SO2和H2O在Cu (100)表面共吸附行为的密度泛函计算
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第12期
论文作者:魏薪 董超芳 陈章华 黄建业 肖葵 李晓刚
文章页码:4102 - 4109
关键词:SO2;H2O;Cu;密度泛函;共吸附;平板模型;吸附能;电荷转移
Key words:SO2; H2O; Cu; density functional theory; co-adsorption; slab model; adsorption energy; charge transfer
摘 要:利用基于密度泛函GGA-rPBE方法的平板模型研究SO2和H2O在面心立方金属Cu (100)表面的共吸附行为。SO2和H2O在Cu (100)表面单分子吸附的计算结果表明,在覆盖度为0.25分子层和0.5分子层的情况,二者均不能以化学键的形式吸附在Cu (100)表面上。针对SO2和H2O在Cu (100)表面的共吸附行为,计算弛豫后的吸附结构、吸附能和电子性质(包括差分电荷密度、价电荷密度、Bader电荷分析和分态密度分析)。结果表明,覆盖度为0.25分子层时,H2O和SO2以化学吸附的形式各自吸附在表面不同Cu原子上;覆盖度为0.5分子层时,H2O分子解离成OH和H,OH吸附在表面Cu原子上,而H与SO2键合后共同远离表面。
Abstract: The co-adsorption behaviors of SO2 and H2O on face-centered cubic Cu (100) ideal surface were studied using the GGA-rPBE method of density functional theory (DFT) with slab models. The optimized structures of single H2O and SO2 on Cu (100) surface were calculated at the coverage of 0.25 ML (molecular layer) and 0.5 ML. The results show that there was no obvious chemical adsorption of them on Cu (100) surface. The adsorbed structures, adsorption energy and electronic properties including difference charge density, valence charge density, Bader charge analysis and partial density of states (PDOS) of co-adsorbed structures of H2O and SO2 were investigated to illustrate the interaction between adsorbates and surface. H2O and SO2 can adsorb on surface of Cu atoms chemically via molecule form at the coverage of 0.25 ML, while H2O dissociated into OH adsorbed on surface and H bonded with SO2 which keeps away from surface at the coverage of 0.5 ML.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 4102-4109
Xin WEI1, Chao-fang DONG1, Zhang-hua CHEN2, Jian-ye HUANG1, Kui XIAO1, Xiao-gang LI1
1. Corrosion and Protection Centre, Institute of Advanced Materials and Technology, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China;
2. School of Mathematics and Physics, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China
Received 3 December 2014; accepted 7 May 2015
Abstract: The co-adsorption behaviors of SO2 and H2O on face-centered cubic Cu (100) ideal surface were studied using the GGA-rPBE method of density functional theory (DFT) with slab models. The optimized structures of single H2O and SO2 on Cu (100) surface were calculated at the coverage of 0.25 ML (molecular layer) and 0.5 ML. The results show that there was no obvious chemical adsorption of them on Cu (100) surface. The adsorbed structures, adsorption energy and electronic properties including difference charge density, valence charge density, Bader charge analysis and partial density of states (PDOS) of co-adsorbed structures of H2O and SO2 were investigated to illustrate the interaction between adsorbates and surface. H2O and SO2 can adsorb on surface of Cu atoms chemically via molecule form at the coverage of 0.25 ML, while H2O dissociated into OH adsorbed on surface and H bonded with SO2 which keeps away from surface at the coverage of 0.5 ML.
Key words: SO2; H2O; Cu; density functional theory; co-adsorption; slab model; adsorption energy; charge transfer
1 Introduction
As a wildly used metal, copper corrodes at negligible rates in unpolluted air, water, and deaerated, nonoxidizing acids. But it appears to show remarkable activity for the sulfur dioxide (SO2) in atmospheric pollutant [1-3]. From the previous studies, atmospheric corrosion of copper and its alloys is so complex for the process occurring in solid/liquid/gaseous phase and their interfaces [4,5]. Overriding pollution or deposition of aerosol particles, the moisture is the role factor affecting atmospheric corrosion. The importance of atmospheric droplets formation uptake to copper surfaces at the initial stage of atmospheric corrosion is widely recognized [6].
As mentioned by LEYGRAF and GRAEDEL [7], the time scale of surface film formation is about 1 μs, which means that it happens too fast to be observed or detected by experiments. Some researchers have studied the corrosion behaviors at the atomic scale [8-13]. There are also recent reports on the adsorption and transformation of SO2 [14-19]. However, usually, it is desirable to build structures that do not rely on the real co-adsorption state. The co-adsorption is not equal to the sum of each molecule adsorption, however, monomolecular adsorption can provide a theoretical basis for it. There are various calculations of adsorption geometries of SO2 on the metal and metallicoxide surface with DFT study [14,15,18,19]. Present structural measurements of SO2 adsorption on copper surface show one consistent result: on copper surface, the molecular plane of SO2 lies perpendicularly to the surface through two O atoms or through one O and one S atom [18,19]. Is there chemical adsorption on the copper surface with SO2? The calculation results of SO2 adsorption on Cu (111) are different when various exchange-correlation functions are used [20-23]. The calculation results whose exchange-correlation functions are GGA-PBE, GGA-PW91 and LDA yield reasonable adsorption energy and bond lengths are consistent with the experiment results. Moreover, the calculated geometries with the molecular plane parallel to the surface give the lowest energy instead of that with the molecular plane perpendicular to the surface from the previous experimental measurements at 0.25 ML coverage. Similar calculation of CASTEP DFT was conducted on Cu (100) surface to investigate the geometry of the adsorption of SO2 at different coverages. Large coverage may not lead to the perpendicular adsorption. The bonding mechanism of SO2 on copper involves electron transfer from Cu to SO2.
