碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)和碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)。而Al3+和Mg2+的存在可以降低镀层中碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)脱水形成无保护作用氧化锌(ZnO)的趋势,增加镀层中碱 性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)和碱性碳酸锌铝(Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O)等腐蚀产物的量。且碱性氯化锌(Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O)和碱式碳酸锌(Zn4CO3(OH)6·H2O)填充于腐蚀裂缝中可以进一步阻止腐蚀的发生,使得镀层表面获得更低的电位从而对阳极的分层扩散驱动力变小,降低切边部位在长期腐蚀中的溶解情况,提高镀层的耐蚀性能和切边保护性能。
REFERENCES
[1] 林 源, 袁训华, 岳崇锋, 江社明, 黎振华, 张启富. 热镀锌铝镁镀层的组织和耐蚀性能[J]. 金属热处理, 2014, 39(4): 31-36.
LIN Yuan, YUAN Xun-hua, YUE Chong-feng, JIANG She-ming, LI Zhen-hua, ZHANG Qi-fu. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of hot dip Zn-Al-Mg coating[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2014, 39(4): 31-36.
[2] KAZUHIKO H, KHSAKU U, WATARU Y. Influence of Si addition to the coating bath on the growth of the Al-Fe alloy layer in hot-dip Zn-Al-Mg alloy-coated steel sheets[J]. ISIJ International, 2011, 51(11): 1895-1902.
[3] 孔 纲, 王丽平, 车淳山. 热浸镀Zn-Al-Mg合金镀层的研究与应用[J]. 材料保护, 2014, 47(4): 45-47.
KONG Gang, WANG Li-ping, CHE Chun-shan. Current research status and application prospect of hot-dipped Zn-Al-Mg alloy coating[J]. Journal of Materials Protection, 2014, 47(4): 45-47.
[4] ELVINS J, SPITTLE J A, SULLIVAN J, WORSLEY D A. The effect of magnesium additions on the microstructure and cut edge corrosion resistance of zinc aluminum alloy galvanized steel[J]. Corrosion Science, 2008, 50(6): 1650-1658.
[5] HISESHI F, RIE K, HIROSHI I. Hot-dip Zn-5%Al alloy-coated steel sheets[J]. JFE Technical Report, 2009, 14(12): 41-45.
[6] TSUJIMURA T, KOMASTUA A, ANDOH A. Influence of Mg content in coating layer and coating structure on corrosion resistance of hot-dip Zn-Al-Mg alloy coated steel sheet[C]// Galvatech’01, 5th International Conference on Zinc and Zinc Alloy Coated Steel Sheet. Brussels, Belgium: Stahl und Eisen, 2001: 145-152.
[7] KIMATA Y, TAKAHASHI A, ASAI K. Corrosion resistance of Zn-11%Al-3%Mg-0.2%Si coated steel sheet after sheltered outdoor exposure test in Miyakojima[C]// Galvatech’07, 7th International Conference on Zinc and Zinc Alloy Coated Steel Sheet. Osaka, Japan: The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, 2007: 586-591.
[8] SOHN H K, LEE J W, YOO Y, MIN J, OH M S, KIM S H, JIN Y S, KIM K Y. Corrosion behaviors of Zn-MgZn2 eutectic structure in Zn-Al-Mg coatings[C]// Galvatech’11, 8th International Conference on Zinc and Zinc Alloy Coated Steel Sheet. Genoa, Italy: Associazione Italiana di Metallurgia, 2011: 144-148.
[9] ISHIKAWA T, UED M, KANDORI K, NAKAYAMA T. Air permeability of the artificially synthesized Zn-Al-Mg-alloy rusts[J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(6): 2547-2556.
[10] 李 锋, 吕家舜, 杨洪刚, 康永林. 热浸镀Zn11Al3Mg0.2Si合金镀层微观组织实验研究[J]. 表面技术, 2011, 40(3): 32-35.
LI Feng,  Jia-shun, YANG Hong-gang, KANG Yong-lin. The experiment research of microstructure of hot-dip galvanized Zn11Al3Mg0.2Si alloy coating[J]. Surface Technology, 2011, 40(3): 32-35.
Jia-shun, YANG Hong-gang, KANG Yong-lin. The experiment research of microstructure of hot-dip galvanized Zn11Al3Mg0.2Si alloy coating[J]. Surface Technology, 2011, 40(3): 32-35.
[11] 李 锋, 吕家舜, 杨洪刚, 徐小连, 钟 彬, 艾芳芳. 锌铝镁镀层在NaCl体系中的腐蚀行为[J]. 中国表面工程, 2011, 24(4): 25-29.
LI Feng,  Jia-shun, YANG Hong-gang, XU Xiao-lian, ZHONG Bin, AI Fang-fang. The corrosion behavior for Zn-Al-Mg coating in NaCl system[J]. China Surface Engineering, 2011, 24(4): 25-29.
Jia-shun, YANG Hong-gang, XU Xiao-lian, ZHONG Bin, AI Fang-fang. The corrosion behavior for Zn-Al-Mg coating in NaCl system[J]. China Surface Engineering, 2011, 24(4): 25-29.
[12] 曹楚南, 张鉴清. 电化学阻抗谱导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 268-282.
CAO Chu-nan, ZHANG Jian-qing. An introduction to electrochemical impedance spectroscopy[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002: 268-282.
[13] 曹楚南. 腐蚀电化学原理[M]. 3版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008: 278-287.
CAO Chu-nan. Theory of corrosion electrochemistry[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008: 278-287.
[14] DUTTA M, HALDER A K, SINGH S B. Morphology and properties of hot dip Zn-Mg and Zn-Al-Mg alloy coatings on steel sheet[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2010, 10(25): 2578-2584.
[15] VOLOVITCH P, ALLELY C, OGLE K. Understanding corrosion via corrosion product characterization: I. Case study of the role of Mg alloying in Zn-Mg coating on steel[J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51(6): 1251-1262.
[16] UEDA K. Corrosion resistance of Zn-11%Al-3%Mg-0.2Si Alloy coated steel sheet in the marine atmospheric after long term outdoor exposure[C]// Galvatech’13, 9th International Conference on Zinc and Zinc Alloy Coated Steel Sheet. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013: 659-662.
[17] 张启富, 刘邦津, 黄建中. 现代钢带连续热镀锌[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2007: 627-636.
ZHANG Qi-fu, LIU Bang-jin, HUANG Jian-zhong. Modern continuous hot dip galvanizing of steel strip[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2007: 627-636.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51071052);国家“十二五”科技支撑计划资助项目(2012BAJ13B03)
收稿日期:2015-01-21;修订日期:2015-05-23
通信作者:袁训华, 高级工程师,博士;电话:010-62182574;E-mail: xhyuan092@sina.com