The adsorption of H2O molecular on copper surface has been investigated with VASP code [24]. The adsorption geometry of single H2O molecule trends to weakly bind to a top position with the molecular plane basically parallel to the Cu surface. Many experimental techniques have been used to regard the adsorption on Cu surfaces [25-34], including infrared reflection adsorption spectroscopy [26], scanning tunneling micro- scope [27] and electron energy loss spectroscopy [31,32]. However, most of the theoretical studies mainly aimed at monomer H2O adsorption [33-35] on Cu surface, and there are still some debates between theoretical studies and experimental techniques. The most stable geometry of H2O adsorption is dimer structure which comprises two water molecules at atop position with tiled H-parallel configuration (one titled up and the other titled down), which is in excellent agreement with the experimental techniques.
There are few existing researches on the adsorption of SO2 in the presence of H2O at the atomic scale. The exact mechanism for this process of initial surface film formation is still obscure and leads to numerous debates. The purpose of this work is to report a DFT study of the co-adsorption of SO2 and H2O on Cu (100) surface. In this work, the structural evolutions and adsorption energy and electronic properties after the full optimization were analyzed, which may show a depiction of surface co-adsorption groups on copper surface.
2 Computational details
The first-principles calculations based on the DFT were performed with the GGA-rPBE exchange- correlation function in the MedeA-VASP 5.3 [36]. The electronic iterations convergence is 1.00×10-5 eV using the normal algorithm and reciprocal space projection operators. The calculations were conducted on 4-layer- slabs of the Cu (100) surface with a 15  vacuum gap. A (2×1) mesh and a (2×2) mesh were used for the adsorption calculation, corresponding to a high adsorbate coverages of 0.5 ML and 0.25 ML. The adsorbates and the two free moving uppermost surface layers were allowed and the two bottom layers were fixed. The slab models were calculated with the (6×6×1) and (6×12×1) Monkorst-Pack grid [37] for a coverage of 0.25 ML and 0.5 ML, respectively. All calculations were performed with a cut off energy of 400 eV.
vacuum gap. A (2×1) mesh and a (2×2) mesh were used for the adsorption calculation, corresponding to a high adsorbate coverages of 0.5 ML and 0.25 ML. The adsorbates and the two free moving uppermost surface layers were allowed and the two bottom layers were fixed. The slab models were calculated with the (6×6×1) and (6×12×1) Monkorst-Pack grid [37] for a coverage of 0.25 ML and 0.5 ML, respectively. All calculations were performed with a cut off energy of 400 eV.
The definition of adsorption energy is as follows:
Ead=Eads+Esub-Eads/sub (1)
where Eads, Esub and Eads/sub are the total energies of isolated adsorbates, the relaxed clean slab and the slab covered with adsorbates, respectively. According to this definition, the higher the adsorption energy is, the stronger the interaction between adsorbates and the substrate is. The property of PDOS was calculated to investigate the interaction among different atoms. From PDOS diagram, the peak shifting indicates that the electronic number of the atom within a certain energy interval has changed. The interaction between different atoms may relate with overlapping of peaks. The difference in the charge density can be defined as
△ρ=ρads/slab-ρslab-ρads (2)
where ρads/slab stands for the charge density of the adsorbed system, ρslab stands for the charge density of the clean surface, and ρads stands for the charge density of adsorbed molecules.
The difference in charge density and Bader charge analysis can characterize the charge transfer among atoms. The charges trend to move towards the middle of two bonding atoms, which can be shown in the figure of valence charge density.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Single H2O adsorption on Cu (100) surface
Table 1 lists the optimized structures of single H2O molecule adsorption on Cu (100) surface at the coverages of 0.25 ML and 0.5 ML, and the related geometric parameters and adsorption energies are listed in Table 2. With respect to the coverage of 0.25 ML, a series of previous calculation results proved that the most stable configuration is similar with our result shown in Table 1 with the parallel molecular plane of H2O tilt to the surface at top site of surface. The distance of Cu—O is 2.732  , which is longer than that of common copper oxide (1.840-2.429
, which is longer than that of common copper oxide (1.840-2.429  ), according to ICSD database and Pearson’s database of MedeA. The H—O bond length and the H—O—H angle are basically in accordance with the experimental values [38] of 0.96
), according to ICSD database and Pearson’s database of MedeA. The H—O bond length and the H—O—H angle are basically in accordance with the experimental values [38] of 0.96  and 104.5°, respectively. The most stable configuration whose coverage is 0.5 ML is not similar to that at the coverage of 0.25 ML, which is possibly due to the intermolecular repulsion of H2O. The distance of Cu—O is 3.301
and 104.5°, respectively. The most stable configuration whose coverage is 0.5 ML is not similar to that at the coverage of 0.25 ML, which is possibly due to the intermolecular repulsion of H2O. The distance of Cu—O is 3.301  and those of two H—O bonds are 0.974
and those of two H—O bonds are 0.974  and 0.994
and 0.994  . As the copper surface mainly interacts with O atoms in H2O molecule, our approach employs the distance of Cu—O in the optimized structure (Table 2) to express the strength of interaction between adsorbate and surface. According to our calculation, H2O prefers to adsorb on Cu (100) surface at the coverage of 0.25 ML more than 0.5 ML. However, in all cases, H2O binding to Cu (100) surface is very weak.
. As the copper surface mainly interacts with O atoms in H2O molecule, our approach employs the distance of Cu—O in the optimized structure (Table 2) to express the strength of interaction between adsorbate and surface. According to our calculation, H2O prefers to adsorb on Cu (100) surface at the coverage of 0.25 ML more than 0.5 ML. However, in all cases, H2O binding to Cu (100) surface is very weak.
Table 1 Adsorbed structures of single H2O and SO2 molecule adsorption on Cu (100) surface
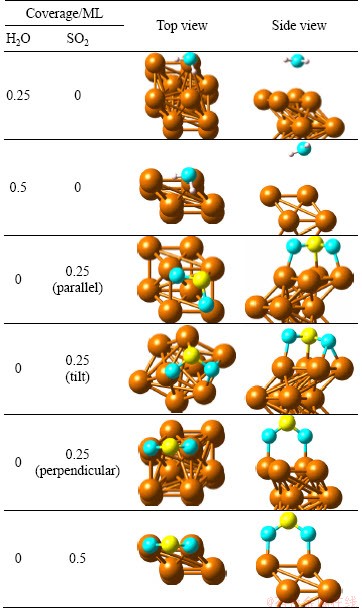
Table 2 Geometrical parameters and adsorption energies of single H2O and SO2 adsorption on optimized Cu (100) surface at coverages of 0.25 ML and 0.5 ML
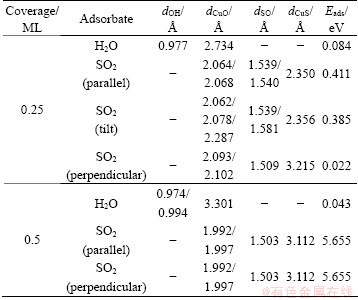
The adsorption energies of H2O on Cu (100) surface are 0.084 eV and 0.043 eV at the coverages of 0.25 ML and 0.5 ML, respectively. The calculated adsorption energy is not consistent with the experimental value [39], which indicates that the experimental adsorption energy is unlikely derived from the single adsorbed water on the ideal flat surfaces.
3.2 Single SO2 adsorption on Cu (100) surface
The stable adsorption structures of SO2 is with the molecular plane parallel to the Cu (111) surface at the coverage of 0.25 ML, which disagrees with the experimental results [40]. In our calculation, the initial structures with SO2 molecular plane parallel, tilt and perpendicular to Cu (100) surface are calculated at the coverages of 0.25 ML and 0.5 ML. The optimized adsorption structures are also listed in Table 1. The geometric parameters and adsorption energies are also listed in Table 2. The SO2 molecular plane of optimized structure is parallel to Cu (100) surface when the initial molecular plane of SO2 is parallel or tilt to the surface at the coverage of 0.25 ML. The Cu atoms interact with S and O atoms. The SO2 molecular plane keeps perpendicular to the Cu (100) surface when the initial SO2 molecular plane is perpendicular to the surface at the coverage of 0.25 ML. The Cu atoms only interact with O atoms. The reason for the above condition is that the energy difference (about 0.4 eV) between the two stable structures is very small. For the coverage of 0.5 ML, in all cases, the SO2 molecular plane of optimized structure keeps perpendicular to the surface and the Cu atoms of the surface interact with O atoms. The molecule plane of SO2 trends to keep perpendicular to the copper surface with the increasing coverage. The distance of Cu—O is shorter at the coverage of 0.5 ML than that at 0.25 ML, which indicates stronger interaction among each other. However, there is still no interaction between Cu atoms and S atoms at the coverage of 0.5 ML. The distance of S—O is longer than 1.43  which is in the SO2 gas for all cases. The adsorption of SO2 leads to a rise in the distance of S—O at the coverage of 0.25 ML corresponding to the coverage of 0.5 ML. The loose strength of S—O chemical bond is attributed to electron transfer from copper surface to the SO2 molecule.
which is in the SO2 gas for all cases. The adsorption of SO2 leads to a rise in the distance of S—O at the coverage of 0.25 ML corresponding to the coverage of 0.5 ML. The loose strength of S—O chemical bond is attributed to electron transfer from copper surface to the SO2 molecule.
The adsorption energy of SO2 is much higher at the coverage of 0.5 ML than that at 0.25 ML, which indicates the shorter distance of Cu—O. In terms of the adsorption energy, we may infer that it is mainly contributed by the interaction of Cu—O instead of Cu—S.
3.3 Co-adsorption of SO2 and H2O on Cu (100) surface
3.3.1 Adsorption structures
The co-adsorption behavior of SO2 and H2O was investigated with the structure of initial SO2 molecular plane perpendicular to the surface. Corresponding to the fixed SO2 configuration of initial co-adsorption structure, the optimized H2O is merged into the slab. The structures of Figs. 1 and 2 present the optimized co-adsorption structures at the coverages of 0.25 ML and 0.5 ML, respectively. For all structures, the lateral movements of the relaxed atoms are negligible and the major variation of the atomic position occurs in the z direction. The H2O molecular plane is perpendicular to the SO2 molecular plane with same height relative to the surface. The geometry parameters and adsorption energies of optimized structure are summarized in Table 3.
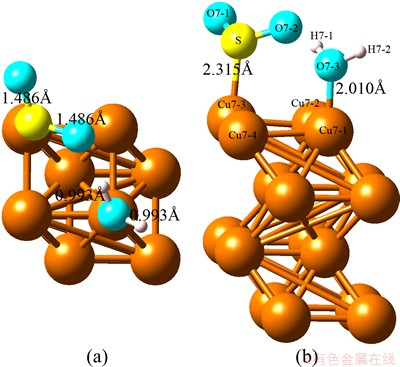
Fig. 1 Optimized top view (a) and side view (b) configurations of co-adsorption of SO2 and H2O on Cu (100) surface at coverage of 0.25 ML
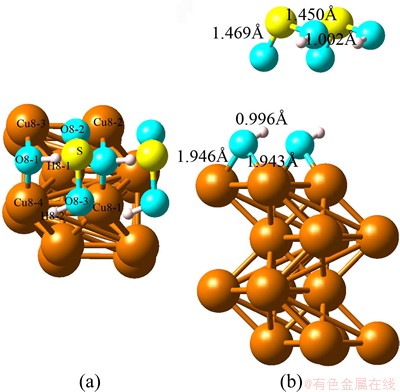
Fig. 2 Optimized top view (a) and side view (b) configurations of co-adsorption of SO2 and H2O on Cu(100) at coverage of 0.5 ML (super cell: 2×1×1)
With regard to the optimized structure shown as Fig. 1, the H2O molecule and SO2 molecule are adsorbed on different Cu atoms with O and S atoms, respectively. The distances of Cu—O and Cu—S are 2.010  and 2.385
and 2.385  , respectively. The shorter distance of Cu—O of the single H2O adsorption geometry illustrates that the existence of SO2 enhances the adsorption of H2O. Meanwhile, the existence of H2O affects the adsorption form of SO2. The elongated O—H distance and shortened S—O distance of the single adsorption illustrate the redistribution of electrons.
, respectively. The shorter distance of Cu—O of the single H2O adsorption geometry illustrates that the existence of SO2 enhances the adsorption of H2O. Meanwhile, the existence of H2O affects the adsorption form of SO2. The elongated O—H distance and shortened S—O distance of the single adsorption illustrate the redistribution of electrons.
Table 3 Geometric parameters and adsorption energies of H2O and SO2 co-adsorption on optimized Cu (100) surface at coverages of 0.25 ML and 0.5 ML

For the optimized structure shown in Fig. 2, one H atom of H—O—H breaks and bonds with SO2 molecule which keeps away from Cu (100) surface. The adsobates are divided into a first layer containing O—H and a second layer containing O—S—O—H after calculation. The splitting results from displacements in the opposite directions, SO2 is moving up while H2O is moving down with respect to the position of the initial mixed layer. Moreover, our calculation results indicate the smallest distance between Cu atom and O atom can be obtained at the level of 1.943  which is much smaller than that of single adsorption.
which is much smaller than that of single adsorption.
Summarily, all the results of adsorbed structure and the configuration of optimized structure are closely related to the coverages of SO2 and H2O. For all structures in this work, the distance of Cu—O illustrates the strength of interaction between adsorbates and surface. According to the distance of Cu—O of single adsorption, it may be inferred that the interaction between SO2 and surface is stronger than that of H2O and surface. Considering the co-adsorption optimized structure, the distance of Cu—O is a little smaller than that of single SO2 adsorption and much smaller than that of single H2O adsorption.
3.3.2 Adsorption energy
The co-adsorption energy of H2O and SO2 (Table 3) is dramatically larger than the sum of the monomolecular adsorption of H2O and SO2. It may be inferred that the considerably large co-adsorption energy is caused by the reaction of adsorbates on Cu surface. The co-adsorption energy consists of the energy released in the reaction energy of SO2 and H2O and the adsorption energy of their reaction product on the Cu surface.
3.3.3 Electronic properties
To illustrate the electronic interactions between adsorbates and Cu (100) surface, we calculated the partial density of states of Cu and O atoms of co-adsorption configuration at the coverages of 0.25 ML and 0.5 ML, and the results are given in Figs. 3 and 4. As shown in Figs. 3(a)-(d) and Figs. 4(a) and (b), the peaks of interacted Cu-3d, O-2p and S-3p shift uptowards in comparison with those of bare Cu atoms, O atoms of H2O and S atoms of SO2. This means that the adsorption occurs to adsorbed molecule on Cu (100) surface, which is the same as the geometrical structure. The electronic peaks of Cu-3d, O-2p and S-3p shift uptowards, which implies that the energy increase is due to the interactions between adsorbates and Cu (100) surface. The resonance of the PDOS peaks of O-2p and Cu-3d shown in Figs. 3(e) and (f) and Fig. 4(c) occurs in the entire energy range, indicating that an interaction happens between Cu atom of the surface and O atom.
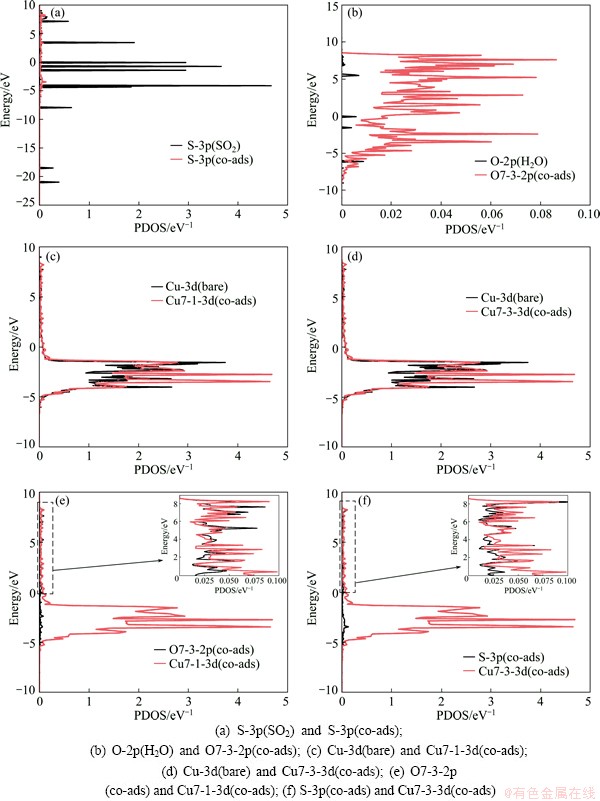
Fig. 3 Partial density of states for co-adsorption of SO2 and H2O at coverage of 0.25 ML
To show clearly the electronic interactions between adsorbates and Cu (100) surface, we give the difference charge density with co-adsorption at the coverages of 0.25 ML and 0.5 ML. The figures of difference charge density show that the Cu atoms of the surface lose electrons and adsorbed molecules gain electrons (Fig. 5). The Bader charge analysis results (Tables 4 and 5) show that Cu atoms, H atom and S atom lose electrons and O atoms get electrons. In order to investigate the bonding of atoms, the valence charge density of co-adsorption at the coverages of 0.25 ML and 0.5 ML is also calculated and shown in Fig. 6. Obviously, the bonding between Cu atom and O may be found at the coverage of 0.5 ML, which indicates a chemical bonding between them. For the coverage of 0.25 ML, the interaction between Cu atoms and O atom or S atom is weaker than that at 0.5 ML.
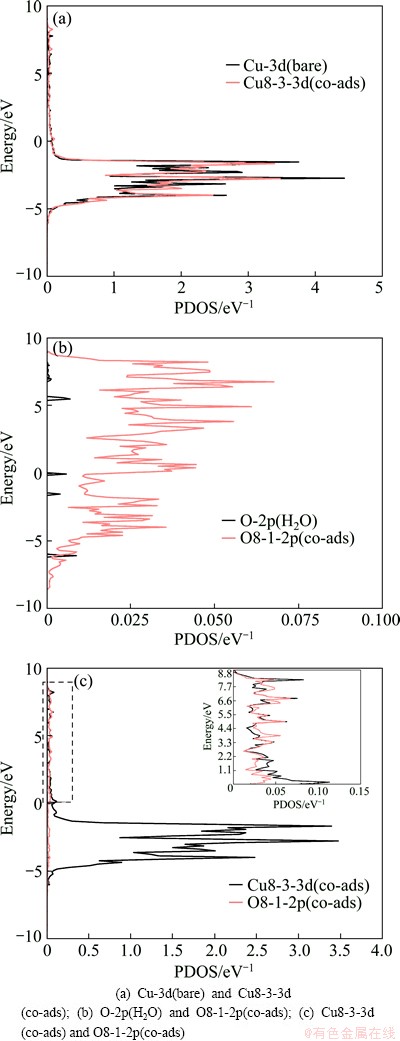
Fig. 4 Partial density of states for co-adsorption of SO2 and H2O at coverage of 0.5 ML
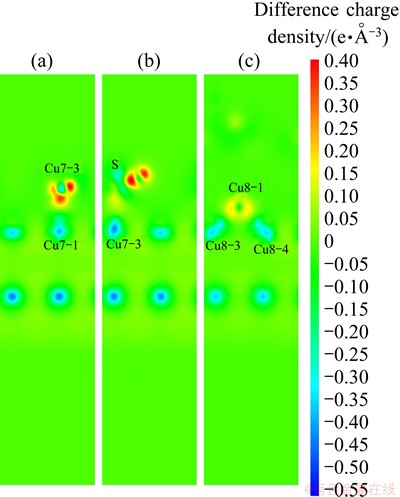
Fig. 5 Difference charge density of Cu atom and O atom (a) and Cu atom and S atom (b) with adsorbates at coverage of 0.25 ML, Cu atom and O atom (c) with adsorbates at coverage of 0.5 ML in co-adsorbed geometry
Table 4 Bader valence electron charges, charge transfer (relative to atoms) of co-adsorption of SO2 and H2O on Cu (100) surface at coverage of 0.25 ML
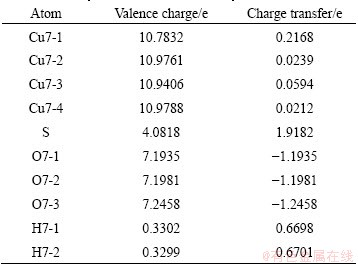
Table 5 Bader valence electron charges, charge transfer (relative to atoms) of co-adsorption of SO2 and H2O on Cu (100) surface at coverage of 0.5 ML

Fig. 6 Valence charge densities of Cu atom and O atom (a) and Cu atom and S atom (b) with adsorbates at coverage of 0.25 ML, Cu atom and O atom (c) with adsorbates at coverage of 0.5 ML in co-adsorbed geometry
4 Conclusions
1) With respect to the co-adsorption, H2O molecule is dissociated and O—H is adsorbed on Cu atom of the surface with O atom, while another H atom of H2O is bonded with O atom of SO2, keeping away from the surface at the coverage of 0.5 ML. The SO2 and H2O are adsorbed on different Cu atoms with S and O atoms at the coverage of 0.25ML, respectively.
2) The co-adsorption energy is not equal to the sum of single adsorption energy of SO2 and H2O, which contains the interaction energy among the adsorbates.
3) The calculation of PDOS, difference charge density, valence charge density and Bader charge analysis illustrate that there are obviously chemical adsorption between Cu (100) surface and adsorbates at the coverage of 0.5 ML. The bonding of SO2 and H2O at 0.5 ML is not as strong as that at 0.25 ML.
4) The adsorption of gases by clean and fresh metal surface is a primary step in atmospheric corrosion, but the detailed mechanisms that drive co-adsorption of H2O and SO2 more easily than individual gas are obscure. The co-adsorption behavior of gases may shed light on further investigation of atmospheric corrosion mechanism.
References
[1] TIDBLAD J, GRAEDEL T E. GILDES model studies of aqueous chemistry. III. Initial SO2-induced atmospheric corrosion of copper [J]. Corrosion Science, 1996, 38: 2201-2224.
[2] RICE D W, PETERSON P, RIGBY E B, PHIPPS P B P, CAPPELL R J. Tremoureux, atmospheric corrosion of copper and silver [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1981, 128: 275-284.
[3] GIOVANNELLI G, NATALI S, ZORTEA L, BOZZINI B. An investigation into the surface layers formed on oxidised copper exposed to SO2 in humid air under hypoxic conditions [J]. Corrosion Science, 2012, 57: 104-113.
[4] HUANG Hua-Liang, PAN Zhi-quan, GUO Xing-peng, QIU Yu-bing. Effect of an alternating electric field on the atmospheric corrosion behaviour of copper under a thin electrolyte layer [J]. Corrosion Science, 2013, 75: 100-105.
[5] HUANG Hua-liang, DONG Ze-hua, CHEN Zhen-yu, GUO Xing-peng. The effects of Cl- ion concentration and relative humidity on atmospheric corrosion behaviour of PCB-Cu under adsorbed thin electrolyte layer [J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53: 1230-1236.
[6] GRAVIER J, VIGNAL V, BISSEY-BRETON S. Influence of residual stress, surface roughness and crystallographic texture induced by machining on the corrosion behavior of copper in salt-frog atmosphere [J]. Corrosion Science, 2012, 61: 162-170.
[7] LEYGRAF C, GRAEDEL T E. Atmospheric corrosion [M]. New York: Wiley-Interscience, 2000.
[8] GUO Li-qiu, ZHAO Xiao-ming, WANG Bao-chang, BAI Yang, QIAO Li-jie. The initial stage of atmospheric corrosion on interstitial free steel investigated by in situ SPM [J]. Corrosion Science, 2013, 70: 188-193.
[9] GUO Li-qiu, LIN Mei-chao, QIAO Li-jie, VOLINSKY A A. Duplex stainless steel passive film electrical properties studied by situ current sensing atomic force microscopy [J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 78: 55-62.
[10] DUAN Yong-hua. Adsorption of fluorine and chlorine on Mg (0001) surface: A density functional theory investigation [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(6): 1844-1852.
[11] WANG Li, FANG Li-hong, GONG Jian-hong. First-principles study of TiC(110) surface [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(1): 170-174.
[12] WEN Zhi-qin, ZHAO Yu-hong, HOU Hua, WANG Nan, FU Li, HAN Pei-de. A first-principlesstudy on interfacial properties of Ni(001)/Ni3Nb(001) [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(5): 1500-1505.
[13] JIANG Yong, XU Can-hui, LAN Guo-qiang, First-principles thermodynamics of metal-oxide surfaces andinterfaces: A case study review [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(1): 180-192.
[14] KH M, AMMAR H Y. Adsorption of SO2 on Li atoms deposited on MgO(100) surface: DFT calculations [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2011, 257: 6049-6058.
[15] ZHAO Ling, LI Xin-yong, HAO Ce, RASTON C L. SO2 adsorption and transformation on calcined NiAl hydrotalcite-like compounds surfaces: An in situ FTIR and DFT study [J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2012, 117-118: 339-345.
[16] JACKSON G J, WOODRUFF D P, CHAN A S Y, JONES R G, COWIE B C C. The local structure of SO2 and SO3 on Ni(111) [J]. Surface Science, 2005, 577: 31-41.
[17] KNIGHT M J, ALLEGRETTI F,  E A, HOGAN K A, SAYAGO D I, LEROTHOLI T J, UNTERBERGER W, WOODRUFF D P. The local structure of SO2 and SO3 on Ni(111): A scanned-energy mode photoelectron diffraction study [J]. Surface Science, 2009, 603: 2062-2073.
E A, HOGAN K A, SAYAGO D I, LEROTHOLI T J, UNTERBERGER W, WOODRUFF D P. The local structure of SO2 and SO3 on Ni(111): A scanned-energy mode photoelectron diffraction study [J]. Surface Science, 2009, 603: 2062-2073.
[18] SAKAI Y, KOYANAGI M, MOGI K, MIYOSHI E. Theoretical study of adsorption of SO2 on Ni(111) and Cu(111) surfaces [J]. Surface Science, 2002, 513: 272-282.
[19] RODRIGUEZ J A, RICART J M, CLOTET A, ILLAS F. Density functional studies on the adsorpton and decomposition of SO2 on Cu(100) [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 2001, 115: 454-464.
[20] MILMAN V, WINKLER B, WHITE J A, PICKARD C J, PAYNE M C, AKHMATSKAYA E V, NOBES R H. Electronic structure, properties, and phase stability of inorganic: A pseudopotential plane-wave study [J]. International Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 2000, 77: 895-910.
[21] HAMMER B, HANSEN L B,  J K. Improved adsorption energetics within density-functional theory using revised Perdew- Burke-Ernzerhof functionals [J]. Physical Review B, 1999, 59: 7413-7421.
J K. Improved adsorption energetics within density-functional theory using revised Perdew- Burke-Ernzerhof functionals [J]. Physical Review B, 1999, 59: 7413-7421.
[22] PERDEW J P, YUE W. Accurate and simple density functional for the electronic exchange energy generalized gradient [J]. Physical Review B, 1986, 33: 8800-8802.
[23] PERDEW J P, BURKE K, ERNZERHOF M. Atoms, molecules, solids, and surfaces: Applications of the generalized gradient approximation for exchange and correlation [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77: 3865-3868.
[24] TANG Qian-lin, CHEN Zhao-Xu. Density functional slab model studies of water adsorption on flat and stepped Cu surfaces [J]. Surface Science, 2007, 601: 954-964.
[25] KAMMLER T,  J. The kinetics of the reaction of gaseous hydrogen atoms with oxygen on Cu(111) surfaces toward water [J]. Journal of Chemical Physics B, 2001, 105: 8369-8374.
J. The kinetics of the reaction of gaseous hydrogen atoms with oxygen on Cu(111) surfaces toward water [J]. Journal of Chemical Physics B, 2001, 105: 8369-8374.
[26] NAKAMURA M, ITO M. Coadsorption of water dimer and ring-hexamer clusters on M(1 1 1) (M = Cu, Ni, Pt) and Ru(0 0 1) surfaces at 25 K as studied by infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2005, 404: 346-350.
[27] MORGENSTERN K, RIEDER K H. Formation of the cyclic ice hexamer via excitation of vibrational molecular modes by the scanning tunneling microscope [J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2002, 116: 5746-5752.
[28] KURAHASHI M, SUZUKI T, JU X, YAMAUCHI Y. A metastable-atom deexcitation spectroscopy (MDS) study of water adsorption on Cu(100): A new feature at around the Fermi level [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2003, 377: 519-522.
[29] AMMON C, BAYER A,  H P, HELD G. Low-temperature partial dissociation of water on Cu(1 1 0) [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2003, 377: 163-169.
H P, HELD G. Low-temperature partial dissociation of water on Cu(1 1 0) [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2003, 377: 163-169.
[30] ANDERSSON K,  A, GLOVER C, NORDLUND D,
A, GLOVER C, NORDLUND D,  H, SCHIROS T, TAKAHASHI O, OGASAWARA H, PETTERSSON L G M, NILSSON A. Molecularly intact and dissociative adsorption of water on clean Cu(110): A comparison with the water/Ru(001) system [J]. Surface Science, 2005, 585: L183-L189.
H, SCHIROS T, TAKAHASHI O, OGASAWARA H, PETTERSSON L G M, NILSSON A. Molecularly intact and dissociative adsorption of water on clean Cu(110): A comparison with the water/Ru(001) system [J]. Surface Science, 2005, 585: L183-L189.
[31] ANDERSSON S, NYBERG C, TENGST L C G. Adsorption of water monomers on Cu(100) and Pd(100) at low temperatures [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 1984, 104: 305-310.
L C G. Adsorption of water monomers on Cu(100) and Pd(100) at low temperatures [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 1984, 104: 305-310.
[32] NYBERG C, TENGST L C G, UVDAL P, ANDERSSON S. Adsorption of water on Cu(100) and Pd(100) at low temperatures: Observation of monomeric water [J]. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 1986, 38: 299-307.
L C G, UVDAL P, ANDERSSON S. Adsorption of water on Cu(100) and Pd(100) at low temperatures: Observation of monomeric water [J]. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 1986, 38: 299-307.
[33] HODGSON A, HAQ S. Water adsorption and the wetting of metal surfaces [J]. Surface Science, 2009, 64: 381-451.
[34] GALLAGHER M E, HAQ S, OMER A, HODGSON A. Water monolayer and multilayer adsorption on Ni(111) [J]. Surface Science, 2007, 601: 268-273.
[35] SCHIROS T, HAQ S, OGASAWARA H, TAKAHASHI O,  H, ANDERSSON K, PETTERSSON L G M, HODGSON A, NILSSON A. Structure of water adsorbed on the open Cu(110) surface:H-up,H-down, or both? [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2006, 4-6: 415-419.
H, ANDERSSON K, PETTERSSON L G M, HODGSON A, NILSSON A. Structure of water adsorbed on the open Cu(110) surface:H-up,H-down, or both? [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2006, 4-6: 415-419.
[36] KRESSE G, FUTHNULLER J. Effienciency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set [J]. Computation Materials Science, 1996, 6: 15-50.
[37] MONKHORST H J, PACK J D. Special points for Brillouim-zone integrations [J]. Physical Review B, 1976, 13: 5188-5192.
[38] BENEDICT W S, GAILAR N, PLYLER E K. Rotation-vibration spectra of deuterated water vapor [J]. Journal of Chemical Physics 1956, 24: 1139-1165.
[39] SEXTON B A, HUGHES A E. A comparison of weak molecular adsorption of organic molecules on clean copper and platinum surfaces [J]. Surface Science, 1984, 140: 227-248.
[40] PANGHER N, WILDE L, POLCIK M, HAASE J. Structure determinations of SO2 and its decomposition product SO adsorbed on Cu(100) by use of X-ray absorption fine-structure measurements [J]. Surface Science, 1997, 392: 211-222.
魏 薪1,董超芳1,陈章华2,黄建业1,肖 葵1,李晓刚1
1. 北京科技大学 新材料技术研究院 腐蚀与防护中心,北京 100083;
2. 北京科技大学 数理学院,北京 100083
摘 要:利用基于密度泛函GGA-rPBE方法的平板模型研究SO2和H2O在面心立方金属Cu (100)表面的共吸附行为。SO2和H2O在Cu (100)表面单分子吸附的计算结果表明,在覆盖度为0.25分子层和0.5分子层的情况,二者均不能以化学键的形式吸附在Cu (100)表面上。针对SO2和H2O在Cu (100)表面的共吸附行为,计算弛豫后的吸附结构、吸附能和电子性质(包括差分电荷密度、价电荷密度、Bader电荷分析和分态密度分析)。结果表明,覆盖度为0.25分子层时,H2O和SO2以化学吸附的形式各自吸附在表面不同Cu原子上;覆盖度为0.5分子层时,H2O分子解离成OH和H,OH吸附在表面Cu原子上,而H与SO2键合后共同远离表面。
关键词:SO2;H2O;Cu;密度泛函;共吸附;平板模型;吸附能;电荷转移
(Edited by Yun-bin HE)
Foundation item: Project (51222106) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (230201306500002) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China; Project (2014CB643300) supported by National Basic Research Program of China
Corresponding author: Chao-fang DONG; Tel: +86-10-62333931-518; Fax: +86-10-62334005; E-mail: cfdong@ustb.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)64059-6

